Clock on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate
A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate
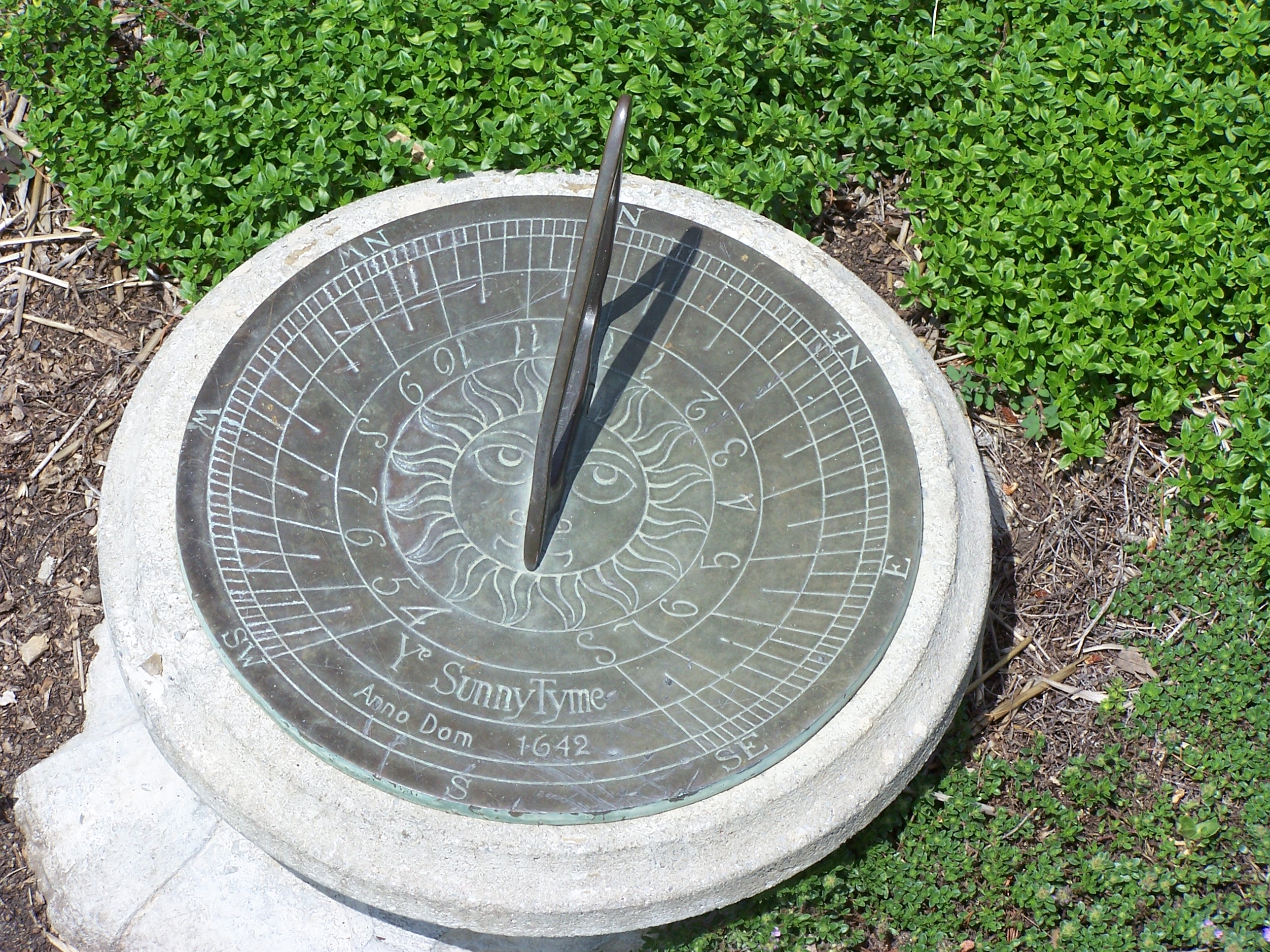 The apparent position of the Sun in the sky moves over the course of each day, reflecting the rotation of the Earth. Shadows cast by stationary objects move correspondingly, so their positions can be used to indicate the time of day. A sundial shows the time by displaying the position of a shadow on a (usually) flat surface, which has markings that correspond to the hours. Sundials can be horizontal, vertical, or in other orientations. Sundials were widely used in
The apparent position of the Sun in the sky moves over the course of each day, reflecting the rotation of the Earth. Shadows cast by stationary objects move correspondingly, so their positions can be used to indicate the time of day. A sundial shows the time by displaying the position of a shadow on a (usually) flat surface, which has markings that correspond to the hours. Sundials can be horizontal, vertical, or in other orientations. Sundials were widely used in
 Many devices can be used to mark the passage of time without respect to reference time (time of day, hours, minutes, etc.) and can be useful for measuring duration or intervals. Examples of such duration timers are candle clocks,
Many devices can be used to mark the passage of time without respect to reference time (time of day, hours, minutes, etc.) and can be useful for measuring duration or intervals. Examples of such duration timers are candle clocks,
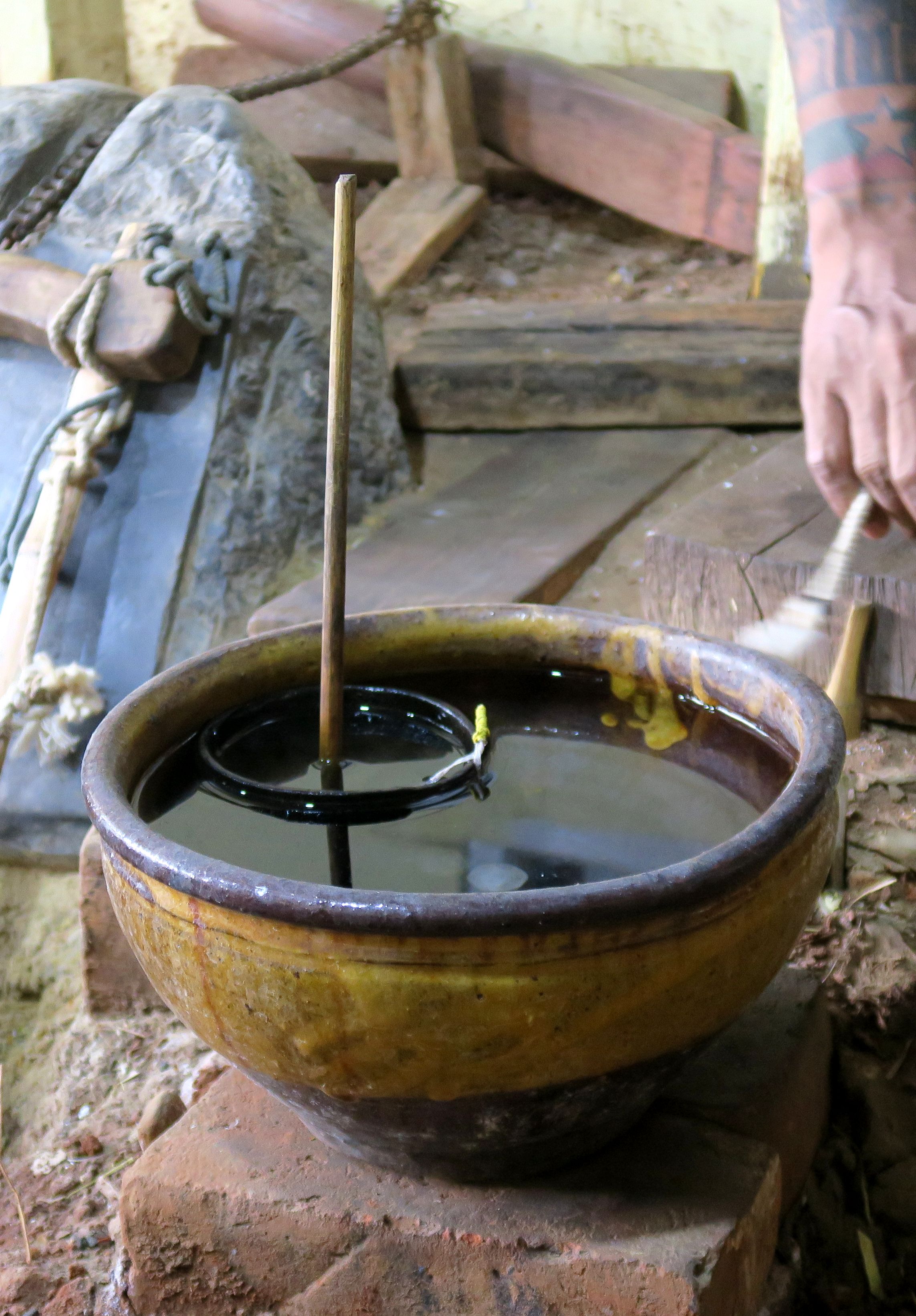 Water clocks, along with the sundials, are possibly the oldest time-measuring instruments, with the only exceptions being the day counting tally stick. Given their great antiquity, where and when they first existed is not known and is perhaps unknowable. The bowl-shaped outflow is the simplest form of a water clock and is known to have existed in Babylon and in Egypt around the 16th century BC. Other regions of the world, including India and China, also have early evidence of water clocks, but the earliest dates are less certain. Some authors, however, write about water clocks appearing as early as 4000 BC in these regions of the world.
Water clocks, along with the sundials, are possibly the oldest time-measuring instruments, with the only exceptions being the day counting tally stick. Given their great antiquity, where and when they first existed is not known and is perhaps unknowable. The bowl-shaped outflow is the simplest form of a water clock and is known to have existed in Babylon and in Egypt around the 16th century BC. Other regions of the world, including India and China, also have early evidence of water clocks, but the earliest dates are less certain. Some authors, however, write about water clocks appearing as early as 4000 BC in these regions of the world.
the Chinese developed their own advanced water clocks
��水鐘)in 725 AD, passing their ideas on to Korea and Japan. Some water clock designs were developed independently and some knowledge was transferred through the spread of trade. Pre-modern societies do not have the same precise timekeeping requirements that exist in modern industrial societies, where every hour of work or rest is monitored, and work may start or finish at any time regardless of external conditions. Instead, water clocks in ancient societies were used mainly for
 A water-powered cogwheel clock was created in China by
A water-powered cogwheel clock was created in China by  In the 13th century, Al-Jazari, an engineer from Mesopotamia (lived 1136–1206) who worked for
In the 13th century, Al-Jazari, an engineer from Mesopotamia (lived 1136–1206) who worked for
Clock that changed the world (H4, 1759) - Flickr - Tatters ❀.jpg, One mechanical clock
(was useful for sailing purposes) Mechanical digital clock.jpg, Mechanical digital clock
(with rolling numbers)
The word (from the Greek —'hour', and —'to tell') was used to describe early mechanical clocks, but the use of this word (still used in several  In Europe, between 1280 and 1320, there was an increase in the number of references to clocks and horologes in church records, and this probably indicates that a new type of clock mechanism had been devised. Existing clock mechanisms that used water power were being adapted to take their driving power from falling weights. This power was controlled by some form of oscillating mechanism, probably derived from existing bell-ringing or alarm devices. This controlled release of power – the escapement – marks the beginning of the true mechanical clock, which differed from the previously mentioned cogwheel clocks. Verge escapement mechanism derived in the surge of true mechanical clocks, which didn't need any kind of fluid power, like water or mercury, to work.
These mechanical clocks were intended for two main purposes: for signalling and notification (e.g. the timing of services and public events), and for modeling the solar system. The former purpose is administrative, the latter arises naturally given the scholarly interests in astronomy, science, astrology, and how these subjects integrated with the religious philosophy of the time. The astrolabe was used both by astronomers and astrologers, and it was natural to apply a clockwork drive to the rotating plate to produce a working model of the solar system.
Simple clocks intended mainly for notification were installed in towers, and did not always require faces or hands. They would have announced the canonical hours or intervals between set times of prayer. Canonical hours varied in length as the times of sunrise and sunset shifted. The more sophisticated astronomical clocks would have had moving dials or hands, and would have shown the time in various time systems, including Italian hours, canonical hours, and time as measured by astronomers at the time. Both styles of clock started acquiring extravagant features such as
In Europe, between 1280 and 1320, there was an increase in the number of references to clocks and horologes in church records, and this probably indicates that a new type of clock mechanism had been devised. Existing clock mechanisms that used water power were being adapted to take their driving power from falling weights. This power was controlled by some form of oscillating mechanism, probably derived from existing bell-ringing or alarm devices. This controlled release of power – the escapement – marks the beginning of the true mechanical clock, which differed from the previously mentioned cogwheel clocks. Verge escapement mechanism derived in the surge of true mechanical clocks, which didn't need any kind of fluid power, like water or mercury, to work.
These mechanical clocks were intended for two main purposes: for signalling and notification (e.g. the timing of services and public events), and for modeling the solar system. The former purpose is administrative, the latter arises naturally given the scholarly interests in astronomy, science, astrology, and how these subjects integrated with the religious philosophy of the time. The astrolabe was used both by astronomers and astrologers, and it was natural to apply a clockwork drive to the rotating plate to produce a working model of the solar system.
Simple clocks intended mainly for notification were installed in towers, and did not always require faces or hands. They would have announced the canonical hours or intervals between set times of prayer. Canonical hours varied in length as the times of sunrise and sunset shifted. The more sophisticated astronomical clocks would have had moving dials or hands, and would have shown the time in various time systems, including Italian hours, canonical hours, and time as measured by astronomers at the time. Both styles of clock started acquiring extravagant features such as

 The world's first fully mechanical water clock the 'Cosmic Engine', was invented by Su Song, a Chinese
The world's first fully mechanical water clock the 'Cosmic Engine', was invented by Su Song, a Chinese
Matthew Norman carriage clock with winding key.jpg, Matthew Norman carriage clock with winding key
1908 Gilbert mantel clock decorated with Memento Mori decoupage.JPG, Decorated William Gilbert mantel clock
Clockmakers developed their art in various ways. Building smaller clocks was a technical challenge, as was improving accuracy and reliability. Clocks could be impressive showpieces to demonstrate skilled craftsmanship, or less expensive, mass-produced items for domestic use. The escapement in particular was an important factor affecting the clock's accuracy, so many different mechanisms were tried.
Spring-driven clocks appeared during the 15th century, although they are often erroneously credited to 
 In 1815,
In 1815,
 The
The
 The timekeeping element in every modern clock is a harmonic oscillator, a physical object (resonator) that vibrates or oscillates repetitively at a precisely constant frequency.
* In mechanical clocks, this is either a pendulum or a
The timekeeping element in every modern clock is a harmonic oscillator, a physical object (resonator) that vibrates or oscillates repetitively at a precisely constant frequency.
* In mechanical clocks, this is either a pendulum or a

 * Synchronous electric clocks do not have an internal oscillator, but count cycles of the 50 or 60 Hz oscillation of the AC power line, which is synchronized by the utility to a precision oscillator. The counting may be done electronically, usually in clocks with digital displays, or, in analog clocks, the AC may drive a
* Synchronous electric clocks do not have an internal oscillator, but count cycles of the 50 or 60 Hz oscillation of the AC power line, which is synchronized by the utility to a precision oscillator. The counting may be done electronically, usually in clocks with digital displays, or, in analog clocks, the AC may drive a
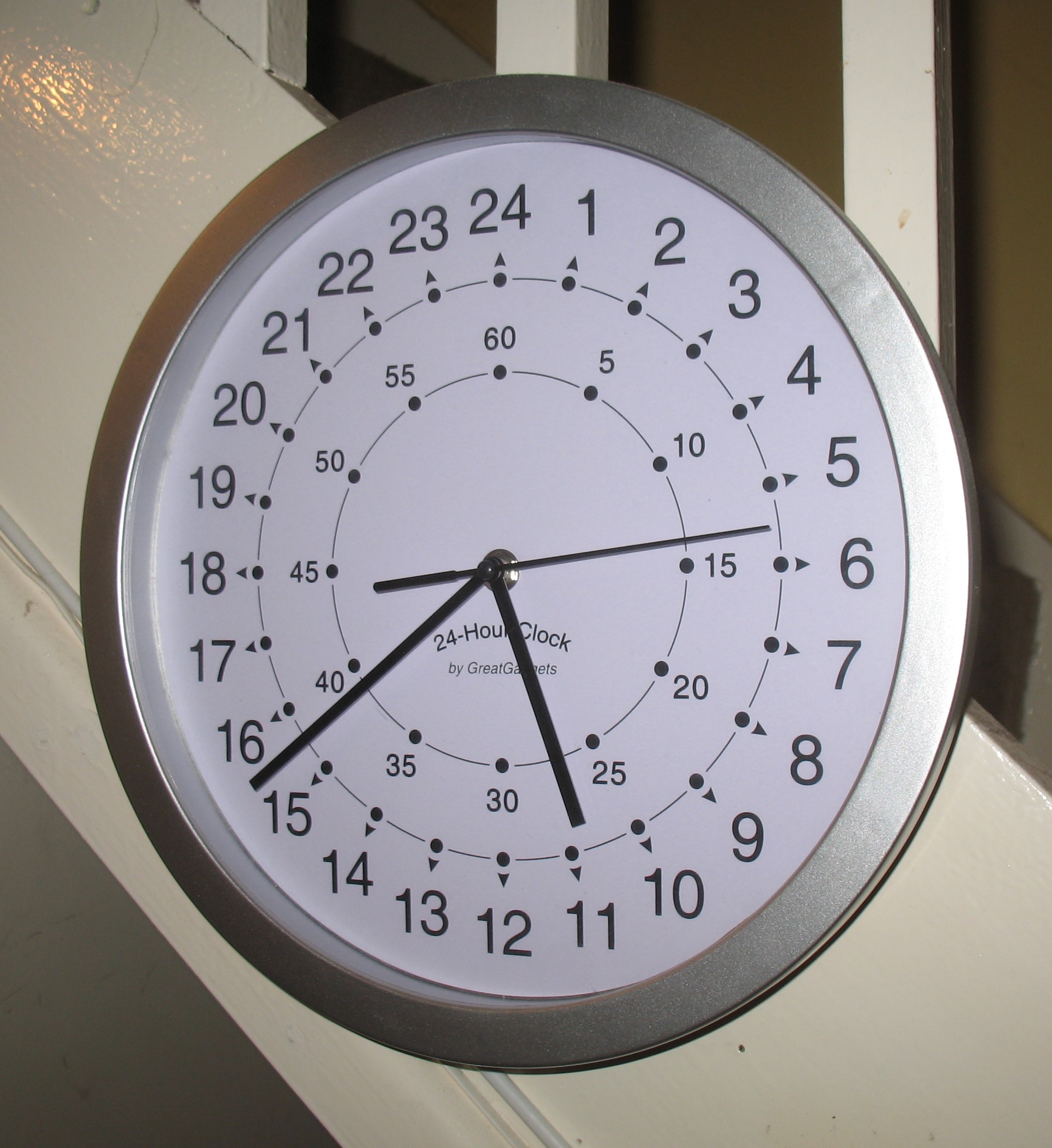

 Analog clocks usually use a clock face which indicates time using rotating pointers called "hands" on a fixed numbered dial or dials. The standard clock face, known universally throughout the world, has a short "hour hand" which indicates the hour on a circular dial of 12 hours, making two revolutions per day, and a longer "minute hand" which indicates the minutes in the current hour on the same dial, which is also divided into 60 minutes. It may also have a "second hand" which indicates the seconds in the current minute. The only other widely used clock face today is the 24 hour analog dial, because of the use of 24 hour time in military organizations and timetables. Before the modern clock face was standardized during the
Analog clocks usually use a clock face which indicates time using rotating pointers called "hands" on a fixed numbered dial or dials. The standard clock face, known universally throughout the world, has a short "hour hand" which indicates the hour on a circular dial of 12 hours, making two revolutions per day, and a longer "minute hand" which indicates the minutes in the current hour on the same dial, which is also divided into 60 minutes. It may also have a "second hand" which indicates the seconds in the current minute. The only other widely used clock face today is the 24 hour analog dial, because of the use of 24 hour time in military organizations and timetables. Before the modern clock face was standardized during the
Kanazawa Station Water Clock.jpg, Digital clock displaying time by controlling valves on the fountain
Digital-clock-radio-basic hf.jpg, Simplistic digital clock radio
Analog clock with digital display.png, Diagram of a mechanical digital display of a flip clock
Digital clocks display a numeric representation of time. Two numeric display formats are commonly used on digital clocks:
* the
 Word clocks are clocks that display the time visually using sentences. E.g.: "It's about three o'clock." These clocks can be implemented in hardware or software.
Word clocks are clocks that display the time visually using sentences. E.g.: "It's about three o'clock." These clocks can be implemented in hardware or software.
 Clocks are in homes, offices and many other places; smaller ones (watches) are carried on the wrist or in a pocket; larger ones are in public places, e.g. a railway station or church. A small clock is often shown in a corner of computer displays, mobile phones and many MP3 players.
The primary purpose of a clock is to ''display'' the time. Clocks may also have the facility to make a loud alert signal at a specified time, typically to waken a sleeper at a preset time; they are referred to as ''alarm clocks''. The alarm may start at a low volume and become louder, or have the facility to be switched off for a few minutes then resume. Alarm clocks with visible indicators are sometimes used to indicate to children too young to read the time that the time for sleep has finished; they are sometimes called ''training clocks''.
A clock mechanism may be used to ''control'' a device according to time, e.g. a central heating system, a
Clocks are in homes, offices and many other places; smaller ones (watches) are carried on the wrist or in a pocket; larger ones are in public places, e.g. a railway station or church. A small clock is often shown in a corner of computer displays, mobile phones and many MP3 players.
The primary purpose of a clock is to ''display'' the time. Clocks may also have the facility to make a loud alert signal at a specified time, typically to waken a sleeper at a preset time; they are referred to as ''alarm clocks''. The alarm may start at a low volume and become louder, or have the facility to be switched off for a few minutes then resume. Alarm clocks with visible indicators are sometimes used to indicate to children too young to read the time that the time for sleep has finished; they are sometimes called ''training clocks''.
A clock mechanism may be used to ''control'' a device according to time, e.g. a central heating system, a

National Association of Watch & Clock Collectors Museum
{{Authority control Time measurement systems Articles containing video clips


 A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate
A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, ...
. The clock is one of the oldest human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month and the year. Devices operating on several physical processes have been used over the millennia
A millennium (plural millennia or millenniums) is a period of one thousand years, sometimes called a kiloannum (ka), or kiloyear (ky). Normally, the word is used specifically for periods of a thousand years that begin at the starting point (ini ...
.
Some predecessors to the modern clock may be considered as "clocks" that are based on movement in nature: A sundial shows the time by displaying the position of a shadow on a flat surface. There is a range of duration timers, a well-known example being the hourglass. Water clocks, along with the sundials, are possibly the oldest time-measuring instruments. A major advance occurred with the invention of the verge escapement, which made possible the first mechanical clocks around 1300 in Europe, which kept time with oscillating timekeepers like balance wheel
A balance wheel, or balance, is the timekeeping device used in mechanical watches and small clocks, analogous to the pendulum in a pendulum clock. It is a weighted wheel that rotates back and forth, being returned toward its center position by a ...
s., pp. 103–104., p. 31.
Traditionally, in horology
Horology (; related to Latin '; ; , interfix ''-o-'', and suffix ''-logy''), . is the study of the measurement of time. Clocks, watches, clockwork, sundials, hourglasses, clepsydras, timers, time recorders, marine chronometers, and atomic clo ...
, the term ''clock'' was used for a striking clock, while a clock that did not strike the hours audibly was called a timepiece. This distinction is no longer made. Watch
A watch is a portable timepiece intended to be carried or worn by a person. It is designed to keep a consistent movement despite the motions caused by the person's activities. A wristwatch is designed to be worn around the wrist, attached b ...
es and other timepieces that can be carried on one's person are usually not referred to as clocks. Spring-driven clocks appeared during the 15th century. During the 15th and 16th centuries, clockmaking flourished. The next development in accuracy occurred after 1656 with the invention of the pendulum clock by Christiaan Huygens. A major stimulus to improving the accuracy and reliability of clocks was the importance of precise time-keeping for navigation. The mechanism of a timepiece with a series of gears driven by a spring or weights is referred to as clockwork
Clockwork refers to the inner workings of either mechanical devices called clocks and watches (where it is also called the movement) or other mechanisms that work similarly, using a series of gears driven by a spring or weight.
A clockwork mec ...
; the term is used by extension for a similar mechanism not used in a timepiece. The electric clock was patented in 1840, and electronic clocks were introduced in the 20th century, becoming widespread with the development of small battery-powered semiconductor devices.
The timekeeping element in every modern clock is a harmonic oscillator, a physical object (resonator
A resonator is a device or system that exhibits resonance or resonant behavior. That is, it naturally oscillates with greater amplitude at some frequencies, called resonant frequencies, than at other frequencies. The oscillations in a resonator ...
) that vibrates or oscillates at a particular frequency.
This object can be a pendulum
A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced sideways from its resting, equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward th ...
, a tuning fork
A tuning fork is an acoustic resonator in the form of a two-pronged fork with the prongs ( tines) formed from a U-shaped bar of elastic metal (usually steel). It resonates at a specific constant pitch when set vibrating by striking it agains ...
, a quartz crystal
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical form ...
, or the vibration of electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no ...
s in atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, ...
s as they emit microwaves.
Clocks have different ways of displaying the time. Analog clocks indicate time with a traditional clock face, with moving hands. Digital clocks display a numeric representation of time. Two numbering systems are in use: 12-hour time notation and 24-hour
The modern 24-hour clock, popularly referred to in the United States as military time, is the convention of timekeeping in which the day runs from midnight to midnight and is divided into 24 hours. This is indicated by the hours (and minutes) pass ...
notation. Most digital clocks use electronic mechanisms and LCD, LED, or VFD
VFD may refer to:
* Factory Workers' Union of Germany, (german: Verband der Fabrikarbeiter Deutschlands, link=no), a former trade union in Germany
* Vacuum fluorescent display, a display device on consumer electronics equipment
* Variable-freque ...
displays. For the blind and for use over telephones, speaking clock
A speaking clock or talking clock is a live or recorded human voice service, usually accessed by telephone, that gives the correct time. The first telephone speaking clock service was introduced in France, in association with the Paris Observ ...
s state the time audibly in words. There are also clocks for the blind that have displays that can be read by touch. The study of timekeeping is known as horology
Horology (; related to Latin '; ; , interfix ''-o-'', and suffix ''-logy''), . is the study of the measurement of time. Clocks, watches, clockwork, sundials, hourglasses, clepsydras, timers, time recorders, marine chronometers, and atomic clo ...
.
Etymology
The word ''clock'' derives from the medievalLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
word for 'bell'——and has cognates in many European languages. Clocks spread to England from the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
, so the English word came from the Middle Low German and Middle Dutch .
The word derives from the Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English ...
, Old North French , or Middle Dutch
Middle Dutch is a collective name for a number of closely related West Germanic dialects whose ancestor was Old Dutch. It was spoken and written between 1150 and 1500. Until the advent of Modern Dutch after 1500 or c. 1550, there was no overarc ...
, all of which mean 'bell', and stem from an Old Irish
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic ( sga, Goídelc, Ogham script: ᚌᚑᚔᚇᚓᚂᚉ; ga, Sean-Ghaeilge; gd, Seann-Ghàidhlig; gv, Shenn Yernish or ), is the oldest form of the Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive writt ...
root.
History of time-measuring devices
Sundials
ancient times
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history cov ...
. With the knowledge of latitude, a well-constructed sundial can measure local solar time
Solar time is a calculation of the passage of time based on the position of the Sun in the sky. The fundamental unit of solar time is the day, based on the synodic rotation period. Two types of solar time are apparent solar time (sundial ti ...
with reasonable accuracy, within a minute or two. Sundials continued to be used to monitor the performance of clocks until the 1830s, with the use of the telegraph and train to standardize time and time zones between cities.
Devices that measure duration, elapsed time and intervals
 Many devices can be used to mark the passage of time without respect to reference time (time of day, hours, minutes, etc.) and can be useful for measuring duration or intervals. Examples of such duration timers are candle clocks,
Many devices can be used to mark the passage of time without respect to reference time (time of day, hours, minutes, etc.) and can be useful for measuring duration or intervals. Examples of such duration timers are candle clocks, incense clock
The incense clock () is a timekeeping device that originated from China during the Song Dynasty (960-1279) and spread to neighboring East Asian countries such as Japan and Korea. The clocks' bodies are effectively specialized censers that hold i ...
s and the hourglass. Both the candle clock and the incense clock work on the same principle wherein the consumption of resources is more or less constant allowing reasonably precise and repeatable estimates of time passages. In the hourglass, fine sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class o ...
pouring through a tiny hole at a constant rate indicates an arbitrary, predetermined passage of time. The resource is not consumed but re-used.
Water clocks
 Water clocks, along with the sundials, are possibly the oldest time-measuring instruments, with the only exceptions being the day counting tally stick. Given their great antiquity, where and when they first existed is not known and is perhaps unknowable. The bowl-shaped outflow is the simplest form of a water clock and is known to have existed in Babylon and in Egypt around the 16th century BC. Other regions of the world, including India and China, also have early evidence of water clocks, but the earliest dates are less certain. Some authors, however, write about water clocks appearing as early as 4000 BC in these regions of the world.
Water clocks, along with the sundials, are possibly the oldest time-measuring instruments, with the only exceptions being the day counting tally stick. Given their great antiquity, where and when they first existed is not known and is perhaps unknowable. The bowl-shaped outflow is the simplest form of a water clock and is known to have existed in Babylon and in Egypt around the 16th century BC. Other regions of the world, including India and China, also have early evidence of water clocks, but the earliest dates are less certain. Some authors, however, write about water clocks appearing as early as 4000 BC in these regions of the world.
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
astronomer Andronicus of Cyrrhus
Andronicus of Cyrrhus or Andronicus Cyrrhestes ( grc-gre, Ἀνδρόνικος Κυρρήστου, ''Andrónikos Kyrrhēstou''), son of Hermias, was a Greek astronomer best known as the architect of the horologion at Athens called the Tower of t ...
supervised the construction of the Tower of the Winds
The Tower of the Winds or the Horologion of Andronikos Kyrrhestes is an octagonal Pentelic marble clocktower in the Roman Agora in Athens that functioned as a ''horologion'' or "timepiece". It is considered the world's first meteorological stat ...
in Athens in the 1st century B.C. The Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Roman civilizations advanced water clock design with improved accuracy. These advances were passed on through Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
and Islamic times, eventually making their way back to Europe. Independentlythe Chinese developed their own advanced water clocks
��水鐘)in 725 AD, passing their ideas on to Korea and Japan. Some water clock designs were developed independently and some knowledge was transferred through the spread of trade. Pre-modern societies do not have the same precise timekeeping requirements that exist in modern industrial societies, where every hour of work or rest is monitored, and work may start or finish at any time regardless of external conditions. Instead, water clocks in ancient societies were used mainly for
astrological
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Dif ...
reasons. These early water clocks were calibrated with a sundial. While never reaching the level of accuracy of a modern timepiece, the water clock was the most accurate and commonly used timekeeping device for millennia, until it was replaced by the more accurate pendulum clock in 17th-century Europe.
Islamic civilization is credited with further advancing the accuracy of clocks with elaborate engineering. In 797 (or possibly 801), the Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
of Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
, Harun al-Rashid, presented Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
with an Asian elephant named Abul-Abbas together with a "particularly elaborate example" of a water clock. Pope Sylvester II
Pope Sylvester II ( – 12 May 1003), originally known as Gerbert of Aurillac, was a French-born scholar and teacher who served as the bishop of Rome and ruled the Papal States from 999 to his death. He endorsed and promoted study of Arab and Gre ...
introduced clocks to northern and western Europe around 1000 AD.
Mechanical water clocks
The first knowngear
A gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth (called ''cogs''), which mesh with another (compatible) toothed part to transmit (convert) torque and speed. The basic ...
ed clock was invented by the great mathematician, physicist, and engineer Archimedes during the 3rd century BC. Archimedes created his astronomical clock that was also a cuckoo clock with birds singing and moving every hour. It is the first carillon clock as it plays music and simultaneously with a person blinking his eyes surprised by the singing birds. Archimedes clock works with a system of four weights, counter weights, and strings regulated by a system of floats in a water container with siphons that regulate the automatic continuation of the clock. The principles of this type of clocks are described by the mathematician and physicist Hero, who says that some of them work with a chain that turns a gear of the mechanism. Another Greek clock probably constructed at the time of Alexander was in Gaza, described by Procopius. The Gaza clock was probably a Meteoroskopeion, i.e. a building showing the celestial phenomena and the time. It had pointer for the time and some automations similar to the Archimedes clock. There were 12 doors opening one every hour with Hercules performing his labors, the Lion at one o'clock, etc., and at night a lamp becomes visible every hour, with 12 windows opening to show the time.
Yi Xing
Yi Xing (, 683–727), born Zhang Sui (), was a Chinese astronomer, Buddhist monk, inventor, mathematician, mechanical engineer, and philosopher during the Tang dynasty. His astronomical celestial globe featured a liquid-driven escapement, the ...
and Liang Lingzan
Liang Lingzan () was a Chinese artist, astronomer, inventor, mechanical engineer and politician of the Kaiyuan era during the Tang Dynasty. He invented a mechanized water clock with the Tantric monk and mathematician Yi Xing (). It was actually a ...
. This is not considered an escapement
An escapement is a mechanical linkage in mechanical watches and clocks that gives impulses to the timekeeping element and periodically releases the gear train to move forward, advancing the clock's hands. The impulse action transfers energy ...
mechanism clock as it was unidirectional, the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
and genius Su Song (1020–1101) incorporated it into his monumental innovation of the astronomical clock-tower of Kaifeng
Kaifeng () is a prefecture-level city in east-central Henan province, China. It is one of the Eight Ancient Capitals of China, having been the capital eight times in history, and is best known for having been the Chinese capital during the No ...
in 1088. His astronomical clock and rotating armillary sphere still relied on the use of either flowing water during the spring, summer, autumn seasons and liquid mercury during the freezing temperature of winter (i.e. hydraulics
Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counte ...
).
In Su Song's waterwheel linkwork device, the action of the escapement's arrest and release was achieved by gravity exerted periodically as the continuous flow of liquid filled containers of a limited size. In a single line of evolution, Su Song's clock therefore united the concept of the clepsydra and the mechanical clock into one device run by mechanics and hydraulics. In his memorial, Su Song wrote about this concept:According to your servant's opinion there have been many systems and designs for astronomical instruments during past dynasties all differing from one another in minor respects. But the principle of the use of water-power for the driving mechanism has always been the same. The heavens move without ceasing but so also does water flow (and fall). Thus if the water is made to pour with perfect evenness, then the comparison of the rotary movements (of the heavens and the machine) will show no discrepancy or contradiction; for the unresting follows the unceasing.Song was also strongly influenced by the earlier armillary sphere created by
Zhang Sixun
Zhang Sixun (, fl. 10th century) was a Chinese astronomer and mechanical engineer from Bazhong, Sichuan during the early Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD).Liu, 577. He is credited with creating an armillary sphere for his astronomical clock tower that ...
(976 AD), who also employed the escapement mechanism and used liquid mercury instead of water in the waterwheel of his astronomical clock tower.The mechanical clockworks for Su Song's astronomical tower featured a great driving-wheel that was 11 feet in diameter, carrying 36 scoops, into each of which water poured at a uniform rate from the "constant-level tank". The main driving shaft of iron, with its cylindrical necks supported on iron crescent-shaped bearings, ended in a pinion, which engaged a gear wheel at the lower end of the main vertical transmission shaft. This great astronomical hydromechanical clock tower was about ten metres high (about 30 feet) and featured a clock escapement
An escapement is a mechanical linkage in mechanical watches and clocks that gives impulses to the timekeeping element and periodically releases the gear train to move forward, advancing the clock's hands. The impulse action transfers energy ...
and was indirectly powered by a rotating wheel either with falling water and liquid mercury. A full-sized working replica of Su Song's clock exists in the Republic of China (Taiwan)'s National Museum of Natural Science, Taichung city. This full-scale, fully functional replica, approximately 12 meters (39 feet) in height, was constructed from Su Song's original descriptions and mechanical drawings. In the 13th century, Al-Jazari, an engineer from Mesopotamia (lived 1136–1206) who worked for
In the 13th century, Al-Jazari, an engineer from Mesopotamia (lived 1136–1206) who worked for Artuqid
The Artuqid dynasty (alternatively Artukid, Ortoqid, or Ortokid; , pl. ; ; ) was a Turkoman dynasty originated from tribe that ruled in eastern Anatolia, Northern Syria and Northern Iraq in the eleventh through thirteenth centuries. The Art ...
king of Diyar-Bakr, Nasir al-Din
Nasir al-Din ( ar, نصیر الدین or or , 'defender of the faith'), was originally a honorific title and is an Arabic masculine given name and surname. There are many variant spellings in English due to transliteration. Notable people with ...
, made numerous clocks of all shapes and sizes. The most reputed clocks included the elephant, scribe, and castle clocks, some of which have been successfully reconstructed. As well as telling the time, these grand clocks were symbols of status, grandeur and wealth of the Urtuq State.
Fully mechanical
(was useful for sailing purposes) Mechanical digital clock.jpg, Mechanical digital clock
(with rolling numbers)
Romance languages
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language ...
) for all timekeepers conceals the true nature of the mechanisms. For example, there is a record that in 1176 Sens Cathedral
Sens Cathedral (french: Cathédrale Saint-Étienne de Sens) is a Catholic cathedral in Sens in Burgundy, eastern France. The cathedral, dedicated to Saint Stephen, is the seat of the Archbishop of Sens.
Sens was the first cathedral to be built in ...
in France installed an ' horologe' but the mechanism used is unknown. According to Jocelyn de Brakelond, in 1198 during a fire at the abbey of St Edmundsbury (now Bury St Edmunds), the monks "ran to the clock" to fetch water, indicating that their water clock had a reservoir large enough to help extinguish the occasional fire. The word ''clock'' (via Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. In this region it served as the primary written language, though local languages were also written to varying degrees. Latin functione ...
from Old Irish
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic ( sga, Goídelc, Ogham script: ᚌᚑᚔᚇᚓᚂᚉ; ga, Sean-Ghaeilge; gd, Seann-Ghàidhlig; gv, Shenn Yernish or ), is the oldest form of the Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive writt ...
, both meaning 'bell'), which gradually supersedes "horologe", suggests that it was the sound of bells which also characterized the prototype mechanical clocks that appeared during the 13th century in Europe.
 In Europe, between 1280 and 1320, there was an increase in the number of references to clocks and horologes in church records, and this probably indicates that a new type of clock mechanism had been devised. Existing clock mechanisms that used water power were being adapted to take their driving power from falling weights. This power was controlled by some form of oscillating mechanism, probably derived from existing bell-ringing or alarm devices. This controlled release of power – the escapement – marks the beginning of the true mechanical clock, which differed from the previously mentioned cogwheel clocks. Verge escapement mechanism derived in the surge of true mechanical clocks, which didn't need any kind of fluid power, like water or mercury, to work.
These mechanical clocks were intended for two main purposes: for signalling and notification (e.g. the timing of services and public events), and for modeling the solar system. The former purpose is administrative, the latter arises naturally given the scholarly interests in astronomy, science, astrology, and how these subjects integrated with the religious philosophy of the time. The astrolabe was used both by astronomers and astrologers, and it was natural to apply a clockwork drive to the rotating plate to produce a working model of the solar system.
Simple clocks intended mainly for notification were installed in towers, and did not always require faces or hands. They would have announced the canonical hours or intervals between set times of prayer. Canonical hours varied in length as the times of sunrise and sunset shifted. The more sophisticated astronomical clocks would have had moving dials or hands, and would have shown the time in various time systems, including Italian hours, canonical hours, and time as measured by astronomers at the time. Both styles of clock started acquiring extravagant features such as
In Europe, between 1280 and 1320, there was an increase in the number of references to clocks and horologes in church records, and this probably indicates that a new type of clock mechanism had been devised. Existing clock mechanisms that used water power were being adapted to take their driving power from falling weights. This power was controlled by some form of oscillating mechanism, probably derived from existing bell-ringing or alarm devices. This controlled release of power – the escapement – marks the beginning of the true mechanical clock, which differed from the previously mentioned cogwheel clocks. Verge escapement mechanism derived in the surge of true mechanical clocks, which didn't need any kind of fluid power, like water or mercury, to work.
These mechanical clocks were intended for two main purposes: for signalling and notification (e.g. the timing of services and public events), and for modeling the solar system. The former purpose is administrative, the latter arises naturally given the scholarly interests in astronomy, science, astrology, and how these subjects integrated with the religious philosophy of the time. The astrolabe was used both by astronomers and astrologers, and it was natural to apply a clockwork drive to the rotating plate to produce a working model of the solar system.
Simple clocks intended mainly for notification were installed in towers, and did not always require faces or hands. They would have announced the canonical hours or intervals between set times of prayer. Canonical hours varied in length as the times of sunrise and sunset shifted. The more sophisticated astronomical clocks would have had moving dials or hands, and would have shown the time in various time systems, including Italian hours, canonical hours, and time as measured by astronomers at the time. Both styles of clock started acquiring extravagant features such as automata
An automaton (; plural: automata or automatons) is a relatively self-operating machine, or control mechanism designed to automatically follow a sequence of operations, or respond to predetermined instructions.Automaton – Definition and More ...
.
In 1283, a large clock was installed at Dunstable Priory in Bedfordshire
Bedfordshire (; abbreviated Beds) is a ceremonial county in the East of England. The county has been administered by three unitary authorities, Borough of Bedford, Central Bedfordshire and Borough of Luton, since Bedfordshire County Council ...
in southern England; its location above the rood screen suggests that it was not a water clock. In 1292, Canterbury Cathedral installed a 'great horloge'. Over the next 30 years there are mentions of clocks at a number of ecclesiastical institutions in England, Italy, and France. In 1322, a new clock was installed in Norwich, an expensive replacement for an earlier clock installed in 1273. This had a large (2 metre) astronomical dial with automata and bells. The costs of the installation included the full-time employment of two clockkeeper
A clockkeeper, sometimes seen as clock keeper, refers to a form of employment seen prevalently during Middle Age Europe involving the tracking of time and the maintaining of clocks and other timekeeping devices. However, the practice and its appea ...
s for two years.
Astronomical

 The world's first fully mechanical water clock the 'Cosmic Engine', was invented by Su Song, a Chinese
The world's first fully mechanical water clock the 'Cosmic Engine', was invented by Su Song, a Chinese polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
, designed and constructed in China in 1092. This great astronomical hydromechanical clock tower was about ten metres high (about 30 feet) and featured a clock escapement
An escapement is a mechanical linkage in mechanical watches and clocks that gives impulses to the timekeeping element and periodically releases the gear train to move forward, advancing the clock's hands. The impulse action transfers energy ...
and was indirectly powered by a rotating wheel with falling water and liquid mercury, and used an armillary sphere capable of calculating complex astronomical problems.
In Europe, there were the clocks constructed by Richard of Wallingford
Richard of Wallingford (1292–1336) was an English mathematician, astronomer, horologist, and cleric who made major contributions to astronomy and horology while serving as abbot of St Albans Abbey in Hertfordshire.
Biography
Richard was bor ...
in Albans by 1336, and by Giovanni de Dondi in Padua
Padua ( ; it, Padova ; vec, Pàdova) is a city and ''comune'' in Veneto, northern Italy. Padua is on the river Bacchiglione, west of Venice. It is the capital of the province of Padua. It is also the economic and communications hub of the ...
from 1348 to 1364. They no longer exist, but detailed descriptions of their design and construction survive,North, John. God's Clockmaker: Richard of Wallingford and the Invention of Time. London: Hambledon and London (2005).King, Henry "Geared to the Stars: the evolution of planetariums, orreries, and astronomical clocks", University of Toronto Press, 1978 and modern reproductions have been made. They illustrate how quickly the theory of the mechanical clock had been translated into practical constructions, and also that one of the many impulses to their development had been the desire of astronomers to investigate celestial phenomena.
The Astrarium of Giovanni Dondi dell'Orologio was a complex astronomical clock built between 1348 and 1364 in Padua
Padua ( ; it, Padova ; vec, Pàdova) is a city and ''comune'' in Veneto, northern Italy. Padua is on the river Bacchiglione, west of Venice. It is the capital of the province of Padua. It is also the economic and communications hub of the ...
, Italy, by the doctor and clock-maker Giovanni Dondi dell'Orologio
Giovanni Dondi dell'Orologio (c. 1330 – 1388), also known as Giovanni de' Dondi, was an Italian physician, astronomer and mechanical engineer in Padua, now in Italy. He is remembered today as a pioneer in the art of clock design and construct ...
. The Astrarium had seven faces and 107 moving gears; it showed the positions of the sun, the moon and the five planets then known, as well as religious feast days. The astrarium stood about 1 metre high, and consisted of a seven-sided brass or iron framework resting on 7 decorative paw-shaped feet. The lower section provided a 24-hour dial and a large calendar drum, showing the fixed feasts of the church, the movable feasts, and the position in the zodiac of the moon's ascending node. The upper section contained 7 dials, each about 30 cm in diameter, showing the positional data for the Primum Mobile
In classical, medieval, and Renaissance astronomy, the Primum Mobile (Latin: "first movable") was the outermost moving sphere in the geocentric model of the universe.
The concept was introduced by Ptolemy to account for the apparent daily motio ...
, Venus, Mercury, the moon, Saturn, Jupiter, and Mars. Directly above the 24-hour dial is the dial of the Primum Mobile
In classical, medieval, and Renaissance astronomy, the Primum Mobile (Latin: "first movable") was the outermost moving sphere in the geocentric model of the universe.
The concept was introduced by Ptolemy to account for the apparent daily motio ...
, so called because it reproduces the diurnal motion of the stars and the annual motion of the sun against the background of stars. Each of the 'planetary' dials used complex clockwork to produce reasonably accurate models of the planets' motion. These agreed reasonably well both with Ptolemaic theory and with observations.
Wallingford's clock had a large astrolabe-type dial, showing the sun, the moon's age, phase, and node, a star map, and possibly the planets. In addition, it had a wheel of fortune and an indicator of the state of the tide at London Bridge. Bells rang every hour, the number of strokes indicating the time. Dondi's clock was a seven-sided construction, 1 metre high, with dials showing the time of day, including minutes, the motions of all the known planets, an automatic calendar of fixed and movable feasts, and an eclipse prediction hand rotating once every 18 years. It is not known how accurate or reliable these clocks would have been. They were probably adjusted manually every day to compensate for errors caused by wear and imprecise manufacture. Water clocks are sometimes still used today, and can be examined in places such as ancient castles and museums. The Salisbury Cathedral clock, built in 1386, is considered to be the world's oldest surviving mechanical clock that strikes the hours.
Spring-driven
Nuremberg
Nuremberg ( ; german: link=no, Nürnberg ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the second-largest city of the German state of Bavaria after its capital Munich, and its 518,370 (2019) inhabitants make it the 14th-largest ...
watchmaker Peter Henlein
Peter Henlein (also spelled Henle or Hele) (1485 - August 1542), a locksmith and clockmaker of Nuremberg, Germany, is often considered the inventor of the watch., p.31 He was one of the first craftsmen to make small ornamental portable clocks wh ...
(or Henle, or Hele) around 1511. The earliest existing spring driven clock is the chamber clock given to Phillip the Good, Duke of Burgundy, around 1430, now in the Germanisches Nationalmuseum
The Germanisches National Museum is a museum in Nuremberg, Germany. Founded in 1852, it houses a large collection of items relating to German culture and art extending from prehistoric times through to the present day. The Germanisches National ...
. Spring power presented clockmakers with a new problem: how to keep the clock movement running at a constant rate as the spring ran down. This resulted in the invention of the '' stackfreed'' and the fusee in the 15th century, and many other innovations, down to the invention of the modern ''going barrel'' in 1760.
Early clock dials did not indicate minutes and seconds. A clock with a dial indicating minutes was illustrated in a 1475 manuscript by Paulus Almanus,p. 529, "Time and timekeeping instruments", ''History of astronomy: an encyclopedia'', John Lankford, Taylor & Francis, 1997, . and some 15th-century clocks in Germany indicated minutes and seconds.
An early record of a seconds hand on a clock dates back to about 1560 on a clock now in the Fremersdorf collection.
During the 15th and 16th centuries, clockmaking flourished, particularly in the metalworking towns of Nuremberg
Nuremberg ( ; german: link=no, Nürnberg ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the second-largest city of the German state of Bavaria after its capital Munich, and its 518,370 (2019) inhabitants make it the 14th-largest ...
and Augsburg
Augsburg (; bar , Augschburg , links=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swabian_German , label=Swabian German, , ) is a city in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, around west of Bavarian capital Munich. It is a university town and regional seat of the ...
, and in Blois
Blois ( ; ) is a commune and the capital city of Loir-et-Cher department, in Centre-Val de Loire, France, on the banks of the lower Loire river between Orléans and Tours.
With 45,898 inhabitants by 2019, Blois is the most populated city of the ...
, France. Some of the more basic table clocks have only one time-keeping hand, with the dial between the hour markers being divided into four equal parts making the clocks readable to the nearest 15 minutes. Other clocks were exhibitions of craftsmanship and skill, incorporating astronomical indicators and musical movements. The cross-beat escapement was invented in 1584 by Jost Bürgi, who also developed the remontoire. Bürgi's clocks were a great improvement in accuracy as they were correct to within a minute a day. These clocks helped the 16th-century astronomer Tycho Brahe
Tycho Brahe ( ; born Tyge Ottesen Brahe; generally called Tycho (14 December 154624 October 1601) was a Danish astronomer, known for his comprehensive astronomical observations, generally considered to be the most accurate of his time. He was ...
to observe astronomical events with much greater precision than before.

Pendulum
The next development in accuracy occurred after 1656 with the invention of the pendulum clock. Galileo had the idea to use a swinging bob to regulate the motion of a time-telling device earlier in the 17th century. Christiaan Huygens, however, is usually credited as the inventor. He determined the mathematical formula that related pendulum length to time (about 99.4 cm or 39.1 inches for the one second movement) and had the first pendulum-driven clock made. The first model clock was built in 1657 inthe Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital o ...
, but it was in England that the idea was taken up. The longcase clock (also known as the ''grandfather clock'') was created to house the pendulum and works by the English clockmaker William Clement in 1670 or 1671. It was also at this time that clock cases began to be made of wood and clock faces to use enamel as well as hand-painted ceramics.
In 1670, William Clement created the anchor escapement
In horology, the anchor escapement is a type of escapement used in pendulum clocks. The escapement is a mechanism in a mechanical clock that maintains the swing of the pendulum by giving it a small push each swing, and allows the clock's wheels ...
, an improvement over Huygens' crown escapement. Clement also introduced the pendulum suspension spring in 1671. The concentric minute hand was added to the clock by Daniel Quare, a London clockmaker and others, and the second hand was first introduced.
Hairspring
In 1675, Huygens and Robert Hooke invented the spiral balance spring, or the hairspring, designed to control the oscillating speed of thebalance wheel
A balance wheel, or balance, is the timekeeping device used in mechanical watches and small clocks, analogous to the pendulum in a pendulum clock. It is a weighted wheel that rotates back and forth, being returned toward its center position by a ...
. This crucial advance finally made accurate pocket watches possible. The great English clockmaker Thomas Tompion
Thomas Tompion, FRS (1639–1713) was an English clockmaker, watchmaker and mechanician who is still regarded to this day as the "Father of English Clockmaking". Tompion's work includes some of the most historic and important clocks and watc ...
, was one of the first to use this mechanism successfully in his pocket watch
A pocket watch (or pocketwatch) is a watch that is made to be carried in a pocket, as opposed to a wristwatch, which is strapped to the wrist.
They were the most common type of watch from their development in the 16th century until wristw ...
es, and he adopted the minute hand which, after a variety of designs were trialled, eventually stabilised into the modern-day configuration. The rack and snail striking mechanism for striking clocks, was introduced during the 17th century and had distinct advantages over the 'countwheel' (or 'locking plate') mechanism. During the 20th century there was a common misconception that Edward Barlow invented '' rack and snail'' striking. In fact, his invention was connected with a repeating mechanism employing the rack and snail. The repeating clock, that chimes the number of hours (or even minutes) on demand was invented by either Quare or Barlow in 1676. George Graham
George Graham (born 30 November 1944), nicknamed "Stroller", is a Scottish former Association football, football player and manager (association football), manager.
In his successful playing career, he made 455 appearances in England's Football ...
invented the deadbeat escapement for clocks in 1720.
Marine chronometer
A major stimulus to improving the accuracy and reliability of clocks was the importance of precise time-keeping for navigation. The position of a ship at sea could be determined with reasonable accuracy if a navigator could refer to a clock that lost or gained less than about 10 seconds per day. This clock could not contain a pendulum, which would be virtually useless on a rocking ship. In 1714, the British government offered large financial rewards to the value of 20,000 pounds for anyone who could determine longitude accurately. John Harrison, who dedicated his life to improving the accuracy of his clocks, later received considerable sums under the Longitude Act. In 1735, Harrison built his first chronometer, which he steadily improved on over the next thirty years before submitting it for examination. The clock had many innovations, including the use of bearings to reduce friction, weighted balances to compensate for the ship's pitch and roll in the sea and the use of two different metals to reduce the problem of expansion from heat. The chronometer was tested in 1761 by Harrison's son and by the end of 10 weeks the clock was in error by less than 5 seconds.Mass production
The British had dominated watch manufacture for much of the 17th and 18th centuries, but maintained a system of production that was geared towards high quality products for the elite. Although there was an attempt to modernise clock manufacture with mass-production techniques and the application of duplicating tools and machinery by the British Watch Company in 1843, it was in the United States that this system took off. In 1816,Eli Terry
Eli Terry Sr. (April 13, 1772 – February 24, 1852) was an inventor and clockmaker in Connecticut. He received a United States patent for a shelf clock mechanism. He introduced mass production to the art of clockmaking, which made clocks a ...
and some other Connecticut clockmakers developed a way of mass-producing clocks by using interchangeable parts. Aaron Lufkin Dennison started a factory in 1851 in Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut Massachusett_writing_systems.html" ;"title="nowiki/> məhswatʃəwiːsət.html" ;"title="Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət">Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət'' En ...
that also used interchangeable parts, and by 1861 was running a successful enterprise incorporated as the Waltham Watch Company.. Reprinted by McGraw-Hill, New York and London, 1926 (); and by Lindsay Publications, Inc., Bradley, Illinois, ().
Early electric
 In 1815,
In 1815, Francis Ronalds
Sir Francis Ronalds FRS (21 February 17888 August 1873) was an English scientist and inventor, and arguably the first electrical engineer. He was knighted for creating the first working electric telegraph over a substantial distance. In 1816 ...
published the first electric clock powered by dry pile batteries. Alexander Bain, Scottish clockmaker, patented the electric clock in 1840. The electric clock's mainspring is wound either with an electric motor or with an electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire wound into a coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated in ...
and armature. In 1841, he first patented the electromagnetic
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions o ...
pendulum. By the end of the nineteenth century, the advent of the dry cell battery made it feasible to use electric power in clocks. Spring or weight driven clocks that use electricity, either alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in whic ...
(AC) or direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or eve ...
(DC), to rewind the spring or raise the weight of a mechanical clock would be classified as an electromechanical clock. This classification would also apply to clocks that employ an electrical impulse to propel the pendulum. In electromechanical clocks the electricity serves no time keeping function. These types of clocks were made as individual timepieces but more commonly used in synchronized time installations in schools, businesses, factories, railroads and government facilities as a master clock and slave clocks.
Where an AC electrical supply of stable frequency is available, timekeeping can be maintained very reliably by using a synchronous motor
A synchronous electric motor is an AC electric motor in which, at steady state,
the rotation of the shaft is synchronized with the frequency of the supply current; the rotation period is exactly equal to an integral number of AC cycles. Syn ...
, essentially counting the cycles. The supply current alternates with an accurate frequency of 50 hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that o ...
in many countries, and 60 hertz in others. While the frequency may vary slightly during the day as the load changes, generators are designed to maintain an accurate number of cycles over a day, so the clock may be a fraction of a second slow or fast at any time, but will be perfectly accurate over a long time. The rotor
Rotor may refer to:
Science and technology
Engineering
* Rotor (electric), the non-stationary part of an alternator or electric motor, operating with a stationary element so called the stator
*Helicopter rotor, the rotary wing(s) of a rotorcraft ...
of the motor rotates at a speed that is related to the alternation frequency. Appropriate gearing converts this rotation speed to the correct ones for the hands of the analog clock. Time in these cases is measured in several ways, such as by counting the cycles of the AC supply, vibration of a tuning fork
A tuning fork is an acoustic resonator in the form of a two-pronged fork with the prongs ( tines) formed from a U-shaped bar of elastic metal (usually steel). It resonates at a specific constant pitch when set vibrating by striking it agains ...
, the behaviour of quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical ...
crystals, or the quantum vibrations of atoms. Electronic circuits divide these high-frequency oscillations to slower ones that drive the time display.
Quartz
 The
The piezoelectric
Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied mechanical stress. The word '' ...
properties of crystalline quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical ...
were discovered by Jacques
Ancient and noble French family names, Jacques, Jacq, or James are believed to originate from the Middle Ages in the historic northwest Brittany region in France, and have since spread around the world over the centuries. To date, there are over ...
and Pierre Curie in 1880. The first crystal oscillator was invented in 1917 by Alexander M. Nicholson, after which the first quartz crystal oscillator was built by Walter G. Cady in 1921. In 1927 the first quartz clock was built by Warren Marrison and J.W. Horton at Bell Telephone Laboratories
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by mult ...
in Canada. The following decades saw the development of quartz clocks as precision time measurement devices in laboratory settings—the bulky and delicate counting electronics, built with vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as ...
s at the time, limited their practical use elsewhere. The National Bureau of Standards (now NIST) based the time standard of the United States on quartz clocks from late 1929 until the 1960s, when it changed to atomic clocks. In 1969, Seiko
, commonly known as Seiko ( , ), is a Japanese maker of watches, clocks, electronic devices, semiconductors, jewelry, and optical products. Founded in 1881 by Kintarō Hattori in Tokyo, Seiko introduced one of the first quartz watches and the ...
produced the world's first quartz wristwatch, the Astron. Their inherent accuracy and low cost of production resulted in the subsequent proliferation of quartz clocks and watches.
Atomic
Currently,atomic clock
An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated with different energy levels, and in transitions betwe ...
s are the most accurate clocks in existence. They are considerably more accurate than quartz clocks as they can be accurate to within a few seconds over trillions of years. Atomic clocks were first theorized by Lord Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, (26 June 182417 December 1907) was a British mathematician, mathematical physicist and engineer born in Belfast. Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53 years, he did important ...
in 1879. In the 1930s the development of magnetic resonance created practical method for doing this. A prototype ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous wa ...
maser device was built in 1949 at the U.S. National Bureau of Standards
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical sci ...
(NBS, now NIST). Although it was less accurate than existing quartz clocks, it served to demonstrate the concept. The first accurate atomic clock, a caesium standard based on a certain transition of the caesium-133 atom, was built by Louis Essen in 1955 at the National Physical Laboratory in the UK. Calibration of the caesium standard atomic clock was carried out by the use of the astronomical time scale '' ephemeris time'' (ET). As of 2013, the most stable atomic clocks are ytterbium
Ytterbium is a chemical element with the symbol Yb and atomic number 70. It is a metal, the fourteenth and penultimate element in the lanthanide series, which is the basis of the relative stability of its +2 oxidation state. However, like the othe ...
clocks, which are stable to within less than two parts in 1 quintillion ().
Operation
The invention of the mechanical clock in the 13th century initiated a change in timekeeping methods from continuous processes, such as the motion of the gnomon's shadow on a sundial or the flow of liquid in a water clock, to periodic oscillatory processes, such as the swing of a pendulum or the vibration of aquartz crystal
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical form ...
, which had the potential for more accuracy. All modern clocks use oscillation.
Although the mechanisms they use vary, all oscillating clocks, mechanical, electric, and atomic, work similarly and can be divided into analogous parts. They consist of an object that repeats the same motion over and over again, an '' oscillator'', with a precisely constant time interval between each repetition, or 'beat'. Attached to the oscillator is a ''controller'' device, which sustains the oscillator's motion by replacing the energy it loses to friction, and converts its oscillations into a series of pulses. The pulses are then counted by some type of ''counter'', and the number of counts is converted into convenient units, usually seconds, minutes, hours, etc. Finally some kind of ''indicator'' displays the result in human readable form.
Power source
Oscillator
 The timekeeping element in every modern clock is a harmonic oscillator, a physical object (resonator) that vibrates or oscillates repetitively at a precisely constant frequency.
* In mechanical clocks, this is either a pendulum or a
The timekeeping element in every modern clock is a harmonic oscillator, a physical object (resonator) that vibrates or oscillates repetitively at a precisely constant frequency.
* In mechanical clocks, this is either a pendulum or a balance wheel
A balance wheel, or balance, is the timekeeping device used in mechanical watches and small clocks, analogous to the pendulum in a pendulum clock. It is a weighted wheel that rotates back and forth, being returned toward its center position by a ...
.
* In some early electronic clocks and watches such as the Accutron, it is a tuning fork
A tuning fork is an acoustic resonator in the form of a two-pronged fork with the prongs ( tines) formed from a U-shaped bar of elastic metal (usually steel). It resonates at a specific constant pitch when set vibrating by striking it agains ...
.
* In quartz clocks and watches, it is a quartz crystal
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical form ...
.
* In atomic clock
An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated with different energy levels, and in transitions betwe ...
s, it is the vibration of electrons in atoms as they emit microwaves.
* In early mechanical clocks before 1657, it was a crude balance wheel or foliot which was not a harmonic oscillator because it lacked a balance spring
A balance spring, or hairspring, is a spring attached to the balance wheel in mechanical timepieces. It causes the balance wheel to oscillate with a resonant frequency when the timepiece is running, which controls the speed at which the wheels of ...
. As a result, they were very inaccurate, with errors of perhaps an hour a day.
The advantage of a harmonic oscillator over other forms of oscillator is that it employs resonance
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied Periodic function, periodic force (or a Fourier analysis, Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system ...
to vibrate at a precise natural resonant frequency or "beat" dependent only on its physical characteristics, and resists vibrating at other rates. The possible precision achievable by a harmonic oscillator is measured by a parameter called its Q, or quality factor, which increases (other things being equal) with its resonant frequency. This is why there has been a long-term trend toward higher frequency oscillators in clocks. Balance wheels and pendulums always include a means of adjusting the rate of the timepiece. Quartz timepieces sometimes include a rate screw that adjusts a capacitor for that purpose. Atomic clocks are primary standards, and their rate cannot be adjusted.
Synchronized or slave clocks
Some clocks rely for their accuracy on an external oscillator; that is, they are automatically synchronized to a more accurate clock: *
Slave clock
In telecommunication and horology, a slave clock is a clock that depends on another clock, the master clock. Modern clocks are synchronized through the Internet or by radio time signals, to Coordinated Universal Time. UTC is based on a network ...
s, used in large institutions and schools from the 1860s to the 1970s, kept time with a pendulum, but were wired to a master clock in the building, and periodically received a signal to synchronize them with the master, often on the hour. Later versions without pendulums were triggered by a pulse from the master clock and certain sequences used to force rapid synchronization following a power failure.
synchronous motor
A synchronous electric motor is an AC electric motor in which, at steady state,
the rotation of the shaft is synchronized with the frequency of the supply current; the rotation period is exactly equal to an integral number of AC cycles. Syn ...
which rotates an exact fraction of a revolution for every cycle of the line voltage, and drives the gear train. Although changes in the grid line frequency due to load variations may cause the clock to temporarily gain or lose several seconds during the course of a day, the total number of cycles per 24 hours is maintained extremely accurately by the utility company, so that the clock keeps time accurately over long periods.
* Computer real time clocks keep time with a quartz crystal, but can be periodically (usually weekly) synchronized over the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
to atomic clocks ( UTC), using the Network Time Protocol (NTP).
* Radio clocks keep time with a quartz crystal, but are periodically synchronized to time signals transmitted from dedicated standard time radio stations or satellite navigation signals, which are set by atomic clocks.
Controller
This has the dual function of keeping the oscillator running by giving it 'pushes' to replace the energy lost to friction, and converting its vibrations into a series of pulses that serve to measure the time. * In mechanical clocks, this is theescapement
An escapement is a mechanical linkage in mechanical watches and clocks that gives impulses to the timekeeping element and periodically releases the gear train to move forward, advancing the clock's hands. The impulse action transfers energy ...
, which gives precise pushes to the swinging pendulum or balance wheel, and releases one gear tooth of the ''escape wheel'' at each swing, allowing all the clock's wheels to move forward a fixed amount with each swing.
* In electronic clocks this is an electronic oscillator circuit that gives the vibrating quartz crystal or tuning fork tiny 'pushes', and generates a series of electrical pulses, one for each vibration of the crystal, which is called the clock signal.
* In atomic clocks the controller is an evacuated microwave cavity attached to a microwave oscillator controlled by a microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circ ...
. A thin gas of caesium atoms is released into the cavity where they are exposed to microwaves. A laser measures how many atoms have absorbed the microwaves, and an electronic feedback control system called a phase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input signal. There are several different types; the simplest is an electronic circuit consisting of a ...
tunes the microwave oscillator until it is at the frequency that causes the atoms to vibrate and absorb the microwaves. Then the microwave signal is divided by digital counters to become the clock signal.
In mechanical clocks, the low Q of the balance wheel or pendulum oscillator made them very sensitive to the disturbing effect of the impulses of the escapement, so the escapement had a great effect on the accuracy of the clock, and many escapement designs were tried. The higher Q of resonators in electronic clocks makes them relatively insensitive to the disturbing effects of the drive power, so the driving oscillator circuit is a much less critical component.
Counter chain
This counts the pulses and adds them up to get traditional time units of seconds, minutes, hours, etc. It usually has a provision for ''setting'' the clock by manually entering the correct time into the counter. * In mechanical clocks this is done mechanically by agear train
A gear train is a mechanical system formed by mounting gears on a frame so the teeth of the gears engage.
Gear teeth are designed to ensure the pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each other without slipping, providing a smooth transmission ...
, known as the wheel train In horology, a wheel train (or just train) is the gear train of a mechanical watch or clock. Although the term is used for other types of gear trains, the long history of mechanical timepieces has created a traditional terminology for their gear tr ...
. The gear train also has a second function; to transmit mechanical power from the power source to run the oscillator. There is a friction coupling called the 'cannon pinion' between the gears driving the hands and the rest of the clock, allowing the hands to be turned to set the time.
* In digital clocks a series of integrated circuit counters or dividers add the pulses up digitally, using binary
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1)
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical operation that ta ...
logic. Often pushbuttons on the case allow the hour and minute counters to be incremented and decremented to set the time.
Indicator
This displays the count of seconds, minutes, hours, etc. in a human readable form. * The earliest mechanical clocks in the 13th century did not have a visual indicator and signalled the time audibly by striking bells. Many clocks to this day are striking clocks which strike the hour. * Analog clocks display time with an analog clock face, which consists of a dial with the numbers 1 through 12 or 24, the hours in the day, around the outside. The hours are indicated with an hour hand, which makes one or two revolutions in a day, while the minutes are indicated by a minute hand, which makes one revolution per hour. In mechanical clocks a gear train drives the hands; in electronic clocks the circuit produces pulses every second which drive astepper motor
A stepper motor, also known as step motor or stepping motor, is a brushless DC electric motor that divides a full rotation into a number of equal steps. The motor's position can be commanded to move and hold at one of these steps without any posi ...
and gear train, which move the hands.
* Digital clocks display the time in periodically changing digits on a digital display. A common misconception is that a digital clock is more accurate than an analog wall clock, but the indicator type is separate and apart from the accuracy of the timing source.
* Talking clock
A talking clock (also called a speaking clock and an auditory clock) is a timekeeping device that presents the time as sounds. It may present the time solely as sounds, such as a phone-based time service (see "Speaking clock") or a clock for the vi ...
s and the speaking clock
A speaking clock or talking clock is a live or recorded human voice service, usually accessed by telephone, that gives the correct time. The first telephone speaking clock service was introduced in France, in association with the Paris Observ ...
services provided by telephone companies speak the time audibly, using either recorded or digitally synthesized voices.
Types
Clocks can be classified by the type of time display, as well as by the method of timekeeping.Time display methods
Analog

 Analog clocks usually use a clock face which indicates time using rotating pointers called "hands" on a fixed numbered dial or dials. The standard clock face, known universally throughout the world, has a short "hour hand" which indicates the hour on a circular dial of 12 hours, making two revolutions per day, and a longer "minute hand" which indicates the minutes in the current hour on the same dial, which is also divided into 60 minutes. It may also have a "second hand" which indicates the seconds in the current minute. The only other widely used clock face today is the 24 hour analog dial, because of the use of 24 hour time in military organizations and timetables. Before the modern clock face was standardized during the
Analog clocks usually use a clock face which indicates time using rotating pointers called "hands" on a fixed numbered dial or dials. The standard clock face, known universally throughout the world, has a short "hour hand" which indicates the hour on a circular dial of 12 hours, making two revolutions per day, and a longer "minute hand" which indicates the minutes in the current hour on the same dial, which is also divided into 60 minutes. It may also have a "second hand" which indicates the seconds in the current minute. The only other widely used clock face today is the 24 hour analog dial, because of the use of 24 hour time in military organizations and timetables. Before the modern clock face was standardized during the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, many other face designs were used throughout the years, including dials divided into 6, 8, 10, and 24 hours. During the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
the French government tried to introduce a 10-hour clock
Decimal time is the representation of the time of day using units which are decimally related. This term is often used specifically to refer to the time system used in France for a few years beginning in 1792 during the French Revolution, whic ...
, as part of their decimal-based metric system
The metric system is a system of measurement that succeeded the decimalised system based on the metre that had been introduced in France in the 1790s. The historical development of these systems culminated in the definition of the Interna ...
of measurement, but it did not achieve widespread use. An Italian 6 hour clock was developed in the 18th century, presumably to save power (a clock or watch striking 24 times uses more power).
Another type of analog clock is the sundial, which tracks the sun continuously, registering the time by the shadow position of its gnomon. Because the sun does not adjust to daylight saving time, users must add an hour during that time. Corrections must also be made for the equation of time
In mathematics, an equation is a formula that expresses the equality of two expressions, by connecting them with the equals sign . The word ''equation'' and its cognates in other languages may have subtly different meanings; for example, in F ...
, and for the difference between the longitudes of the sundial and of the central meridian of the time zone
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude, because it ...
that is being used (i.e. 15 degrees east of the prime meridian for each hour that the time zone is ahead of GMT
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is the mean solar time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London, counted from midnight. At different times in the past, it has been calculated in different ways, including being calculated from noon; as a cons ...
). Sundials use some or part of the 24 hour analog dial. There also exist clocks which use a digital display despite having an analog mechanism—these are commonly referred to as flip clocks. Alternative systems have been proposed. For example, the "Twelv" clock indicates the current hour using one of twelve colors, and indicates the minute by showing a proportion of a circular disk, similar to a moon phase
Concerning the lunar month of ~29.53 days as viewed from Earth, the lunar phase or Moon phase is the shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion, which can be expressed quantitatively using areas or angles, or described qualitatively using the t ...
.
Digital
24-hour notation
The modern 24-hour clock, popularly referred to in the United States as military time, is the convention of timekeeping in which the day runs from midnight to midnight and is divided into 24 hours. This is indicated by the hours (and minutes) pass ...
with hours ranging 00–23;
* the 12-hour notation with AM/PM indicator, with hours indicated as 12AM, followed by 1AM–11AM, followed by 12PM, followed by 1PM–11PM (a notation mostly used in domestic environments).
Most digital clocks use electronic mechanisms and LCD, LED, or VFD
VFD may refer to:
* Factory Workers' Union of Germany, (german: Verband der Fabrikarbeiter Deutschlands, link=no), a former trade union in Germany
* Vacuum fluorescent display, a display device on consumer electronics equipment
* Variable-freque ...
displays; many other display technologies are used as well ( cathode-ray tubes, nixie tube
A Nixie tube ( ), or cold cathode display, is an electronic device used for displaying numerals or other information using glow discharge.
The glass tube contains a wire-mesh anode and multiple cathodes, shaped like numerals or other symbo ...
s, etc.). After a reset, battery change or power failure, these clocks without a backup battery or capacitor either start counting from 12:00, or stay at 12:00, often with blinking digits indicating that the time needs to be set. Some newer clocks will reset themselves based on radio or Internet time servers that are tuned to national atomic clock
An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated with different energy levels, and in transitions betwe ...
s. Since the advent of digital clocks in the 1960s, the use of analog clocks has declined significantly.
Some clocks, called ' flip clocks', have digital displays that work mechanically. The digits are painted on sheets of material which are mounted like the pages of a book. Once a minute, a page is turned over to reveal the next digit. These displays are usually easier to read in brightly lit conditions than LCDs or LEDs. Also, they do not go back to 12:00 after a power interruption. Flip clocks generally do not have electronic mechanisms. Usually, they are driven by AC-synchronous motor
A synchronous electric motor is an AC electric motor in which, at steady state,
the rotation of the shaft is synchronized with the frequency of the supply current; the rotation period is exactly equal to an integral number of AC cycles. Syn ...
s.
Hybrid (analog-digital)
Clocks with analog quadrants, with a digital component, usually minutes and hours displayed analogously and seconds displayed in digital mode.Auditory
For convenience, distance, telephony or blindness, auditory clocks present the time as sounds. The sound is either spoken natural language, (e.g. "The time is twelve thirty-five"), or as auditory codes (e.g. number of sequential bell rings on the hour represents the number of the hour like the bell, Big Ben). Most telecommunication companies also provide aspeaking clock
A speaking clock or talking clock is a live or recorded human voice service, usually accessed by telephone, that gives the correct time. The first telephone speaking clock service was introduced in France, in association with the Paris Observ ...
service as well.
Word
 Word clocks are clocks that display the time visually using sentences. E.g.: "It's about three o'clock." These clocks can be implemented in hardware or software.
Word clocks are clocks that display the time visually using sentences. E.g.: "It's about three o'clock." These clocks can be implemented in hardware or software.
Projection
Some clocks, usually digital ones, include an optical projector that shines a magnified image of the time display onto a screen or onto a surface such as an indoor ceiling or wall. The digits are large enough to be easily read, without using glasses, by persons with moderately imperfect vision, so the clocks are convenient for use in their bedrooms. Usually, the timekeeping circuitry has a battery as a backup source for an uninterrupted power supply to keep the clock on time, while the projection light only works when the unit is connected to an A.C. supply. Completely battery-powered portable versions resembling flashlights are also available.Tactile
Auditory and projection clocks can be used by people who are blind or have limited vision. There are also clocks for the blind that have displays that can be read by using the sense of touch. Some of these are similar to normal analog displays, but are constructed so the hands can be felt without damaging them. Another type is essentially digital, and uses devices that use a code such asBraille
Braille (Pronounced: ) is a tactile writing system used by people who are visually impaired, including people who are blind, deafblind or who have low vision. It can be read either on embossed paper or by using refreshable braille disp ...
to show the digits so that they can be felt with the fingertips.
Multi-display
Some clocks have several displays driven by a single mechanism, and some others have several completely separate mechanisms in a single case. Clocks in public places often have several faces visible from different directions, so that the clock can be read from anywhere in the vicinity; all the faces show the same time. Other clocks show the current time in several time-zones. Watches that are intended to be carried by travellers often have two displays, one for the local time and the other for the time at home, which is useful for making pre-arranged phone calls. Some equation clocks have two displays, one showing mean time and the othersolar time
Solar time is a calculation of the passage of time based on the position of the Sun in the sky. The fundamental unit of solar time is the day, based on the synodic rotation period. Two types of solar time are apparent solar time (sundial ti ...
, as would be shown by a sundial. Some clocks have both analog and digital displays. Clocks with Braille displays usually also have conventional digits so they can be read by sighted people.
Purposes
 Clocks are in homes, offices and many other places; smaller ones (watches) are carried on the wrist or in a pocket; larger ones are in public places, e.g. a railway station or church. A small clock is often shown in a corner of computer displays, mobile phones and many MP3 players.
The primary purpose of a clock is to ''display'' the time. Clocks may also have the facility to make a loud alert signal at a specified time, typically to waken a sleeper at a preset time; they are referred to as ''alarm clocks''. The alarm may start at a low volume and become louder, or have the facility to be switched off for a few minutes then resume. Alarm clocks with visible indicators are sometimes used to indicate to children too young to read the time that the time for sleep has finished; they are sometimes called ''training clocks''.
A clock mechanism may be used to ''control'' a device according to time, e.g. a central heating system, a
Clocks are in homes, offices and many other places; smaller ones (watches) are carried on the wrist or in a pocket; larger ones are in public places, e.g. a railway station or church. A small clock is often shown in a corner of computer displays, mobile phones and many MP3 players.
The primary purpose of a clock is to ''display'' the time. Clocks may also have the facility to make a loud alert signal at a specified time, typically to waken a sleeper at a preset time; they are referred to as ''alarm clocks''. The alarm may start at a low volume and become louder, or have the facility to be switched off for a few minutes then resume. Alarm clocks with visible indicators are sometimes used to indicate to children too young to read the time that the time for sleep has finished; they are sometimes called ''training clocks''.
A clock mechanism may be used to ''control'' a device according to time, e.g. a central heating system, a VCR
A videocassette recorder (VCR) or video recorder is an electromechanical device that records analog audio and analog video from broadcast television or other source on a removable, magnetic tape videocassette, and can play back the recording. ...
, or a time bomb (see: digital counter). Such mechanisms are usually called timer
A timer is a specialized type of clock used for measuring specific time intervals.
Timers can be categorized into two main types.
The word "timer" is usually reserved for devices that counts down from a specified time interval, while devices th ...
s. Clock mechanisms are also used to drive devices such as solar trackers and astronomical telescopes, which have to turn at accurately controlled speeds to counteract the rotation of the Earth.
Most digital computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These program ...
s depend on an internal signal at constant frequency to synchronize processing; this is referred to as a clock signal. (A few research projects are developing CPUs based on asynchronous circuits.) Some equipment, including computers, also maintains time and date for use as required; this is referred to as time-of-day clock, and is distinct from the system clock signal, although possibly based on counting its cycles.
In Chinese culture, giving a clock () is often taboo, especially to the elderly as the term for this act is a homophone with the term for the act of attending another's funeral ().http://www.sohu.com/a/160882715_578225 别人过节喜庆的时候,不送钟表。送终和送钟谐音。
This homonymic pair works in both Mandarin and Cantonese, although in most parts of China only clocks and large bells, and not watches, are called "''zhong''", and watches are commonly given as gifts in China.
However, should such a gift be given, the "unluckiness" of the gift can be countered by exacting a small monetary payment so the recipient is buying the clock and thereby counteracting the ("give") expression of the phrase.
Time standards
For some scientific work timing of the utmost accuracy is essential. It is also necessary to have a standard of the maximum accuracy against which working clocks can be calibrated. An ideal clock would give the time to unlimited accuracy, but this is not realisable. Many physical processes, in particular including some transitions between atomicenergy level
A quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound—that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy, called energy levels. This contrasts with classical particles, which can have any amount of energy. The t ...
s, occur at exceedingly stable frequency; counting cycles of such a process can give a very accurate and consistent time—clocks which work this way are usually called atomic clocks. Such clocks are typically large, very expensive, require a controlled environment, and are far more accurate than required for most purposes; they are typically used in a standards laboratory.
Navigation
Until advances in the late twentieth century, navigation depended on the ability to measurelatitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
and longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east– west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lette ...
. Latitude can be determined through celestial navigation; the measurement of longitude requires accurate knowledge of time. This need was a major motivation for the development of accurate mechanical clocks. John Harrison created the first highly accurate marine chronometer in the mid-18th century. The Noon gun in Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
still fires an accurate signal to allow ships to check their chronometers. Many buildings near major ports used to have (some still do) a large ball mounted on a tower or mast arranged to drop at a pre-determined time, for the same purpose. While satellite navigation systems such as GPS require unprecedentedly accurate knowledge of time, this is supplied by equipment on the satellites; vehicles no longer need timekeeping equipment.
Specific types
See also
* 24-hour analog dial * Allan variance * Allen-Bradley Clock Tower at Rockwell Automation Headquarters Building (Wisconsin) * American Watchmakers-Clockmakers Institute * BaselWorld * Biological clock * Castle clock * Clockarium * Clock as herald of the Industrial Revolution (Lewis Mumford) * Clock face * Clock drift *Clock ident
A clock ident is a form of television ident in which a clock is displayed, reading the current time, and usually alongside the logo of that particular television station. Clock idents are typically used before news bulletins and closedown, thoug ...
* Clock network
* Clock of the Long Now
* Clock signal (digital circuits)
* Clockkeeper
A clockkeeper, sometimes seen as clock keeper, refers to a form of employment seen prevalently during Middle Age Europe involving the tracking of time and the maintaining of clocks and other timekeeping devices. However, the practice and its appea ...
* Clockmaker
A clockmaker is an artisan who makes and/or repairs clocks. Since almost all clocks are now factory-made, most modern clockmakers only repair clocks. Modern clockmakers may be employed by jewellers, antique shops, and places devoted strictly to ...
* Colgate Clock (Indiana)
* Colgate Clock (New Jersey), largest clock in USA
* Corpus Clock
The Corpus Clock, also known as the Grasshopper clock, is a large sculptural clock at street level on the outside of the Taylor Library at Corpus Christi College, Cambridge University, in the United Kingdom, at the junction of Bene't Street ...
* Cosmo Clock 21
Cosmo Clock 21 is a 112.5 metre tall ferris wheel at the Cosmo World amusement park in the Minato Mirai 21 district of Yokohama, Japan. When it first opened, it was the world's tallest Ferris wheel, until the completion of the Igosu 108 in Sh ...
, world's largest clock
* Cox's timepiece
* Cuckooland Museum
The Cuckooland Museum, previously known as the ''Cuckoo Clock Museum'', is a museum that exhibits mainly cuckoo clocks, located in Tabley, Cheshire, England. The collection comprises 300 years of cuckoo clock-making history, since the very earlie ...
* Date and time representation by country
Different conventions exist around the world for date and time representation, both written and spoken.
Differences
Differences can exist in:
*The calendar that is used.
*The order in which the year, month, and day are represented. (Year-mon ...
* Debt clock
A debt clock is a public counter, which displays the government debt (also known as ''public debt'' or ''national debt'') of a public corporation, usually of a state, and which visualizes the progression through an update every second. Because of ...
* Le Défenseur du Temps (automata)
* Department of Defense master clock (U.S.)
* Doomsday Clock
* Earth clock
* Equation clock
* Federation of the Swiss Watch Industry FH
* Guard tour patrol system (watchclocks)
* Iron Ring Clock
* Jens Olsen's World Clock
* Jewel bearing
* List of biggest clock faces
* List of clocks
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby unio ...
* List of international common standards
* List of largest cuckoo clocks
* Metrology
* Mora clock
Gustavian Mora clocks are a type of longcase clock which were made in, and derived their name from, the town of Mora in Dalarna province, Sweden. Production began in the late 18th century and continued through most of the 19th century, finally ...
* National Association of Watch and Clock Collectors
The National Association of Watch & Clock Collectors, Inc. (NAWCC) is a nonprofit association of people who share a passion for collecting watches and clocks and studying horology (the art and science of time and timekeeping). The NAWCC's global m ...
* Projection clock
* Replica watch
A counterfeit watch (or replica watch) is an unauthorised copy of an authentic watch. High-end luxury watches such as Rolex, Patek Philippe and Richard Mille are frequently counterfeited and sold on city streets and online. With technological adv ...
* Rubik's Clock
* Star clock
* Singing bird box
A singing bird box (''boîte à oiseau chanteur'' in French) is a box, usually rectangular-shaped, which contains within a miniature automaton singing bird concealed below an oval lid and activated by means of an operating lever.
Its origins are ...
* System time
In computer science and computer programming, system time represents a computer system's notion of the passage of time. In this sense, ''time'' also includes the passing of days on the calendar.
System time is measured by a ''system clock'', w ...
* Time to digital converter
* Timeline of time measurement technology
The history of timekeeping devices dates back to when ancient civilizations first observed astronomical bodies as they moved across the sky. Devices and methods for keeping time have since then improved through a long series of new inventions ...
* Timer
A timer is a specialized type of clock used for measuring specific time intervals.
Timers can be categorized into two main types.
The word "timer" is usually reserved for devices that counts down from a specified time interval, while devices th ...
* Watch
A watch is a portable timepiece intended to be carried or worn by a person. It is designed to keep a consistent movement despite the motions caused by the person's activities. A wristwatch is designed to be worn around the wrist, attached b ...
* Watchmaker
A watchmaker is an artisan who makes and repairs watches. Since a majority of watches are now factory-made, most modern watchmakers only repair watches. However, originally they were master craftsmen who built watches, including all their part ...
Notes and references
Bibliography
* Baillie, G.H., O. Clutton, & C.A. Ilbert. ''Britten's Old Clocks and Watches and Their Makers'' (7th ed.). Bonanza Books (1956). * Bolter, David J. ''Turing's Man: Western Culture in the Computer Age''. The University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill, NC (1984). pbk. Summary of the role of "the clock" in its setting the direction of philosophic movement for the "Western World". Cf. picture on p. 25 showing the ''verge'' and ''foliot''. Bolton derived the picture from Macey, p. 20. * * * * Edey, Winthrop. ''French Clocks''. New York: Walker & Co. (1967). * Kak, Subhash, Babylonian and Indian Astronomy: Early Connections. 2003. * Kumar, Narendra "Science in Ancient India" (2004). . * Landes, David S. ''Revolution in Time: Clocks and the Making of the Modern World''. Cambridge: Harvard University Press (1983). * Landes, David S. ''Clocks & the Wealth of Nations'', Daedalus Journal, Spring 2003. * Lloyd, Alan H. "Mechanical Timekeepers", ''A History of Technology,'' Vol. III. Edited by Charles Joseph Singer et al. Oxford: Clarendon Press (1957), pp. 648–675. * Macey, Samuel L., ''Clocks and the Cosmos: Time in Western Life and Thought'', Archon Books, Hamden, Conn. (1980). * * North, John. ''God's Clockmaker: Richard of Wallingford and the Invention of Time''. London: Hambledon and London (2005). * Palmer, Brooks. ''The Book of American Clocks'', The Macmillan Co. (1979). * Robinson, Tom. ''The Longcase Clock''. Suffolk, England: Antique Collector's Club (1981). * Smith, Alan. ''The International Dictionary of Clocks''. London: Chancellor Press (1996). * Tardy. ''French Clocks the World Over''. Part I and II. Translated with the assistance of Alexander Ballantyne. Paris: Tardy (1981). * * Yoder, Joella Gerstmeyer. ''Unrolling Time: Christiaan Huygens and the Mathematization of Nature''. New York: Cambridge University Press (1988). * Zea, Philip, & Robert Cheney. ''Clock Making in New England: 1725–1825''. Old Sturbridge Village (1992).External links
* *National Association of Watch & Clock Collectors Museum
{{Authority control Time measurement systems Articles containing video clips