Christendom on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The terms Christendom or Christian world commonly refer to the global Christian community, Christian states, Christian-majority countries or countries in which
Merriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christendom"
/ref> Following the spread of Christianity from the
 Early Christianity spread in the Greek/Roman world and beyond as a 1st-century
Early Christianity spread in the Greek/Roman world and beyond as a 1st-century
 "Christendom" has referred to the
"Christendom" has referred to the
 An
An
 Christian art began, about two centuries after Christ, by borrowing motifs from Roman Imperial imagery,
Christian art began, about two centuries after Christ, by borrowing motifs from Roman Imperial imagery,
 Christian architecture encompasses a wide range of both secular and religious styles from the foundation of Christianity to the present day, influencing the design and construction of buildings and structures in Christian culture.Fletcher, Banister. ''A History of Architecture''
Buildings were at first adapted from those originally intended for other purposes but, with the rise of distinctively ecclesiastical architecture, church buildings came to influence secular ones which have often imitated religious architecture. In the 20th century, the use of new materials, such as concrete, as well as simpler styles has had its effect upon the design of churches and arguably the flow of influence has been reversed. From the birth of Christianity to the present, the most significant period of transformation for Christian architecture in the west was the Gothic cathedral. In the east,
Christian architecture encompasses a wide range of both secular and religious styles from the foundation of Christianity to the present day, influencing the design and construction of buildings and structures in Christian culture.Fletcher, Banister. ''A History of Architecture''
Buildings were at first adapted from those originally intended for other purposes but, with the rise of distinctively ecclesiastical architecture, church buildings came to influence secular ones which have often imitated religious architecture. In the 20th century, the use of new materials, such as concrete, as well as simpler styles has had its effect upon the design of churches and arguably the flow of influence has been reversed. From the birth of Christianity to the present, the most significant period of transformation for Christian architecture in the west was the Gothic cathedral. In the east,

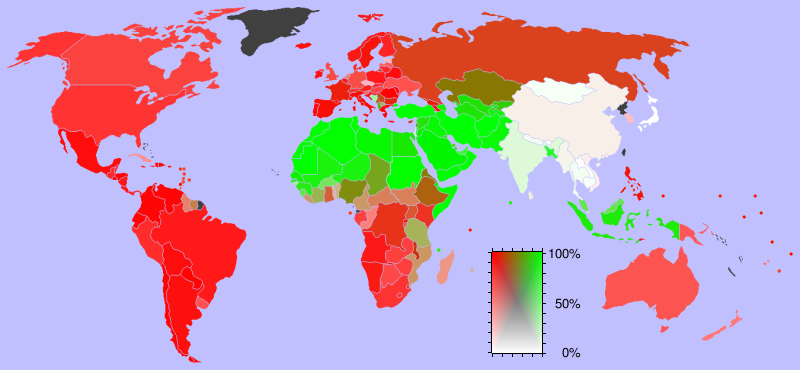 In 2009, according to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', Christianity was the majority religion in Europe (including Russia) with 80%,
In 2009, according to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', Christianity was the majority religion in Europe (including Russia) with 80%,
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
is dominant or prevails.SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christendom"
/ref> Following the spread of Christianity from the
Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
to Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
and North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
during the early Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, Christendom has been divided in the pre-existing Greek East and Latin West
Greek East and Latin West are terms used to distinguish between the two parts of the Greco-Roman world and of medieval Christendom, specifically the eastern regions where Greek was the ''lingua franca'' (Greece, Anatolia, the southern Balkans, ...
. After the Great schism of 1054, two main branches within Christianity emerged, centred around the cities of Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
(Western Christianity
Western Christianity is one of two subdivisions of Christianity (Eastern Christianity being the other). Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Protestantism, Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the O ...
, whose community was called Western or Latin Christendom) and Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
(Eastern Christianity
Eastern Christianity comprises Christianity, Christian traditions and Christian denomination, church families that originally developed during Classical antiquity, classical and late antiquity in the Eastern Mediterranean region or locations fu ...
, whose community was called Eastern Christendom or Byzantine commonwealth). After the fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city was captured on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 55-da ...
in 1453, Latin Christendom rose to a central role in the Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to various nations and state (polity), states in Western Europe, Northern America, and Australasia; with some debate as to whether those in Eastern Europe and Latin America also const ...
. Following the reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
, protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
emerged as the third main branch of Christianity in the 16th century. The history of the Christian world spans about 2,000 years and includes a variety of socio-political developments, as well as advancements in the arts
The arts or creative arts are a vast range of human practices involving creativity, creative expression, storytelling, and cultural participation. The arts encompass diverse and plural modes of thought, deeds, and existence in an extensive ...
, architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
, literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially novels, Play (theatre), plays, and poetry, poems. It includes both print and Electroni ...
, science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
, philosophy
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
, politics
Politics () is the set of activities that are associated with decision-making, making decisions in social group, groups, or other forms of power (social and political), power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of Social sta ...
and technology.
Terminology
TheAnglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
term ''crīstendōm'' appears to have been coined in the 9th century by a scribe somewhere in southern England, possibly at the court of king Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great ( ; – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who both died when Alfr ...
of Wessex
The Kingdom of the West Saxons, also known as the Kingdom of Wessex, was an Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy, kingdom in the south of Great Britain, from around 519 until Alfred the Great declared himself as King of the Anglo-Saxons in 886.
The Anglo-Sa ...
. The scribe was translating Paulus Orosius' book ''History Against the Pagans'' () and in need for a term to express the concept of the universal culture focused on Jesus Christ
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
. It had the sense now taken by ''Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
'' (as is still the case with the cognate Dutch ''christendom'', where it denotes mostly the religion itself, just like the German ''Christentum'').
The current sense of the word of "lands where Christianity is the dominant religion" emerged in Late Middle English (by ).
Canadian theology professor Douglas John Hall stated (1997) that "Christendom" ..means literally the dominion or sovereignty of the Christian religion." Thomas John Curry, Roman Catholic auxiliary bishop of Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
, defined (2001) Christendom as "the system dating from the fourth century by which governments upheld and promoted Christianity." Curry states that the end of Christendom came about because modern governments refused to "uphold the teachings, customs, ethos, and practice of Christianity." British church historian
Church history or ecclesiastical history as an academic discipline studies the history of Christianity and the way the Christian Church has developed since its inception.
Henry Melvill Gwatkin defined church history as "the spiritual side of th ...
Diarmaid MacCulloch described (2010) Christendom as "the union between Christianity and secular power."
There is a common and nonliteral sense of the word that is much like the terms ''Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to various nations and state (polity), states in Western Europe, Northern America, and Australasia; with some debate as to whether those in Eastern Europe and Latin America also const ...
'', '' known world'' or '' Free World''. The notion of "Europe" and the "Western World
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to various nations and state (polity), states in Western Europe, Northern America, and Australasia; with some debate as to whether those in Eastern Europe and Latin America also const ...
" has been intimately connected with the concept of "Christianity and Christendom"; many even attribute Christianity for being the link that created a unified European identity.
History
Rise of Christendom
 Early Christianity spread in the Greek/Roman world and beyond as a 1st-century
Early Christianity spread in the Greek/Roman world and beyond as a 1st-century Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
sect, which historians refer to as Jewish Christianity. It may be divided into two distinct phases: the apostolic period, when the first apostles were alive and organizing the Church, and the post-apostolic period, when an early episcopal structure developed, whereby bishoprics were governed by bishops
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...
(overseers).
The post-apostolic period concerns the time roughly after the death of the apostles when bishops emerged as overseers of urban Christian populations. The earliest recorded use of the terms ''Christianity'' (Greek ) and ''catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
'' (Greek ), dates to this period, the 2nd century, attributed to Ignatius of Antioch
Ignatius of Antioch (; ; died 108/140), also known as Ignatius Theophorus (), was an early Christian writer and Patriarch of Antioch. While en route to Rome, where he met his Christian martyrs, martyrdom, Ignatius wrote a series of letters. This ...
''c.'' 107. Early Christendom would close at the end of imperial persecution of Christians after the ascension of Constantine the Great
Constantine I (27 February 27222 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a Constantine the Great and Christianity, pivotal ro ...
and the Edict of Milan
The Edict of Milan (; , ''Diatagma tōn Mediolanōn'') was the February 313 agreement to treat Christians benevolently within the Roman Empire. Frend, W. H. C. (1965). ''The Early Church''. SPCK, p. 137. Western Roman Emperor Constantine I and ...
in AD 313 and the First Council of Nicaea
The First Council of Nicaea ( ; ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in the Bithynian city of Nicaea (now İznik, Turkey) by the Roman Emperor Constantine I. The Council of Nicaea met from May until the end of July 325.
This ec ...
in 325.
According to Malcolm Muggeridge
Thomas Malcolm Muggeridge (24 March 1903 – 14 November 1990) was a conservative British journalist and satirist. His father, H. T. Muggeridge, was a socialist politician and one of the early Labour Party Members of Parliament (for Romford, i ...
(1980), Christ founded Christianity, but Constantine founded Christendom. Canadian theology professor Douglas John Hall dates the 'inauguration of Christendom' to the 4th century, with Constantine playing the primary role (so much so that he equates Christendom with "Constantinianism") and Theodosius I (Edict of Thessalonica
An edict is a decree or announcement of a law, often associated with monarchies, but it can be under any official authority. Synonyms include "dictum" and "pronouncement". ''Edict'' derives from the Latin wikt:edictum#Latin, edictum.
Notable ed ...
, 380) and Justinian I
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
secondary roles.Hall (2002), p. 1–9.
Late Antiquity and Early Middle Ages
medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
and renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
notion of the ''Christian world'' as a polity
A polity is a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of political Institutionalisation, institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources.
A polity can be any group of people org ...
. In essence, the earliest vision of Christendom was a vision of a Christian theocracy
Theocracy is a form of autocracy or oligarchy in which one or more deity, deities are recognized as supreme ruling authorities, giving divine guidance to human intermediaries, with executive and legislative power, who manage the government's ...
, a government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive (government), execu ...
founded upon and upholding Christian values, whose institutions are spread through and over with Christian doctrine
Christian theology is the theology – the systematic study of the divine and religion – of Christianity, Christian belief and practice. It concentrates primarily upon the texts of the Old Testament and of the New Testament, as well as on Ch ...
. In this period, members of the Christian clergy
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
wield political authority. The specific relationship between the political leaders and the clergy
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
varied but, in theory, the national and political divisions were at times subsumed under the leadership of the church as an institution. This model of church-state relations was accepted by various Church leaders and political leaders in European history.
The Church gradually became a defining institution of the Roman Empire. Emperor Constantine issued the Edict of Milan
The Edict of Milan (; , ''Diatagma tōn Mediolanōn'') was the February 313 agreement to treat Christians benevolently within the Roman Empire. Frend, W. H. C. (1965). ''The Early Church''. SPCK, p. 137. Western Roman Emperor Constantine I and ...
in 313 proclaiming toleration for the Christian religion, and convoked the First Council of Nicaea
The First Council of Nicaea ( ; ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in the Bithynian city of Nicaea (now İznik, Turkey) by the Roman Emperor Constantine I. The Council of Nicaea met from May until the end of July 325.
This ec ...
in 325 whose Nicene Creed
The Nicene Creed, also called the Creed of Constantinople, is the defining statement of belief of Nicene Christianity and in those Christian denominations that adhere to it.
The original Nicene Creed was first adopted at the First Council of N ...
included belief in "one holy catholic and apostolic Church". Emperor Theodosius I
Theodosius I ( ; 11 January 347 – 17 January 395), also known as Theodosius the Great, was Roman emperor from 379 to 395. He won two civil wars and was instrumental in establishing the Nicene Creed as the orthodox doctrine for Nicene C ...
made Nicene Christianity the state church of the Roman Empire
In the year before the First Council of Constantinople in 381, Nicene Christianity, Nicean Christianity became the official religion of the Roman Empire when Theodosius I, emperor of the East, Gratian, emperor of the West, and Gratian's junior co-r ...
with the Edict of Thessalonica
An edict is a decree or announcement of a law, often associated with monarchies, but it can be under any official authority. Synonyms include "dictum" and "pronouncement". ''Edict'' derives from the Latin wikt:edictum#Latin, edictum.
Notable ed ...
of 380. In terms of prosperity and cultural life, the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
was one of the peaks in Christian history and Christian civilization,. and Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
remained the leading city of the Christian world in size, wealth, and culture. There was a renewed interest in classical Greek philosophy, as well as an increase in literary output in vernacular Greek..
As the Western Roman Empire
In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. ...
disintegrated into feudal kingdoms and principalities
A principality (or sometimes princedom) is a type of monarchical state or feudal territory ruled by a prince or princess. It can be either a sovereign state or a constituent part of a larger political entity. The term "principality" is often ...
, the concept of Christendom changed as the western church became one of five patriarchates of the Pentarchy and the Christians of the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
developed. The Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
was the last bastion of Christendom. Christendom would take a turn with the rise of the Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
, a Germanic tribe who converted to the Christian faith and entered into communion with Rome.
On Christmas Day 800 AD, Pope Leo III crowned Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
, resulting in the creation of another Christian king beside the Christian emperor in the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
state. The Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Franks, Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as List of Frankish kings, kings of the Franks since ...
created a definition of ''Christendom'' in juxtaposition with the Byzantine Empire, that of a distributed versus centralized culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
respectively.
The classical heritage flourished throughout the Middle Ages in both the Byzantine Greek East and the Latin West. In the Greek philosopher Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the writte ...
's ideal state there are three major classes, which was representative of the idea of the "tripartite soul", which is expressive of three functions or capacities of the human soul: "reason", "the spirited element", and "appetites" (or "passions"). Will Durant made a convincing case that certain prominent features of Plato's ideal community where discernible in the organization, dogma and effectiveness of "the" Medieval Church in Europe:
... For a thousand years Europe was ruled by an order of guardians considerably like that which was visioned by our philosopher. During the Middle Ages it was customary to classify the population of Christendom into ''laboratores'' (workers), ''bellatores'' (soldiers), and ''oratores'' (clergy). The last group, though small in number, monopolized the instruments and opportunities of culture, and ruled with almost unlimited sway half of the most powerful continent on the globe. The clergy, like Plato's guardians, were placed in authority... by their talent as shown in ecclesiastical studies and administration, by their disposition to a life of meditation and simplicity, and ... by the influence of their relatives with the powers of state and church. In the latter half of the period in which they ruled 00 AD onwards the clergy were as free from family cares as even Plato could desire or such guardians.. lericalCelibacy was part of the psychological structure of the power of the clergy; for on the one hand they were unimpeded by the narrowing egoism of the family, and on the other their apparent superiority to the call of the flesh added to the awe in which lay sinners held them....''''
Later Middle Ages and Renaissance
After the collapse of Charlemagne's empire, the southern remnants of theHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
became a collection of states loosely connected to the Holy See of Rome. Tensions between Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III (; born Lotario dei Conti di Segni; 22 February 1161 – 16 July 1216) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 until his death on 16 July 1216.
Pope Innocent was one of the most power ...
and secular rulers ran high, as the pontiff exerted control over their temporal counterparts in the west and vice versa. The pontificate of Innocent III is considered the height of temporal power of the papacy. The '' Corpus Christianum'' described the then-current notion of the community
A community is a social unit (a group of people) with a shared socially-significant characteristic, such as place, set of norms, culture, religion, values, customs, or identity. Communities may share a sense of place situated in a given g ...
of all Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
united under the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
. The community was to be guided by Christian values in its politics, economics and social life. Its legal basis was the '' corpus iuris canonica'' (body of canon law).
In the East, Christendom became more defined as the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
's gradual loss of territory to an expanding Islam and the Muslim conquest of Persia
As part of the early Muslim conquests, which were initiated by Muhammad in 622, the Rashidun Caliphate conquered the Sasanian Empire between 632 and 654. This event led to the decline of Zoroastrianism, which had been the official religion of ...
. This caused Christianity to become important to the Byzantine identity. Before the East–West Schism
The East–West Schism, also known as the Great Schism or the Schism of 1054, is the break of communion (Christian), communion between the Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church. A series of Eastern Orthodox – Roman Catholic eccle ...
which divided the Church religiously, there had been the notion of a ''universal Christendom'' that included the East and the West. After the East–West Schism, hopes of regaining religious unity with the West were ended by the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
, when Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding ...
conquered the Byzantine capital of Constantinople and hastened the decline of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire experienced cycles of growth and decay over the course of nearly a thousand years, including major losses during the early Muslim conquests of the 7th century. But the Empire's final decline started in the 11th century, and e ...
on the path to its destruction. With the breakup of the Byzantine Empire into individual nations with nationalist Orthodox Churches, the term Christendom described Western Europe, Catholicism, Orthodox Byzantines, and other Eastern rites of the Church.
The Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
's peak of authority over all European Christians and their common endeavours of the Christian community—for example, the Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding t ...
, the fight against the Moors
The term Moor is an Endonym and exonym, exonym used in European languages to designate the Muslims, Muslim populations of North Africa (the Maghreb) and the Iberian Peninsula (particularly al-Andalus) during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a s ...
in the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
and against the Ottomans
Ottoman may refer to:
* Osman I, historically known in English as "Ottoman I", founder of the Ottoman Empire
* Osman II, historically known in English as "Ottoman II"
* Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empir ...
in the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
—helped to develop a sense of communal identity against the obstacle of Europe's deep political divisions. The popes, formally just the bishops of Rome, claimed to be the focus of all Christendom, which was largely recognised in Western Christendom from the 11th century until the Reformation, but not in Eastern Christendom. Moreover, this authority was also sometimes abused, and fostered the Inquisition
The Inquisition was a Catholic Inquisitorial system#History, judicial procedure where the Ecclesiastical court, ecclesiastical judges could initiate, investigate and try cases in their jurisdiction. Popularly it became the name for various med ...
and anti-Jewish pogroms, to root out divergent elements and create a religiously uniform community. Ultimately, the Inquisition was done away with by order of Pope Innocent III.
Christendom ultimately was led into specific crisis in the late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the Periodization, period of History of Europe, European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period ( ...
, when the kings of France managed to establish a French national church during the 14th century and the papacy became ever more aligned with the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation. Known as the Western Schism, western Christendom was a split between three men, who were driven by politics rather than any real theological disagreement for simultaneously claiming to be the true pope. The Avignon Papacy
The Avignon Papacy (; ) was the period from 1309 to 1376 during which seven successive popes resided in Avignon (at the time within the Kingdom of Arles, part of the Holy Roman Empire, now part of France) rather than in Rome (now the capital of ...
developed a reputation for corruption that estranged major parts of Western Christendom. The Avignon schism was ended by the Council of Constance.
Before the modern period, Christendom was in a general crisis at the time of the Renaissance Popes because of the moral laxity of these pontiffs and their willingness to seek and rely on temporal power as secular rulers did. Many in the Catholic Church's hierarchy in the Renaissance became increasingly entangled with insatiable greed for material wealth and temporal power, which led to many reform movements, some merely wanting a moral reformation of the Church's clergy, while others repudiated the Church and separated from it in order to form new sects. The Italian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance ( ) was a period in History of Italy, Italian history between the 14th and 16th centuries. The period is known for the initial development of the broader Renaissance culture that spread across Western Europe and marked t ...
produced ideas or institutions by which men living in society could be held together in harmony. In the early 16th century, Baldassare Castiglione (''The Book of the Courtier
''The Book of the Courtier'' ( ) by Baldassare Castiglione is a lengthy philosophical dialogue on the topic of what constitutes an ideal courtier or (in the third chapter) court lady, worthy to befriend and advise a prince or political leader. ...
'') laid out his vision of the ideal gentleman and lady, while Machiavelli cast a jaundiced eye on "la verità effetuale delle cose"—the actual truth of things—in ''The Prince
''The Prince'' ( ; ) is a 16th-century political treatise written by the Italian diplomat, philosopher, and Political philosophy, political theorist Niccolò Machiavelli in the form of a realistic instruction guide for new Prince#Prince as gener ...
'', composed, humanist style, chiefly of parallel ancient and modern examples of Virtù. Some Protestant movements grew up along lines of mysticism
Mysticism is popularly known as becoming one with God or the Absolute (philosophy), Absolute, but may refer to any kind of Religious ecstasy, ecstasy or altered state of consciousness which is given a religious or Spirituality, spiritual meani ...
or renaissance humanism (cf.
The abbreviation cf. (short for either Latin or , both meaning 'compare') is generally used in writing to refer the reader to other material to make a comparison with the topic being discussed. However some sources offer differing or even contr ...
Erasmus
Desiderius Erasmus Roterodamus ( ; ; 28 October c. 1466 – 12 July 1536), commonly known in English as Erasmus of Rotterdam or simply Erasmus, was a Dutch Christian humanist, Catholic priest and Catholic theology, theologian, educationalist ...
). The Catholic Church fell partly into general neglect under the Renaissance Popes, whose inability to govern the Church by showing personal example of high moral standards set the climate for what would ultimately become the Protestant Reformation. During the Renaissance, the papacy was mainly run by the wealthy families and also had strong secular interests. To safeguard Rome and the connected Papal States the popes became necessarily involved in temporal matters, even leading armies, as the great patron of arts Pope Julius II
Pope Julius II (; ; born Giuliano della Rovere; 5 December 144321 February 1513) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1503 to his death, in February 1513. Nicknamed the Warrior Pope, the Battle Pope or the Fearsome ...
did. During these intermediate times, popes strove to make Rome the capital of Christendom while projecting it through art, architecture, and literature as the center of a Golden Age of unity, order, and peace.
Professor Frederick J. McGinness described Rome as essential in understanding the legacy the Church and its representatives encapsulated best by The Eternal City: No other city in Europe matches Rome in its traditions, history, legacies, and influence in the Western world. Rome in the Renaissance under the papacy not only acted as guardian and transmitter of these elements stemming from the Roman Empire but also assumed the role as artificer and interpreter of its myths and meanings for the peoples of Europe from the Middle Ages to modern times... Under the patronage of the popes, whose wealth and income were exceeded only by their ambitions, the city became a cultural center for master architects, sculptors, musicians, painters, and artisans of every kind...In its myth and message, Rome had become the sacred city of the popes, the prime symbol of a triumphant Catholicism, the center of orthodox Christianity, a new Jerusalem.It is clearly noticeable that the popes of the Italian Renaissance have been subjected by many writers with an overly harsh tone. Pope Julius II, for example, was not only an effective secular leader in military affairs, a deviously effective politician but foremost one of the greatest patron of the Renaissance period and person who also encouraged open criticism from noted humanists. The blossoming of renaissance humanism was made very much possible due to the universality of the institutions of Catholic Church and represented by personalities such as Pope Pius II,
Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath who formulated a mathematical model, model of Celestial spheres#Renaissance, the universe that placed heliocentrism, the Sun rather than Earth at its cen ...
, Leon Battista Alberti
Leon Battista Alberti (; 14 February 1404 – 25 April 1472) was an Italian Renaissance humanist author, artist, architect, poet, Catholic priest, priest, linguistics, linguist, philosopher, and cryptography, cryptographer; he epitomised the natu ...
, Desiderius Erasmus
Desiderius Erasmus Roterodamus ( ; ; 28 October c. 1466 – 12 July 1536), commonly known in English as Erasmus of Rotterdam or simply Erasmus, was a Dutch Christian humanist, Catholic priest and Catholic theology, theologian, educationalist ...
, sir Thomas More
Sir Thomas More (7 February 1478 – 6 July 1535), venerated in the Catholic Church as Saint Thomas More, was an English lawyer, judge, social philosopher, author, statesman, theologian, and noted Renaissance humanist. He also served Henry VII ...
, Bartolomé de Las Casas
Bartolomé de las Casas, Dominican Order, OP ( ; ); 11 November 1484 – 18 July 1566) was a Spanish clergyman, writer, and activist best known for his work as an historian and social reformer. He arrived in Hispaniola as a layman, then became ...
, Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 1452 - 2 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested o ...
and Teresa of Ávila. George Santayana in his work '' The Life of Reason'' postulated the tenets of the all encompassing order the Church had brought and as the repository of the legacy of classical antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the inter ...
:
The enterprise of individuals or of small aristocratic bodies has meantime sown the world which we call civilised with some seeds and nuclei of order. There are scattered about a variety of churches, industries, academies, and governments. But the universal order once dreamt of and nominally almost established, the empire of universal peace, all-permeating rational art, and philosophical worship, is mentioned no more. An unformulated conception, the prerational ethics of private privilege and national unity, fills the background of men's minds. It represents feudal traditions rather than the tendency really involved in contemporary industry, science, or philanthropy. Those dark ages, from which our political practice is derived, had a political theory which we should do well to study; for their theory about a universal empire and a Catholic church was in turn the echo of a former age of reason, when a few men conscious of ruling the world had for a moment sought to survey it as a whole and to rule it justly.
Reformation and Early Modern era
Developments inwestern philosophy
Western philosophy refers to the Philosophy, philosophical thought, traditions and works of the Western world. Historically, the term refers to the philosophical thinking of Western culture, beginning with the ancient Greek philosophy of the Pre ...
and European events brought change to the notion of the ''Corpus Christianum''. The Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy ...
accelerated the process of transforming France from a feudal monarchy to a centralized state. The rise of strong, centralized monarchies denoted the European transition from feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was a combination of legal, economic, military, cultural, and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe from the 9th to 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of struc ...
to capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
. By the end of the Hundred Years' War, both France and England were able to raise enough money through taxation to create independent standing armies. In the Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses, known at the time and in following centuries as the Civil Wars, were a series of armed confrontations, machinations, battles and campaigns fought over control of the English throne from 1455 to 1487. The conflict was fo ...
, Henry Tudor took the crown of England. His heir, the absolute king Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
establishing the English church.
In modern history
The modern era or the modern period is considered the current historical period of human history. It was originally applied to the history of Europe and Western history for events that came after the Middle Ages, often from around the year 1500, ...
, the Reformation and rise of modernity
Modernity, a topic in the humanities and social sciences, is both a historical period (the modern era) and the ensemble of particular Society, socio-Culture, cultural Norm (social), norms, attitudes and practices that arose in the wake of the ...
in the early 16th century entailed a change in the ''Corpus Christianum''. In the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, the Peace of Augsburg of 1555 officially ended the idea among secular leaders that all Christians must be united under one church. The principle of '' cuius regio, eius religio'' ("whose the region is, his religion") established the religious, political and geographic divisions of Christianity, and this was established with the Treaty of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two Peace treaty, peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy R ...
in 1648, which legally ended the concept of a single Christian hegemony in the territories of the Holy Roman Empire, despite the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
's doctrine that it alone is the one true Church founded by Christ.
Subsequently, each government determined the religion of their own state. Christians living in states where their denomination was ''not'' the established one were guaranteed the right to practice their faith in public during allotted hours and in private at their will. At times there were mass expulsions of dissenting faiths as happened with the Salzburg Protestants
The Salzburg Protestants () were Protestantism, Protestant refugees who had lived in the Catholic Archbishopric of Salzburg until the 18th century. In a series of persecutions ending in 1731, over 20,000 Protestants were expelled from their homel ...
. Some people passed as adhering to the official church, but instead lived as Nicodemite
A Nicodemite () is a person suspected of publicly misrepresenting their religious faith to conceal their true beliefs. The term is sometimes defined as referring to a Protestantism, Protestant Christian who lived in a Roman Catholic country and es ...
s or crypto-protestants.
The European wars of religion
The European wars of religion were a series of wars waged in Europe during the 16th, 17th and early 18th centuries. Fought after the Protestant Reformation began in 1517, the wars disrupted the religious and political order in the Catholic Chu ...
are usually taken to have ended with the Treaty of Westphalia (1648), or arguably, including the Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War was a European great power conflict from 1688 to 1697 between Kingdom of France, France and the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance. Although largely concentrated in Europe, fighting spread to colonial poss ...
and the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish E ...
in this period, with the Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaty, peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vac ...
of 1713. In the 18th century, the focus shifts away from religious conflicts, either between Christian factions or against the external threat of Islamic factions.
End of Christendom
The European Miracle, theAge of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment (also the Age of Reason and the Enlightenment) was a Europe, European Intellect, intellectual and Philosophy, philosophical movement active from the late 17th to early 19th century. Chiefly valuing knowledge gained th ...
and the formation of the great colonial empire
A colonial empire is a sovereign state, state engaging in colonization, possibly establishing or maintaining colony, colonies, infused with some form of coloniality and colonialism. Such states can expand contiguous as well as Territory#Overseas ...
s, together with the beginning decline of the Ottoman Empire, mark the end of the geopolitical "history of Christendom". Instead, the focus of Western history shifts to the development of the nation-state
A nation state, or nation-state, is a political entity in which the state (a centralized political organization ruling over a population within a territory) and the nation (a community based on a common identity) are (broadly or ideally) con ...
, accompanied by increasing atheism
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the Existence of God, existence of Deity, deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the ...
and secularism
Secularism is the principle of seeking to conduct human affairs based on naturalistic considerations, uninvolved with religion. It is most commonly thought of as the separation of religion from civil affairs and the state and may be broadened ...
, culminating with the French Revolution and the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
at the turn of the 19th century.
In his 1964 encyclical letter '' Ecclesiam Suam'', Pope Paul VI
Pope Paul VI (born Giovanni Battista Enrico Antonio Maria Montini; 26 September 18976 August 1978) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 21 June 1963 until his death on 6 August 1978. Succeeding John XXII ...
observed thatWriting in 1997, Canadian theology
Theology is the study of religious belief from a Religion, religious perspective, with a focus on the nature of divinity. It is taught as an Discipline (academia), academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itse ...
professor Douglas John Hall argued that Christendom had either fallen already or was in its death throes; although its end was gradual and not as clear to pin down as its 4th-century establishment, the "transition to the post-Constantinian, or post-Christendom, situation (...) has already been in process for a century or two", beginning with the 18th-century rationalist Enlightenment and the French Revolution (the first attempt to topple the Christian establishment). American Catholic bishop Thomas John Curry stated in 2001 that the end of Christendom came about because modern governments refused to "uphold the teachings, customs, ethos, and practice of Christianity". He argued the First Amendment to the United States Constitution
The First Amendment (Amendment I) to the United States Constitution prevents Federal government of the United States, Congress from making laws respecting an Establishment Clause, establishment of religion; prohibiting the Free Exercise Cla ...
(1791) and the Second Vatican Council
The Second Ecumenical Council of the Vatican, commonly known as the or , was the 21st and most recent ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. The council met each autumn from 1962 to 1965 in St. Peter's Basilica in Vatican City for session ...
's Declaration on Religious Freedom (1965) are two of the most important documents setting the stage for its end. According to British historian Diarmaid MacCulloch (2010), Christendom was 'killed' by the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
(1914–18), which led to the fall of the three main Christian empires ( Russian, German and Austrian) of Europe, as well as the Ottoman Empire, rupturing the Eastern Christian communities that had existed on its territory. The Christian empires were replaced by secular, even anti-clerical republics seeking to definitively keep the churches out of politics. The only surviving monarchy with an established church, Britain, was severely damaged by the war, lost most of Ireland due to Catholic–Protestant infighting, and was starting to lose grip on its colonies.MacCulloch (2010), p. 1024–1030.
Changes in worldwide Christianity over the last century have been significant, since 1900, Christianity has spread rapidly in the Global South
Global North and Global South are terms that denote a method of grouping countries based on their defining characteristics with regard to socioeconomics and politics. According to UN Trade and Development (UNCTAD), the Global South broadly com ...
and Third World countries. The late 20th century has shown the shift of Christian adherence to the Third World
The term Third World arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact. The United States, Canada, Taiwan, Japan, South Korea, the Southern Cone, NATO, Western European countries and oth ...
and the Southern Hemisphere in general, by 2010 about 157 countries and territories in the world had Christian majorities.
Classical culture
Western culture
Western culture, also known as Western civilization, European civilization, Occidental culture, Western society, or simply the West, refers to the Cultural heritage, internally diverse culture of the Western world. The term "Western" encompas ...
, throughout most of its history, has been nearly equivalent to Christian culture, and many of the population of the Western hemisphere could broadly be described as cultural Christians. The notion of "Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
" and the "Western World
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to various nations and state (polity), states in Western Europe, Northern America, and Australasia; with some debate as to whether those in Eastern Europe and Latin America also const ...
" has been intimately connected with the concept of "Christianity and Christendom"; many even attribute Christianity for being the link that created a unified European identity. Historian
A historian is a person who studies and writes about the past and is regarded as an authority on it. Historians are concerned with the continuous, methodical narrative and research of past events as relating to the human species; as well as the ...
Paul Legutko of Stanford University
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth ...
said the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
is "at the center of the development of the values, ideas, science, laws, and institutions which constitute what we call Western civilization."
Though Western culture contained several polytheistic religions during its early years under the Greek and Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
s, as the centralized Roman power waned, the dominance of the Catholic Church was the only consistent force in Western Europe. Until the Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment (also the Age of Reason and the Enlightenment) was a Europe, European Intellect, intellectual and Philosophy, philosophical movement active from the late 17th to early 19th century. Chiefly valuing knowledge gained th ...
, Christian culture guided the course of philosophy, literature, art, music and science. Christian disciplines of the respective arts have subsequently developed into Christian philosophy
Christian philosophy includes all philosophy carried out by Christians, or in relation to the religion of Christianity.
Christian philosophy emerged with the aim of reconciling science and faith, starting from natural rational explanations wit ...
, Christian art
Christian art is sacred art which uses subjects, themes, and imagery from Christianity. Most Christian groups use or have used art to some extent, including early Christian art and architecture and Christian media.
Images of Jesus and narrative ...
, Christian music
Christian music is a genre of music that has been written to express either personal or a communal belief regarding Christianity, Christian life and faith. Common themes of Christian music include praise, worship, penitence and lament, and its f ...
, Christian literature
Christian literature is the literary aspect of Christian media, and it constitutes a huge body of extremely varied writing.
History
The Christian genre spans a variety of media and art forms that highlight Christian beliefs, narratives, and m ...
etc. Art and literature, law, education, and politics were preserved in the teachings of the Church, in an environment that, otherwise, would have probably seen their loss. The Church founded many cathedrals
A cathedral is a church (building), church that contains the of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, Annual conferences within Methodism, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually s ...
, universities
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
, monasteries and seminaries, some of which continue to exist today. Medieval Christianity created the first modern universities. The Catholic Church established a hospital system in medieval Europe that vastly improved upon the Roman ''valetudinaria''. These hospitals were established to cater to "particular social groups marginalized by poverty, sickness, and age," according to historian of hospitals, Guenter Risse. Christianity also had a strong impact on all other aspects of life: marriage and family, education, the humanities and sciences, the political and social order, the economy, and the arts.
Christianity had a significant impact on education and science and medicine as the church created the bases of the Western system of education, and was the sponsor of founding universities
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
in the Western world as the university is generally regarded as an institution that has its origin in the Medieval Christian setting.Rüegg, Walter: "Foreword. The University as a European Institution", in: ''A History of the University in Europe. Vol. 1: Universities in the Middle Ages'', Cambridge University Press, 1992, , pp. XIX–XX Many clerics
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
throughout history have made significant contributions to science and Jesuits
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
in particular have made numerous significant contributions to the development of science. The cultural influence of Christianity includes social welfare
Welfare spending is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specifically to social insurance p ...
, founding hospitals, economics (as the Protestant work ethic
The Protestant work ethic, also known as the Calvinist work ethic or the Puritan work ethic, is a work ethic concept in sociology, economics, and history. It emphasizes that a person's subscription to the values espoused by the Protestantism, Pro ...
), natural law
Natural law (, ) is a Philosophy, philosophical and legal theory that posits the existence of a set of inherent laws derived from nature and universal moral principles, which are discoverable through reason. In ethics, natural law theory asserts ...
(which would later influence the creation of international law
International law, also known as public international law and the law of nations, is the set of Rule of law, rules, norms, Customary law, legal customs and standards that State (polity), states and other actors feel an obligation to, and generall ...
), politics, architecture,Sir Banister Fletcher, ''History of Architecture on the Comparative Method''. literature, personal hygiene, and family life. Christianity played a role in ending practices common among pagan societies
A society () is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. ...
, such as human sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease deity, gods, a human ruler, public or jurisdictional demands for justice by capital punishment, an authoritative/prie ...
, slavery
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
, infanticide
Infanticide (or infant homicide) is the intentional killing of infants or offspring. Infanticide was a widespread practice throughout human history that was mainly used to dispose of unwanted children, its main purpose being the prevention of re ...
and polygamy
Polygamy (from Late Greek , "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marriage, marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, it is called polygyny. When a woman is married to more tha ...
.
Art and literature
Writings and poetry
Christian literature
Christian literature is the literary aspect of Christian media, and it constitutes a huge body of extremely varied writing.
History
The Christian genre spans a variety of media and art forms that highlight Christian beliefs, narratives, and m ...
is writing that deals with Christian themes and incorporates the Christian world view. This constitutes a huge body of extremely varied writing. Christian poetry is any poetry
Poetry (from the Greek language, Greek word ''poiesis'', "making") is a form of literature, literary art that uses aesthetics, aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language to evoke meaning (linguistics), meanings in addition to, or in ...
that contains Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
teachings, themes, or references. The influence of Christianity on poetry
Poetry (from the Greek language, Greek word ''poiesis'', "making") is a form of literature, literary art that uses aesthetics, aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language to evoke meaning (linguistics), meanings in addition to, or in ...
has been great in any area that Christianity has taken hold. Christian poems often directly reference the Bible
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) originally writt ...
, while others provide allegory
As a List of narrative techniques, literary device or artistic form, an allegory is a wikt:narrative, narrative or visual representation in which a character, place, or event can be interpreted to represent a meaning with moral or political signi ...
.
Supplemental arts
Christian art
Christian art is sacred art which uses subjects, themes, and imagery from Christianity. Most Christian groups use or have used art to some extent, including early Christian art and architecture and Christian media.
Images of Jesus and narrative ...
is art produced in an attempt to illustrate, supplement and portray in tangible form the principles of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
. Virtually all Christian groupings use or have used art to some extent. The prominence of art and the media, style, and representations change; however, the unifying theme is ultimately the representation of the life and times of Jesus
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
and in some cases the Old Testament
The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Isr ...
. Depictions of saints are also common, especially in Anglicanism
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
, Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, and Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
.
Illumination
 An
An illuminated manuscript
An illuminated manuscript is a formally prepared manuscript, document where the text is decorated with flourishes such as marginalia, borders and Miniature (illuminated manuscript), miniature illustrations. Often used in the Roman Catholic Churc ...
is a manuscript
A manuscript (abbreviated MS for singular and MSS for plural) was, traditionally, any document written by hand or typewritten, as opposed to mechanically printed or reproduced in some indirect or automated way. More recently, the term has ...
in which the text
Text may refer to:
Written word
* Text (literary theory)
In literary theory, a text is any object that can be "read", whether this object is a work of literature, a street sign, an arrangement of buildings on a city block, or styles of clothi ...
is supplemented by the addition of decoration. The earliest surviving substantive illuminated manuscripts are from the period AD 400 to 600, primarily produced in Ireland, Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
and Italy. The majority of surviving manuscripts are from the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, although many illuminated manuscripts survive from the 15th century Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, along with a very limited number from Late Antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown (historian), Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodiza ...
.
Most illuminated manuscripts were created as codices
The codex (: codices ) was the historical ancestor format of the modern book. Technically, the vast majority of modern books use the codex format of a stack of pages bound at one edge, along the side of the text. But the term ''codex'' is now r ...
, which had superseded scrolls; some isolated single sheets survive. A very few illuminated manuscript fragments survive on papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can a ...
. Most medieval manuscripts, illuminated or not, were written on parchment
Parchment is a writing material made from specially prepared Tanning (leather), untanned skins of animals—primarily sheep, calves and goats. It has been used as a writing medium in West Asia and Europe for more than two millennia. By AD 400 ...
(most commonly of calf, sheep, or goat skin), but most manuscripts important enough to illuminate were written on the best quality of parchment, called vellum
Vellum is prepared animal skin or membrane, typically used as writing material. It is often distinguished from parchment, either by being made from calfskin (rather than the skin of other animals), or simply by being of a higher quality. Vellu ...
, traditionally made of unsplit calfskin, though high quality parchment from other skins was also called ''parchment''.
Iconography
 Christian art began, about two centuries after Christ, by borrowing motifs from Roman Imperial imagery,
Christian art began, about two centuries after Christ, by borrowing motifs from Roman Imperial imagery, classical Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archa ...
and Roman religion and popular art. Religious images are used to some extent by the Abrahamic
The term Abrahamic religions is used to group together monotheistic religions revering the Biblical figure Abraham, namely Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The religions share doctrinal, historical, and geographic overlap that contrasts them wit ...
Christian faith, and often contain highly complex iconography, which reflects centuries of accumulated tradition. In the Late Antique period iconography began to be standardised, and to relate more closely to Biblical
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) biblical languages ...
texts, although many gaps in the canonical Gospel narratives were plugged with matter from the apocryphal gospels
Apocrypha () are biblical or related writings not forming part of the accepted canon of scripture, some of which might be of doubtful authorship or authenticity. In Christianity, the word ''apocryphal'' (ἀπόκρυφος) was first applied to ...
. Eventually the Church would succeed in weeding most of these out, but some remain, like the ox and ass in the Nativity of Christ.
An icon
An icon () is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, in the cultures of the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, Catholic Church, Catholic, and Lutheranism, Lutheran churches. The most common subjects include Jesus, Mary, mother of ...
is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, from Eastern Christianity
Eastern Christianity comprises Christianity, Christian traditions and Christian denomination, church families that originally developed during Classical antiquity, classical and late antiquity in the Eastern Mediterranean region or locations fu ...
. Christianity has used symbolism from its very beginnings. In both East and West, numerous iconic types of Christ
Jesus ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Christianity, central figure of Christianity, the M ...
, Mary and saints and other subjects were developed; the number of named types of icons of Mary, with or without the infant Christ, was especially large in the East, whereas Christ Pantocrator was much the commonest image of Christ.
Christian symbolism invests objects or actions with an inner meaning expressing Christian ideas. Christianity has borrowed from the common stock of significant symbols known to most periods and to all regions of the world. Religious symbolism is effective when it appeals to both the intellect and the emotions. Especially important depictions of Mary include the Hodegetria and Panagia types. Traditional models evolved for narrative paintings, including large cycles covering the events of the Life of Christ, the Life of the Virgin, parts of the Old Testament, and, increasingly, the lives of popular saint
In Christianity, Christian belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of sanctification in Christianity, holiness, imitation of God, likeness, or closeness to God in Christianity, God. However, the use of the ...
s. Especially in the West, a system of attributes developed for identifying individual figures of saints by a standard appearance and symbolic objects held by them; in the East they were more likely to identified by text labels.
Each saint has a story and a reason why he or she led an exemplary life. Symbols
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise different concep ...
have been used to tell these stories throughout the history of the Church. A number of Christian saints are traditionally represented by a symbol or iconic motif associated with their life, termed an attribute or emblem
An emblem is an abstract art, abstract or representational pictorial image that represents a concept, like a moral truth, or an allegory, or a person, like a monarch or saint.
Emblems vs. symbols
Although the words ''emblem'' and ''symbol'' ...
, in order to identify them. The study of these forms part of iconography
Iconography, as a branch of art history, studies the identification, description and interpretation of the content of images: the subjects depicted, the particular compositions and details used to do so, and other elements that are distinct fro ...
in Art history
Art history is the study of Work of art, artistic works made throughout human history. Among other topics, it studies art’s formal qualities, its impact on societies and cultures, and how artistic styles have changed throughout history.
Tradit ...
.
Architecture
 Christian architecture encompasses a wide range of both secular and religious styles from the foundation of Christianity to the present day, influencing the design and construction of buildings and structures in Christian culture.Fletcher, Banister. ''A History of Architecture''
Buildings were at first adapted from those originally intended for other purposes but, with the rise of distinctively ecclesiastical architecture, church buildings came to influence secular ones which have often imitated religious architecture. In the 20th century, the use of new materials, such as concrete, as well as simpler styles has had its effect upon the design of churches and arguably the flow of influence has been reversed. From the birth of Christianity to the present, the most significant period of transformation for Christian architecture in the west was the Gothic cathedral. In the east,
Christian architecture encompasses a wide range of both secular and religious styles from the foundation of Christianity to the present day, influencing the design and construction of buildings and structures in Christian culture.Fletcher, Banister. ''A History of Architecture''
Buildings were at first adapted from those originally intended for other purposes but, with the rise of distinctively ecclesiastical architecture, church buildings came to influence secular ones which have often imitated religious architecture. In the 20th century, the use of new materials, such as concrete, as well as simpler styles has had its effect upon the design of churches and arguably the flow of influence has been reversed. From the birth of Christianity to the present, the most significant period of transformation for Christian architecture in the west was the Gothic cathedral. In the east, Byzantine architecture
Byzantine architecture is the architecture of the Byzantine Empire, or Eastern Roman Empire, usually dated from 330 AD, when Constantine the Great established a new Roman capital in Byzantium, which became Constantinople, until the Fall of Cons ...
was a continuation of Roman architecture
Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical ancient Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often con ...
.
Philosophy
Christian philosophy
Christian philosophy includes all philosophy carried out by Christians, or in relation to the religion of Christianity.
Christian philosophy emerged with the aim of reconciling science and faith, starting from natural rational explanations wit ...
is a term to describe the fusion of various fields of philosophy
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
with the theological doctrines of Christianity. Scholasticism
Scholasticism was a medieval European philosophical movement or methodology that was the predominant education in Europe from about 1100 to 1700. It is known for employing logically precise analyses and reconciling classical philosophy and Ca ...
, which means "that hichbelongs to the school", and was a method of learning taught by the academic
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of tertiary education. The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 386 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the go ...
s (or ''school people'') of medieval universities
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
c. 1100–1500. Scholasticism
Scholasticism was a medieval European philosophical movement or methodology that was the predominant education in Europe from about 1100 to 1700. It is known for employing logically precise analyses and reconciling classical philosophy and Ca ...
originally started to reconcile the philosophy
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
of the ancient classical philosophers with medieval Christian theology. Scholasticism is not a philosophy or theology in itself but a tool and method for learning which places emphasis on dialectical reasoning.
Christian civilization

Medieval conditions
TheByzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
, which was the most sophisticated culture during antiquity, suffered under Muslim conquests The Muslim conquests, Muslim invasions, Islamic conquests, including Arab conquests, Arab Islamic conquests, also Iranian Muslim conquests, Turkic Muslim conquests etc.
*Early Muslim conquests
** Ridda Wars
**Muslim conquest of Persia
*** Muslim co ...
limiting its scientific prowess during the Medieval period
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
. Christian Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean ...
had suffered a catastrophic loss of knowledge following the fall of the Western Roman Empire
In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. ...
. But thanks to the Church scholars such as Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas ( ; ; – 7 March 1274) was an Italian Dominican Order, Dominican friar and Catholic priest, priest, the foremost Scholasticism, Scholastic thinker, as well as one of the most influential philosophers and theologians in the W ...
and Buridan, the West carried on at least the spirit of scientific inquiry which would later lead to Europe's taking the lead in science during the Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of History of science, modern science during the early modern period, when developments in History of mathematics#Mathematics during the Scientific Revolution, mathemati ...
using translations of medieval works.
Medieval technology refers to the technology
Technology is the application of Conceptual model, conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible too ...
used in medieval Europe
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
under Christian rule. After the Renaissance of the 12th century
The Renaissance of the 12th century was a period of many changes at the outset of the High Middle Ages. It included social, political and economic transformations, and an intellectual revitalization of Western Europe with strong philosophical and ...
, medieval Europe saw a radical change in the rate of new inventions, innovations in the ways of managing traditional means of production, and economic growth. The period saw major technological
Technology is the application of conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible tools such as ute ...
advances, including the adoption of gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, charcoal (which is mostly carbon), and potassium nitrate, potassium ni ...
and the astrolabe
An astrolabe (; ; ) is an astronomy, astronomical list of astronomical instruments, instrument dating to ancient times. It serves as a star chart and Model#Physical model, physical model of the visible celestial sphere, half-dome of the sky. It ...
, the invention of spectacles
Glasses, also known as eyeglasses (American English), spectacles (Commonwealth English), or colloquially as specs, are Visual perception, vision eyewear with clear or tinted lens (optics), lenses mounted in a frame that holds them in front ...
, and greatly improved water mill
A watermill or water mill is a mill that uses hydropower. It is a structure that uses a water wheel or water turbine to drive a mechanical process such as milling (grinding), rolling, or hammering. Such processes are needed in the production ...
s, building
A building or edifice is an enclosed Structure#Load-bearing, structure with a roof, walls and window, windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, a ...
techniques, agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
in general, clock
A clock or chronometer is a device that measures and displays time. The clock is one of the oldest Invention, human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month, a ...
s, and ship
A ship is a large watercraft, vessel that travels the world's oceans and other Waterway, navigable waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research and fishing. Ships are generally disti ...
s. The latter advances made possible the dawn of the Age of Exploration
The Age of Discovery (), also known as the Age of Exploration, was part of the early modern period and overlapped with the Age of Sail. It was a period from approximately the 15th to the 17th century, during which Seamanship, seafarers fro ...
. The development of water mills was impressive, and extended from agriculture to sawmill
A sawmill (saw mill, saw-mill) or lumber mill is a facility where logging, logs are cut into lumber. Modern sawmills use a motorized saw to cut logs lengthwise to make long pieces, and crosswise to length depending on standard or custom sizes ...
s both for timber and stone, probably derived from Roman technology. By the time of the Domesday Book
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by ...
, most large villages in Britain had mills. They also were widely used in mining
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasib ...
, as described by Georg Agricola in De Re Metallica for raising ore from shafts, crushing ore, and even powering bellows.
Significant in this respect were advances within the fields of navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the motion, movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navig ...
. The compass
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself with No ...
and astrolabe
An astrolabe (; ; ) is an astronomy, astronomical list of astronomical instruments, instrument dating to ancient times. It serves as a star chart and Model#Physical model, physical model of the visible celestial sphere, half-dome of the sky. It ...
along with advances in shipbuilding, enabled the navigation of the World Oceans and thus domination of the worlds economic trade. Gutenberg's printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a printing, print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in whi ...
made possible a dissemination of knowledge to a wider population, that would not only lead to a gradually more egalitarian society, but one more able to dominate other cultures, drawing from a vast reserve of knowledge and experience.
Renaissance innovations
During theRenaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, great advances occurred in geography, astronomy, chemistry, physics, math, manufacturing, and engineering. The rediscovery of ancient scientific texts was accelerated after the Fall of Constantinople, and the invention of printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The ...
which would democratize learning and allow a faster propagation of new ideas. '' Renaissance technology'' is the set of artifacts and customs, spanning roughly the 14th through the 16th century. The era is marked by such profound technical advancements like the printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a printing, print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in whi ...
, linear perspectivity, patent law
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A ...
, double shell domes or Bastion fortresses. Draw-books of the Renaissance artist-engineers such as Taccola and Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 1452 - 2 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested o ...
give a deep insight into the mechanical technology then known and applied.
Renaissance science spawned the Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of History of science, modern science during the early modern period, when developments in History of mathematics#Mathematics during the Scientific Revolution, mathemati ...
; science and technology began a cycle of mutual advancement. The ''Scientific Renaissance'' was the early phase of the Scientific Revolution. In the two-phase model of early modern
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
science: a ''Scientific Renaissance'' of the 15th and 16th centuries, focused on the restoration of the natural knowledge of the ancients; and a ''Scientific Revolution'' of the 17th century, when scientists shifted from recovery to innovation. Some scholars and historians attributes Christianity to having contributed to the rise of the Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of History of science, modern science during the early modern period, when developments in History of mathematics#Mathematics during the Scientific Revolution, mathemati ...
.
Professor Noah J Efron says that "Generations of historians and sociologists have discovered many ways in which Christians, Christian beliefs, and Christian institutions played crucial roles in fashioning the tenets, methods, and institutions of what in time became modern science. They found that some forms of Christianity provided the motivation to study nature systematically..." Virtually all modern scholars and historians agree that Christianity moved many early-modern intellectuals to study nature systematically.
Demographics
Geographic spread
 In 2009, according to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', Christianity was the majority religion in Europe (including Russia) with 80%,
In 2009, according to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', Christianity was the majority religion in Europe (including Russia) with 80%, Latin America
Latin America is the cultural region of the Americas where Romance languages are predominantly spoken, primarily Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Latin America is defined according to cultural identity, not geogr ...
with 92%, North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
with 81%, and Oceania
Oceania ( , ) is a region, geographical region including Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is generally considered a continent, while Mainland Australia is regarded as its co ...
with 79%. There are also large Christian communities in other parts of the world, such as China, India and Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
, where Christianity is the second-largest religion after Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
. The United States is home to the world's largest Christian population, followed by Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
and Mexico.
Many Christians not only live under, but also have an official status in, a state religion of the following nations: Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
(Roman Catholic Church), Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
(Armenian Apostolic Church
The Armenian Apostolic Church () is the Autocephaly, autocephalous national church of Armenia. Part of Oriental Orthodoxy, it is one of the most ancient Christianity, Christian churches. The Armenian Apostolic Church, like the Armenian Catholic ...
), Costa Rica
Costa Rica, officially the Republic of Costa Rica, is a country in Central America. It borders Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, as well as Maritime bo ...
(Roman Catholic Church), Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
( Church of Denmark), El Salvador
El Salvador, officially the Republic of El Salvador, is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south by the Pacific Ocean. El Salvador's capital and largest city is S ...
(Roman Catholic Church), England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
(Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
), Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
(Georgian Orthodox Church
The Apostolic Autocephalous Orthodox Church of Georgia ( ka, საქართველოს სამოციქულო ავტოკეფალური მართლმადიდებელი ეკლესია, tr), commonl ...
), Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
( Church of Greece), Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ...
( Church of Iceland), Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (, ; ; ), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein ( ), is a Landlocked country#Doubly landlocked, doubly landlocked Swiss Standard German, German-speaking microstate in the Central European Alps, between Austria in the east ...
(Roman Catholic Church), Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
(Roman Catholic Church), Monaco
Monaco, officially the Principality of Monaco, is a Sovereign state, sovereign city-state and European microstates, microstate on the French Riviera a few kilometres west of the Regions of Italy, Italian region of Liguria, in Western Europe, ...
(Roman Catholic Church), Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
(Romanian Orthodox Church
The Romanian Orthodox Church (ROC; , ), or Romanian Patriarchate, is an autocephalous Eastern Orthodox church in full communion with other Eastern Orthodox Christian denomination, Christian churches, and one of the nine patriarchates in the East ...
), Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
(Church of Norway
The Church of Norway (, , , ) is an Lutheranism, evangelical Lutheran denomination of Protestant Christianity and by far the largest Christian church in Norway. Christianity became the state religion of Norway around 1020, and was established a ...
), Vatican City
Vatican City, officially the Vatican City State (; ), is a Landlocked country, landlocked sovereign state and city-state; it is enclaved within Rome, the capital city of Italy and Bishop of Rome, seat of the Catholic Church. It became inde ...
(Roman Catholic Church), Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
(Roman Catholic Church, Swiss Reformed Church and Christian Catholic Church of Switzerland).
Number of adherents
The estimated number ofChristians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
in the world ranges from 2.2 billion33.39% of ~7.2 billion world population (under the section 'People') to 2.4 billion people. The faith represents approximately one-third of the world's population and is the largest religion in the world, with the three largest groups of Christians being the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
, and the Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, and also called the Greek Orthodox Church or simply the Orthodox Church, is List of Christian denominations by number of members, one of the three major doctrinal and ...
. The largest Christian denomination is the Catholic Church, with an estimated 1.2 billion adherents.
Notable Christian organizations
Areligious order
A religious order is a subgroup within a larger confessional community with a distinctive high-religiosity lifestyle and clear membership. Religious orders often trace their lineage from revered teachers, venerate their Organizational founder, ...
is a lineage of communities and organizations of people who live in some way set apart from society in accordance with their specific religious devotion, usually characterized by the principles of its founder's religious practice. In contrast, the term Holy Orders
In certain Christian denominations, holy orders are the ordination, ordained ministries of bishop, priest (presbyter), and deacon, and the sacrament or rite by which candidates are ordained to those orders. Churches recognizing these orders inclu ...
is used by many Christian churches to refer to ordination or to a group of individuals who are set apart for a special role or ministry. Historically, the word "order" designated an established civil body or corporation with a hierarchy, and ordination meant legal incorporation into an ordo. The word "holy" refers to the Church. In context, therefore, a holy order is set apart for ministry in the Church. Religious orders are composed of initiates (laity) and, in some traditions, ordained clergies.
Various organizations include:
* In the Roman Catholic Church, religious institute
In the Catholic Church, a religious institute is "a society in which members, according to proper law, pronounce public religious vows, vows, either perpetual or temporary which are to be renewed, however, when the period of time has elapsed, a ...
s and secular institute
In the Catholic Church, a secular institute is one of the forms of consecrated life recognized in Canon law of the Catholic Church, Church law (1983 Code of Canon Law Canons 710–730).
Secular consecrated persons profess the Evangelical couns ...
s are the major forms of institutes of consecrated life, similar to which are societies of apostolic life. They are organizations of laity or clergy who live a common life under the guidance of a fixed rule and the leadership of a superior. (ed., see : Catholic orders and societies for a particular listing.)
* Anglican religious orders are communities of laity or clergy in the Anglican churches who live under a common rule of life. (ed., see : Anglican organizations for a particular listing)
Christianity law and ethics
Church and state framing
Within the framework of Christianity, there are at least three possible definitions for Church law. One is the Torah/Mosaic Law (from what Christians consider to be theOld Testament
The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Isr ...
) also called Divine Law
Divine law is any body of law that is perceived as deriving from a Transcendence (religion), transcendent source, such as the will of God or godsin contrast to man-made law or to secular law. According to Angelos Chaniotis and Rudolph F. Peters, di ...
or Biblical law. Another is the instructions of Jesus of Nazareth in the Gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christianity, Christian message ("the gospel"), but in the second century Anno domino, AD the term (, from which the English word originated as a calque) came to be used also for the books in which the message w ...
(sometimes referred to as the Law of Christ or the New Commandment or the New Covenant
The New Covenant () is a biblical interpretation which was originally derived from a Book of Jeremiah#Sections of the Book, phrase which is contained in the Book of Jeremiah (Jeremiah 31:31–34), in the Hebrew Bible (or the Old Testament of the ...
). A third is canon law
Canon law (from , , a 'straight measuring rod, ruler') is a set of ordinances and regulations made by ecclesiastical jurisdiction, ecclesiastical authority (church leadership) for the government of a Christian organization or church and its membe ...
which is the internal ecclesiastical
{{Short pages monitor