Christmas traditions on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Christmas traditions include a variety of customs, religious practices, rituals, and folklore associated with the celebration of
Christmas traditions include a variety of customs, religious practices, rituals, and folklore associated with the celebration of
 The practice of putting up special decorations at Christmas has a long history. In the 15th century, it was recorded that in London it was the custom at Christmas for every house and all the parish churches to be "decked with holm, ivy,
The practice of putting up special decorations at Christmas has a long history. In the 15th century, it was recorded that in London it was the custom at Christmas for every house and all the parish churches to be "decked with holm, ivy,  Nativity scenes are known from 10th-century Rome. They were popularised by Saint
Nativity scenes are known from 10th-century Rome. They were popularised by Saint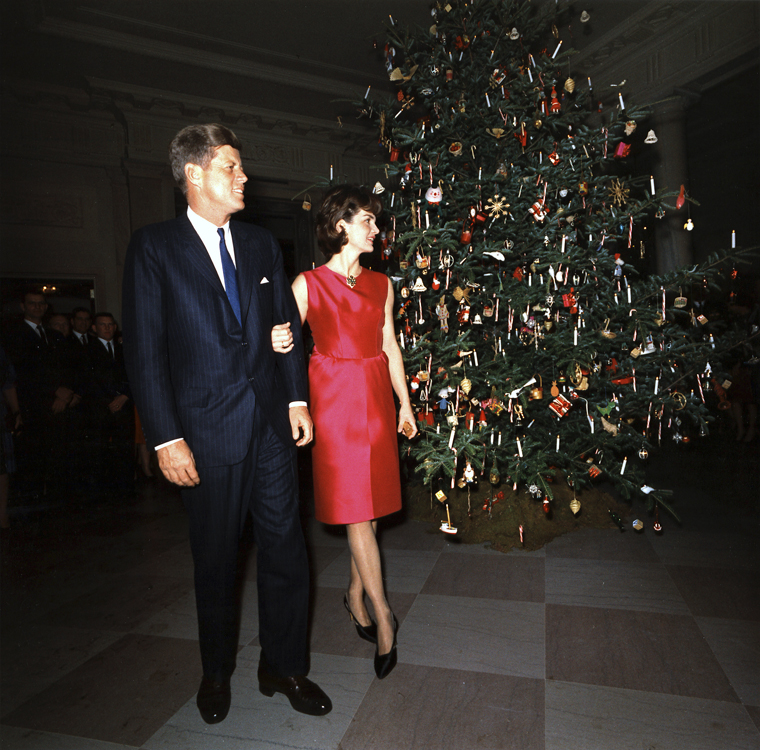  The Christmas tree was first used by German Lutherans in the 16th century, with records indicating that a Christmas tree was placed in the Cathedral of Strassburg in 1539, under the leadership of the Protestant Reformer,
The Christmas tree was first used by German Lutherans in the 16th century, with records indicating that a Christmas tree was placed in the Cathedral of Strassburg in 1539, under the leadership of the Protestant Reformer,
Christ
, ''Online Etymology Dictionary'', 2001. and represents an importation from the German language.van Renterghem, Tony. ''When Santa was a shaman.'' St. Paul: Since the 16th century, the
Since the 16th century, the  Other traditional decorations include
Other traditional decorations include
 For the Christian celebration of Christmas, the viewing of the
For the Christian celebration of Christmas, the viewing of the
 The songs now known specifically as carols were originally communal folk songs sung during celebrations such as "harvest tide" as well as Christmas. It was only later that carols began to be sung in church. Traditionally, carols have often been based on medieval chord patterns, and it is this that gives them their uniquely characteristic musical sound. Some carols like "
The songs now known specifically as carols were originally communal folk songs sung during celebrations such as "harvest tide" as well as Christmas. It was only later that carols began to be sung in church. Traditionally, carols have often been based on medieval chord patterns, and it is this that gives them their uniquely characteristic musical sound. Some carols like "
 A special Christmas family meal is traditionally an important part of the holiday's celebration, and the food that is served varies greatly from country to country. Some regions have special meals for Christmas Eve, such as Sicily, where 12 kinds of fish are served. In the United Kingdom and countries influenced by its traditions, a standard Christmas meal includes turkey, goose or other large bird, gravy, potatoes, vegetables, sometimes bread and cider. Special desserts are also prepared, such as
A special Christmas family meal is traditionally an important part of the holiday's celebration, and the food that is served varies greatly from country to country. Some regions have special meals for Christmas Eve, such as Sicily, where 12 kinds of fish are served. In the United Kingdom and countries influenced by its traditions, a standard Christmas meal includes turkey, goose or other large bird, gravy, potatoes, vegetables, sometimes bread and cider. Special desserts are also prepared, such as  In Poland and other parts of eastern Europe and Scandinavia, fish often is used for the traditional main course, but richer meat such as lamb is increasingly served. In Sweden it is common with a special variety of smörgåsbord, where ham, meatballs and herring play a prominent role. In Germany, France, and Austria, goose and pork are favored. Beef, ham, and chicken in various recipes are popular throughout the world. The Maltese traditionally serve '' Imbuljuta tal-Qastan'', a chocolate and chestnuts beverage, after
In Poland and other parts of eastern Europe and Scandinavia, fish often is used for the traditional main course, but richer meat such as lamb is increasingly served. In Sweden it is common with a special variety of smörgåsbord, where ham, meatballs and herring play a prominent role. In Germany, France, and Austria, goose and pork are favored. Beef, ham, and chicken in various recipes are popular throughout the world. The Maltese traditionally serve '' Imbuljuta tal-Qastan'', a chocolate and chestnuts beverage, after
 Christmas cards are illustrated messages of greeting exchanged between friends and family members during the weeks preceding Christmas Day. The traditional greeting reads "wishing you a Merry Christmas and a Happy New Year", much like that of the first commercial Christmas card, produced by
Christmas cards are illustrated messages of greeting exchanged between friends and family members during the weeks preceding Christmas Day. The traditional greeting reads "wishing you a Merry Christmas and a Happy New Year", much like that of the first commercial Christmas card, produced by 
 The exchanging of gifts is one of the core aspects of the modern Christmas celebration, making it the most profitable time of year for retailers and businesses throughout the world. On Christmas, people exchange gifts based on the Christian tradition associated with
The exchanging of gifts is one of the core aspects of the modern Christmas celebration, making it the most profitable time of year for retailers and businesses throughout the world. On Christmas, people exchange gifts based on the Christian tradition associated with
 A number of figures are associated with Christmas and the seasonal giving of gifts. Among these are
A number of figures are associated with Christmas and the seasonal giving of gifts. Among these are
"The Claus That Refreshes"
, Snopes.com, 2006. and continues through the present day. Father Christmas, a jolly, stout, bearded man who typified the spirit of good cheer at Christmas, predates the Santa Claus character. He is first recorded in early 17th century England, but was associated with holiday merrymaking and
Father Christmas, a jolly, stout, bearded man who typified the spirit of good cheer at Christmas, predates the Santa Claus character. He is first recorded in early 17th century England, but was associated with holiday merrymaking and
 Christmas traditions include a variety of customs, religious practices, rituals, and folklore associated with the celebration of
Christmas traditions include a variety of customs, religious practices, rituals, and folklore associated with the celebration of Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A feast central to the Christian liturgical year, ...
. Many of these traditions vary by country or region, while others are practiced in a virtually identical manner across the world.
Traditions associated with the Christmas holiday are diverse in their origins and nature, with some having an exclusively Christian character with origins from within the religion, while others have been described as more cultural or secular in nature and have originated from outside the realm of Christian influence. Christmas traditions have also changed and evolved significantly in the centuries since Christmas was first instituted as a holiday, with celebrations often taking on an entirely different quality or atmosphere depending on the time period and geographical region.
Church attendance
Christmas Day (inclusive of its vigil, Christmas Eve), is a Festival in the Lutheran Church, a Solemnity in the Roman Catholic Church, and aPrincipal Feast
Principal Feasts are a type of observance in some churches of the Anglican Communion, including the Church of England, the Episcopal Church (United States), and the Anglican Church of Canada. All Principal Feasts are also Principal Holy Days, shari ...
of the Anglican Communion
The Anglican Communion is the third largest Christian communion after the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches. Founded in 1867 in London, the communion has more than 85 million members within the Church of England and other ...
. Other Christian denominations do not rank their feast days but nevertheless place importance on Christmas Eve/Christmas Day, as with other Christian feasts like Easter, Ascension Day, and Pentecost. As such, for Christians, attending a Christmas Eve or Christmas Day church service
A church service (or a service of worship) is a formalized period of Christian communal worship, often held in a church building. It often but not exclusively occurs on Sunday, or Saturday in the case of those churches practicing seventh-day Sa ...
plays an important part in the recognition of the Christmas season
The Christmas season or the festive season (also known in some countries as the holiday season or the holidays) is an annually recurring period recognized in many Western and other countries that is generally considered to run from late Novembe ...
. Christmas, along with Easter, is the period of highest annual church attendance. A 2010 survey by Lifeway Christian Resources
Lifeway Christian Resources, based in Nashville, Tennessee, is the Christian media publishing and distribution division of the Southern Baptist Convention and provider of church business services. Until the end of their physical retail presen ...
found that six in ten Americans attend church services during this time. In the United Kingdom, the Church of England reported an estimated attendance of people at Christmas services in 2015.
Decorations
 The practice of putting up special decorations at Christmas has a long history. In the 15th century, it was recorded that in London it was the custom at Christmas for every house and all the parish churches to be "decked with holm, ivy,
The practice of putting up special decorations at Christmas has a long history. In the 15th century, it was recorded that in London it was the custom at Christmas for every house and all the parish churches to be "decked with holm, ivy, bays
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a na ...
, and whatsoever the season of the year afforded to be green". The heart-shaped leaves of ivy
''Hedera'', commonly called ivy (plural ivies), is a genus of 12–15 species of evergreen climbing or ground-creeping woody plants in the family Araliaceae, native to western, central and southern Europe, Macaronesia, northwestern Africa and ...
were said to symbolize the coming to earth of Jesus, while holly
''Ilex'' (), or holly, is a genus of over 570 species of flowering plants in the family Aquifoliaceae, and the only living genus in that family. ''Ilex'' has the most species of any woody dioecious angiosperm genus. The species are evergreen o ...
was seen as protection against pagans and witches, its thorns and red berries held to represent the Crown of Thorns
According to the New Testament, a woven crown of thorns ( or grc, ἀκάνθινος στέφανος, akanthinos stephanos, label=none) was placed on the head of Jesus during the events leading up to his crucifixion. It was one of the inst ...
worn by Jesus at the crucifixion and the blood he shed.
Francis of Assisi
Giovanni di Pietro di Bernardone, better known as Saint Francis of Assisi ( it, Francesco d'Assisi; – 3 October 1226), was a mystic Italian Catholic friar, founder of the Franciscans, and one of the most venerated figures in Christian ...
from 1223, quickly spreading across Europe.Collins, Ace, ''Stories Behind the Great Traditions of Christmas'', Zondervan, (2003), p.47. Different types of decorations developed across the Christian world, dependent on local tradition and available resources, and can vary from simple representations of the crib to far more elaborate sets – renowned manger scene traditions include the colourful ''Kraków szopka
Kraków szopki or nativity scenes (crib, crèche) ( pl, szopka krakowska) are a Christmas tradition originating from Kraków, Poland, and dating back to the 19th century. An unusual and characteristic feature of the szopka is the use of historica ...
'' in Poland, which imitate Kraków's historical buildings as settings, the elaborate Italian ''presepi'' (Neapolitan
Neapolitan means of or pertaining to Naples, a city in Italy; or to:
Geography and history
* Province of Naples, a province in the Campania region of southern Italy that includes the city
* Duchy of Naples, in existence during the Early and Hig ...
, Genoese and Bolognese
Bologna (, , ; egl, label= Emilian, Bulåggna ; lat, Bononia) is the capital and largest city of the Emilia-Romagna region in Northern Italy. It is the seventh most populous city in Italy with about 400,000 inhabitants and 150 different nati ...
), or the Provençal crèches in southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
France, using hand-painted terracotta figurines called ''santons
A santon is a small hand-painted figurine cast in terracotta or a similar material that is used for building nativity scenes. Santons are a traditional product of the Provence region of southeastern France. A maker of santons is called a ''s ...
''. In certain parts of the world, notably Sicily, living nativity scenes following the tradition of Saint Francis are a popular alternative to static crèches. The first commercially produced decorations appeared in Germany in the 1860s, inspired by paper chains made by children.Collins p. 83. In countries where a representation of the Nativity scene
In the Christian tradition, a nativity scene (also known as a manger scene, crib, crèche ( or ), or in Italian ''presepio'' or ''presepe'', or Bethlehem) is the special exhibition, particularly during the Christmas season, of art objects rep ...
is very popular, people are encouraged to compete and create the most original or realistic ones. Within some families, the pieces used to make the representation are considered a valuable family heirloom
In popular usage, an heirloom is something that has been passed down for generations through family members. Examples are a Family Bible, antiques, weapons or jewellery.
The term originated with the historical principle of an heirloom in ...
.
The traditional colors of Christmas decorations are red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondary ...
, green, and gold. Red symbolizes the blood of Jesus, which was shed in his crucifixion
Crucifixion is a method of capital punishment in which the victim is tied or nailed to a large wooden cross or beam and left to hang until eventual death from exhaustion and asphyxiation. It was used as a punishment by the Persians, Carthagin ...
, while green symbolizes eternal life, and in particular the evergreen tree, which does not lose its leaves in the winter, and gold is the first color associated with Christmas, as one of the three gifts of the Magi
Magi (; singular magus ; from Latin ''magus'', cf. fa, مغ ) were priests in Zoroastrianism and the earlier religions of the western Iranians. The earliest known use of the word ''magi'' is in the trilingual inscription written by Darius the ...
, symbolizing royalty.
 The Christmas tree was first used by German Lutherans in the 16th century, with records indicating that a Christmas tree was placed in the Cathedral of Strassburg in 1539, under the leadership of the Protestant Reformer,
The Christmas tree was first used by German Lutherans in the 16th century, with records indicating that a Christmas tree was placed in the Cathedral of Strassburg in 1539, under the leadership of the Protestant Reformer, Martin Bucer
Martin Bucer ( early German: ''Martin Butzer''; 11 November 1491 – 28 February 1551) was a German Protestant reformer based in Strasbourg who influenced Lutheran, Calvinist, and Anglican doctrines and practices. Bucer was originally a me ...
. In the United States, these "German Lutherans brought the decorated Christmas tree with them; the Moravians put lighted candles on those trees." When decorating the Christmas tree, many individuals place a star at the top of the tree symbolizing the Star of Bethlehem, a fact recorded by ''The School Journal'' in 1897. Professor David Albert Jones of Oxford University writes that in the 19th century, it became popular for people to also use an angel to top the Christmas tree in order to symbolize the angels mentioned in the accounts of the Nativity of Jesus
The nativity of Jesus, nativity of Christ, birth of Jesus or birth of Christ is described in the biblical gospels of Luke and Matthew. The two accounts agree that Jesus was born in Bethlehem in Judaea, his mother Mary was engaged to a man na ...
. The Christmas tree is considered by some as Christianisation
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
of pagan tradition and ritual surrounding the Winter Solstice, which included the use of evergreen boughs, and an adaptation of pagan tree worship
Trees are significant in many of the world's mythologies, and have been given deep and sacred meanings throughout the ages. Human beings, observing the growth and death of trees, and the annual death and revival of their foliage, have often seen ...
; according to eighth-century biographer Æddi Stephanus
Stephen of Ripon was the author of the eighth-century hagiographic text ''Vita Sancti Wilfrithi'' ("Life of Saint Wilfrid"). Other names once traditionally attributed to him are Eddius Stephanus or Æddi Stephanus, but these names are no longer p ...
, Saint Boniface (634–709), who was a missionary in Germany, took an axe to an oak tree dedicated to Thor and pointed out a fir tree, which he stated was a more fitting object of reverence because it pointed to heaven
Heaven or the heavens, is a common religious cosmological or transcendent supernatural place where beings such as deities, angels, souls, saints, or venerated ancestors are said to originate, be enthroned, or reside. According to the belie ...
and it had a triangular shape, which he said was symbolic of the Trinity. The English language phrase "Christmas tree" is first recorded in 1835Harper, DouglasChrist
, ''Online Etymology Dictionary'', 2001. and represents an importation from the German language.van Renterghem, Tony. ''When Santa was a shaman.'' St. Paul:
Llewellyn Publications
Llewellyn Worldwide (formerly Llewellyn Publications) is a New Age publisher based in Woodbury, Minnesota. Llewellyn's mission is to "serve the trade and consumers worldwide with options and tools for exploring new worlds of mind & spirit, there ...
, 1995. .
From Germany the custom was introduced to Britain, first via Queen Charlotte
Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz (Sophia Charlotte; 19 May 1744 – 17 November 1818) was Queen of Great Britain and of Ireland as the wife of King George III from their marriage on 8 September 1761 until the union of the two kingdoms ...
, wife of George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
, and then more successfully by Prince Albert during the reign of Queen Victoria. By 1841 the Christmas tree had become even more widespread throughout Britain.Lejeune, ''Marie Claire''. ''Compendium of symbolic and ritual plants in Europe'', p.550. University of Michigan . By the 1870s, people in the United States had adopted the custom of putting up a Christmas tree.Shoemaker, Alfred Lewis. (1959) ''Christmas in Pennsylvania: a folk-cultural study.'' Edition 40. pp. 52, 53. Stackpole Books 1999. . Christmas trees may be decorated with lights and ornaments.
 Since the 16th century, the
Since the 16th century, the poinsettia
The poinsettia ( or ) (''Euphorbia pulcherrima'') is a commercially important flowering plant species of the diverse spurge family Euphorbiaceae. Indigenous to Mexico and Central America, the poinsettia was first described by Europeans in 1834 ...
, a native plant from Mexico, has been associated with Christmas carrying the Christian symbolism of the Star of Bethlehem; in that country it is known in Spanish as the ''Flower of the Holy Night''. Other popular holiday plants include holly, mistletoe, red amaryllis
''Amaryllis'' () is the only genus in the subtribe Amaryllidinae (tribe Amaryllideae). It is a small genus of flowering bulbs, with two species. The better known of the two, ''Amaryllis belladonna'', is a native of the Western Cape region of ...
, and Christmas cactus
''Schlumbergera'' is a small genus of cacti with six to nine species found in the coastal mountains of south-eastern Brazil. These plants grow on trees or rocks in habitats that are generally shady with high humidity, and can be quite different ...
. Along with a Christmas tree, the interior of a home may be decorated with these plants, along with garlands and evergreen foliage. The display of Christmas village
A Christmas village (or putz) is a decorative, miniature-scale village often set up during the Christmas season. These villages are rooted in the elaborate Christmas traditions of the Moravian church, a Protestant denomination. Mass-produced ca ...
s has also become a tradition in many homes during this season. The outside of houses may be decorated with lights and sometimes with illuminated sleighs
A sled, skid, sledge, or sleigh is a land vehicle that slides across a surface, usually of ice or snow. It is built with either a smooth underside or a separate body supported by two or more smooth, relatively narrow, longitudinal runners s ...
, snowmen, and other Christmas figures. Mistletoe features prominently in European myth and folklore (for example the legend of Baldr
Baldr (also Balder, Baldur) is a god in Germanic mythology. In Norse mythology, Baldr (Old Norse: ) is a son of the god Odin and the goddess Frigg, and has numerous brothers, such as Thor and Váli. In wider Germanic mythology, the god was kn ...
), it is an evergreen parasitic plant which grows on trees, especially apple and poplar, and turns golden when it is dried. It is customary to hang a sprig of mistletoe in the house at Christmas, and anyone standing underneath it may be kissed. Mistletoe has sticky white berries, one of which was traditionally removed whenever someone was kissed under it. This is probably a fertility ritual. The mistletoe berry juice resembles semen.
 Other traditional decorations include
Other traditional decorations include bells
Bells may refer to:
* Bell, a musical instrument
Places
* Bells, North Carolina
* Bells, Tennessee
* Bells, Texas
* Bells Beach, Victoria, an internationally famous surf beach in Australia
* Bells Corners, Ontario
Music
* Bells, directly st ...
, candles, candy canes
A candy cane is a cane-shaped stick candy often associated with Christmastide, as well as Saint Nicholas Day. It is traditionally white with red stripes and flavored with peppermint, but they also come in a variety of other flavors and colors.
...
, stockings, wreaths, and angels
In various theistic religious traditions an angel is a supernatural spiritual being who serves God.
Abrahamic religions often depict angels as benevolent celestial intermediaries between God (or Heaven) and humanity. Other roles include ...
. Both the displaying of wreaths and candles in each window are a more traditional Christmas display. The concentric assortment of leaves, usually from an evergreen, make up Christmas wreaths and are designed to prepare Christians for the Advent season. Candles in each window are meant to demonstrate the fact that Christians believe that Jesus Christ is the ultimate light of the world.
Christmas lights and banners may be hung along streets, music played from speakers, and Christmas trees placed in prominent places. It is common in many parts of the world for town squares and consumer shopping areas to sponsor and display decorations. Rolls of brightly colored paper with secular or religious Christmas motifs are manufactured for the purpose of wrapping gifts. In some countries, Christmas decorations are traditionally taken down on Twelfth Night.
Nativity play
 For the Christian celebration of Christmas, the viewing of the
For the Christian celebration of Christmas, the viewing of the Nativity play
A Nativity play or Christmas pageant is a play which recounts the story of the Nativity of Jesus. It is usually performed at Christmas, the feast of the Nativity.
Liturgical
The term "Nativity Drama" is used by Wellesz in his discussion of the ...
is one of the oldest Christmastime traditions, with the first reenactment of the Nativity of Jesus
The nativity of Jesus, nativity of Christ, birth of Jesus or birth of Christ is described in the biblical gospels of Luke and Matthew. The two accounts agree that Jesus was born in Bethlehem in Judaea, his mother Mary was engaged to a man na ...
taking place in A.D. 1223. In that year, Francis of Assisi
Giovanni di Pietro di Bernardone, better known as Saint Francis of Assisi ( it, Francesco d'Assisi; – 3 October 1226), was a mystic Italian Catholic friar, founder of the Franciscans, and one of the most venerated figures in Christian ...
assembled a Nativity scene
In the Christian tradition, a nativity scene (also known as a manger scene, crib, crèche ( or ), or in Italian ''presepio'' or ''presepe'', or Bethlehem) is the special exhibition, particularly during the Christmas season, of art objects rep ...
outside of his church in Italy and children sang Christmas carols celebrating the birth of Jesus. Each year, this grew larger and people travelled from afar to see Francis' depiction of the Nativity of Jesus that came to feature drama and music. Nativity plays eventually spread throughout all of Europe, where they remain popular. Christmas Eve and Christmas Day church services often came to feature Nativity plays, as did schools and theatres. In France, Germany, Mexico and Spain, Nativity plays are often reenacted outdoors in the streets.
Music and carols
The earliest extant specifically Christmas hymns appear in fourth-century Rome. Latin hymns such as "Veni redemptor gentium
"Veni redemptor gentium" (Come, Redeemer of the nations) is a Latin Advent or Christmas hymn by Ambrose of Milan in iambic tetrameter. The hymn is assigned to the Office of Readings for Advent, from December 17 through December 24, in the Liturg ...
", written by Ambrose
Ambrose of Milan ( la, Aurelius Ambrosius; ), venerated as Saint Ambrose, ; lmo, Sant Ambroeus . was a theologian and statesman who served as Bishop of Milan from 374 to 397. He expressed himself prominently as a public figure, fiercely promot ...
, Archbishop of Milan, were austere statements of the theological doctrine of the Incarnation in opposition to Arianism
Arianism ( grc-x-koine, Ἀρειανισμός, ) is a Christological doctrine first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter from Alexandria, Egypt. Arian theology holds that Jesus Christ is the Son of God, who was begotten by God ...
. "Corde natus ex Parentis" ("Of the Father's love begotten") by the Spanish poet Prudentius
Aurelius Prudentius Clemens () was a Roman Christian poet, born in the Roman province of Tarraconensis (now Northern Spain) in 348.H. J. Rose, ''A Handbook of Classical Literature'' (1967) p. 508 He probably died in the Iberian Peninsula some tim ...
(d. 413) is still sung in some churches today. In the 9th and 10th centuries, the Christmas "Sequence" or "Prose" was introduced in North European monasteries, developing under Bernard of Clairvaux
Bernard of Clairvaux, O. Cist. ( la, Bernardus Claraevallensis; 109020 August 1153), venerated as Saint Bernard, was an abbot, mystic, co-founder of the Knights Templars, and a major leader in the reformation of the Benedictine Order through ...
into a sequence of rhymed stanzas. In the 12th century the Parisian monk Adam of St. Victor began to derive music from popular songs, introducing something closer to the traditional Christmas carol
A Christmas carol is a carol (a song or hymn) on the theme of Christmas, traditionally sung at Christmas itself or during the surrounding Christmas holiday season. The term noel has sometimes been used, especially for carols of French or ...
.
By the 13th century, in France, Germany, and particularly, Italy, under the influence of Francis of Assisi
Giovanni di Pietro di Bernardone, better known as Saint Francis of Assisi ( it, Francesco d'Assisi; – 3 October 1226), was a mystic Italian Catholic friar, founder of the Franciscans, and one of the most venerated figures in Christian ...
, a strong tradition of popular Christmas songs in the native language developed. Christmas carols in English first appear in a 1426 work of John Awdlay, a Shropshire chaplain, who lists twenty-five "caroles of Cristemas", probably sung by groups of wassailers, who went from house to house.
 The songs now known specifically as carols were originally communal folk songs sung during celebrations such as "harvest tide" as well as Christmas. It was only later that carols began to be sung in church. Traditionally, carols have often been based on medieval chord patterns, and it is this that gives them their uniquely characteristic musical sound. Some carols like "
The songs now known specifically as carols were originally communal folk songs sung during celebrations such as "harvest tide" as well as Christmas. It was only later that carols began to be sung in church. Traditionally, carols have often been based on medieval chord patterns, and it is this that gives them their uniquely characteristic musical sound. Some carols like "Personent hodie
"Personent hodie" is a Christmas carol originally published in the 1582 Finnish song book ''Piae Cantiones'', a volume of 74 Medieval songs with Latin texts collected by Jacobus Finno (Jaakko Suomalainen), a Swedish Lutheran cleric, and publish ...
", "Good King Wenceslas
"Good King Wenceslas" is a Christmas carol that tells a story of a Bohemian king who goes on a journey, braving harsh winter weather, to give alms to a poor peasant on the Feast of Stephen (December 26, the Second Day of Christmas). During th ...
", and "The Holly and the Ivy
"The Holly and the Ivy" is a traditional British folk Christmas carol, listed as number 514 in the Roud Folk Song Index. The song can be traced only as far as the early nineteenth century, but the lyrics reflect an association between holly a ...
" can be traced directly back to the Middle Ages. They are among the oldest musical compositions still regularly sung. " Adeste Fideles" (O Come all ye faithful) appears in its current form in the mid-18th century, although the words may have originated in the 13th century.
Singing of carols initially suffered a decline in popularity after the Protestant Reformation in northern Europe, although some Reformers, like Martin Luther, wrote carols and encouraged their use in worship. Carols largely survived in rural communities until the revival of interest in popular songs in the 19th century. The 18th-century English reformer Charles Wesley
Charles Wesley (18 December 1707 – 29 March 1788) was an English leader of the Methodist movement. Wesley was a prolific hymnwriter who wrote over 6,500 hymns during his lifetime. His works include " And Can It Be", " Christ the Lord Is Risen ...
understood the importance of music to worship. In addition to setting many psalms to melodies, which were influential in the Great Awakening in the United States, he wrote texts for at least three Christmas carols. The best known was originally entitled "Hark! How All the Welkin Rings", later renamed " Hark! the Herald Angels Sing".
Felix Mendelssohn wrote a melody adapted to fit Wesley's words. In Austria in 1818 Mohr and Gruber made a major addition to the genre when they composed " Silent Night" for the St. Nicholas Church, Oberndorf. William Sandys' ''Christmas Carols Ancient and Modern'' (1833) contained the first appearance in print of many now-classic English carols, and contributed to the mid-Victorian revival of the festival.
Completely secular Christmas seasonal songs emerged in the late 18th century. " Deck the Halls" dates from 1784, and the American " Jingle Bells" was copyrighted in 1857. In the 19th and 20th century, African American spirituals and songs about Christmas, based in their tradition of spirituals, became more widely known. An increasing number of seasonal holidays songs were commercially produced in the 20th century, including jazz and blues variations. In addition, there was a revival of interest in early music, from groups singing folk music, such as The Revels, to performers of early medieval and classical music. John Rutter has composed many carols including " All Bells in Paradise", " Angels' Carol", " Candlelight Carol", " Donkey Carol", " Jesus Child", " Shepherd's Pipe Carol" and " Star Carol".
Traditional cuisine
Christmas pudding
Christmas pudding is sweet dried-fruit pudding traditionally served as part of Christmas dinner in Britain and other countries to which the tradition has been exported. It has its origins in medieval England, with early recipes making use of d ...
, mince pies, fruit cake
Fruitcake (or fruit cake or fruit bread) is a cake made with candied or dried fruit, nuts, and spices, and optionally soaked in spirits. In the United Kingdom, certain rich versions may be iced and decorated.
Fruitcakes are typically served ...
and Yule log cake.
 In Poland and other parts of eastern Europe and Scandinavia, fish often is used for the traditional main course, but richer meat such as lamb is increasingly served. In Sweden it is common with a special variety of smörgåsbord, where ham, meatballs and herring play a prominent role. In Germany, France, and Austria, goose and pork are favored. Beef, ham, and chicken in various recipes are popular throughout the world. The Maltese traditionally serve '' Imbuljuta tal-Qastan'', a chocolate and chestnuts beverage, after
In Poland and other parts of eastern Europe and Scandinavia, fish often is used for the traditional main course, but richer meat such as lamb is increasingly served. In Sweden it is common with a special variety of smörgåsbord, where ham, meatballs and herring play a prominent role. In Germany, France, and Austria, goose and pork are favored. Beef, ham, and chicken in various recipes are popular throughout the world. The Maltese traditionally serve '' Imbuljuta tal-Qastan'', a chocolate and chestnuts beverage, after Midnight Mass
In many Western Christian traditions Midnight Mass is the first liturgy of Christmastide that is celebrated on the night of Christmas Eve, traditionally beginning at midnight when Christmas Eve gives way to Christmas Day. This popular Christmas c ...
and throughout the Christmas season. Slovenes prepare the traditional Christmas bread potica
Slovenian potica ( sl, Slovenska potica) is a nut roll and a traditional festive pastry from Slovenia.
The name of potica is distinctly Slovenian and developed etymologically from earlier Slovenian forms such as povitica, povtica, potvitsa. This ...
, '' bûche de Noël'' in France, ''panettone
Panettone (, ; lmo, label=Milanese, panetton ) is an Italian type of sweet bread, and fruitcake, originally from Milan, usually prepared and enjoyed for Christmas and New Year in Western, Southern, and Southeastern Europe as well as in South ...
'' in Italy, and elaborate tarts and cakes. The eating of sweets and chocolates has become popular worldwide, and sweeter Christmas delicacies include the German '' stollen'', marzipan cake or candy, and Jamaican rum fruit cake. As one of the few fruits traditionally available to northern countries in winter, oranges have been long associated with special Christmas foods. Eggnog
Eggnog (), historically also known as a milk punch or an egg milk punch when alcoholic beverages are added, is a rich, chilled, sweetened, dairy-based beverage. It is traditionally made with milk, cream, sugar, egg yolks, and whipped egg white ...
is a sweetened dairy-based beverage
A drink or beverage is a liquid intended for human consumption. In addition to their basic function of satisfying thirst, drinks play important roles in human culture. Common types of drinks include plain drinking water, milk, juice, smoothies ...
traditionally made with milk, cream, sugar, and whipped eggs (which gives it a frothy texture). Spirits
Spirit or spirits may refer to:
Liquor and other volatile liquids
* Spirits, a.k.a. liquor, distilled alcoholic drinks
* Spirit or tincture, an extract of plant or animal material dissolved in ethanol
* Volatile (especially flammable) liquids, ...
such as brandy, rum or bourbon are often added. The finished serving is often garnished with a sprinkling of ground cinnamon or nutmeg.
Cards
 Christmas cards are illustrated messages of greeting exchanged between friends and family members during the weeks preceding Christmas Day. The traditional greeting reads "wishing you a Merry Christmas and a Happy New Year", much like that of the first commercial Christmas card, produced by
Christmas cards are illustrated messages of greeting exchanged between friends and family members during the weeks preceding Christmas Day. The traditional greeting reads "wishing you a Merry Christmas and a Happy New Year", much like that of the first commercial Christmas card, produced by Sir Henry Cole
Sir Henry Cole FRSA (15 July 1808 – 18 April 1882) was a British civil servant and inventor who facilitated many innovations in commerce and education in the 19th century in the United Kingdom. Cole is credited with devising the concept of ...
in London in 1843. The custom of sending them has become popular among a wide cross-section of people with the emergence of the modern trend towards exchanging E-cards.
Christmas cards are purchased in considerable quantities, and feature artwork, commercially designed and relevant to the season. The content of the design might relate directly to the Christmas narrative, with depictions of the Nativity of Jesus, or Christian symbols
Christian symbolism is the use of symbols, including archetypes, acts, artwork or events, by Christianity. It invests objects or actions with an inner meaning expressing Christian ideas.
The symbolism of the early Church was characterized by bei ...
such as the Star of Bethlehem, or a white dove, which can represent both the Holy Spirit and Peace on Earth. Other Christmas cards are more secular and can depict Christmas tradition
Christmas traditions include a variety of customs, religious practices, rituals, and folklore associated with the celebration of Christmas. Many of these traditions vary by country or region, while others are practiced in a virtually identical m ...
s, mythical figures such as Santa Claus
Santa Claus, also known as Father Christmas, Saint Nicholas, Saint Nick, Kris Kringle, or simply Santa, is a legendary figure originating in Western Christian culture who is said to bring children gifts during the late evening and overnigh ...
, objects directly associated with Christmas such as candles, holly and baubles, or a variety of images associated with the season, such as Christmastide activities, snow scenes and the wildlife of the northern winter. There are even humorous cards and genres depicting nostalgic scenes of the past such as crinolined shoppers in idealized 19th-century streetscapes.
Some prefer cards with a poem, prayer, or Biblical verse; while others distance themselves from religion with an all-inclusive "Season's greetings".

Commemorative stamps
A number of nations have issuedcommemorative stamp
A commemorative stamp is a postage stamp, often issued on a significant date such as an anniversary, to honor or commemorate a place, event, person, or object. The ''subject'' of the commemorative stamp is usually spelled out in print, unlike defi ...
s at Christmastide. Postal customers will often use these stamps to mail Christmas cards, and they are popular with philatelists
Philately (; ) is the study of postage stamps and postal history. It also refers to the collection and appreciation of stamps and other philatelic products. Philately involves more than just stamp collecting or the study of postage; it is possi ...
. These stamps are regular postage stamps, unlike Christmas seal
Christmas seals are labels placed on mail during the Christmas season to raise funds and awareness for charitable programs. They have become particularly associated with lung diseases such as tuberculosis, and with child welfare. Christmas seals ...
s, and are valid for postage year-round. They usually go on sale some time between early October and early December, and are printed in considerable quantities.
Gift giving
 The exchanging of gifts is one of the core aspects of the modern Christmas celebration, making it the most profitable time of year for retailers and businesses throughout the world. On Christmas, people exchange gifts based on the Christian tradition associated with
The exchanging of gifts is one of the core aspects of the modern Christmas celebration, making it the most profitable time of year for retailers and businesses throughout the world. On Christmas, people exchange gifts based on the Christian tradition associated with Saint Nicholas
Saint Nicholas of Myra, ; la, Sanctus Nicolaus (traditionally 15 March 270 – 6 December 343), also known as Nicholas of Bari, was an early Christian bishop of Greeks, Greek descent from the maritime city of Myra in Asia Minor (; modern-da ...
, and the gifts of gold, frankincense, and myrrh which were given to the baby Jesus by the Magi
Magi (; singular magus ; from Latin ''magus'', cf. fa, مغ ) were priests in Zoroastrianism and the earlier religions of the western Iranians. The earliest known use of the word ''magi'' is in the trilingual inscription written by Darius the ...
. The practice of gift giving in the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
celebration of Saturnalia may have influenced Christian Christmas customs, but on the other hand the Christian "core dogma of the Incarnation, however, solidly established the giving and receiving of gifts as the structural principle of that recurrent yet unique event", because it was the Biblical Magi, "together with all their fellow men, who received the gift of God through man's renewed participation in the divine life."
Gift-bearing figures

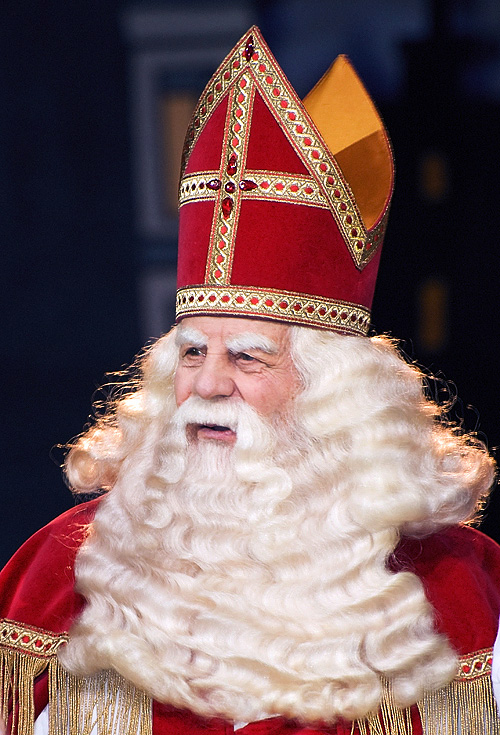
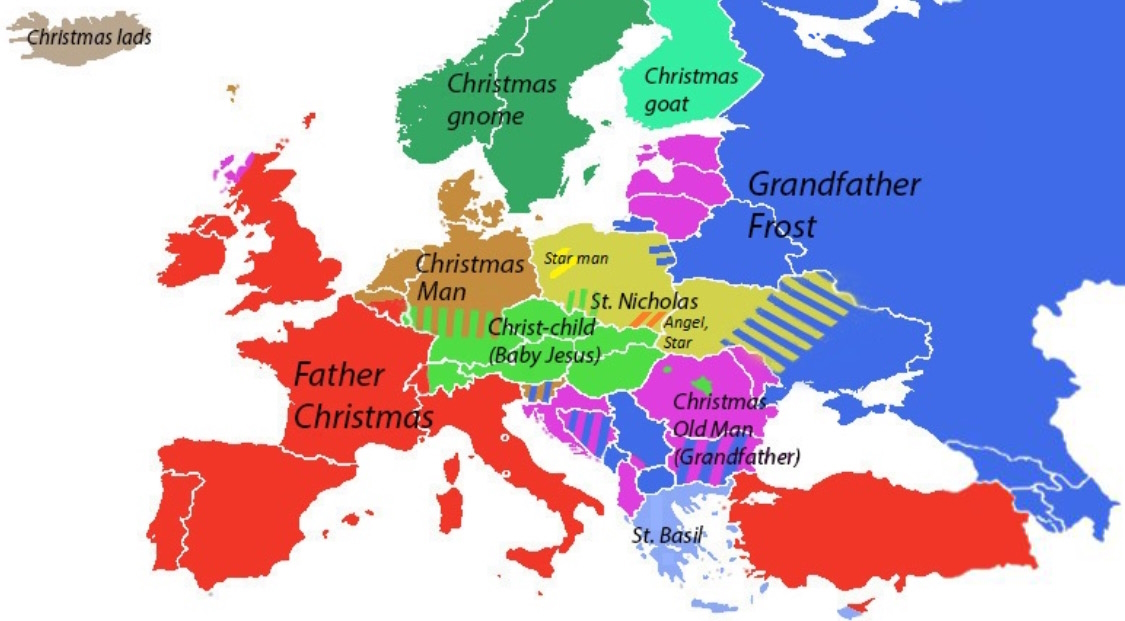
 A number of figures are associated with Christmas and the seasonal giving of gifts. Among these are
A number of figures are associated with Christmas and the seasonal giving of gifts. Among these are Father Christmas
Father Christmas is the traditional English name for the personification of Christmas. Although now known as a Christmas gift-bringer, and typically considered to be synonymous with Santa Claus, he was originally part of a much older and unrela ...
, also known as Santa Claus
Santa Claus, also known as Father Christmas, Saint Nicholas, Saint Nick, Kris Kringle, or simply Santa, is a legendary figure originating in Western Christian culture who is said to bring children gifts during the late evening and overnigh ...
(derived from the Dutch for Saint Nicholas), Père Noël, and the Weihnachtsmann
Santa Claus, also known as Father Christmas, Saint Nicholas, Saint Nick, Kris Kringle, or simply Santa, is a legendary figure originating in Western Christian culture who is said to bring children gifts during the late evening and overnigh ...
; Saint Nicholas
Saint Nicholas of Myra, ; la, Sanctus Nicolaus (traditionally 15 March 270 – 6 December 343), also known as Nicholas of Bari, was an early Christian bishop of Greeks, Greek descent from the maritime city of Myra in Asia Minor (; modern-da ...
or Sinterklaas
Sinterklaas () or Sint-Nicolaas () is a legendary figure based on Saint Nicholas, patron saint of children. Other Dutch names for the figure include ''De Sint'' ("The Saint"), ''De Goede Sint'' ("The Good Saint") and ''De Goedheiligman'' ("The ...
; the Christkind
The Christkind (; ), also called ''Christkindl'', is the traditional Christmas gift-bringer in Austria, Switzerland, southern and western Germany, the Czech Republic, Croatia, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, the eastern part of Belgium, Portugal, Sl ...
; Kris Kringle; Joulupukki
Joulupukki is a Finnish Christmas figure. The name ''joulupukki'' literally means "Christmas goat" or " Yule Goat" in Finnish; the word ''pukki'' comes from the Germanic root ''bock'', which is a cognate of the English " buck", and means "billy ...
; tomte/nisse; Babbo Natale; Saint Basil
Basil of Caesarea, also called Saint Basil the Great ( grc, Ἅγιος Βασίλειος ὁ Μέγας, ''Hágios Basíleios ho Mégas''; cop, Ⲡⲓⲁⲅⲓⲟⲥ Ⲃⲁⲥⲓⲗⲓⲟⲥ; 330 – January 1 or 2, 379), was a bishop of Ca ...
; and Ded Moroz
Ded Moroz (russian: Дед Мороз, ; Russian diminutive: russian: Дедушка Мороз, Dedushka Moroz, label=none; sk, Dedo Mráz; pl, Dziadek Mróz) or Morozko (russian: Морозко) is a legendary figure similar to Saint Nicho ...
. The Scandinavian tomte (also called nisse) is sometimes depicted as a gnome instead of Santa Claus.
The best known of these figures today is red-dressed Santa Claus, of diverse origins. The name Santa Claus can be traced back to the Dutch ''Sinterklaas'', which means simply Saint Nicholas. Nicholas was a 4th-century Greek bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
of Myra, a city in the Roman province of Lycia, whose ruins are from modern Demre in southwest Turkey. Among other saintly attributes, he was noted for the care of children, generosity, and the giving of gifts. His feast day, December 6, came to be celebrated in many countries with the giving of gifts.Forbes, Bruce David, ''Christmas: a candid history'', University of California Press, 2007, , pp. 68–79.
Saint Nicholas traditionally appeared in bishop's attire, accompanied by helpers, inquiring about the behaviour of children during the past year before deciding whether they deserved a gift or not. By the 13th century, Saint Nicholas was well known in the Netherlands, and the practice of gift-giving in his name spread to other parts of central and southern Europe. During the Reformation in 16th–17th-century Europe, many Protestants changed the gift bringer to the Christ Child or ''Christkindl'', corrupted in English to Kris Kringle, and the date of giving gifts changed from December 6 to Christmas Eve.
The modern popular image of Santa Claus, however, was created in the United States, and in particular in New York. The transformation was accomplished with the aid of notable contributors including Washington Irving
Washington Irving (April 3, 1783 – November 28, 1859) was an American short-story writer, essayist, biographer, historian, and diplomat of the early 19th century. He is best known for his short stories " Rip Van Winkle" (1819) and "The Legen ...
and the German-American cartoonist Thomas Nast
Thomas Nast (; ; September 26, 1840December 7, 1902) was a German-born American caricaturist and editorial cartoonist often considered to be the "Father of the American Cartoon".
He was a critic of Democratic Representative "Boss" Tweed and t ...
(1840–1902). Following the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, some of the inhabitants of New York City sought out symbols of the city's non-English past. New York had originally been established as the Dutch colonial town of New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam ( nl, Nieuw Amsterdam, or ) was a 17th-century Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''factory'' gave rise ...
and the Dutch Sinterklaas tradition was reinvented as Saint Nicholas.
In 1809, the New-York Historical Society
The New-York Historical Society is an American history museum and library in New York City, along Central Park West between 76th and 77th Streets, on the Upper West Side of Manhattan. The society was founded in 1804 as New York's first museum. ...
convened and retroactively named ''Sancte Claus'' the patron saint of Nieuw Amsterdam, the Dutch name for New York City. At his first American appearance in 1810, Santa Claus was drawn in bishops' robes. However, as new artists took over, Santa Claus developed more secular attire. Nast drew a new image of "Santa Claus" annually, beginning in 1863. By the 1880s, Nast's Santa had evolved into the modern vision of the figure, perhaps based on the English figure of Father Christmas. The image was standardized by advertisers in the 1920sMikkelson, Barbara and David P."The Claus That Refreshes"
, Snopes.com, 2006. and continues through the present day.
 Father Christmas, a jolly, stout, bearded man who typified the spirit of good cheer at Christmas, predates the Santa Claus character. He is first recorded in early 17th century England, but was associated with holiday merrymaking and
Father Christmas, a jolly, stout, bearded man who typified the spirit of good cheer at Christmas, predates the Santa Claus character. He is first recorded in early 17th century England, but was associated with holiday merrymaking and drunkenness
Alcohol intoxication, also known as alcohol poisoning, commonly described as drunkenness or inebriation, is the negative behavior and physical effects caused by a recent consumption of alcohol. In addition to the toxicity of ethanol, the main p ...
rather than the bringing of gifts. In Victorian Britain
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwardian ...
, his image was remade to match that of Santa. The French Père Noël evolved along similar lines, eventually adopting the Santa image. In Italy, Babbo Natale acts as Santa Claus, while La Befana
In Italian folklore, the Befana () is an old woman who delivers gifts to children throughout Italy on Epiphany Eve (the night of January 5) in a similar way to Santa Claus or the Three Magi Kings.Illes, Judika. ''Encyclopedia of Spirits: The ...
is the bringer of gifts and arrives on the eve of the Epiphany
Epiphany may refer to:
* Epiphany (feeling), an experience of sudden and striking insight
Religion
* Epiphany (holiday), a Christian holiday celebrating the revelation of God the Son as a human being in Jesus Christ
** Epiphany season, or Epipha ...
. It is said that La Befana set out to bring the baby Jesus gifts, but got lost along the way. Now, she brings gifts to all children. In some cultures Santa Claus is accompanied by Knecht Ruprecht, or Black Peter. In other versions, elves
An elf () is a type of humanoid supernatural being in Germanic mythology and folklore. Elves appear especially in Norse mythology, North Germanic mythology. They are subsequently mentioned in Snorri Sturluson's Icelandic Prose Edda. He dis ...
make the toys. His wife is referred to as Mrs. Claus
Mrs. Claus (also known as Mrs. Santa Claus or Mrs. Santa) is the legendary wife of Santa Claus, the Christmas gift-bringer in Western Christmas tradition.
She is known for making cookies with the elves, caring for the reindeer, and preparing t ...
.
There has been some opposition to the narrative of the American evolution of Saint Nicholas into the modern Santa. It has been claimed that the Saint Nicholas Society was not founded until 1835, almost half a century after the end of the American War of Independence. Moreover, a study of the "children's books, periodicals and journals" of New Amsterdam by Charles Jones revealed no references to Saint Nicholas or Sinterklaas. However, not all scholars agree with Jones's findings, which he reiterated in a book-length study in 1978; Howard G. Hageman, of New Brunswick Theological Seminary, maintains that the tradition of celebrating Sinterklaas in New York was alive and well from the early settlement of the Hudson Valley
The Hudson Valley (also known as the Hudson River Valley) comprises the valley of the Hudson River and its adjacent communities in the U.S. state of New York. The region stretches from the Capital District including Albany and Troy south to Yo ...
on.
Current tradition in several Latin American countries (such as Venezuela and Colombia) holds that while Santa makes the toys, he then gives them to the Baby Jesus, who is the one who actually delivers them to the children's homes, a reconciliation between traditional religious beliefs and the iconography of Santa Claus imported from the United States.
In South Tyrol (Italy), Austria, Czech Republic, Southern Germany, Hungary, Liechtenstein, Slovakia, and Switzerland, the Christkind
The Christkind (; ), also called ''Christkindl'', is the traditional Christmas gift-bringer in Austria, Switzerland, southern and western Germany, the Czech Republic, Croatia, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, the eastern part of Belgium, Portugal, Sl ...
( Ježíšek in Czech, Jézuska in Hungarian and Ježiško in Slovak) brings the presents. Greek children get their presents from Saint Basil
Basil of Caesarea, also called Saint Basil the Great ( grc, Ἅγιος Βασίλειος ὁ Μέγας, ''Hágios Basíleios ho Mégas''; cop, Ⲡⲓⲁⲅⲓⲟⲥ Ⲃⲁⲥⲓⲗⲓⲟⲥ; 330 – January 1 or 2, 379), was a bishop of Ca ...
on New Year's Eve, the eve of that saint's liturgical feast. The German St. Nikolaus is not identical with the Weihnachtsmann (who is the German version of Santa Claus / Father Christmas). St. Nikolaus wears a bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
's dress and still brings small gifts (usually candies, nuts, and fruits) on December 6 and is accompanied by Knecht Ruprecht. Although many parents around the world routinely teach their children about Santa Claus and other gift bringers, some have come to reject this practice, considering it deceptive.
Multiple gift-giver figures exist in Poland, varying between regions and individual families. St Nicholas (''Święty Mikołaj'') dominates Central and North-East areas, the Starman (''Gwiazdor'') is most common in Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; german: Großpolen, sv, Storpolen, la, Polonia Maior), is a historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest city ...
, Baby Jesus (''Dzieciątko'') is unique to Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( pl, Górny Śląsk; szl, Gůrny Ślůnsk, Gōrny Ślōnsk; cs, Horní Slezsko; german: Oberschlesien; Silesian German: ; la, Silesia Superior) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, locate ...
, with the Little Star (''Gwiazdka'') and the Little Angel (''Aniołek'') being common in the South and the South-East. Grandfather Frost (''Dziadek Mróz'') is less commonly accepted in some areas of Eastern Poland. It is worth noting that across all of Poland, St Nicholas is the gift giver on the Saint Nicholas Day on December 6.
References
{{Authority control