Ceramics processing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 Ceramic engineering is the science and technology of creating objects from inorganic, non-metallic materials. This is done either by the action of heat, or at lower temperatures using precipitation reactions from high-purity chemical solutions. The term includes the purification of raw materials, the study and production of the chemical compounds concerned, their formation into components and the study of their structure, composition and properties.
Ceramic engineering is the science and technology of creating objects from inorganic, non-metallic materials. This is done either by the action of heat, or at lower temperatures using precipitation reactions from high-purity chemical solutions. The term includes the purification of raw materials, the study and production of the chemical compounds concerned, their formation into components and the study of their structure, composition and properties.
 Abraham Darby first used coke in 1709 in Shropshire, England, to improve the yield of a smelting process. Coke is now widely used to produce carbide ceramics. Potter
Abraham Darby first used coke in 1709 in Shropshire, England, to improve the yield of a smelting process. Coke is now widely used to produce carbide ceramics. Potter
 The
The
 *Recently, there have been advances in ceramics which include bio-ceramics, such as dental implants and synthetic bones. Hydroxyapatite, the natural mineral component of bone, has been made synthetically from a number of biological and chemical sources and can be formed into ceramic materials. Orthopaedic implants made from these materials bond readily to bone and other tissues in the body without rejection or inflammatory reactions. Because of this, they are of great interest for gene delivery and
*Recently, there have been advances in ceramics which include bio-ceramics, such as dental implants and synthetic bones. Hydroxyapatite, the natural mineral component of bone, has been made synthetically from a number of biological and chemical sources and can be formed into ceramic materials. Orthopaedic implants made from these materials bond readily to bone and other tissues in the body without rejection or inflammatory reactions. Because of this, they are of great interest for gene delivery and
 Glass-ceramic materials share many properties with both glasses and ceramics. Glass-ceramics have an amorphous phase and one or more crystalline phases and are produced by a so-called "controlled crystallization", which is typically avoided in glass manufacturing. Glass-ceramics often contain a crystalline phase which constitutes anywhere from 30% /mto 90% /mof its composition by volume, yielding an array of materials with interesting thermomechanical properties.
In the processing of glass-ceramics, molten glass is cooled down gradually before reheating and annealing. In this heat treatment the glass partly
Glass-ceramic materials share many properties with both glasses and ceramics. Glass-ceramics have an amorphous phase and one or more crystalline phases and are produced by a so-called "controlled crystallization", which is typically avoided in glass manufacturing. Glass-ceramics often contain a crystalline phase which constitutes anywhere from 30% /mto 90% /mof its composition by volume, yielding an array of materials with interesting thermomechanical properties.
In the processing of glass-ceramics, molten glass is cooled down gradually before reheating and annealing. In this heat treatment the glass partly
 *Milling is the process by which materials are reduced from a large size to a smaller size. Milling may involve breaking up cemented material (in which case individual particles retain their shape) or pulverization (which involves grinding the particles themselves to a smaller size). Milling is generally done by mechanical means, including ''attrition'' (which is particle-to-particle collision that results in agglomerate break up or particle shearing), ''compression'' (which applies a forces that results in fracturing), and ''impact'' (which employs a milling medium or the particles themselves to cause fracturing). Attrition milling equipment includes the wet scrubber (also called the planetary mill or wet attrition mill), which has paddles in water creating vortexes in which the material collides and break up. Compression mills include the jaw crusher, roller crusher and cone crusher. Impact mills include the ball mill, which has media that tumble and fracture the material. Shaft impactors cause particle-to particle attrition and compression.
*Batching is the process of weighing the oxides according to recipes, and preparing them for mixing and drying.
*Mixing occurs after batching and is performed with various machines, such as dry mixing ribbon mixers (a type of cement mixer), Mueller mixers, and
*Milling is the process by which materials are reduced from a large size to a smaller size. Milling may involve breaking up cemented material (in which case individual particles retain their shape) or pulverization (which involves grinding the particles themselves to a smaller size). Milling is generally done by mechanical means, including ''attrition'' (which is particle-to-particle collision that results in agglomerate break up or particle shearing), ''compression'' (which applies a forces that results in fracturing), and ''impact'' (which employs a milling medium or the particles themselves to cause fracturing). Attrition milling equipment includes the wet scrubber (also called the planetary mill or wet attrition mill), which has paddles in water creating vortexes in which the material collides and break up. Compression mills include the jaw crusher, roller crusher and cone crusher. Impact mills include the ball mill, which has media that tumble and fracture the material. Shaft impactors cause particle-to particle attrition and compression.
*Batching is the process of weighing the oxides according to recipes, and preparing them for mixing and drying.
*Mixing occurs after batching and is performed with various machines, such as dry mixing ribbon mixers (a type of cement mixer), Mueller mixers, and
NASA/TM-2013-217910, January 2009, accessed 17 November 2020. These forming techniques are well known for providing tools and other components with dimensional stability, surface quality, high (near theoretical) density and microstructural uniformity. The increasing use and diversity of speciality forms of ceramics adds to the diversity of process technologies to be used. Thus, reinforcing fibres and filaments are mainly made by polymer, sol-gel, or CVD processes, but melt processing also has applicability. The most widely used speciality form is layered structures, with tape casting for electronic substrates and packages being pre-eminent. Photo-lithography is of increasing interest for precise patterning of conductors and other components for such packaging. Tape casting or forming processes are also of increasing interest for other applications, ranging from open structures such as fuel cells to ceramic composites. The other major layer structure is coating, where melt spraying is very important, but chemical and physical vapour deposition and chemical (e.g., sol-gel and polymer pyrolysis) methods are all seeing increased use. Besides open structures from formed tape, extruded structures, such as honeycomb catalyst supports, and highly porous structures, including various foams, for example,
 Substantial interest has arisen in recent years in fabricating ceramic composites. While there is considerable interest in composites with one or more non-ceramic constituents, the greatest attention is on composites in which all constituents are ceramic. These typically comprise two ceramic constituents: a continuous matrix, and a dispersed phase of ceramic particles, whiskers, or short (chopped) or continuous ceramic fibres. The challenge, as in wet chemical processing, is to obtain a uniform or homogeneous distribution of the dispersed particle or fibre phase.Hull, D. and Clyne, T.W. (1996) ''An Introduction to Composite Materials''. Cambridge Solid State Science Series, Cambridge University Press
Barbero, E.J. (2010) ''Introduction to Composite Materials Design'', 2nd Edn., CRC Press.
Consider first the processing of particulate composites. The particulate phase of greatest interest is tetragonal zirconia because of the toughening that can be achieved from the
Substantial interest has arisen in recent years in fabricating ceramic composites. While there is considerable interest in composites with one or more non-ceramic constituents, the greatest attention is on composites in which all constituents are ceramic. These typically comprise two ceramic constituents: a continuous matrix, and a dispersed phase of ceramic particles, whiskers, or short (chopped) or continuous ceramic fibres. The challenge, as in wet chemical processing, is to obtain a uniform or homogeneous distribution of the dispersed particle or fibre phase.Hull, D. and Clyne, T.W. (1996) ''An Introduction to Composite Materials''. Cambridge Solid State Science Series, Cambridge University Press
Barbero, E.J. (2010) ''Introduction to Composite Materials Design'', 2nd Edn., CRC Press.
Consider first the processing of particulate composites. The particulate phase of greatest interest is tetragonal zirconia because of the toughening that can be achieved from the  In processing particulate composites, the issue is not only homogeneity of the size and spatial distribution of the dispersed and matrix phases, but also control of the matrix grain size. However, there is some built-in self-control due to inhibition of matrix grain growth by the dispersed phase. Particulate composites, though generally offer increased resistance to damage, failure, or both, are still quite sensitive to inhomogeneities of composition as well as other processing defects such as pores. Thus they need good processing to be effective.
Particulate composites have been made on a commercial basis by simply mixing powders of the two constituents. Although this approach is inherently limited in the homogeneity that can be achieved, it is the most readily adaptable for existing ceramic production technology. However, other approaches are of interest.
In processing particulate composites, the issue is not only homogeneity of the size and spatial distribution of the dispersed and matrix phases, but also control of the matrix grain size. However, there is some built-in self-control due to inhibition of matrix grain growth by the dispersed phase. Particulate composites, though generally offer increased resistance to damage, failure, or both, are still quite sensitive to inhomogeneities of composition as well as other processing defects such as pores. Thus they need good processing to be effective.
Particulate composites have been made on a commercial basis by simply mixing powders of the two constituents. Although this approach is inherently limited in the homogeneity that can be achieved, it is the most readily adaptable for existing ceramic production technology. However, other approaches are of interest.
 From the technological standpoint, a particularly desirable approach to fabricating particulate composites is to coat the matrix or its precursor onto fine particles of the dispersed phase with good control of the starting dispersed particle size and the resultant matrix coating thickness. One should in principle be able to achieve the ultimate in homogeneity of distribution and thereby optimize composite performance. This can also have other ramifications, such as allowing more useful composite performance to be achieved in a body having porosity, which might be desired for other factors, such as limiting thermal conductivity.
There are also some opportunities to utilize melt processing for fabrication of ceramic, particulate, whisker and short-fibre, and continuous-fibre composites. Clearly, both particulate and whisker composites are conceivable by solid-state precipitation after solidification of the melt. This can also be obtained in some cases by sintering, as for precipitation-toughened, partially stabilized zirconia. Similarly, it is known that one can directionally solidify ceramic eutectic mixtures and hence obtain uniaxially aligned fibre composites. Such composite processing has typically been limited to very simple shapes and thus suffers from serious economic problems due to high machining costs.
Clearly, there are possibilities of using melt casting for many of these approaches. Potentially even more desirable is using melt-derived particles. In this method, quenching is done in a solid solution or in a fine eutectic structure, in which the particles are then processed by more typical ceramic powder processing methods into a useful body. There have also been preliminary attempts to use melt spraying as a means of forming composites by introducing the dispersed particulate, whisker, or fibre phase in conjunction with the melt spraying process.
Other methods besides melt infiltration to manufacture ceramic composites with long fibre reinforcement are chemical vapour infiltration and the infiltration of fibre preforms with organic
From the technological standpoint, a particularly desirable approach to fabricating particulate composites is to coat the matrix or its precursor onto fine particles of the dispersed phase with good control of the starting dispersed particle size and the resultant matrix coating thickness. One should in principle be able to achieve the ultimate in homogeneity of distribution and thereby optimize composite performance. This can also have other ramifications, such as allowing more useful composite performance to be achieved in a body having porosity, which might be desired for other factors, such as limiting thermal conductivity.
There are also some opportunities to utilize melt processing for fabrication of ceramic, particulate, whisker and short-fibre, and continuous-fibre composites. Clearly, both particulate and whisker composites are conceivable by solid-state precipitation after solidification of the melt. This can also be obtained in some cases by sintering, as for precipitation-toughened, partially stabilized zirconia. Similarly, it is known that one can directionally solidify ceramic eutectic mixtures and hence obtain uniaxially aligned fibre composites. Such composite processing has typically been limited to very simple shapes and thus suffers from serious economic problems due to high machining costs.
Clearly, there are possibilities of using melt casting for many of these approaches. Potentially even more desirable is using melt-derived particles. In this method, quenching is done in a solid solution or in a fine eutectic structure, in which the particles are then processed by more typical ceramic powder processing methods into a useful body. There have also been preliminary attempts to use melt spraying as a means of forming composites by introducing the dispersed particulate, whisker, or fibre phase in conjunction with the melt spraying process.
Other methods besides melt infiltration to manufacture ceramic composites with long fibre reinforcement are chemical vapour infiltration and the infiltration of fibre preforms with organic
 The products of technical ceramics include tiles used in the
The products of technical ceramics include tiles used in the
 * Artificial bone; Dentistry applications, teeth.
* Biodegradable splints; Reinforcing bones recovering from osteoporosis
*Implant material
* Artificial bone; Dentistry applications, teeth.
* Biodegradable splints; Reinforcing bones recovering from osteoporosis
*Implant material
 Silicification is quite common in the biological world and occurs in bacteria, single-celled organisms, plants, and animals (invertebrates and vertebrates). Crystalline minerals formed in such environment often show exceptional physical properties (e.g. strength, hardness, fracture toughness) and tend to form hierarchical structures that exhibit microstructural order over a range of length or spatial scales. The minerals are crystallized from an environment that is undersaturated with respect to silicon, and under conditions of neutral pH and low temperature (0–40 °C). Formation of the mineral may occur either within or outside of the cell wall of an organism, and specific biochemical reactions for mineral deposition exist that include lipids, proteins and carbohydrates.
Most natural (or biological) materials are complex composites whose mechanical properties are often outstanding, considering the weak constituents from which they are assembled. These complex structures, which have risen from hundreds of million years of evolution, are inspiring the design of novel materials with exceptional physical properties for high performance in adverse conditions. Their defining characteristics such as hierarchy, multifunctionality, and the capacity for self-healing, are currently being investigated.
The basic building blocks begin with the 20 amino acids and proceed to polypeptides, polysaccharides, and polypeptides–saccharides. These, in turn, compose the basic proteins, which are the primary constituents of the 'soft tissues' common to most biominerals. With well over 1000 proteins possible, current research emphasizes the use of collagen, chitin, keratin, and elastin. The 'hard' phases are often strengthened by crystalline minerals, which nucleate and grow in a biomediated environment that determines the size, shape and distribution of individual crystals. The most important mineral phases have been identified as hydroxyapatite, silica, and
Silicification is quite common in the biological world and occurs in bacteria, single-celled organisms, plants, and animals (invertebrates and vertebrates). Crystalline minerals formed in such environment often show exceptional physical properties (e.g. strength, hardness, fracture toughness) and tend to form hierarchical structures that exhibit microstructural order over a range of length or spatial scales. The minerals are crystallized from an environment that is undersaturated with respect to silicon, and under conditions of neutral pH and low temperature (0–40 °C). Formation of the mineral may occur either within or outside of the cell wall of an organism, and specific biochemical reactions for mineral deposition exist that include lipids, proteins and carbohydrates.
Most natural (or biological) materials are complex composites whose mechanical properties are often outstanding, considering the weak constituents from which they are assembled. These complex structures, which have risen from hundreds of million years of evolution, are inspiring the design of novel materials with exceptional physical properties for high performance in adverse conditions. Their defining characteristics such as hierarchy, multifunctionality, and the capacity for self-healing, are currently being investigated.
The basic building blocks begin with the 20 amino acids and proceed to polypeptides, polysaccharides, and polypeptides–saccharides. These, in turn, compose the basic proteins, which are the primary constituents of the 'soft tissues' common to most biominerals. With well over 1000 proteins possible, current research emphasizes the use of collagen, chitin, keratin, and elastin. The 'hard' phases are often strengthened by crystalline minerals, which nucleate and grow in a biomediated environment that determines the size, shape and distribution of individual crystals. The most important mineral phases have been identified as hydroxyapatite, silica, and  High-resolution scanning electron microscope (SEM) observations were performed of the microstructure of the mother-of-pearl (or nacre) portion of the abalone shell. Those shells exhibit the highest mechanical strength and fracture toughness of any non-metallic substance known. The nacre from the shell of the abalone has become one of the more intensively studied biological structures in materials science. Clearly visible in these images are the neatly stacked (or ordered) mineral tiles separated by thin organic sheets along with a macrostructure of larger periodic growth bands which collectively form what scientists are currently referring to as a hierarchical composite structure. (The term hierarchy simply implies that there are a range of structural features which exist over a wide range of length scales).
Future developments reside in the synthesis of bio-inspired materials through processing methods and strategies that are characteristic of biological systems. These involve nanoscale self-assembly of the components and the development of hierarchical structures.
High-resolution scanning electron microscope (SEM) observations were performed of the microstructure of the mother-of-pearl (or nacre) portion of the abalone shell. Those shells exhibit the highest mechanical strength and fracture toughness of any non-metallic substance known. The nacre from the shell of the abalone has become one of the more intensively studied biological structures in materials science. Clearly visible in these images are the neatly stacked (or ordered) mineral tiles separated by thin organic sheets along with a macrostructure of larger periodic growth bands which collectively form what scientists are currently referring to as a hierarchical composite structure. (The term hierarchy simply implies that there are a range of structural features which exist over a wide range of length scales).
Future developments reside in the synthesis of bio-inspired materials through processing methods and strategies that are characteristic of biological systems. These involve nanoscale self-assembly of the components and the development of hierarchical structures.
The American Ceramic SocietyCeramic Tile Institute of America
{{Authority control Materials science Ceramic materials Engineering disciplines Industrial processes


 Ceramic engineering is the science and technology of creating objects from inorganic, non-metallic materials. This is done either by the action of heat, or at lower temperatures using precipitation reactions from high-purity chemical solutions. The term includes the purification of raw materials, the study and production of the chemical compounds concerned, their formation into components and the study of their structure, composition and properties.
Ceramic engineering is the science and technology of creating objects from inorganic, non-metallic materials. This is done either by the action of heat, or at lower temperatures using precipitation reactions from high-purity chemical solutions. The term includes the purification of raw materials, the study and production of the chemical compounds concerned, their formation into components and the study of their structure, composition and properties.
Ceramic materials
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, ...
may have a crystalline or partly crystalline structure, with long-range order on atomic scale. Glass ceramics may have an amorphous or glassy structure, with limited or short-range atomic order. They are either formed from a molten mass that solidifies on cooling, formed and matured by the action of heat, or chemically synthesized at low temperatures using, for example, hydrothermal
Hydrothermal circulation in its most general sense is the circulation of hot water (Ancient Greek ὕδωρ, ''water'',Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with th ...
or sol-gel synthesis.
The special character of ceramic materials gives rise to many applications in materials engineering, electrical engineering, chemical engineering
Chemical engineering is an engineering field which deals with the study of operation and design of chemical plants as well as methods of improving production. Chemical engineers develop economical commercial processes to convert raw materials int ...
and mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, an ...
. As ceramics are heat resistant, they can be used for many tasks for which materials like metal and polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
s are unsuitable. Ceramic materials are used in a wide range of industries, including mining, aerospace, medicine, refinery, food and chemical industries, packaging science, electronics, industrial and transmission electricity, and guided lightwave transmission.Kingery, W.D., Bowen, H.K., and Uhlmann, D.R., ''Introduction to Ceramics'', p. 690 (Wiley-Interscience, 2nd Edition, 2006)
History
The word "ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
" is derived from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
word () meaning pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and ...
. It is related to the older Indo-European language root "to burn". "Ceramic" may be used as a noun in the singular to refer to a ceramic material or the product of ceramic manufacture, or as an adjective. Ceramics is the making of things out of ceramic materials. Ceramic engineering, like many sciences, evolved from a different discipline by today's standards. Materials science engineering is grouped with ceramics engineering to this day.
 Abraham Darby first used coke in 1709 in Shropshire, England, to improve the yield of a smelting process. Coke is now widely used to produce carbide ceramics. Potter
Abraham Darby first used coke in 1709 in Shropshire, England, to improve the yield of a smelting process. Coke is now widely used to produce carbide ceramics. Potter Josiah Wedgwood
Josiah Wedgwood (12 July 1730 – 3 January 1795) was an English potter, entrepreneur and abolitionist. Founding the Wedgwood company in 1759, he developed improved pottery bodies by systematic experimentation, and was the leader in the indus ...
opened the first modern ceramics factory in Stoke-on-Trent, England, in 1759. Austrian chemist Carl Josef Bayer, working for the textile industry in Russia, developed a process
A process is a series or set of activities that interact to produce a result; it may occur once-only or be recurrent or periodic.
Things called a process include:
Business and management
*Business process, activities that produce a specific se ...
to separate alumina from bauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO ...
ore in 1888. The Bayer process is still used to purify alumina for the ceramic and aluminium industries. Brothers Pierre and Jacques Curie
In computing, a CURIE (or ''Compact URI'') defines a generic, abbreviated syntax for expressing Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs). It is an abbreviated URI expressed in a compact syntax, and may be found in both XML and non-XML grammars. A CURIE ...
discovered piezoelectricity
Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied mechanical stress. The word ''p ...
in Rochelle salt . Piezoelectricity is one of the key properties of electroceramics Electroceramics is a class of ceramic materials used primarily for their electrical properties.
While ceramics have traditionally been admired and used for their mechanical, thermal and chemical stability, their unique electrical, optical and magne ...
.
E.G. Acheson heated a mixture of coke and clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
in 1893, and invented carborundum, or synthetic silicon carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal s ...
. Henri Moissan
Ferdinand Frédéric Henri Moissan (28 September 1852 – 20 February 1907) was a French chemist and pharmacist who won the 1906 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work in isolating fluorine from its compounds. Moissan was one of the original mem ...
also synthesized SiC and tungsten carbide
Tungsten carbide (chemical formula: WC) is a chemical compound (specifically, a carbide) containing equal parts of tungsten and carbon atoms. In its most basic form, tungsten carbide is a fine gray powder, but it can be pressed and formed into ...
in his electric arc furnace
An electric arc furnace (EAF) is a furnace that heats material by means of an electric arc.
Industrial arc furnaces range in size from small units of approximately one-tonne capacity (used in foundries for producing cast iron products) up to ...
in Paris about the same time as Acheson. Karl Schröter used liquid-phase sintering
Clinker nodules produced by sintering
Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by pressure or heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction.
Sintering happens as part of a manufacturing ...
to bond or "cement" Moissan's tungsten carbide particles with cobalt in 1923 in Germany. Cemented (metal-bonded) carbide
In chemistry, a carbide usually describes a compound composed of carbon and a metal. In metallurgy, carbiding or carburizing is the process for producing carbide coatings on a metal piece.
Interstitial / Metallic carbides
The carbides of th ...
edges greatly increase the durability of hardened steel
The term hardened steel is often used for a medium or high carbon steel that has been given heat treatment and then quenching followed by tempering. The quenching results in the formation of metastable martensite, the fraction of which is reduced ...
cutting tools. W.H. Nernst developed cubic-stabilized zirconia in the 1920s in Berlin. This material is used as an oxygen sensor in exhaust systems. The main limitation on the use of ceramics in engineering is brittleness.
Military
 The
The military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
requirements of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
encouraged developments, which created a need for high-performance materials and helped speed the development of ceramic science and engineering. Throughout the 1960s and 1970s, new types of ceramics were developed in response to advances in atomic energy, electronics, communications, and space travel. The discovery of ceramic superconductors in 1986 has spurred intense research to develop superconducting ceramic parts for electronic devices, electric motors, and transportation equipment.
There is an increasing need in the military sector for high-strength, robust materials which have the capability to transmit light around the visible (0.4–0.7 micrometers) and mid-infrared (1–5 micrometers) regions of the spectrum. These materials are needed for applications requiring transparent armour. Transparent armour is a material or system of materials designed to be optically transparent, yet protect from fragmentation or ballistic impacts. The primary requirement for a transparent armour system is to not only defeat the designated threat but also provide a multi-hit capability with minimized distortion of surrounding areas. Transparent armour windows must also be compatible with night vision equipment. New materials that are thinner, lightweight, and offer better ballistic performance are being sought.
Such solid-state components have found widespread use for various applications in the electro-optical field including: optical fibres
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means t ...
for guided lightwave transmission, optical
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultravio ...
switches
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type of ...
, laser amplifiers and lenses
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), ...
, hosts for solid-state lasers
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The fir ...
and optical window materials for gas lasers, and infrared (IR) heat seeking devices for missile guidance
Missile guidance refers to a variety of methods of guiding a missile or a guided bomb to its intended target. The missile's target accuracy is a critical factor for its effectiveness. Guidance systems improve missile accuracy by improving its P ...
systems and IR night vision.Harris, D.C., "Materials for Infrared Windows and Domes: Properties and Performance", SPIE PRESS Monograph, Vol. PM70 (Int. Society of Optical Engineers, Bellingham WA, 2009)
Modern industry
Now a multibillion-dollar a year industry, ceramic engineering and research has established itself as an important field of science. Applications continue to expand as researchers develop new kinds of ceramics to serve different purposes.Richerson, D.W., ''Modern Ceramic Engineering'', 2nd Ed., (Marcel Dekker Inc., 1992) . *Zirconium dioxide
Zirconium dioxide (), sometimes known as zirconia (not to be confused with zircon), is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium. Its most naturally occurring form, with a monoclinic crystalline structure, is the mineral baddeleyite. A dopant stabi ...
ceramics are used in the manufacture of knives. The blade of the ceramic knife
A ceramic knife is a knife with a ceramic blade typically made from zirconium dioxide (ZrO2; also known as zirconia), rather than the steel used for most knives. Ceramic knife blades are usually produced through the dry-pressing and firing of pow ...
will stay sharp for much longer than that of a steel knife, although it is more brittle and can be snapped by dropping it on a hard surface.
*Ceramics such as alumina, boron carbide and silicon carbide have been used in bulletproof vests to repel small arms rifle fire. Such plates are known commonly as ballistic plate
A ballistic plate, also known as an armour plate, is a protective armoured plate inserted into a carrier or bulletproof vest, that can be used stand-alone, or in conjunction with other armour. "Hard armour" usually denotes armour that uses balli ...
s. Similar material is used to protect cockpits of some military aircraft, because of the low weight of the material.
*Silicon nitride
Silicon nitride is a chemical compound of the elements silicon and nitrogen. is the most thermodynamically stable and commercially important of the silicon nitrides, and the term "silicon nitride" commonly refers to this specific composition. It ...
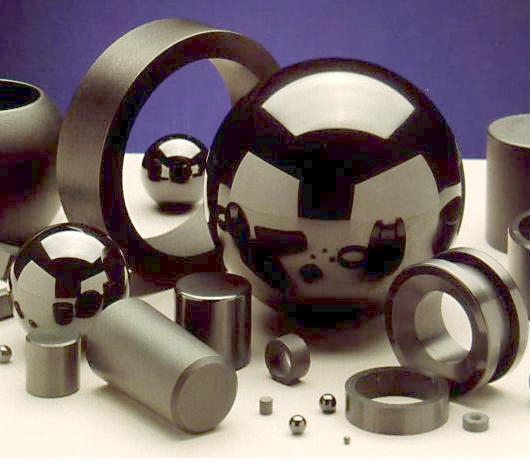
parts are used in ceramic ball bearings. Their higher hardness means that they are much less susceptible to wear and can offer more than triple lifetimes. They also deform less under load meaning they have less contact with the bearing retainer walls and can roll faster. In very high speed applications, heat from friction during rolling can cause problems for metal bearings; problems which are reduced by the use of ceramics. Ceramics are also more chemically resistant and can be used in wet environments where steel bearings would rust. The major drawback to using ceramics is a significantly higher cost. In many cases their electrically insulating properties may also be valuable in bearings.
*In the early 1980s, Toyota
is a Japanese multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Toyota City, Aichi, Japan. It was founded by Kiichiro Toyoda and incorporated on . Toyota is one of the largest automobile manufacturers in the world, producing about 10 ...
researched production of an adiabatic ceramic engine which can run at a temperature of over 6000 °F (3300 °C). Ceramic engines do not require a cooling system and hence allow a major weight reduction and therefore greater fuel efficiency. Fuel efficiency of the engine is also higher at high temperature, as shown by Carnot's theorem. In a conventional metallic engine, much of the energy released from the fuel must be dissipated as waste heat
Waste heat is heat that is produced by a machine, or other process that uses energy, as a byproduct of doing work. All such processes give off some waste heat as a fundamental result of the laws of thermodynamics. Waste heat has lower utility ...
in order to prevent a meltdown of the metallic parts. Despite all of these desirable properties, such engines are not in production because the manufacturing of ceramic parts in the requisite precision and durability is difficult. Imperfection in the ceramic leads to cracks, which can lead to potentially dangerous equipment failure. Such engines are possible in laboratory settings, but mass-production is not feasible with current technology.
*Work is being done in developing ceramic parts for gas turbine
A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the directio ...
engines
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power g ...
. Currently, even blades made of advanced metal alloys used in the engines' hot section require cooling and careful limiting of operating temperatures. Turbine engines made with ceramics could operate more efficiently, giving aircraft greater range and payload for a set amount of fuel.
 *Recently, there have been advances in ceramics which include bio-ceramics, such as dental implants and synthetic bones. Hydroxyapatite, the natural mineral component of bone, has been made synthetically from a number of biological and chemical sources and can be formed into ceramic materials. Orthopaedic implants made from these materials bond readily to bone and other tissues in the body without rejection or inflammatory reactions. Because of this, they are of great interest for gene delivery and
*Recently, there have been advances in ceramics which include bio-ceramics, such as dental implants and synthetic bones. Hydroxyapatite, the natural mineral component of bone, has been made synthetically from a number of biological and chemical sources and can be formed into ceramic materials. Orthopaedic implants made from these materials bond readily to bone and other tissues in the body without rejection or inflammatory reactions. Because of this, they are of great interest for gene delivery and tissue engineering
Tissue engineering is a biomedical engineering discipline that uses a combination of cells, engineering, materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to restore, maintain, improve, or replace different types of biolog ...
scaffolds. Most hydroxyapatite ceramics are very porous and lack mechanical strength and are used to coat metal orthopaedic devices to aid in forming a bond to bone or as bone fillers. They are also used as fillers for orthopaedic plastic screws to aid in reducing the inflammation and increase absorption of these plastic materials. Work is being done to make strong, fully dense nano crystalline hydroxyapatite ceramic materials for orthopaedic weight bearing devices, replacing foreign metal and plastic orthopaedic materials with a synthetic, but naturally occurring, bone mineral. Ultimately these ceramic materials may be used as bone replacements or with the incorporation of protein collagens, synthetic bones.
*Durable actinide-containing ceramic materials have many applications such as in nuclear fuels for burning excess Pu and in chemically-inert sources of alpha irradiation for power supply of unmanned space vehicles or to produce electricity for microelectronic devices. Both use and disposal of radioactive actinides require their immobilisation in a durable host material. Nuclear waste long-lived radionuclides such as actinides are immobilised using chemically-durable crystalline materials based on polycrystalline ceramics and large single crystals.
Glass-ceramics
 Glass-ceramic materials share many properties with both glasses and ceramics. Glass-ceramics have an amorphous phase and one or more crystalline phases and are produced by a so-called "controlled crystallization", which is typically avoided in glass manufacturing. Glass-ceramics often contain a crystalline phase which constitutes anywhere from 30% /mto 90% /mof its composition by volume, yielding an array of materials with interesting thermomechanical properties.
In the processing of glass-ceramics, molten glass is cooled down gradually before reheating and annealing. In this heat treatment the glass partly
Glass-ceramic materials share many properties with both glasses and ceramics. Glass-ceramics have an amorphous phase and one or more crystalline phases and are produced by a so-called "controlled crystallization", which is typically avoided in glass manufacturing. Glass-ceramics often contain a crystalline phase which constitutes anywhere from 30% /mto 90% /mof its composition by volume, yielding an array of materials with interesting thermomechanical properties.
In the processing of glass-ceramics, molten glass is cooled down gradually before reheating and annealing. In this heat treatment the glass partly crystallizes
Crystallization is the process by which solid forms, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal. Some ways by which crystals form are precipitating from a solution, freezing, or more rarely dep ...
. In many cases, so-called 'nucleation agents' are added in order to regulate and control the crystallization process. Because there is usually no pressing and sintering, glass-ceramics do not contain the volume fraction of porosity typically present in sintered ceramics.
The term mainly refers to a mix of lithium and aluminosilicate
Aluminosilicate minerals ( IMA symbol: Als) are minerals composed of aluminium, silicon, and oxygen, plus countercations. They are a major component of kaolin and other clay minerals.
Andalusite, kyanite, and sillimanite are naturall ...
s which yields an array of materials with interesting thermomechanical properties. The most commercially important of these have the distinction of being impervious to thermal shock. Thus, glass-ceramics have become extremely useful for countertop cooking. The negative thermal expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions.
Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kinetic ...
coefficient (TEC) of the crystalline ceramic phase can be balanced with the positive TEC of the glassy phase. At a certain point (~70% crystalline) the glass-ceramic has a net TEC near zero. This type of glass-ceramic
Glass-ceramics are polycrystalline materials produced through controlled crystallization of base glass, producing a fine uniform dispersion of crystals throughout the bulk material. Crystallization is accomplished by subjecting suitable glasses to ...
exhibits excellent mechanical properties and can sustain repeated and quick temperature changes up to 1000 °C.
Processing steps
The traditional ceramic process generally follows this sequence: Milling → Batching → Mixing → Forming → Drying → Firing → Assembly. *Milling is the process by which materials are reduced from a large size to a smaller size. Milling may involve breaking up cemented material (in which case individual particles retain their shape) or pulverization (which involves grinding the particles themselves to a smaller size). Milling is generally done by mechanical means, including ''attrition'' (which is particle-to-particle collision that results in agglomerate break up or particle shearing), ''compression'' (which applies a forces that results in fracturing), and ''impact'' (which employs a milling medium or the particles themselves to cause fracturing). Attrition milling equipment includes the wet scrubber (also called the planetary mill or wet attrition mill), which has paddles in water creating vortexes in which the material collides and break up. Compression mills include the jaw crusher, roller crusher and cone crusher. Impact mills include the ball mill, which has media that tumble and fracture the material. Shaft impactors cause particle-to particle attrition and compression.
*Batching is the process of weighing the oxides according to recipes, and preparing them for mixing and drying.
*Mixing occurs after batching and is performed with various machines, such as dry mixing ribbon mixers (a type of cement mixer), Mueller mixers, and
*Milling is the process by which materials are reduced from a large size to a smaller size. Milling may involve breaking up cemented material (in which case individual particles retain their shape) or pulverization (which involves grinding the particles themselves to a smaller size). Milling is generally done by mechanical means, including ''attrition'' (which is particle-to-particle collision that results in agglomerate break up or particle shearing), ''compression'' (which applies a forces that results in fracturing), and ''impact'' (which employs a milling medium or the particles themselves to cause fracturing). Attrition milling equipment includes the wet scrubber (also called the planetary mill or wet attrition mill), which has paddles in water creating vortexes in which the material collides and break up. Compression mills include the jaw crusher, roller crusher and cone crusher. Impact mills include the ball mill, which has media that tumble and fracture the material. Shaft impactors cause particle-to particle attrition and compression.
*Batching is the process of weighing the oxides according to recipes, and preparing them for mixing and drying.
*Mixing occurs after batching and is performed with various machines, such as dry mixing ribbon mixers (a type of cement mixer), Mueller mixers, and pug mill
A pugmill or pug mill is a machine in which clay or other materials are mixed into a plastic state or a similar machine for the trituration of ore. Industrial applications are found in pottery, bricks, cement and some parts of the concrete and asp ...
s. Wet mixing generally involves the same equipment.
*Forming is making the mixed material into shapes, ranging from toilet bowls to spark plug insulators. Forming can involve: (1) Extrusion, such as extruding "slugs" to make bricks, (2) Pressing to make shaped parts, (3) Slip casting
Slip casting, or slipcasting, is a ceramic forming technique for pottery and other ceramics, especially for shapes not easily made on a wheel. In this method, a liquid clay body slip (usually mixed in a blunger) is poured into plaster mo ...
, as in making toilet bowls, wash basins and ornamentals like ceramic statues. Forming produces a "green" part, ready for drying. Green parts are soft, pliable, and over time will lose shape. Handling the green product will change its shape. For example, a green brick can be "squeezed", and after squeezing it will stay that way.
*Drying is removing the water or binder from the formed material. Spray drying
Spray drying is a method of changing a dry powder from a liquid or slurry by rapidly drying with a hot gas. This is the preferred method of drying of many thermally-sensitive materials such as foods and pharmaceuticals, or materials which may requ ...
is widely used to prepare powder for pressing operations. Other dryers are tunnel dryers and periodic dryers. Controlled heat is applied in this two-stage process. First, heat removes water. This step needs careful control, as rapid heating causes cracks and surface defects. The dried part is smaller than the green part, and is brittle, necessitating careful handling, since a small impact will cause crumbling and breaking.
*Sintering is where the dried parts pass through a controlled heating process, and the oxides are chemically changed to cause bonding and densification. The fired part will be smaller than the dried part.
Forming methods
Ceramic forming techniques Ceramic forming techniques are ways of forming ceramics, which are used to make everything from tableware such as teapots to engineering ceramics such as computer parts. Pottery techniques include the potter's wheel, slip casting and many others. ...
include throwing, slipcasting
Slip casting, or slipcasting, is a ceramic forming technique for pottery and other ceramics, especially for shapes not easily made on a wheel. In this method, a liquid clay body slip (usually mixed in a blunger) is poured into plaster mo ...
, tape casting Tape casting (also called doctor blading, knife coating, and shank shifting) is a casting process used in the manufacture of thin ceramic tapes and sheets from ceramic slurry. The ceramic slurry is cast in a thin layer onto a flat surface and then d ...
, freeze-casting, injection moulding, dry pressing, isostatic pressing, hot isostatic pressing (HIP), 3D printing and others. Methods for forming ceramic powders into complex shapes are desirable in many areas of technology. Such methods are required for producing advanced, high-temperature structural parts such as heat engine components and turbines
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful Work (physics), work. The work produced by a turbine can be used ...
. Materials other than ceramics which are used in these processes may include: wood, metal, water, plaster and epoxy—most of which will be eliminated upon firing. A ceramic-filled epoxy, such as Martyte, is sometimes used to protect structural steel under conditions of rocket exhaust impingement.Refractory Materials for Flame Deflector Protection System Corrosion Control: Similar Industries and/or Launch Facilities SurveyNASA/TM-2013-217910, January 2009, accessed 17 November 2020. These forming techniques are well known for providing tools and other components with dimensional stability, surface quality, high (near theoretical) density and microstructural uniformity. The increasing use and diversity of speciality forms of ceramics adds to the diversity of process technologies to be used. Thus, reinforcing fibres and filaments are mainly made by polymer, sol-gel, or CVD processes, but melt processing also has applicability. The most widely used speciality form is layered structures, with tape casting for electronic substrates and packages being pre-eminent. Photo-lithography is of increasing interest for precise patterning of conductors and other components for such packaging. Tape casting or forming processes are also of increasing interest for other applications, ranging from open structures such as fuel cells to ceramic composites. The other major layer structure is coating, where melt spraying is very important, but chemical and physical vapour deposition and chemical (e.g., sol-gel and polymer pyrolysis) methods are all seeing increased use. Besides open structures from formed tape, extruded structures, such as honeycomb catalyst supports, and highly porous structures, including various foams, for example,
reticulated foam
Reticulated foam is a very porous, low density solid foam. 'Reticulated' means like a net. Reticulated foams are extremely open foams i.e. there are few, if any, intact bubbles or cell windows. In contrast, the foam formed by soap bubbles is compo ...
, are of increasing use.
Densification of consolidated powder bodies continues to be achieved predominantly by (pressureless) sintering. However, the use of pressure sintering by hot pressing is increasing, especially for non-oxides and parts of simple shapes where higher quality (mainly microstructural homogeneity) is needed, and larger size or multiple parts per pressing can be an advantage.
The sintering process
The principles of sintering-based methods are simple ("sinter" has roots in the English "cinder
Cinder is an alternate term for scoria.
Cinder or Cinders may also refer to:
In computing
*Cinder (programming library), a C++ programming library for visualization
*Cinder, OpenStack's block storage component
* Cyber Insider Threat, CINDER, a ...
"). The firing is done at a temperature below the melting point of the ceramic. Once a roughly-held-together object called a "green body" is made, it is baked in a kiln
A kiln is a thermally insulated chamber, a type of oven, that produces temperatures sufficient to complete some process, such as hardening, drying, or chemical changes. Kilns have been used for millennia to turn objects made from clay int ...
, where atomic and molecular diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemica ...
processes give rise to significant changes in the primary microstructural features. This includes the gradual elimination of porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measur ...
, which is typically accompanied by a net shrinkage and overall densification
Urban density is a term used in urban planning and urban design to refer to the number of people inhabiting a given urbanized area. As such it is to be distinguished from other measures of population density. Urban density is considered an importan ...
of the component. Thus, the pores in the object may close up, resulting in a denser product of significantly greater strength
Strength may refer to:
Physical strength
*Physical strength, as in people or animals
* Hysterical strength, extreme strength occurring when people are in life-and-death situations
*Superhuman strength, great physical strength far above human c ...
and fracture toughness.
Another major change in the body during the firing or sintering process will be the establishment of the polycrystalline
A crystallite is a small or even microscopic crystal which forms, for example, during the cooling of many materials. Crystallites are also referred to as grains.
Bacillite is a type of crystallite. It is rodlike with parallel longulites.
Stru ...
nature of the solid. Significant grain growth tends to occur during sintering, with this growth depending on temperature and duration of the sintering process. The growth of grains will result in some form of grain size distribution, which will have a significant impact on the ultimate physical properties of the material. In particular, abnormal grain growth
Abnormal or discontinuous grain growth, also referred to as exaggerated or secondary recrystallisation grain growth, is a grain growth phenomenon through which certain energetically favorable grains ( crystallites) grow rapidly in a matrix of fin ...
in which certain grains grow very large in a matrix of finer grains will significantly alter the physical and mechanical properties of the obtained ceramic. In the sintered body, grain sizes are a product of the thermal processing parameters as well as the initial particle size
Particle size is a notion introduced for comparing dimensions of solid particles ('' flecks''), liquid particles ('' droplets''), or gaseous particles ('' bubbles''). The notion of particle size applies to particles in colloids, in ecology, in ...
, or possibly the sizes of aggregates or particle cluster
may refer to:
Science and technology Astronomy
* Cluster (spacecraft), constellation of four European Space Agency spacecraft
* Asteroid cluster, a small asteroid family
* Cluster II (spacecraft), a European Space Agency mission to study t ...
s which arise during the initial stages of processing.
The ultimate microstructure
Microstructure is the very small scale structure of a material, defined as the structure of a prepared surface of material as revealed by an optical microscope above 25× magnification. The microstructure of a material (such as metals, polymers ...
(and thus the physical properties) of the final product will be limited by and subject to the form of the structural template or precursor which is created in the initial stages of chemical synthesis
As a topic of chemistry, chemical synthesis (or combination) is the artificial execution of chemical reactions to obtain one or several products. This occurs by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions. In mod ...
and physical forming. Hence the importance of chemical powder
A powder is a dry, bulk solid composed of many very fine particles that may flow freely when shaken or tilted. Powders are a special sub-class of granular materials, although the terms ''powder'' and '' granular'' are sometimes used to distin ...
and polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
processing
Processing is a free graphical library and integrated development environment (IDE) built for the electronic arts, new media art, and visual design communities with the purpose of teaching non-programmers the fundamentals of computer programming ...
as it pertains to the synthesis of industrial ceramics, glasses and glass-ceramics.
There are numerous possible refinements of the sintering process. Some of the most common involve pressing the green body to give the densification a head start and reduce the sintering time needed. Sometimes organic binders such as polyvinyl alcohol
Poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVOH, PVA, or PVAl) is a water-soluble synthetic polymer. It has the idealized formula H2CH(OH)sub>''n''. It is used in papermaking, textile warp sizing, as a thickener and emulsion stabilizer in polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) ...
are added to hold the green body together; these burn out during the firing (at 200–350 °C). Sometimes organic lubricants are added during pressing to increase densification. It is common to combine these, and add binders and lubricants to a powder, then press. (The formulation of these organic chemical additives is an art in itself. This is particularly important in the manufacture of high performance ceramics such as those used by the billions for electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
, in capacitors, inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists of an insulated wire wound into a c ...
s, sensors, etc.)
A slurry can be used in place of a powder, and then cast into a desired shape, dried and then sintered. Indeed, traditional pottery is done with this type of method, using a plastic mixture worked with the hands. If a mixture of different materials is used together in a ceramic, the sintering temperature is sometimes above the melting point of one minor component – a ''liquid phase'' sintering. This results in shorter sintering times compared to solid state sintering. Such liquid phase sintering involves in faster diffusion processes and may result in abnormal grain growth
Abnormal or discontinuous grain growth, also referred to as exaggerated or secondary recrystallisation grain growth, is a grain growth phenomenon through which certain energetically favorable grains ( crystallites) grow rapidly in a matrix of fin ...
.
Strength of ceramics
A material's strength is dependent on its microstructure. The engineering processes to which a material is subjected can alter its microstructure. The variety of strengthening mechanisms that alter the strength of a material include the mechanism ofgrain boundary strengthening
In materials science, grain-boundary strengthening (or Hall–Petch strengthening) is a method of strengthening materials by changing their average crystallite (grain) size. It is based on the observation that grain boundaries are insurmountabl ...
. Thus, although yield strength is maximized with decreasing grain size, ultimately, very small grain sizes make the material brittle. Considered in tandem with the fact that the yield strength is the parameter that predicts plastic deformation in the material, one can make informed decisions on how to increase the strength of a material depending on its microstructural properties and the desired end effect.
The relation between yield stress and grain size is described mathematically by the Hall-Petch equation which is
:
where ''ky'' is the strengthening coefficient (a constant unique to each material), ''σo'' is a materials constant for the starting stress for dislocation movement (or the resistance of the lattice to dislocation motion), ''d'' is the grain diameter, and ''σy'' is the yield stress.
Theoretically, a material could be made infinitely strong if the grains are made infinitely small. This is, unfortunately, impossible because the lower limit of grain size is a single unit cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector, for example) does not necessaril ...
of the material. Even then, if the grains of a material are the size of a single unit cell, then the material is in fact amorphous, not crystalline, since there is no long range order, and dislocations can not be defined in an amorphous material. It has been observed experimentally that the microstructure with the highest yield strength is a grain size of about 10 nanometres, because grains smaller than this undergo another yielding mechanism, grain boundary sliding. Producing engineering materials with this ideal grain size is difficult because of the limitations of initial particle sizes inherent to nanomaterials
*
Nanomaterials describe, in principle, materials of which a single unit is sized (in at least one dimension) between 1 and 100 nm (the usual definition of nanoscale).
Nanomaterials research takes a materials science-based approach to na ...
and nanotechnology.
Theory of chemical processing
Microstructural uniformity
In the processing of fine ceramics, the irregular particle sizes and shapes in a typical powder often lead to non-uniform packing morphologies that result in packingdensity
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematical ...
variations in the powder compact. Uncontrolled agglomeration
Agglomeration may refer to:
* Urban agglomeration, in standard English
* Megalopolis, in Chinese English, as defined in China's ''Standard for basic terminology of urban planning'' (GB/T 50280—98). Also known as " city cluster".
* Economies of ag ...
of powders due to attractive van der Waals forces
In molecular physics, the van der Waals force is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical electronic bond; they are comparatively weak and th ...
can also give rise to in microstructural inhomogeneities.
Differential stresses that develop as a result of non-uniform drying shrinkage are directly related to the rate at which the solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
can be removed, and thus highly dependent upon the distribution of porosity. Such stresses have been associated with a plastic-to-brittle transition in consolidated bodies,
and can yield to crack propagation
Fracture mechanics is the field of mechanics concerned with the study of the propagation of cracks in materials. It uses methods of analytical solid mechanics to calculate the driving force on a crack and those of experimental solid mechanics t ...
in the unfired body if not relieved.
In addition, any fluctuations in packing density in the compact as it is prepared for the kiln are often amplified during the sintering process, yielding inhomogeneous densification.
Some pores and other structural defect
A defect is a physical, functional, or aesthetic attribute of a product or service that exhibits that the product or service failed to meet one of the desired specifications. Defect, defects or defected may also refer to:
Examples
* Angular defec ...
s associated with density variations have been shown to play a detrimental role in the sintering process by growing and thus limiting end-point densities.
Differential stresses arising from inhomogeneous densification have also been shown to result in the propagation of internal cracks, thus becoming the strength-controlling flaws.
It would therefore appear desirable to process a material in such a way that it is physically uniform with regard to the distribution of components and porosity, rather than using particle size distributions which will maximize the green density. The containment of a uniformly dispersed assembly of strongly interacting particles in suspension requires total control over particle-particle interactions. Monodisperse colloids provide this potential.
Monodisperse powders of colloidal silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
, for example, may therefore be stabilized sufficiently to ensure a high degree of order in the colloidal crystal A colloidal crystal is an ordered array of colloid particles and fine grained materials analogous to a standard crystal whose repeating subunits are atoms or molecules. A natural example of this phenomenon can be found in the gem opal, where sphere ...
or polycrystalline colloidal solid which results from aggregation. The degree of order appears to be limited by the time and space allowed for longer-range correlations to be established.
Such defective polycrystalline colloidal structures would appear to be the basic elements of submicrometer colloidal materials science, and, therefore, provide the first step in developing a more rigorous understanding of the mechanisms involved in microstructural evolution in inorganic systems such as polycrystalline ceramics.
Self-assembly

Self-assembly
Self-assembly is a process in which a disordered system of pre-existing components forms an organized structure or pattern as a consequence of specific, local interactions among the components themselves, without external direction. When the ...
is the most common term in use in the modern scientific community to describe the spontaneous aggregation of particles (atoms, molecules, colloids, micelles, etc.) without the influence of any external forces. Large groups of such particles are known to assemble themselves into thermodynamic
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws of the ...
ally stable, structurally well-defined arrays, quite reminiscent of one of the 7 crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macro ...
systems found in metallurgy and mineralogy (e.g. face-centred cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.
There are three main varieties of ...
, body-centred cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.
There are three main varieties of ...
, etc.). The fundamental difference in equilibrium structure is in the spatial scale of the unit cell (or lattice parameter
A lattice constant or lattice parameter is one of the physical dimensions and angles that determine the geometry of the unit cells in a crystal lattice, and is proportional to the distance between atoms in the crystal. A simple cubic crystal has o ...
) in each particular case.
Thus, self-assembly is emerging as a new strategy in chemical synthesis and nanotechnology. Molecular self-assembly has been observed in various biological systems and underlies the formation of a wide variety of complex biological structures. Molecular crystals, liquid crystals, colloids, micelles, emulsions, phase-separated polymers, thin films and self-assembled monolayers all represent examples of the types of highly ordered structures which are obtained using these techniques. The distinguishing feature of these methods is self-organization in the absence of any external forces.
In addition, the principal mechanical characteristics and structures of biological ceramics, polymer composites, elastomers
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of ''elastic p ...
, and cellular
Cellular may refer to:
*Cellular automaton, a model in discrete mathematics
* Cell biology, the evaluation of cells work and more
* ''Cellular'' (film), a 2004 movie
*Cellular frequencies, assigned to networks operating in cellular RF bands
*Cell ...
materials are being re-evaluated, with an emphasis on bioinspired materials and structures. Traditional approaches focus on design methods of biological materials using conventional synthetic materials. This includes an emerging class of mechanically superior biomaterials
A biomaterial is a substance that has been engineered to interact with biological systems for a medical purpose, either a therapeutic (treat, augment, repair, or replace a tissue function of the body) or a diagnostic one. As a science, biomateria ...
based on microstructural features and designs found in nature. The new horizons have been identified in the synthesis of bioinspired materials through processes that are characteristic of biological systems in nature. This includes the nanoscale self-assembly of the components and the development of hierarchical structures.
Ceramic composites
 Substantial interest has arisen in recent years in fabricating ceramic composites. While there is considerable interest in composites with one or more non-ceramic constituents, the greatest attention is on composites in which all constituents are ceramic. These typically comprise two ceramic constituents: a continuous matrix, and a dispersed phase of ceramic particles, whiskers, or short (chopped) or continuous ceramic fibres. The challenge, as in wet chemical processing, is to obtain a uniform or homogeneous distribution of the dispersed particle or fibre phase.Hull, D. and Clyne, T.W. (1996) ''An Introduction to Composite Materials''. Cambridge Solid State Science Series, Cambridge University Press
Barbero, E.J. (2010) ''Introduction to Composite Materials Design'', 2nd Edn., CRC Press.
Consider first the processing of particulate composites. The particulate phase of greatest interest is tetragonal zirconia because of the toughening that can be achieved from the
Substantial interest has arisen in recent years in fabricating ceramic composites. While there is considerable interest in composites with one or more non-ceramic constituents, the greatest attention is on composites in which all constituents are ceramic. These typically comprise two ceramic constituents: a continuous matrix, and a dispersed phase of ceramic particles, whiskers, or short (chopped) or continuous ceramic fibres. The challenge, as in wet chemical processing, is to obtain a uniform or homogeneous distribution of the dispersed particle or fibre phase.Hull, D. and Clyne, T.W. (1996) ''An Introduction to Composite Materials''. Cambridge Solid State Science Series, Cambridge University Press
Barbero, E.J. (2010) ''Introduction to Composite Materials Design'', 2nd Edn., CRC Press.
Consider first the processing of particulate composites. The particulate phase of greatest interest is tetragonal zirconia because of the toughening that can be achieved from the phase transformation
In chemistry, thermodynamics, and other related fields, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic states of ...
from the metastable tetragonal to the monoclinic crystalline phase, aka transformation toughening. There is also substantial interest in dispersion of hard, non-oxide phases such as SiC, TiB, TiC, boron, carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
and especially oxide matrices like alumina and mullite
Mullite or porcelainite is a rare silicate mineral formed during contact metamorphism of clay minerals. It can form two stoichiometric forms: 3 Al2 O32 SiO2 or 2Al2O3 SiO2. Unusually, mullite has no charge-balancing cations present. As a result, th ...
. There is also interest too incorporating other ceramic particulates, especially those of highly anisotropic thermal expansion. Examples include Al2O3, TiO2, graphite, and boron nitride.
 In processing particulate composites, the issue is not only homogeneity of the size and spatial distribution of the dispersed and matrix phases, but also control of the matrix grain size. However, there is some built-in self-control due to inhibition of matrix grain growth by the dispersed phase. Particulate composites, though generally offer increased resistance to damage, failure, or both, are still quite sensitive to inhomogeneities of composition as well as other processing defects such as pores. Thus they need good processing to be effective.
Particulate composites have been made on a commercial basis by simply mixing powders of the two constituents. Although this approach is inherently limited in the homogeneity that can be achieved, it is the most readily adaptable for existing ceramic production technology. However, other approaches are of interest.
In processing particulate composites, the issue is not only homogeneity of the size and spatial distribution of the dispersed and matrix phases, but also control of the matrix grain size. However, there is some built-in self-control due to inhibition of matrix grain growth by the dispersed phase. Particulate composites, though generally offer increased resistance to damage, failure, or both, are still quite sensitive to inhomogeneities of composition as well as other processing defects such as pores. Thus they need good processing to be effective.
Particulate composites have been made on a commercial basis by simply mixing powders of the two constituents. Although this approach is inherently limited in the homogeneity that can be achieved, it is the most readily adaptable for existing ceramic production technology. However, other approaches are of interest.
 From the technological standpoint, a particularly desirable approach to fabricating particulate composites is to coat the matrix or its precursor onto fine particles of the dispersed phase with good control of the starting dispersed particle size and the resultant matrix coating thickness. One should in principle be able to achieve the ultimate in homogeneity of distribution and thereby optimize composite performance. This can also have other ramifications, such as allowing more useful composite performance to be achieved in a body having porosity, which might be desired for other factors, such as limiting thermal conductivity.
There are also some opportunities to utilize melt processing for fabrication of ceramic, particulate, whisker and short-fibre, and continuous-fibre composites. Clearly, both particulate and whisker composites are conceivable by solid-state precipitation after solidification of the melt. This can also be obtained in some cases by sintering, as for precipitation-toughened, partially stabilized zirconia. Similarly, it is known that one can directionally solidify ceramic eutectic mixtures and hence obtain uniaxially aligned fibre composites. Such composite processing has typically been limited to very simple shapes and thus suffers from serious economic problems due to high machining costs.
Clearly, there are possibilities of using melt casting for many of these approaches. Potentially even more desirable is using melt-derived particles. In this method, quenching is done in a solid solution or in a fine eutectic structure, in which the particles are then processed by more typical ceramic powder processing methods into a useful body. There have also been preliminary attempts to use melt spraying as a means of forming composites by introducing the dispersed particulate, whisker, or fibre phase in conjunction with the melt spraying process.
Other methods besides melt infiltration to manufacture ceramic composites with long fibre reinforcement are chemical vapour infiltration and the infiltration of fibre preforms with organic
From the technological standpoint, a particularly desirable approach to fabricating particulate composites is to coat the matrix or its precursor onto fine particles of the dispersed phase with good control of the starting dispersed particle size and the resultant matrix coating thickness. One should in principle be able to achieve the ultimate in homogeneity of distribution and thereby optimize composite performance. This can also have other ramifications, such as allowing more useful composite performance to be achieved in a body having porosity, which might be desired for other factors, such as limiting thermal conductivity.
There are also some opportunities to utilize melt processing for fabrication of ceramic, particulate, whisker and short-fibre, and continuous-fibre composites. Clearly, both particulate and whisker composites are conceivable by solid-state precipitation after solidification of the melt. This can also be obtained in some cases by sintering, as for precipitation-toughened, partially stabilized zirconia. Similarly, it is known that one can directionally solidify ceramic eutectic mixtures and hence obtain uniaxially aligned fibre composites. Such composite processing has typically been limited to very simple shapes and thus suffers from serious economic problems due to high machining costs.
Clearly, there are possibilities of using melt casting for many of these approaches. Potentially even more desirable is using melt-derived particles. In this method, quenching is done in a solid solution or in a fine eutectic structure, in which the particles are then processed by more typical ceramic powder processing methods into a useful body. There have also been preliminary attempts to use melt spraying as a means of forming composites by introducing the dispersed particulate, whisker, or fibre phase in conjunction with the melt spraying process.
Other methods besides melt infiltration to manufacture ceramic composites with long fibre reinforcement are chemical vapour infiltration and the infiltration of fibre preforms with organic precursor
Precursor or Precursors may refer to:
* Precursor (religion), a forerunner, predecessor
** The Precursor, John the Baptist
Science and technology
* Precursor (bird), a hypothesized genus of fossil birds that was composed of fossilized parts of u ...
, which after pyrolysis
The pyrolysis (or devolatilization) process is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures, often in an inert atmosphere. It involves a change of chemical composition. The word is coined from the Greek-derived elements ''py ...
yield an amorphous ceramic matrix, initially with a low density. With repeated cycles of infiltration and pyrolysis one of those types of ceramic matrix composite
In materials science, ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) are a subgroup of composite materials and a subgroup of ceramics. They consist of ceramic fibers embedded in a ceramic matrix. The fibers and the matrix both can consist of any ceramic mate ...
s is produced. Chemical vapour infiltration is used to manufacture carbon/carbon and silicon carbide reinforced with carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
or silicon carbide fibres.
Besides many process improvements, the first of two major needs for fibre composites is lower fibre costs. The second major need is fibre compositions or coatings, or composite processing, to reduce degradation that results from high-temperature composite exposure under oxidizing conditions.
Applications
 The products of technical ceramics include tiles used in the
The products of technical ceramics include tiles used in the Space Shuttle program
The Space Shuttle program was the fourth human spaceflight program carried out by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), which accomplished routine transportation for Earth-to-orbit crew and cargo from 1981 to 2011. I ...
, gas burner nozzles, ballistic protection, nuclear fuel uranium oxide pellets, bio-medical implants, jet engine turbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced by a turbine can be used for generating ...
blades, and missile
In military terminology, a missile is a guided airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight usually by a jet engine or rocket motor. Missiles are thus also called guided missiles or guided rockets (when a previously unguided rocke ...
nose cones.
Its products are often made from materials other than clay, chosen for their particular physical properties. These may be classified as follows:
* Oxides: silica, alumina, zirconia
Zirconium dioxide (), sometimes known as zirconia (not to be confused with zircon), is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium. Its most naturally occurring form, with a monoclinic crystalline structure, is the mineral baddeleyite. A dopant sta ...
*Non-oxides: carbides, boride A boride is a compound between boron and a less electronegative element, for example silicon boride (SiB3 and SiB6). The borides are a very large group of compounds that are generally high melting and are covalent more than ionic in nature. Some bo ...
s, nitride
In chemistry, a nitride is an inorganic compound of nitrogen. The "nitride" anion, N3- ion, is very elusive but compounds of nitride are numerous, although rarely naturally occuring. Some nitrides have a find applications, such as wear-resistant ...
s, silicide
A silicide is a type of chemical compound that combines silicon and a (usually) more electropositive element.
Silicon is more electropositive than carbon. Silicides are structurally closer to borides than to carbides.
Similar to borides and carb ...
s
*Composite
Composite or compositing may refer to:
Materials
* Composite material, a material that is made from several different substances
** Metal matrix composite, composed of metal and other parts
** Cermet, a composite of ceramic and metallic materials
...
s: particulate or whisker reinforced matrices, combinations of oxides and non-oxides (e.g. polymers).
Ceramics can be used in many technological industries. One application is the ceramic tiles on NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
's Space Shuttle, used to protect it and the future supersonic space planes from the searing heat of re-entry into the Earth's atmosphere. They are also used widely in electronics and optics. In addition to the applications listed here, ceramics are also used as a coating in various engineering cases. An example would be a ceramic bearing coating over a titanium frame used for an aircraft. Recently the field has come to include the studies of single crystals or glass fibres, in addition to traditional polycrystalline materials, and the applications of these have been overlapping and changing rapidly.
Aerospace
*Engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power ...
s: shielding a hot running aircraft engine from damaging other components.
* Airframes: used as a high-stress, high-temp and lightweight bearing and structural component.
*Missile nose-cones: shielding the missile internals from heat.
*Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program ...
tiles
* Space-debris ballistic shields: ceramic fiber woven shields offer better protection to hypervelocity (~7 km/s) particles than aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
shields of equal weight.
*Rocket nozzles: focusing high-temperature exhaust gases from the rocket booster.
* Unmanned Air Vehicles: ceramic engine utilization in aeronautical applications (such as Unmanned Air Vehicles) may result in enhanced performance characteristics and less operational costs.
Biomedical
 * Artificial bone; Dentistry applications, teeth.
* Biodegradable splints; Reinforcing bones recovering from osteoporosis
*Implant material
* Artificial bone; Dentistry applications, teeth.
* Biodegradable splints; Reinforcing bones recovering from osteoporosis
*Implant material
Electronics
*Capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
The effect of ...
s
* Integrated circuit packages
*Transducer
A transducer is a device that converts energy from one form to another. Usually a transducer converts a signal in one form of energy to a signal in another.
Transducers are often employed at the boundaries of automation, measurement, and cont ...
s
*Insulators
Insulator may refer to:
* Insulator (electricity), a substance that resists electricity
** Pin insulator, a device that isolates a wire from a physical support such as a pin on a utility pole
** Strain insulator, a device that is designed to work ...
Optical
*Optical fibres, guided lightwave transmission *Switches *Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The fi ...
amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It may increase the power significantly, or its main effect may be to boost t ...
s
*Lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements ...
es
*Infrared heat-seeking devices
Automotive
* Heat shield * Exhaust heat managementBiomaterials
 Silicification is quite common in the biological world and occurs in bacteria, single-celled organisms, plants, and animals (invertebrates and vertebrates). Crystalline minerals formed in such environment often show exceptional physical properties (e.g. strength, hardness, fracture toughness) and tend to form hierarchical structures that exhibit microstructural order over a range of length or spatial scales. The minerals are crystallized from an environment that is undersaturated with respect to silicon, and under conditions of neutral pH and low temperature (0–40 °C). Formation of the mineral may occur either within or outside of the cell wall of an organism, and specific biochemical reactions for mineral deposition exist that include lipids, proteins and carbohydrates.
Most natural (or biological) materials are complex composites whose mechanical properties are often outstanding, considering the weak constituents from which they are assembled. These complex structures, which have risen from hundreds of million years of evolution, are inspiring the design of novel materials with exceptional physical properties for high performance in adverse conditions. Their defining characteristics such as hierarchy, multifunctionality, and the capacity for self-healing, are currently being investigated.
The basic building blocks begin with the 20 amino acids and proceed to polypeptides, polysaccharides, and polypeptides–saccharides. These, in turn, compose the basic proteins, which are the primary constituents of the 'soft tissues' common to most biominerals. With well over 1000 proteins possible, current research emphasizes the use of collagen, chitin, keratin, and elastin. The 'hard' phases are often strengthened by crystalline minerals, which nucleate and grow in a biomediated environment that determines the size, shape and distribution of individual crystals. The most important mineral phases have been identified as hydroxyapatite, silica, and
Silicification is quite common in the biological world and occurs in bacteria, single-celled organisms, plants, and animals (invertebrates and vertebrates). Crystalline minerals formed in such environment often show exceptional physical properties (e.g. strength, hardness, fracture toughness) and tend to form hierarchical structures that exhibit microstructural order over a range of length or spatial scales. The minerals are crystallized from an environment that is undersaturated with respect to silicon, and under conditions of neutral pH and low temperature (0–40 °C). Formation of the mineral may occur either within or outside of the cell wall of an organism, and specific biochemical reactions for mineral deposition exist that include lipids, proteins and carbohydrates.
Most natural (or biological) materials are complex composites whose mechanical properties are often outstanding, considering the weak constituents from which they are assembled. These complex structures, which have risen from hundreds of million years of evolution, are inspiring the design of novel materials with exceptional physical properties for high performance in adverse conditions. Their defining characteristics such as hierarchy, multifunctionality, and the capacity for self-healing, are currently being investigated.
The basic building blocks begin with the 20 amino acids and proceed to polypeptides, polysaccharides, and polypeptides–saccharides. These, in turn, compose the basic proteins, which are the primary constituents of the 'soft tissues' common to most biominerals. With well over 1000 proteins possible, current research emphasizes the use of collagen, chitin, keratin, and elastin. The 'hard' phases are often strengthened by crystalline minerals, which nucleate and grow in a biomediated environment that determines the size, shape and distribution of individual crystals. The most important mineral phases have been identified as hydroxyapatite, silica, and aragonite
Aragonite is a carbonate mineral, one of the three most common naturally occurring crystal forms of calcium carbonate, (the other forms being the minerals calcite and vaterite). It is formed by biological and physical processes, including pre ...
. Using the classification of Wegst and Ashby, the principal mechanical characteristics and structures of biological ceramics, polymer composites, elastomers, and cellular materials have been presented. Selected systems in each class are being investigated with emphasis on the relationship between their microstructure over a range of length scales and their mechanical response.
Thus, the crystallization of inorganic materials in nature generally occurs at ambient temperature and pressure. Yet the vital organisms through which these minerals form are capable of consistently producing extremely precise and complex structures. Understanding the processes in which living organisms control the growth of crystalline minerals such as silica could lead to significant advances in the field of materials science, and open the door to novel synthesis techniques for nanoscale composite materials, or nanocomposites.
 High-resolution scanning electron microscope (SEM) observations were performed of the microstructure of the mother-of-pearl (or nacre) portion of the abalone shell. Those shells exhibit the highest mechanical strength and fracture toughness of any non-metallic substance known. The nacre from the shell of the abalone has become one of the more intensively studied biological structures in materials science. Clearly visible in these images are the neatly stacked (or ordered) mineral tiles separated by thin organic sheets along with a macrostructure of larger periodic growth bands which collectively form what scientists are currently referring to as a hierarchical composite structure. (The term hierarchy simply implies that there are a range of structural features which exist over a wide range of length scales).
Future developments reside in the synthesis of bio-inspired materials through processing methods and strategies that are characteristic of biological systems. These involve nanoscale self-assembly of the components and the development of hierarchical structures.
High-resolution scanning electron microscope (SEM) observations were performed of the microstructure of the mother-of-pearl (or nacre) portion of the abalone shell. Those shells exhibit the highest mechanical strength and fracture toughness of any non-metallic substance known. The nacre from the shell of the abalone has become one of the more intensively studied biological structures in materials science. Clearly visible in these images are the neatly stacked (or ordered) mineral tiles separated by thin organic sheets along with a macrostructure of larger periodic growth bands which collectively form what scientists are currently referring to as a hierarchical composite structure. (The term hierarchy simply implies that there are a range of structural features which exist over a wide range of length scales).
Future developments reside in the synthesis of bio-inspired materials through processing methods and strategies that are characteristic of biological systems. These involve nanoscale self-assembly of the components and the development of hierarchical structures.
See also
* * * * * * * * * * * * * *References
External links
The American Ceramic Society
{{Authority control Materials science Ceramic materials Engineering disciplines Industrial processes