Christianity in the 11th century on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Christianity in the 11th century is marked primarily by the Great Schism of the Church, which formally divided the
 The first major phase of the struggle between
The first major phase of the struggle between
 Emperor
Emperor
 The
The
The Orthodox East perceived the Papacy as taking on monarch type characteristics that were not in line with the church's historical tradition. The "official" schism in 1054 was the excommunication of Patriarch
 The primary causes of the Schism were disputes over conflicting claims of jurisdiction, in particular over papal authority—
The primary causes of the Schism were disputes over conflicting claims of jurisdiction, in particular over papal authority—

 In March 1095 at the
In March 1095 at the
 The
The
Schaff's ''The Seven Ecumenical Councils
{{DEFAULTSORT:Christianity In The 11th Century 11 11
State church of the Roman Empire
Christianity became the official religion of the Roman Empire when Emperor Theodosius I issued the Edict of Thessalonica in 380, which recognized the catholic orthodoxy of Nicene Christians in the Great Church as the Roman Empire's state religion. ...
into Eastern (Greek) and Western (Latin) branches.
In 1054, following the death of the Patriarch of Rome Leo IX
Pope Leo IX (21 June 1002 – 19 April 1054), born Bruno von Egisheim-Dagsburg, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 February 1049 to his death in 1054. Leo IX is considered to be one of the most historically ...
, papal legates
300px, A woodcut showing Henry II of England greeting the pope's legate.
A papal legate or apostolic legate (from the ancient Roman title '' legatus'') is a personal representative of the pope to foreign nations, or to some part of the Catholic ...
(representatives of the Pope) from Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (Romulus and Remus, legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
...
traveled to Constantinople to deny Michael Cerularius
Michael I Cerularius or Keroularios ( el, Μιχαήλ Α΄ Κηρουλάριος; 1000 – 21 January 1059 AD) was the Patriarch of Constantinople from 1043 to 1059 AD. His disputes with Pope Leo IX over church practices in the 11th century p ...
, the reigning Patriarch of Constantinople
The ecumenical patriarch ( el, Οἰκουμενικός Πατριάρχης, translit=Oikoumenikós Patriárchēs) is the archbishop of Constantinople (Istanbul), New Rome and ''primus inter pares'' (first among equals) among the heads of th ...
, the title of Ecumenical
Ecumenism (), also spelled oecumenism, is the concept and principle that Christians who belong to different Christian denominations should work together to develop closer relationships among their churches and promote Christian unity. The adjec ...
Patriarch and to insist that he recognize the Church of Rome's claim to be the head and mother of the churches. Cerularius refused, resulting in the leader of the contingent from Rome excommunicating Cerularius and the legates in turn being excommunicated by Constantinople. Though this event, in and of itself, was relatively insignificant (and the authority of the legates in their actions was dubious) it ultimately marked the end of any pretense of a union between the eastern
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
* Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
* Eastern Air ...
and western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
branches of the Church. Though efforts were made at reconciliation at various times, they remained divided, each claiming to be the true Christian Church
In ecclesiology, the Christian Church is what different Christian denominations conceive of as being the true body of Christians or the original institution established by Jesus. "Christian Church" has also been used in academia as a synonym for ...
.
Investiture Controversy
 The first major phase of the struggle between
The first major phase of the struggle between Church and state in medieval Europe
Church and state in medieval Europe was the relationship between the Catholic Church and the various monarchies and other states in Europe during the Middle Ages (between the end of Roman authority in the West in the fifth century to their ...
was marked by the Investiture Controversy
The Investiture Controversy, also called Investiture Contest ( German: ''Investiturstreit''; ), was a conflict between the Church and the state in medieval Europe over the ability to choose and install bishops (investiture) and abbots of monas ...
between emperor and Pope over the right to make church appointments. The Papacy were the initial victors, but as Italians divided between Guelphs and Ghibellines
The Guelphs and Ghibellines (, , ; it, guelfi e ghibellini ) were factions supporting the Pope and the Holy Roman Emperor, respectively, in the Italian city-states of Central Italy and Northern Italy.
During the 12th and 13th centuries, rival ...
in factions that were often passed down through families or states until the end of the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, the dispute gradually weakened the Papacy, not least by drawing it into politics. In 1059 the Church attempted to control, or exact a price for, most marriages among the great by prohibiting marriages involving consanguinity
Consanguinity ("blood relation", from Latin '' consanguinitas'') is the characteristic of having a kinship with another person (being descended from a common ancestor).
Many jurisdictions have laws prohibiting people who are related by blood fro ...
(blood kin) and affinity
Affinity may refer to:
Commerce, finance and law
* Affinity (law), kinship by marriage
* Affinity analysis, a market research and business management technique
* Affinity Credit Union, a Saskatchewan-based credit union
* Affinity Equity Par ...
(kin by marriage) to the seventh degree of relationship. Under these rules, almost all great marriages required a dispensation. The rules were relaxed to the fourth degree in 1215.
The Investiture Controversy, or Lay investiture controversy, was the most significant conflict between secular and religious powers in medieval Europe. It began as a dispute in the 11th century between the Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperator ...
Henry IV, and Pope Gregory VII
Pope Gregory VII ( la, Gregorius VII; 1015 – 25 May 1085), born Hildebrand of Sovana ( it, Ildebrando di Soana), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 22 April 1073 to his death in 1085. He is venerated as a saint ...
concerning who would appoint bishops (investiture
Investiture (from the Latin preposition ''in'' and verb ''vestire'', "dress" from ''vestis'' "robe") is a formal installation or ceremony that a person undergoes, often related to membership in Christian religious institutes as well as Christian k ...
). The end of lay investiture threatened to undercut the power of the empire and the ambitions of noblemen for the benefit of Church reform.
Bishops collected revenues from estates attached to their bishopric. Noblemen who held lands hereditarily passed those lands on within their family. However, because bishops had no legitimate children, when a bishop died it was the king's right to appoint a successor. So, while a king had little recourse in preventing noblemen from acquiring powerful domains via inheritance and dynastic marriages, a king could keep careful control of lands under the domain of his bishops. Kings would bestow bishoprics to members of noble families whose friendship he wished to secure. Furthermore, if a king left a bishopric vacant, then he collected the estates' revenues until a bishop was appointed, when in theory he was to repay the earnings. The infrequence of this repayment was an obvious source of dispute. The Church wanted to end this lay investiture because of the potential corruption, not only from vacant sees but also from other practices such as simony
Simony () is the act of selling church offices and roles or sacred things. It is named after Simon Magus, who is described in the Acts of the Apostles as having offered two disciples of Jesus payment in exchange for their empowering him to im ...
.
Pope Gregory VII issued the ''Dictatus Papae
''Dictatus papae'' is a compilation of 27 statements of authority claimed by the pope that was included in Pope Gregory VII's register under the year 1075.
Principles
The principles expressed in ''Dictatus Papae'' are mostly those expressed by ...
'', which declared that the Pope alone could appoint or depose bishops or translate them to other sees. Henry IV's rejection of the decree lead to his excommunication and a ducal revolt; eventually Henry received absolution after dramatic public penance barefoot in Alpine snow and cloaked in a hairshirt
A cilice , also known as a sackcloth, was originally a garment or undergarment made of coarse cloth or animal hair (a hairshirt) worn close to the skin. It is used by members of various Christian traditions (including the Catholic, Lutheran, ...
, though the revolt and conflict of investiture continued. Likewise, a similar controversy occurred in England between King Henry I and St. Anselm, Archbishop of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Canterbury. The current archbishop is Jus ...
, over investiture and ecclesiastical revenues collected by the king during an episcopal vacancy. The English dispute was resolved by the Concordat of London in 1107, where the king renounced his claim to invest bishops but continued to require an oath of fealty from them upon their election. This was a partial model for the Concordat of Worms
The Concordat of Worms(; ) was an agreement between the Catholic Church and the Holy Roman Empire which regulated the procedure for the appointment of bishops and abbots in the Empire. Signed on 23 September 1122 in the German city of Worms by P ...
(''Pactum Calixtinum''), which resolved the imperial investiture controversy with a compromise that allowed secular authorities some measure of control but granted the selection of bishops to their cathedral canons. As a symbol of the compromise, lay authorities invested bishops with their secular authority symbolised by the lance, and ecclesiastical authorities invested bishops with their spiritual authority symbolised by the ring
Ring may refer to:
* Ring (jewellery), a round band, usually made of metal, worn as ornamental jewelry
* To make a sound with a bell, and the sound made by a bell
:(hence) to initiate a telephone connection
Arts, entertainment and media Film and ...
and the staff.
Byzantine conquest of Bulgaria
 Emperor
Emperor Basil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus ( gr, Βασίλειος Πορφυρογέννητος ;) and, most often, the Purple-born ( gr, ὁ πορφυρογέννητος, translit=ho porphyrogennetos).. 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar ...
Porphyrogenitus sought to restore former territories of the Byzantine Empire. By 1000, Basil II had fought off his own nobility and defeated the Islamic threat from the east, and so led another invasion of Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Maced ...
. Bulgaria had been partly subjugated by John I Tzimiskes
John I Tzimiskes (; 925 – 10 January 976) was the senior Byzantine emperor from 969 to 976. An intuitive and successful general, he strengthened the Empire and expanded its borders during his short reign.
Background
John I Tzimiskes ...
after the invasion
An invasion is a military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitical entity aggressively enter territory owned by another such entity, generally with the objective of either: conquering; liberating or re-establishing con ...
of Svyatoslav I of Kiev
; (943 – 26 March 972), also spelled Svyatoslav, was Grand Prince of Kiev famous for his persistent campaigns in the east and south, which precipitated the collapse of two great powers of Eastern Europe, Khazaria and the First Bulgarian Empire. He ...
but parts of the country had remained outside Byzantine control under the leadership of Samuel and his brothers.
This time instead of marching into the middle of the country, he annexed it bit by bit. Eventually, after denying Bulgaria of about a third of its land, the Bulgarians risked everything in one battle in 1014. The Battle of Kleidion
The Battle of Kleidion ( grc-gre, Κλειδίον; or Clidium, after the medieval name of the village of Klyuch, "(the) key"; also known as the Battle of Belasitsa) took place on July 29, 1014, between the Byzantine Empire and the Bulgarian Em ...
was a disaster for the Bulgarians and the Byzantine army captured 15,000 prisoners; 99 out of every 100 was blinded and the 100th was spared one eye to guide the rest back to their homes. The Bulgarians resisted until 1018 when they finally submitted to Basil II's rule.
Following his final subjugation of the Bulgarian state in 1018, Basil II, to underscore the Byzantine victory, established the Archbishopric of Ohrid
The Archbishopric of Ohrid, also known as the Bulgarian Archbishopric of Ohrid
*T. Kamusella in The Politics of Language and Nationalism in Modern Central Europe, Springer, 2008, p. 276
*Aisling Lyon, Decentralisation and the Management of Ethni ...
by downgrading the Bulgarian patriarchate to the rank of the archbishopric. The now archbishopric remained an autocephalous
Autocephaly (; from el, αὐτοκεφαλία, meaning "property of being self-headed") is the status of a hierarchical Christian church whose head bishop does not report to any higher-ranking bishop. The term is primarily used in Eastern Ort ...
church, separate from the Patriarchate of Constantinople
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople ( el, Οἰκουμενικὸν Πατριαρχεῖον Κωνσταντινουπόλεως, translit=Oikoumenikón Patriarkhíon Konstantinoupóleos, ; la, Patriarchatus Oecumenicus Constanti ...
. However, while the archbishopric was completely independent in any other aspect, its primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including hum ...
was selected by the emperor from a list of three candidates submitted by the local church synod
A synod () is a council of a Christian denomination, usually convened to decide an issue of doctrine, administration or application. The word ''synod'' comes from the meaning "assembly" or "meeting" and is analogous with the Latin word meani ...
. In three '' sigillia'' issued in 1020 Basil II gave extensive privileges to the new see.
Although the first appointed archbishop (John of Debar John of Debar ( bg, Йоан Дебърски; fl. 1018–1037) was an 11th-century Bulgarian clergyman. He was a bishop under Emperor Samuel of Bulgaria. According to Srđan Pirivatrić he became the last Bulgarian patriarch David in 1016. He r ...
) was a Bulgarian, his successors, as well as the whole higher clergy, were selected from Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
s. The monks and the ordinary priests continued to be predominantly Bulgarian. To a large extent the archbishopric preserved its national character, upheld the Slavonic liturgy, and continued its contribution to the development of Bulgarian literature.
Theology
Western theology before Scholasticism
With the division and decline of theCarolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the ...
, notable theological activity was preserved in some of the Cathedral schools that had begun to rise to prominence under it – for instance at Auxerre
Auxerre ( , ) is the capital of the Yonne department and the fourth-largest city in Burgundy. Auxerre's population today is about 35,000; the urban area (''aire d'attraction'') comprises roughly 113,000 inhabitants. Residents of Auxerre are ref ...
in the 9th century or Chartres
Chartres () is the prefecture of the Eure-et-Loir department in the Centre-Val de Loire region in France. It is located about southwest of Paris. At the 2019 census, there were 170,763 inhabitants in the metropolitan area of Chartres (as de ...
in the 11th. Intellectual influences from the Arabic world (including works of classical authors preserved by Islamic scholars) percolated into the Christian West via Spain, influencing such theologians as Gerbert of Aurillac
Pope Sylvester II ( – 12 May 1003), originally known as Gerbert of Aurillac, was a French-born scholar and teacher who served as the bishop of Rome and ruled the Papal States from 999 to his death. He endorsed and promoted study of Arab and Gre ...
, who went on to become Pope Sylvester II and mentor to Otto III
Otto III (June/July 980 – 23 January 1002) was Holy Roman Emperor from 996 until his death in 1002. A member of the Ottonian dynasty, Otto III was the only son of the Emperor Otto II and his wife Theophanu.
Otto III was crowned as King of G ...
. (Otto was the fourth ruler of the Germanic Ottonian
The Ottonian dynasty (german: Ottonen) was a Saxon dynasty of German monarchs (919–1024), named after three of its kings and Holy Roman Emperors named Otto, especially its first Emperor Otto I. It is also known as the Saxon dynasty after th ...
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 un ...
, successor to the Carolingian Empire). With hindsight, one might say that a new note was struck when a controversy about the meaning of the eucharist blew up around Berengar of Tours
Berengar of Tours (died 6 January 1088), in Latin Berengarius Turonensis, was an 11th-century French Christian theologian and archdeacon of Angers, a scholar whose leadership of the cathedral school at Chartres set an example of intellectual i ...
in the 11th century: hints of a new confidence in the intellectual investigation of the faith that perhaps foreshadowed the explosion of theological argument that was to take place in the 12th century.
Notable authors include:
* Fulbert of Chartres
Fulbert of Chartres (french: Fulbert de Chartres; 952–970–10 April 1028) was the Bishop of Chartres from 1006 to 1028 and a teacher at the Cathedral school there. Fulbert was a pupil of Gerbert of Aurillac, who would later become Pope S ...
(died 1028)
* Berengar of Tours
Berengar of Tours (died 6 January 1088), in Latin Berengarius Turonensis, was an 11th-century French Christian theologian and archdeacon of Angers, a scholar whose leadership of the cathedral school at Chartres set an example of intellectual i ...
(c.999-1088)
* Lanfranc
Lanfranc, OSB (1005 1010 – 24 May 1089) was a celebrated Italian jurist who renounced his career to become a Benedictine monk at Bec in Normandy. He served successively as prior of Bec Abbey and abbot of St Stephen in Normandy and the ...
(died 1089)
Monasticism
One of the major developments in monasticism during the 11th century was the height of theCluniac reforms
The Cluniac Reforms (also called the Benedictine Reform) were a series of changes within medieval monasticism of the Western Church focused on restoring the traditional monastic life, encouraging art, and caring for the poor. The movement began wit ...
, which centred upon Cluny Abbey
Cluny Abbey (; , formerly also ''Cluni'' or ''Clugny''; ) is a former Benedictine monastery in Cluny, Saône-et-Loire, France. It was dedicated to Saint Peter.
The abbey was constructed in the Romanesque architectural style, with three churche ...
in Burgundy, which controlled a large centralised order with over two hundred monasteries throughout Western Christendom. Cluny championed a revived Papacy during this century and encouraged stricter monastic discipline with a return to the principles of the Benedictine Rule
The ''Rule of Saint Benedict'' ( la, Regula Sancti Benedicti) is a book of precepts written in Latin in 516 by St Benedict of Nursia ( AD 480–550) for monks living communally under the authority of an abbot.
The spirit of Saint Benedict's Ru ...
. Cluny Abbey promoted art and literature, and the liturgy at the Romanesque abbey church was an ornate formal affair dedicated to glorifying God. Together with the revived Papacy, Cluny worked for greater devotion among men in the Church. Towards the end of the 12th century, the wealth and power of Cluny was criticised by many monastics in the Church, especially those that broke from the Cluniac order to form the Cistercians
The Cistercians, () officially the Order of Cistercians ( la, (Sacer) Ordo Cisterciensis, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint ...
, who devoted themselves with much greater rigor to manual labour and severe austerity.
Spread of Christianity
Poland
The spread Christianity was reversed temporarily in Poland, as thepagan reaction in Poland
The pagan reaction in Poland ( pl, Reakcja pogańska w Polsce) was a series of events in the Kingdom of Poland in the 1030s that culminated in a popular uprising or rebellion, or possibly a series of these, that destabilized the Kingdom of Poland. ...
saw many churches and monasteries burned, and priests killed.
Scandinavia
Scandinavia was the last part of Germanic Europe to convert and most resistant. From theHigh Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD 1500 ...
, the territories of Northern Europe were gradually converted to Christianity under German leadership. German and Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swed ...
n noblemen extended their power to Finnic, Samic, Baltic and some Slavic peoples
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
.
Migrations of peoples, although not strictly part of the 'Migration Age', continued beyond 1000, marked by Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
, Magyar, Turkic and Mongol invasions
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire ( 1206-1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastatio ...
, also had significant effects, especially in eastern Europe.
Goths
Many Goths converted to Christianity as individuals outside the Roman Empire. Most members of other tribes converted Christian when their respective tribes settled within the empire, and most Franks and Anglo-Saxons converted a few generations later. During the later centuries following theFall of Rome
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vas ...
, as the Roman Church gradually split between the diocese
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associat ...
s loyal to the Patriarch of Rome
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholic Churches are termed patriarchs (and in certai ...
in the West and those loyal to the other Patriarch
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholic Churches are termed patriarchs (and in certain ...
s in the East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fa ...
, most of the Germanic peoples (excepting the Crimean Goths
The Crimean Goths were Greuthungi- Gothic tribes who remained in the lands around the Black Sea, especially in Crimea. They were the longest-lasting of the Gothic communities. Their existence is well attested through the ages, though the exact p ...
and a few other eastern groups) gradually became strongly allied with the Western Church, particularly as a result of the reign of Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Em ...
.
Georgia
In 1010, the church in the unifiedKingdom of Georgia
The Kingdom of Georgia ( ka, საქართველოს სამეფო, tr), also known as the Georgian Empire, was a medieval Eurasian monarchy that was founded in circa 1008 AD. It reached its Golden Age of political and economic ...
became autocephalous
Autocephaly (; from el, αὐτοκεφαλία, meaning "property of being self-headed") is the status of a hierarchical Christian church whose head bishop does not report to any higher-ranking bishop. The term is primarily used in Eastern Ort ...
(self-governing), and its catholicos ( Melchizedek I) was elevated to the rank of patriarch
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholic Churches are termed patriarchs (and in certain ...
and obtained the official title of Catholicos-Patriarch of All Georgia
''Catholicos-Patriarch'' has been the title of the heads of the Georgian Orthodox Church since 1010. The first Catholicos-Patriarch of All Georgia was Melkisedek I (1010–1033). In the 15th century the Georgian Orthodox Church was divided into th ...
.
East-West Schism
 The
The East-West Schism
East West (or East and West) may refer to:
*East–West dichotomy, the contrast between Eastern and Western society or culture
Arts and entertainment
Books, journals and magazines
*'' East, West'', an anthology of short stories written by Salm ...
, or Great Schism, separated the Church into Western (Latin) and Eastern (Greek) branches, i.e., Western Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy. It was the first major division since certain groups in the East rejected the decrees of the Council of Chalcedon (see Oriental Orthodoxy
The Oriental Orthodox Churches are Eastern Christian churches adhering to Miaphysite Christology, with approximately 60 million members worldwide. The Oriental Orthodox Churches are part of the Nicene Christian tradition, and represent o ...
) and was far more significant. Relations between East and West had long been embittered by political and ecclesiastical differences and theological disputes.
There were doctrinal issues like the filioque clause
( ; ) is a Latin term ("and from the Son") added to the original Niceno-Constantinopolitan Creed (commonly known as the Nicene Creed), and which has been the subject of great controversy between Eastern and Western Christianity. It is a term ...
and the authority of the Pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
involved in the split, but these were exacerbated by cultural and linguistic differences between Latins and Greeks. Prior to that, the Eastern and Western halves of the Church had frequently been in conflict, particularly during the periods of iconoclasm
Iconoclasm (from Greek: grc, εἰκών, lit=figure, icon, translit=eikṓn, label=none + grc, κλάω, lit=to break, translit=kláō, label=none)From grc, εἰκών + κλάω, lit=image-breaking. ''Iconoclasm'' may also be conside ...
and the Photian schism
The Photian Schism was a four-year (863–867) schism between the episcopal sees of Rome and Constantinople. The issue centred on the right of the Byzantine Emperor to depose and appoint a patriarch without approval from the papacy.
In 857, ...
br>The Orthodox East perceived the Papacy as taking on monarch type characteristics that were not in line with the church's historical tradition. The "official" schism in 1054 was the excommunication of Patriarch
Michael Cerularius
Michael I Cerularius or Keroularios ( el, Μιχαήλ Α΄ Κηρουλάριος; 1000 – 21 January 1059 AD) was the Patriarch of Constantinople from 1043 to 1059 AD. His disputes with Pope Leo IX over church practices in the 11th century p ...
of Constantinople, followed by his excommunication of papal legates. Both groups are descended from the Early Church
Early Christianity (up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325) spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewish ...
, both acknowledge the apostolic succession
Apostolic succession is the method whereby the ministry of the Christian Church is held to be derived from the apostles by a continuous succession, which has usually been associated with a claim that the succession is through a series of bish ...
of each other's bishops and the validity of each other's sacrament
A sacrament is a Christian rite that is recognized as being particularly important and significant. There are various views on the existence and meaning of such rites. Many Christians consider the sacraments to be a visible symbol of the rea ...
s. Though both acknowledge the primacy of the Bishop of Rome, Eastern Orthodoxy understands this as a primacy of honour with limited or no ecclesiastical authority in other dioceses. The Orthodox East perceived the Papacy as taking on monarch type characteristics that were not in line with the church's tradition.
Ecclesiology
At the root of what became the Great Schism is the question ofecclesiology
In Christian theology, ecclesiology is the study of the Church, the origins of Christianity, its relationship to Jesus, its role in salvation, its polity, its discipline, its eschatology, and its leadership.
In its early history, one of the C ...
. The Eastern Churches maintained the idea that every local city-church with its bishop, presbyters, deacons and people celebrating the Eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was institu ...
constituted the whole Church. In this view called Eucharistic ecclesiology (or more recently holographic ecclesiology), every bishop is Saint Peter
) (Simeon, Simon)
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Bethsaida, Gaulanitis, Syria, Roman Empire
, death_date = Between AD 64–68
, death_place = probably Vatican Hill, Rome, Italia, Roman Empire
, parents = John (or Jonah; Jona)
, occupa ...
's successor in his church ("the Church") and the churches form what Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος ; 260/265 – 30 May 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilus (from the grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος τοῦ Παμφίλου), was a Greek historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christi ...
called a common union of churches. This implied that all bishops were ontologically equal, although functionally particular bishops could be granted special privileges by other bishops and serve as metropolitans, archbishops or patriarchs. Early on, the ecclesiology of the Roman Church was universal in nature, with the idea that the Church was a worldwide organism with a divinely (not functionally) appointed center: the Church/Bishop of Rome.
Language and culture
The dominant language of the West wasLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, whilst that of the East was Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
. Soon after the fall of the Western Empire, the number of individuals who spoke both Latin and Greek began to dwindle, and communication between East and West grew much more difficult. With linguistic unity gone, cultural unity began to crumble as well. The two halves of the Church were naturally divided along similar lines; they developed different rite Rite may refer to:
* Ritual, an established ceremonious act
* Rite of passage, a ceremonious act associated with social transition
Religion
* Rite (Christianity), a sacred ritual or liturgical tradition in various Christian denominations
* Cath ...
s and had different approaches to religious doctrines.
Papal Supremacy
Pope Leo IX
Pope Leo IX (21 June 1002 – 19 April 1054), born Bruno von Egisheim-Dagsburg, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 February 1049 to his death in 1054. Leo IX is considered to be one of the most historically ...
claimed he held authority over the four Eastern patriarch
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholic Churches are termed patriarchs (and in certain ...
s and over the insertion of the Filioque clause
( ; ) is a Latin term ("and from the Son") added to the original Niceno-Constantinopolitan Creed (commonly known as the Nicene Creed), and which has been the subject of great controversy between Eastern and Western Christianity. It is a term ...
into the Nicene Creed
The original Nicene Creed (; grc-gre, Σύμβολον τῆς Νικαίας; la, Symbolum Nicaenum) was first adopted at the First Council of Nicaea in 325. In 381, it was amended at the First Council of Constantinople. The amended form is a ...
by the Western patriarch in 1014. Eastern Orthodoxy states that the 28th Canon of the Council of Chalcedon explicitly proclaimed the equality of the Bishops of Rome and Constantinople and that it established the highest court of ecclesiastical appeal in Constantinople. The seventh canon of the Council of Ephesus declared:
:It is unlawful for any man to bring forward, or to write, or to compose a different (ἑτέραν) Faith as a rival to that established by the holy Fathers assembled with the Holy Ghost in Nicæa. But those who shall dare to compose a different faith, or to introduce or offer it to persons desiring to turn to the acknowledgment of the truth, whether from Heathenism or from Judaism, or from any heresy whatsoever, shall be deposed, if they be bishops or clergymen; bishops from the episcopate and clergymen from the clergy; and if they be laymen, they shall be anathematized
Anathema, in common usage, is something or someone detested or shunned. In its other main usage, it is a formal excommunication. The latter meaning, its ecclesiastical sense, is based on New Testament usage. In the Old Testament, anathema was a cr ...
Eastern Orthodoxy also observes that this canon of the Council of Ephesus in 431 explicitly prohibited modification of the Nicene Creed drawn up by the First Council of Nicaea
The First Council of Nicaea (; grc, Νίκαια ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in the Bithynian city of Nicaea (now İznik, Turkey) by the Roman Emperor Constantine I in AD 325.
This ecumenical council was the first effort ...
in 325 and modified by the second Ecumenical Council
The First Council of Constantinople ( la, Concilium Constantinopolitanum; grc-gre, Σύνοδος τῆς Κωνσταντινουπόλεως) was a council of Christian bishops convened in Constantinople (now Istanbul, Turkey) in AD 38 ...
in 381. Thus to change "who proceeds from the Father" to "who proceeds from the Father and the Son" (Latin "filioque
( ; ) is a Latin term ("and from the Son") added to the original Niceno-Constantinopolitan Creed (commonly known as the Nicene Creed), and which has been the subject of great controversy between Eastern and Western Christianity. It is a term ...
" added) is rejected by the Orthodox both as illicit and doctrinally incorrect.
In the Orthodox view, the Bishop of Rome (i.e. the Pope) would have universal primacy in a reunited Christendom, as ''primus inter pares
''Primus inter pares'' is a Latin phrase meaning first among equals. It is typically used as an honorary title for someone who is formally equal to other members of their group but is accorded unofficial respect, traditionally owing to their sen ...
'' without power of jurisdiction.
Other points of conflict
Many other issues increased tensions. * The Western Church's insertion of "Filioque
( ; ) is a Latin term ("and from the Son") added to the original Niceno-Constantinopolitan Creed (commonly known as the Nicene Creed), and which has been the subject of great controversy between Eastern and Western Christianity. It is a term ...
" into the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
version of the Nicene Creed
The original Nicene Creed (; grc-gre, Σύμβολον τῆς Νικαίας; la, Symbolum Nicaenum) was first adopted at the First Council of Nicaea in 325. In 381, it was amended at the First Council of Constantinople. The amended form is a ...
.
* Disputes in the Balkans, Southern Italy, and Sicily
Sicily ( it, Sicilia , ) is the list of islands in the Mediterranean, largest island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. The Strait of Messina divides it from the region of Calabria in Southern Italy. I ...
over whether Rome or Constantinople had ecclesiastical jurisdiction.
* As a result of the Muslim conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests ( ar, الْفُتُوحَاتُ الإسْلَامِيَّة, ), also referred to as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. He estab ...
of the territories of the patriarchates of Alexandria, Antioch and Jerusalem, only two rival powerful centres of ecclesiastical authority, Constantinople and Rome, remained.
* Certain liturgical
Liturgy is the customary public ritual of worship performed by a religious group. ''Liturgy'' can also be used to refer specifically to public worship by Christians. As a religious phenomenon, liturgy represents a communal response to and partici ...
practices in the West that the East believed represented illegitimate innovation: the use of unleavened bread
Unleavened bread is any of a wide variety of breads which are prepared without using rising agents such as yeast. Unleavened breads are generally flat breads; however, not all flat breads are unleavened. Unleavened breads, such as the tortil ...
for the Eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was institu ...
, for example (see Azymite).
* Celibacy among Western priests (both monastic and parish), as opposed to the Eastern discipline whereby parish priests could be married men.
Mutual excommunication of 1054
The dispute about the authority of Roman bishops reached a climax in 1054, when Michael I Cerularius tried to bolster his position as the "Patriarch of Constantinople", seeming to set himself up as a rival of Pope Leo IX, as the Popes previously had forbidden calling Constantinople a patriarchate. The dispute ended when the Pope's legate, Cardinal Humbert, excommunicated Cerularius and, in exchange, Michael excommunicated the papal legates. It was suspected by the Patriarch that the bull of excommunication, placed on the altar of Hagia Sophia, had been tampered with by Argyros, the commander of Southern Italy, who had a drawn-out controversy with Michael I Cerularius. Although this is commonly viewed as the "Great Schism", historically the event did little to change the relationship between East and West at that time. Michael himself knew that the Pope was a prisoner of the Normans at the time that Humbert arrived, and by the time Michael was excommunicated Pope Leo had already died, voiding the papal legates of authority. Moreover, Michael did not excommunicate the Pope, nor even the Western Church, but only the papal delegation. Most of the direct causes of the Great Schism, however, are far less grandiose than the famous ''Filioque
( ; ) is a Latin term ("and from the Son") added to the original Niceno-Constantinopolitan Creed (commonly known as the Nicene Creed), and which has been the subject of great controversy between Eastern and Western Christianity. It is a term ...
''. The relations between the Papacy and the Byzantine court were good in the years leading up to 1054. The emperor Constantine IX
Constantine IX Monomachos ( grc-x-medieval, Κωνσταντῖνος Μονομάχος, translit=Kōnstantinos IX Monomachos; 1004 – 11 January 1055), reigned as Byzantine emperor from June 1042 to January 1055. Empress Zoë Porphyrogenita ...
and the Pope Leo IX
Pope Leo IX (21 June 1002 – 19 April 1054), born Bruno von Egisheim-Dagsburg, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 February 1049 to his death in 1054. Leo IX is considered to be one of the most historically ...
were allied through the mediation of the Lombard catepan of Italy
The Catepanate (or Catapanate) of Italy ( el, ''Katepaníkion Italías'') was a province of the Byzantine Empire from 965 until 1071. At its greatest extent, it comprised mainland Italy south of a line drawn from Monte Gargano to the Gulf of S ...
, Argyrus, who had spent years in Constantinople, originally as a political prisoner.
Cerularius ordered a letter to be written to the bishop of Trani
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Trani-Barletta-Bisceglie ( la, Archidioecesis Tranensis-Barolensis-Vigiliensis (-Nazarensis)) is a Latin rite archbishopric in the administrative province of Barletta-Andria-Trani, in the southeastern Italian regi ...
in which he attacked the " Judaistic" practices of the West, namely the use of unleavened bread. The letter was to be sent by John to all the bishops of the West, including the Pope. John promptly complied, and the letter was passed to Humbert of Mourmoutiers
Humbert of Silva Candida, O.S.B., also known as Humbert of Moyenmoutier (between 1000 and 1015 – 5 May 1061), was a French Benedictine abbot and later a cardinal. It was his act of excommunicating the Patriarch of Constantinople Michael I Ce ...
, the cardinal-bishop of Silva Candida, who translated the letter into Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
and brought it to the Pope, who ordered a reply to be made to each charge and a defence of papal supremacy
Papal supremacy is the doctrine of the Catholic Church that the Pope, by reason of his office as Vicar of Christ, the visible source and foundation of the unity both of the bishops and of the whole company of the faithful, and as pastor of the ...
to be laid out in a response.
Michael was convinced to cool the debate and thus attempt to prevent the impending breach. However, Humbert and the Pope made no concessions and the former was sent with legatine powers to the imperial capital to solve the questions raised once and for all. Humbert, Frederick of Lorraine, and Peter, Archbishop of Amalfi
The Archdiocese of Amalfi-Cava de' Tirreni ( la, Archidioecesis Amalphitana-Cavensis) is an archdiocese of the Latin Rite of the Catholic Church, with its episcopal see at Amalfi, not far from Naples. It was named Archdiocese of Amalfi until p ...
arrived in April 1054 and were met with a hostile reception; they stormed out of the palace, leaving the papal response with Michael, who in turn was even more angered by their actions. The patriarch refused to recognise their authority or, practically, their existence. When Pope Leo died on April 19, 1054, the legates' authority legally ceased, but they effectively ignored this technicality.
In response to Michael's refusal to address the issues at hand, the legatine mission took the extreme measure of entering the church of the Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia ( 'Holy Wisdom'; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque ( tr, Ayasofya-i Kebir Cami-i Şerifi), is a mosque and major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The cathedral was originally built as a Greek Ortho ...
during the divine liturgy and placing a Bull of Excommunication (1054) on the altar.
The legates left for Rome two days after issuing the Bull of Excommunication, leaving behind a city near riot. The patriarch had the immense support of the people against the emperor, who had supported the legates to his own detriment. To assuage popular anger, the bull was burnt, and the legates were anathema
Anathema, in common usage, is something or someone detested or shunned. In its other main usage, it is a formal excommunication. The latter meaning, its ecclesiastical sense, is based on New Testament usage. In the Old Testament, anathema was a c ...
tised. Only the legates were anathematised and, once again, there was no explicit indication that the entire Western church was being anathematised.
In the bull of excommunication issued against Patriarch Michael by the papal legates, one of the reasons cited was the Eastern Church's deletion of the "Filioque
( ; ) is a Latin term ("and from the Son") added to the original Niceno-Constantinopolitan Creed (commonly known as the Nicene Creed), and which has been the subject of great controversy between Eastern and Western Christianity. It is a term ...
" from the original Nicene Creed. In fact, it was the opposite: the Eastern Church did not delete anything. It was the Western Church that added this phrase to the Nicene-Constantinopolitan Creed.
Peace and Truce of God
Violence was endemic amongst the nobility of the Middle Ages with the Church seeking to prevent ecclesiastical land and the clergy becoming involved. Clerics and peasants were granted immunity from violence by the Peace of God (''Pax Dei''), fighting was banned on holy days by the Truce of God (''Treuga Dei'') and the concept ofchivalry
Chivalry, or the chivalric code, is an informal and varying code of conduct developed in Europe between 1170 and 1220. It was associated with the medieval Christian institution of knighthood; knights' and gentlemen's behaviours were governed b ...
developed. The wealthy lords and nobles would give the monasteries estates in exchange for the conduction of mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementa ...
es for the soul of a deceased loved one. Though this was likely not the original intent of Benedict, the efficiency of his cenobitic
Cenobitic (or coenobitic) monasticism is a monastic tradition that stresses community life. Often in the West the community belongs to a religious order, and the life of the cenobitic monk is regulated by a religious rule, a collection of prece ...
Rule in addition to the stability of the monasteries made such estates very productive; the general monk was then raised to a level of nobility, for the serf
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which developed ...
s of the estate would tend to the labor, while the monk was free to study. The monasteries thus attracted many of the best people in society, and during this period the monasteries were the central storehouses and producers of knowledge.
Crusades

Background
Until the Islamic conquests of the 7th and 8th centuries the Holy Land was part of theRoman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
and then Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. In 1009, when the Fatimid
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a dyn ...
Caliph al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah
Abū ʿAlī Manṣūr (13 August 985 – 13 February 1021), better known by his regnal name al-Ḥākim bi-Amr Allāh ( ar, الحاكم بأمر الله, lit=The Ruler by the Order of God), was the sixth Fatimid caliph and 16th Ismaili imam ...
destroyed the Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, hy, Սուրբ Հարության տաճար, la, Ecclesia Sancti Sepulchri, am, የቅዱስ መቃብር ቤተክርስቲያን, he, כנסיית הקבר, ar, كنيسة القيامة is a church i ...
, but in 1039 his successor was paid a large sum by the Byzantine Empire to rebuild it. Western Christians were allowed to visit the sacred places in the Holy Land. In 1063, Pope Alexander II
Pope Alexander II (1010/1015 – 21 April 1073), born Anselm of Baggio, was the head of the Roman Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1061 to his death in 1073. Born in Milan, Anselm was deeply involved in the Pataria reform ...
had given his blessing to Iberian Christians in their wars against the Muslims, granting both a papal standard, the , and an indulgence
In the teaching of the Catholic Church, an indulgence (, from , 'permit') is "a way to reduce the amount of punishment one has to undergo for sins". The ''Catechism of the Catholic Church'' describes an indulgence as "a remission before God o ...
to those killed in battle. Both sides of the Investiture Controversy tried to marshal public opinion in their favour creating personal engagement, awakening of intense Christian piety and public interest in religious affairs. This was strengthened by religious propaganda advocating Just War
The just war theory ( la, bellum iustum) is a doctrine, also referred to as a tradition, of military ethics which is studied by military leaders, theologians, ethicists and policy makers. The purpose of the doctrine is to ensure that a war is ...
in order to recover control of the holy places in Jerusalem where the death
Death is the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain an organism. For organisms with a brain, death can also be defined as the irreversible cessation of functioning of the whole brain, including brainstem, and brain ...
, resurrection
Resurrection or anastasis is the concept of coming back to life after death. In a number of religions, a dying-and-rising god is a deity which dies and is resurrected. Reincarnation is a similar process hypothesized by other religions, which ...
and ascension into heaven
Heaven or the heavens, is a common religious cosmological or transcendent supernatural place where beings such as deities, angels, souls, saints, or venerated ancestors are said to originate, be enthroned, or reside. According to the belie ...
of Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
took place. The '' Reconquista'' was not the only European/Muslim conflict. The Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
adventurer Robert Guiscard
Robert Guiscard (; Modern ; – 17 July 1085) was a Norman adventurer remembered for the conquest of southern Italy and Sicily. Robert was born into the Hauteville family in Normandy, went on to become count and then duke of Apulia and Calabria ...
conquered Calabria in 1057 and held traditionally Byzantine territory from the Muslims of Sicily
Sicily ( it, Sicilia , ) is the list of islands in the Mediterranean, largest island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. The Strait of Messina divides it from the region of Calabria in Southern Italy. I ...
. The maritime states of Pisa
Pisa ( , or ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, central Italy, straddling the Arno just before it empties into the Ligurian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa. Although Pisa is known worldwide for its leaning tower, the city ...
, Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of Ge ...
and Catalonia were all actively fighting Islamic strongholds in Majorca
Mallorca, or Majorca, is the largest island in the Balearic Islands, which are part of Spain and located in the Mediterranean.
The capital of the island, Palma, is also the capital of the autonomous community of the Balearic Islands. The Ba ...
reducing raiding on the coasts of Italy and Catalonia. This long history of losing territories to a religious enemy created a powerful motive to respond to Byzantine Emperor Alexius I's call for holy war to defend Christendom and to recapture the lost lands starting with Jerusalem. The Papacy of Pope Gregory VII
Pope Gregory VII ( la, Gregorius VII; 1015 – 25 May 1085), born Hildebrand of Sovana ( it, Ildebrando di Soana), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 22 April 1073 to his death in 1085. He is venerated as a saint ...
struggled with the doctrinal validity of holy war. Saint Augustine of Hippo
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Afr ...
had justified the use of force in the service of Christ in ''The City of God
''On the City of God Against the Pagans'' ( la, De civitate Dei contra paganos), often called ''The City of God'', is a book of Christian philosophy written in Latin by Augustine of Hippo in the early 5th century AD. The book was in response ...
'', and a Christian just war
The just war theory ( la, bellum iustum) is a doctrine, also referred to as a tradition, of military ethics which is studied by military leaders, theologians, ethicists and policy makers. The purpose of the doctrine is to ensure that a war is ...
although this might enhance the Papacy's standing in Europe, stem violence amongst the western nobility as the "Peace of God" movement had failed and provide leverage the claims of supremacy over the Patriarch of Constantinople
The ecumenical patriarch ( el, Οἰκουμενικός Πατριάρχης, translit=Oikoumenikós Patriárchēs) is the archbishop of Constantinople (Istanbul), New Rome and ''primus inter pares'' (first among equals) among the heads of th ...
, which had resulted in the Great Schism of 1054. However, Gregory's conflict with the German emperor over the Investiture Controversy meant no crusade materialised. For Gregory's successor, Pope Urban II, a crusade would serve to reunite Christendom, bolster the Papacy, and perhaps bring the East under his control.
Council of Clermont
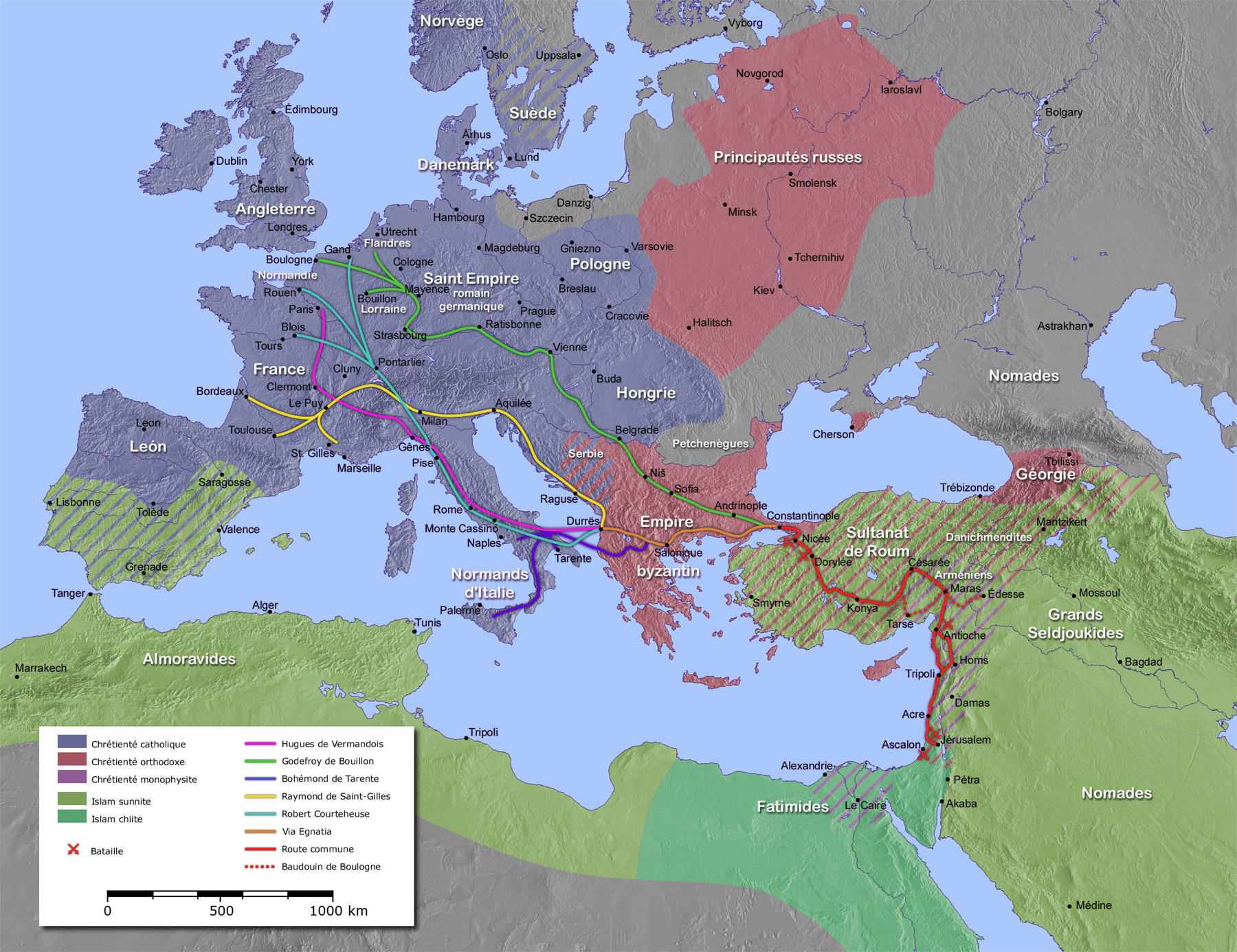
 In March 1095 at the
In March 1095 at the Council of Piacenza The Council of Piacenza was a mixed synod of ecclesiastics and laymen of the Roman Catholic Church, which took place from March 1 to March 7, 1095, at Piacenza.
The Council was held at the end of Pope Urban II's tour of Italy and France, which he m ...
, ambassadors sent by Byzantine Emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as le ...
Alexius I
Alexios I Komnenos ( grc-gre, Ἀλέξιος Κομνηνός, 1057 – 15 August 1118; Latinized Alexius I Comnenus) was Byzantine emperor from 1081 to 1118. Although he was not the first emperor of the Komnenian dynasty, it was during ...
called for help with defending his empire against the Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
. Urban II called for support from the Western nobility at the Council of Clermont
The Council of Clermont was a mixed synod of ecclesiastics and laymen of the Catholic Church, called by Pope Urban II and held from 17 to 27 November 1095 at Clermont, Auvergne, at the time part of the Duchy of Aquitaine.
Pope Urban's speec ...
on 27 November 1095, combining the idea of pilgrimage to the Holy Land with that of waging a holy war against infidels. Later that year, at Clermont, Pope Urban II called upon all Christians to join a war against the Turks, promising those who died in the endeavor would receive immediate remission of their sins.
First Crusade, 1095–1099
 The
The Siege of Antioch
The siege of Antioch took place during the First Crusade in 1097 and 1098, on the crusaders' way to Jerusalem through Syria. Two sieges took place in succession. The first siege, by the crusaders against the city held by the Seljuk Empire, last ...
took place shortly before the siege on Jerusalem during the first Crusade. Antioch fell to the Franks in May 1098 but not before a lengthy siege. The ruler of Antioch was not sure how the Christians living within his city would react, and he forced them to live outside the city during the siege, though he promised to protect their wives and children from harm, while Jews and Muslims fought together. The siege only came to end when the city was betrayed and the Franks entered through the water-gate of the town causing the leader to flee. Once inside the city, as was standard military practice at the time, the Franks then massacred the civilians, destroyed mosques and pillaged the city.Arab Historians of the Crusades, trans. F. Gabrieli, trans. E. J. Costello. London: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1984. The crusaders finally marched to the walls of Jerusalem with only a fraction of their original forces. The Jews and Muslims fought together to defend Jerusalem against the invading Franks. They were unsuccessful though and on 15 July 1099 the crusaders entered the city. Again, they proceeded to massacre the remaining Jewish and Muslim civilians and pillaged or destroyed mosques and the city.Trumpbour, John. "Crusades." In The Oxford Encyclopedia of the Islamic World. , edited by John L. Esposito. Oxford Islamic Studies Online, http://www.oxfordislamicstudies.com/article (accessed February 17, 2008). One historian has written that the "isolation, alienation and fear"Riley-Smith, Jonathan. ''The Oxford History of the Crusades'' New York: Oxford University Press, 1999. . felt by the Franks so far from home helps to explain the atrocities they committed, including the cannibalism which was recorded after the Siege of Maarat
The Siege of Ma'arra occurred in late 1098 in the city of Ma'arrat al-Numan, in what is modern-day Syria, during the First Crusade. It is infamous for the claims of widespread cannibalism displayed by the Crusaders.
Prologue
After the Crusader ...
in 1098.
The Crusaders also tried to gain control of the city of Tyre but were defeated by the Muslims. The people of Tyre asked Zahir al-Din Atabek, the leader of Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
, for help defending their city from the Franks with the promise to surrender Tyre to him. When the Franks were defeated the people of Tyre did not surrender the city, but Zahir al-Din simply said "What I have done I have done only for the sake of God and the Muslims, nor out of desire for wealth and kingdom."
Aftermath
After gaining control of Jerusalem the Crusaders created four Crusader states: theKingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem ( la, Regnum Hierosolymitanum; fro, Roiaume de Jherusalem), officially known as the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem or the Frankish Kingdom of Palestine,Example (title of works): was a Crusader state that was establish ...
, the County of Edessa
The County of Edessa (Latin: ''Comitatus Edessanus'') was one of the Crusader states in the 12th century. Ferdinandi, Sergio (2017). La Contea Franca di Edessa. Fondazione e Profilo Storico del Primo Principato Crociato nel Levante (1098-115 ...
, the Principality of Antioch
The Principality of Antioch was one of the crusader states created during the First Crusade which included parts of modern-day Turkey and Syria. The principality was much smaller than the County of Edessa or the Kingdom of Jerusalem. It extende ...
and the County of Tripoli. Initially, Muslims did very little about the Crusader states due to internal conflicts. In the Kingdom of Jerusalem at most 120,000 Franks (predominantly French-speaking Western Christians) ruled over 350,000 Muslims, Jews, and native Eastern Christians.Benjamin Z. Kedar, "The Subjected Muslims of the Frankish Levant", in ''The Crusades: The Essential Readings'', ed. Thomas F. Madden, Blackwell, 2002, p.244. Originally published in ''Muslims Under Latin Rule, 1100–1300'', ed. James M. Powell, Princeton University Press, 1990. Kedar quotes his numbers from Joshua Prawer
Joshua Prawer ( he, יהושע פרַאוֶור; November 22, 1917 – April 30, 1990) was a notable Israeli historian and a scholar of the Crusades and Kingdom of Jerusalem.
His work often attempted to portray Crusader society as a forerunner ...
, ''Histoire du royaume latin de Jérusalem'', tr. G. Nahon, Paris, 1969, vol. 1, pp.498, 568-572.
Timeline
See also
*History of Christianity
The history of Christianity concerns the Christianity, Christian religion, Christendom, Christian countries, and the Christians with their various Christian denomination, denominations, from the Christianity in the 1st century, 1st century ...
*History of the Roman Catholic Church
The history of the Catholic Church is the formation, events, and historical development of the Catholic Church through time.
The tradition of the Catholic Church claims the Catholic Church began with Jesus Christ and his teachings; the Catholi ...
*History of the Eastern Orthodox Church
The History of the Eastern Orthodox Church is the formation, events, and transformation of the Eastern Orthodox Church through time.
According to the Eastern Orthodox tradition the history of the Eastern Orthodox Church is traced back to Jesus ...
* History of Christian theology
*History of Oriental Orthodoxy
Oriental Orthodoxy is the communion of Eastern Christian Churches that recognize only three ecumenical councils—the First Council of Nicaea, the First Council of Constantinople and the Council of Ephesus. They reject the dogmatic definitions of ...
*Christianization
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
* Reconquista
* German Pilgrimage of 1064-1065
* Timeline of Christianity
*Timeline of Christian missions
This timeline of Christian missions chronicles the global expansion of Christianity through a listing of the most significant missionary outreach events.
Apostolic Age
Earliest dates must all be considered approximate
* 33 – Great Commissi ...
* Timeline of the Roman Catholic Church
*Chronological list of saints and blesseds in the 11th century
A list of people, who died during the 11th century, who have received recognition as Blessed (through beatification) or Saint (through canonization) from the Catholic Church:
See also
The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (2020). 'Vladim ...
References
Further reading
* Esler, Philip F. ''The Early Christian World''. Routledge (2004). . * White, L. Michael. ''From Jesus to Christianity''. HarperCollins (2004). . * Freedman, David Noel (Ed). ''Eerdmans Dictionary of the Bible''. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing (2000). . * Pelikan, Jaroslav Jan. ''The Christian Tradition: The Emergence of the Catholic Tradition (100-600)''. University of Chicago Press (1975). .External links
Schaff's ''The Seven Ecumenical Councils
{{DEFAULTSORT:Christianity In The 11th Century 11 11