Carlos Menem on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Carlos Saúl Menem (2 July 1930 – 14 February 2021) was an Argentine lawyer and politician who served as the President of Argentina from 1989 to 1999. Ideologically, he identified as a
''Encyclopædia Britannica'' but later converted to
 Menem was elected governor of La Rioja in 1973 when the proscription of Peronism was lifted. He was deposed during the 1976 Argentine coup d'état that overthrew President Isabel Perón. He was accused of corruption and having links with the guerrillas of the
Menem was elected governor of La Rioja in 1973 when the proscription of Peronism was lifted. He was deposed during the 1976 Argentine coup d'état that overthrew President Isabel Perón. He was accused of corruption and having links with the guerrillas of the

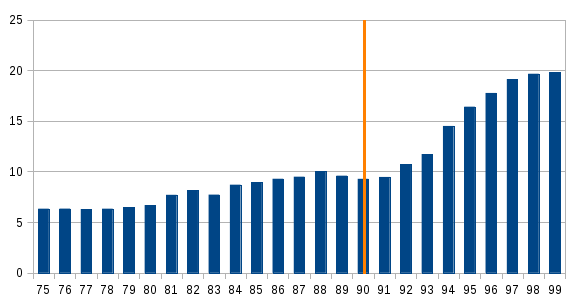 Hyperinflation forced Menem to abandon party
Hyperinflation forced Menem to abandon party  Although the Convertibility plan had positive consequences in the short term, it caused problems that surfaced later. Large numbers of employees of privatized state enterprises were fired, and unemployment grew to over 10%. Big compensation payments prevented an immediate public reaction. Free trade and the expensive costs in dollars forced private companies to reduce the number of workers as well, or risk bankruptcy. Unions were unable to resist the changes. People with low incomes, such as retirees and state workers, suffered under tax increases while their wages remained frozen. Some provinces, such as
Although the Convertibility plan had positive consequences in the short term, it caused problems that surfaced later. Large numbers of employees of privatized state enterprises were fired, and unemployment grew to over 10%. Big compensation payments prevented an immediate public reaction. Free trade and the expensive costs in dollars forced private companies to reduce the number of workers as well, or risk bankruptcy. Unions were unable to resist the changes. People with low incomes, such as retirees and state workers, suffered under tax increases while their wages remained frozen. Some provinces, such as
 The
The  Growing unemployment increased popular resistance against Menem after his re-election. There were several riots and demonstrations in the provinces, unions opposed the economic policies, and the opposing parties organized the first '' cacerolazos''.
Growing unemployment increased popular resistance against Menem after his re-election. There were several riots and demonstrations in the provinces, unions opposed the economic policies, and the opposing parties organized the first '' cacerolazos''.
 During Menem's presidency, Argentina aligned with the
During Menem's presidency, Argentina aligned with the
 Menem also settled all remaining border issues with
Menem also settled all remaining border issues with
 Argentina was still divided by the aftermath of the
Argentina was still divided by the aftermath of the
 The Israeli embassy suffered a terrorist car bomb attack on 17 March 1992. It was perceived as a consequence of Argentina's involvement in the
The Israeli embassy suffered a terrorist car bomb attack on 17 March 1992. It was perceived as a consequence of Argentina's involvement in the
 Menem ran in 2003 and won the greatest number of votes, 24%, in the first round of the 27 April 2003
Menem ran in 2003 and won the greatest number of votes, 24%, in the first round of the 27 April 2003 
 Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Collar of the Order of the Nile
* :
**
Collar of the Order of the Nile
* :
** First Class of the
First Class of the  Grand Cross of the Order of Vytautas the Great
* :
**
Grand Cross of the Order of Vytautas the Great
* :
** Knight Grand Cross with Collar
Knight Grand Cross with Collar  Collar of the Order of Manuel Amador Guerrero
* :
**
Collar of the Order of Manuel Amador Guerrero
* :
** Collar of the
Collar of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Collar of the
Collar of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Cordon of the Order of the Republic of
Grand Cordon of the Order of the Republic of  Medal of the Oriental Republic of Uruguay (1994).
* :
**
Medal of the Oriental Republic of Uruguay (1994).
* :
** Honorary Knight Grand Cross of the
Honorary Knight Grand Cross of the
Launch of new faction (from the BBC)Chile declines extradition request (from the BBC)Menem arrives on Argentine soil (from the BBC)Biography by CIDOB
(in Spanish) * {{DEFAULTSORT:Menem, Carlos Saul 1930 births 2021 deaths 20th-century Argentine politicians 20th-century Argentine writers 20th-century male writers 21st-century Argentine politicians Argentine Roman Catholics Argentine former Muslims Argentine anti-communists 20th-century Argentine lawyers Argentine male writers Argentine people of Syrian descent Argentine politicians convicted of corruption Articles containing video clips Converts to Roman Catholicism from Islam Deaths from kidney failure Governors of La Rioja Province, Argentina Heads of government who were later imprisoned Honorary Knights Grand Cross of the Order of St Michael and St George Infectious disease deaths in Argentina Justicialist Party politicians Members of the Argentine Senate for La Rioja
Peronist
Peronism, also called justicialism,. The Justicialist Party is the main Peronist party in Argentina, it derives its name from the concept of social justice., name=, group= is an Argentine political movement based on the ideas and legacy of A ...
and supported economically liberal
Economic liberalism is a political and economic ideology that supports a market economy based on individualism and private property in the means of production. Adam Smith is considered one of the primary initial writers on economic liberali ...
policies. He led Argentina as president during the 1990s and implemented a free market
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any ot ...
liberalization
Liberalization or liberalisation (British English) is a broad term that refers to the practice of making laws, systems, or opinions less severe, usually in the sense of eliminating certain government regulations or restrictions. The term is used m ...
. He served as President of the Justicialist Party
The Justicialist Party ( es, Partido Justicialista, ; abbr. PJ) is a major political party in Argentina, and the largest branch within Peronism.
Current president Alberto Fernández belongs to the Justicialist Party (and has, since 2021, serve ...
for thirteen years (from 1990 to 2001 and again from 2001 to 2003), and his political approach became known as Federal Peronism.
Born in Anillaco to a Syrian family, Menem was raised as a Muslim,"Carlos Menem"''Encyclopædia Britannica'' but later converted to
Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
to pursue a political career. Menem became a Peronist
Peronism, also called justicialism,. The Justicialist Party is the main Peronist party in Argentina, it derives its name from the concept of social justice., name=, group= is an Argentine political movement based on the ideas and legacy of A ...
during a visit to Buenos Aires. He led the party in his home province of La Rioja and was elected governor in 1973. He was deposed and detained during the 1976 Argentine coup d'état and was elected governor again in 1983. He defeated the Buenos Aires governor Antonio Cafiero
Antonio Francisco Cafiero (12 September 1922 – 13 October 2014) was an Argentine Justicialist Party politician. Cafiero held a number of important posts throughout his career, including, most notably, the governorship of Buenos Aires Province f ...
in the primary elections for the 1989 presidential elections. Hyperinflation and riots forced outgoing president Raúl Alfonsín to resign early, shortening the presidential transition.
Menem supported the Washington Consensus and tackled inflation with the Convertibility plan in 1991. The plan was complemented by a series of privatization
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
s and was initially a success. Argentina re-established diplomatic relations with the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, suspended since the 1982 Falklands War
The Falklands War ( es, link=no, Guerra de las Malvinas) was a ten-week undeclared war between Argentina and the United Kingdom in 1982 over two British dependent territories in the South Atlantic: the Falkland Islands and its territorial ...
, and developed special relations with the United States. The country suffered two terrorist attacks. The Peronist victory in the 1993 midterm elections allowed him to persuade Alfonsín (by then leader of the opposition party UCR) to sign the Pact of Olivos for the 1994 amendment of the Argentine Constitution
The 1994 amendment to the Constitution of Argentina was approved on 22 August 1994 by a Constitutional Assembly that met in the twin cities of Santa Fe and Paraná. The calling for elections for the Constitutional Convention and the main issues t ...
. This amendment allowed Menem to run for re-election in 1995, which he won. A new economic crisis began, and the opposing parties formed a political coalition winning the 1997 midterm elections and the 1999 presidential election.
He was investigated on various criminal and corruption charges, including illegal arms trafficking (he was sentenced to seven years in prison), embezzlement of public funds (he was sentenced four and half years to prison), extortion
Extortion is the practice of obtaining benefit through coercion. In most jurisdictions it is likely to constitute a criminal offence; the bulk of this article deals with such cases. Robbery is the simplest and most common form of extortion, ...
and bribery (in both of which he was declared innocent). His position as senator earned him immunity from incarceration.
Menem ran for the presidency again in 2003, but faced with a likely defeat in a ballotage against Néstor Kirchner, he chose to pull out, effectively handing the presidency to Kirchner. He was elected senator for La Rioja in 2005. By the time of his death in 2021 at age 90, he was the oldest living former Argentine president. He is regarded as a polarizing figure in Argentina, mostly due to corruption and economic mismanagement throughout his Presidency.
Early life and education
Carlos Saúl Menem was born on 2 July 1930 in Anillaco, a small town in the mountainous north of La Rioja Province, Argentina. His parents, Saúl Menem and Mohibe Akil, wereSyria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
n nationals from Yabroud who had emigrated to Argentina. He attended elementary and high school in La Rioja, and joined a basketball team during his university studies. He visited Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
in 1951 with the team, and met the president Juan Perón
Juan Domingo Perón (, , ; 8 October 1895 – 1 July 1974) was an Argentine Army general and politician. After serving in several government positions, including Minister of Labour and Vice President of a military dictatorship, he was elected ...
and his wife Eva Perón. This influenced Menem to become a Peronist
Peronism, also called justicialism,. The Justicialist Party is the main Peronist party in Argentina, it derives its name from the concept of social justice., name=, group= is an Argentine political movement based on the ideas and legacy of A ...
. He studied law at the National University of Córdoba, graduating in 1955.
After President Juan Perón's overthrow in 1955, Menem was briefly incarcerated. He later joined the successor to the Peronist Party, the Justicialist Party
The Justicialist Party ( es, Partido Justicialista, ; abbr. PJ) is a major political party in Argentina, and the largest branch within Peronism.
Current president Alberto Fernández belongs to the Justicialist Party (and has, since 2021, serve ...
''(Partido Justicialista)'' (PJ). He was elected president of its La Rioja Province chapter in 1973. In that capacity, he was included in the flight to Spain that brought Perón back to Argentina after his long exile. According to the Peronist politician Juan Manuel Abal Medina, Menem played no special part in the event.
Governor of La Rioja
1st term (1973–1976) and arrest
 Menem was elected governor of La Rioja in 1973 when the proscription of Peronism was lifted. He was deposed during the 1976 Argentine coup d'état that overthrew President Isabel Perón. He was accused of corruption and having links with the guerrillas of the
Menem was elected governor of La Rioja in 1973 when the proscription of Peronism was lifted. He was deposed during the 1976 Argentine coup d'état that overthrew President Isabel Perón. He was accused of corruption and having links with the guerrillas of the Dirty War
The Dirty War ( es, Guerra sucia) is the name used by the military junta or civic-military dictatorship of Argentina ( es, dictadura cívico-militar de Argentina, links=no) for the period of state terrorism in Argentina from 1974 to 1983 a ...
. He was detained on 25 March, kept for a week at a local barracks, and then moved to a temporary prison on the ship ''33 Orientales'' in Buenos Aires. He was detained alongside former ministers Antonio Cafiero
Antonio Francisco Cafiero (12 September 1922 – 13 October 2014) was an Argentine Justicialist Party politician. Cafiero held a number of important posts throughout his career, including, most notably, the governorship of Buenos Aires Province f ...
, Jorge Taiana, Miguel Unamuno, José Deheza, and Pedro Arrighi, the unionists Jorge Triaca, Diego Ibáñez, and Lorenzo Miguel, the diplomat Jorge Vázquez, the journalist Osvaldo Papaleo, and the former president Raúl Lastiri
Raúl Alberto Lastiri (11 September 1915 – 11 December 1978) was an Argentine politician who was interim president of Argentina from July 13, 1973 until October 12, 1973. Lastiri, who presided over the Argentine Chamber of Deputies, was promot ...
. He shared a cell with Pedro Eladio Vázquez, Juan Perón's personal physician. During this time he helped the chaplain Lorenzo Lavalle, despite still being a Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
. In July he was sent to Magdalena, to a permanent prison. His wife Zulema visited him every week, but rejected his conversion to Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. His mother died during the time he was a prisoner, and dictator Jorge Rafael Videla denied his request to attend her funeral. He was released on 29 July 1978, on the condition that he live in a city outside his home province without leaving it. He settled in Mar del Plata
Mar del Plata is a city on the coast of the Atlantic Ocean, in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. It is the seat of General Pueyrredón district. Mar del Plata is the second largest city in Buenos Aires Province. The name "Mar del Plata" is a sh ...
.
Menem met Admiral Eduardo Massera, who intended to run for president, and had public meetings with personalities such as Carlos Monzón, Susana Giménez
María Susana Giménez Aubert (born 29 January 1944), known as Susana Giménez (), is an Argentine TV host, actress, model and businesswoman. In 2012, she was considered the biggest celebrity in Argentine television by the media firm that pub ...
, and Alberto Olmedo. As a result, he was forced to reside in another city, Tandil. He had to report daily to Chief of Police Hugo Zamora. This forced residence was lifted in February 1980. He returned to Buenos Aires, and then to La Rioja. He resumed his political activities, despite the prohibition, and was detained again. His new forced residence was in Las Lomitas
Las Lomitas is a city in northern Argentina. It is located in the Patiño Department in the center of Formosa Province. It has a population of 12,399 inhabitants as of the . This represented a 20% increase in the population compared to the whic ...
in the province of Formosa
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is an island country located in East Asia. The main island of Taiwan, formerly known in the Western political circles, press and literature as Formosa, makes up 99% of the land area of the territori ...
. He was one of the last politicians to be released from prison by the National Reorganization Process.
2nd and 3rd terms (1983–1989)
Military rule ended in 1983, and the Radical Raúl Alfonsín was elected president. Menem ran for governor again and was elected by a clear margin. The province benefited from tax regulations established by the military, which allowed increased industrial growth. His party gained control of the provincial legislature, and he was re-elected in 1987 with 63% of the vote. The Partido Justicialista at the time was divided into two factions, the conservatives that still supported the political doctrines of Juan and Isabel Perón, and those who proposed a renovation of the party. The internal disputes ceased in 1987. Menem, with his prominent victory in his district, was one of the leading figures of the party and disputed its leadership.Presidential elections

Antonio Cafiero
Antonio Francisco Cafiero (12 September 1922 – 13 October 2014) was an Argentine Justicialist Party politician. Cafiero held a number of important posts throughout his career, including, most notably, the governorship of Buenos Aires Province f ...
, who had been elected governor of Buenos Aires Province, led the renewal of the Partido Justicialista, and was considered their most likely candidate for the presidency. Menem, on the other hand, was seen as a populist leader. Using a big tent
A big tent party, or catch-all party, is a term used in reference to a political party's policy of permitting or encouraging a broad spectrum of views among its members. This is in contrast to other kinds of parties, which defend a determined i ...
approach, he got support from several unrelated political figures. As a result, he defeated Cafiero in the primary elections. He sought alliances with Bunge and Born, union leaders, former members of Montoneros, and the AAA, people from the church, " Carapintadas", etc. He promised a "revolution of production" and huge wage increases, but it was not clear exactly which policies he was proposing. The rival candidate, Eduardo Angeloz, tried to point out the mistakes made by Menem and Alfonsín. Jacques de Mahieu, a French ideologue of the Peronist movement (and former Vichy
Vichy (, ; ; oc, Vichèi, link=no, ) is a city in the Allier department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of central France, in the historic province of Bourbonnais.
It is a spa and resort town and in World War II was the capital of ...
collaborator), was photographed campaigning for Menem. His campaign slogans were ''¡Siganme!'' (Follow me!) and ''¡No los voy a defraudar!'' (I won't let you down!)
The elections were held on 14 May 1989. Menem won by a wide margin, and became the president-elect of Argentina. He was scheduled to take office on 10 December, but inflation levels took a turn for the worse, growing into hyperinflation, causing public riots. The outgoing president Alfonsín resigned and transferred power to Menem five months early, on 8 July. Menem's accession marked the first time since Hipólito Yrigoyen
Juan Hipólito del Sagrado Corazón de Jesús Yrigoyen (; 12 July 1852 – 3 July 1933) was an Argentine politician of the Radical Civic Union and two-time President of Argentina, who served his first term from 1916 to 1922 and his second ...
took office in 1916 that an incumbent president peacefully transferred power to an elected successor from the opposition.Edwards, p. 162
Presidency
Economic policy
 Hyperinflation forced Menem to abandon party
Hyperinflation forced Menem to abandon party orthodoxy
Orthodoxy (from Greek: ) is adherence to correct or accepted creeds, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical councils in Antiquity, but different Church ...
in favour of a fiscally conservative, market-oriented economic policy.
At the time, most economists thought that the ideal solution was the Washington Consensus; i.e. reduce expenditures below the amount of money earned by the state, and open international commerce to free trade
Free trade is a trade policy that does not restrict imports or exports. It can also be understood as the free market idea applied to international trade. In government, free trade is predominantly advocated by political parties that hold econ ...
. Alfonsín had proposed similar reforms in the past, alongside some limited privatization
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
of state-owned enterprise
A state-owned enterprise (SOE) is a government entity which is established or nationalised by the ''national government'' or ''provincial government'' by an executive order or an act of legislation in order to earn profit for the governmen ...
s; those projects were resisted by the Partido Justicialistal opposition party, whose internal factions were actually benefiting from the prevailing protectionist policies.
The magnitude of the crisis, however, convinced most politicians to change their minds. Menem, fearing that the crisis might force him to resign as well, embraced the Washington Consensus and rejected the traditional policies of Peronism.
The president invited several conservative figures into his cabinet, such as Álvaro Alsogaray
Álvaro Carlos Alsogaray (22 June 1913 – 1 April 2005) was an Argentine politician and economist. He was Minister of Economy and was the principal proponent of classical liberalism in Argentina.
He founded the Union of the Democratic Cen ...
, as well as a businessman from Bunge and Born; Miguel Roig, the company's then-vice president, became Menem's first appointed minister of economy
A finance minister is an executive or cabinet position in charge of one or more of government finances, economic policy and financial regulation.
A finance minister's portfolio has a large variety of names around the world, such as "treasury", ...
on 30 May, although he would be replaced just five days after taking office due to his sudden death by myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which ma ...
; in his place was appointed Néstor Mario Rapanelli, who had succeeded Roig as vice president at Bunge and Born.
Congress passed the economic emergency and state reform laws. The first allowed president Menem to reduce or remove subsidies at his discretion, and the latter to privatize state enterprises – the first being telephones and airlines. These privatizations were beneficial to foreign creditors, who replaced their bonds with company shares.Romero, p. 289 Despite increased tax revenue and the money gained from privatizations, the economy was still unstable. The Bunge and Born businessmen left the government in late 1989, amid a second round of hyperinflation.
The first measure of the new minister of economy, Antonio Erman González
Antonio Erman González (16 May 1935 – 2 February 2007) was an Argentinian politician. He occupied many charges during the presidency of Carlos Menem, like Minister of Economy, Minister of Health, Minister of Defense, Minister of Labour and Pr ...
, was a mandatory conversion of time deposits into government bonds: the BONEX plan. It exacerbated the recession but was successful in reducing the inflation rate, which was its intended purpose.Edwards, p. 103Romero, p. 290 González also lowered social welfare spending, including that for people with disabilities.
His fourth minister of economy, Domingo Cavallo, was appointed in 1991 and deepened the liberalization
Liberalization or liberalisation (British English) is a broad term that refers to the practice of making laws, systems, or opinions less severe, usually in the sense of eliminating certain government regulations or restrictions. The term is used m ...
of the economy. The Convertibility plan was sanctioned by Congress, setting a one-to-one fixed exchange rate between the United States dollar
The United States dollar ( symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the officia ...
and the new peso
The peso is the monetary unit of several countries in the Americas, and the Philippines. Originating in the Spanish Empire, the word translates to "weight". In most countries the peso uses the same sign, "$", as many currencies named " doll ...
, which replaced the austral. The law also limited public expenditures, but this was frequently ignored. Under Cavallo, there was increased free trade
Free trade is a trade policy that does not restrict imports or exports. It can also be understood as the free market idea applied to international trade. In government, free trade is predominantly advocated by political parties that hold econ ...
, alongside a general reduction of tariff
A tariff is a tax imposed by the government of a country or by a supranational union on imports or exports of goods. Besides being a source of revenue for the government, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and p ...
s on imports and state regulations to tackle inflation, and high taxes on sales and earnings to reduce the deficit caused by it. Initially, the plan was a success: the capital flight ended, interest rates were lowered, inflation fell to single digits, and economic activity increased; in that year alone, the gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is of ...
grew at a rate of 10.5%.
The money from privatizations allowed Argentina to repurchase many of the Brady Bonds issued during the crisis. The privatizations of electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as describe ...
, water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
, and gas services were more successful than previous ones. YPF, the national oil refinery, was partially privatized as well, with the state keeping a good portion of its shares. The project to privatize the pension fund
A pension fund, also known as a superannuation fund in some countries, is any plan, fund, or scheme which provides retirement income.
Pension funds typically have large amounts of money to invest and are the major investors in listed and priva ...
s was resisted in Congress and was approved as a mixed system that allowed both public and private options for workers. The national state also signed a fiscal pact with the provinces, so that they reduced their local deficits as well; Buenos Aires Province
Buenos Aires (), officially the Buenos Aires Province (''Provincia de Buenos Aires'' ), is the largest and most populous Argentine province. It takes its name from the city of Buenos Aires, the capital of the country, which used to be part of th ...
was aided with a fund that gave the governor a million pesos daily.
 Although the Convertibility plan had positive consequences in the short term, it caused problems that surfaced later. Large numbers of employees of privatized state enterprises were fired, and unemployment grew to over 10%. Big compensation payments prevented an immediate public reaction. Free trade and the expensive costs in dollars forced private companies to reduce the number of workers as well, or risk bankruptcy. Unions were unable to resist the changes. People with low incomes, such as retirees and state workers, suffered under tax increases while their wages remained frozen. Some provinces, such as
Although the Convertibility plan had positive consequences in the short term, it caused problems that surfaced later. Large numbers of employees of privatized state enterprises were fired, and unemployment grew to over 10%. Big compensation payments prevented an immediate public reaction. Free trade and the expensive costs in dollars forced private companies to reduce the number of workers as well, or risk bankruptcy. Unions were unable to resist the changes. People with low incomes, such as retirees and state workers, suffered under tax increases while their wages remained frozen. Some provinces, such as Santiago del Estero
Santiago del Estero (, Spanish for ''Saint-James-Upon-The-Lagoon'') is the capital of Santiago del Estero Province in northern Argentina. It has a population of 252,192 inhabitants, () making it the twelfth largest city in the country, with a surf ...
, Jujuy
San Salvador de Jujuy (), commonly known as Jujuy and locally often referred to as San Salvador, is the capital and largest city of Jujuy Province in northwest Argentina. Also, it is the seat of the Doctor Manuel Belgrano Department. It lies ne ...
, and San Juan San Juan, Spanish for Saint John, may refer to:
Places Argentina
* San Juan Province, Argentina
* San Juan, Argentina, the capital of that province
* San Juan, Salta, a village in Iruya, Salta Province
* San Juan (Buenos Aires Underground), ...
, endured violent riots as well. To compensate for these issues, the government started a number of social welfare programs and restored protectionist policies over some sectors of the economy. It was difficult for Argentine companies to export, and easy imports damaged most national producers. The national budget soon slid into a deficit.
Cavallo soon began the second wave of privatizations, this time targeting the national postal service, the Correo Argentino, and the country's nuclear power plants. He also limited the amount of money released to the provinces. He still had the full support of Menem, despite growing opposition within the Justicialist Party.
The Mexican Tequila Crisis of 1994 impacted the national economy, causing the deficit, recession, and a growth in unemployment. The government further reduced public expenditures, the wages of state workers, and raised taxes. The deficit and recession were reduced, but unemployment stayed high. External debt increased. The crisis also proved that the economic system was vulnerable to capital flight.
The growing discontent over unemployment and the scandals caused by the privatization of the postal service led to Cavallo's removal as a minister, and his replacement by Roque Fernández
Roque Benjamín Fernández (born April 30, 1947) is an Argentine economist, former President of the Central Bank and Minister of Economy, and the only member of the Chicago Boys ever to have been the chief economic policy maker in Argentina.
...
.Romero, pp. 308–309 Fernández maintained Cavallo's fiscal austerity
Austerity is a set of political-economic policies that aim to reduce government budget deficits through spending cuts, tax increases, or a combination of both. There are three primary types of austerity measures: higher taxes to fund spend ...
; he increased the price of fuels, sold the remaining state shares of YPF to Repsol, fired state employees, and raised the value-added tax to 21%. New labor law was met with resistance, both by Peronists, opposition parties, and unions, and could not be approved by Congress.
The 1997 Asian financial crisis
The Asian financial crisis was a period of financial crisis that gripped much of East Asia and Southeast Asia beginning in July 1997 and raised fears of a worldwide economic meltdown due to financial contagion. However, the recovery in 1998– ...
and the 1998 Russian financial crisis
The Russian financial crisis (also called the ruble crisis or the Russian flu) began in Russia on 17 August 1998. It resulted in the Russian government and the Russian Central Bank devaluing the ruble and defaulting on its debt. The crisis had ...
also affected the country with consequences that lasted longer than the Tequila Crisis and started a depression.
Domestic policy
Menem began his presidency assuming a non-confrontational approach, appointing people from the conservative opposition, and business people to his cabinet. To prevent successful legal cases against the projected privatizations, theSupreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
's numbers were increased from five to nine judges; the new judges ruled in support of Menem and usually had the majority. Other institutions that restrained or limited executive power were controlled as well. When Congress resisted some of his proposals, he used the Necessity and Urgency Decree as an alternative to sending bills to it. He even considered it feasible to dissolve Congress and rule by decree, but this step was never implemented. In addition, he developed a ''bon vivant'' lifestyle, taking advantage of his authority. For instance, he made a journey from Buenos Aires to Pinamar driving a Ferrari Testarossa in less than two hours, violating speed limits. He divorced his wife Zulema Yoma and expanded the Quinta de Olivos presidential residence with a golf course, a small zoo, servants, a barber, and even a buffoon.
 The
The swiftgate
"Swiftgate" was the name given to a 1991 corruption scandal in Argentina during the presidency of Carlos Menem.
Background
Swift, an American food processing company, wanted to apply for a grant to keep open its facilities in the province of Sant ...
scandal broke out in 1990, as American investors were damaged by a case of corruption, and asked for assistance from the United States' Ambassador Terence Todman. Most of the ministers resigned as a result of it. Cavallo was reassigned as minister of economy, and his successful economic plan turned him into a prominent figure in Menem's cabinet. Cavallo brought a number of independent economists to the cabinet, and Menem supported him by replacing Peronist politicians. Both teams complemented each other. Both Menem and Cavallo tried to be recognized as the designer of the convertibility plan.
Antonio Cafiero
Antonio Francisco Cafiero (12 September 1922 – 13 October 2014) was an Argentine Justicialist Party politician. Cafiero held a number of important posts throughout his career, including, most notably, the governorship of Buenos Aires Province f ...
, a rival of Menem in the Partido Justicialistal, was unable to amend the constitution of the province of Buenos Aires to run for re-election. Duhalde stepped down from the vice presidency and became the new governor in the 1991 elections, turning the province into a powerful bastion. Menem also selected famous people with no political background to run for office in those elections, including the singer Palito Ortega
Ramón Bautista Ortega (; born February 28, 1941) is an Argentine singer and actor, better known as Palito Ortega (). Ortega is an icon of Argentine popular music, and is considered one of the main representatives of the musical style called N ...
and racing driver Carlos Reutemann. The elections were a big success for the Partido Justicialistal, . After these elections, all of the Partido Justicialistal, was aligned with Menem's leadership, with the exception of a small number of legislators known as the "Group of Eight". The opposition from the UCR was minimal, as the party was still discredited by the 1989 crisis. With such political influence, Menem began his proposal to amend the constitution to allow a re-election. The party did not have the required supermajority in the Congress to call for it. The Partido Justicialistal was divided, as other politicians intended to replace Menem in 1995 or negotiate their support. The UCR was divided as well, as Alfonsín opposed the proposal, but governors Angeloz and Massaccesi were open for negotiations. The victory in the 1993 elections strengthened his proposal, which was approved by the Senate. Menem called for a non-binding referendum on the proposal, to increase pressure on the Radical deputies. He also sent a bill to Congress to modify the majority requirements. Alfonsín met with Menem and agreed to support the proposal in exchange for amendments that would place limits on presidential power. This negotiation is known as the Pact of Olivos. The capital city of Buenos Aires would be allowed to elect its own chief of government. Presidential elections would use a system of ballotage, and the president could only be re-elected once. The electoral college was abolished, replaced by direct elections. The provinces would be allowed to elect a third senator; two for the majority party and one for the first minority. The Council of Magistracy of the Nation would have the power to propose new judges, and the Necessity and Urgency Decrees would have a reduced scope.
Despite the internal opposition of Fernando de la Rúa, Alfonsín got his party to approve the pact. He reasoned that Menem would be supported by the eventual referendum, that many legislators would turn to his side, and he would eventually be able to amend the constitution reinforcing presidential power rather than limiting it. Still, as both sides feared a betrayal, all the contents of the pact were included as a single proposal, not allowing the Constituent Assembly to discuss each one separately. The Broad Front, a new political party composed of former Peronists, led by Carlos Álvarez, grew in the elections for the Constituent Assembly. Both the Partido Justicialistal, and the UCR respected the pact, which was completely approved. Duhalde made a similar amendment to the constitution of Buenos Aires province, in order to be re-elected in 1995. Menem won the elections with more than 50% of the vote, followed by José Octavio Bordón
José Octavio Bordón (born 22 December 1945) is an Argentine politician and diplomat. He was governor of Mendoza Province from 1987 to 1991, and served in both houses of the National Congress as a National Deputy and a National Senator. Most ...
, and Carlos Álvarez. The UCR finished third in the elections for the first time.
 Growing unemployment increased popular resistance against Menem after his re-election. There were several riots and demonstrations in the provinces, unions opposed the economic policies, and the opposing parties organized the first '' cacerolazos''.
Growing unemployment increased popular resistance against Menem after his re-election. There were several riots and demonstrations in the provinces, unions opposed the economic policies, and the opposing parties organized the first '' cacerolazos''. Estanislao Esteban Karlic
Estanislao Esteban Karlic (born 7 February 1926) is an Argentine cardinal of the Catholic Church. He served as Archbishop of Paraná from 1986 to 2003, and was elevated to the cardinalate in 2007.
Biography
Estanislao Karlic was born in Oliva ...
replaced Antonio Quarracino as the head of the Argentine Episcopal Conference The Argentine Episcopal Conference ( es, Conferencia Episcopal Argentina) is an episcopal conference of the Roman Catholic Church of Argentina that gathers the bishops of the country in order to discuss pastoral issues and in general all matters tha ...
, which led to a growing opposition to Menem from the Church. The teachers' unions established a "white tent" at the Congressional plaza as a form of protest. The first '' piqueteros'' operated in Cutral Có
Cutral Có is a city in the Confluencia Department of Neuquén Province in Argentina. It is part of the statistical area formed with neighboring Plaza Huincul.
The settlement is located in the desert, it was founded in 1933 after the discovery of ...
, and this protest method was soon imitated in the rest of the country. Menem's authority in the Partido Justicialistal, was also held in doubt, as he was unable to run for another re-election and the party sought a candidate for the 1999 elections. This led to a fierce rivalry with Duhalde, the most likely candidate. Menem attempted to undermine his chances, and proposed a new amendment to the constitution allowing him to run for an unlimited number of re-elections. He also started a judicial case, claiming that his inability to run for a third term was a proscription. Several scandals erupted, such as the scandal over Argentine arms sales to Ecuador and Croatia, the Río Tercero explosion that may have destroyed evidence, the murder of the journalist José Luis Cabezas, and the suicide of Alfredo Yabrán, who may have ordered it. The Partido Justicialistal, lost the 1997 midterm elections against the UCR and the FREPASO united in a political coalition, the Alliance for Work, Justice and Education (Alianza). The Supreme Court confirmed that Menem was unable to run for a third re-election. Duhalde became the candidate for the presidential elections, and lost to the candidate for the Alianza ticket, Fernando de la Rúa.
Foreign policy
 During Menem's presidency, Argentina aligned with the
During Menem's presidency, Argentina aligned with the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, and had special relations with the country. Menem had good relations with U.S. president George H. W. Bush, and his successor Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and again ...
from 1993 on.
The country left the Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 120 countries that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. After the United Nations, it is the largest grouping of states worldwide.
The movement originated in the aftermath ...
, and the Cóndor missile program was discontinued. Argentina supported all the international positions of the U.S., and sent forces to the Gulf War
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Iraq were carried out in two key phases: ...
, and the peace keeping efforts after the Kosovo War
The Kosovo War was an armed conflict in Kosovo that started 28 February 1998 and lasted until 11 June 1999. It was fought by the forces of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (i.e. Serbia and Montenegro), which controlled Kosovo before the war ...
.Romero, p. 303
The country was accepted as a major non-NATO ally
Major non-NATO ally (MNNA) is a designation given by the United States government to close allies that have strategic working relationships with the US Armed Forces but are not members of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). While the s ...
, but not as a full member.
Menem's government re-established relations with the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, suspended since the Falklands War
The Falklands War ( es, link=no, Guerra de las Malvinas) was a ten-week undeclared war between Argentina and the United Kingdom in 1982 over two British dependent territories in the South Atlantic: the Falkland Islands and its territorial ...
, after Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher (; 13 October 19258 April 2013) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 1975 to 1990. She was the first female British prime ...
left office in 1990. The discussions on the Falkland Islands sovereignty dispute were temporarily given a lower priority, and the focus shifted to discussions of fishing rights.
In 1991 Menem became the first head of state of Argentina to make a diplomatic visit to Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
. He proposed mediating between Israel and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
in their negotiations over the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
. The diplomatic relations between Argentina and Israel were later damaged by the lack of results in the investigations over the terrorist attacks against the Israeli embassy and the AMIA center in Buenos Aires.
In 1998, Menem visited Russia, and met with Russian president Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin ( rus, Борис Николаевич Ельцин, p=bɐˈrʲis nʲɪkɐˈla(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈjelʲtsɨn, a=Ru-Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin.ogg; 1 February 1931 – 23 April 2007) was a Soviet and Russian politician wh ...
, where Menem expressed his anticommunist sentiments and congratulated Yeltsin for "defeating communism" in Russia.
Chile
 Menem also settled all remaining border issues with
Menem also settled all remaining border issues with Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
. The Lago del Desierto dispute had an international arbitration, favourable to Argentina. The only exception was the dispute over the Southern Patagonian Ice Field, which is still open.
Previously and contrary to other Peronist authorities, Menem voted for the Treaty of Peace and Friendship of 1984 between Chile and Argentina
The Treaty of Peace and Friendship of 1984 between Chile and Argentina ( es, Tratado de Paz y Amistad de 1984 entre Chile y Argentina, see the text in thUnited Nations was signed into agreement at the Vatican on 29 November 1984.
It was ratified ...
. Chilean president Patricio Aylwin was at first sceptical towards his Argentine counterpart whom he according to Emol considered "scruffy" ( es, destartalado). Over time however Aylwin changed his opinion, saying at one point "this Turk
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic o ...
wins everybody over" (''este turco se los conquista a todos''). Aylwin's successor, Eduardo Frei Ruiz-Tagle, had particularly warm relations with Menem. Former Chilean foreign minister José Miguel Insulza recalls of meetings with Menem and Eduardo Frei Ruiz-Tagle in Anillaco in the 1990s where they enjoyed talking about politics and football. All of this made the critics of Menem label him "pro-Chilean". President of Chile Sebastián Piñera posthumously called him "a good friend of Chile". Similarly, José Miguel Insulza called Menem "one of the best friends of Chile".
Armed forces
 Argentina was still divided by the aftermath of the
Argentina was still divided by the aftermath of the Dirty War
The Dirty War ( es, Guerra sucia) is the name used by the military junta or civic-military dictatorship of Argentina ( es, dictadura cívico-militar de Argentina, links=no) for the period of state terrorism in Argentina from 1974 to 1983 a ...
(the dirty war ended in 1983, Menem's presidency began in 1989). Menem proposed an agenda of national reconciliation. First, he arranged the repatriation
Repatriation is the process of returning a thing or a person to its country of origin or citizenship. The term may refer to non-human entities, such as converting a foreign currency into the currency of one's own country, as well as to the pro ...
of the body of Juan Manuel de Rosas, a controversial 19th century governor, and proposed to reconcile his legacy with those of Bartolomé Mitre
Bartolomé Mitre Martínez (26 June 1821 – 19 January 1906) was an Argentine statesman, soldier and author. He was President of Argentina from 1862 to 1868 and the first president of unified Argentina.
Mitre is known as the most versatile s ...
and Domingo Faustino Sarmiento, who also fought in the Argentine Civil Wars
The Argentine Civil Wars were a series of civil conflicts of varying intensity that took place through the territories of Argentina from 1814 to 1853. Initiation concurrently with the Argentine War of Independence (1810–1820), the conflict p ...
. Menem intended to use the reconciliation of these historical Argentine figures as a metaphor for the reconciliation of the Dirty War. However, although the repatriation and acceptance of Rosas was a success, the acceptance of the military regime was not.
The military leaders of the National Reorganization Process, convicted in the 1985 Trial of the Juntas
The Trial of the Juntas ( es, Juicio a las Juntas) was the judicial trial of the members of the ''de facto'' military government that ruled Argentina during the dictatorship of the Proceso de Reorganización Nacional (''el proceso''), which last ...
, received presidential pardons, despite popular opposition to them. This was an old request of the '' Carapintadas'' in previous years. However, Menem did not apply their proposed changes to the military. The colonel, Mohamed Alí Seineldín, who was also pardoned, started a new mutiny, killing two military men. Unlike the mutinies that took place during the presidency of Alfonsín, the military fully obeyed Menem's orders for a forceful repression. Seineldín was utterly defeated, and sentenced to life imprisonment. This was the last military mutiny in Argentina.
The president effected drastic cuts to the military budget, and privatized military factories. Menem appointed Lt. Gen. Martín Balza, who had performed well during the repression of Seineldín's mutiny, as the Army's General Chief of Staff (head of the military hierarchy). The death of a conscript soldier in 1994, victim of abuses by his superiors, led to the abolition of conscription in the country. The following year, Balza voiced the first institutional self-criticism of the armed forces during the Dirty War, saying that obedience did not justify the actions committed in those years.
Terrorist attacks
Gulf War
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Iraq were carried out in two key phases: ...
. Although Hezbollah claimed responsibility for it, the Supreme Court investigated several other hypotheses. The Court wrote a report in 1996 suggesting that it could have been the explosion of an arms cache stored in the basement. Another hypothesis was that the attack could have been performed by Jewish extremists, in order to cast blame on Muslims and thwart the peace negotiations. The Court finally held Hezbollah responsible for the attack in May 1999.
The Argentine Israelite Mutual Association suffered a terrorist attack with another car bomb
A car bomb, bus bomb, lorry bomb, or truck bomb, also known as a vehicle-borne improvised explosive device (VBIED), is an improvised explosive device designed to be detonated in an automobile or other vehicles.
Car bombs can be roughly divided ...
on 18 July 1994, killing eighty-five people. It was the most destructive terrorist attack in the history of Latin America. The attack was universally condemned and 155,000 people demonstrated at the Congressional plaza, but Menem did not attend.Ruggiero, p. 90 The legal case stayed unresolved during the remainder of Menem's presidency. Menem had suggested, in the first press conference, that former ''Carapintada'' leaders may be responsible for the attack, but this idea was rejected by the minister of defense several hours later. The CIA
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
office in Buenos Aires initially considered it a joint Iranian-Syrian attack, but some days later considered it just an Iranian attack. Menem and Mossad also preferred this line of investigation. As a result of the attack, the Jewish community in Argentina had increased influence over Argentine politics. Years later, the prosecutor Alberto Nisman
Natalio Alberto Nisman (5 December 1963 – 18 January 2015) was an Argentine lawyer who worked as a federal prosecutor, noted for being the chief investigator of the 1994 car bombing of a Jewish center in Buenos Aires, which killed 85 people, th ...
charged Menem with covering up a local connection to the attack, as the local terrorists may have been distant Syrian relatives of the Menem family. However, Menem was never tried for this suspected cover-up, and on 18 January 2015, Nisman was found dead of a gunshot to his head at his home in Buenos Aires.
On 15 March 1995, Menem's son died while piloting a Bell 206B-3 helicopter, along with Silvio Oltra who was riding as a passenger. The helicopter reportedly struck overhead power lines
An overhead power line is a structure used in electric power transmission and distribution to transmit electrical energy across large distances. It consists of one or more uninsulated electrical cables (commonly multiples of three for three-ph ...
near Ramallo in the north of the province of Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
and crashed, killing both men. Later on, remains of Menem Jr. were exhumed amid murder claims by his mother Zulema Yoma. Menem had accused the Lebanese Shia
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mos ...
Islamist group, Hezbollah, of killing his son.
Post-presidency
 Menem ran in 2003 and won the greatest number of votes, 24%, in the first round of the 27 April 2003
Menem ran in 2003 and won the greatest number of votes, 24%, in the first round of the 27 April 2003 presidential election
A presidential election is the election of any head of state whose official title is President.
Elections by country
Albania
The president of Albania is elected by the Assembly of Albania who are elected by the Albanian public.
Chile
The p ...
; but votes were split among numerous parties. Under the 1994 amendment, a presidential candidate can win outright by winning 45% of the vote, or 40% if the margin of victory is 10 or more percentage points. This set the stage for Argentina's first-ever ballotage between Menem and second-place finisher, and fellow Peronist, Néstor Kirchner, who had received 22%. It was scheduled for 18 May. However, by that time, Menem had become very unpopular. Polls predicted that he faced almost certain defeat by Kirchner in the runoff. Most polls showed Kirchner taking at least 60 percent of the vote, and at least one poll showed Menem losing by as many as 50 points. To avoid a humiliating defeat, Menem withdrew his candidacy on 14 May, effectively handing the presidency to Kirchner.

Ángel Maza
Ángel Eduardo Maza (born 18 December 1954) is an Argentine Justicialist Party (PJ) politician. He was the governor of La Rioja Province during several terms, until he was ousted by impeachment in 2007. His sister, Ada Maza, is a national senator. ...
, the elected governor of La Rioja, was allied with Menem, and had campaigned for him. However, weak provincial finances forced Maza to switch his support to Kirchner, which weakened Menem's influence even further. In June 2004 Menem announced that he had founded a new faction within the Partido Justicialista, called "People's Peronism". He announced his intention to run in the 2007 election. In 2005, the press reported that he was trying to form an alliance with his former minister of economy Cavallo to fight in the parliamentary elections. Menem said that there had been only preliminary conversations and an alliance did not result. In the 23 October 2005 elections, Menem won the minority seat in the Senate representing his province of birth. The two seats allocated to the majority were won by President Kirchner's faction, locally led by Ángel Maza.
Menem ran for Governor of La Rioja in August 2007, but was defeated. He finished in third place with about 22% of the vote. This was viewed as a catastrophic defeat, signaling the end of his political dominance in La Rioja. It was the first time in 30 years that Menem had lost an election. Following this defeat in his home province, he withdrew his candidacy for president. At the end of 2009 he announced that he intended to run for the presidency again in the 2011 elections. but ran for a new term as a senator instead. In 2019, he eventually sat in the Frente de Todos' Senatebench until his death in 2021.
Corruption charges
On 7 June 2001, Menem was arrested over a weapons export scandal. The scheme was based on exports toEcuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
and Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = " Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capi ...
in 1991 and 1996. He was held under house arrest until November. He appeared before a judge in late August 2002 and denied all charges. Menem and his Chilean second wife Cecilia Bolocco
Cecilia Carolina Bolocco Fonck (born May 19, 1965) is a Chilean actress, TV host, and beauty queen who was crowned Miss Universo Chile 1987 and Miss Universe 1987.
Bolocco has worked as a journalist on the Spanish language edition of CNN, on ...
, who had had a child since their marriage in 2001, fled to Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
. Argentine judicial authorities repeatedly requested Menem's extradition to face embezzlement charges. This request was rejected by the Chilean Supreme Court as under Chilean law, people cannot be extradited for questioning. On 22 December 2004, after the arrest warrants were cancelled, Menem returned with his family to Argentina. He still faced charges of embezzlement and failing to declare illegal funds in a Swiss bank
Banking in Switzerland dates to the early eighteenth century through Switzerland's merchant trade and has, over the centuries, grown into a complex, regulated, and international industry. Banking is seen as emblematic of Switzerland, along wit ...
. He was declared innocent of those charges in 2013.
In August 2008, the BBC reported that Menem was under investigation for his role in the 1995 Río Tercero explosion, which is alleged to have been part of the weapons scandal involving Croatia and Ecuador. Following an Appeals Court ruling that found Menem guilty of aggravated smuggling, he was sentenced to seven years in prison on 13 June 2013, for his role in illegally smuggling weapons to Ecuador and Croatia; his position as senator earned him immunity from incarceration, and his advanced age (82) afforded him the possibility of house arrest. His minister of defence during the weapons sales, Oscar Camilión, was concurrently sentenced to five and a half years. Menem was scheduled to attend a trial on the matter in which he was charged with "indirect responsibility", on 24 February 2021; but died ten days before that.
In December 2008, the German multinational Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad.
The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', ''E ...
agreed to pay an $800 million fine to the United States government, and approximately €700 million to the German government, to settle allegations of bribery. The settlement revealed that Menem had received about US$2 million in bribes from Siemens in exchange for awarding the national ID card and passport production contract to Siemens; Menem denied the charges but nonetheless agreed to pay a fine.
On 1 December 2015, Menem was also found guilty of embezzlement, and sentenced four and half years to prison. Domingo Cavallo, his economy minister, and Raúl Granillo Ocampo, Menem's former minister of justice, also received prison sentences of more than three years for participating in the scheme, and were ordered to repay hundreds of thousands of pesos’ worth of illegal bonuses.
Illness and death
On 13 June 2020, Menem was hospitalized due to a severe case ofpneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severit ...
and placed in intensive care; he tested negative for COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quick ...
and was discharged on 29 June 2020, three days before his 90th birthday. On 15 December 2020, he was hospitalized again at the Los Arcos Sanatorium due to a urinary infection. On 24 December 2020, Menem was induced into coma after a kidney failure.
He died on 14 February 2021 at the Sanatorio Los Arcos in Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
from complications of urinary tract infection. The national government issued three days of national mourning
A national day of mourning is a day or days marked by mourning and memorial activities observed among the majority of a country's populace. They are designated by the national government. Such days include those marking the death or funeral of ...
, and had a public funeral at the Palace of the Argentine National Congress. It was attended by several politicians, including the president Alberto Fernández, and by hundreds of people. He was buried at the San Justo Islamic cemetery the following day, next to his son. His daughter confirmed that he had died as a Catholic, but he would be buried according to Muslim rites in the Islamic Cemetery to be with his family.
Although former presidents are meant to have a bust at the Hall of Busts of the Casa Rosada 8 years after they leave office, By the time of his death Menem never received such honor. Casa Rosada actually has a bust of Menem donated by artist Fernando Pugliese, but never disclosed it. President Alberto Fernández told Zulema Menem that the intention was to make a ceremony once Menem recovered from his health problems; unfortunately, he died.
Style and legacy
In the early days, Menem sported an image similar to the old '' caudillos'', such as Facundo Quiroga and Chacho Peñaloza. He groomed his sideburns in a similar style. His presidential inauguration was attended by several gauchos. Contrary to Peronist tradition, Menem did not prepare huge rallies in the Plaza de Mayo to address the people from the balcony of the Casa Rosada. Instead, he took full advantage ofmass media
Mass media refers to a diverse array of media technologies that reach a large audience via mass communication. The technologies through which this communication takes place include a variety of outlets.
Broadcast media transmit informati ...
, such as television.
Menem's administration was exalted by libertarians Javier Milei and Diego Giacomini in the late 2010s, after being strongly criticized during and by Kirchnerism. Some liberal economists such as José Luis Espert
José Luis Espert (born 21 November 1961) is an Argentine economist and politician. He is known to be one of the strongest supporters of economic liberalism in Argentina. Since the 2021 Argentine legislative election, he has been a Argentine Cha ...
and Alberto Benegas Lynch have also taken a critical approach towards Menem's presidency.
Honours
Foreign honours
* : ** Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the Grand Order of King Tomislav
The Grand Order of King Tomislav ( hr, Velered kralja Tomislava), or officially the Grand Order of King Tomislav with Sash and Great Morning Star (''Velered kralja Tomislava s lentom i Velikom Danicom''), is the highest state order of Croatia. It ...
* :
** Collar of the Order of the Nile
* :
**
Collar of the Order of the Nile
* :
** First Class of the
First Class of the Order of Jamaica
The Order of Jamaica is the fifth of the six orders in the Jamaican honours system. The Order was established in 1969, and it is considered the equivalent of a knighthood in the British honours system.
Membership in the Order can be conferred upon ...
* :
** Grand Cross of the Order of Vytautas the Great
* :
**
Grand Cross of the Order of Vytautas the Great
* :
**Order of Merit of the Italian Republic
The Order of Merit of the Italian Republic ( it, Ordine al Merito della Repubblica Italiana) is the senior Italian order of merit. It was established in 1951 by the second President of the Italian Republic, Luigi Einaudi.
The highest-rankin ...
(1992)
* :
** Honorary Recipient of the Order of the Crown of the Realm (1991).
* :
** Collar of the Order of Manuel Amador Guerrero
* :
**
Collar of the Order of Manuel Amador Guerrero
* :
** Collar of the
Collar of the Order of the Sun of Peru
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
* :
** Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the Order of Merit of the Republic of Poland
The Order of Merit of the Republic of Poland ( pl, Order Zasługi Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej) is a Polish order of merit created in 1974, awarded to persons who have rendered great service to Poland. It is granted to foreigners or Poles resident a ...
* :
**Order of Isabella the Catholic
The Order of Isabella the Catholic ( es, Orden de Isabel la Católica) is a Spanish civil order and honor granted to persons and institutions in recognition of extraordinary services to the homeland or the promotion of international relations a ...
* :
** Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the Order of Good Hope
The Order of Good Hope or Order of the Cape of Good Hope is a dormant order of merit of the Republic of South Africa.
History
The Order of Good Hope was founded in 1973, by the republican government of South Africa, to grant those who had disti ...
* :
** Grand Cordon of the Order of the Republic of
Grand Cordon of the Order of the Republic of Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
(1997)
*:
** Medal of the Oriental Republic of Uruguay (1994).
* :
**
Medal of the Oriental Republic of Uruguay (1994).
* :
**Order of St Michael and St George
The Most Distinguished Order of Saint Michael and Saint George is a British order of chivalry founded on 28 April 1818 by George IV, Prince of Wales, while he was acting as prince regent for his father, King George III.
It is named in honour ...
(1998).
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * *External links
Launch of new faction (from the BBC)
(in Spanish) * {{DEFAULTSORT:Menem, Carlos Saul 1930 births 2021 deaths 20th-century Argentine politicians 20th-century Argentine writers 20th-century male writers 21st-century Argentine politicians Argentine Roman Catholics Argentine former Muslims Argentine anti-communists 20th-century Argentine lawyers Argentine male writers Argentine people of Syrian descent Argentine politicians convicted of corruption Articles containing video clips Converts to Roman Catholicism from Islam Deaths from kidney failure Governors of La Rioja Province, Argentina Heads of government who were later imprisoned Honorary Knights Grand Cross of the Order of St Michael and St George Infectious disease deaths in Argentina Justicialist Party politicians Members of the Argentine Senate for La Rioja
Carlos
Carlos may refer to:
Places
;Canada
* Carlos, Alberta, a locality
;United States
* Carlos, Indiana, an unincorporated community
* Carlos, Maryland, a place in Allegany County
* Carlos, Minnesota, a small city
* Carlos, West Virginia
;Elsewhere ...
National University of Córdoba alumni
Opposition to Fidel Castro
People from La Rioja Province, Argentina
Presidents of Argentina
Prisoners and detainees of Argentina
Recipients of the Medal of the Oriental Republic of Uruguay
Recipients of the Order of Prince Yaroslav the Wise, 1st class