Charing Cross Railway Station on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Charing Cross railway station (also known as London Charing Cross) is a central London railway terminus between the
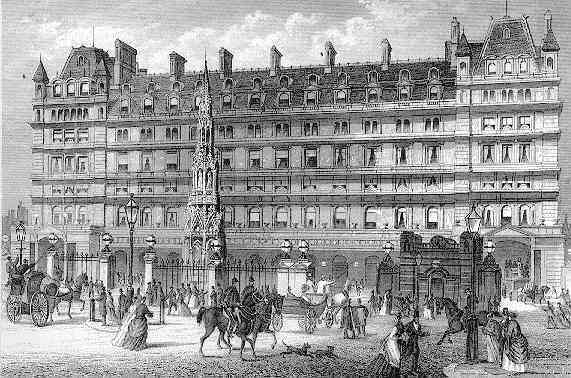 The station was designed by Sir John Hawkshaw, and featured a single span
The station was designed by Sir John Hawkshaw, and featured a single span
 Contemporary with the Charing Cross Hotel was a replica of the
Contemporary with the Charing Cross Hotel was a replica of the

 The station is served by two
The station is served by two
Station information
on Charing Cross railway station from
Strand
Strand may refer to:
Topography
*The flat area of land bordering a body of water, a:
** Beach
** Shoreline
* Strand swamp, a type of swamp habitat in Florida
Places Africa
* Strand, Western Cape, a seaside town in South Africa
* Strand Street ...
and Hungerford Bridge
The Hungerford Bridge crosses the River Thames in London, and lies between Waterloo Bridge and Westminster Bridge. Owned by Network Rail Infrastructure Ltd (who use its official name of Charing Cross Bridge) it is a steel truss railway brid ...
in the City of Westminster
The City of Westminster is a city and borough in Inner London. It is the site of the United Kingdom's Houses of Parliament and much of the British government. It occupies a large area of central Greater London, including most of the West En ...
. It is the terminus of the South Eastern Main Line
The South Eastern Main Line is a major long-distance railway route in South East England, UK, one of the three main routes crossing the county of Kent, going via Sevenoaks, Tonbridge, Ashford and Folkestone to Dover. The other routes are t ...
to Dover
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maids ...
via Ashford Ashford may refer to:
Places
Australia
*Ashford, New South Wales
*Ashford, South Australia
*Electoral district of Ashford, South Australia
Ireland
*Ashford, County Wicklow
*Ashford Castle, County Galway
United Kingdom
*Ashford, Kent, a town
**B ...
. All trains are operated by Southeastern
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sep ...
, which provides the majority of commuter and regional services to south-east London and Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
. It is connected to Charing Cross Underground station
Charing Cross (sometimes informally abbreviated as Charing +, Charing X, CHX or CH+) is a London Underground station at Charing Cross in the City of Westminster. The station is served by the Bakerloo line, Bakerloo and Northern line, Northern ...
and is near to Embankment Underground station and Embankment Pier.
The station was originally opened by the South Eastern Railway in 1864. It takes its name from its proximity to the road junction Charing Cross
Charing Cross ( ) is a junction in Westminster, London, England, where six routes meet. Clockwise from north these are: the east side of Trafalgar Square leading to St Martin's Place and then Charing Cross Road; the Strand leading to the City ...
, the notional "centre of London" from which distances from the city are measured. During the 19th century the station became the main London terminus for continental traffic via boat train
A boat train is a passenger train operating to a port for the specific purpose of making connection with a passenger ship, such as a ferry, ocean liner, or cruise ship. Through ticketing is normally available. __NOTOC__
Notable named boat tr ...
s, and served several prestigious international services. It was badly damaged by an engineering accident in 1905 and extensively rebuilt, subsequently becoming an important meeting point for military and government traffic during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
. By this time, Charing Cross station was seen as out of date by some politicians and proposals were made to replace Hungerford Bridge with a road bridge or road/rail combination, with the station moving to the south bank of the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
in the case of a road-only replacement. The station was bombed several times during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, and was rebuilt afterwards, re-opening in 1951. In the late 1980s, the station complex was redesigned by Terry Farrell and rebuilt to accommodate a modern office block, now known as Embankment Place.
Location
Charing Cross station is located at the western end of theStrand
Strand may refer to:
Topography
*The flat area of land bordering a body of water, a:
** Beach
** Shoreline
* Strand swamp, a type of swamp habitat in Florida
Places Africa
* Strand, Western Cape, a seaside town in South Africa
* Strand Street ...
in the City of Westminster
The City of Westminster is a city and borough in Inner London. It is the site of the United Kingdom's Houses of Parliament and much of the British government. It occupies a large area of central Greater London, including most of the West En ...
, east of Trafalgar Square
Trafalgar Square ( ) is a public square in the City of Westminster, Central London, laid out in the early 19th century around the area formerly known as Charing Cross. At its centre is a high column bearing a statue of Admiral Nelson comm ...
and northeast of Whitehall
Whitehall is a road and area in the City of Westminster, Central London. The road forms the first part of the A3212 road from Trafalgar Square to Chelsea. It is the main thoroughfare running south from Trafalgar Square towards Parliament Sq ...
. It is close to the Embankment Pier, providing river services along the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
. The railway leads directly out onto Hungerford Bridge
The Hungerford Bridge crosses the River Thames in London, and lies between Waterloo Bridge and Westminster Bridge. Owned by Network Rail Infrastructure Ltd (who use its official name of Charing Cross Bridge) it is a steel truss railway brid ...
and across the river towards the London Borough of Lambeth
Lambeth () is a London borough in South London, England, which forms part of Inner London. Its name was recorded in 1062 as ''Lambehitha'' ("landing place for lambs") and in 1255 as ''Lambeth''. The geographical centre of London is at Frazier S ...
.
The station code is CHX. It is one of twenty stations in Great Britain that are managed by Network Rail
Network Rail Limited is the owner (via its subsidiary Network Rail Infrastructure Limited, which was known as Railtrack plc before 2002) and infrastructure manager of most of the railway network in Great Britain. Network Rail is an "arm's len ...
and is the 15th busiest station in the country. A number of key bus routes run in the area, and are designated "Trafalgar Square for Charing Cross".
History
The station was planned as the London terminus of the South Eastern Railway (SER). They had wanted to extend the line fromBricklayers Arms
Bricklayers Arms is the road intersection of the A2 and the London Inner Ring Road where Bermondsey meets Walworth and Elephant & Castle in south London. It is the junction of Tower Bridge Road, Old Kent Road, New Kent Road and Great Dover ...
towards Hungerford Bridge, but a bill presented in 1846 was unsuccessful. In 1857, they proposed to Parliament that they would build a railway terminus in the West End, hoping to use Victoria, before reaching an agreement with the London, Brighton & South Coast Railway to build a line west from .
Later in the year, the SER secretary Samuel Smiles looked for potential routes and decided the best location would be on the site of the former Hungerford Market
Hungerford Market was a produce market in London, at Charing Cross on the Strand. It existed in two different buildings on the same site, the first built in 1682, the second in 1832. The market was first built on the site of Hungerford House, ...
adjacent to The Strand, and that the line should be directly connected to Waterloo, allowing a link with London and South Western Railway
The London and South Western Railway (LSWR, sometimes written L&SWR) was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Originating as the London and Southampton Railway, its network extended to Dorchester and Weymouth, to Salisbury, Exeter ...
services. The Charing Cross Railway Company was formed in 1859 in order to build the extension, and the SER paid £300,000 (now £) in capital to help build this. The line towards Charing Cross was expensive to build as it traversed a heavily built-up area, which was exacerbated in 1862 when the company chose to upgrade the two running lines to three, and doubled the capacity over the bridge to four tracks. The bridge replaced the original suspension bridge designed by Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel (; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was a British civil engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history," "one of the 19th-century engineering giants," and "on ...
which opened in 1845. Work began in June 1860 and took around three years. The old suspension bridge remained open until the new bridge was suitable to carry foot traffic. A trial run over the new line took place on 1 December 1863.
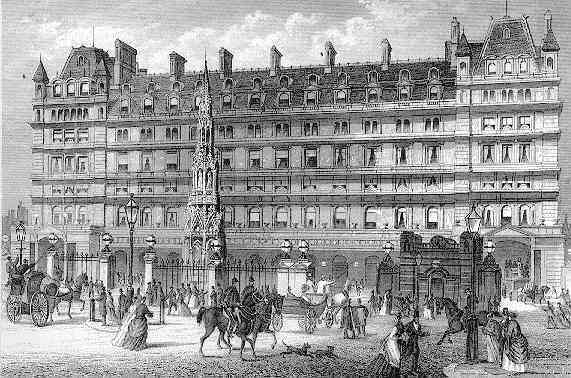 The station was designed by Sir John Hawkshaw, and featured a single span
The station was designed by Sir John Hawkshaw, and featured a single span wrought iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.08%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4%). It is a semi-fused mass of iron with fibrous slag inclusions (up to 2% by weight), which give it a wood-like "grain" ...
roof, long and wide, arching over the six platforms on its relatively cramped site. It was built on a brick arched viaduct, the level of the rails above the ground varying up to . The space underneath the line was used as wine cellar
A wine cellar is a storage room for wine in bottles or barrels, or more rarely in carboys, amphorae, or plastic containers. In an ''active'' wine cellar, important factors such as temperature and humidity are maintained by a climate control system ...
s. The roof above the tracks is a single wide great arch, rising to at its highest point. The station was built by Lucas Brothers.
Charing Cross station opened on 11 January 1864. The Charing Cross Railway was absorbed into the SER on 1 September, shortly after the station opened.
The , designed by Edward Middleton Barry
Edward Middleton Barry RA (7 June 1830 – 27 January 1880) was an English architect of the 19th century.
Biography
Edward Barry was the third son of Sir Charles Barry, born in his father's house, 27 Foley Place, London. In infancy he was ...
, and built by Lucas Brothers, opened on 15 May 1865 and gave the station an ornate frontage in the French Renaissance style. It had 250 bedrooms spread over seven floors and extended along Villiers Street as well as the front of the Strand. The public rooms had balconies overlooking the main station concourse. It quickly became popular and was profitable, leading to a 90-bedroom annexe on the other side of Villiers Street opening in 1878. A bridge over the street connected the two parts of the hotel together.
In 1887, Hungerford Bridge was widened to in order to provide three more tracks into the station. On 1 January 1899, the SER merged with the London, Chatham & Dover Railway to form the South Eastern & Chatham Railway (SECR), which took over operations at Charing Cross.
Eleanor Cross
 Contemporary with the Charing Cross Hotel was a replica of the
Contemporary with the Charing Cross Hotel was a replica of the Eleanor Cross
The Eleanor crosses were a series of twelve tall and lavishly decorated stone monuments topped with crosses erected in a line down part of the east of England. King Edward I had them built between 1291 and about 1295 in memory of his beloved wi ...
in Red Mansfield stone, also designed by Edward Middleton Barry
Edward Middleton Barry RA (7 June 1830 – 27 January 1880) was an English architect of the 19th century.
Biography
Edward Barry was the third son of Sir Charles Barry, born in his father's house, 27 Foley Place, London. In infancy he was ...
, that was erected in the station forecourt. It was based on the original Whitehall Cross built in 1291, that had been demolished in 1647 by order of Parliament. Distances in London are officially measured from the original site of the cross, now the statue of Charles I facing Whitehall
Whitehall is a road and area in the City of Westminster, Central London. The road forms the first part of the A3212 road from Trafalgar Square to Chelsea. It is the main thoroughfare running south from Trafalgar Square towards Parliament Sq ...
, and not from this replica.
The cross deteriorated over time until it was in such a vulnerable condition that it was placed on English Heritage
English Heritage (officially the English Heritage Trust) is a charity that manages over 400 historic monuments, buildings and places. These include prehistoric sites, medieval castles, Roman forts and country houses.
The charity states that i ...
's "Heritage At Risk Register" in 2008. A ten-month project to repair and restore the cross was completed in August 2010. This work included recreating and attaching almost 100 missing ornamental features including heraldic shields, an angel, pinnacles, crockets and finials; securing weak or fractured masonry with stainless steel pins and rods and re-attaching decorative items which had previously been removed after becoming loose.
International services
After opening, Charing Cross became the main terminus of all SER services instead of London Bridge, includingboat train
A boat train is a passenger train operating to a port for the specific purpose of making connection with a passenger ship, such as a ferry, ocean liner, or cruise ship. Through ticketing is normally available. __NOTOC__
Notable named boat tr ...
s to Continental Europe. Along with Victoria, it became the main departure point from London to abroad, and was called "the Gates of the World" by Percy Fitzgerald. Thomas Cook
Thomas Cook (22 November 1808 – 18 July 1892) was an English businessman. He is best known for founding the travel agency Thomas Cook & Son. He was also one of the initial developers of the "package tour" including travel, accommodatio ...
established a travel office on the corner of the station forecourt. The SER route became the shortest from London to Dover after a diversion at Sevenoaks was built in 1868, and by 1913 it was possible to travel from Charing Cross to Paris in six and a half hours.
Owing to its international connections, Charing Cross played an important part in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
as the main departure point for both the military and government towards the Western Front Western Front or West Front may refer to:
Military frontiers
* Western Front (World War I), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (World War II), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (Russian Empire), a maj ...
. All civilian and public boat services were suspended on 3 August 1914. Return journeys from Dover carried the sick and wounded towards Charing Cross and hence to hospitals around the country. Over the course of the war, 283 journeys departed from the station. On 26 December 1918, shortly after the war, the US President Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
met King George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936.
Born during the reign of his grandmother Qu ...
at Charing Cross. Commercial cross-Channel services resumed to Ostend
Ostend ( nl, Oostende, ; french: link=no, Ostende ; german: link=no, Ostende ; vls, Ostende) is a coastal city and municipality, located in the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It comprises the boroughs of Mariakerk ...
on 18 January 1919, Boulogne
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the C ...
on 3 February and Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's prefecture is its third-largest city of Arras. Th ...
on 8 January 1920, but by this time, Victoria had been expanded to accommodate the strict wartime immigration and customs checks, and Charing Cross ceased to be important as an international terminal.
1905 roof collapse
A length of the original roof structure, comprising the two end bays at the south of the station, and part of the western wall collapsed at 3:57 p.m. on 5 December 1905. A gang of men were employed at the time in repairing, glazing and painting the section of roof which fell. Shortly after 3:45 p.m, the roof emitted a loud noise, which was when someone noticed that one of the main tie rods had broken and was hanging down. Part of the roof began to sag and the western wall began to crack. It was another 12 minutes before the collapse occurred, which enabled trains and platforms to be evacuated and incoming trains to be held back. The roof, girders and debris fell across four passenger trains, blocking all tracks. The part of the western wall that fell had crashed through the wall and roof of the neighbouring Royal Avenue Theatre (now thePlayhouse Theatre
The Playhouse Theatre is a West End theatre in the City of Westminster, located in Northumberland Avenue, near Trafalgar Square, central London. The Theatre was built by F. H. Fowler and Hill with a seating capacity of 1,200. It was rebuilt i ...
) in Northumberland Avenue, which was being reconstructed at the time. Six people died (two workmen on the roof, a W.H. Smith bookstall vendor and three workmen on the Royal Avenue Theatre site).
At the Board Of Trade Inquiry into the accident, expert witnesses expressed doubts about the design of the roof, even though the cause of the failure was attributed to a faulty weld in a tie rod. Though the SECR believed the roof had a lifespan of at least forty more years, they decided not to repair it but to replace it entirely. A travelling timber gantry had to be constructed to take the remainder of the station roof down safely. The replacement was a utilitarian post and girder structure supporting a ridge and furrow roof. The curve of the original roof design can still be seen on the interior brickwork. The station was partially re-opened on 19 March 1906.
The old booking offices were demolished and the various rooms on the ground floor were rearranged. A new booking hall was constructed, along with a separate ladies' waiting-room. The additional remedial work was completed in 1913.

Proposed closure and relocation
By the late-19th century, Charing Cross was seen as being inconveniently placed. In 1889, the newly formedLondon County Council
London County Council (LCC) was the principal local government body for the County of London throughout its existence from 1889 to 1965, and the first London-wide general municipal authority to be directly elected. It covered the area today kn ...
's John Burns
John Elliot Burns (20 October 1858 – 24 January 1943) was an English trade unionist and politician, particularly associated with London politics and Battersea. He was a socialist and then a Liberal Member of Parliament and Minister. He was ...
proposed that the station and its approach should be demolished, with a road bridge put in place. The idea gained support within the council as it would allow the Strand to be widened and put a road crossing over the Thames that could bypass Whitehall. When the SECR went to Parliament asking for an act to strengthen the bridge in 1916, Burns suggested the station was in the wrong place and should be rebuilt on the south side of the Thames. The following year, an act was passed to reconstruct the bridge, with strict conditions about its appearance and a ban on enlarging the station building itself.
Ownership of Charing Cross passed to the Southern Railway (SR) in 1923 following the Big Four grouping. The line was electrified in 1926 to cater for suburban services. The lighter load of multiple-unit electric trains was found to put far less strain on the bridge, and so traffic was redesigned so that local services ran on the older section, with mainline services using the 1887 extension.
In 1926, the Royal Commission on Cross River Traffic proposed that Hungerford Bridge should be replaced by a double deck road / rail bridge, and a new Charing Cross station built to the east of the old one. The SR approved the idea as it would allow them to expand the station. Two years later, a proposal appeared again to build just a road bridge and relocate the station south of the Thames, as it was significantly cheaper. The Prime Minister Stanley Baldwin
Stanley Baldwin, 1st Earl Baldwin of Bewdley, (3 August 186714 December 1947) was a British Conservative Party politician who dominated the government of the United Kingdom between the world wars, serving as prime minister on three occasions, ...
urged the SR to accept the proposal, as "a matter of national importance", but the bill failed in 1930 after the select committee Select committee may refer to:
*Select committee (parliamentary system) A select committee is a committee made up of a small number of parliamentary members appointed to deal with particular areas or issues originating in the Westminster system o ...
did not accept building a new Charing Cross on the south bank. The proposal was formally rejected in 1936 by the London & Home Counties Traffic Advisory Committee, which revived the double-deck bridge option. The plans were all abandoned following the outbreak of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
.
World War II
Charing Cross sustained substantial damage in air-raids during the war. On 8 October 1940, a train was hit during a daylight raid on Whitehall. On the evening of 16/17 April 1941, the hotel was damaged by fire and explosives, four trains caught fire and there were several fires on the bridge. Aparachute mine
A parachute mine is a naval mine dropped from an aircraft by parachute. They were mostly used in the Second World War by the Luftwaffe and initially by the Royal Air Force (RAF) Bomber Command.
Frequently, they were dropped on land targets.
Histo ...
landed next to platform 4. The station was closed to repair the damage and defuse the mine. A further raid took place on the night of 10/11 May, leading to the station's closure again. On 18 June 1944, a bomb took out a span of the bridge. Normal operation did not resume until 4 December.
Following the war, the hotel received extensive repairs in 1951. This consisted of a whole new set of top floors, while the mansard roof
A mansard or mansard roof (also called a French roof or curb roof) is a four-sided gambrel-style hip roof characterised by two slopes on each of its sides, with the lower slope, punctured by dormer windows, at a steeper angle than the upper. Th ...
of the upper floors of the hotel was rebuilt in a plain neo-Georgian white brick.
Modernisation
The booking hall and ticket offices were modernised in 1974. Electronic ticket printing was first trialled at the station in 1983. In 1986, redevelopment began over most of the area above the platforms. The new buildings were named Embankment Place, apostmodern
Postmodernism is an intellectual stance or Rhetorical modes, mode of discourseNuyen, A.T., 1992. The Role of Rhetorical Devices in Postmodernist Discourse. Philosophy & Rhetoric, pp.183–194. characterized by philosophical skepticism, skepticis ...
office and shopping complex designed by Terry Farrell and Partners
Farrells is an architecture and urban design firm founded by British architect-planner Terry Farrell with offices in London, Manchester, Hong Kong, and Shanghai. The firm has won numerous awards for their characteristic mixed-use schemes, tr ...
. This development led to the replacement of almost the whole of the 1906 roof. The rear two spans of this structure – immediately adjacent to the existing concourse roof – were retained as part of an enlarged waiting area. In addition the original retaining side walls of the station which once supported it remain in near complete condition. The works were completed in November 1990. Most of the Embankment Place complex is office space, with a selection of restaurants on the ground floor.
Services
The station has six platforms. All trains call atWaterloo East
Waterloo East railway station, also known as London Waterloo East, is a railway station in central London on the line from through London Bridge towards Kent, in the south-east of England. It is to the east of London Waterloo railway station ...
and London Bridge
Several bridges named London Bridge have spanned the River Thames between the City of London and Southwark, in central London. The current crossing, which opened to traffic in 1973, is a box girder bridge built from concrete and steel. It re ...
.
All services at London Charing Cross are operated by Southeastern
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sep ...
using , , , and EMUs
Emus may refer to:
* Emu
The emu () (''Dromaius novaehollandiae'') is the second-tallest living bird after its ratite relative the ostrich. It is endemic to Australia where it is the largest native bird and the only extant member of the ...
.
The typical off-peak service in trains per hour is:
* 4 tph to via of which 2 continue to
* 4 tph to via
* 2 tph to via
* 1 tph to
* 1 tph to via
* 2 tph to via (1 semi-fast, 1 stopping)
* 1 tph to via
London Underground
 The station is served by two
The station is served by two London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or by its nickname the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England.
The ...
stations, both within walking distance of the mainline terminal and sited at each end: Charing Cross
Charing Cross ( ) is a junction in Westminster, London, England, where six routes meet. Clockwise from north these are: the east side of Trafalgar Square leading to St Martin's Place and then Charing Cross Road; the Strand leading to the City ...
(to the north), and Embankment
Embankment may refer to:
Geology and geography
* A levee, an artificial bank raised above the immediately surrounding land to redirect or prevent flooding by a river, lake or sea
* Embankment (earthworks), a raised bank to carry a road, railway ...
(to the south). Both stations have an Oyster Out of Station Interchange, which allows passengers to change lines while still being charged as a single journey.
Numerous proposals for underground connections for the mainline station were considered in the decades after its opening. Almost as soon as work was complete on the station, the SER wanted to build a connection from Charing Cross to the railway terminals further north. Soon after Charing Cross station opened, the North Western and Charing Cross Railway
The North Western and Charing Cross Railway (NW&CCR) was a railway company established in 1864 to construct an underground railway in London. The NW&CCR was one of many underground railway schemes proposed for London following the opening in 1863 ...
Act was passed, a joint act between the SER and the London and North Western Railway
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR, L&NWR) was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. In the late 19th century, the L&NWR was the largest joint stock company in the United Kingdom.
In 1923, it became a constituent of the Lo ...
(LNWR) that proposed a shallow sub-surface line to . The scheme collapsed in 1866 due to a shortage of funding caused by a banking crisis. The scheme was revived with the London Central Railway, that proposed to link Charing Cross to Euston and , but was again abandoned in 1874.
The first underground railway to serve Charing Cross was the District Railway
The Metropolitan District Railway, also known as the District Railway, was a passenger railway that served London from 1868 to 1933. Established in 1864 to complete an " inner circle" of lines connecting railway termini in London, the first par ...
(now the District line
The District line is a London Underground line running from in the east and Edgware Road in the west to in west London, where it splits into multiple branches. One branch runs to in south-west London and a short branch, with a limited serv ...
), which opened its station at Charing Cross on 30 May 1870.
In the 1884, bills were submitted to parliament by the Charing Cross and Euston Railway and the London Central Subway for sub-surface underground lines between Charing Cross and Euston and Charing Cross and King's Cross respectively and by the King's Cross, Charing Cross and Waterloo Subway for a deep-level railway linking the three terminals in its name. None of the three plans proceeded.
The Baker Street and Waterloo Railway
The Baker Street and Waterloo Railway (BS&WR), also known as the Bakerloo tube, was a railway company established in 1893 that built a deep-level underground "tube" railway in London. The company struggled to fund the work, and construction di ...
(now the Bakerloo line
The Bakerloo line () is a London Underground line that goes from in suburban north-west London to in south London, via the West End. Printed in brown on the Tube map, it serves 25 stations, 15 of which are underground, over . It runs partl ...
) constructed a deep-level tube line on the west side of the station in the late 19th century, which opened on 10 March 1906 with a new station in Trafalgar Square and an interchange with the District Railway's station. The link between Charing Cross and Euston was finally built by the Charing Cross, Euston and Hampstead Railway
The Charing Cross, Euston and Hampstead Railway (CCE&HR), also known as the Hampstead Tube, was a railway company established in 1891 that constructed a deep-level underground "tube" railway in London. Construction of the CCE&HR was delayed for ...
(now part of the Northern line
The Northern line is a London Underground line that runs from North London to South London. It is printed in black on the Tube map. The Northern line is unique on the Underground network in having two different routes through central London, t ...
) as a deep-level tube line in 1906 which opened its station under the forecourt of the mainline station on 22 June 1907.
Originally, Embankment tube station was called Charing Cross, while the present Charing Cross tube station was the separate Trafalgar Square (Bakerloo line) and Strand (Northern line) stations. The two northern stations were combined under the current name when connected by the development of the Jubilee line
The Jubilee line is a London Underground line that runs between in east London and in the suburban north-west, via the Docklands, South Bank and West End. Opened in 1979, it is the newest line on the Underground network, although some secti ...
. New below ground passageways were constructed linking the platforms so that an interchange could be made. The Northern line's Strand station was temporarily closed from 1974 to enable new escalators to be installed and it reopened along with the opening of the Jubilee line on 1 May 1979. The Jubilee line platforms were closed on 20 November 1999, following the extension of the Jubilee line where it was diverted to Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, B ...
and onwards south of the River Thames.
Accidents and incidents
On 25 October 1913, two trains collided in thick fog at Waterloo junction, killing three people. On 31 July 1925, there was a minor side-on collision near platform 2. In May 1927, a trunk was deposited in Charing Cross station's cloakroom that contained the five severed body parts of Minnie Alice Bonati. She was later identified as having been murdered inRochester Row
Rochester Row is a street in the City of Westminster in London that runs between Greycoat Place in the north and Vauxhall Bridge Road in the south.
It is joined by Greycoat Street, Rochester Street, Vincent Square, Emery Hill Street, Vane Stre ...
by John Robinson, who was convicted of the Charing Cross Trunk Murder, for which he was later executed.
Cultural references
The statue ''A Conversation With Oscar Wilde'' is directly opposite the station. It was erected in 1998 and designed for people to sit on the monument and have a virtual conversation withOscar Wilde
Oscar Fingal O'Flahertie Wills Wilde (16 October 185430 November 1900) was an Irish poet and playwright. After writing in different forms throughout the 1880s, he became one of the most popular playwrights in London in the early 1890s. He is ...
.
Charing Cross is referenced in numerous Sherlock Holmes
Sherlock Holmes () is a fictional detective created by British author Arthur Conan Doyle. Referring to himself as a " consulting detective" in the stories, Holmes is known for his proficiency with observation, deduction, forensic science and ...
stories. In ''The Adventure of the Abbey Grange
"The Adventure of the Abbey Grange", one of the 56 Sherlock Holmes short stories written by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, is one of 13 stories in the cycle collected as ''The Return of Sherlock Holmes'' (1905). It was first published in ''The Strand ...
'', Holmes and Watson catch a train from the station towards the fictional Abbey Grange in Kent, while in '' The Adventure of the Golden Pince-Nez'', they travel to from the station.
References
Notes Citations Sources * * * * * * * * * *External links
Station information
on Charing Cross railway station from
Network Rail
Network Rail Limited is the owner (via its subsidiary Network Rail Infrastructure Limited, which was known as Railtrack plc before 2002) and infrastructure manager of most of the railway network in Great Britain. Network Rail is an "arm's len ...
{{Authority control
Railway termini in London
Railway stations in the City of Westminster
Network Rail managed stations
Former South Eastern Railway (UK) stations
Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1864
Railway stations served by Southeastern
Terry Farrell buildings
John Hawkshaw railway stations
Train driver depots in England
London station group
1864 establishments in England
Edward Middleton Barry buildings