Caucasus Albania on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Caucasian Albania is a modern
''
 Aghuank (
Aghuank (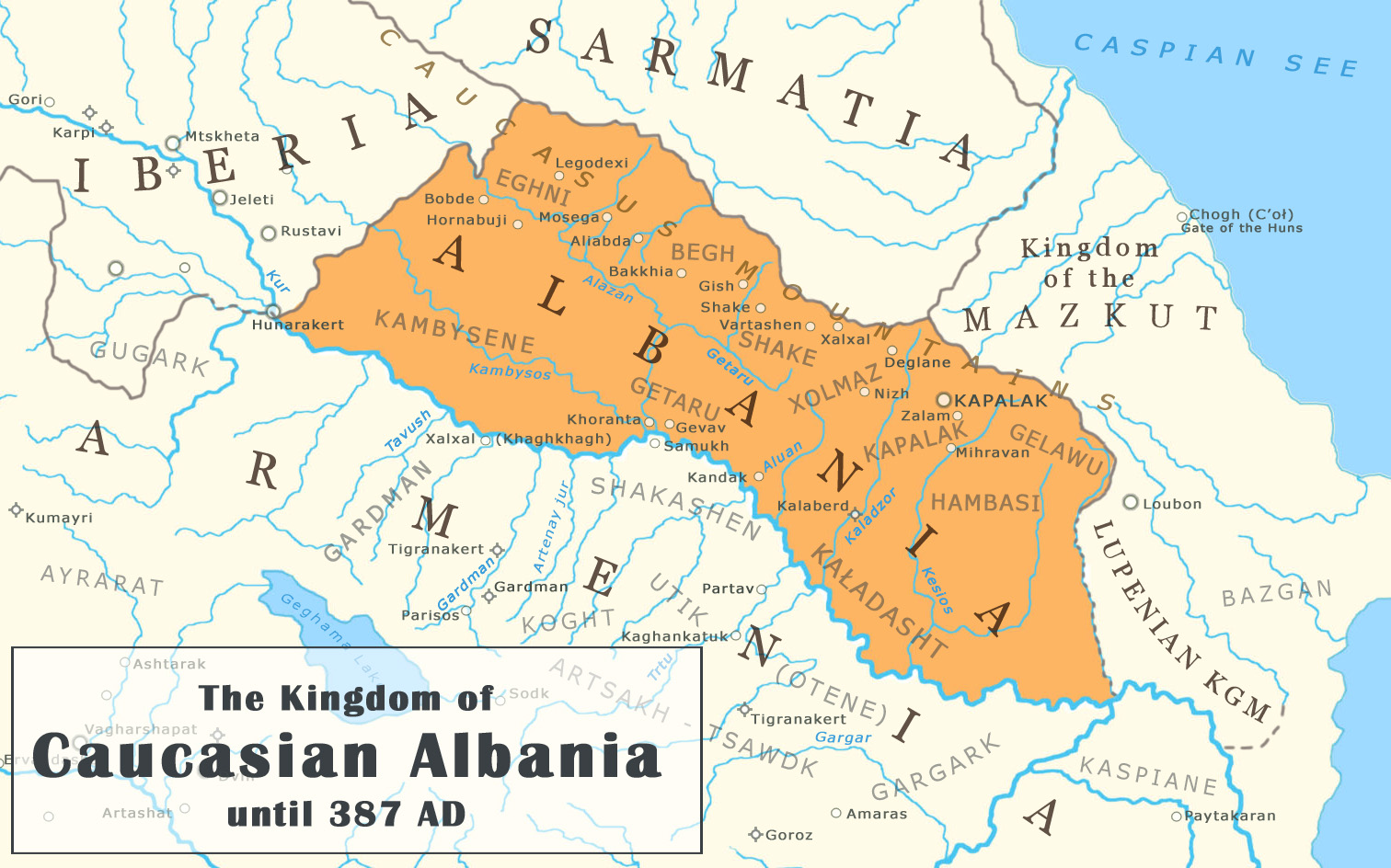 The Parthian name for the region was '' Ardhan'' (
The Parthian name for the region was '' Ardhan'' (
The lands of Greater Asia
'. These boundaries, though, were probably never static—at times the territory of Caucasian Albania included land to the west of the river Kura. Albania or Arran in Islamic times was a triangle of land, lowland in the east and mountainous in the west, formed by the junction of the Kura and Aras rivers, Mil plain and parts of the
В 6 т. Т. 2. Восток в средние века. М., «Восточная литература», 2002. (History of the East. In 6 volumes. Volume 2. Moscow, publishing house of the Russian Academy of sciences «East literature»): The multi-ethnic population of Albania left-bank at this time is increasingly moving to the Persian language. Mainly this applies to cities of Aran and Shirwan, as begin from 9-10 centuries named two main areas in the territory of Azerbaijan. With regard to the rural population, it would seem, mostly retained for a long time, their old languages, related to modern Daghestanian family, especially Lezgin. (Russian text: Пестрое в этническом плане население левобережной Албании в это время все больше переходит на персидский язык. Главным образом это относится к городам Арана и Ширвана, как стали в IX-Х вв. именоваться два главные области на территории Азербайджана. Что касается сельского населения, то оно, по-видимому, в основном сохраняло еще долгое время свои старые языки, родственные современным дагестанским, прежде всего лезгинскому. and subsequently
 A Caucasian Albanian alphabet of fifty-two letters, bearing resemblance to Georgian, Ethiopian and Armenian characters,See sample of script with letters that resemble other alphabets, specifically Georgian (19 letters), Ethiopian (14 letters) and Armenian (10 letters) i
A Caucasian Albanian alphabet of fifty-two letters, bearing resemblance to Georgian, Ethiopian and Armenian characters,See sample of script with letters that resemble other alphabets, specifically Georgian (19 letters), Ethiopian (14 letters) and Armenian (10 letters) i
"The Albanian Script: The Process How Its Secrets Were Revealed,"
by Zaza Aleksidze and Betty Blair survived through a few inscriptions, and an Armenian manuscript dating from the 15th century. This manuscript, Matenadaran No. 7117, first published by Ilia Abuladze in 1937 is a language manual, presenting different alphabets for comparison – Armenian alphabet,
The Eastern Orthodox Encyclopædia.
 The Greek historian Arrian mentions (perhaps anachronistically) the Caucasian Albanians for the first time in the
The Greek historian Arrian mentions (perhaps anachronistically) the Caucasian Albanians for the first time in the
Moskva, «Vostochnaya Literatura», 2002.
 There was an enduring relation of Albania with
There was an enduring relation of Albania with  Albania is also mentioned by
Albania is also mentioned by
The Arsacids
''Encyclopædia Iranica''. excerpt:"Whatever the sporadic suzerainty of Rome, the country was now a part—together with Iberia (East Georgia) and (Caucasian) Albania, where other Arsacid branched reigned—of a pan-Arsacid family federation. Culturally, the predominance of Hellenism, as under the Artaxiads, was now followed by a predominance of "Iranianism," and, symptomatically, instead of Greek, as before, Parthian became the language of the educated" Whatever the sporadic suzerainty of Rome, the country was now a part—together with Iberia (East Georgia) and (Caucasian) Albania, where other Arsacid branches reigned—of a pan-Arsacid family federation. Culturally, the predominance of Hellenism, as under the Artaxiads, was now followed by a predominance of "Iranianism", and, symptomatically, instead of Greek, as before, Parthian became the language of the educated. An incursion in this era was made by the
 In Kaghankatvatsi's ''History'' and in the historical text of the Armenian early medieval author
In Kaghankatvatsi's ''History'' and in the historical text of the Armenian early medieval author
/ref> Both
Movses Kalankatuatsi. ''The History of Aluank''
Translated from Old Armenian (Grabar) by Sh.V.Smbatian, Yerevan, 1984.
Koriun, ''The Life of Mashtots''
translated from Old Armenian (Grabar) by Bedros Norehad. * Movses Kalankatuatsi. ''History of Albania''. Translated by L. Davlianidze-Tatishvili, Tbilisi, 1985. * Movses Khorenats
Translated from Old Armenian (Grabar) by
About the Caucasian Albania (section 10)
Caucasian History
{{Authority control 705 disestablishments Former countries in Europe Geographic history of Azerbaijan History of Dagestan Roman client kingdoms
exonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
for a former state located in ancient times in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
: mostly in what is now Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of t ...
(where both of its capitals were located). The modern endonyms for the area are ''Aghwank'' and ''Aluank'', among the Udi people
Udis (endonym ''Udi'' or ''Uti'') are a native people of the Caucasus that currently live mainly in Russia and Azerbaijan, with smaller populations in Georgia, Armenia, Kazakhstan, Ukraine and other countries. Their total number is about 10,000 pe ...
, who regard themselves as descended from the inhabitants of Caucasian Albania. However, its original endonym is unknown.Robert H. Hewsen. "Ethno-History and the Armenian Influence upon the Caucasian Albanians", in: Samuelian, Thomas J. (Ed.), ''Classical Armenian Culture. Influences and Creativity''. Chicago: 1982, pp. 27-40. Bosworth, Clifford E.br>Arran''
Encyclopædia Iranica
''Encyclopædia Iranica'' is a project whose goal is to create a comprehensive and authoritative English language encyclopedia about the history, culture, and civilization of Iranian peoples from prehistory to modern times.
Scope
The ''Encyc ...
''.
The name Albania is derived from the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
name and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
. James Stuart Olson. An Ethnohistorical Dictionary of the Russian and Soviet Empires. The prefix "Caucasian" is used purely to avoid confusion with modern Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
of the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, which has no known geographical or historical connections to Caucasian Albania.
Little is known of the region's prehistory, including the origins of Caucasian Albania as a geographical and/or ethnolinguistic concept. In the 1st century BC and the 1st century AD, the area south of the Greater Caucasus
The Greater Caucasus ( az, Böyük Qafqaz, Бөјүк Гафгаз, بيوک قافقاز; ka, დიდი კავკასიონი, ''Didi K’avk’asioni''; russian: Большой Кавказ, ''Bolshoy Kavkaz'', sometimes translat ...
and north of the Lesser Caucasus
The Lesser Caucasus, also called Caucasus Minor, is the second of the two main mountain ranges of Caucasus mountains, of length about . The western portion of the Lesser Caucasus overlaps and converges with east Turkey and northwest Iran.
It runs ...
was divided between Caucasian Albania in the east, Caucasian Iberia
In Greco-Roman geography, Iberia (Ancient Greek: ''Iberia''; la, Hiberia) was an exonym for the Georgian kingdom of Kartli ( ka, ქართლი), known after its core province, which during Classical Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages ...
in the center, Kolchis in the west, Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
in the southwest and Atropatene
Atropatene ( peo, Ātṛpātakāna; grc, Ἀτροπατηνή), also known as Media Atropatene, was an ancient Iranian kingdom established in by the Persian satrap Atropates. The kingdom, centered in present-day northern Iran, was ruled by A ...
to the southeast.
In 252, Caucasian Albania acknowledged the suzerainty of the Sasanian Empire, appearing among its provinces in Shapur I's inscription at the Ka'ba-ye Zartosht
Shapur I's Ka'ba-ye Zartosht inscription (shortened as Shapur-KZ, ŠKZ, SKZ), also referred to as The Great Inscription of Shapur I, and ''Res Gestae Divi Saporis'' (RGDS), is a trilingual inscription made during the reign of the Sasanian king S ...
. The kingdom would remain an integral part of the empire until its fall. By the end of the 3rd-century, the kings of Caucasian Albania were replaced with an Arsacid family, and would later be succeeded by another Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
royal family in the 5th century AD, the Mihranids The Mihranids were an Iranian family which ruled several regions of Caucasus from 330 to 821. They claimed to be of Sasanian Persian descent but were of Parthian origin.
History
The dynasty was founded when a certain Mihran, a distant relative o ...
.
Geonyms
 Aghuank (
Aghuank (Old Armenian
Classical Armenian (, in Eastern Armenian pronunciation: Grabar, Western Armenian: Krapar; meaning "literary anguage; also Old Armenian or Liturgical Armenian) is the oldest attested form of the Armenian language. It was first written down at ...
: Աղուանք ''Ałuankʿ'', Modern Armenian
Modern Armenian ( hy, աշխարհաբար, ''ashkharhabar'' or ''ašxarhabar'', literally the "secular/lay language") is the modern vernacular (vulgar) form of the Armenian language. Although it first appeared in the 14th century, it was not until ...
: Աղվանք ''Aġvank’'') is the Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
n name for Caucasian Albania. Armenian authors mention that the name derived from the word " ału" («աղու») meaning amiable
Amiable (1891–1915) was a British Thoroughbred racehorse that won the 1894 Epsom Oaks and 1,000 Guineas Stakes despite having severe stringhalt in both hind limbs. Amiable raced until she was three years old, retiring in 1895 to the Duke ...
in Armenian. The term ''Aghuank'' is polysemous
Polysemy ( or ; ) is the capacity for a sign (e.g. a symbol, a morpheme, a word, or a phrase) to have multiple related meanings. For example, a word can have several word senses. Polysemy is distinct from ''monosemy'', where a word has a single ...
and is also used in Armenian sources to denote the region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics ( physical geography), human impact characteristics ( human geography), and the interaction of humanity an ...
between the Kur and Araxes rivers as part of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
. In the latter case it is sometimes used in the form "Armenian Aghuank" or "Hay-Aghuank".
The Armenian historian of the region, Movses Kaghankatvatsi Movses Kaghankatvatsi ( hy, Մովսէս Կաղանկատուացի ''Movses Kaġankatvac’i''), or Movses Daskhurantsi ( ''Movses Dasxuranc’i'') is the reputed author (or authors) of a tenth-century Classical Armenian historiographical work on C ...
, who left the only more or less complete historical account about the region, explains the name Aghvank as a derivation from the word '' ału'' (Armenian for sweet, soft, tender), which, he said, was the nickname of Caucasian Albania's first governor Arran and referred to his lenient personality. Movses Kaghankatvatsi and other ancient sources explain ''Arran'' or ''Arhan'' as the name of the legendary founder of Caucasian Albania (Aghvan) or even of the Iranian tribe known as Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
(Alani), who in some versions was a son of Noah's son Yafet. James Darmesteter
James Darmesteter (28 March 184919 October 1894) was a French author, orientalist, and antiquarian.
Biography
He was born of Jewish parents at Château-Salins, in Lorraine. The family name had originated in their earlier home of Darmstadt. He was ...
, translator of the Avesta
The Avesta () is the primary collection of religious texts of Zoroastrianism, composed in the Avestan language.
The Avesta texts fall into several different categories, arranged either by dialect, or by usage. The principal text in the lit ...
, compared ''Arran'' with '' Airyana Vaego'' which he also considered to have been in the Araxes- Ararat region, although modern theories tend to place this in the east of Iran.
 The Parthian name for the region was '' Ardhan'' (
The Parthian name for the region was '' Ardhan'' (Middle Persian
Middle Persian or Pahlavi, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg () in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasanian Empire. For some time after the Sasanian collapse, Middle ...
: ''Arran''). The Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
was ''ar-Rān''.V. Minorsky. ''Caucasica IV''. Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies, University of London, Vol. 15, No. 3. (1953), p. 504 In Georgian, it was known as რანი (''Rani''). In Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
, it was called . What its inhabitants were called is unknown.
Geography
In pre-Islamic times, Caucasian Albania/Arran was a wider concept than that of post-Islamic Arran. Ancient Arran covered all eastern Transcaucasia, which included most of the territory of the modern-day Azerbaijan Republic and part of the territory of Dagestan. However, in post-Islamic times the geographic notion of Arran reduced to the territory between the rivers of Kura and Araks. Ancient Caucasian Albania lay on the south-eastern part of theGreater Caucasus
The Greater Caucasus ( az, Böyük Qafqaz, Бөјүк Гафгаз, بيوک قافقاز; ka, დიდი კავკასიონი, ''Didi K’avk’asioni''; russian: Большой Кавказ, ''Bolshoy Kavkaz'', sometimes translat ...
mountains. It was bounded by Caucasian Iberia
In Greco-Roman geography, Iberia (Ancient Greek: ''Iberia''; la, Hiberia) was an exonym for the Georgian kingdom of Kartli ( ka, ქართლი), known after its core province, which during Classical Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages ...
(present-day Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
) to the west, by Sarmatia
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th c ...
to the north, by the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
to the east, and by the provinces of Artsakh and Utik
Utik ( hy, Ուտիք, also known as Uti, Utiq, or Outi) was a historic province of the Kingdom of Armenia. It was ceded to Caucasian Albania following the partition of Armenia between Sassanid Persia and the Eastern Roman Empire in 387 AD. Most ...
in Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
to the west along the river Kura.Anon. ''Armenian "Geography" («Աշխարհացոյց»), Sec. IV, AsiaThe lands of Greater Asia
'. These boundaries, though, were probably never static—at times the territory of Caucasian Albania included land to the west of the river Kura. Albania or Arran in Islamic times was a triangle of land, lowland in the east and mountainous in the west, formed by the junction of the Kura and Aras rivers, Mil plain and parts of the
Mughan plain
Mughan plain ( az, Muğan düzü, مغان دوزو; ) is a plain stretching from northwestern Iran to the southern part of the Republic of Azerbaijan. The highest density of irrigation canals is in the section of the Mughan plain which lies in ...
, and in the pre-Islamic times, corresponded roughly to the territory of the modern-day Republic of Azerbaijan
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th ...
.
The districts of Albania were:
* Cambysene Cambysene was a region first attested in the ''Geographica'' ("Geography") of the ancient geographer and historian Strabo (64/3 BC – AD). According to Strabo, it comprised one of the northernmost provinces of the ancient Kingdom of Armenia, and ...
* Getaru
* Elni/Xeni
* Begh
* Shake
* Xolmaz
* Kapalak
* Hambasi
* Gelavu
* Hejeri
* Kaladasht
The kingdom's capital during antiquity was Qabala
Qabala ( az, Qəbələ) is a city and the administrative centre of the Qabala District of Azerbaijan. The municipality consists of the city of Gabala and the village of Küsnat. Before the city was known as Kutkashen, but after the Republic of ...
(Gabala; Kapalak).
Classical sources are unanimous in making the Kura River (Cyros) the frontier between Armenia and Albania after the conquest of the territories on the right bank of Kura by Armenians in the 2nd century BC.
The original territory of Albania was approximately 23,000 km2. Yeremyan, Suren T. ''«Հայաստանը ըստ «Աշխարհացույցի»'' (''Armenia According to the "Ashkharhatsuyts"''). Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Armenia (NAS RA) ( hy, Հայաստանի Հանրապետության գիտությունների ազգային ակադեմիա, ՀՀ ԳԱԱ, ''Hayastani Hanrapetut’yan gitut’yunneri az ...
, 1963, p. 34. After 387 AD the territory of Caucasian Albania, sometimes referred to by scholars as "Greater Albania," grew to about 45,000 km². In the 5th century the capital was transferred to Partav
Barda ( az, Bərdə ) is a city and the capital of the Barda District in Azerbaijan, located south of Yevlax and on the left bank of the Tartar river. It served as the capital of Caucasian Albania by the end of the 5th-century. Barda became the ch ...
in Utik', reported to have been built in the mid-5th century by the King Vache II of Albania,Minorsky, Vladimir. ''A History of Sharvan and Darband in the 10th-11th Centuries''. Cambridge, 1958. but according to M. L. Chaumont, it existed earlier as an Armenian city.
In a medieval chronicle "''Ajayib-ad-Dunia''", written in the 13th century by an unknown author, Arran is said to have been 30 '' farsakhs'' (200 km) in width, and 40 ''farsakhs'' (270 km) in length. All the right bank of the Kura River until it joined with the Aras was attributed to Arran (the left bank of the Kura was known as Shirvan
Shirvan (from fa, شروان, translit=Shirvān; az, Şirvan; Tat: ''Şirvan''), also spelled as Sharvān, Shirwan, Shervan, Sherwan and Šervān, is a historical Iranian region in the eastern Caucasus, known by this name in both pre-Islam ...
). The boundaries of Arran have shifted throughout history, sometimes encompassing the entire territory of the present-day Republic of Azerbaijan, and at other times only parts of the South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
. In some instances, Arran was a part of Armenia.
Medieval Islamic geographers gave descriptions of Arran in general, and of its towns, which included Barda, Beylagan
Beylagan District ( az, Beyləqan rayonu) is one of the 66 districts of Azerbaijan. It is located in the centre of the country and belongs to the Central Aran Economic Region. The district borders the districts of Fuzuli, Aghjabadi, Zardab, Imis ...
, and Ganja, along with others.
Ethnogenesis
Originally, at least some of the Caucasian Albanians probably spoke Lezgic languages close to those found in modernDaghestan
Dagestan ( ; rus, Дагеста́н, , dəɡʲɪˈstan, links=yes), officially the Republic of Dagestan (russian: Респу́блика Дагеста́н, Respúblika Dagestán, links=no), is a republic of Russia situated in the North Ca ...
; overall, though, as many as 26 different languages may have been spoken in Caucasian Albania.
After the Caucasian Albanians were Christianized in the 4th century, part of the population was assimilated by the Armenians (who dominated in the provinces of Artsakh and Utik
Utik ( hy, Ուտիք, also known as Uti, Utiq, or Outi) was a historic province of the Kingdom of Armenia. It was ceded to Caucasian Albania following the partition of Armenia between Sassanid Persia and the Eastern Roman Empire in 387 AD. Most ...
that were earlier detached from the Kingdom of Armenia) and Georgians (in the north), while the eastern parts of Caucasian Albania were Islamized and absorbed by Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
История ВостокаВ 6 т. Т. 2. Восток в средние века. М., «Восточная литература», 2002. (History of the East. In 6 volumes. Volume 2. Moscow, publishing house of the Russian Academy of sciences «East literature»): The multi-ethnic population of Albania left-bank at this time is increasingly moving to the Persian language. Mainly this applies to cities of Aran and Shirwan, as begin from 9-10 centuries named two main areas in the territory of Azerbaijan. With regard to the rural population, it would seem, mostly retained for a long time, their old languages, related to modern Daghestanian family, especially Lezgin. (Russian text: Пестрое в этническом плане население левобережной Албании в это время все больше переходит на персидский язык. Главным образом это относится к городам Арана и Ширвана, как стали в IX-Х вв. именоваться два главные области на территории Азербайджана. Что касается сельского населения, то оно, по-видимому, в основном сохраняло еще долгое время свои старые языки, родственные современным дагестанским, прежде всего лезгинскому. and subsequently
Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging t ...
(modern Azerbaijanis). Small remnants of this group continue to exist independently, and are known as the Udi people
Udis (endonym ''Udi'' or ''Uti'') are a native people of the Caucasus that currently live mainly in Russia and Azerbaijan, with smaller populations in Georgia, Armenia, Kazakhstan, Ukraine and other countries. Their total number is about 10,000 pe ...
.
The pre-Islamic population of Caucasian Albania might have played a role in the ethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is "the formation and development of an ethnic group".
This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification.
The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th century neologism that was later introd ...
of a number of modern ethnicities, including the Azerbaijanis of Qabala, Zaqatala, Shaki, and Oguz. the Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
of Vartashen and Shaki, the Georgians of Kakhetia and Hereti
The Kingdom of Hereti ( ka, ჰერეთის სამეფო ''heretis samepo'') was a medieval monarchy which emerged in Caucasus on the Iberian- Albanian frontier. Nowadays it roughly corresponds to the southeastern corner of Georgia's K ...
( Ingiloy), the Laks, the Lezgins
Lezgins or Leks ( lez, Лезгияр, Лекьер. lezgijar) are a Northeast Caucasian ethnic group native predominantly to southern Dagestan, a republic of Russia, and northeastern Azerbaijan. The Lezgin are predominantly Sunni Muslims and s ...
and the Tsakhurs of Daghestan
Dagestan ( ; rus, Дагеста́н, , dəɡʲɪˈstan, links=yes), officially the Republic of Dagestan (russian: Респу́блика Дагеста́н, Respúblika Dagestán, links=no), is a republic of Russia situated in the North Ca ...
.
Alphabet and languages
Caucasian Albanian language
According to Armenian medieval historiansMovses Khorenatsi
Movses Khorenatsi (ca. 410–490s AD; hy, Մովսէս Խորենացի, , also written as ''Movses Xorenac‘i'' and Moses of Khoren, Moses of Chorene, and Moses Chorenensis in Latin sources) was a prominent Armenian historian from the late a ...
, Movses Kaghankatvatsi Movses Kaghankatvatsi ( hy, Մովսէս Կաղանկատուացի ''Movses Kaġankatvac’i''), or Movses Daskhurantsi ( ''Movses Dasxuranc’i'') is the reputed author (or authors) of a tenth-century Classical Armenian historiographical work on C ...
and Koryun
Koriun ( hy, Կորիւն, reformed spelling: Կորյուն; also transliterated as ''Koriwn'', ''Koryun'') was the earliest Armenian-language author. Writing in the fifth century, his ''Life of Mashtots'' contains many details about the evangel ...
, the Caucasian Albanian (the Armenian name for the language is Aghvank, the native name of the language is unknown) alphabet was created by Mesrob Mashtots,К. В. Тревер. Очерки по истории и культуре Кавказской Албании. М—Л., 1959:''"Как известно, в V в. Месроп Маштоц, создавая албанский алфавит, в основу его положил гаргарское наречие албанского языка («создал письмена гаргарского языка, богатого горловыми звуками»). Это последнее обстоятельство позволяет высказать предположение, что именно гаргары являлись наиболее культурным и ведущим албанским племенем".'' the Armenian monk
A monk (, from el, μοναχός, ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a person who practices religious asceticism by monastic living, either alone or with any number of other monks. A monk may be a person who decides to dedica ...
, theologian
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the ...
and translator
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transl ...
who is also credited with creating the Armenian alphabet
The Armenian alphabet ( hy, Հայոց գրեր, ' or , ') is an alphabetic writing system used to write Armenian. It was developed around 405 AD by Mesrop Mashtots, an Armenian linguist and ecclesiastical leader. The system originally had ...
. This alphabet was used to write down the Udi language
The Udi language, spoken by the Udi people, is a member of the Lezgic branch of the Northeast Caucasian language family. It is believed an earlier form of it was the main language of Caucasian Albania, which stretched from south Dagestan to cur ...
, which was probably the main language of the Caucasian Albanians.
Koryun
Koriun ( hy, Կորիւն, reformed spelling: Կորյուն; also transliterated as ''Koriwn'', ''Koryun'') was the earliest Armenian-language author. Writing in the fifth century, his ''Life of Mashtots'' contains many details about the evangel ...
, a pupil of Mesrob Mashtots, in his book ''The Life of Mashtots'', wrote about how his tutor created the alphabet:
Then there came and visited them an elderly man, an Albanian named Benjamin. And he (Mashtots) inquired and examined the barbaric diction of the Albanian language, and then through his usual God-given keenness of mind invented an alphabet, which he, through the grace of Christ, successfully organized and put in order.
 A Caucasian Albanian alphabet of fifty-two letters, bearing resemblance to Georgian, Ethiopian and Armenian characters,See sample of script with letters that resemble other alphabets, specifically Georgian (19 letters), Ethiopian (14 letters) and Armenian (10 letters) i
A Caucasian Albanian alphabet of fifty-two letters, bearing resemblance to Georgian, Ethiopian and Armenian characters,See sample of script with letters that resemble other alphabets, specifically Georgian (19 letters), Ethiopian (14 letters) and Armenian (10 letters) i"The Albanian Script: The Process How Its Secrets Were Revealed,"
by Zaza Aleksidze and Betty Blair survived through a few inscriptions, and an Armenian manuscript dating from the 15th century. This manuscript, Matenadaran No. 7117, first published by Ilia Abuladze in 1937 is a language manual, presenting different alphabets for comparison – Armenian alphabet,
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, Syriac Syriac may refer to:
*Syriac language, an ancient dialect of Middle Aramaic
*Sureth, one of the modern dialects of Syriac spoken in the Nineveh Plains region
* Syriac alphabet
** Syriac (Unicode block)
** Syriac Supplement
* Neo-Aramaic languages a ...
, Georgian, Coptic, and Caucasian Albanian among them. The alphabet was titled: ''"Ałuanicʿ girn ē"'' ( hy, Աղուանից գիրն Է, meaning, "These are Albanian letters").
In 1996, Zaza Aleksidze of the Georgian Centre of Manuscripts discovered at Saint Catherine's Monastery
Saint Catherine's Monastery ( ar, دير القدّيسة كاترين; grc-gre, Μονὴ τῆς Ἁγίας Αἰκατερίνης), officially the Sacred Autonomous Royal Monastery of Saint Katherine of the Holy and God-Trodden Mount Sinai, ...
at Mount Sinai
Mount Sinai ( he , הר סיני ''Har Sinai''; Aramaic: ܛܘܪܐ ܕܣܝܢܝ ''Ṭūrāʾ Dsyny''), traditionally known as Jabal Musa ( ar, جَبَل مُوسَىٰ, translation: Mount Moses), is a mountain on the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt. It is ...
, Egypt, a text written on parchment
Parchment is a writing material made from specially prepared untanned skins of animals—primarily sheep, calves, and goats. It has been used as a writing medium for over two millennia. Vellum is a finer quality parchment made from the skins o ...
that had been reused in a Georgian palimpsest
In textual studies, a palimpsest () is a manuscript page, either from a scroll or a book, from which the text has been scraped or washed off so that the page can be reused for another document. Parchment was made of lamb, calf, or kid skin an ...
. In 2001 Aleksidze identified its script as Caucasian Albanian, and the text as an early lectionary dating to perhaps before the 6th century. Many of the letters discovered in it were not in the Albanian alphabet listed in the 15th-century Armenian manuscript.
Muslim geographers Al-Muqaddasi, Ibn-Hawqal and Estakhri
Abu Ishaq Ibrahim ibn Muhammad al-Farisi al-Istakhri () (also ''Estakhri'', fa, استخری, i.e. from the Iranian city of Istakhr, b. - d. 346 AH/AD 957) was a 10th-century travel-author and geographer who wrote valuable accounts in Arab ...
recorded that a language which they called Arranian was still spoken in the capital Barda and the rest of Arran in the 10th century.
Iranian languages
Iranian contact in the region goes back to the Median andAchaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
times. During this Arsacid Dynasty of Caucasian Albania, the Parthian language spread in the region. It is possible that the language and literature for administration and record-keeping of the imperial chancellery for external affairs naturally became Parthian, based on the Aramaic alphabet. According to Toumanoff: "the predominance of Hellenism, as under the Artaxiads, was now followed by a predominance of "Iranianism", and, symptomatically, instead of Greek, as before, Parthian became the language of the educated".
With the establishment of the Sassanids, Middle Persian
Middle Persian or Pahlavi, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg () in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasanian Empire. For some time after the Sasanian collapse, Middle ...
, a closely related language to Parthian, became an official language of the Sassanid Empire.Benjamin W. Fortson, "Indo-European Language and Culture: An Introduction", John Wiley and Sons, 2009. pg 242: " Middle Persian was the official language of the Sassanian dynasty" At this time, Persian enjoyed even more success than the Caucasian Albanian language and the region was greatly affected by Iran.Shnirelman, V.A.(2001), 'The value of the Past: Myths, Identity and Politics in Transcaucasia', Osaka: National Museum of Ethnology. pp 79: "Yet, even at the time of Caucasian Albania and later on, as well, the region was greatly affected by Iran and Persian enjoyed even more success than the Albanian language". According to Vladimir Minorsky
Vladimir Fyodorovich Minorsky (russian: Владимир Фёдорович Минорский; – March 25, 1966) was a Russian Orientalist best known for his contributions to the study of Persian, Lurish and Kurdish history, geography, ...
: "The presence of Iranian settlers in Transcaucasia, and especially in the proximity of the passes, must have played an important role in absorbing and pushing back the aboriginal inhabitants. Such names as Sharvan, Layzan, Baylaqan, etc., suggest that the Iranian immigration proceeded chiefly from Gilan and other regions on the southern coast of the Caspian". The presence of the Persian language and Iranian culture continued during the Islamic era.
Religion
The original population of the Caucasus followed different pagan religions. UnderAchaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
, Parthian and especially Sassanid
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
influence, Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheisti ...
also grew in the region. Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
started to spread in the late 4th century in the Sassanid era.
The Arab conquest and the Chalcedonian crisis led to severe disintegration of the Church of Caucasian Albania. Starting from the 8th century, much of the local population converted to Islam
Religious conversion is the adoption of a set of beliefs identified with one particular religious denomination to the exclusion of others. Thus "religious conversion" would describe the abandoning of adherence to one denomination and affiliatin ...
. By the 11th century there already were conciliar mosques in Partaw, Qabala
Qabala ( az, Qəbələ) is a city and the administrative centre of the Qabala District of Azerbaijan. The municipality consists of the city of Gabala and the village of Küsnat. Before the city was known as Kutkashen, but after the Republic of ...
and Shaki; the cities that were the creed of Caucasian Albanian Christianity.
These Islamised groups would later be known as Lezgins
Lezgins or Leks ( lez, Лезгияр, Лекьер. lezgijar) are a Northeast Caucasian ethnic group native predominantly to southern Dagestan, a republic of Russia, and northeastern Azerbaijan. The Lezgin are predominantly Sunni Muslims and s ...
and Tsakhurs or mix with the Turkic and Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
population to form present-day Azeris
Azerbaijanis (; az, Azərbaycanlılar, ), Azeris ( az, Azərilər, ), or Azerbaijani Turks ( az, Azərbaycan Türkləri, ) are a Turkic people living mainly in northwestern Iran and the Republic of Azerbaijan. They are the second-most nume ...
, whereas those that remained Christian were gradually absorbed by Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
or continued to exist on their own and be known as the Udi people
Udis (endonym ''Udi'' or ''Uti'') are a native people of the Caucasus that currently live mainly in Russia and Azerbaijan, with smaller populations in Georgia, Armenia, Kazakhstan, Ukraine and other countries. Their total number is about 10,000 pe ...
.
The Caucasian Albanian tribes of Hereti
The Kingdom of Hereti ( ka, ჰერეთის სამეფო ''heretis samepo'') was a medieval monarchy which emerged in Caucasus on the Iberian- Albanian frontier. Nowadays it roughly corresponds to the southeastern corner of Georgia's K ...
were converted to Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") ...
by Dinar, Queen of Hereti in the 10th century. The religious affairs of this small principality were now officially administered by the Georgian Orthodox Church
The Apostolic Autocephalous Orthodox Church of Georgia ( ka, საქართველოს სამოციქულო ავტოკეფალური მართლმადიდებელი ეკლესია, tr), commonly ...
. In 1010, Hereti became absorbed into the neighbouring Georgian kingdom of Kakheti. Eventually, in the early 12th century, these lands became part of the Georgian Kingdom under David the Builder finalising the process of their Georgianisation.Caucasian AlbaniaThe Eastern Orthodox Encyclopædia.
History
The history of Albania before the 6th century BC is unknown.Median and Achaemenid era
According to one hypothesis, Caucasian Albania was incorporated in the Median empire, as early as the 7th or 6th century BC. However, an increasingPersia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
n influence on the region is usually believed to be connected with the defence of Persia's northern frontiers, from invading nomads. As early as the Achaemenid empire, measures may have been taken to fortify the Caucasian passes. By the mid-6th century BC, Albania has been incorporated in the Achaemenid empire; it was later controlled by the Achaemenid satrapy of Media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Media (communication), tools used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Broadcast media, communications delivered over mass e ...
. The building of fortifications and gates in and around Darband is traditionally ascribed to the Sassanid Empire.
Hellenistic era
 The Greek historian Arrian mentions (perhaps anachronistically) the Caucasian Albanians for the first time in the
The Greek historian Arrian mentions (perhaps anachronistically) the Caucasian Albanians for the first time in the battle of Gaugamela
The Battle of Gaugamela (; grc, Γαυγάμηλα, translit=Gaugámela), also called the Battle of Arbela ( grc, Ἄρβηλα, translit=Árbela), took place in 331 BC between the forces of the Army of Macedon under Alexander the Great ...
, where the Albanians, Medes, Cadussi and Sacae were under the command of Atropates
Atropates ( peo, *Ātr̥pātaʰ and Middle Persian ; grc, Ἀτροπάτης ; c. 370 BC - after 321 BC) was a Persian nobleman who served Darius III, then Alexander the Great, and eventually founded an independent kingdom and dynasty that wa ...
. Albania first appears in history as a vassal state in the empire of Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
(95-56 BC). The kingdom of Albania emerged in the eastern Caucasus in 2nd or 1st century BC and along with the Georgians and Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
formed one of the three nations of the Southern Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
. Albania came under strong Armenian religious and cultural influence.Istorija Vostoka. V 6 t. T. 2, Vostok v srednije vekaMoskva, «Vostochnaya Literatura», 2002.
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
, Strabo, and other classical authors repeatedly mention the Caspians
The Caspians ( fa, کاسپیها, ''Kaspyn''; el, Κάσπιοι, ''Káspioi''; Aramaic: ܟܣܦܝ, ''kspy''; xcl, Կասպք, ''Kaspk’''; la, Caspi, ''Caspiani'') were a people of antiquity who dwelt along the southwestern shores of the ...
but do not seem to know much about them; they are grouped with other inhabitants of the southern shore of the Caspian Sea, like the Amardi, Anariacae, Cadusii, Albani (see below), and Vitii (Eratosthenes apud Strabo, 11.8.8), and their land ( Caspiane) is said to be part of Albania (Theophanes Mytilenaeus apud Strabo, 11.4.5).
In the 2nd century BC parts of Albania were conquered by the Kingdom of Armenia, presumably from Medes
The Medes ( Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, ...
(although possibly it was earlier part of Orontid Armenia).
The original population of the territories on the right bank of Kura before the Armenian conquest consisted of various autochthonous people. Ancient chronicles provide the names of several peoples that populated these districts, including the regions of Artsakh and Utik
Utik ( hy, Ուտիք, also known as Uti, Utiq, or Outi) was a historic province of the Kingdom of Armenia. It was ceded to Caucasian Albania following the partition of Armenia between Sassanid Persia and the Eastern Roman Empire in 387 AD. Most ...
. These were Utians, Mycians, Caspians
The Caspians ( fa, کاسپیها, ''Kaspyn''; el, Κάσπιοι, ''Káspioi''; Aramaic: ܟܣܦܝ, ''kspy''; xcl, Կասպք, ''Kaspk’''; la, Caspi, ''Caspiani'') were a people of antiquity who dwelt along the southwestern shores of the ...
, Gargarians, Sakasenians, Gelians, Sodians, Lupenians, Balas knians, Parsians and Parrasians. According to Robert H. Hewsen, these tribes were "certainly not of Armenian origin", and "although certain Iranian peoples must have settled here during the long period of Persian and Median rule, most of the natives were not even Indo-Europeans". He also states that the several peoples of the right bank of Kura "were highly Armenicized and that many were actually Armenians ''per se'' cannot be doubted". Many of those people were still being cited as distinct ethnic entities when the right bank of Kura was acquired by the Caucasian Albanians in 387 AD.
Roman Empire
 There was an enduring relation of Albania with
There was an enduring relation of Albania with Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC ...
.
The Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
rock inscription close to Boyukdash mountain in Gobustan, Baku, which mentions Legio XII Fulminata
Legio XII Fulminata ("Thunderbolt Twelfth Legion"), also known as ''Paterna'', ''Victrix'', ''Antiqua'', ''Certa Constans'', and ''Galliena'', was a legion of the Imperial Roman army. It was originally levied by Julius Caesar in 58 BC, and the leg ...
, is the world's easternmost Roman evidence known. In Albania, Romans reached the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
for the first time.
The Roman coins
Roman currency for most of Roman history consisted of gold, silver, bronze, orichalcum and copper coinage. From its introduction to the Republic, during the third century BC, well into Imperial times, Roman currency saw many changes in form, denom ...
circulated in Caucasian Albania till the end of the 3rd century AD. Two denarii
The denarius (, dēnāriī ) was the standard Roman silver coin from its introduction in the Second Punic War to the reign of Gordian III (AD 238–244), when it was gradually replaced by the antoninianus. It continued to be minted in very ...
, which were unearthed in the 2nd-century BC layer, were minted by Clodius and Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
. The coins of Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
are ubiquitous. The Qabala treasures revealed the denarii of Otho
Marcus Otho (; born Marcus Salvius Otho; 28 April 32 – 16 April 69) was the seventh Roman emperor, ruling for three months from 15 January to 16 April 69. He was the second emperor of the Year of the Four Emperors.
A member of a noble Etr ...
, Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empi ...
, Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
and Hadrian.
In 69-68 BC Lucullus
Lucius Licinius Lucullus (; 118–57/56 BC) was a Roman general and statesman, closely connected with Lucius Cornelius Sulla. In culmination of over 20 years of almost continuous military and government service, he conquered the eastern kingd ...
, having overcome Armenian ruler Tigranes II, approached the borders of Caucasian Albania and was succeeded by Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
.
After the 66-65 BC wintering Pompey launched the Iberian campaign. It is reported by Strabo upon the account of Theophanes of Mytilene
Theophanes of Mytilene ( grc-gre, Θεοφάνης ὁ Μυτιληναῖος) was an intellectual and historian from the town of Mytilene on the island of Lesbos who lived in the middle of the 1st century BC. He was a friend of Pompey and wrot ...
who participated in it. As testified by Kamilla Trever
Kamilla Vasilyevna Trever (russian: Камилла Васильевна Тревер; 25 January 1892, Saint Petersburg – 11 November 1974, Leningrad) was a Russian historian, numismatist and orientalist, and a corresponding member of the Russ ...
, Pompey reached the Albanian border at modern Qazakh District
Qazax District (; az, Qazax rayonu) is one of the 66 districts of Azerbaijan. It is located in the north-west of the country and belongs to the Gazakh-Tovuz Economic Region. The district borders the district of Aghstafa, and the Tavush Province o ...
of Azerbaijan. Igrar Aliyev
Igrar Habib oglu Aliyev ( az, İqrar Əliyev) (14 March 1924, Baku – 11 June 2004, Baku) was a Soviet and Azerbaijani historian. Aliyev was the author of 160 peer reviewed journal publications and books. Many of his books are devoted to the Mede ...
showed that this region called Cambysene was inhabited mainly by stock-breeders at the time. When fording the Alazan river, he was attacked by forces of Oroezes, King of Albania, and eventually defeated them. According to Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for hi ...
, Albanians "were led by a brother of the king, named Cosis, who as soon as the fighting was at close quarters, rushed upon Pompey himself and smote him with a javelin on the fold of his breastplate; but Pompey ran him through the body and killed him". Plutarch also reported that "after the battle, Pompey set out to march to the Caspian Sea, but was turned back by a multitude of deadly reptiles when he was only three days march distant, and withdrew into Lesser Armenia". The first kings of Albania were certainly the representatives of the local tribal nobility, to which attest their non-Armenian and non-Iranian names (Oroezes, Cosis and Zober in Greek sources).
The population of Caucasian Albania of the Roman period is believed to have belonged to either the Northeast Caucasian peoples or the South Caucasian peoples.
According to Strabo, the Albanians were a group of 26 tribes which lived to the north of the Kura river and each of them had its own king and language. Sometime before the 1st century BC they federated into one state and were ruled by one king.
Strabo wrote of the Caucasian Albanians in the 1st century BC:
 Albania is also mentioned by
Albania is also mentioned by Dionysius Periegetes
Dionysius Periegetes ( grc-gre, Διονύσιος ὁ Περιηγητής, literally Dionysius the Voyager or Traveller, often Latinized to ''Dionysius Periegeta''), also known as Dionysius of Alexandria or Dionysius the African,''Encyclopædia ...
(2nd or 3rd century AD) who describes Albanians as a nation of warriors, living by the Iberians and the Georgians.
In 1899 a silver plate featuring Roman toreutics
The term ''toreutics'', relatively rarely used in English, refers to artistic metalworking – hammering gold or silver (or other materials), engraving, or using repoussé and chasing to form minute detailed reliefs or small engraved patterns. To ...
was excavated near Azerbaijani village of Qalagah.
The rock inscription near the south-eastern part of Boyukdash's foot (70 km from Baku) was discovered on June 2, 1948 by Azerbaijani archaeologist Ishag Jafarzadeh. The legend is IMPDOMITIANO CAESARE·AVG GERMANIC L·IVLIVS MAXIMVS> LEG XII·FVL. According to Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Fl ...
's titles in it, the related march took place between 84 and 96. The inscription was studied by Russian expert Yevgeni Pakhomov, who assumed that the associated campaign was launched to control the Derbent Gate and that the XII Fulminata has marched out either from Melitene, its permanent base, or Armenia, where it might have moved from before. Pakhomov supposed that the legion proceeded to the spot continually along the Aras River
, az, Araz, fa, ارس, tr, Aras
The Aras (also known as the Araks, Arax, Araxes, or Araz) is a river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan excl ...
. The later version, published in 1956, states that the legion was stationing in Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Re ...
by that time whereas the centurion might have been in Albania with some diplomatic mission because for the talks with the Eastern rulers the Roman commanders were usually sending centurions.
In 1953 twelve denarii of Augustus were unearthed. In 1958 one denarius, coined in c. 82 AD, was revealed in the Şamaxı
Shamakhi ( az, Şamaxı, ) is a city in Azerbaijan and the administrative centre of the Shamakhi District. The city's estimated population was 31,704. It is famous for its traditional dancers, the Shamakhi Dancers, and also for perhaps giving i ...
trove.
During the reign of Roman emperor Hadrian (117-138) Albania was invaded by the Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
, an Iranian nomadic group. This invasion promoted an alliance between Rome and the Albanians that was reinforced under Antoninus Pius
Antoninus Pius ( Latin: ''Titus Aelius Hadrianus Antoninus Pius''; 19 September 86 – 7 March 161) was Roman emperor from 138 to 161. He was the fourth of the Five Good Emperors from the Nerva–Antonine dynasty.
Born into a senatori ...
in 140 AD. Sassanians occupied the area around 240 Ad but after a few years, the Roman Empire regained control of Caucasian Albania.
Indeed, in 297 the treaty of Nisibis stipulated the reestablishment of the Roman protectorate over Caucasian Iberia
In Greco-Roman geography, Iberia (Ancient Greek: ''Iberia''; la, Hiberia) was an exonym for the Georgian kingdom of Kartli ( ka, ქართლი), known after its core province, which during Classical Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages ...
and Albania. But fifty years later Rome lost the area that since then remained an integral part of the Sasanian Empire.
Parthian period
Under Parthian rule, Iranian political and cultural influence increased in the region.Toumanoff, Cyril
Cyril Leo Toumanoff (russian: Кирилл Львович Туманов; 13 October 1913 – 4 February 1997) was a Russian-born Georgian historian and genealogist who mostly specialized in the history and genealogies of medieval Georgia, Armenia, ...
The Arsacids
''Encyclopædia Iranica''. excerpt:"Whatever the sporadic suzerainty of Rome, the country was now a part—together with Iberia (East Georgia) and (Caucasian) Albania, where other Arsacid branched reigned—of a pan-Arsacid family federation. Culturally, the predominance of Hellenism, as under the Artaxiads, was now followed by a predominance of "Iranianism," and, symptomatically, instead of Greek, as before, Parthian became the language of the educated" Whatever the sporadic suzerainty of Rome, the country was now a part—together with Iberia (East Georgia) and (Caucasian) Albania, where other Arsacid branches reigned—of a pan-Arsacid family federation. Culturally, the predominance of Hellenism, as under the Artaxiads, was now followed by a predominance of "Iranianism", and, symptomatically, instead of Greek, as before, Parthian became the language of the educated. An incursion in this era was made by the
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
who between 134 and 136 attacked Albania, Media, and Armenia, penetrating as far as Cappadocia. But Vologases persuaded them to withdraw, probably by paying them.
Sassanid period
In 252-253, Caucasian Albania, along withCaucasian Iberia
In Greco-Roman geography, Iberia (Ancient Greek: ''Iberia''; la, Hiberia) was an exonym for the Georgian kingdom of Kartli ( ka, ქართლი), known after its core province, which during Classical Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages ...
and Greater Armenia
Greater Armenia ( hy, Մեծ Հայք, translit=Mets Hayk) is the name given to the Armenian state that emerged on the Armenian Highlands during the reign of King Artaxias I at the turn of the 2nd century BC. The term was used to refer princ ...
, was conquered and annexed by the Sassanid Empire. Albania became a vassal state
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to ...
of the Sassanid Empire, but retained its monarchy; the Albanian king had no real power and most civil, religious, and military authority lay with the Sassanid marzban
Marzbān, or Marzpān (Middle Persian transliteration: mrzwpn, derived from ''marz'' "border, boundary" and the suffix ''-pān'' "guardian"; Modern Persian: ''Marzbān'') were a class of margraves, warden of the marches, and by extension milita ...
(military governor) of the territory.Nevertheless, "despite being one of the chief vassals of Sasanian ''Shahanshah
Shah (; fa, شاه, , ) is a royal title that was historically used by the leading figures of Iranian monarchies.Yarshater, EhsaPersia or Iran, Persian or Farsi, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII no. 1 (1989) It was also used by a variety of ...
'', the Albanian king had only a semblance of authority, and the Sassanid marzban
Marzbān, or Marzpān (Middle Persian transliteration: mrzwpn, derived from ''marz'' "border, boundary" and the suffix ''-pān'' "guardian"; Modern Persian: ''Marzbān'') were a class of margraves, warden of the marches, and by extension milita ...
(military governor) held most civil, religious, and military authority.
The Roman Empire again obtained control of Caucasian Albania as a vassal state for a few years around 300 AD, but then the Sassanids regained control and subsequently dominated the area for centuries until the Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
invasions.
Albania was mentioned among the Sassanid provinces listed in the trilingual inscription of Shapur I at Naqsh-e Rustam.
In the middle of the 4th century, King Urnayr of Albania arrived in Armenia and was baptized by Gregory the Illuminator
Gregory the Illuminator ( Classical hy, Գրիգոր Լուսաւորիչ, reformed: Գրիգոր Լուսավորիչ, ''Grigor Lusavorich'';, ''Gregorios Phoster'' or , ''Gregorios Photistes''; la, Gregorius Armeniae Illuminator, cu, Svyas ...
, but Christianity spread in Albania only gradually, and the Albanian king remained loyal to the Sassanids. After the partition of Armenia between Byzantium and Persia (in 387 AD), Albania with Sassanid help was able to seize from Armenia all the right bank of the river Kura up to river Araxes, including Artsakh and Utik.
In the mid-5th century, the Sassanid King Yazdegerd II passed an edict requiring all the Christians in his empire to convert to Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheisti ...
, fearing that Christians might ally with Roman Empire, which had recently adopted Christianity as its official religion. This led to a rebellion of Albanians, along with Armenians and Georgians. At the Battle of Avarayr
The Battle of Avarayr ( hy, Ավարայրի ճակատամարտ ''Avarayri čakatamart'') was fought on 2 June 451 on the Avarayr Plain in Vaspurakan between a Christian Armenian army under Vardan Mamikonian and Sassanid Persia. It is conside ...
, the allied forces of Caucasian Albania, Georgia, and Armenia, devoted to Christianity, suffered defeat at the hands of the Sassanid army. Many of the Armenian nobility fled to the mountainous regions of Albania, particularly to Artsakh, which had become a center for resistance to Sassanid Persia. The religious center of the Albanian state also moved here. However, King Vache of Albania, a relative of Yazdegerd II, was forced to convert to Zoroastrianism, but soon thereafter converted back to Christianity.
According to ''The History of the Country of Albania
''The History of the Caucasian Albanians'' (or ''The History of the World of Aghvank''; hy, Պատմութիւն Աղուանից աշխարհի) by Movses Kaghankatvatsi is a history of eastern territories of Armenia ( Artsakh and Utik), as well ...
'', Peroz ordered the Albanian king Vache II to have the city of Perozapat ("the city of Peroz" or "Prosperous Peroz") constructed. However, this is unlikely as the Kingdom of Caucasian Albania had been abolished by Peroz after suppressing a revolt by Vache II in the mid-460s. The city was seemingly founded by Peroz himself after the removal of the ruling family in Caucasian Albania. Due to its more secure location, it was made the new residence of the Iranian . Albania remained kingless until 485, when Vachagan III
Vachagan III the Pious () or Vachagan II (according to some authors) was the last Arsacid king of Caucasian Albania, ruling approximately from 485 to 523.
Background
His lineage is uncertain. Murtazali Gadjiev considers him a son (or nephew) of ...
() was installed on the throne by Peroz's brother and successor Balash (). In 552, the seat of the Albanian Catholicos was also transferred to Partaw.
By the end of the 5th century, the ancient Arsacid royal house of Albania, a branch of the ruling dynasty of Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
, became extinct, and in the 6th century, it was replaced by princes of the Persian or Parthian Mihranid The Mihranids were an Iranian family which ruled several regions of Caucasus from 330 to 821. They claimed to be of Sasanian Persian descent but were of Parthian origin.
History
The dynasty was founded when a certain Mihran, a distant relative o ...
family, who claimed descent from the Sassanids. They assumed the Persian title of Arranshah (i.e. the Shah
Shah (; fa, شاه, , ) is a royal title that was historically used by the leading figures of Iranian monarchies.Yarshater, EhsaPersia or Iran, Persian or Farsi, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII no. 1 (1989) It was also used by a variety of ...
of Arran, the Persian name of Albania). The ruling dynasty was named after its Persian founder Mihran, who was a distant relative of the Sasanians. The Mihranid dynasty survived under Muslim suzerainty until 821-22.
In the late 6th to early 7th centuries the territory of Albania became an arena of wars between Sassanid Persia, Byzantium, and the Khazar Khanate
The Khazars ; he, כּוּזָרִים, Kūzārīm; la, Gazari, or ; zh, 突厥曷薩 ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a semi-nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire coveri ...
, the latter two very often acting as allies against Sassanid Persia. In 628, during the Third Perso-Turkic War
The Third Perso-Turkic War was the third and final conflict between the Sassanian Empire and the Western Turkic Khaganate. Unlike the previous two wars, it was not fought in Central Asia, but in Transcaucasia. Hostilities were initiated in 627 ...
, the Khazars invaded Albania, and their leader Ziebel
Tong Yabghu Qaghan (r. 618–628 or 630) (also known as T'ung Yabghu, Tong Yabghu Khagan, and Tong Yabğu, Traditional Chinese 統葉護可汗, Simplified Chinese: 统叶护可汗, pinyin ''Tǒng Yèhù Kěhán'', Wade-Giles: ''T'ung Yeh-hu K'o-h ...
declared himself Lord of Albania, levying a tax on merchants and the fishermen of the Kura and Araxes rivers "in accordance with the land survey of the kingdom of Persia". Most of Transcaucasia was under Khazar rule before the arrival of the Arabs. However, some other sources state that the Khazars later left the region because of political instability.
According to Peter Golden, "steady pressure from Turkic nomads was typical of the Khazar era, although there are no unambiguous references to permanent settlements", while Vladimir Minorsky
Vladimir Fyodorovich Minorsky (russian: Владимир Фёдорович Минорский; – March 25, 1966) was a Russian Orientalist best known for his contributions to the study of Persian, Lurish and Kurdish history, geography, ...
stated that, in Islamic times, "the town of Qabala lying between Shirvan
Shirvan (from fa, شروان, translit=Shirvān; az, Şirvan; Tat: ''Şirvan''), also spelled as Sharvān, Shirwan, Shervan, Sherwan and Šervān, is a historical Iranian region in the eastern Caucasus, known by this name in both pre-Islam ...
and Shakki was a place where Khazars were probably settled".
Impact of Armenian politics, culture and civilization
Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
n politics, culture and civilization played a critical role in the entire history of Caucasian Albania (Aghvank, in Armenian). This, due to the fact that after the partition of the Kingdom of Armenia by Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
and Byzantium in 387 AD, the Armenian provinces of Artsakh and Utik
Utik ( hy, Ուտիք, also known as Uti, Utiq, or Outi) was a historic province of the Kingdom of Armenia. It was ceded to Caucasian Albania following the partition of Armenia between Sassanid Persia and the Eastern Roman Empire in 387 AD. Most ...
were disassociated from the Armenian kingdom and included by Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
into a single province (marzpanate) called Aghvank (Arran). This new unit included: the original Caucasian Albania, found between the River Kura and the Great Caucasus; tribes living along the Caspian shore; as well as Artsakh and Utik, two territories now detached from Armenia.Моисей Хоренский. Армянская География VII в. Перевод Патканова К.П. СПб., 1877. стр. 40,17
The Armenian medieval atlas Ashkharatsuits (Աշխարացույց), compiled in the 7th century by Anania Shirakatsi
Anania Shirakatsi ( hy, Անանիա Շիրակացի, ''Anania Širakac’i'', anglicized: Ananias of Shirak) was a 7th-century Armenian polymath and natural philosopher, author of extant works covering mathematics, astronomy, geography, chronol ...
(Անանիա Շիրակացի, but sometimes attributed to Movses Khorenatsi
Movses Khorenatsi (ca. 410–490s AD; hy, Մովսէս Խորենացի, , also written as ''Movses Xorenac‘i'' and Moses of Khoren, Moses of Chorene, and Moses Chorenensis in Latin sources) was a prominent Armenian historian from the late a ...
as well), categorizes Artsakh and Utik as provinces of Armenia despite their presumed detachment from the Armenian Kingdom
The Kingdom of Armenia, also the Kingdom of Greater Armenia, or simply Greater Armenia ( hy, Մեծ Հայք '; la, Armenia Maior), sometimes referred to as the Armenian Empire, was a monarchy in the Ancient Near East which existed from 331 BC ...
and their political association with Caucasian Albania and Persia at the time of his writing. Shirakatsi specifies that Artsakh and Utik are "now detached" from Armenia and included in "Aghvank," and he takes care to distinguish this new entity from the old "Aghvank strictly speaking" (Բուն Աղվանք) situated north of the river Kura. Because it was more homogeneous and more developed than the original tribes to the north of the Kura, the Armenian element took over Caucasian Albania's political life and was progressively able to impose its language and culture.Robert H. Hewsen, "Ethno-History and the Armenian Influence upon the Caucasian Albanians," in Classical Armenian Culture: Influences and Creativity, ed. Thomas J. Samuelian (Philadelphia: Scholars Press, 1982)
The Armenian population of Artsakh and Utik remained in place as did the entire political, social, cultural and military structure of the provinces. In the 5th century, early medieval historian Khorenatsi (Խորենացի) testifies that the population of Artsakh and Utik spoke Armenian, with the River Kura, in his words, marking the "boundary of Armenian speech" (... զեզերս հայկական խօսիցս). though this does not mean that its population consisted exclusively of ethnic Armenians.
Whatever little is known about Caucasian Albania after 387 AD comes from the Old Armenian text ''History of the Land of Aghvank'' (Պատմություն Աղվանից Աշխարհի) by the Armenian author Movses Kaghankatvatsi Movses Kaghankatvatsi ( hy, Մովսէս Կաղանկատուացի ''Movses Kaġankatvac’i''), or Movses Daskhurantsi ( ''Movses Dasxuranc’i'') is the reputed author (or authors) of a tenth-century Classical Armenian historiographical work on C ...
(also known as Movses Daskhurantsi),''The History of the Caucasian Albanians'' by Movsēs Dasxuranc'i. Translated by Charles Dowsett. London: Oxford University Press, 1961, pp. 3-4 "Introduction" which in essence is the history of Armenia's provinces of Artsakh and Utik. Kaghankatvatsi, repeating Khorenatsi, mentions that the very name "Aghvank"/"Albania" is of Armenian origin, and relates it to the Armenian word "aghu" (աղու, meaning "kind," "benevolent". Khorenatsi states that "aghu" was a nickname given to Prince Arran, whom the Armenian King Vologases I (Vagharsh I) appointed as governor of northeastern provinces bordering on Armenia. According to a legend reported by Khorenatsi, Arran was a descendant of Sisak, the ancestor of the Siunids of Armenia's province of Syunik, and thus a great-grandson of the ancestral eponym of the Armenians, the Forefather Hayk. Kaghankatvatsi and another Armenian author, Kirakos Gandzaketsi, confirm Arran's belonging to Hayk's bloodline by calling Arranshahiks "a Haykazian dynasty".
 In Kaghankatvatsi's ''History'' and in the historical text of the Armenian early medieval author
In Kaghankatvatsi's ''History'' and in the historical text of the Armenian early medieval author Agathangelos
Agathangelos (in xcl, Ագաթանգեղոս Agatʿangełos, in Greek "bearer of good news" or angel, 5th century AD ) is the pseudonym of the author of a life of the first apostle of Armenia, Gregory the Illuminator, who died about 332.
He ...
, the Kingdom of Aghvank's feudal system, including its political terminology, was Armenian. As in Armenia, nobles of Aghvank are referred to by the terms nakharar
''Nakharar'' ( hy, նախարար ''naxarar'', from Parthian ''naxvadār'' "holder of the primacy""նախարար" in H. Ačaṙean (1926–35), ''Hayerēn Armatakan Baṙaran'' (Yerevan: Yerevan State University), 2nd ed., 1971–79) was a here ...
s (նախարար), azat
Azat ( hy, ազատ; plural ազատք ''azatkʿ'', collective ազատանի ''azatani'') was a class of Armenian nobility; the term came to designate the middle and lower nobility originally, in contrast to the ''naxarark'' who were the great ...
s (ազատ), hazarapets (հազարապետ), marzpets (մարզպետ), shinakans (շինական), etc.
Princely families, which were later mentioned in Kaghankatvatsi's ''History'' were included in the Table of Ranks called "Gahnamak" (direct translation: "List of Thrones," Arm. Գահնամակ) of the Kingdom of Armenia, which defined Armenia's aristocratic hierarchy. Princely families of Caucasian Albania were also included in the Table of Armies called "Zoranamak" (Arm. Զորանամակ) of the Kingdom of Armenia which determined military obligations of key aristocratic families before the Armenian King in times of war.
As in Armenia, the "Albanian" clergy used exclusively Armenian church terms for clerical hierarchy (katholikos/կաթողիկոս, vardapet/վարդապետ, sargavag/սարգավագ, etc.) Identifiably Armenian are also most if not all toponyms found in the ''History.'' Not only are the names of most towns, villages, mountains, and rivers uniquely Armenian morphologically, exactly the same toponyms were and are still found in other parts of historical Armenia. They include the root kert ("town") for towns (Arm.: կերտ, such Dastakert, Hnarakert – compare with Tigranakert or modern Stapanakert in Nagorno Karabakh), shen and kan (village) for villages (Arm. շեն, and կան, such as Karashen or Dyutakan), etc.
First names of most rulers, commoners and clergy in Kaghankatvatsi's ''History'' are uniquely Armenian. Many of these names survived for centuries and are still used only by modern Armenians. These include: Vachagan (Վախագան), Vache (Վաչե), Bakur (Բակուր), Taguhi (Թագուհի), Vrtanes (Վրթաննես), Viro (Վիրո), Varaz-Trdat (Վարազ-Տրդաթ), Marut (Մարութ), etc. Some of these names can be translated from Armenian as common words: e.g. Taguhi means "queen" and Varaz means "wild boar". In fact, Armenians to this day use the first name Aghvan (Աղվան) that directly refers to the Kingdom of Aghvank.
After the partition, the capital city of Caucasian Albania was moved from the territories on the eastern bank of the River Kura (referred to by Armenians "Aghvank Proper," Arm. Բուն Աղվանք) to Partav, located in the former Armenian province of Utik. This was followed by the transfer of the Seat of the Kingdom of Albania's religious leader (Katholicos) from territories north of Kura to Partav.
The Kingdom of Albania was converted to Christianity at the start of the 4th century by none other than the Armenian evangelizer St. Gregory the Enlightener (Arm. Սբ. Գրիգոր Լուսավորիչ), who baptized Armenia into the first Christian state by 301 AD.Movses Kalankatuatsi. ''History of the Land of Aluank'', translated from Old Armenian by Sh. V. Smbatian. Yerevan: Matenadaran (Institute of Ancient Manuscripts), 1984, p. 27 In about 330 AD, the grandson of St. Gregory, St. Grigoris, ecumenical head of the eastern provinces of Armenia, was designated bishop for the Kingdom of Aghvank. Mausoleum interning Grigoris’ remains, the Amaras Monastery
Amaras Monastery ( hy, Ամարաս վանք) is an Armenian monastery near the village of Sos, ''de facto'' in the Martuni Province of the Republic of Artsakh, ''de jure'' in the Khojavend District of Azerbaijan, in the disputed region of Nago ...
stands as the oldest dated monument in Nagorno Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh ( ) is a landlocked region in the South Caucasus, within the mountainous range of Karabakh, lying between Lower Karabakh and Syunik, and covering the southeastern range of the Lesser Caucasus mountains. The region is mos ...
. Amaras was started by St. Gregory and completed by St. Grigoris himself.
According to tradition, the Amaras Monastery housed the first Armenian school in historical Armenia, which was opened early in the 5th century by the inventor of the Armenian alphabet St. Mesrob Mashtots. St. Mesrob Mashtots was intensely active in preaching Gospel in Artsakh and Utik. Movses Kaghankatvatsi's ''History'' dedicates four separate chapters to St. Mashtots’ mission, referring to him as "enlightener" and "saint" (chapters 27, 28 and 29 of Book One, and chapter 3 of Book Two).Movses Kalankatuatsi. ''History of the Land of Aluank'', Book I, chapters 27, 28 and 29; Book II, chapter 3 Overall, St. Mesrob made three trips to the Kingdom of Albania where he toured not only the Armenian lands of Artsakh and Utik but also territories to the north of the River Kura.
Kaghankatvatsi's ''History'' describes Armenian influence on the Church of Aghvank, whose jurisdiction extended from Artsakh and Utik to regions to the north of the River Kura, in the territories of the "original", "pre-Armenian" Caucasian Albania.Chorbajian, Levon; Donabedian Patrick; Mutafian, Claude. The Caucasian Knot: The History and Geo-Politics of Nagorno-Karabagh. NJ: Zed Books, 1994, Albanian episode One of the consequences of this was that the Armenian language progressively supplanted Albanian as the language of church and state (and only if there was any single "Albanian" language in the first place which is doubtful because the population of Albania/Aghvank was described as consisting of as many 26 different tribes). In the same 7th century, Armenian poet Davtak Kertogh
Davtak Kertogh (''Davtak the Poet'') was a 7th-century Armenian poet, the first secular writer in Armenian literature.The Heritage of Armenian Literature: By Agop Jack Hacikyan, Gabriel Basmajian, Edward S. Franchuk, Nourhan Ouzounian, Wayne State ...
writes his ''Elegy on the Death of Grand Prince Juansher'', where each passage begins with a letter of Armenian script in alphabetical order.Agop Jack Hacikyan, Gabriel Basmajian, Edward S. Franchuk. ''The Heritage of Armenian Literature''. Wayne State University Press (December 2002), pp. 94–99
Christianization
The polytheistic religion of Albania was centered on the worship of three divinities, designated by ''Interpretatio Romana
''Interpretatio graeca'' (Latin, "Greek translation") or "interpretation by means of Greek odels is a discourse used to interpret or attempt to understand the mythology and religion of other cultures; a comparative methodology using ancient Gr ...
'' as Sol, Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label= genitive Boeotian Aeolic and Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label= genitive el, Δίας, ''Días'' () is the sky and thunder god in ancient Greek reli ...
, and Luna
Luna commonly refers to:
* Earth's Moon, named "Luna" in Latin
* Luna (goddess), the ancient Roman personification of the Moon
Luna may also refer to:
Places Philippines
* Luna, Apayao
* Luna, Isabela
* Luna, La Union
* Luna, San Jose
Roma ...
.
Christianity started to enter Caucasian Albania at an early date, according to Movses Kaghankatvatsi Movses Kaghankatvatsi ( hy, Մովսէս Կաղանկատուացի ''Movses Kaġankatvac’i''), or Movses Daskhurantsi ( ''Movses Dasxuranc’i'') is the reputed author (or authors) of a tenth-century Classical Armenian historiographical work on C ...
, as early as during the 1st century. The first Christian church in the region was built by St. Eliseus, a disciple of Thaddeus of Edessa
According to Eastern Christian tradition, Addai of Edessa ( Syriac: ܡܪܝ ܐܕܝ, Mar Addai or Mor Aday sometimes Latinized Addeus) or Thaddeus of Edessa was one of the seventy disciples of Jesus. He is possibly identical with Thaddaeus, on ...
, at a place called Gis. Shortly after Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
adopted Christianity as its state religion (301 AD), the Caucasian Albanian king Urnayr went to the See of the Armenian Apostolic Church
, native_name_lang = hy
, icon = Armenian Apostolic Church logo.svg
, icon_width = 100px
, icon_alt =
, image = Էջմիածնի_Մայր_Տաճար.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, a ...
to receive baptism from St. Gregory the Illuminator
Gregory the Illuminator ( Classical hy, Գրիգոր Լուսաւորիչ, reformed: Գրիգոր Լուսավորիչ, ''Grigor Lusavorich'';, ''Gregorios Phoster'' or , ''Gregorios Photistes''; la, Gregorius Armeniae Illuminator, cu, Svyas ...
, the first Patriarch of Armenia.
King Vachagan III
Vachagan III the Pious () or Vachagan II (according to some authors) was the last Arsacid king of Caucasian Albania, ruling approximately from 485 to 523.
Background
His lineage is uncertain. Murtazali Gadjiev considers him a son (or nephew) of ...
helped to implant Christianity in Caucasian Albania, through a synod allowing the church legal rights in some domestic issues. In 498 AD (in other sources, 488 AD) in the settlement named Aluen (Aghuen) (present-day Agdam District
Aghdam District ( az, Ağdam rayonu) is one of the 66 administrative divisions of Azerbaijan. It is located in the west of the country and belongs to the Karabakh Economic Region. The district borders the districts of Khojaly, Kalbajar, Tartar, ...
of Azerbaijan), an Albanian church council convened to adopt laws further strengthening the position of Christianity in Albania.
Albanian churchmen took part in missionary efforts in the Caucasus and Pontic regions. In 682, the '' catholicos'', Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, led an unsuccessful delegation to convert Alp Iluetuer
Alp Ilutuer was the Ilutuer (vassal ruler) of the North Caucasian Huns during the 680s CE.
He is mentioned in the account of Bishop Israel of Caucasian Albania, who travelled to Alp Ilutuer's court. During his stay in the land of Huns in 681— ...
, the ruler of the North Caucasian Huns, to Christianity. The Albanian Church maintained a number of monasteries in the Holy Land. In the 7th century, Varaz-Grigor, ruler of Albania, and "his nation" were christened by Emperor Heraclius at Gardman.
After the overthrow of Nerses in 705, the Caucasian Albanian elite decided to reestablish the tradition of having their Catholicoi ordained through the Patriarch of Armenia, as it was the case before 590. This event is generally regarded as the abolition of the Church of Caucasian Albania, and the lowering of its denominational status to that of a Catholicate within the body of the Armenian Apostolic Church.
Islamic era
Sassanid Albania fell to theIslamic conquest of Persia
The Muslim conquest of Persia, also known as the Arab conquest of Iran, was carried out by the Rashidun Caliphate from 633 to 654 AD and led to the fall of the Sasanian Empire as well as the eventual decline of the Zoroastrian religion.
The r ...
in the mid-7th century and was incorporated into the Rashidun Caliphate. King Javanshir
Javanshir (alternate spellings: Javansher, Juansher, Ĵovenšēr, Jivanshir; '' pal, Juvānšēr''; literally "young lion"), was the prince of Caucasian Albania from 637 to 680, hailing from the region of Gardman. His life and deeds were the subje ...
of Albania, the most prominent ruler of Mihranid The Mihranids were an Iranian family which ruled several regions of Caucasus from 330 to 821. They claimed to be of Sasanian Persian descent but were of Parthian origin.
History
The dynasty was founded when a certain Mihran, a distant relative o ...
dynasty, fought against the Arab invasion of caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
Uthman
Uthman ibn Affan ( ar, عثمان بن عفان, ʿUthmān ibn ʿAffān; – 17 June 656), also spelled by Colloquial Arabic, Turkish and Persian rendering Osman, was a second cousin, son-in-law and notable companion of the Islamic prop ...
on the side of Sassanid Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. Facing the threat of the Arab invasion on the south and the Khazar
The Khazars ; he, כּוּזָרִים, Kūzārīm; la, Gazari, or ; zh, 突厥曷薩 ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a semi-nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire coverin ...
offensive on the north, Javanshir had to recognize the caliph's suzerainty. The Arabs then reunited the territory with Armenia under one governor.
By the 8th century, "Albania" had been reduced to a strictly geographical and titular
Titular may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Title character in a narrative work, the character referred to in its title
Religion
* Titular (Catholicism), a cardinal who holds a titulus, one of the main churches of Rome
** Titular bisho ...
ecclesiastical connotation, and was referred to as such by medieval Armenian historians; on its place sprang a number principalities, such as that of the Armenian principality and kingdom of Khachen
The Principality of Khachen ( hy, Խաչենի իշխանություն, Khacheni ishkhanutyun) was a medieval Armenian principality on the territory of historical Artsakh (present-day Nagorno-Karabakh). The provinces of Artsakh and Utik were ...
, along with various Caucasian, Iranian and Arabic principalities: the principality of Shaddadid
The Shaddadids were a Kurdish Sunni Muslim dynasty. who ruled in various parts of Armenia and Arran from 951 to 1199 AD. They were established in Dvin. Through their long tenure in Armenia, they often intermarried with the Bagratuni royal fami ...
s, the principality of Shirvan
Shirvan (from fa, شروان, translit=Shirvān; az, Şirvan; Tat: ''Şirvan''), also spelled as Sharvān, Shirwan, Shervan, Sherwan and Šervān, is a historical Iranian region in the eastern Caucasus, known by this name in both pre-Islam ...
, the principality of Derbent
Derbent (russian: Дербе́нт; lez, Кьвевар, Цал; az, Дәрбәнд, italic=no, Dərbənd; av, Дербенд; fa, دربند), formerly romanized as Derbend, is a city in Dagestan, Russia, located on the Caspian Sea. It i ...
. Most of the region was ruled by the Persian Sajid Dynasty
The Sajid dynasty ( fa, ساجیان, sajyan), was an Iranian Muslim dynasty that ruled from 889/890 until 929. The Sajids ruled Azerbaijan and parts of Armenia first from Maragha and Barda and then from Ardabil.''Azerbaijan IV'', C.E. Bosworth, ' ...
from 890 to 929. The region was at times part of the Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
province of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
based on numismatic and historical evidence.
Early Muslim ruling dynasties of the time included Rawadids, Sajids, Salarids, Shaddadids, Shirvanshahs
''Shirvanshah'' ( fa, شروانشاه), also spelled as ''Shīrwān Shāh'' or ''Sharwān Shāh'', was the title of the rulers of Shirvan from the mid-9th century to the early 16th century. The title remained in a single family, the Yazidids, ...
, and the Sheki and Tiflis
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), is the capital and the largest city of Georgia, lying on the banks of the Kura River with a population of approximately 1.5 million pe ...
emirates. The principal cities of Arran in early medieval times were Barda (Partav) and Ganja. Barda reached prominence in the 10th century, and was used to house a mint
MiNT is Now TOS (MiNT) is a free software alternative operating system kernel for the Atari ST system and its successors. It is a multi-tasking alternative to TOS and MagiC. Together with the free system components fVDI device drivers, XaA ...
. Barda was sacked by the Rus and Norse several times in the 10th century as a result of the Caspian expeditions of the Rus Caspian can refer to:
*The Caspian Sea
*The Caspian Depression, surrounding the northern part of the Caspian Sea
*The Caspians, the ancient people living near the Caspian Sea
*Caspian languages, collection of languages and dialects of Caspian peopl ...
. Barda never revived after these raids and was replaced as capital by Baylaqan
Beylagan ( az, Beyləqan ) is the administrative centre of the Beylagan District of Azerbaijan. During the Soviet era, it was renamed Zhdanov (russian: Жданов) after Stalinist politician Andrei Zhdanov. This move was reverted in 1991 when t ...
, which in turn was sacked by the Mongols in 1221. After this Ganja rose to prominence and became the central city of the region. The capital of the Shaddadid dynasty, Ganja was considered the "mother city of Arran" during their reign.
The territory of Arran became a part of the Seljuk empire, followed by the Ildegizid state. It was taken briefly by the Khwarizmid dynasty and then overran by Mongol Hulagu empire
The Ilkhanate, also spelled Il-khanate ( fa, ایل خانان, ''Ilxānān''), known to the Mongols as ''Hülegü Ulus'' (, ''Qulug-un Ulus''), was a khanate established from the southwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. The Ilkhanid realm, ...
in the 13th century. Later, it became a part of Chobanid, Jalayirid
The Jalayirid Sultanate was a culturally Persianate, Mongol Jalayir dynasty which ruled over Iraq and western Persia after the breakup of the Mongol khanate of Persia in the 1330s.Bayne Fisher, William. ''The Cambridge History of Iran'', p.3: ...
, Timurid, and Safavid states.
In Azerbaijani historiography
The history of Caucasian Albania has been a major topic of Azerbaijani revisionist theories, which came under criticism in Western and Russian academic and analytical circles, and were often characterized as "bizarre" and "futile".Thomas De Waal. The Caucasus: An Introduction. Oxford University Press, USA. 2010, p. 108 In his article "The Albanian Myth", Russian historian and anthropologistVictor Schnirelmann
Victor Alexandrovich Schnirelmann (russian: Виктор Александрович Шнирельман, b. 18 May 1949, Moscow; frequently spelled Shnirelman in his English-language publications) is a Russian historian, ethnologist and a member o ...
states that Azerbaijani academics have been "renaming prominent medieval Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
political leaders, historians and writers, who lived in Nagorno Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh ( ) is a landlocked region in the South Caucasus, within the mountainous range of Karabakh, lying between Lower Karabakh and Syunik, and covering the southeastern range of the Lesser Caucasus mountains. The region is mos ...
and Armenia into "Albanians". Schnirelmann argues that these efforts were first launched in the 1950s and were directed towards "ripping the population of early medieval Nagorno Karabakh off from their Armenian heritage" and "cleansing Azerbaijan of Armenian history". In the 1970s, Azerbaijan made a transition from ignoring, discounting or concealing Armenian historical heritage in Soviet Azerbaijan to misattributing and mischaracterizing it as examples of Azerbaijani culture by arbitrarily declaring "Caucasian Albanians" as ancestors of modern Azerbaijanis. In this regard, Thomas de Waal
Thomas Patrick Lowndes de Waal (born 1966) is a British journalist and writer on the Caucasus. He is a senior fellow at Carnegie Europe. He is best known for his 2003 book '' Black Garden: Armenia and Azerbaijan Through Peace and War''.
Lif ...
, a scholar at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, writes about the political context of Azerbaijan's historical revisionism:
This rather bizarre argument has the strong political subtext that Nagorno Karabakh had in fact been Caucasian Albanian and that Armenians had no claim to it.Schnirelmann states that a significant revisionist method used by Azerbaijani scholars was "re-publishing of ancient and medieval sources, where the term "Armenian state" was routinely and systematically removed and replaced with "Albanian state".Esayi Hasan Jalaeants (Author), George A. Bournoutian (Translator). Brief History of the Aghuank Region: (Patmut'iwn Hamarot Aghuanits Erkri). Mazda Publishers (July 2009), Introduction, pp. 9-21 American author George Bournoutian gives examples of how that was done by
Ziya Bunyadov
Ziya Musa oglu Bunyadov ( az, Ziya Bünyadov sometimes spelled in English as Zia Buniatov or Bunyatov) (21 December 1923, Astara – 21 February 1997, Baku) was an Azerbaijani historian, academician, and Vice-President of the National Academy o ...
, vice-chairman of Azerbaijani Academy of Sciences, who earned the nickname of "Azerbaijan’s foremost Armenophobe".
According to de Waal:
Buniatov’s scholarly credentials were dubious. It later transpired that the two articles he published in 1960 and 1965 on Caucasian Albania were direct plagiarism. Under his own name, he had simply published, unattributed, translations of two articles, originally written in English by Western scholars C.F.J. Dowsett andHewsen, a historian from Rowan College and the acknowledged authority in this field, wrote in his volume ''Armenia: A Historical Atlas'', published byRobert Hewsen Robert H. Hewsen (May 20, 1934 – November 17, 2018) was an American historian and professor of history at Rowan University. He was an expert on the ancient history of the South Caucasus. Hewsen is the author of ''Armenia: A Historical Atlas'' ( ....
University of Chicago Press
The University of Chicago Press is the largest and one of the oldest university presses in the United States. It is operated by the University of Chicago and publishes a wide variety of academic titles, including ''The Chicago Manual of Style'', ...
:
According to de Waal, a disciple of Bunyadov, Farida Mammadova, has "taken the Albanian theory and used it to push Armenians out of the Caucasus altogether. She had relocated Caucasian Albania into what is now the Republic of Armenia. All those lands, churches, and monasteries in the Republic of Armenia—all had been Albanian. No sacred Armenian fact was left un-attacked". De Waal describes Mammadova as a sophisticated end of what "in Azerbaijan has become a very blunt instrument indeed".Thomas de Waal, Black Garden, chapter "Urekavank", in Russian, 2005/ref> Both
Ziya Bunyadov
Ziya Musa oglu Bunyadov ( az, Ziya Bünyadov sometimes spelled in English as Zia Buniatov or Bunyatov) (21 December 1923, Astara – 21 February 1997, Baku) was an Azerbaijani historian, academician, and Vice-President of the National Academy o ...
and Farida Mammadova are known for their anti-Armenian public pronouncements and pamphlets.
Historical revisionism in Azerbaijan supported a number of policies on the ground, including cultural vandalism directed against Armenian monuments in Soviet and post-Soviet Azerbaijan. Armenian memorial stone crosses known as "'' khachkars'' on the territory of Azerbaijan were regularly misrepresented as "Caucasian Albanian" both before and after Azerbaijan's independence. Furthermore, mischaracterization of Armenian ''khachkars'' as supposedly non-Armenian monuments of Caucasian Albania was associated with acts of cultural vandalism against Armenian historical monuments in Nakhichevan. The Khachkar destruction in Nakhchivan refer to the systematic campaign by the government of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of t ...
to completely demolish the Armenian cemetery in Julfa
The Armenian cemetery in Julfa ( hy, Ջուղայի գերեզմանատուն, ''Jughayi gerezmanatun'') was a cemetery near the town of Julfa (known as Jugha in Armenian), in the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan that originally housed around ...
with thousands of Armenian ''khachkars'' near the town of Julfa (known as Jugha in Armenian), Nakhchivan. Claims by Armenians that Azerbaijan was undertaking a systematic campaign to destroy and remove the monuments first arose in late 1998 and those charges were renewed in 2002 and 2005. Adam T. Smith, an anthropologist and associate professor of anthropology at the University of Chicago
The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, U of C, or UChi) is a private university, private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Its main campus is located in Chicago's Hyde Park, Chicago, Hyde Park neighborhood. The University of Chic ...
, called the removal of the khachkars "a shameful episode in humanity's relation to its past, a deplorable act on the part of the government of Azerbaijan which requires both explanation and repair". Smith and other scholars, as well as several United States Senators
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and powe ...
, signed a letter to the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
and other organizations condemning Azerbaijan's government. Azerbaijan instead contends that the monuments were not of Armenian, but of Caucasian Albanian
Caucasian Albania is a modern exonym for a former state located in ancient times in the Caucasus: mostly in what is now Azerbaijan (where both of its capitals were located). The modern endonyms for the area are ''Aghwank'' and ''Aluank'', among ...
, origin, which, per Thomas De Waal
Thomas Patrick Lowndes de Waal (born 1966) is a British journalist and writer on the Caucasus. He is a senior fellow at Carnegie Europe. He is best known for his 2003 book '' Black Garden: Armenia and Azerbaijan Through Peace and War''.
Lif ...
, did not protect "the graveyard from an act in the history wars".
Anti-Armenian cultural vandalism in Azerbaijan perpetrated with the use of revisionist theories on Caucasian Albania was also noted in northern Azerbaijan, where Norwegian archeologists were involved in the restoration of an Armenian-Georgian church in the village of Kish near the city of Shaki. Azerbaijanis erased Armenian inscriptions on the church's walls, which led to by an official complaint by Norwegian foreign ministry.
Furthermore, revisionist theories about Caucasian Albania have also been used by Azerbaijani statesmen in the ongoing Azerbaijani-Georgian dispute over the territorial status of David Gareja monastery complex
David Gareja ( ka, დავითგარეჯის სამონასტრო კომპლექსი) is a rock-hewn Georgian Orthodox monastery complex located in the Kakheti region of Eastern Georgia, on the half-desert slopes o ...
, a Georgian spiritual and historical monument partially located on the territory of Azerbaijani Republic. David Gareja is a rock-hewn Georgian Orthodox monastery complex in the Kakheti region of Eastern Georgia, on the semi-desert slopes of Mount Gareja, some 60–70 km southeast of Georgia's capital Tbilisi. Giorgi Manjgaladze, Georgia's deputy foreign minister proposed that Georgia would be willing to exchange other territory for the remainder of David Gareja because of its historical and cultural significance to the Georgians. Baku disapproves of this land swap, and in April 2007, Azerbaijan's deputy foreign minister Khalaf Khalafov told a press conference in Baku that it was "out of the question" for Azerbaijan to "give up its claims to the borderlands" including David Gareja. Khalafov then stated that the monastery "was home to the Caucasian Albanians, who are believed to have been the earliest inhabitants of Azerbaijan". Georgian art historian Dimitri Tumanishvili dismissed this claim and stated that the complex "is covered in the work of Georgian masters". "There are Georgian inscriptions everywhere dating back to the sixth century," he said "There are no traces of another culture there. After that, I don’t think you need any further proof".
See also
* Arsacid Dynasty of Caucasian Albania * Arts of Caucasian Albania * Artsakh * Church of Caucasian Albania *Shirvan
Shirvan (from fa, شروان, translit=Shirvān; az, Şirvan; Tat: ''Şirvan''), also spelled as Sharvān, Shirwan, Shervan, Sherwan and Šervān, is a historical Iranian region in the eastern Caucasus, known by this name in both pre-Islam ...
Notes
Footnotes
References
* * Marco Bais ''Albania caucasica: ethnos, storia, territorio attraverso le fonti greche, latine e armene''. Mimesis Edizioni. Roma, 2001Movses Kalankatuatsi. ''The History of Aluank''
Translated from Old Armenian (Grabar) by Sh.V.Smbatian, Yerevan, 1984.
Koriun, ''The Life of Mashtots''
translated from Old Armenian (Grabar) by Bedros Norehad. * Movses Kalankatuatsi. ''History of Albania''. Translated by L. Davlianidze-Tatishvili, Tbilisi, 1985. * Movses Khorenats
Translated from Old Armenian (Grabar) by
Gagik Sargsyan
Gagik Sargsyan ( hy, Գագիկ Խորենի Սարգսյան; 6 April 1926, in Yerevan – 25 August 1998, in Yerevan) was an Armenian historian, who served as the vice president of the Armenian Academy of Sciences.
Biography
He studied at Yer ...
, Yerevan, 1990.
* Ilia Abuladze. "About the discovery of the alphabet of the Caucasian Albanians". ''Bulletin of the Institute of Language, History and Material Culture (ENIMK)'', Vol. 4, Ch. I, Tbilisi, 1938.
*
*
*
*
External links
About the Caucasian Albania (section 10)
Caucasian History
{{Authority control 705 disestablishments Former countries in Europe Geographic history of Azerbaijan History of Dagestan Roman client kingdoms