Coccidioidomycosis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Coccidioidomycosis (, ), commonly known as cocci, Valley fever, as well as California fever, desert rheumatism, or San Joaquin Valley fever, is a mammalian fungal disease caused by '' Coccidioides immitis'' or ''
disseminated coccidioidomycosis
Therefore, coccidioidomycosis may be divided into the following types: :* Acute coccidioidomycosis, sometimes described in literature as primary pulmonary coccidioidomycosis :* Chronic coccidioidomycosis :*
 An estimated 60% of people infected with the fungi responsible for coccidioidomycosis have minimal to no symptoms, while 40% will have a range of possible clinical symptoms. Of those who do develop symptoms, the primary infection is most often respiratory, with symptoms resembling
An estimated 60% of people infected with the fungi responsible for coccidioidomycosis have minimal to no symptoms, while 40% will have a range of possible clinical symptoms. Of those who do develop symptoms, the primary infection is most often respiratory, with symptoms resembling

 Rain starts the cycle of initial growth of the fungus in the soil. In soil (and in agar media), ''Coccidioides'' exist in filament form. It forms
Rain starts the cycle of initial growth of the fungus in the soil. In soil (and in agar media), ''Coccidioides'' exist in filament form. It forms
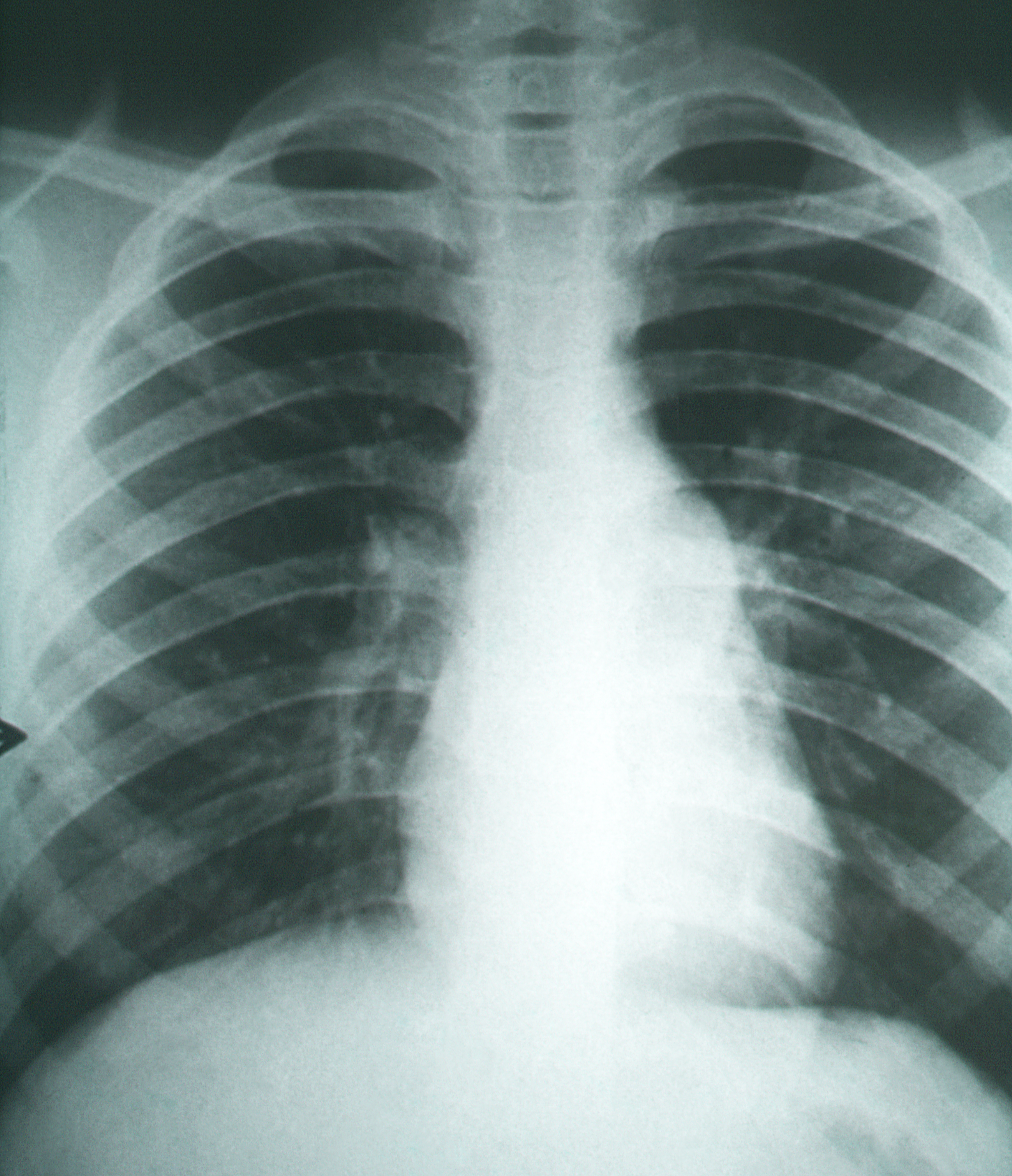 Coccidioidomycosis diagnosis relies on a combination of an infected person's signs and symptoms, findings on radiographic imaging, and laboratory results.
The disease is commonly misdiagnosed as bacterial community-acquired pneumonia. The fungal infection can be demonstrated by microscopic detection of diagnostic cells in body fluids, exudates,
Coccidioidomycosis diagnosis relies on a combination of an infected person's signs and symptoms, findings on radiographic imaging, and laboratory results.
The disease is commonly misdiagnosed as bacterial community-acquired pneumonia. The fungal infection can be demonstrated by microscopic detection of diagnostic cells in body fluids, exudates, 
 Valley fever is not contagious.
In dogs, the most common symptom of coccidioidomycosis is a chronic cough, which can be dry or moist. Other symptoms include fever (in approximately 50% of cases), weight loss, anorexia, lethargy, and depression. The disease can disseminate throughout the dog's body, most commonly causing
Valley fever is not contagious.
In dogs, the most common symptom of coccidioidomycosis is a chronic cough, which can be dry or moist. Other symptoms include fever (in approximately 50% of cases), weight loss, anorexia, lethargy, and depression. The disease can disseminate throughout the dog's body, most commonly causing
Image:Spherule and endospore forms of Coccidioides immitis 01ee057 lores.jpg, Spherule and endospore forms of Coccidioides immitis
Image:Mature spherule with endospores of Coccidioides immitis PHIL 480.tif, Mature spherule with endospores of Coccidioides immitis
U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention page on coccidioidomycosis
{{Mycoses Biological weapons Animal fungal diseases Neglected American diseases Fungal diseases
Coccidioides posadasii
''Coccidioides posadasii'' is a pathogenic fungus that, along with ''Coccidioides immitis'', is the causative agent of coccidioidomycosis, or valley fever in humans. It resides in the soil in certain parts of the Southwestern United States ...
''. Coccidioidomycosis is endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
in certain parts of the United States in Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
, California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. N ...
, New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
, Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to its ...
, and northern Mexico.
''C. immitis'' is a dimorphic saprophytic fungus that grows as a mycelium
Mycelium (plural mycelia) is a root-like structure of a fungus consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. Fungal colonies composed of mycelium are found in and on soil and many other substrates. A typical single spore germinates ...
in the soil and produces a spherule
A sphere () is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the ...
form in the host organism. It resides in the soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former ...
in certain parts of the southwestern United States, most notably in California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
and Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
. It is also commonly found in northern Mexico, and parts of Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known a ...
and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
. ''C. immitis'' is dormant during long dry spells, then develops as a mold
A mold () or mould () is one of the structures certain fungi can form. The dust-like, colored appearance of molds is due to the formation of spores containing fungal secondary metabolites. The spores are the dispersal units of the fungi. Not ...
with long filaments that break off into airborne spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, ...
s when it rains. The spores, known as arthroconidia, are swept into the air by disruption of the soil, such as during construction, farming, low-wind or singular dust events, or an earthquake. Windstorms may also cause epidemics far from endemic areas. In December 1977, a windstorm in an endemic area around Arvin, California led to several hundred cases, including deaths, in non-endemic areas hundreds of miles away.
Coccidioidomycosis is a common cause of community-acquired pneumonia in the endemic areas of the United States. Infections usually occur due to inhalation of the arthroconidial spores after soil disruption. The disease is not contagious. In some cases the infection may recur or become chronic.
It was reported in 2022 that valley fever had been increasing in California's Central Valley for years (1,000 cases in Kern county in 2014, 3,000 in 2021); experts said that cases could rise across the American west as the climate makes the landscape drier and hotter. Article gives judgement of medical director and earth system scientist.
Classification
After ''Coccidioides'' infection, coccidioidomycosis begins with Valley fever, which is its initial acute form. Valley fever may progress to the chronic form and then tdisseminated coccidioidomycosis
Therefore, coccidioidomycosis may be divided into the following types: :* Acute coccidioidomycosis, sometimes described in literature as primary pulmonary coccidioidomycosis :* Chronic coccidioidomycosis :*
Disseminated coccidioidomycosis
Disseminated coccidioidomycosis is a systemic infection with ''Coccidioides immitis'', in which 15-20% of people develop skin lesions.
See also
* Coccidioidomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis (, ), commonly known as cocci, Valley fever, as well as C ...
, which includes primary cutaneous coccidioidomycosis
Primary cutaneous coccidioidomycosis is a skin condition caused by Coccidioides immitis following a definite history of inoculation or a colonized splinter found in the skin lesion.
See also
* Coccidioidomycosis
* List of cutaneous conditions
...
Valley fever is not a contagious disease
A contagious disease is an infectious disease that is readily spread (that is, communicated) by transmission of a pathogen through contact (direct or indirect) with an infected person.
A disease is often known to be contagious before medical ...
.
Signs and symptoms
 An estimated 60% of people infected with the fungi responsible for coccidioidomycosis have minimal to no symptoms, while 40% will have a range of possible clinical symptoms. Of those who do develop symptoms, the primary infection is most often respiratory, with symptoms resembling
An estimated 60% of people infected with the fungi responsible for coccidioidomycosis have minimal to no symptoms, while 40% will have a range of possible clinical symptoms. Of those who do develop symptoms, the primary infection is most often respiratory, with symptoms resembling bronchitis
Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi (large and medium-sized airways) in the lungs that causes coughing. Bronchitis usually begins as an infection in the nose, ears, throat, or sinuses. The infection then makes its way down to the bronchi. ...
or pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severit ...
that resolve over a matter of a few weeks. In endemic regions, coccidioidomycosis is responsible for 20% of cases of community-acquired pneumonia. Notable coccidioidomycosis signs and symptoms include a profound feeling of tiredness, loss of smell and taste, fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
, cough, headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
s, rash
A rash is a change of the human skin which affects its color, appearance, or texture.
A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, c ...
, muscle pain, and joint pain. Fatigue can persist for many months after initial infection. The classic triad of coccidioidomycosis known as "desert rheumatism" includes the combination of fever, joint pains, and erythema nodosum
Erythema nodosum (EN) is an inflammatory condition characterized by inflammation of the fat cells under the skin, resulting in tender red nodules or lumps that are usually seen on both shins. It can be caused by a variety of conditions, and typi ...
.
A minority (3–5%) of infected individuals do not recover from the initial acute infection and develop a chronic infection. This can take the form of chronic lung infection or widespread disseminated infection (affecting the tissues lining the brain, soft tissues, joints, and bone). Chronic infection is responsible for most of the morbidity and mortality. Chronic fibrocavitary disease is manifested by cough (sometimes productive of mucus), fevers, night sweats and weight loss. Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the ...
, including involvement of the spine, and meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion or ...
may occur months to years after initial infection. Severe lung disease may develop in HIV-infected persons.
Complications
Serious complications may occur in patients who have weakened immune systems, including severepneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severit ...
with respiratory failure and bronchopleural fistulas requiring resection, lung nodules, and possible disseminated form, where the infection spreads throughout the body. The disseminated form of coccidioidomycosis can devastate the body, causing skin ulcers, abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends ...
es, bone lesions, swollen joints with severe pain, heart inflammation, urinary tract
The urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, c ...
problems, and inflammation of the brain's lining, which can lead to death.
Cause
hypha
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium.
Structure
A hypha consists of one or ...
e in both horizontal and vertical directions. Over a prolonged dry period, cells within hyphae degenerate to form alternating barrel-shaped cells ( arthroconidia) which are light in weight and carried by air currents. This happens when the soil is disturbed, often by clearing trees, construction or farming. As the population grows, so do all these activities, causing a potential cascade effect. The more land that is cleared and the more arid the soil, the riper the environment for ''Coccidioides''. These spores can be easily inhaled unknowingly. On reaching alveoli Alveolus (; pl. alveoli, adj. alveolar) is a general anatomical term for a concave cavity or pit.
Uses in anatomy and zoology
* Pulmonary alveolus, an air sac in the lungs
** Alveolar cell or pneumocyte
** Alveolar duct
** Alveolar macrophage
* M ...
they enlarge in size to become spherules, and internal septations develop. This division of cells is made possible by the optimal temperature inside the body. Septations develop and form endospore
An endospore is a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by some bacteria in the phylum Bacillota. The name "endospore" is suggestive of a spore or seed-like form (''endo'' means 'within'), but it is not a true spore (i.e., n ...
s within the spherule. Rupture of spherules release these endospores, which in turn repeat the cycle and spread the infection to adjacent tissues within the body of the infected individual. Nodules can form in lungs surrounding these spherules. When they rupture, they release their contents into bronchi, forming thin-walled cavities. These cavities can cause symptoms including characteristic chest pain, coughing up blood, and persistent cough. In individuals with a weakened immune system, the infection can spread through the blood. The fungus can also, rarely, enter the body through a break in the skin and cause infection.
Diagnosis
 Coccidioidomycosis diagnosis relies on a combination of an infected person's signs and symptoms, findings on radiographic imaging, and laboratory results.
The disease is commonly misdiagnosed as bacterial community-acquired pneumonia. The fungal infection can be demonstrated by microscopic detection of diagnostic cells in body fluids, exudates,
Coccidioidomycosis diagnosis relies on a combination of an infected person's signs and symptoms, findings on radiographic imaging, and laboratory results.
The disease is commonly misdiagnosed as bacterial community-acquired pneumonia. The fungal infection can be demonstrated by microscopic detection of diagnostic cells in body fluids, exudates, sputum
Sputum is mucus that is coughed up from the lower airways (the trachea and bronchi). In medicine, sputum samples are usually used for a naked eye examination, microbiological investigation of respiratory infections and cytological investigatio ...
and biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a dise ...
tissue by methods of Papanicolaou or Grocott's methenamine silver stain
In pathology, the Grocott-Gomori's (or Gömöri) methenamine silver stain, abbreviated GMS, is a popular staining method in histology. The stain was originally named after György Gömöri, the Hungarian physician who developed the stain.
It is ...
ing. These stains can demonstrate spherules and surrounding inflammation.
With specific nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecu ...
primers, ''C. immitis'' DNA can be amplified by polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) ...
(PCR). It can also be detected in culture by morphological identification or by using molecular probes that hybridize with ''C. immitis'' RNA. ''C. immitis'' and ''C. posadasii'' cannot be distinguished on cytology or by symptoms, but only by DNA PCR.
An indirect demonstration of fungal infection can be achieved also by serologic analysis detecting fungal antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respon ...
or host IgM or IgG
Immunoglobulin G (Ig G) is a type of antibody. Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies in humans, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. Each IgG an ...
antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of t ...
produced against the fungus. The available tests include the tube-precipitin (TP) assays, complement fixation assays, and enzyme immunoassays. TP antibody is not found in cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the ...
(CSF). TP antibody is specific and is used as a confirmatory test, whereas ELISA is sensitive and thus used for initial testing.
If the meninges are affected, CSF will show abnormally low glucose levels, an increased level of protein, and lymphocytic pleocytosis. Rarely, CSF eosinophilia is present.

Imaging
Chest X-rays
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
rarely demonstrate nodules or cavities in the lungs, but these images commonly demonstrate lung opacification, pleural effusion
A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung.
Under normal conditions, pleural fluid is secreted by the parietal pleural capillaries at a rate of 0.6 millilitre per k ...
s, or enlargement of lymph nodes associated with the lungs. Computed tomography scans of the chest are more sensitive than chest X-rays to detect these changes.
Prevention
Preventing Valley fever is challenging because it is difficult to avoid breathing in the fungus should it be present; however, the public health effect of the disease is essential to understand in areas where the fungus is endemic. Enhancing surveillance of coccidioidomycosis is key to preparedness in the medical field in addition to improving diagnostics for early infections. Currently there are no completely effective preventive measures available for people who live or travel through Valley fever-endemic areas. Recommended preventive measures include avoiding airborne dust or dirt, but this does not guarantee protection against infection. People in certain occupations may be advised to wear face masks. The use of air filtration indoors is also helpful, in addition to keeping skin injuries clean and covered to avoid skin infection. In 1998–2011, there were 111,117 cases of coccidioidomycosis in the U.S. that were logged into the National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System (NNDSS). Since many U.S. states do not require reporting of coccidioidomycosis, the actual numbers may be higher. The United States' Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) called the disease a "silent epidemic" and acknowledged that there is no proven anticoccidioidal vaccine available. A 2001cost-effectiveness analysis
Cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA) is a form of economic analysis that compares the relative costs and outcomes (effects) of different courses of action. Cost-effectiveness analysis is distinct from cost–benefit analysis, which assigns a monetar ...
indicated that a potential vaccine could improve health as well as reducing total health care expenditures among infants, teens, and immigrant adults, and more modestly improve health but increase total health care expenditures in older age groups.
Raising both surveillance and awareness of the disease while medical researchers are developing a human vaccine can positively contribute towards prevention efforts. Research demonstrates that patients from endemic areas who are aware of the disease are most likely to request diagnostic testing for coccidioidomycosis. Presently, Meridian Bioscience manufactures the so-called ''EIA test'' to diagnose the Valley fever, which however is known for producing a fair quantity of false positives. Currently, recommended prevention measures can include type-of-exposure-based respirator protection for persons engaged in agriculture, construction and others working outdoors in endemic areas. Dust control measures such as planting grass and wetting the soil, and also limiting exposure to dust storms are advisable for residential areas in endemic regions.
Treatment
Significant disease develops in fewer than 5% of those infected and typically occurs in those with a weakened immune system. Mild asymptomatic cases often do not require any treatment. Those with severe symptoms may benefit from antifungal therapy, which requires 3–6 months or more of treatment depending on the response to the treatment. There is a lack of prospective studies that examine optimal antifungal therapy for coccidioidomycosis. On the whole, oralfluconazole
Fluconazole is an antifungal medication used for a number of fungal infections. This includes candidiasis, blastomycosis, coccidiodomycosis, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, dermatophytosis, and pityriasis versicolor. It is also used to prev ...
and intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrie ...
amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcosis ...
are used in progressive or disseminated disease, or in immunocompromised individuals. Amphotericin B was originally the only available treatment, but alternatives, including itraconazole and ketoconazole
Ketoconazole, sold under the brand name Nizoral among others, is an antiandrogen and antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. Applied to the skin it is used for fungal skin infections such as tinea, cutaneous ca ...
, became available for milder disease. Fluconazole is the preferred medication for coccidioidal meningitis, due to its penetration into CSF. Intrathecal or intraventricular amphotericin B therapy is used if infection persists after fluconazole treatment. Itraconazole is used for cases that involve treatment of infected person's bones and joints. The antifungal medications posaconazole
Posaconazole, sold under the brand name Noxafil among others, is a triazole antifungal medication.
It was approved for medical use in the United States in September 2006, and is available as a generic medication.
Medical uses
Posaconazole is u ...
and voriconazole
Voriconazole, sold under the brand name Vfend among others, is an antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. This includes aspergillosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, penicilliosis, and infections by ' ...
have also been used to treat coccidioidomycosis. Because the symptoms of coccidioidomycosis are similar to the common flu, pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severit ...
, and other respiratory diseases, it is important for public health professionals to be aware of the rise of coccidioidomycosis and the specifics of diagnosis. Greyhound
The English Greyhound, or simply the Greyhound, is a breed of dog, a sighthound which has been bred for coursing, greyhound racing and hunting. Since the rise in large-scale adoption of retired racing Greyhounds, the breed has seen a resurgenc ...
dogs often get coccidioidomycosis; their treatment regimen involves 6–12 months of ketoconazole taken with food.
A particular severe case of meningitis caused by valley fever initially received several incorrect diagnoses such as sinus infections and cluster headaches. The patient became unable to work during diagnosis and original search for treatments. Eventually the right treatment was found—albeit with severe side effects—requiring four pills a day and medication administered directly into the brain every 16 weeks.
Toxicity
Conventional ''amphotericin B desoxycholate
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcosis. Fo ...
'' (AmB: used since the 1950s as a primary agent) is known to be associated with increased drug-induced nephrotoxicity impairing kidney function. Other formulations have been developed such as lipid-soluble formulations to mitigate side-effects such as direct proximal and distal tubular cytotoxicity
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are an immune cell or some types of venom, e.g. from the puff adder (''Bitis arietans'') or brown recluse spider (''Loxosceles reclusa'').
Cell physiology
Treating c ...
. These include liposomal amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcos ...
, ''amphotericin B lipid complex'' such as Abelcet (brand) ''amphotericin B phospholipid complex'' also as ''AmBisome Intravenous'', or ''Amphotec Intravenous'' (Generic; Amphotericin B Cholesteryl Sul), and ''amphotericin B colloidal dispersion'', all shown to exhibit a decrease in nephrotoxicity. The latter was not as effective in one study as ''amphotericin B desoxycholate'' which had a 50% murine
The Old World rats and mice, part of the subfamily Murinae in the family Muridae, comprise at least 519 species. Members of this subfamily are called murines. In terms of species richness, this subfamily is larger than all mammal families ex ...
(rat and mouse) morbidity rate versus zero for the AmB colloidal dispersion.
The cost of the nephrotoxic AmB deoxycholate, in 2015, for a patient of at 1 mg/kg/day dosage, was approximately US$63.80, compared to $1318.80 for 5 mg/kg/day of the less toxic liposomal AmB.
Epidemiology
Coccidioidomycosis is endemic to the western hemisphere between 40°N and 40°S. The ecological niches are characterized by hot summers and mild winters with an annual rainfall of 10–50 cm. The species are found in alkaline sandy soil, typically 10–30 cm below the surface. In harmony with the mycelium life cycle, incidence increases with periods of dryness after a rainy season; this phenomenon, termed "grow and blow", refers to growth of the fungus in wet weather, producing spores which are spread by the wind during succeeding dry weather. While the majority of cases are observed in the endemic region, cases reported outside the area are generally visitors, who contact the infection and return to their native areas before becoming symptomatic.North America
In the United States, ''C. immitis'' is endemic to southern and central California with the highest presence in theSan Joaquin Valley
The San Joaquin Valley ( ; es, Valle de San Joaquín) is the area of the Central Valley of the U.S. state of California that lies south of the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta and is drained by the San Joaquin River. It comprises seven ...
. ''C. posadassi'' is most prevalent in Arizona, although it can be found in a wider region spanning from Utah, New Mexico, Texas, and Nevada. An estimated 150,000 infections occur annually, with 25,000 new infections occurring every year. The incidence of coccidioidomycosis in the United States in 2011 (42.6 per 100,000) was almost ten times higher than the incidence reported in 1998 (5.3 per 100,000). In area where it is most prevalent, the infection rate is 2-4%.
Incidence varies widely across the west and southwest. In Arizona, for instance, in 2007, there were 3,450 cases in Maricopa County
Maricopa County is in the south-central part of the U.S. state of Arizona. As of the 2020 census, the population was 4,420,568, making it the state's most populous county, and the fourth-most populous in the United States. It contains about ...
, which in 2007 had an estimated population of 3,880,181 for an incidence of approximately 1 in 1,125. In contrast, though southern New Mexico is considered an endemic region, there were 35 cases in the entire state in 2008 and 23 in 2007, in a region that had an estimated 2008 population of 1,984,356, for an incidence of approximately 1 in 56,695.
Infection rates vary greatly by county, and although population density is important, so are other factors that have not been proven yet. Greater construction activity may disturb spores in the soil. In addition, the effect of altitude on fungi growth and morphology has not been studied, and altitude can range from sea level to 10,000 feet or higher across California, Arizona, Utah and New Mexico.
In California from 2000 to 2007, there were 16,970 reported cases (5.9 per 100,000 people) and 752 deaths of the 8,657 people hospitalized. The highest incidence was in the San Joaquin Valley with 76% of the 16,970 cases (12,855) occurring in the area. Following the 1994 Northridge earthquake
The 1994 Northridge earthquake was a moment 6.7 (), blind thrust earthquake that occurred on January 17, 1994, at 4:30:55 a.m. PST in the San Fernando Valley region of the City of Los Angeles.
The quake had a duration of approximately 1 ...
, there was a sudden increase of cases in the areas affected by the quake, at a pace of over 10 times baseline.
There was an outbreak in the summer of 2001 in Colorado, away from where the disease was considered endemic. A group of archeologists visited Dinosaur National Monument
Dinosaur National Monument is an American national monument located on the southeast flank of the Uinta Mountains on the border between Colorado and Utah at the confluence of the Green and Yampa rivers. Although most of the monument area is i ...
, and eight members of the crew, along with two National Park Service workers were diagnosed with Valley fever.
California state prisons, beginning in 1919, have been particularly affected by coccidioidomycosis. In 2005 and 2006, the Pleasant Valley State Prison near Coalinga and Avenal State Prison near Avenal
Avenal (Spanish for "Oat field") is a city in Kings County, California, United States. Avenal is located southwest of Hanford, at an elevation of . It is part of the Hanford– Corcoran Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA Code 25260), which e ...
on the western side of the San Joaquin Valley
The San Joaquin Valley ( ; es, Valle de San Joaquín) is the area of the Central Valley of the U.S. state of California that lies south of the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta and is drained by the San Joaquin River. It comprises seven ...
had the highest incidence in 2005, of at least 3,000 per 100,000. The receiver appointed in ''Plata v. Schwarzenegger
''Plata v. Newsom'', Docket No. 4:01-cv-01351-JST ( N.D. Cal.), is a federal class action civil rights lawsuit alleging that the California Department of Corrections and Rehabilitation's (CDCR) medical services are inadequate and violate the Eig ...
'' issued an order in May 2013 requiring relocation of vulnerable populations in those prisons.
The incidence rate has been increasing, with rates as high as 7% during 2006–2010. The cost of care and treatment is $23 million in California prisons. A lawsuit was filed against the state in 2014 on behalf of 58 inmates stating that the Avenal and Pleasant valley state prisons did not take necessary steps to prevent infections.
Population risk factors
There are several populations that have a higher risk for contracting coccidioidomycosis and developing the advanced disseminated version of the disease. Populations with exposure to the airborne arthroconidia working in agriculture and construction have a higher risk. Outbreaks have also been linked to earthquakes, windstorms and military training exercises where the ground is disturbed. Historically, an infection is more likely to occur in males than females, although this could be attributed to occupation rather than being sex-specific. Women who are pregnant and immediately postpartum are at a high risk of infection and dissemination. There is also an association between stage of pregnancy and severity of the disease, with third trimester women being more likely to develop dissemination. Presumably this is related to highly elevated hormonal levels, which stimulate growth and maturation of spherules and subsequent release of endospores. Certain ethnic populations are more susceptible to disseminated coccidioidomycosis. The risk of dissemination is 175 times greater in Filipinos and 10 times greater in African Americans than non-Hispanic whites. Individuals with a weakened immune system are also more susceptible to the disease. In particular, individuals with HIV and diseases that impairT-cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
function. Individuals with pre-existing conditions such as diabetes are also at a higher risk. Age also affects the severity of the disease, with more than one-third of deaths being in the 65-84 age group.
History
The first case of what was later named coccidioidomycosis was described in 1892 inBuenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
by Alejandro Posadas
Alejandro Posadas (December 28, 1870 – November 21, 1902) was an Argentinian physician and surgeon specializing in pediatric surgery. He was the first person to film an operation and brought the first x-ray to the country of Argentina.
Posadas ...
, a medical intern at the Hospital de Clínicas "José de San Martín"
The Hospital de Clínicas "José de San Martín" is a teaching hospital located in Buenos Aires, Argentina. It belongs to the University of Buenos Aires (UBA) Faculty of Medical Sciences, currently the best ranked university in that country.
H ...
. Posadas established an infectious character of the disease after being able to transfer it in laboratory conditions to lab animals. In the U.S., Dr. E. Rixford, a physician from a San Francisco hospital, and T. C. Gilchrist, a pathologist at Johns Hopkins Medical School, became early pioneers of clinical studies of the infection. They decided that the causative organism was a ''Coccidia
Coccidia (Coccidiasina) are a subclass of microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled obligate intracellular parasites belonging to the apicomplexan class Conoidasida.
As obligate intracellular parasites, they must live and reproduce within an a ...
''-type protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histo ...
n and named it ''Coccidioides immitis'' (resembling ''Coccidia'', not mild).
Dr. William Ophüls, a professor at Stanford University Hospital (San Francisco), discovered that the causative agent of the disease that was at first called ''Coccidioides'' infection and later coccidioidomycosis was a fungal pathogen, and coccidioidomycosis was also distinguished from Histoplasmosis and Blastomycosis
Blastomycosis or blasto is a fungal infection caused by inhaling spores of a ''Blastomyces'' fungus. Only about half of people with the disease have symptoms, which can include fever, cough, night sweats, muscle pains, weight loss, chest pain, ...
. Further, ''Coccidioides immitis'' was identified as the culprit of respiratory disorders previously called San Joaquin Valley fever, desert fever, and Valley fever, and a serum precipitin test was developed by Charles E. Smith that was able to detect an acute form of the infection. In retrospect, Smith played a major role in both medical research and raising awareness about coccidioidomycosis, especially when he became dean of the School of Public Health at the University of California at Berkeley in 1951.
''Coccidioides immitis'' was considered by the United States during the 1950s and 1960s as a potential biological weapon. The strain selected for investigation was designated with the military symbol OC, and initial expectations were for its deployment as a human incapacitant. Medical research suggested that OC might have had some lethal effects on the populace, and ''Coccidioides immitis'' started to be classified by the authorities as a threat to public health. However, ''Coccidioides immitis'' was never weaponized to the public's knowledge, and most of the military research in the mid-1960s was concentrated on developing a human vaccine. Currently, it is not on the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the U.S. federal government created to protect the health of all Americans and providing essential human services. Its motto is " ...
' or Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's list of select agents and toxins.
In 2002, ''Coccidioides posadasii
''Coccidioides posadasii'' is a pathogenic fungus that, along with ''Coccidioides immitis'', is the causative agent of coccidioidomycosis, or valley fever in humans. It resides in the soil in certain parts of the Southwestern United States ...
'' was identified as genetically distinct from ''Coccidioides immitis'' despite their morphologic similarities and can also cause coccidioidomycosis.
Research
As of 2013, there is no vaccine available to prevent infection with '' Coccidioides immitis'' or ''Coccidioides posadasii'', but efforts to develop such a vaccine are underway.Other animals
 Valley fever is not contagious.
In dogs, the most common symptom of coccidioidomycosis is a chronic cough, which can be dry or moist. Other symptoms include fever (in approximately 50% of cases), weight loss, anorexia, lethargy, and depression. The disease can disseminate throughout the dog's body, most commonly causing
Valley fever is not contagious.
In dogs, the most common symptom of coccidioidomycosis is a chronic cough, which can be dry or moist. Other symptoms include fever (in approximately 50% of cases), weight loss, anorexia, lethargy, and depression. The disease can disseminate throughout the dog's body, most commonly causing osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the ...
(infection of the bone), which leads to lameness. Dissemination can cause other symptoms, depending on which organs are infected. If the fungus infects the heart or pericardium
The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made ...
, it can cause heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, ...
and death.
In cats, symptoms may include skin lesions, fever, and loss of appetite, with skin lesions being the most common.
Other species in which Valley fever has been found include livestock such as cattle and horses; llamas; marine mammals, including sea otters; zoo animals such as monkeys and apes, kangaroos, tigers, etc.; and wildlife native to the geographic area where the fungus is found, such as cougars, skunks, and javelinas.
Additional images
In Popular Culture
* In the Season 1 episode of Bones called "The Man in the Fallout Shelter
"The Man in the Fallout Shelter" is the ninth episode of the first season of the television series, ''Bones''. Originally aired on December 13, 2005 on FOX network, the episode is written by Hart Hanson and directed by Greg Yaitanes. The plot feat ...
" the entire lab is exposed to coccidioidomycosis through inhalation of bone dust. Erroneously, the team is forced to quarantine in the lab on Christmas Eve to prevent the disease from spreading to the public (in real life, the disease is not contagious).
** The lab is later exposed to it again in the Season 2 episode "The Priest in the Churchyard
''Bones'' is an American crime drama television series that premiered on September 13, 2005, on Fox.
The show is based on forensic anthropology and forensic archaeology, with each episode focusing on an FBI case concerning the mystery behind ...
" from contaminated graveyard soil but only receives a series of injections rather than be forced to quarantine.
* '' Everything in Between'', a 2022 Australian feature film, contains references to coccidioidomycosis.
* In Doctor House, season 3 episode 4 "Line in the Sand", a 17 years old patient has a Coccidioides infection.
See also
* '' Coccidioides'' * '' Coccidioides immitis'' * ''Coccidioides posadasii
''Coccidioides posadasii'' is a pathogenic fungus that, along with ''Coccidioides immitis'', is the causative agent of coccidioidomycosis, or valley fever in humans. It resides in the soil in certain parts of the Southwestern United States ...
''
* Zygomycosis
* Medical geology
* List of cutaneous conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier agai ...
* ''Thunderhead'', a 1998 novel by Douglas Preston
Douglas Jerome Preston (born May 31, 1956) is an American journalist and author. Although he is best known for his thrillers in collaboration with Lincoln Child (including the '' Agent Pendergast'' series and ''Gideon Crew'' series), he has also ...
and Lincoln Child
Lincoln Child (13 October 1957) is an American author of techno-thriller and horror novels. Though he is most well known for his collaborations with Douglas Preston (including the Agent Pendergast series and the Gideon Crew series, among other ...
which uses the fungus and illness as a central plot point.
References
Further reading
* (Review). * (Review).External links
U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention page on coccidioidomycosis
{{Mycoses Biological weapons Animal fungal diseases Neglected American diseases Fungal diseases