Cat predation on wildlife on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cat predation on wildlife is the result of the natural instincts and
 Many islands host ecologically naive animal species. That is, animals that do not have predator responses for dealing with predators such as cats. Pet cats introduced to such islands have had a devastating impact on these islands'
Many islands host ecologically naive animal species. That is, animals that do not have predator responses for dealing with predators such as cats. Pet cats introduced to such islands have had a devastating impact on these islands'
"The Domestic Cat: Bird Killer, Mouser and Destroyer of Wildlife: Means of Utilizing and Controlling It"
Commonwealth of Massachusetts, State Board of Agriculture, Economic Biology Bulletin 42, 1916. Wildlife on islands faces unique challenges. A 2001 study attributed the decline of several island bird species, such as the
The Royal Society for the Protection of Birds, accessed 23 June 2014. Nick Forde, a trustee of the UK charity SongBird Survival, said the RSPB's claim of no evidence was disingenuous because adequate studies had not been done. In the UK, it is common to allow pet cats access to the outdoors. SongBird Survival considers that "the prevailing line that 'there is no scientific evidence that predation by cats is having any impact on bird populations in UK' is simply no longer tenable", and that "no study has ever examined the impact of cats on songbirds at the population level; evidence shows that the recovering sparrowhawk population in the 1970-80s resulted in the decline of some songbird populations; cats kill around 3 times as many songbirds as sparrowhawks; the mere presence of cats near birds' nests was found to decrease provision of food by a third while the resultant mobbing clamour from parent birds led in turn to increased nest predation by crows and magpies; nd thatit is therefore far more likely that cats have an even greater impact on songbird populations than sparrowhawks".
 The relationship between cats and humans began as a commensal relationship due to their predation on rodents, dating back to 7500 B.C. in connection to the inception of commensal rodents near
The relationship between cats and humans began as a commensal relationship due to their predation on rodents, dating back to 7500 B.C. in connection to the inception of commensal rodents near
 Various methods of population control are used to reduce the number of feral cats in areas where they are too abundant, thereby reducing the adverse effects that they often have on wildlife in those areas. Some of the methods most used, particularly in urban areas, are " Trap-Neuter-Return" (TNR) and "Trap-Euthanize" programs, as well as neutering kittens and allowing them to be adopted. Scientific research has not found TNR to be an effective means of controlling the feral cat population. Literature reviews have found that when studies documented TNR colonies that declined in population, those declines were being driven primarily by substantial percentages of colony cats being permanently removed by a combination of rehoming and euthanasia on an ongoing basis, as well as by an unusually high rate of death and disappearance. TNR colonies often increase in population because cats breed quickly and the trapping and sterilization rates are frequently too low to stop this population growth, because food is usually being provided to the cats, and because public awareness of a TNR colony tends to encourage people in the surrounding community to dump their own unwanted pet cats there. The growing popularity of TNR, even near areas of particular ecological sensitivity, has been attributed in part to a lack of public interest regarding the environmental harm caused by feral cats, and the unwillingness of both scientific communities and TNR advocates to engage.
Because hunting behavior in cats is driven by instinct and not by hunger, feeding cats (as in TNR colonies) does nothing to stop them from hunting, even if the cats are overfed. Feeding cats can allow a state of hyperpredation to come about, where human intervention causes an unnaturally high predator population density to continue indefinitely, even if the local prey populations collapse.
Housecats are common in western societies which has an effect on how society views the moral implication of feral cat population management. A study was done in rural and urban
Various methods of population control are used to reduce the number of feral cats in areas where they are too abundant, thereby reducing the adverse effects that they often have on wildlife in those areas. Some of the methods most used, particularly in urban areas, are " Trap-Neuter-Return" (TNR) and "Trap-Euthanize" programs, as well as neutering kittens and allowing them to be adopted. Scientific research has not found TNR to be an effective means of controlling the feral cat population. Literature reviews have found that when studies documented TNR colonies that declined in population, those declines were being driven primarily by substantial percentages of colony cats being permanently removed by a combination of rehoming and euthanasia on an ongoing basis, as well as by an unusually high rate of death and disappearance. TNR colonies often increase in population because cats breed quickly and the trapping and sterilization rates are frequently too low to stop this population growth, because food is usually being provided to the cats, and because public awareness of a TNR colony tends to encourage people in the surrounding community to dump their own unwanted pet cats there. The growing popularity of TNR, even near areas of particular ecological sensitivity, has been attributed in part to a lack of public interest regarding the environmental harm caused by feral cats, and the unwillingness of both scientific communities and TNR advocates to engage.
Because hunting behavior in cats is driven by instinct and not by hunger, feeding cats (as in TNR colonies) does nothing to stop them from hunting, even if the cats are overfed. Feeding cats can allow a state of hyperpredation to come about, where human intervention causes an unnaturally high predator population density to continue indefinitely, even if the local prey populations collapse.
Housecats are common in western societies which has an effect on how society views the moral implication of feral cat population management. A study was done in rural and urban
behavior
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions of Individual, individuals, organisms, systems or Artificial intelligence, artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or or ...
of both feral
A feral (; ) animal or plant is one that lives in the wild but is descended from domesticated individuals. As with an introduced species, the introduction of feral animals or plants to non-native regions may disrupt ecosystems and has, in som ...
and owned house cats to hunt small prey
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not ki ...
, including wildlife
Wildlife refers to domestication, undomesticated animals and uncultivated plant species which can exist in their natural habitat, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wilderness, wild in an area without being species, introdu ...
. Some people view this as a desirable trait, such as in the case of barn cats and other cats kept for the intended purpose of pest control in rural settings; but scientific evidence does not support the popular use of cats to control urban rat populations, and ecologists oppose their use for this purpose because of the disproportionate harm they do to native wildlife. Recognized as both invasive species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native spec ...
and predators, cats have been shown to cause significant ecological harm across various ecosystems.
Due to cats' natural hunting instinct, their ability to adapt to different environments, and the wide range of small animals they prey upon, both feral and free-ranging pet
A pet, or companion animal, is an animal kept primarily for a person's company or entertainment rather than as a working animal, livestock, or a laboratory animal. Popular pets are often considered to have attractive/ cute appearances, inte ...
cats are responsible for predation on wildlife, and in some environments, considerable ecological harm. Cats are disease carriers and can spread diseases to animals in their community and marine life. There are methods to help mitigate the environmental impact imposed by feral cats through different forms of population management. Reducing cats' impact on the environment is limited by perceptions society has towards cats because humans have a relationship with cats as pets.
In Australia, hunting by feral cats helped to drive at least 20 native mammals to extinction, and continues to threaten at least 124 more. Their introduction into island ecosystems has caused the extinction of at least 33 endemic species on islands throughout the world. A 2013 systematic review in ''Nature Communications
''Nature Communications'' is a peer-reviewed, open access, scientific journal published by Nature Portfolio since 2010. It is a multidisciplinary journal that covers the natural sciences, including physics, chemistry, earth sciences, medic ...
'' of data from 17 studies found that feral and domestic cats are estimated to kill billions of birds in the United States every year.
In a global 2023 assessment, cats were found to prey on 2,084 different species, of which 347 (or 16.5%) were of conservation concern. Birds, reptiles, and small mammals accounted for 90% of killed species. Island animals of conservation concern had three times more species predated upon than continental species.
Consequences of introduction
 Many islands host ecologically naive animal species. That is, animals that do not have predator responses for dealing with predators such as cats. Pet cats introduced to such islands have had a devastating impact on these islands'
Many islands host ecologically naive animal species. That is, animals that do not have predator responses for dealing with predators such as cats. Pet cats introduced to such islands have had a devastating impact on these islands' biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
.
They have been implicated in the extinction of several species and local extinctions, such as the hutia
Hutias (known in Spanish as jutía) are moderately large cavy-like rodents of the subfamily Capromyinae that inhabit the Caribbean islands. Most species are restricted to Cuba, but species are known from all of the Greater Antilles, as well as ...
s from the Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
, the Guadalupe storm petrel from the Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
coast of Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
, and the Lyall's wren
Lyall's wren or the Stephens Island wren (''Traversia lyalli'') was a small, flightless passerine belonging to the family Acanthisittidae, the New Zealand wrens. Now extinct, it was once found throughout New Zealand, but when it came to the a ...
from New Zealand. In a statistical study, they were a significant cause for the extinction of 40% of the species studied. Moors and Atkinson wrote, in 1984, "no other alien predator has had such a universally damaging effect".
The large animal population of the remote Kerguelen Islands
The Kerguelen Islands ( or ; in French commonly ' but officially ', ), also known as the Desolation Islands (' in French), are a group of islands in the subantarctic, sub-Antarctic region. They are among the Extremes on Earth#Remoteness, most i ...
in the Southern Indian Ocean comprises introduced species, including cats, rabbits, some seabirds, and sheep
Sheep (: sheep) or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to d ...
. Although exotic mammals form the bulk of their diet, cats' impact on seabirds is very important.
Restoration
Because of the damage cats cause in islands and some ecosystems, many conservationists working in the field ofisland restoration
The ecological restoration of islands, or island restoration, is the application of the principles of ecological restoration to islands and island groups. Islands, due to their isolation, are home to many of the world's endemic (ecology), endemic ...
have worked to remove feral cats. (Island restoration involves the removal of introduced species and reintroducing native species.) , 48 islands have had their feral cat populations eradicated, including New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
's network of offshore island bird reserves and Australia's Macquarie Island
Macquarie Island is a subantarctic island in the south-western Pacific Ocean, about halfway between New Zealand and Antarctica. It has been governed as a part of Tasmania, Australia, since 1880. It became a Protected areas of Tasmania, Tasmania ...
.
Larger projects have also been undertaken, including their complete removal from Ascension Island
Ascension Island is an isolated volcanic island, 7°56′ south of the Equator in the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic Ocean. It is about from the coast of Africa and from the coast of South America. It is governed as part of the British Overs ...
. The cats, introduced in the 19th century, caused a collapse in populations of nesting seabird
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adaptation, adapted to life within the marine ecosystem, marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent ...
s. The project to remove them from the island began in 2002, and the island was cleared of cats by 2004. As of 2007, five species of seabirds had re-established colonies on the main island.
In some cases, the removal of cats had unintended consequences
In the social sciences, unintended consequences (sometimes unanticipated consequences or unforeseen consequences, more colloquially called knock-on effects) are outcomes of a purposeful action that are not intended or foreseen. The term was po ...
. An example is Macquarie Island
Macquarie Island is a subantarctic island in the south-western Pacific Ocean, about halfway between New Zealand and Antarctica. It has been governed as a part of Tasmania, Australia, since 1880. It became a Protected areas of Tasmania, Tasmania ...
, where the removal of cats caused an explosion in the number of rabbits, that started feeding off the island's vegetation, thus leaving the birds without protection from other predators, like rats and other birds. even if the eradication was positioned within an integrated pest management framework. The removal of the rats and rabbits was scheduled for 2007 and it could take up to seven years and cost $24 million.
Birds
A 2013 study by Scott R. Loss and colleagues from the Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute and the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service identified free-ranging domestic cats as the leading human-caused threat to birds and small mammals in the United States. The study estimated that cats kill between 1.3 and 3.7 billion birds and between 6.3 and 22.3 billion mammals each year, with unowned cats being responsible for the majority of these deaths. These figures were much higher than previous estimates for the U.S. Unspecified species of birds native to the U.S. and mammals includingmice
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
, shrew
Shrews ( family Soricidae) are small mole-like mammals classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, West Indies shrews, or marsupial shrews, which belong to dif ...
s, vole
Voles are small rodents that are relatives of lemmings and hamsters, but with a stouter body; a longer, hairy tail; a slightly rounder head; smaller eyes and ears; and differently formed molars (high-crowned with angular cusps instead of lo ...
s, squirrel
Squirrels are members of the family Sciuridae (), a family that includes small or medium-sized rodents. The squirrel family includes tree squirrels, ground squirrels (including chipmunks and prairie dogs, among others), and flying squirrel ...
s and rabbit
Rabbits are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also includes the hares), which is in the order Lagomorpha (which also includes pikas). They are familiar throughout the world as a small herbivore, a prey animal, a domesticated ...
s were considered most likely to be preyed upon by cats.
Perhaps the first U.S. study that pointed to predation by cats on wildlife, as a concern was ornithologist Edward Howe Forbush's 1916 report for the Massachusetts State Board of Agriculture, ''The Domestic Cat: Bird Killer, Mouser and Destroyer of Wildlife: Means of Utilizing and Controlling It''.Edward Howe Forbush"The Domestic Cat: Bird Killer, Mouser and Destroyer of Wildlife: Means of Utilizing and Controlling It"
Commonwealth of Massachusetts, State Board of Agriculture, Economic Biology Bulletin 42, 1916. Wildlife on islands faces unique challenges. A 2001 study attributed the decline of several island bird species, such as the
Townsend's shearwater
Townsend's shearwater (''Puffinus auricularis'') is a rare seabird of the tropics from the family Procellariidae.
Taxonomy
Its relationships are unresolved. Its closest relatives are probably, but not certainly, the Hawaiian shearwater (''Puffi ...
, socorro dove
The Socorro dove or Grayson's dove (''Zenaida graysoni'') is a dove species which is extinct in the wild. It was endemic to Socorro Island in the Revillagigedo Islands off the west coast of Mexico. The last sighting in its natural habitat was i ...
, and the Marquesan ground dove to predation by domestic cats.
in ''Encyclopedia of Biodiversity'' The study concluded that habitat loss and degradation were the primary threats to endangered bird species, impacting at least 52% of them, while introduced species
An introduced species, alien species, exotic species, adventive species, immigrant species, foreign species, non-indigenous species, or non-native species is a species living outside its native distributional range, but which has arrived ther ...
, including domestic cats, rat
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents. Species of rats are found throughout the order Rodentia, but stereotypical rats are found in the genus ''Rattus''. Other rat genera include '' Neotoma'' (pack rats), '' Bandicota'' (bandicoo ...
s and mustelids, accounted for 6% of endangered birds. Other studies caution that removing domestic cats from islands can have unintended ecological consequences, including surges in rat populations, which may further endanger native bird and mammal species.
Mammals
Rodents are the primary prey of the african wild cat, the primary ancestors of thedomestic cat
The cat (''Felis catus''), also referred to as the domestic cat or house cat, is a small Domestication, domesticated carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species of the family Felidae. Advances in archaeology and genetics have sh ...
. However, cats are generalist predators that hunt a broad range of prey including mammals, birds, fish, reptiles, amphibians, and invertebrates. One study in Italy found that cats there returned 207 different species of prey, while another on Great Britain found cats were hunting 20 different species of mammal, 44 species of bird, four reptile species and three species of amphibian. Small mammals usually make up the majority of captured prey, but this varies with whatever types of prey are locally available. In this context, cats are also frequently used as a form of pest control.
Cats are sometimes intentionally released into urban environments on the popular assumption that they will control the rat population; but there is little scientific basis for this. The reality is that cats find rats to be large and formidable prey, and so they preferentially hunt defenseless wildlife such as lizards and songbirds instead. Scientists and conservationists oppose the use of cats as a form of rodent control because they are so inefficient at destroying pest species that the harm they do to native species in the process outweighs any benefit.
Despite this, cat rescue groups sometimes release unadoptable feral cats into rat-infested neighborhoods under the pretext of giving the cats "jobs" as rat control, as is being done in Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
and Brooklyn
Brooklyn is a Boroughs of New York City, borough of New York City located at the westernmost end of Long Island in the New York (state), State of New York. Formerly an independent city, the borough is coextensive with Kings County, one of twelv ...
; the cats will largely ignore the rats and instead will beg for food from people or eat garbage and whatever small wildlife they can catch. Jamie Childs, a public health researcher who has studied urban feral cats, told ''The Atlantic'' that he sees cats and rats peaceably eating from the same pile of garbage at the same time. Studies have found that house mouse and rat infestations are more common in locations near where outdoor cats are being fed, despite occasional predation by the cats.
Impact on island ecosystems
Around half of the scientific literature on cat predation of wildlife is focused on oceanic islands. The emphasis is due in part to the unique vulnerability of island fauna, which makes declines and extinctions due to cats easier to document on islands than elsewhere. In many cases, it is easier to eradicate cats from islands than from mainland areas, which allows studies on the effects of the removal on native prey species. Island species are particularly vulnerable to predation by invasive cats due to their evolutionary isolation. Many of these species lack natural defenses against mammalian predators because they have evolved in environments free from threats. The introduction of cats has led to significant population declines among vertebrate species, especially in ecosystems where prey populations are small and isolated, making it difficult for them to recover from ongoing predation. Their predation onnative species
In biogeography, a native species is indigenous to a given region or ecosystem if its presence in that region is the result of only local natural evolution (though often popularised as "with no human intervention") during history. The term is equi ...
can reduce populations to critically low levels, resulting in cascading effects on other species that occupy similar ecological roles. In the pacific, cats have caused declines in seabird populations, including Hawaiian petrel and Townsend's shearwater
Townsend's shearwater (''Puffinus auricularis'') is a rare seabird of the tropics from the family Procellariidae.
Taxonomy
Its relationships are unresolved. Its closest relatives are probably, but not certainly, the Hawaiian shearwater (''Puffi ...
, both of which play vital roles in nutrient cycling by transferring marine-derived nutrients to terrestrial habitats. In the Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
, cats have significantly impacted reptiles such as iguanas, destabilizing population dynamics and interrupting essential ecosystem functions like herbivory and seed dispersal.
Impact by location
Australia
Cats in Australia have been found to have European origins. This is important to note because of their effect on native species. Feral cats in Australia have been linked to the decline and extinction of various native animals. They have been shown to cause a significant impact on ground nesting birds and small native mammals. Feral cats have also hampered any attempts to re-introduce threatened species back into areas where they have become extinct as the cats have hunted and killed the newly released animals. Numerous Australian environmentalists claim the feral cat has been an ecological disaster in Australia, inhabiting most ecosystems except denserainforest
Rainforests are forests characterized by a closed and continuous tree Canopy (biology), canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforests can be generally classified as tropi ...
, and being implicated in the extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
of several marsupial
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a r ...
and placental
Placental mammals (infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguished ...
mammal species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
. Some inhabitants have begun eating cat meat to mitigate the harm that wild cats do to the local wildlife.
In 2020, it was reported that a culling of feral cats that had recently begun in Dryandra Woodland, in Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Aust ...
, had caused the population of numbats to triple in number, the largest number of the endangered marsupial to have been recorded there since the 1990s.
Feral and pet cats in Australia are estimated to kill around 650 million lizards and snakes per year, or about 225 reptiles per cat on average. Cats were found to be actively hunting and killing over 250 different species of reptiles in Australia, with 11 of which being considered endangered species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
. Cats consume so many lizards in Australia that there was a single cat found with the parts of 40 individual lizards inside of its stomach, the highest amount recorded thus far.
Canada
A 2013 study estimated that between 100 and 350 million birds are killed annually by pet cats in Canada.China
Domestic cats are common throughout China, and the number of pet cats in the country increased at a rate of 8.6% from 2018 to 2019. A 2021 estimate based on a public survey estimated that outdoor cats kill "1.61–4.95 billion invertebrates, 1.61–3.58 billion fishes, 1.13–3.82 billion amphibians, 1.48–4.31 billion reptiles, 2.69–5.52 billion birds, and 3.61–9.80 billion mammals" there each year. The authors recommended policies be implemented, such as a public education initiative to encourage people to keep their cats indoors, and building more animal shelters. They also recommended that TNR programs "should be limited until rigorous, peer-reviewed studies are able to show that such efforts consistently attain the sterilization rates needed to result in stabilization and permanent decline of unowned cat populations", as they said that most TNR programs fail to do this.New Zealand
The fauna ofNew Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
has evolved in isolation for millions of years without the presence of mammals (apart from a few bat species). Consequently, birds dominated the niches occupied by mammals and many became flightless. The introduction of mammals after settlement by Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Co ...
from about the 12th century had a huge effect on indigenous biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
. Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
an explorers and settlers brought cats on their ships and the presence of feral cats was recorded from the latter decades of the 19th century.
It is estimated that feral cats have been responsible for the extinction of six endemic bird species and over 70 localised subspecies as well as depleting bird and lizard species.
South Africa
In a 2020 study, approximately 300,000 domestic cats inCape Town
Cape Town is the legislature, legislative capital city, capital of South Africa. It is the country's oldest city and the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. Cape Town is the country's List of municipalities in South Africa, second-largest ...
kill 27.5 million animals a year; this equates to a cat killing 90 animals per year. Cats on the urban edge of the city of Cape Town kill more than 200,000 animals in the Table Mountain National Park
Table Mountain National Park, previously known as the Cape Peninsula National Park, is a national park in Cape Town, South Africa, proclaimed on 29 May 1998, for the purpose of protecting the natural environment of the Table Mountain chain, and ...
annually. Reptiles constituted 50% of killed prey, but only 17% of prey brought home; mammals constituted 24% of prey, but 54% of prey brought home. Non-native species accounted for only 6% of animals killed by cats from the urban edge, and 17% from deep urban cats.
United Kingdom
Sir David Attenborough in his Christmas Day, 2013, edition ofBBC Radio 4
BBC Radio 4 is a British national radio station owned and operated by the BBC. The station replaced the BBC Home Service on 30 September 1967 and broadcasts a wide variety of spoken-word programmes from the BBC's headquarters at Broadcasti ...
programme Tweet Of The Day said "cats kill an extraordinarily high number of birds in British gardens". Asked whether cat owners should buy bell collars for their pets at Christmas, he replied: "that would be good for the robins, yes". In the UK, the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds
The Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) is a Charitable_organization#United_Kingdom, charitable organisation registered in Charity Commission for England and Wales, England and Wales and in Office of the Scottish Charity Regulator, ...
says there is no scientific evidence that predation by cats is having any effect on the population of birds UK-wide."Are cats causing bird declines?"The Royal Society for the Protection of Birds, accessed 23 June 2014. Nick Forde, a trustee of the UK charity SongBird Survival, said the RSPB's claim of no evidence was disingenuous because adequate studies had not been done. In the UK, it is common to allow pet cats access to the outdoors. SongBird Survival considers that "the prevailing line that 'there is no scientific evidence that predation by cats is having any impact on bird populations in UK' is simply no longer tenable", and that "no study has ever examined the impact of cats on songbirds at the population level; evidence shows that the recovering sparrowhawk population in the 1970-80s resulted in the decline of some songbird populations; cats kill around 3 times as many songbirds as sparrowhawks; the mere presence of cats near birds' nests was found to decrease provision of food by a third while the resultant mobbing clamour from parent birds led in turn to increased nest predation by crows and magpies; nd thatit is therefore far more likely that cats have an even greater impact on songbird populations than sparrowhawks".
United States
The United States is estimated to house a population of 60-80 million cats, and they are estimated to kill 2.4 billion birds per year, making them the leading human-caused threat to the survival of bird species in the country. The majority of these kills are by feral cats, rather than owned cats. In California, a study found that in areas where humans feed feral cats, they will continue to hunt large numbers of native birds even without the intention of eating them. This has resulted in the disappearance of native bird species, such as the California quail (''Callipepla california'') andCalifornia thrasher
The California thrasher (''Toxostoma redivivum'') is a large member of family Mimidae found primarily in chaparral habitat in California in the United States and Baja California in Mexico. It is the only species of the genus ''Toxostoma'' throu ...
(''Toxostoma redivivum''), in those areas where they once resided.
In Maryland, a study showed that due to cats overhunting chipmunks, the natural prey of many raptor species, the Cooper's hawk (''Accipiter cooperii'') population struggled to find food and had to switch to preying on harder-to-catch songbirds, which lengthened their hunting times and increased their nestlings mortality rate.
In Hawaii, cats were introduced by European sailing ships that used them for pest control. They prey on songbirds and many other birds that nest on the ground and in burrows. Nestlings unable to fly are especially vulnerable. Cats successfully hunt in a variety of habitats. A study was made in endangered birds' habitats with an infrared camera to learn how much cats affected the population of birds. The study found that up to 11% of palila nests were depredated yearly. The critically endangered palila produces few eggs per year and the nestlings develop slowly, so that depredation rate could result in extinction.
In New York City, cats are commonly brought into businesses to combat the city's rat problem. Studies done in New York City determined that cats are not effective predators against rats and much more of a threat to other urban wildlife. Research conducted at a Brooklyn waste management facility observed minimal predation on Norway rats, with only three successful or attempted kills recorded over 79 days of observation. Instead, feral cats tend to focus on smaller, easier prey such as birds and mice.
Ecology of fear
Ecology of fear or "fear effect": is a negative impact on prey that leads to a decrease in their population due to predators' presence or scent. The study "Urban bird declines and the fear of cats" refers to how native species are reproducing less to avoid predators, even if predator mortality is low. This study indicates how small predator mortality is, which is less than 1%, but it has a considerable impact on the birds' fecundity and reduces the abundance of birds to 95%. The fear effect is one indirect way cats affect native species besides diseases. The presence of cats altered the prey foraging, movement, and stress response and significantly impacted survival and reproduction.Cat attack outcomes
Wildlife that are attacked by cats fare poorly, even when provided with veterinary treatment by licensed wildlife rehabilitators (over 70% of mammals and over 80% of birds died in spite of treatment in one study). Even those that had no visible injuries from the cat attack often died (55.8% of birds, 33.9% of mammals). Typical wildlife injuries caused by cats include cuts, degloving (the stripping off of skin), and small puncture wounds caused by prey being gripped by the cat's teeth that are easily hidden by fur or feathers. Systemic infection, usually caused by '' Pasteurella multocida'', a highly pathogenic bacterial species that's found naturally in cat mouths, can kill small animals in as little as 15 hours. Additionally, the study revealed that even when wildlife survive the immediate effects of a cat attack, they often left weakened and vulnerable to secondary threats, such as predation or disease. Few other causes of injury that are commonly seen by wildlife care facilities lead to death as rapidly or as frequently as interaction with a cat.Cat owner perspective
A 2018 study published in '' People and Nature'' highlighted, that resolving the environmental impact of cat predation requires greater awareness and responsibility from cat owners Surveys of cat owners find they often view the depredation of wildlife as a normal thing that cats do, and rarely feel and may not feel a strong personal obligation to mitigate it. They may experience some level ofcognitive dissonance
In the field of psychology, cognitive dissonance is described as a mental phenomenon in which people unknowingly hold fundamentally conflicting cognitions. Being confronted by situations that challenge this dissonance may ultimately result in some ...
toward the subject, because when surveyed they're more likely than the general public to believe that cat predation isn't harmful to wildlife, despite the likelihood they have witnessed acts of predation firsthand, and in many cases have been receiving "gifts" of animal carcasses from their cats. Others express concern but believe they cannot manage their cat's behavior without compromising its welfare Some cat owners take pride in the animals their cats return home, believing it represents the cat's authenticity or skill.
Popular press depictions
According to a 2021 study of English-language media coverage since 1990, journalists who cover stories involving outdoor cats rarely include the views of researchers and conservationists, oversimplify the issues, and often only present the unbalanced views of cat advocacy groups, contributing to public misunderstanding of the science, including the public not understanding that outdoor cats present environmental problems.Human interaction
 The relationship between cats and humans began as a commensal relationship due to their predation on rodents, dating back to 7500 B.C. in connection to the inception of commensal rodents near
The relationship between cats and humans began as a commensal relationship due to their predation on rodents, dating back to 7500 B.C. in connection to the inception of commensal rodents near Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
sedentary communities. There is some debate regarding exactly how early domestication began, but there is enough evidence (DNA and Art) to conclude that humans started domesticating cats in Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
. Ancient Egyptians found cats to be beneficial for pest reduction. Human influence on cat evolution can be seen morphologically after the domestication of the cat and the increase of global trade routes, as cats were recruited for rodent control.
Unlike other wild predators, cats are given different forms of aid from humans such as food, shelter, and medical treatment. Aid given by humans present cats with a survival advantage which would not be seen otherwise in the wild, leading to high populations As opportunistic hunters, cats are extremely adaptive to their environments, even if they are a house cat living in a home.
Spreading diseases
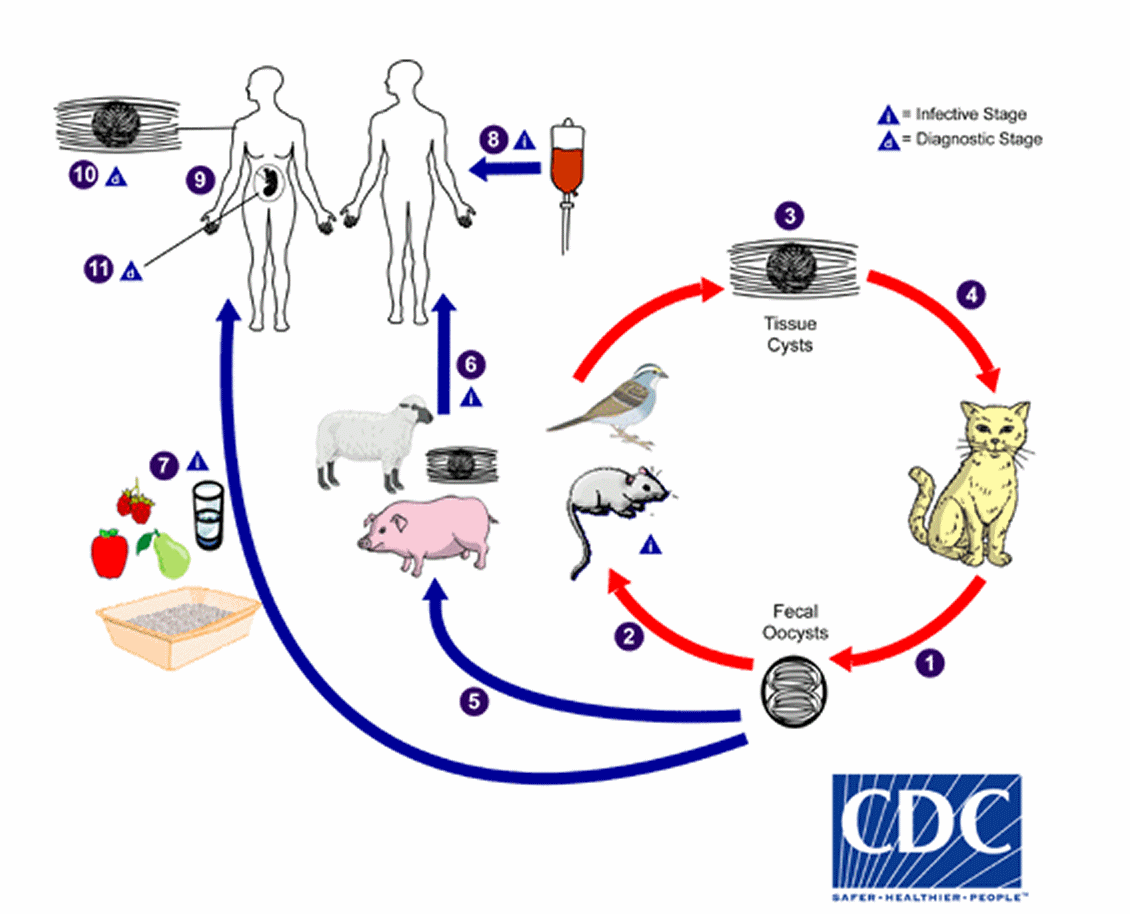
A secondary effect of cat predation on wildlife is the ability to transmit a range ofdisease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical condi ...
s mediated by or acquired from prey to other animals. Whether through interaction or indirectly, cats can spread diseases to prey and non-prey animals, including marine animals and humans. Some of the diseases that can be transmitted from cats to humans include Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by ''Toxoplasma gondii'', an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis are associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric and behavioral conditions. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or month ...
, Hookworm
Hookworms are Gastrointestinal tract, intestinal, Hematophagy, blood-feeding, parasitic Nematode, roundworms that cause types of infection known as helminthiases. Hookworm infection is found in many parts of the world, and is common in areas with ...
s (''Uncinaria stenocephala
''Uncinaria stenocephala'' is a nematode that parasitizes dogs, cats, and foxes, as well as humans. It is rare to find in cats in the United States. ''U. stenocephala'' is the most common canine hookworm in cooler regions, such as Canada and th ...
'', '' Ancylostoma tubaeforme'', ''Ancylostoma braziliense
''Ancylostoma braziliense'' is a species of hookworm belonging to the genus ''Ancylostoma''. It is an intestinal parasite of domestic cats and dogs. Severe infection is often fatal to these pets, especially in puppies and kittens. The infection i ...
'' and '' Ancylostoma ceylanicum''), Cat-scratch disease
Cat-scratch disease (CSD) is an infectious disease that most often results from a scratch or bite of a cat. Symptoms typically include a non-painful bump or blister at the site of injury and painful and swollen lymph nodes. People may feel tire ...
(bartonellosis), Rickettsia disease (''Rickettesia typhi''), Tularemia
Tularemia, also known as rabbit fever, is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium '' Francisella tularensis''. Symptoms may include fever, skin ulcers, and enlarged lymph nodes. Occasionally, a form that results in pneumonia or a throat ...
(''Francisella tularensis''), and Plague (''Yersinia pestis'').
Toxoplasmosis

Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by ''Toxoplasma gondii'', an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis are associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric and behavioral conditions. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or month ...
is caused by the single-celled coccidian parasite ''Toxoplasma gondii'' that only reproduces in cats but is capable of affecting all warm-blooded animals. It has been reported in mammalian, avian, marine, marsupial, sheep, and goat species. Its reproduction mechanism requires cats, the definitive hosts, to prey on the animals that had ingested material contaminated with feline feces. The occurrence of toxoplasmosis therefore depends on cat predation. In mice and rats, it reduces the innate fear of cats by injuring neural tissues to facilitate predation. In Hawaii, the disease has been found to be fatal to the endangered Hawaiian crow, the near-threatened nene, the red-footed booby, and the endangered Hawaiian monk seal. In California, it has had a lethal impact on sea otter
The sea otter (''Enhydra lutris'') is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern Pacific Ocean, North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between , making them the heaviest members of ...
s. Toxoplasmosis in marine life has been traced to freshwater runoff and sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewerage, sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged fro ...
containing oocysts
Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organism ...
in cat feces. Australian marsupials are also highly susceptible to toxoplasmosis.
Tularemia
Tularemia
Tularemia, also known as rabbit fever, is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium '' Francisella tularensis''. Symptoms may include fever, skin ulcers, and enlarged lymph nodes. Occasionally, a form that results in pneumonia or a throat ...
, also known as "rabbit fever" caused by the bacterium ''Francisella tularensis
''Francisella tularensis'' is a pathogenic species of Gram-negative coccobacillus, an aerobic bacterium. It is nonspore-forming, nonmotile, and the causative agent of tularemia, the pneumonic form of which is often lethal without treatment. It i ...
'', is a zoonotic disease that can affect various species, including cats. Cats typically contract tularemia through interactions with infected wildlife, including prey such as rabbits and rodents, or via vectors like ticks and insect bites. The transmission of the disease from cats to other animals is not well-documented. There is potential for tularemia transmission to humans, particularly through bites, scratches, or close contact.
Feral cat population management
 Various methods of population control are used to reduce the number of feral cats in areas where they are too abundant, thereby reducing the adverse effects that they often have on wildlife in those areas. Some of the methods most used, particularly in urban areas, are " Trap-Neuter-Return" (TNR) and "Trap-Euthanize" programs, as well as neutering kittens and allowing them to be adopted. Scientific research has not found TNR to be an effective means of controlling the feral cat population. Literature reviews have found that when studies documented TNR colonies that declined in population, those declines were being driven primarily by substantial percentages of colony cats being permanently removed by a combination of rehoming and euthanasia on an ongoing basis, as well as by an unusually high rate of death and disappearance. TNR colonies often increase in population because cats breed quickly and the trapping and sterilization rates are frequently too low to stop this population growth, because food is usually being provided to the cats, and because public awareness of a TNR colony tends to encourage people in the surrounding community to dump their own unwanted pet cats there. The growing popularity of TNR, even near areas of particular ecological sensitivity, has been attributed in part to a lack of public interest regarding the environmental harm caused by feral cats, and the unwillingness of both scientific communities and TNR advocates to engage.
Because hunting behavior in cats is driven by instinct and not by hunger, feeding cats (as in TNR colonies) does nothing to stop them from hunting, even if the cats are overfed. Feeding cats can allow a state of hyperpredation to come about, where human intervention causes an unnaturally high predator population density to continue indefinitely, even if the local prey populations collapse.
Housecats are common in western societies which has an effect on how society views the moral implication of feral cat population management. A study was done in rural and urban
Various methods of population control are used to reduce the number of feral cats in areas where they are too abundant, thereby reducing the adverse effects that they often have on wildlife in those areas. Some of the methods most used, particularly in urban areas, are " Trap-Neuter-Return" (TNR) and "Trap-Euthanize" programs, as well as neutering kittens and allowing them to be adopted. Scientific research has not found TNR to be an effective means of controlling the feral cat population. Literature reviews have found that when studies documented TNR colonies that declined in population, those declines were being driven primarily by substantial percentages of colony cats being permanently removed by a combination of rehoming and euthanasia on an ongoing basis, as well as by an unusually high rate of death and disappearance. TNR colonies often increase in population because cats breed quickly and the trapping and sterilization rates are frequently too low to stop this population growth, because food is usually being provided to the cats, and because public awareness of a TNR colony tends to encourage people in the surrounding community to dump their own unwanted pet cats there. The growing popularity of TNR, even near areas of particular ecological sensitivity, has been attributed in part to a lack of public interest regarding the environmental harm caused by feral cats, and the unwillingness of both scientific communities and TNR advocates to engage.
Because hunting behavior in cats is driven by instinct and not by hunger, feeding cats (as in TNR colonies) does nothing to stop them from hunting, even if the cats are overfed. Feeding cats can allow a state of hyperpredation to come about, where human intervention causes an unnaturally high predator population density to continue indefinitely, even if the local prey populations collapse.
Housecats are common in western societies which has an effect on how society views the moral implication of feral cat population management. A study was done in rural and urban England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, to determine the perspective of cat owners on managing cat predation of local wildlife. The majority of cat owners agreed that cats should not remain inside to prevent them from hunting. Many cat owners were more concerned about an individual cat's safety than their predation on other animals.
Cat-exclusion zones (CEZ) have been proposed in conservation areas where certain species are vulnerable to predation by cats. These zones are intended for Rural–urban fringe
Peri-urbanisation relates to the processes of scattered and dispersive urban growth that create hybrid landscapes of fragmented and mixed urban and rural characteristics. Such areas may be referred to as the rural–urban fringe, the outskirts ...
areas serving as a buffer zone to mitigate cat predation from urban cats in rural areas. Cat-exclusion zones were presented in response to the lack of success from existing forms of population management. There is probable controversy associated with this policy as it can be perceived as restricting one's freedom, due to the relationship between humans and cats.
Fencing
The Newhaven Wildlife Sanctuary in Central Australia is spearheading a major biodiversity project by establishing a 650-square-Kilometer feral cat-free zone. This initiative involves constructing a 1,600-kilometer predator-proof fence and eradicating feral cats within the sanctuary to create a safe environment for reintroducing endangered species. Feral cats pose a severe threat to Australian Wildlife, not only by preying on native animals but also by spreading diseases. Introduced during European settlement in the 1800s to control rodents and rabbits, feral cats quickly adapted to Australia's environment, thriving on abundant prey and surviving with minimal water. Today, an estimated 6 million feral cats in Australia kill around 1,000 native animals per cat annually, highlighting the urgent need for such conservation efforts.Reducing cat predation through dietary and behavioral enrichment
A study found that providing domestic cats with high meat content diets and engaging them in object play significantly reduced their predation on wildlife. Cats fed a meat-rich diet reduced their hunting activity by 36%, while daily play sessions decreased prey capture by 25%. These findings suggest that improving cats' diets and offering alternative outlets for their hunting instincts can effectively mitigate their impact on wildlife.See also
* Surplus killing, biology *References
Further reading
* * *{{cite web , url=https://www.theextinctions.com/articles-1/the-flightless-wren-and-the-lighthousekeepers-cat , title=The Flightless Wren and the Lighthouse Cat , first=Søren Bay Kruse , last=Thomsen , work=TheExtinctions.com , date=11 November 2022 Animal welfare Cats Invasive mammal species Predation