Caspians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Caspians ( fa, کاسپیها, ''Kaspyn''; el, Κάσπιοι, ''Káspioi'';
The Caspians ( fa, کاسپیها, ''Kaspyn''; el, Κάσπιοι, ''Káspioi'';
Caspians
in ''
 The Caspians ( fa, کاسپیها, ''Kaspyn''; el, Κάσπιοι, ''Káspioi'';
The Caspians ( fa, کاسپیها, ''Kaspyn''; el, Κάσπιοι, ''Káspioi''; Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated i ...
: ܟܣܦܝ, ''kspy''; xcl, Կասպք, ''Kaspk’''; la, Caspi, ''Caspiani'') were a people of antiquity
Antiquity or Antiquities may refer to:
Historical objects or periods Artifacts
*Antiquities, objects or artifacts surviving from ancient cultures
Eras
Any period before the European Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries) but still within the histo ...
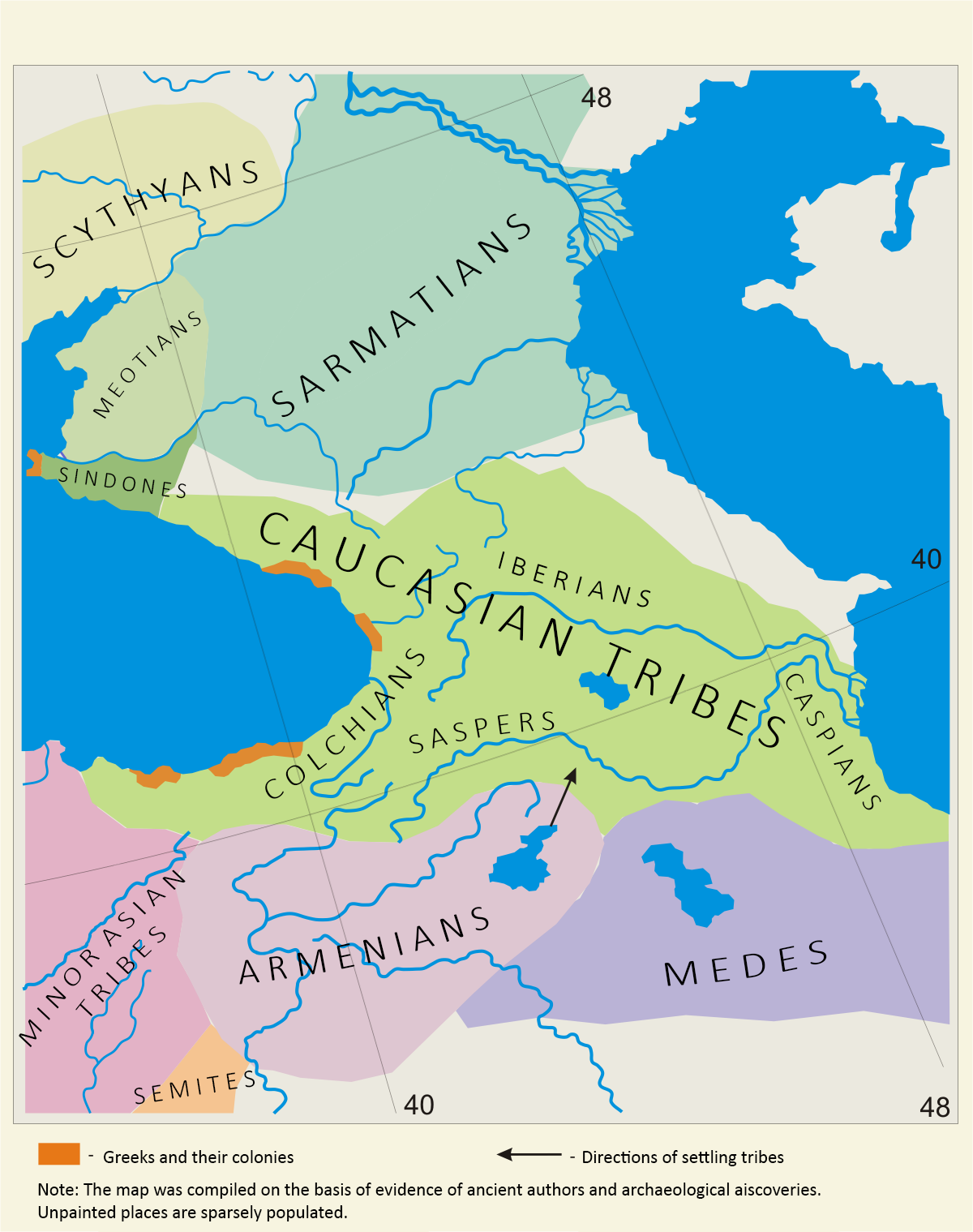
who dwelt along the southwestern shores of the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central A ...
, in the region known as Caspiane Caspiane or Kaspiane ( gr, Κασπιανή, hy, Կասպք ''Kaspkʿ'') was the land populated by the tribe of Caspians, after whom it received its name. Originally a province of the Medes in the 3rd-2nd centuries BC, the land of the Caspians was ...
. ''Caspian'' is the English version of the Greek ethnonym
An ethnonym () is a name applied to a given ethnic group. Ethnonyms can be divided into two categories: exonyms (whose name of the ethnic group has been created by another group of people) and autonyms, or endonyms (whose name is created and us ...
''Kaspioi'', mentioned twice by Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known fo ...
among the Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with cons ...
ies of Darius the Great
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his d ...
and applied by Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
. The name is not attested in Old Iranian
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian languages are grouped ...
.Rüdiger SchmittCaspians
in ''
Encyclopedia Iranica
An encyclopedia (American English) or encyclopædia (British English) is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge either general or special to a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles ...
''. Accessed on 4 April 2010.
The Caspians have generally been regarded as a pre-Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Du ...
people. They have been identified by Ernst Herzfeld
Ernst Emil Herzfeld (23 July 1879 – 20 January 1948) was a German archaeologist and Iranologist.
Life
Herzfeld was born in Celle, Province of Hanover. He studied architecture in Munich and Berlin, while also taking classes in Assyriology, a ...
with the Kassites
The Kassites () were people of the ancient Near East, who controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire c. 1531 BC and until c. 1155 BC (short chronology).
They gained control of Babylonia after the Hittite sack of Babylo ...
, who spoke a language not identified with any other known language group and whose origins have long been the subject of debate. However, onomastic
Onomastics (or, in older texts, onomatology) is the study of the etymology, history, and use of proper names. An '' orthonym'' is the proper name of the object in question, the object of onomastic study.
Onomastics can be helpful in data mining, ...
evidence bearing on this point has been discovered in Aramaic papyri
Hebrew and Aramaic papyri have increasingly been discovered from the 1960s onwards, although these papyri remain rare compared to papyri written in Koine Greek and Demotic Egyptian (no relation except in name, "popular," to modern demotic Greek). ...
from Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
published by P. Grelot, in which several of the Caspian names that are mentioned—and identified under the gentilic כספי ''kaspai''—are, in part, etymologically Iranian. The Caspians of the Egyptian papyri are therefore generally considered as either an Iranian people
Iranians or Iranian people may refer to:
* Iranian peoples, Indo-European ethno-linguistic group living predominantly in Iran and other parts of the Middle East and the Caucasus, as well as parts of Central Asia and South Asia
** Persians, Irania ...
or strongly under Iranian cultural influence.
In the 5th century BC, during the Persian rule in Egypt, a regiment (Aramaic ''degel'') of Caspians was stationed in Elephantine
Elephantine ( ; ; arz, جزيرة الفنتين; el, Ἐλεφαντίνη ''Elephantíne''; , ) is an island on the Nile, forming part of the city of Aswan in Upper Egypt. The archaeological sites on the island were inscribed on the UNESCO ...
, as attested in the Elephantine papyri
The Elephantine Papyri and Ostraca consist of thousands of documents from the Egyptian border fortresses of Elephantine and Aswan, which yielded hundreds of papyri and ostraca in hieratic and demotic Egyptian, Aramaic, Koine Greek, Latin and Co ...
. They are called ''kspy'' in Aramaic and shared their regiment with Khwarezmians, Bactrians
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southw ...
and other Iranian peoples
The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of Indo-European peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities.
The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate ...
. They were not the only garrison on Elephantine. There was also a regiment of Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
.
The Caspians are called ''Caspiani'' in Mela's ''De situ orbis'', ''Caspi'' in Pliny's '' Natural History'', and ''Caspiadae'' in Valerius Flaccus' ''Argonautica''. In the last work, the Caspians are allies of King Perses of Colchis
In Greek mythology, Perses (; grc, Πέρσης, Pérsēs, destroyer) is the brother of Aeëtes, Aloeus, Circe and Pasiphaë, which makes him a son of Helios, the god of the sun, by Perse, an Oceanid nymph.
Etymology
His name is derived fro ...
and appear amongst the Scythian peoples. They are said to have fighting dogs that they take to their graves. This might in fact reflect a variant of the Zoroastrian
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheisti ...
custom of sky burial
Sky burial (, "bird-scattered") is a funeral practice in which a human corpse is placed on a mountaintop to decompose while exposed to the elements or to be eaten by scavenging animals, especially carrion birds. It is a specific type of the ...
, one in which the deceased is left for the dogs to devour.
The Caspiadeans reappear in the medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
''Historia de via Hierosolymitana
The ''Historia de via Hierosolymitana'' is a Latin epic verse history of the First Crusade. Originally composed before 1120 as a work in five books by Gilo of Toucy, it was expanded by the addition of four more by an anonymous poet known as "F ...
'' among the people arrayed against the forces of the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic ...
(1096–1099). The anonymous poet, drawing on Flaccus, probably sought to connect the Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
, the Crusaders' actual enemy, with the ancient Scythians.Nicholas Morton, ''Encountering Islam on the First Crusade'' (Cambridge University Press, 2016), p. 203.
References
{{reflist, 2 Ancient history of Azerbaijan Ancient history of Iran Historical Iranian peoples Ancient peoples of Asia Ancient peoples of Europe History of Talysh