Cortical Column on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A cortical column is a group of 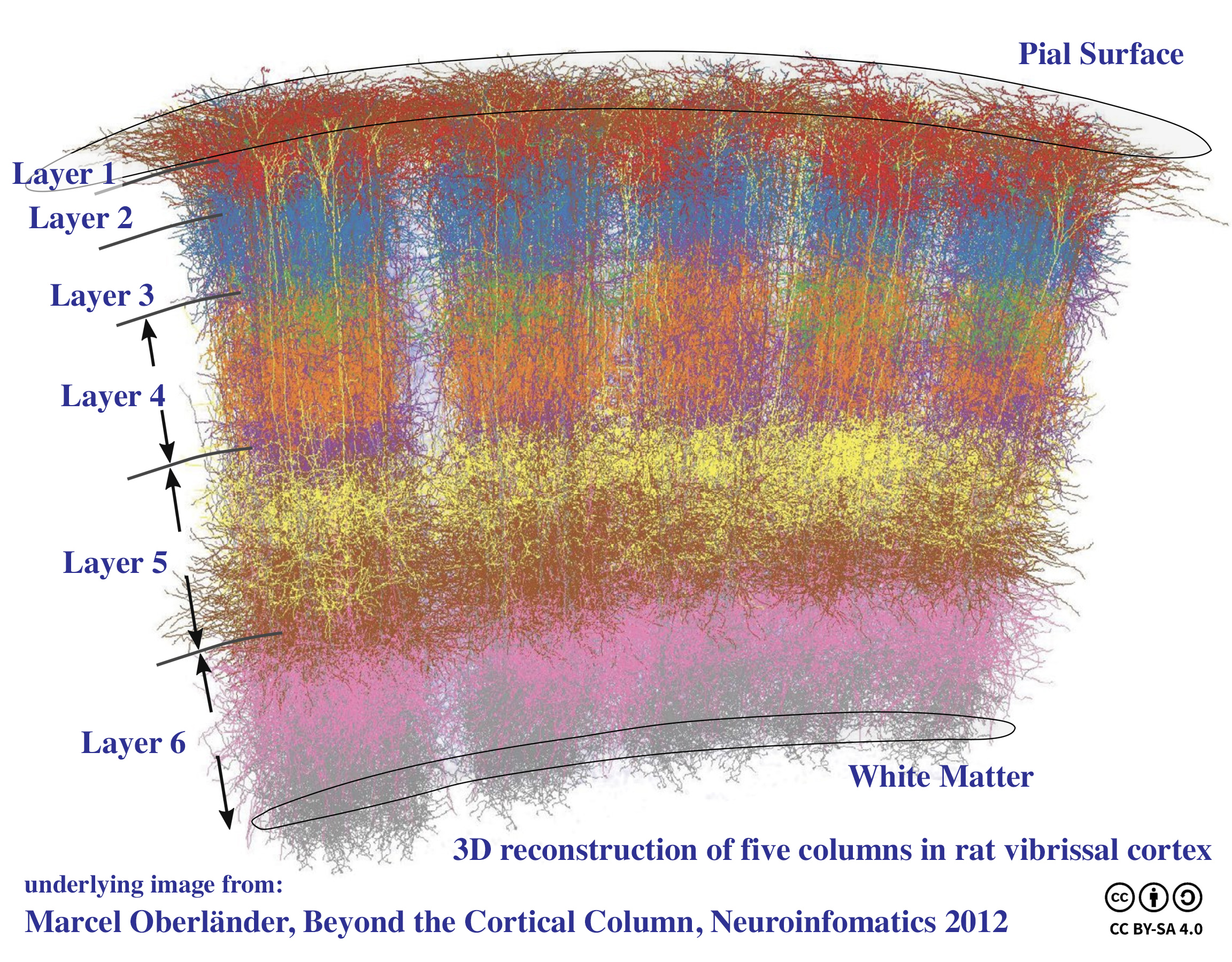 The columnar hypothesis states that the cortex is composed of discrete, modular columns of neurons, characterized by a consistent connectivity profile. The columnar organization hypothesis is currently the most widely adopted to explain the cortical processing of information.
The columnar hypothesis states that the cortex is composed of discrete, modular columns of neurons, characterized by a consistent connectivity profile. The columnar organization hypothesis is currently the most widely adopted to explain the cortical processing of information.
simulate a cortical column
*
neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
s forming a cylindrical structure through the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of Neuron, neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays ...
of the brain perpendicular to the cortical surface. The structure was first identified by Vernon Benjamin Mountcastle in 1957. He later identified minicolumns as the basic units of the neocortex which were arranged into columns. Each contains the same types of neurons, connectivity, and firing properties. Columns are also called hypercolumn, macrocolumn, functional column or sometimes cortical module. Neurons within a minicolumn (microcolumn) encode similar features, whereas a hypercolumn "denotes a unit containing a full set of values for any given set of receptive field parameters". A cortical module is defined as either synonymous with a hypercolumn (Mountcastle) or as a tissue block of multiple overlapping hypercolumns.
Cortical columns are proposed to be the canonical microcircuits for predictive coding
In neuroscience, predictive coding (also known as predictive processing) is a theory of brain function which postulates that the brain is constantly generating and updating a " mental model" of the environment. According to the theory, such a men ...
, in which the process of cognition is implemented through a hierarchy of identical microcircuits. The evolutionary benefit to this duplication allowed human neocortex to increase in size by almost 3-fold over just the last 3 million years.
 The columnar hypothesis states that the cortex is composed of discrete, modular columns of neurons, characterized by a consistent connectivity profile. The columnar organization hypothesis is currently the most widely adopted to explain the cortical processing of information.
The columnar hypothesis states that the cortex is composed of discrete, modular columns of neurons, characterized by a consistent connectivity profile. The columnar organization hypothesis is currently the most widely adopted to explain the cortical processing of information.
Mammalian cerebral cortex
Themammalian
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of Neuron, neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays ...
, the grey matter
Grey matter, or gray matter in American English, is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil ( dendrites and unmyelinated axons), glial cells ( astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, ...
encapsulating the white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called Nerve tract, tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distr ...
, is composed of layers
Layer or layered may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Layers'' (Kungs album)
* ''Layers'' (Les McCann album)
* ''Layers'' (Royce da 5′9″ album)
*“Layers”, the title track of Royce da 5′9″’s sixth studio album
* Layer, a ...
. The human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
cortex is between 2 and 3 mm thick. The number of layers is the same in most mammals, but varies throughout the cortex. 6 layers can be recognized in the neocortex, although many regions lack one or more layers. For example, fewer layers are present in the archipallium and the paleopallium
In anatomy of animals, the paleocortex, or paleopallium, is a region within the telencephalon in the vertebrate brain. This type of cortical tissue consists of three cortical laminae (layers of neuronal cell bodies). In comparison, the neocortex ...
.
Columnar functional organization
The columnar functional organization, as originally framed byVernon Mountcastle
Vernon Benjamin Mountcastle (July 15, 1918 – January 11, 2015) was an American neurophysiologist and Professor Emeritus of Neuroscience at Johns Hopkins University. He discovered and characterized the columnar organization of the cerebral co ...
, suggests that neurons that are horizontally more than 0.5 mm (500 μm) from each other do not have overlapping sensory receptive fields, and other experiments give similar results: 200–800 μm. Various estimates suggest there are 50 to 100 cortical minicolumn A cortical minicolumn (also called cortical microcolumn) is a vertical column through the cortical layers of the brain. Neurons within the microcolumn "receive common inputs, have common outputs, are interconnected, and may well constitute a fundam ...
s in a hypercolumn, each comprising around 80 neurons. Their role is best understood as 'functional units of information processing.'
An important distinction is that the columnar organization is functional by definition, and reflects the local connectivity of the cerebral cortex. Connections "up" and "down" within the thickness of the cortex are much denser than connections that spread from side to side.
Hubel and Wiesel studies
David Hubel
David Hunter Hubel (February 27, 1926 – September 22, 2013) was an American Canadian neurophysiologist noted for his studies of the structure and function of the visual cortex. He was co-recipient with Torsten Wiesel of the 1981 Nobel Pr ...
and Torsten Wiesel
Torsten Nils Wiesel (born 3 June 1924) is a Swedish Neurophysiology, neurophysiologist. With David H. Hubel, he received the 1981 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, for their discoveries concerning information processing in the visual system; ...
followed up on Mountcastle's discoveries in the somatic sensory cortex with their own studies in vision. A part of the discoveries that resulted in them winning the 1981 Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; ; ) are awards administered by the Nobel Foundation and granted in accordance with the principle of "for the greatest benefit to humankind". The prizes were first awarded in 1901, marking the fifth anniversary of Alfred N ...
was that there were cortical columns in vision
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to:
Perception Optical perception
* Visual perception, the sense of sight
* Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight
* Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain und ...
as well, and that the neighboring columns were also related in function in terms of the orientation of lines that evoked the maximal discharge. Hubel and Wiesel followed up on their own studies with work demonstrating the impact of environmental changes on cortical organization, and the sum total of these works resulted in their Nobel Prize.
Number of cortical columns
There are about 200 million (2×108) cortical minicolumns in the human neocortex with up to about 110 neurons each, and with estimates of 21–26 billion (2.1×1010–2.6×1010) neurons in the neocortex. With 50 to 100 cortical minicolumns per cortical column a human would have 2–4 million (2×106–4×106) cortical columns. There may be more if the columns can overlap, as suggested by Tsunoda ''et al''. Jeff Hawkins claims that there are only 150,000 columns in the human neocortex, based on research made by his company Numenta. There are claims that minicolumns may have as many as 400 principal cells, but it is not clear if that includes glia cells. Some contradict the previous estimates, claiming the original research is too arbitrary. The authors propose a uniform neocortex, and choose a fixed width and length to calculate the cell numbers. Later research pointed out that the neocortex is indeed not uniform for other species, and studying nine primate species they found that "the number of neurons underneath 1 mm2 of the cerebral cortical surface ... varies by three times across species." The neocortex is not uniform across species. The actual number of neurons within a single column is variable, and depends on the cerebral areas and thus the function of the column.See also
*Cortical minicolumn A cortical minicolumn (also called cortical microcolumn) is a vertical column through the cortical layers of the brain. Neurons within the microcolumn "receive common inputs, have common outputs, are interconnected, and may well constitute a fundam ...
*Ocular dominance column Ocular dominance columns are stripes of neurons in the visual cortex of certain mammals (including humans) that respond preferentially to input from one eye or the other. The columns span multiple cortical layers, and are laid out in a striped pa ...
*Predictive coding
In neuroscience, predictive coding (also known as predictive processing) is a theory of brain function which postulates that the brain is constantly generating and updating a " mental model" of the environment. According to the theory, such a men ...
* Radial unit hypothesis
References
External links
* * The Blue Brain Project aims tsimulate a cortical column
*
On Intelligence
''On Intelligence: How a New Understanding of the Brain will Lead to the Creation of Truly Intelligent Machines'' is a 2004 book by Jeff Hawkins and Sandra Blakeslee. The book explains Hawkins' memory-prediction framework theory of the brain an ...
—a popular science
Popular science (also called pop-science or popsci) is an interpretation of science intended for a general audience. While science journalism focuses on recent scientific developments, popular science is more broad ranging. It may be written ...
book about column function by Jeff Hawkins
Jeffrey Hawkins is an American businessman, computer scientist, neuroscientist and engineer. He co-founded Palm Computing — where he co-created the PalmPilot and Treo — and Handspring.
He subsequently turned to work on neuroscience, fou ...
* Summarizes what is known and corrects some misconceptions.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cortical Column
Neural circuitry