Columbia River basalts on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Columbia River Basalt Group is the youngest, smallest and one of the best-preserved continental flood basalt province on Earth, covering over mainly eastern
The Columbia River Basalt Group is the youngest, smallest and one of the best-preserved continental flood basalt province on Earth, covering over mainly eastern
 During the middle to late
During the middle to late
 Prior to 17.5 million years ago, the Western
Prior to 17.5 million years ago, the Western
 The hot spot hypothesis is not universally accepted as it has not resolved several questions. The Yellowstone hot spot volcanism track shows a large apparent bow in the hot-spot track that does not correspond to changes in plate motion if the northern CRBG floods are considered. Further, the Yellowstone images show necking of the plume at and , which may correspond to phase changes or may reflect still-to-be-understood viscosity effects. Additional data collection and further modeling will be required to achieve a consensus on the actual mechanism.
The hot spot hypothesis is not universally accepted as it has not resolved several questions. The Yellowstone hot spot volcanism track shows a large apparent bow in the hot-spot track that does not correspond to changes in plate motion if the northern CRBG floods are considered. Further, the Yellowstone images show necking of the plume at and , which may correspond to phase changes or may reflect still-to-be-understood viscosity effects. Additional data collection and further modeling will be required to achieve a consensus on the actual mechanism.
 Three major tools are used to date the CRBG flows: Stratigraphy, radiometric dating, and magnetostratigraphy. These techniques have been key to correlating data from disparate basalt exposures and boring samples over five states.
Major eruptive pulses of flood basalt lavas are laid down stratigraphically. The layers can be distinguished by physical characteristics and chemical composition. Each distinct layer is typically assigned a name usually based on area (valley, mountain, or region) where that formation is exposed and available for study. Stratigraphy provides a relative ordering (ordinal ranking) of the CRBG layers.
Absolute dates, subject to a statistical uncertainty, are determined through
Three major tools are used to date the CRBG flows: Stratigraphy, radiometric dating, and magnetostratigraphy. These techniques have been key to correlating data from disparate basalt exposures and boring samples over five states.
Major eruptive pulses of flood basalt lavas are laid down stratigraphically. The layers can be distinguished by physical characteristics and chemical composition. Each distinct layer is typically assigned a name usually based on area (valley, mountain, or region) where that formation is exposed and available for study. Stratigraphy provides a relative ordering (ordinal ranking) of the CRBG layers.
Absolute dates, subject to a statistical uncertainty, are determined through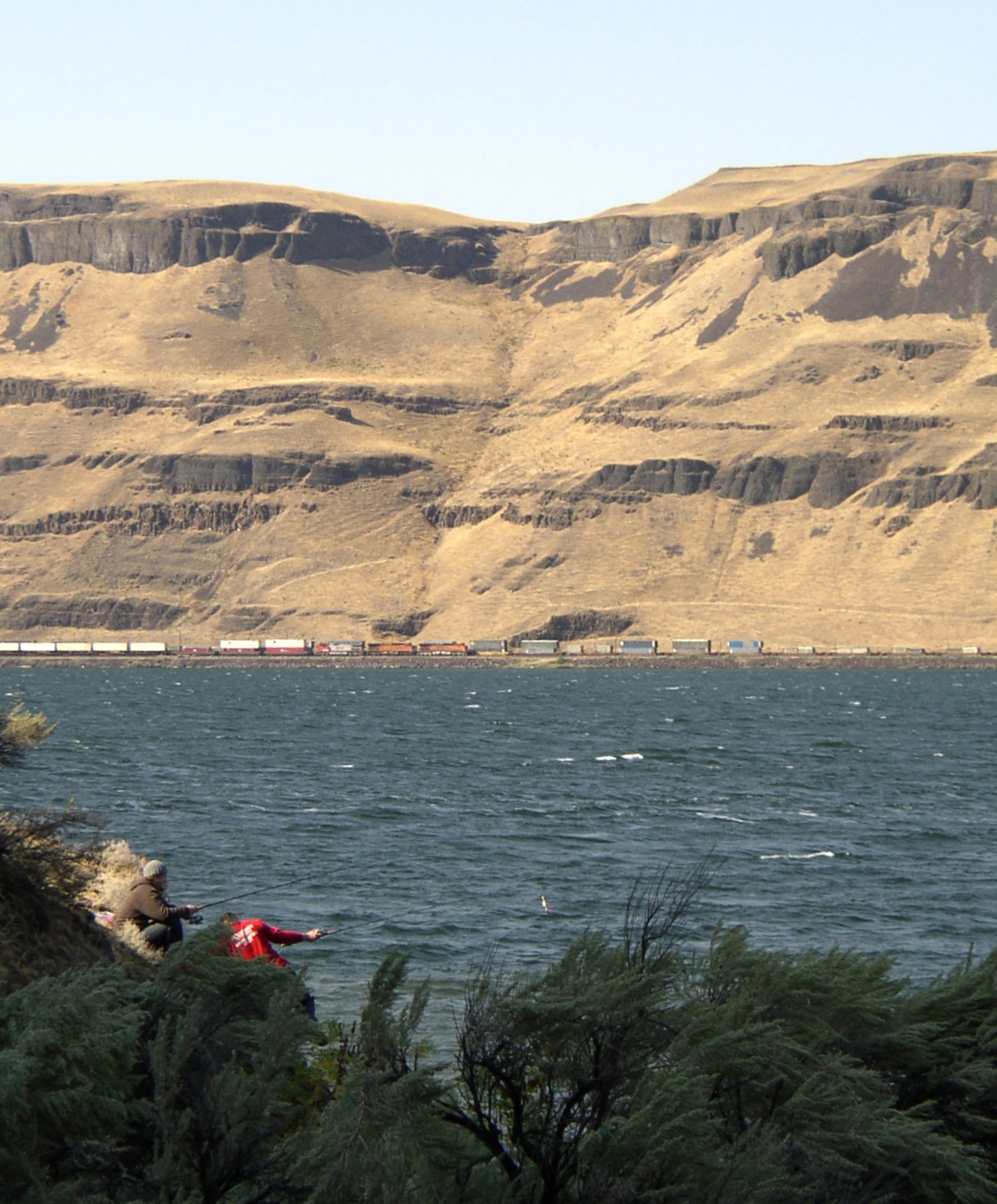 
 The Steens Basalt flows covered about of the Oregon Plateau in sections up to thick. It contains the earliest identified eruption of the CRBG large igneous province. The type locality for the Steens basalt, which covers a large portion of the Oregon Plateau, is an approximately face of Steens Mountain showing multiple layers of basalt. The oldest of the flows considered part of the Columbia River Basalt Group, the Steens basalt, includes flows geographically separated but roughly concurrent with the Imnaha flows. Older Imnaha basalt north of Steens Mountain overlies the chemically distinct lowermost flows of Steens basalt; hence some flows of the Imnaha are stratigraphically younger than the lowermost Steens basalt.
One geomagnetic field reversal occurred during the Steens Basalt eruptions at approximately 16.7 Ma, as dated using 40Ar/39Ar ages and the geomagnetic polarity timescale. Steens Mountain and related sections of Oregon Plateau flood basalts at Catlow Peak and Poker Jim Ridge to the southeast and west of Steens Mountain, provide the most detailed magnetic field reversal data (reversed-to-normal polarity transition) yet reported in volcanic rocks.
The observed trend in feeder dyke swarms associated with the Steens Basalt flow are considered to be atypical of other dyke swarm trends associated with the CRBG. These swarms, characterized by a maintained trend of N20°E, trace the northward continuation of the Nevada shear zone and have been attributed to magmatic rise through this zone on a regional scale.
The Steens Basalt flows covered about of the Oregon Plateau in sections up to thick. It contains the earliest identified eruption of the CRBG large igneous province. The type locality for the Steens basalt, which covers a large portion of the Oregon Plateau, is an approximately face of Steens Mountain showing multiple layers of basalt. The oldest of the flows considered part of the Columbia River Basalt Group, the Steens basalt, includes flows geographically separated but roughly concurrent with the Imnaha flows. Older Imnaha basalt north of Steens Mountain overlies the chemically distinct lowermost flows of Steens basalt; hence some flows of the Imnaha are stratigraphically younger than the lowermost Steens basalt.
One geomagnetic field reversal occurred during the Steens Basalt eruptions at approximately 16.7 Ma, as dated using 40Ar/39Ar ages and the geomagnetic polarity timescale. Steens Mountain and related sections of Oregon Plateau flood basalts at Catlow Peak and Poker Jim Ridge to the southeast and west of Steens Mountain, provide the most detailed magnetic field reversal data (reversed-to-normal polarity transition) yet reported in volcanic rocks.
The observed trend in feeder dyke swarms associated with the Steens Basalt flow are considered to be atypical of other dyke swarm trends associated with the CRBG. These swarms, characterized by a maintained trend of N20°E, trace the northward continuation of the Nevada shear zone and have been attributed to magmatic rise through this zone on a regional scale.
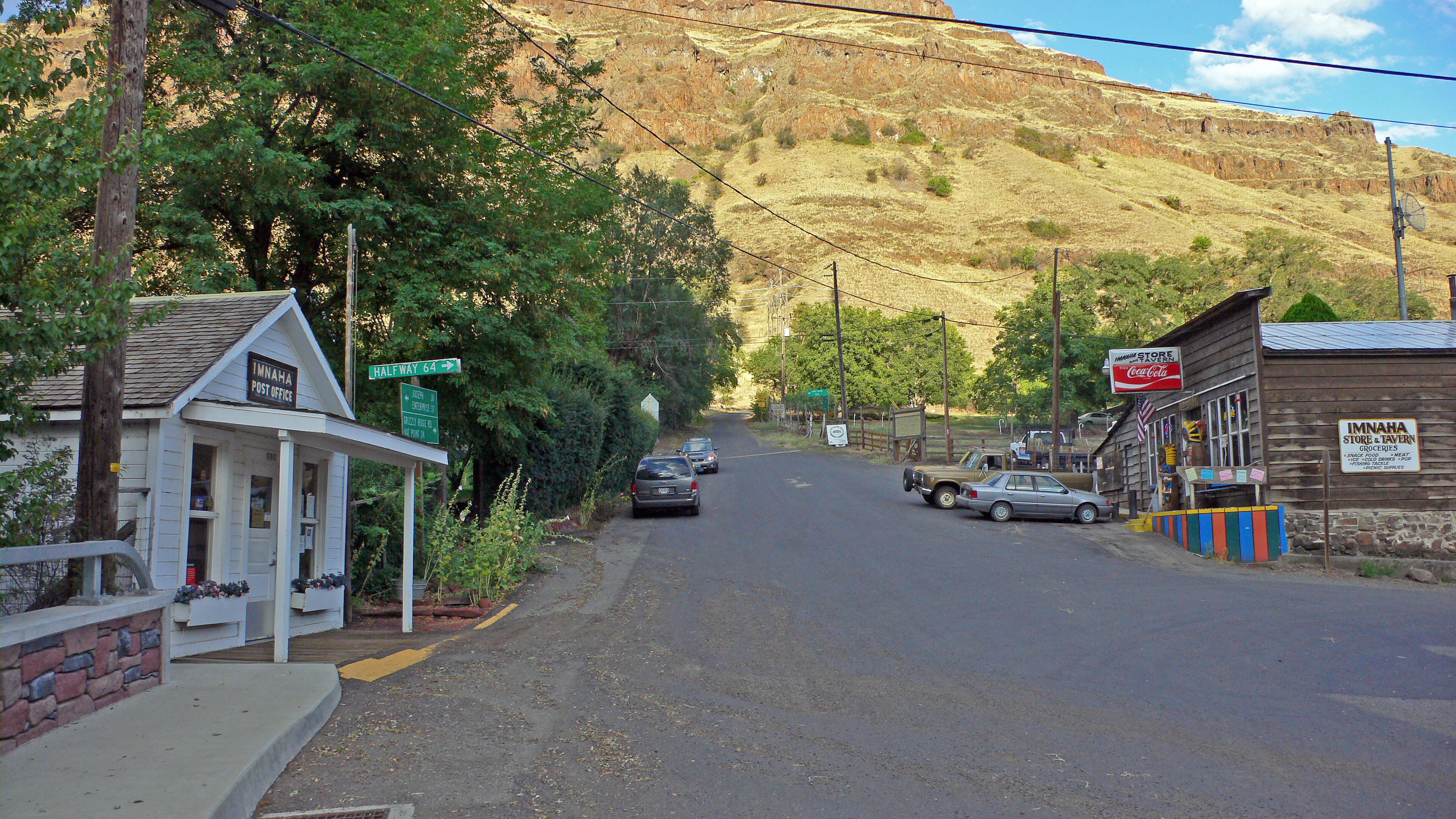 Virtually coeval with the oldest of the flows, the Imnaha basalt flows welled up across northeastern Oregon. There were 26 major flows over the period, one roughly every 15,000 years. Although estimates are that this amounts to about 10% of the total flows, they have been buried under more recent flows, and are visible in few locations. They can be seen along the lower benches of the
Virtually coeval with the oldest of the flows, the Imnaha basalt flows welled up across northeastern Oregon. There were 26 major flows over the period, one roughly every 15,000 years. Although estimates are that this amounts to about 10% of the total flows, they have been buried under more recent flows, and are visible in few locations. They can be seen along the lower benches of the
 The next oldest of the flows, from 17 million to 15.6 million years ago, make up the Grande Ronde Basalt. Units (flow zones) within the Grande Ronde Basalt include the Meyer Ridge and the Sentinel Bluffs units. Geologists estimate that the Grande Ronde Basalt comprises about 85 percent of the total flow volume. It is characterized by a number of
The next oldest of the flows, from 17 million to 15.6 million years ago, make up the Grande Ronde Basalt. Units (flow zones) within the Grande Ronde Basalt include the Meyer Ridge and the Sentinel Bluffs units. Geologists estimate that the Grande Ronde Basalt comprises about 85 percent of the total flow volume. It is characterized by a number of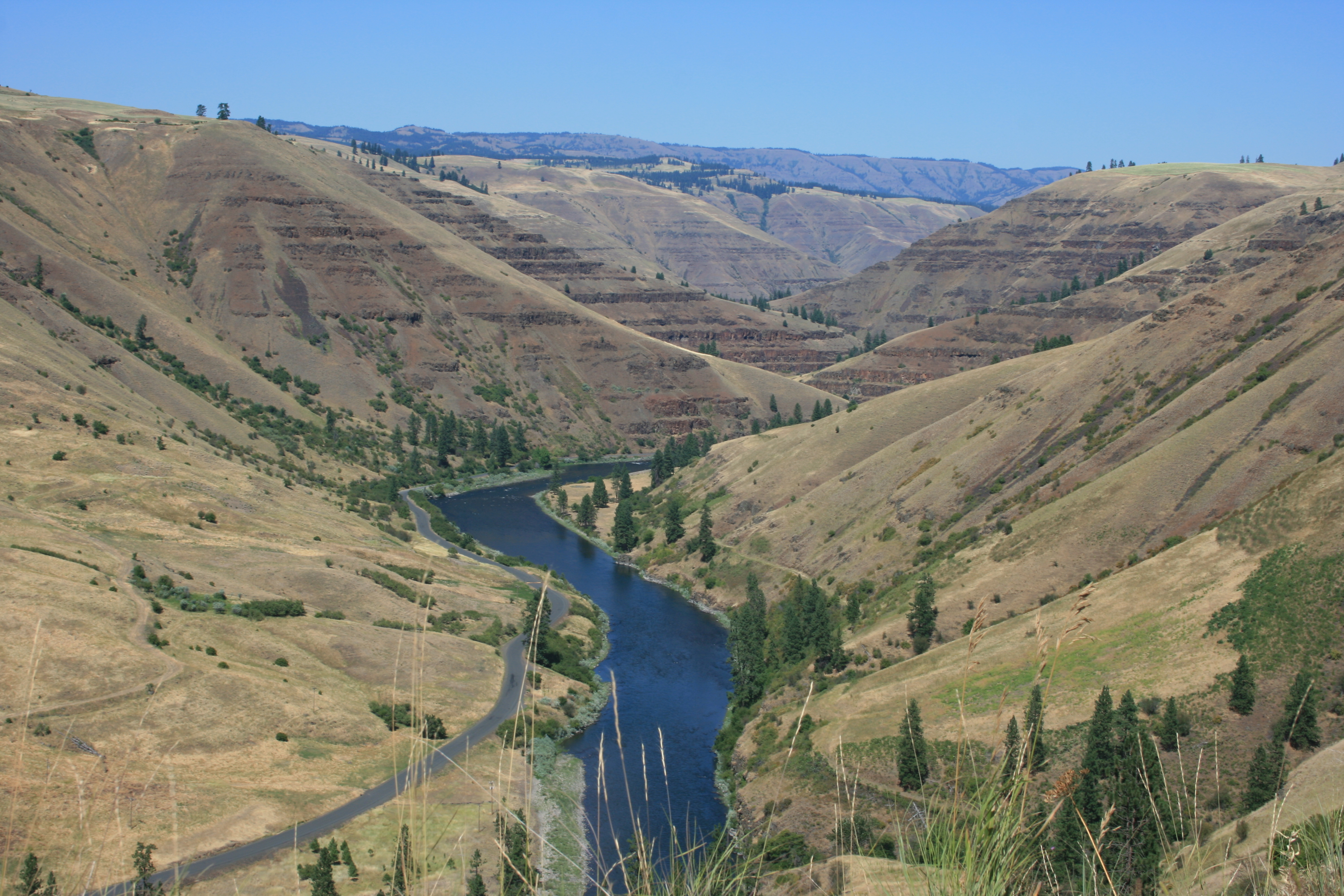  The Grande Ronde basalt flows flooded down the ancestral Columbia River channel to the west of the
The Grande Ronde basalt flows flooded down the ancestral Columbia River channel to the west of the 

 observed that the Oregon High Lava Plains is a complementary system of propagating rhyolite eruptions, with the same point of origin. The two phenomena occurred concurrently, with the High Lava Plains propagating westward since ~10 Ma, while the Snake River Plains propagated eastward.
observed that the Oregon High Lava Plains is a complementary system of propagating rhyolite eruptions, with the same point of origin. The two phenomena occurred concurrently, with the High Lava Plains propagating westward since ~10 Ma, while the Snake River Plains propagated eastward.
USGS - Page on Columbia Plateau
- ''(source of much of this page)''
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20080514031955/http://volcano.und.edu/vwdocs/volc_images/north_america/crb.html Volcano World: page on Columbia River Flood Basalt Province {{Volcanoes of Oregon Large igneous provinces Miocene volcanism Pliocene volcanism Plateaus of the United States Volcanism of Idaho Volcanism of Oregon Volcanism of Washington (state) Columbia River Yellowstone hotspot Miocene geology Pliocene geology Paleogene United States Geologic provinces of the United States
 The Columbia River Basalt Group is the youngest, smallest and one of the best-preserved continental flood basalt province on Earth, covering over mainly eastern
The Columbia River Basalt Group is the youngest, smallest and one of the best-preserved continental flood basalt province on Earth, covering over mainly eastern Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
and Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
, western Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Monta ...
, and part of northern Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. N ...
. The basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
group includes the Steens and Picture Gorge basalt formations.
Introduction
 During the middle to late
During the middle to late Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
epoch
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided ...
, the Columbia River flood basalt
A flood basalt (or plateau basalt) is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot reac ...
s engulfed about of the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Thou ...
, forming a large igneous province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation ...
with an estimated volume of . Eruptions were most vigorous 17–14 million years ago, when over 99 percent of the basalt was released. Less extensive eruptions continued 14–6 million years ago.
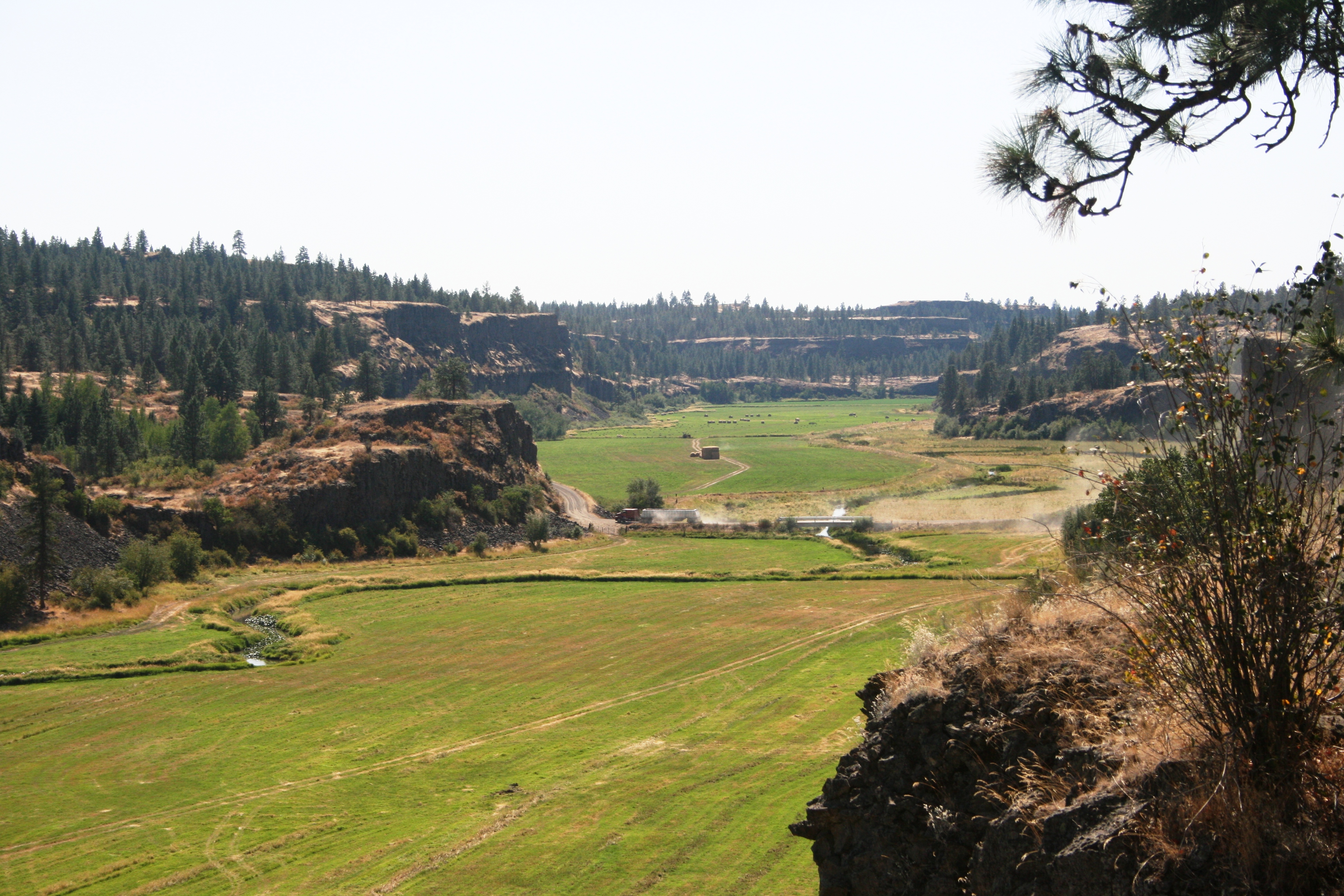
Erosion resulting from the Missoula Floods has extensively exposed these lava flows, laying bare many layers of the basalt flows at Wallula Gap
Wallula Gap () is a large water gap of the Columbia River in the northwest United States in southeast Washington. It cuts through the Horse Heaven Hills basalt anticlines in the Columbia River Basin, just south of the confluence of the Wa ...
, the lower Palouse River, the Columbia River Gorge
The Columbia River Gorge is a canyon of the Columbia River in the Pacific Northwest of the United States. Up to deep, the canyon stretches for over as the river winds westward through the Cascade Range, forming the boundary between the st ...
and throughout the Channeled Scablands
The Channeled Scablands are a relatively barren and soil-free region of interconnected relict and dry flood channels, coulees and cataracts eroded into Palouse loess and the typically flat-lying basalt flows that remain after cataclysmic floods ...
.
The Columbia River Basalt Group is thought to be a potential link to the Chilcotin Group
The Chilcotin Group, also called the Chilcotin Plateau Basalts, is a large area of basaltic lava that forms a volcanic plateau running parallel with the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt in south-central British Columbia, Canada.
Predominantly, during Mio ...
in south-central British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, for ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
. The Latah Formation
The Latah Formation is a series of late Miocene lacustrine sedimentary deposits which outcrop in eastern Washington and northwestern Idaho. The lake beds are interbedded with igneous rock of the Columbia River Basalt Group. The formation was ...
sediments of Washington and Idaho are interbedded with a number of the Columbia River Basalt Group flows, and outcrop across the region.
Absolute dates, subject to a statistical uncertainty, are determined through radiometric dating
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares ...
using isotope ratios such as 40Ar/39Ar dating, which can be used to identify the date of solidifying basalt. In the CRBG deposits 40Ar, which is produced by 40K decay, only accumulates after the melt solidifies.
Other flood basalts include the Deccan Traps
The Deccan Traps is a large igneous province of west-central India (17–24°N, 73–74°E). It is one of the largest volcanic features on Earth, taking the form of a large shield volcano. It consists of numerous layers of solidified flo ...
(late Cretaceous period
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of t ...
), that cover an area of 500,000 km2 (200,000 sq mi) in west-central India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
; the Emeishan Traps
The Emeishan Traps constitute a flood basalt volcanic province, or large igneous province, in south-western China, centred in Sichuan province. It is sometimes referred to as the Permian Emeishan Large Igneous Province or Emeishan Flood Basalts. Li ...
(Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleo ...
), which cover more than 250,000 square kilometers in southwestern China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
; and Siberian Traps
The Siberian Traps (russian: Сибирские траппы, Sibirskiye trappy) is a large region of volcanic rock, known as a large igneous province, in Siberia, Russia. The massive eruptive event that formed the traps is one of the largest ...
(late Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleo ...
) that cover (800,000 sq mi) in Russia.
Formation of the Columbia River Basalt Group
Some time during a 10–15 million-year period, lava flow after lava flow poured out of multiple dikes which trace along an old fault line running from south-eastern Oregon through to western British Columbia. The many layers of lava eventually reached a thickness of more than . As the molten rock came to the surface, the Earth's crust gradually sank into the space left by the rising lava. This subsidence of the crust produced a large, slightly depressed lava plain now known as the Columbia Basin orColumbia River Plateau
The Columbia Plateau is a geologic and geographic region that lies across parts of the U.S. states of Washington, Oregon, and Idaho. It is a wide flood basalt plateau between the Cascade Range and the Rocky Mountains, cut through by the Columbi ...
. The northwesterly advancing lava forced the ancient Columbia River
The Columbia River ( Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia ...
into its present course. The lava, as it flowed over the area, first filled the stream valleys, forming dams that in turn caused impoundments or lakes. In these ancient lake beds are found fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
leaf impressions, petrified wood
Petrified wood, also known as petrified tree (from Ancient Greek meaning 'rock' or 'stone'; literally 'wood turned into stone'), is the name given to a special type of '' fossilized wood'', the fossilized remains of terrestrial vegetation. ' ...
, fossil insects, and bones of vertebrate animals.
In the middle Miocene, 17 to 15 Ma, the Columbia Plateau and the Oregon Basin and Range of the Pacific Northwest were flooded with lava flows. Both flows are similar in both composition and age, and have been attributed to a common source, the Yellowstone hotspot
The Yellowstone hotspot is a volcanic hotspot in the United States responsible for large scale volcanism in Idaho, Montana, Nevada, Oregon, and Wyoming, formed as the North American tectonic plate moved over it. It formed the eastern Snake Riv ...
. The ultimate cause of the volcanism is still up for debate, but the most widely accepted idea is that the mantle plume
A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the Earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic hot ...
or upwelling (similar to that associated with present-day Hawaii) initiated the widespread and voluminous basaltic volcanism about 17 million years ago. As hot mantle plume materials rise and reach lower pressures, the hot materials melt and interact with the materials in the upper mantle, creating magma. Once that magma breaches the surface, it flows as lava and then solidifies into basalt.
Transition to flood volcanism
 Prior to 17.5 million years ago, the Western
Prior to 17.5 million years ago, the Western Cascade
Cascade, Cascades or Cascading may refer to:
Science and technology Science
*Cascade waterfalls, or series of waterfalls
* Cascade, the CRISPR-associated complex for antiviral defense (a protein complex)
* Cascade (grape), a type of fruit
* Bioc ...
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with a summit crater and peri ...
es erupted with periodic regularity for over 20 million years, even as they do today. An abrupt transition to shield volcanic flooding took place in the mid-Miocene. The flows can be divided into four major categories: The Steens Basalt, Grande Ronde Basalt, the Wanapum Basalt, and the Saddle Mountains Basalt. The various lava flows have been dated by radiometric dating—particularly through measurement of the ratios of isotopes of potassium to argon. The Columbia River flood basalt province comprises more than 300 individual basalt lava flows that have an average volume of .
The transition to flood volcanism in the Columbia River Basalt Group (CRBG), similar to other large igneous province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation ...
s, was also marked by atmospheric loading through the mass exsolution and emission of volatiles, via the process of volcanic degassing. Comparative analysis of volatile concentrations in source feeder dykes to associated extruded flow units have been quantitatively measured to determine the magnitude of degassing exhibited in CRBG eruptions. Of the more than 300 individual flows associated with the CRBG, the Roza flow contains some of the most well chemically preserved basalts for volatile analysis. Contained within the Wanapum formation, Roza is one of the most extensive members of the CRBG with an area of 40,300 square kilometres and a volume of 1,300 cubic kilometres. With magmatic volatile values assumed at 1 - 1.5 percent by weight concentration for source feeder dykes, the emission of sulphur for the Roza flow is calculated to be on the order of 12Gt (12,000 million tonnes) at a rate of 1.2Gt (1,200 million tonnes) annually, in the form of sulphur dioxide. However, other research through petrologic analysis has yielded SO2 mass degassing values at 0.12% - 0.28% of the total erupted mass of the magma, translating to lower emission estimates in the range of 9.2Gt of sulfur dioxide for the Roza flow. Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular fo ...
, a by-product of emitted sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic a ...
and atmospheric interactions, has been calculated to be 1.7Gt annually for the Roza flow and 17Gt in total. Analysis of glass inclusions within phenocryst
300px, feldspathic phenocrysts. This granite, from the Switzerland">Swiss side of the Mont Blanc massif, has large white plagioclase phenocrysts, triclinic minerals that give trapezoid shapes when cut through). 1 euro coins, 1 euro coin (diameter ...
s of the basaltic deposits have yielded emission volumes on the magnitude of 310 Mt of hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the dige ...
, and 1.78 Gt of hydrofluoric acid
Hydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride (HF) in water. Solutions of HF are colourless, acidic and highly corrosive. It is used to make most fluorine-containing compounds; examples include the commonly used pharmaceutical antidepres ...
, additionally.
Cause of the volcanism
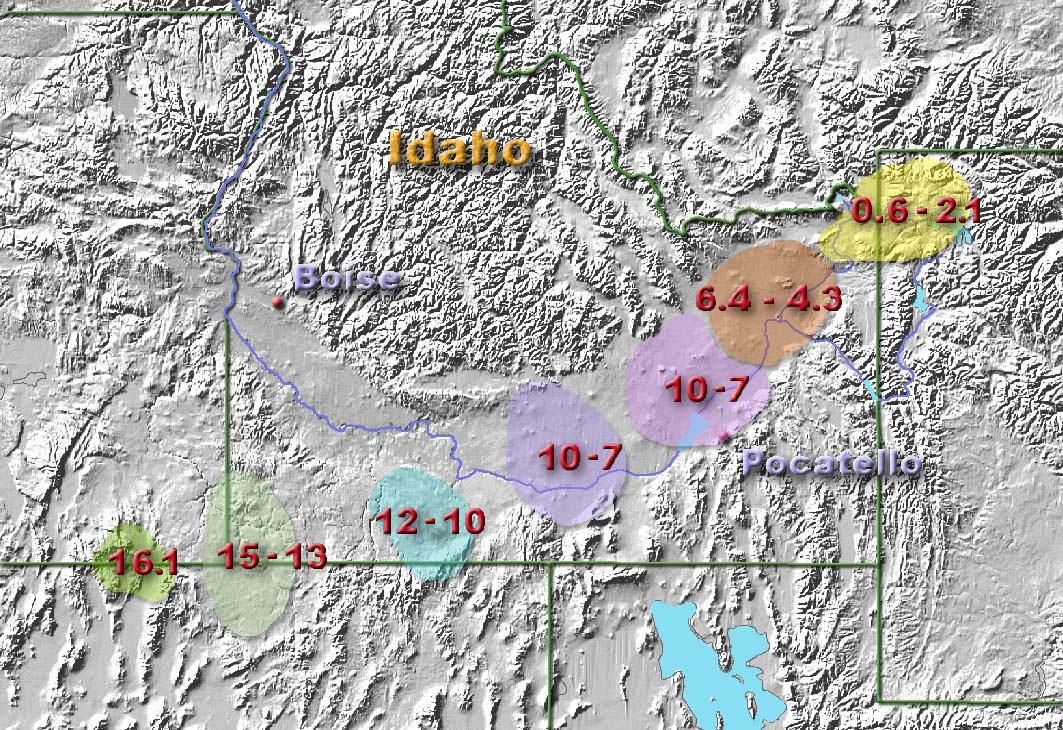
Major hot-spots have often been tracked back to flood-basalt events. In this case theYellowstone hotspot
The Yellowstone hotspot is a volcanic hotspot in the United States responsible for large scale volcanism in Idaho, Montana, Nevada, Oregon, and Wyoming, formed as the North American tectonic plate moved over it. It formed the eastern Snake Riv ...
's initial flood-basalt event occurred near Steens Mountain when the Imnaha and Steens eruptions began. As the North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of , it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Paci ...
moved several centimeters per year westward, the eruptions progressed through the Snake River Plain
The Snake River cutting through the plain leaves many canyons and Canyon#List of gorges">gorges, such as this one near Twin Falls, Idaho
The Snake River Plain is a geologic feature located primarily within the U.S. state of Idaho. It stre ...
across Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Monta ...
and into Wyoming
Wyoming () is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the southwest, and Colorado to t ...
. Consistent with the hot spot hypothesis, the lava flows are progressively younger as one proceeds east along this path.
There is additional confirmation that Yellowstone is associated with a deep hot spot. Using tomographic images based on seismic waves, relatively narrow, deeply seated, active convective plumes have been detected under Yellowstone and several other hot spots. These plumes are much more focused than the upwelling observed with large-scale plate-tectonics circulation.
 The hot spot hypothesis is not universally accepted as it has not resolved several questions. The Yellowstone hot spot volcanism track shows a large apparent bow in the hot-spot track that does not correspond to changes in plate motion if the northern CRBG floods are considered. Further, the Yellowstone images show necking of the plume at and , which may correspond to phase changes or may reflect still-to-be-understood viscosity effects. Additional data collection and further modeling will be required to achieve a consensus on the actual mechanism.
The hot spot hypothesis is not universally accepted as it has not resolved several questions. The Yellowstone hot spot volcanism track shows a large apparent bow in the hot-spot track that does not correspond to changes in plate motion if the northern CRBG floods are considered. Further, the Yellowstone images show necking of the plume at and , which may correspond to phase changes or may reflect still-to-be-understood viscosity effects. Additional data collection and further modeling will be required to achieve a consensus on the actual mechanism.
Speed of flood basalt emplacement
The Columbia River Basalt Group flows exhibit essentially uniform chemical properties through the bulk of individual flows, suggesting rapid placement. Ho and Cashman (1997) characterized the -long Ginkgo flow of the Frenchman Springs Member, determining that it had been formed in roughly a week, based on the measured melting temperature along the flow from the origin to the most distant point of the flow, combined with hydraulics considerations. The Ginkgo basalt was examined over its flow path from a Ginkgo flow feeder dike nearKahlotus, Washington
Kahlotus () is a city in Franklin County, Washington, United States. The population was 193 at the 2010 census. The Washington State Office of Financial Management's 2015 estimate placed the population at 190.
History
The first organized settl ...
to the flow terminus in the Pacific Ocean at Yaquina Head, Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
. The basalt had an upper melting temperature of and a lower temperature to this indicates that the maximum temperature drop along the Ginkgo flow was 20 °C. The lava must have spread quickly to achieve this uniformity. Analyses indicate that the flow must remain laminar, as turbulent flow would cool more quickly. This could be accomplished by sheet flow, which can travel at velocities of without turbulence and minimal cooling, suggesting that the Ginkgo flow occurred in less than a week. The cooling/hydraulics analyses are supported by an independent indicator; if longer periods were required, external water from temporarily dammed rivers would intrude, resulting in both more dramatic cooling rates and increased volumes of pillow lava
Pillow lavas are lavas that contain characteristic pillow-shaped structures that are attributed to the extrusion of the lava underwater, or ''subaqueous extrusion''. Pillow lavas in volcanic rock are characterized by thick sequences of discont ...
. Ho's analysis is consistent with the analysis by Reidel, Tolan, & Beeson (1994), who proposed a maximum Pomona flow emplacement duration of several months based on the time required for rivers to be reestablished in their canyons following a basalt flow interruption.
Dating of the flood basalt flows
 Three major tools are used to date the CRBG flows: Stratigraphy, radiometric dating, and magnetostratigraphy. These techniques have been key to correlating data from disparate basalt exposures and boring samples over five states.
Major eruptive pulses of flood basalt lavas are laid down stratigraphically. The layers can be distinguished by physical characteristics and chemical composition. Each distinct layer is typically assigned a name usually based on area (valley, mountain, or region) where that formation is exposed and available for study. Stratigraphy provides a relative ordering (ordinal ranking) of the CRBG layers.
Absolute dates, subject to a statistical uncertainty, are determined through
Three major tools are used to date the CRBG flows: Stratigraphy, radiometric dating, and magnetostratigraphy. These techniques have been key to correlating data from disparate basalt exposures and boring samples over five states.
Major eruptive pulses of flood basalt lavas are laid down stratigraphically. The layers can be distinguished by physical characteristics and chemical composition. Each distinct layer is typically assigned a name usually based on area (valley, mountain, or region) where that formation is exposed and available for study. Stratigraphy provides a relative ordering (ordinal ranking) of the CRBG layers.
Absolute dates, subject to a statistical uncertainty, are determined through radiometric dating
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares ...
using isotope ratios such as 40Ar/39Ar dating, which can be used to identify the date of solidifying basalt. In the CRBG deposits 40Ar, which is produced by 40K decay, only accumulates after the melt solidifies.
Magnetostratigraphy
Magnetostratigraphy is a geophysical correlation technique used to date sedimentary and volcanic sequences. The method works by collecting oriented samples at measured intervals throughout the section. The samples are analyzed to determine their '' ...
is also used to determine age. This technique uses the pattern of magnetic polarity zones of CRBG layers by comparison to the magnetic polarity timescale. The samples are analyzed to determine their characteristic remanent magnetization from the Earth's magnetic field at the time a stratum was deposited. This is possible as magnetic minerals precipitate in the melt (crystallize), they orient themselves with Earth's magnetic field.
The Steens Basalt captured a highly detailed record of the earth's magnetic reversal that occurred roughly 15 million years ago. Over a 10,000-year period, more than 130 flows solidified – roughly one flow every 75 years. As each flow cooled below about , it captured the magnetic field's orientation-normal, reversed, or in one of several intermediate positions. Most of the flows froze with a single magnetic orientation. However, several of the flows, which freeze from both the upper and lower surfaces, progressively toward the center, captured substantial variations in magnetic field direction as they froze. The observed change in direction was reported as 50⁰ over 15 days.
The major Columbia River Basalt Group flows
Steens Basalt
 The Steens Basalt flows covered about of the Oregon Plateau in sections up to thick. It contains the earliest identified eruption of the CRBG large igneous province. The type locality for the Steens basalt, which covers a large portion of the Oregon Plateau, is an approximately face of Steens Mountain showing multiple layers of basalt. The oldest of the flows considered part of the Columbia River Basalt Group, the Steens basalt, includes flows geographically separated but roughly concurrent with the Imnaha flows. Older Imnaha basalt north of Steens Mountain overlies the chemically distinct lowermost flows of Steens basalt; hence some flows of the Imnaha are stratigraphically younger than the lowermost Steens basalt.
One geomagnetic field reversal occurred during the Steens Basalt eruptions at approximately 16.7 Ma, as dated using 40Ar/39Ar ages and the geomagnetic polarity timescale. Steens Mountain and related sections of Oregon Plateau flood basalts at Catlow Peak and Poker Jim Ridge to the southeast and west of Steens Mountain, provide the most detailed magnetic field reversal data (reversed-to-normal polarity transition) yet reported in volcanic rocks.
The observed trend in feeder dyke swarms associated with the Steens Basalt flow are considered to be atypical of other dyke swarm trends associated with the CRBG. These swarms, characterized by a maintained trend of N20°E, trace the northward continuation of the Nevada shear zone and have been attributed to magmatic rise through this zone on a regional scale.
The Steens Basalt flows covered about of the Oregon Plateau in sections up to thick. It contains the earliest identified eruption of the CRBG large igneous province. The type locality for the Steens basalt, which covers a large portion of the Oregon Plateau, is an approximately face of Steens Mountain showing multiple layers of basalt. The oldest of the flows considered part of the Columbia River Basalt Group, the Steens basalt, includes flows geographically separated but roughly concurrent with the Imnaha flows. Older Imnaha basalt north of Steens Mountain overlies the chemically distinct lowermost flows of Steens basalt; hence some flows of the Imnaha are stratigraphically younger than the lowermost Steens basalt.
One geomagnetic field reversal occurred during the Steens Basalt eruptions at approximately 16.7 Ma, as dated using 40Ar/39Ar ages and the geomagnetic polarity timescale. Steens Mountain and related sections of Oregon Plateau flood basalts at Catlow Peak and Poker Jim Ridge to the southeast and west of Steens Mountain, provide the most detailed magnetic field reversal data (reversed-to-normal polarity transition) yet reported in volcanic rocks.
The observed trend in feeder dyke swarms associated with the Steens Basalt flow are considered to be atypical of other dyke swarm trends associated with the CRBG. These swarms, characterized by a maintained trend of N20°E, trace the northward continuation of the Nevada shear zone and have been attributed to magmatic rise through this zone on a regional scale.
Imnaha Basalt
 Virtually coeval with the oldest of the flows, the Imnaha basalt flows welled up across northeastern Oregon. There were 26 major flows over the period, one roughly every 15,000 years. Although estimates are that this amounts to about 10% of the total flows, they have been buried under more recent flows, and are visible in few locations. They can be seen along the lower benches of the
Virtually coeval with the oldest of the flows, the Imnaha basalt flows welled up across northeastern Oregon. There were 26 major flows over the period, one roughly every 15,000 years. Although estimates are that this amounts to about 10% of the total flows, they have been buried under more recent flows, and are visible in few locations. They can be seen along the lower benches of the Imnaha River
The Imnaha River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed May 3, 2011 tributary of the Snake River in the U.S. state of Oregon. Flowing generally east near the headwaters a ...
and Snake River
The Snake River is a major river of the greater Pacific Northwest region in the United States. At long, it is the largest tributary of the Columbia River, in turn, the largest North American river that empties into the Pacific Ocean. The Snake ...
in Wallowa county.
The Imnaha lavas have been dated using the K–Ar technique, and show a broad range of dates. The oldest is 17.67±0.32 Ma with younger lava flows ranging to 15.50±0.40 Ma. Although the Imnaha Basalt overlies Lower Steens Basalt, it has been suggested that it is interfingered with Upper Steens Basalt.
Grande Ronde Basalt
 The next oldest of the flows, from 17 million to 15.6 million years ago, make up the Grande Ronde Basalt. Units (flow zones) within the Grande Ronde Basalt include the Meyer Ridge and the Sentinel Bluffs units. Geologists estimate that the Grande Ronde Basalt comprises about 85 percent of the total flow volume. It is characterized by a number of
The next oldest of the flows, from 17 million to 15.6 million years ago, make up the Grande Ronde Basalt. Units (flow zones) within the Grande Ronde Basalt include the Meyer Ridge and the Sentinel Bluffs units. Geologists estimate that the Grande Ronde Basalt comprises about 85 percent of the total flow volume. It is characterized by a number of dikes
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to:
General uses
* Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian"
* Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment
* Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess of moral justice
* Dikes ...
called the Chief Joseph Dike Swarm near Joseph
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the m ...
, Enterprise
Enterprise (or the archaic spelling Enterprize) may refer to:
Business and economics
Brands and enterprises
* Enterprise GP Holdings, an energy holding company
* Enterprise plc, a UK civil engineering and maintenance company
* Enterprise ...
, Troy
Troy ( el, Τροία and Latin: Troia, Hittite: 𒋫𒊒𒄿𒊭 ''Truwiša'') or Ilion ( el, Ίλιον and Latin: Ilium, Hittite: 𒃾𒇻𒊭 ''Wiluša'') was an ancient city located at Hisarlik in present-day Turkey, south-west of Ç ...
and Walla Walla through which the lava upwelling occurred (estimates range to up to 20,000 such dikes). Many of the dikes were fissures wide and up to in length, allowing for huge quantities of magma upwelling. Much of the lava flowed north into Washington as well as down the Columbia River channel to the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
; the tremendous flows created the Columbia River Plateau
The Columbia Plateau is a geologic and geographic region that lies across parts of the U.S. states of Washington, Oregon, and Idaho. It is a wide flood basalt plateau between the Cascade Range and the Rocky Mountains, cut through by the Columbi ...
. The weight of this flow (and the emptying of the underlying magma chamber) caused central Washington to sink, creating the broad Columbia Basin in Washington. The type locality for the formation is the canyon of the Grande Ronde River. Grande Ronde basalt flows and dikes can also be seen in the exposed walls of Joseph Canyon along Oregon Route 3
Oregon Route 3 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Oregon. It is located entirely within Wallowa County. OR 3 is the lowest numbered highway in the state of Oregon, of any type (state, federal, or Interstate). OR 3 traverses the Ent ...
.
 The Grande Ronde basalt flows flooded down the ancestral Columbia River channel to the west of the
The Grande Ronde basalt flows flooded down the ancestral Columbia River channel to the west of the Cascade Mountains
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as the North Cascades, a ...
. It can be found exposed along the Clackamas River
The Clackamas River is an approximately tributary of the Willamette River in northwestern Oregon, in the United States. Draining an area of about , the Clackamas flows through mostly forested and rugged mountainous terrain in its upper reaches, a ...
and at Silver Falls State Park where the falls plunge over multiple layers of the Grande Ronde basalt. Evidence of eight flows can be found in the Tualatin Mountains
The Tualatin Mountains (also known as the West Hills or Southwest Hills of Portland) are a range on the western border of Multnomah County, Oregon, United States. A spur of the Northern Oregon Coast Range, they separate the Tualatin Basin of Was ...
on the west side of Portland.
Individual flows included large quantities of basalt. The McCoy Canyon flow of the Sentinel Bluffs Member released of basalt in layers of in thickness. The Umtanum flow has been estimated at in layers deep. The Pruitt Draw flow of the Teepee Butte Member released about with layers of basalt up to thick.
Wanapum Basalt
The Wanapum Basalt is made up of the Eckler Mountain Member (15.6 million years ago), the Frenchman Springs Member (15.5 million years ago), the Roza Member (14.9 million years ago) and the Priest Rapids Member (14.5 million years ago). They originated from vents betweenPendleton, Oregon
Pendleton is a city and the county seat of Umatilla County, Oregon. The population was 17,107 at the time of the 2020 census, which includes approximately 1,600 people who are incarcerated at Eastern Oregon Correctional Institution.
Pendleton ...
and Hanford, Washington.
The Frenchman Springs Member flowed along similar paths as the Grande Ronde basalts, but can be identified by different chemical characteristics. It flowed west to the Pacific, and can be found in the Columbia Gorge, along the upper Clackamas River, the hills south of Oregon City
)
, image_skyline = McLoughlin House.jpg
, imagesize =
, image_caption = The McLoughlin House, est. 1845
, image_flag =
, image_seal = Oregon City seal.png
, image_map ...
. and as far west as Yaquina Head near Newport, Oregon
Newport is a city in Lincoln County, Oregon, United States. It was incorporated in 1882, though the name dates back to the establishment of a post office in 1868. Newport was named for Newport, Rhode Island. As of the 2010 census, the city h ...
– a distance of .
Saddle Mountains Basalt
The Saddle Mountains Basalt, seen prominently at theSaddle Mountains
The Saddle Mountains consists of an upfolded anticline ridge of basalt in Grant County of central Washington state. The ridge, reaching to 2,700 feet, terminates in the east south of Othello, Washington near the foot of the Drumheller Channe ...
, is made up of the Umatilla Member flows, the Wilbur Creek Member flows, the Asotin Member flows (13 million years ago), the Weissenfels Ridge Member flows, the Esquatzel Member flows, the Elephant Mountain Member flows (10.5 million years ago), the Bujford Member flows, the Ice Harbor Member flows (8.5 million years ago) and the Lower Monumental Member flows (6 million years ago).
Related geologic structures
Oregon High Lava Plains
 observed that the Oregon High Lava Plains is a complementary system of propagating rhyolite eruptions, with the same point of origin. The two phenomena occurred concurrently, with the High Lava Plains propagating westward since ~10 Ma, while the Snake River Plains propagated eastward.
observed that the Oregon High Lava Plains is a complementary system of propagating rhyolite eruptions, with the same point of origin. The two phenomena occurred concurrently, with the High Lava Plains propagating westward since ~10 Ma, while the Snake River Plains propagated eastward.
See also
* Grand Coulee *Channeled scablands
The Channeled Scablands are a relatively barren and soil-free region of interconnected relict and dry flood channels, coulees and cataracts eroded into Palouse loess and the typically flat-lying basalt flows that remain after cataclysmic floods ...
* Wallula Gap
Wallula Gap () is a large water gap of the Columbia River in the northwest United States in southeast Washington. It cuts through the Horse Heaven Hills basalt anticlines in the Columbia River Basin, just south of the confluence of the Wa ...
* Interior Plateau
The Interior Plateau comprises a large region of the Interior of British Columbia, and lies between the Cariboo and Monashee Mountains on the east, and the Hazelton Mountains, Coast Mountains and Cascade Range on the west.''Landforms of British C ...
* Basin and Range Province
The Basin and Range Province is a vast physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, characterized by abrupt changes in elevation, alternating ...
References
Sources
* * Not WP:RS. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
USGS - Page on Columbia Plateau
- ''(source of much of this page)''
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20080514031955/http://volcano.und.edu/vwdocs/volc_images/north_america/crb.html Volcano World: page on Columbia River Flood Basalt Province {{Volcanoes of Oregon Large igneous provinces Miocene volcanism Pliocene volcanism Plateaus of the United States Volcanism of Idaho Volcanism of Oregon Volcanism of Washington (state) Columbia River Yellowstone hotspot Miocene geology Pliocene geology Paleogene United States Geologic provinces of the United States