Calvary on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Calvary ( la, Calvariae or ) or Golgotha ( grc-gre, Γολγοθᾶ, ''Golgothâ'') was a site immediately outside
Calvary ( la, Calvariae or ) or Golgotha ( grc-gre, Γολγοθᾶ, ''Golgothâ'') was a site immediately outside
Lucas 23:33
( Thorpe ed.) ''Caluerie'', and ''Calueri'' which were later standardized as ''Calvary''. While the Gospels merely identify Golgotha as a "place",Maththaion 27:33
(Greek) Iōanēn 19:17
(Greek) ''Golgathân'' (),NestleMarkon 15:22
(Greek) ''kraníou tópos'' (), ''Kraníou tópos'' (), ''Kraníon'' (),NestleLoukan 23:33
(Greek) and ''Kraníou tópon'' (). Golgotha's
in German television ZDF, April 11, 2007
/ref>
 The traditional location of Golgotha derives from its identification by Queen Mother Helena, mother of
The traditional location of Golgotha derives from its identification by Queen Mother Helena, mother of
 Prior to Helena's identification, the site had been a
Prior to Helena's identification, the site had been a
''New Advent encyclopedia'', accessed 25 March 2014. and the etching "DOMINVS IVIMVS", meaning "Lord, we went", lending possible support to the statement by Melito of Sardis' asserting that early Christians identified Golgotha as being in the middle of Hadrian's city, rather than outside.
 During 1973–1978 restoration works and excavations inside the Church of the Holy Sepulchre and under the nearby Muristan, it was found that the area was originally a quarry, from which white Meleke
During 1973–1978 restoration works and excavations inside the Church of the Holy Sepulchre and under the nearby Muristan, it was found that the area was originally a quarry, from which white Meleke
 The Itinerarium Burdigalense speaks of Golgotha in 333: "... On the left hand is the little hill of Golgotha where the Lord was crucified. About a stone's throw from thence is a vault (crypta) wherein His body was laid, and rose again on the third day. There, at present, by the command of the Emperor Constantine, has been built a basilica, that is to say, a church of wondrous beauty," Cyril of Jerusalem, a distinguished theologian of the early Church, and eyewitness to the early days of Constantine's edifice, speaks of Golgotha in eight separate passages, sometimes as near to the church where he and his listeners assembled: "Golgotha, the holy hill standing above us here, bears witness to our sight: the Holy Sepulchre bears witness, and the stone which lies there to this day." And just in such a way the pilgrim Egeria often reported in 383: "… the church, built by Constantine, which is situated in Golgotha …" and also bishop Eucherius of Lyon wrote to the island presbyter Faustus in 440: "Golgotha is in the middle between the Anastasis and the Martyrium, the place of the Lord's passion, in which still appears that rock which once endured the very cross on which the Lord was." Breviarius de Hierosolyma reports in 530: "From there (the middle of the basilica), you enter into Golgotha, where there is a large court. Here the Lord was crucified. All around that hill, there are silver screens." (See also:
The Itinerarium Burdigalense speaks of Golgotha in 333: "... On the left hand is the little hill of Golgotha where the Lord was crucified. About a stone's throw from thence is a vault (crypta) wherein His body was laid, and rose again on the third day. There, at present, by the command of the Emperor Constantine, has been built a basilica, that is to say, a church of wondrous beauty," Cyril of Jerusalem, a distinguished theologian of the early Church, and eyewitness to the early days of Constantine's edifice, speaks of Golgotha in eight separate passages, sometimes as near to the church where he and his listeners assembled: "Golgotha, the holy hill standing above us here, bears witness to our sight: the Holy Sepulchre bears witness, and the stone which lies there to this day." And just in such a way the pilgrim Egeria often reported in 383: "… the church, built by Constantine, which is situated in Golgotha …" and also bishop Eucherius of Lyon wrote to the island presbyter Faustus in 440: "Golgotha is in the middle between the Anastasis and the Martyrium, the place of the Lord's passion, in which still appears that rock which once endured the very cross on which the Lord was." Breviarius de Hierosolyma reports in 530: "From there (the middle of the basilica), you enter into Golgotha, where there is a large court. Here the Lord was crucified. All around that hill, there are silver screens." (See also:
 In 1842, Otto Thenius, a theologian and biblical scholar from
In 1842, Otto Thenius, a theologian and biblical scholar from
Golgotha Rediscovered
– proposes that Golgotha was outside Lions' Gate
Polish Calvaries: Architecture as a Stage for the Passion of Christ
{{coord, 31, 46, 43, N, 35, 13, 46, E, source:kolossus-jawiki_type:landmark, display=title Crucifixion of Jesus New Testament places
 Calvary ( la, Calvariae or ) or Golgotha ( grc-gre, Γολγοθᾶ, ''Golgothâ'') was a site immediately outside
Calvary ( la, Calvariae or ) or Golgotha ( grc-gre, Γολγοθᾶ, ''Golgothâ'') was a site immediately outside Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
's walls where Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
was said to have been crucified according to the canonical Gospels
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words a ...
. Since at least the early medieval period, it has been a destination for pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a journey, often into an unknown or foreign place, where a person goes in search of new or expanded meaning about their self, others, nature, or a higher good, through the experience. It can lead to a personal transformation, aft ...
. The exact location of Calvary has been traditionally associated with a place now enclosed within one of the southern chapels of the multidenominational Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, hy, Սուրբ Հարության տաճար, la, Ecclesia Sancti Sepulchri, am, የቅዱስ መቃብር ቤተክርስቲያን, he, כנסיית הקבר, ar, كنيسة القيامة is a church i ...
, a site said to have been recognized by the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
empress Helena
Helena may refer to:
People
*Helena (given name), a given name (including a list of people and characters with the name)
*Katri Helena (born 1945), Finnish singer
*Helena, mother of Constantine I
Places
Greece
* Helena (island)
Guyana
* H ...
, mother of Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
, during her visit to the Holy Land in 325. Other locations have been suggested: in the 19th century, Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
scholars proposed a different location near the Garden Tomb on Green Hill (now "Skull Hill") about north of the traditional site and historian Joan Taylor has more recently proposed a location about to its south-southeast.
Biblical references and names
TheEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
names Calvary and Golgotha derive from the Vulgate Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
, and (all meaning "place of the Skull" or "a Skull"), and used by Jerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian priest, confessor, theologian, and historian; he is co ...
in his translations of Matthew 27:33, Mark 15:22, Luke 23:33, and John 19
John 19 is the nineteenth chapter of the Gospel of John in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. The book containing this chapter is anonymous, but early Christian tradition uniformly affirmed that John composed this Gospel.Holman Illustrate ...
:17. Versions of these names have been used in English since at least the 10th century
The 10th century was the period from 901 ( CMI) through 1000 ( M) in accordance with the Julian calendar, and the last century of the 1st millennium.
In China the Song dynasty was established. The Muslim World experienced a cultural zenith, ...
, a tradition shared with most European languages including French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
(), Spanish and Italian (), pre-Luther
Luther may refer to:
People
* Martin Luther (1483–1546), German monk credited with initiating the Protestant Reformation
* Martin Luther King Jr. (1929-1968), American minister and leader in the American civil rights movement
* Luther (gi ...
an German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
(), Polish (), and Lithuanian (). The 1611 King James Version
The King James Version (KJV), also the King James Bible (KJB) and the Authorized Version, is an English translation of the Christian Bible for the Church of England, which was commissioned in 1604 and published in 1611, by sponsorship of K ...
borrowed the Latin forms directly, while Wycliffe and other translators anglicized them in forms like ''Caluarie'', Đa Halgan GodspelLucas 23:33
( Thorpe ed.) ''Caluerie'', and ''Calueri'' which were later standardized as ''Calvary''. While the Gospels merely identify Golgotha as a "place",
Christian tradition
Christian tradition is a collection of traditions consisting of practices or beliefs associated with Christianity. These ecclesiastical traditions have more or less authority based on the nature of the practices or beliefs and on the group in que ...
has described the location as a hill
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct summit.
Terminology
The distinction between a hill and a mountain is unclear and largely subjective, but a hill is universally considered to be not a ...
or mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher ...
since at least the 6th century. It has thus often been referenced as in English hymns and literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to ...
.
In the 1769 King James Version
The King James Version (KJV), also the King James Bible (KJB) and the Authorized Version, is an English translation of the Christian Bible for the Church of England, which was commissioned in 1604 and published in 1611, by sponsorship of K ...
, the relevant verses of the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chris ...
are:
* And when they were come unto a place called Golgatha, that is to say, a place of a skull, They gave him vinegar to drink mingled with gall: and when he had tasted thereof, he would not drink. And they crucified him, and parted his garments, casting lots...
* And they bring him unto the place Golgotha, which is, being interpreted, The place of a skull. And they gave him to drink wine mingled with myrrh: but he received it not. And when they had crucified him, they parted his garments, casting lots upon them, what every man should take.
* And when they were come to the place, which is called Calvary, there they crucified him, and the malefactors, one on the right hand, and the other on the left.
* And he bearing his cross went forth into a place called the place of a skull, which is called in the Hebrew Golgotha: Where they crucified him, and two other with him, on either side one, and Jesus in the midst.
In the standard Koine Greek
Koine Greek (; Koine el, ἡ κοινὴ διάλεκτος, hē koinè diálektos, the common dialect; ), also known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek or New Testament Greek, was the common supra-reg ...
texts of the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chris ...
, the relevant terms appear as ''Golgothâ'' (),Nestle(Greek)
(Greek) ''Golgathân'' (),Nestle
(Greek)
(Greek)
Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
equivalent would be ''Gulgōleṯ'' (, "skull"), ultimately from the verb ''galal'' () meaning "to roll".. The form preserved in the Greek text, however, is actually closer to Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated i ...
''Golgolta'', which also appears in reference to a head count in the Samaritan version of Numbers 1
Bemidbar, BeMidbar, B'midbar, Bamidbar, or Bamidbor ( — Hebrew for "in the wilderness of" inai the fifth overall and first distinctive word in the parashah), is the 34th weekly Torah portion (, ''parashah'') in the annual Jewish cycle of Tor ...
:18,. although the term is traditionally considered to derive from Syriac ''Gāgūlṯā'' () instead. Although Latin can mean either "a skull" or "the skull" depending on context and numerous English translations render the relevant passages or "Place of the Skull", the Greek forms of the name grammatically refer to the place of ''a'' skull and a place named Skull. (The Greek word does more specifically mean the cranium, the upper part of the skull, but it has been used metonymously since antiquity to refer to skulls and heads more generally.)
The Fathers of the Church offered various interpretations of the name and its origin. Jerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian priest, confessor, theologian, and historian; he is co ...
considered it a place of execution by beheading (), Pseudo-Tertullian describes it as a place resembling a head, and Origen
Origen of Alexandria, ''Ōrigénēs''; Origen's Greek name ''Ōrigénēs'' () probably means "child of Horus" (from , "Horus", and , "born"). ( 185 – 253), also known as Origen Adamantius, was an early Christian scholar, ascetic, and the ...
associated it with legends concerning the skull of Adam. This buried skull of Adam appears in noncanonical medieval legends, including the ''Kitab al-Magall'', the '' Conflict of Adam and Eve with Satan'', the '' Cave of Treasures'', and the works of Eutychius, the 9th-century patriarch of Alexandria. The usual form of the legend is that Shem and Melchizedek retrieved the body of Adam from the resting place of Noah's ark
Ark or ARK may refer to:
Biblical narratives and religion Hebrew word ''teva''
* Noah's Ark, a massive vessel said to have been built to save the world's animals from a flood
* Ark of bulrushes, the boat of the infant Moses
Hebrew ''aron''
* ...
on Mount Ararat
Mount Ararat or , ''Ararat''; or is a snow-capped and dormant compound volcano in the extreme east of Turkey. It consists of two major volcanic cones: Greater Ararat and Little Ararat. Greater Ararat is the highest peak in Turkey and th ...
and were led by angels to Golgotha, a skull-shaped hill at the center of the earth where Adam had previously crushed the serpent's head following the Fall of Man.
In the 19th century, Wilhelm Ludwig Krafft proposed an alternative derivation of these names, suggesting that the place had actually been known as "Gol Goatha"which he interpreted to mean "heap of death" or "hill of execution"and had become associated with the similar sounding Semitic words for "skull" in folk etymologies
Folk etymology (also known as popular etymology, analogical reformation, reanalysis, morphological reanalysis or etymological reinterpretation) is a change in a word or phrase resulting from the replacement of an unfamiliar form by a more famili ...
.. (German) James Fergusson identified this "Goatha" with the ''Goʿah'' () mentioned in Jeremiah 31:39 as a place near Jerusalem, although Krafft himself identified that location with the separate ''Gennáth'' () of Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
, the "Garden Gate" west of the Temple Mount
The Temple Mount ( hbo, הַר הַבַּיִת, translit=Har haBayīt, label=Hebrew, lit=Mount of the House f the Holy}), also known as al-Ḥaram al-Sharīf (Arabic: الحرم الشريف, lit. 'The Noble Sanctuary'), al-Aqsa Mosque compou ...
.
Location
There is no consensus as to the location of the site. John describes the crucifixion site as being "near the city". According toHebrews
The terms ''Hebrews'' (Hebrew: / , Modern: ' / ', Tiberian: ' / '; ISO 259-3: ' / ') and ''Hebrew people'' are mostly considered synonymous with the Semitic-speaking Israelites, especially in the pre-monarchic period when they were still ...
, it was "outside the city gate". and both note that the location would have been accessible to "passers-by". Thus, locating the crucifixion site involves identifying a site that, in the city of Jerusalem some four decades before its destruction in AD70, would have been outside a major gate near enough to the city that the passers-by could not only see him, but also read the inscription 'Jesus the Nazarene, King of the Jews'.
Church of the Holy Sepulchre
Christian tradition since the fourth century has favoured a location now within theChurch of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, hy, Սուրբ Հարության տաճար, la, Ecclesia Sancti Sepulchri, am, የቅዱስ መቃብር ቤተክርስቲያን, he, כנסיית הקבר, ar, كنيسة القيامة is a church i ...
. This places it well within today's walls of Jerusalem, which surround the Old City Old City often refers to old town, the historic or original core of a city or town.
Old City may refer to several places:
Historical cities or regions of cities
''(by country)''
*Old City (Baku), Azerbaijan
* Old City (Dhaka), Bangladesh, also ca ...
and were rebuilt in the 16th century by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
. Proponents of the traditional Holy Sepulchre location point out at the fact that first-century Jerusalem had a different shape and size from the 16th-century city, leaving the church's site outside the pre-AD 70 city walls. Those opposing it doubt this.
Defenders of the traditional site have argued that the site of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre was only brought within the city limits by Herod Agrippa (41–44), who built the so-called Third Wall around a newly settled northern district, while at the time of Jesus' crucifixion around AD 30 it would still have been just outside the city.
Henry Chadwick (2003) argued that when Hadrian's builders replanned the old city, they "incidentally confirm dthe bringing of Golgotha inside a new town wall."
In 2007 Dan Bahat
Dan Bahat ( he, דן בהט, born 1938) is an Israeli archaeologist especially known for his excavations in Jerusalem , particularly at the Western Wall tunnels.
Biography
Dan Bahat was born in Poland to parents who were citizens of Mandatory Pal ...
, the former City Archaeologist of Jerusalem and Professor of Land of Israel Studies at Bar-Ilan University, stated that "Six graves from the first century were found on the area of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre. That means, this place asoutside of the city, without any doubt…".Dan Bahain German television ZDF, April 11, 2007
/ref>
Church of the Holy Sepulchre
 The traditional location of Golgotha derives from its identification by Queen Mother Helena, mother of
The traditional location of Golgotha derives from its identification by Queen Mother Helena, mother of Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
, in 325. Less than away, Helena also identified the location of the tomb of Jesus and claimed to have discovered the True Cross
The True Cross is the cross upon which Jesus was said to have been crucified, particularly as an object of religious veneration. There are no early accounts that the apostles or early Christians preserved the physical cross themselves, althoug ...
; her son, Constantine, then built the Church of the Holy Sepulchre around the whole site. In 333, the author of the '' Itinerarium Burdigalense'', entering from the east, described the result:
In Nazénie Garibian de Vartavan's doctoral thesis, now published as ''La Jérusalem Nouvelle et les premiers sanctuaires chrétiens de l'Arménie. Méthode pour l'étude de l'église comme temple de Dieu,'' she concluded, through multiple arguments (mainly theological and archaeological), that the true site of Golgotha was precisely at the vertical of the now buried Constantinian basilica's altar and away from where the traditional rock of Golgotha is situated. The plans published in the book indicate the location of the Golgotha within a precision of less than two meters, below the circular passage situated a metre away from where the blood stained shirt of Christ was traditionally recovered and immediately before the stairs leading down to St. Helena's Chapel (the above-mentioned mother of Emperor Constantine), alternatively called St. Vartan's Chapel.
Temple to Aphrodite
temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
to Aphrodite
Aphrodite ( ; grc-gre, Ἀφροδίτη, Aphrodítē; , , ) is an ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, and procreation. She was syncretized with the Roman goddess . Aphrodite's major symbols incl ...
. Constantine's construction took over most of the site of the earlier temple enclosure, and the ''Rotunda'' and cloister
A cloister (from Latin ''claustrum'', "enclosure") is a covered walk, open gallery, or open arcade running along the walls of buildings and forming a quadrangle or garth. The attachment of a cloister to a cathedral or church, commonly against ...
(which was replaced after the 12th century by the present '' Catholicon'' and ''Calvary chapel'') roughly overlap with the temple building itself; the basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its nam ...
church Constantine built over the remainder of the enclosure was destroyed at the turn of the 11th century, and has not been replaced. Christian tradition
Christian tradition is a collection of traditions consisting of practices or beliefs associated with Christianity. These ecclesiastical traditions have more or less authority based on the nature of the practices or beliefs and on the group in que ...
claims that the location had originally been a Christian place of veneration, but that Hadrian had deliberately buried these Christian sites and built his own temple on top, on account of his alleged hatred for Christianity.
There is certainly evidence that circa 160, at least as early as 30 years after Hadrian's temple had been built, Christians associated it with the site of ''Golgotha''; Melito of Sardis, an influential mid-2nd century bishop in the region, described the location as "in the middle of the street, in the middle of the city", which matches the position of Hadrian's temple within the mid-2nd century city.
The Romans typically built a city according to a Hippodamian
Hippodamus of Miletus (; Greek: Ἱππόδαμος ὁ Μιλήσιος, ''Hippodamos ho Milesios''; 498 – 408 BC) was an ancient Greek architect, urban planner, physician, mathematician, meteorologist and philosopher, who is considered to ...
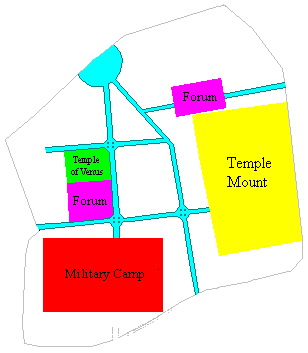
grid plan – a north–south arterial road, the Cardo (which is now the Suq Khan-ez-Zeit), and an east–west arterial road, the Decumanus Maximus (which is now the Via Dolorosa). The forum would traditionally be located on the intersection of the two roads, with the main temples adjacent. However, due to the obstruction posed by the Temple Mount, as well as the Tenth Legion encampment on the Western Hill, Hadrian's city had two ''Cardo'', two ''Decumanus Maximus'', two forums, and several temples. The Western Forum (now the Muristan) is located on the crossroads of the West Cardo and what is now El-Bazar/David Street, with the Temple of Aphrodite adjacent, on the intersection of the Western Cardo and the Via Dolorosa. The Northern Forum is located north of the Temple Mount, on the junction of the Via Dolorosa and the Eastern Cardo (the Tyropoeon), adjacent to the Temple of Jupiter Capitolinus, intentionally built atop the Temple Mount. Another popular holy site that Hadrian converted to a pagan temple was the Pool of Bethesda, possibly referenced to in the fifth chapter of the Gospel of John, Jerome Murphy-O'Connor, ''The Holy Land'', (2008), p. 29 on which was built the Temple of Asclepius
Asclepius (; grc-gre, Ἀσκληπιός ''Asklēpiós'' ; la, Aesculapius) is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Greek religion and mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis, or Arsinoe, or of Apollo alone. Asclepius represen ...
and Serapis. While the positioning of the Temple of Aphrodite may be, in light of the common Colonia layout, entirely unintentional, Hadrian is known to have concurrently built pagan temples on top of other holy sites in Jerusalem as part of an overall "Romanization
Romanization or romanisation, in linguistics, is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, a ...
" policy.
Archaeological excavations under the Church of the Holy Sepulchre have revealed Christian pilgrims' graffiti, dating from the period that the Temple of Aphrodite was still present, of a ship, a common early Christian symbolNave''New Advent encyclopedia'', accessed 25 March 2014. and the etching "DOMINVS IVIMVS", meaning "Lord, we went", lending possible support to the statement by Melito of Sardis' asserting that early Christians identified Golgotha as being in the middle of Hadrian's city, rather than outside.
Rockface
 During 1973–1978 restoration works and excavations inside the Church of the Holy Sepulchre and under the nearby Muristan, it was found that the area was originally a quarry, from which white Meleke
During 1973–1978 restoration works and excavations inside the Church of the Holy Sepulchre and under the nearby Muristan, it was found that the area was originally a quarry, from which white Meleke limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms w ...
was struck; surviving parts of the quarry to the north-east of the chapel of St. Helena are now accessible from within the chapel (by permission). Inside the church is a rock, about 7 m long by 3 m wide by 4.8 m high, that is traditionally believed to be all that now remains visible of ''Golgotha''; the design of the church means that the ''Calvary Chapel'' contains the upper foot or so of the rock, while the remainder is in the chapel beneath it (known as the ''tomb of Adam''). Virgilio Corbo, a Franciscan
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size = 200px
, caption = A cross, Christ's arm and Saint Francis's arm, a universal symbol of the Franciscans
, abbreviation = OFM
, predecessor =
, ...
priest and archaeologist, present at the excavations, suggested that from the city the little hill (which still exists) could have looked like a skull.Hesemann 1999, p. 170: "Von der Stadt aus muß er tatsächlich wie eine Schädelkuppe ausgesehen haben," and p. 190: a sketch; and p. 172: a sketch of the geological findings by C. Katsimbinis, 1976: "der Felsblock ist zu 1/8 unterhalb des Kirchenbodens, verbreitert sich dort auf etwa 6,40 Meter und verläuft weiter in die Tiefe"; and p. 192, a sketch by Corbo, 1980: Golgotha is distant 10 meters outside from the southwest corner of the Martyrion-basilica
During a 1986 repair to the floor of the ''Calvary Chapel'' by the art historian George Lavas and architect Theo Mitropoulos, a round slot of diameter was discovered in the rock, partly open on one side (Lavas attributes the open side to accidental damage during his repairs);George Lavas, ''The Rock of Calvary'', published (1996) in ''The Real and Ideal Jerusalem in Jewish, Christian and Islamic Art'' (proceedings of the 5th International Seminar in Jewish Art), pp. 147–150 although the dating of the slot is uncertain, and could date to Hadrian's temple of Aphrodite, Lavas suggested that it could have been the site of the crucifixion, as it would be strong enough to hold in place a wooden trunk of up to in height (among other things). The same restoration work also revealed a crack running across the surface of the rock, which continues down to the ''Chapel of Adam''; the crack is thought by archaeologists to have been a result of the quarry workmen encountering a flaw in the rock.
Based on the late 20th century excavations of the site, there have been a number of attempted reconstructions of the profile of the cliff face. These often attempt to show the site as it would have appeared to Constantine. However, as the ground level in Roman times was about lower and the site housed Hadrian's temple to Aphrodite, much of the surrounding rocky slope must have been removed long before Constantine built the church on the site. The height of the ''Golgotha'' rock itself would have caused it to jut through the platform level of the Aphrodite temple, where it would be clearly visible. The reason for Hadrian not cutting the rock down is uncertain, but Virgilio Corbo suggested that a statue, probably of Aphrodite, was placed on it, a suggestion also made by Jerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian priest, confessor, theologian, and historian; he is co ...
. Some archaeologists have suggested that prior to Hadrian's use, the rock outcrop had been a ''nefesh'' – a Jewish funeral monument, equivalent to the stele.
Pilgrimages to Constantine's Church
 The Itinerarium Burdigalense speaks of Golgotha in 333: "... On the left hand is the little hill of Golgotha where the Lord was crucified. About a stone's throw from thence is a vault (crypta) wherein His body was laid, and rose again on the third day. There, at present, by the command of the Emperor Constantine, has been built a basilica, that is to say, a church of wondrous beauty," Cyril of Jerusalem, a distinguished theologian of the early Church, and eyewitness to the early days of Constantine's edifice, speaks of Golgotha in eight separate passages, sometimes as near to the church where he and his listeners assembled: "Golgotha, the holy hill standing above us here, bears witness to our sight: the Holy Sepulchre bears witness, and the stone which lies there to this day." And just in such a way the pilgrim Egeria often reported in 383: "… the church, built by Constantine, which is situated in Golgotha …" and also bishop Eucherius of Lyon wrote to the island presbyter Faustus in 440: "Golgotha is in the middle between the Anastasis and the Martyrium, the place of the Lord's passion, in which still appears that rock which once endured the very cross on which the Lord was." Breviarius de Hierosolyma reports in 530: "From there (the middle of the basilica), you enter into Golgotha, where there is a large court. Here the Lord was crucified. All around that hill, there are silver screens." (See also:
The Itinerarium Burdigalense speaks of Golgotha in 333: "... On the left hand is the little hill of Golgotha where the Lord was crucified. About a stone's throw from thence is a vault (crypta) wherein His body was laid, and rose again on the third day. There, at present, by the command of the Emperor Constantine, has been built a basilica, that is to say, a church of wondrous beauty," Cyril of Jerusalem, a distinguished theologian of the early Church, and eyewitness to the early days of Constantine's edifice, speaks of Golgotha in eight separate passages, sometimes as near to the church where he and his listeners assembled: "Golgotha, the holy hill standing above us here, bears witness to our sight: the Holy Sepulchre bears witness, and the stone which lies there to this day." And just in such a way the pilgrim Egeria often reported in 383: "… the church, built by Constantine, which is situated in Golgotha …" and also bishop Eucherius of Lyon wrote to the island presbyter Faustus in 440: "Golgotha is in the middle between the Anastasis and the Martyrium, the place of the Lord's passion, in which still appears that rock which once endured the very cross on which the Lord was." Breviarius de Hierosolyma reports in 530: "From there (the middle of the basilica), you enter into Golgotha, where there is a large court. Here the Lord was crucified. All around that hill, there are silver screens." (See also: Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος ; 260/265 – 30 May 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilus (from the grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος τοῦ Παμφίλου), was a Greek historian of Christianity, exegete, and Chris ...
in 338.)
Gordon's Calvary
Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label= Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, was the first to publish a proposal that the rocky knoll north of Damascus Gate was the biblical ''Golgotha''. He relied heavily on the research of Edward Robinson. In 1882–83, Major-General Charles George Gordon endorsed this view; subsequently the site has sometimes been known as Gordon's Calvary. The location, usually referred to today as '' Skull Hill'', is beneath a cliff that contains two large sunken holes, which Gordon regarded as resembling the eyes of a skull. He and a few others before him believed that the skull-like appearance would have caused the location to be known as Golgotha.
Nearby is an ancient rock-cut tomb known today as the Garden Tomb
The Garden Tomb ( he, גן הקבר) is a rock-cut tomb in Jerusalem, which was unearthed in 1867 and is considered by some Protestants to be the site of the burial and resurrection of Jesus. The tomb has been dated by Israeli archaeologist ...
, which Gordon proposed as the tomb of Jesus. The Garden Tomb contains several ancient burial places, although the archaeologist Gabriel Barkay
Gabriel Barkay (Hebrew: גבריאל ברקאי; sometimes transcribed from the Hebrew Gavriel Barkai) is an Israeli archaeologist.
Early life and studies
Born in 1944 in the Budapest Ghetto, Hungary, he immigrated to Israel in 1950.
Barkay stud ...
has proposed that the tomb dates to the 7th century BC and that the site may have been abandoned by the 1st century.
Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος ; 260/265 – 30 May 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilus (from the grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος τοῦ Παμφίλου), was a Greek historian of Christianity, exegete, and Chris ...
comments that Golgotha was in his day (the 4th century) pointed out ''north of Mount Zion''.Eusebius, '' Onomasticon'', 365 While ''Mount Zion'' was used previously in reference to the Temple Mount itself, Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
, the first-century AD historian who knew the city as it was before the Roman destruction of Jerusalem, identified Mount Zion as being the Western Hill (the current Mount Zion), which is south of both the Garden Tomb and the Holy Sepulchre. Eusebius' comment therefore offers no additional argument for either location.
See also
*Crucifixion of Jesus
The crucifixion and death of Jesus occurred in 1st-century Judea, most likely in AD 30 or AD 33. It is described in the four canonical gospels, referred to in the New Testament epistles, attested to by other ancient sources, and consider ...
References
External links
Golgotha Rediscovered
– proposes that Golgotha was outside Lions' Gate
Polish Calvaries: Architecture as a Stage for the Passion of Christ
{{coord, 31, 46, 43, N, 35, 13, 46, E, source:kolossus-jawiki_type:landmark, display=title Crucifixion of Jesus New Testament places