Calcitonin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Calcitonin is a 32 amino acid
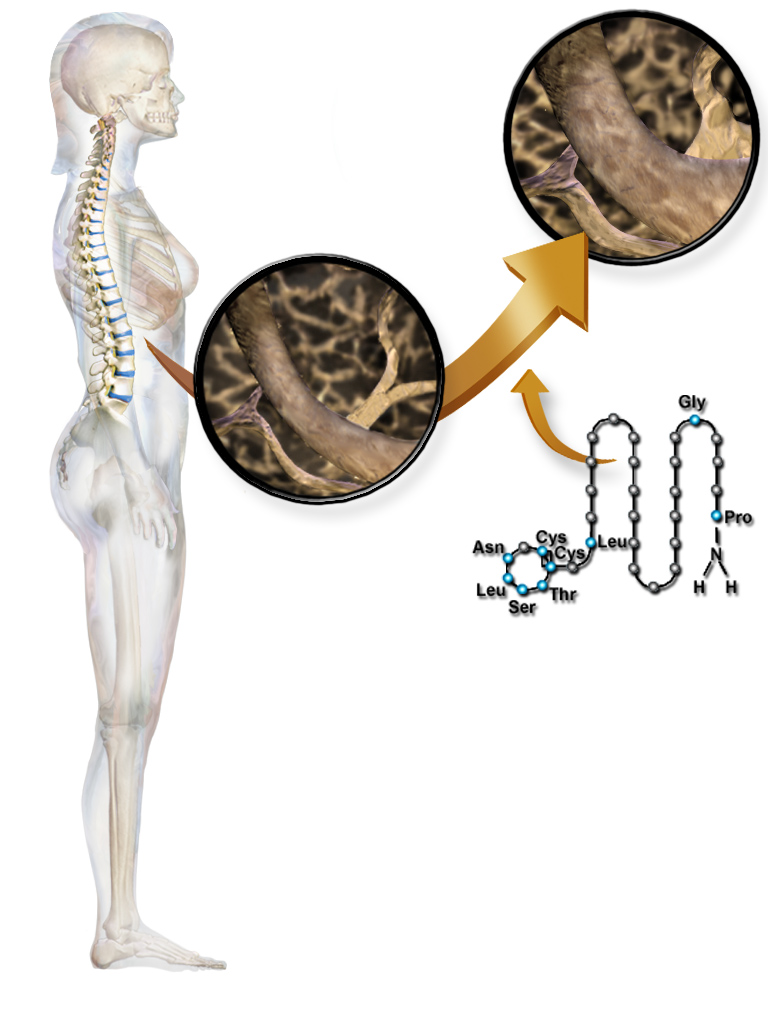 Calcitonin can be used therapeutically for the treatment of
Calcitonin can be used therapeutically for the treatment of
The Calcitonin Protein
* {{Amyloidosis Peptide hormones Hormones of the thyroid gland Human hormones Hormones of calcium metabolism Tumor markers Thyroid
peptide hormone
Peptide hormones or protein hormones are hormones whose molecules are peptide, or proteins, respectively. The latter have longer amino acid chain lengths than the former. These hormones have an effect on the endocrine system of animals, including h ...
secreted by parafollicular cells (also known as C cells) of the thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The ...
(or endostyle
The endostyle is an anatomical feature found in invertebrate chordates and larval lampreys. It is an organ which assists chordates in filter-feeding. It is found in adult urochordates and cephalochordates, as well as in the larvae of the vertebra ...
) in humans and other chordates
A chordate () is an animal of the phylum Chordata (). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five synapomorphies, or primary physical characteristics, that distinguish them from all the other taxa. These five ...
. in the ultimopharyngeal body. It acts to reduce blood calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar ...
(Ca2+), opposing the effects of parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called parathormone or parathyrin, is a peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates the serum calcium concentration through its effects on bone, kidney, and intestine.
PTH influences bone ...
(PTH).
Its importance in humans has not been as well established as its importance in other animals, as its function is usually not significant in the regulation of normal calcium homeostasis. It belongs to the calcitonin-like protein family.
Historically calcitonin has also been called thyrocalcitonin.
Biosynthesis and regulation
Calcitonin is formed by theproteolytic
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called prote ...
cleavage of a larger prepropeptide, which is the product of the CALC1 gene (). It is functionally an antagonist with PTH and Vitamin D3. The CALC1 gene belongs to a superfamily of related protein hormone precursors including islet amyloid precursor protein, calcitonin gene-related peptide
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is a member of the calcitonin family of peptides consisting of calcitonin, amylin, adrenomedullin, adrenomedullin 2 ( intermedin) and calcitonin‑receptor‑stimulating peptide. Calcitonin is mainly produ ...
, and the precursor of adrenomedullin
Adrenomedullin (ADM or AM) is a vasodilator peptide hormone of uncertain significance in human health and disease. It was initially isolated in 1993 from a pheochromocytoma, a tumor of the adrenal medulla: hence the name.
In humans ADM is encoded ...
.
Secretion of calcitonin is stimulated by:
:* an increase in serum a2+:* gastrin
Gastrin is a peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid (HCl) by the parietal cells of the stomach and aids in gastric motility. It is released by G cells in the pyloric antrum of the stomach, duodenum, and the pancreas.
Gast ...
and pentagastrin.
Function
The hormone participates incalcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar ...
(Ca2+) metabolism. In many ways, calcitonin counteracts parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called parathormone or parathyrin, is a peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates the serum calcium concentration through its effects on bone, kidney, and intestine.
PTH influences bone ...
(PTH) and vitamin D.
More specifically, calcitonin lowers blood Ca2+ levels in two ways:
:* Major effect: Inhibits osteoclast
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated pro ...
activity in bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
s, which break down the bone
:* Minor effect: Inhibits renal tubular cell reabsorption of Ca2+ and phosphate, allowing them to be excreted in the urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cellul ...
High concentrations of calcitonin may be able to increase urinary excretion of calcium and phosphate via the renal
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; bloo ...
tubules. leading to marked hypocalcemia. However, this is a minor effect with no physiological significance in humans. It is also a short-lived effect because the kidneys become resistant to calcitonin, as demonstrated by the kidney's unaffected excretion of calcium in patients with thyroid tumors that secrete excessive calcitonin.
In its skeleton-preserving actions, calcitonin protects against calcium loss from the skeleton during periods of calcium mobilization, such as pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
and, especially, lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The proces ...
. The protective mechanisms include the direct inhibition of bone resorption and the indirect effect through the inhibition of the release of prolactin from the pituitary gland. The reason provided is that prolactin
Prolactin (PRL), also known as lactotropin, is a protein best known for its role in enabling mammals to produce milk. It is influential in over 300 separate processes in various vertebrates, including humans. Prolactin is secreted from the pi ...
induces the release of PTH related peptide which enhances bone resorption, but is still under investigation.
Other effects are in preventing postprandial hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia, also spelled hypercalcaemia, is a high calcium (Ca2+) level in the blood serum. The normal range is 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L), with levels greater than 2.6 mmol/L defined as hypercalcem ...
resulting from absorption of Ca2+. Also, calcitonin inhibits food intake in rats and monkeys, and may have CNS action involving the regulation of feeding and appetite.
Calcitonin lowers blood calcium and phosphorus mainly through its inhibition of osteoclasts. Osteoblasts do not have calcitonin receptors and are therefore not directly affected by calcitonin levels. However, since bone resorption and bone formation are coupled processes, eventually calcitonin's inhibition of osteoclastic activity leads to increased osteoblast
Osteoblasts (from the Greek language, Greek combining forms for "bone", ὀστέο-, ''osteo-'' and βλαστάνω, ''blastanō'' "germinate") are cell (biology), cells with a single Cell nucleus, nucleus that synthesize bone. However, in the p ...
ic activity (as an indirect effect).
Receptor
Thecalcitonin receptor
The calcitonin receptor (CT) is a G protein-coupled receptor that binds the peptide hormone calcitonin and is involved in maintenance of calcium homeostasis, particularly with respect to bone formation and metabolism.
CT works by activating the ...
is a G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related p ...
localized to osteoclasts as well kidney and brain cells. It is coupled to a Gsα subunit, thus stimulating cAMP
Camp may refer to:
Outdoor accommodation and recreation
* Campsite or campground, a recreational outdoor sleeping and eating site
* a temporary settlement for nomads
* Camp, a term used in New England, Northern Ontario and New Brunswick to descri ...
production by adenylate cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction:
:A ...
in target cells. It may also affect the ovaries in women and the testes in men.
Discovery
Calcitonin was first purified in 1962 by Douglas Harold Copp and B. Cheney at theUniversity of British Columbia
The University of British Columbia (UBC) is a public research university with campuses near Vancouver and in Kelowna, British Columbia. Established in 1908, it is British Columbia's oldest university. The university ranks among the top thr ...
, Canada. It was initially thought to be secreted by the parathyroid gland
Parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands in the neck of humans and other tetrapods. Humans usually have four parathyroid glands, located on the back of the thyroid gland in variable locations. The parathyroid gland produces and secretes pa ...
but was shown by Iain Macintyre and his team at the Royal Postgraduate Medical School, London, to be secreted by parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thy ...
. Dr. Copp named the discovered hormone calcitonin because of its role in 'maintaining normal calcium tone'.
Medical significance
Calcitonin assay is used in identifying patients with nodular thyroid diseases. It is helpful in making an early diagnosis of medullary carcinoma of thyroid. A malignancy of the parafollicular cells, i.e. Medullary thyroid cancer, typically produces an elevated serum calcitonin level. Prognosis of MTC depends on early detection and treatment. Calcitonin also has significantly impactedmolecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and phys ...
, as the gene encoding calcitonin was the first gene discovered in mammalian cells to be alternatively spliced
Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins. In this process, particular exons of a gene may b ...
, now known to be a ubiquitous mechanism in eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacter ...
s.
Pharmacology
Calcitonin has clinically been used for metabolic bone disorders for more than 50 years. Salmon calcitonin is used for the treatment of: * Postmenopausalosteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone a ...
* Hypercalcaemia
* Bone metastases
Bone metastasis, or osseous metastatic disease, is a category of cancer metastases that results from primary tumor invasion to bone. Bone-originating primary tumors such as osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, and Ewing's sarcoma are rare; the most co ...
* Paget's disease
* Phantom limb pain
It has been investigated as a possible non-operative treatment for spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis is an abnormal narrowing of the spinal canal or neural foramen that results in pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. Symptoms may include pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs. Symptoms are typically gradual i ...
.
The following information is from the UK Electronic Medicines Compendium
General characteristics of the active substance
Salmon calcitonin is rapidly absorbed and eliminated. Peak plasma concentrations are attained within the first hour of administration. Animal studies have shown that calcitonin is primarily metabolised via proteolysis in the kidney following parenteral administration. The metabolites lack the specificbiological activity
In pharmacology, biological activity or pharmacological activity describes the beneficial or adverse effects of a drug on living matter. When a drug is a complex chemical mixture, this activity is exerted by the substance's active ingredient or ...
of calcitonin. Bioavailability following subcutaneous and intramuscular injection in humans is high and similar for the two routes of administration (71% and 66%, respectively).
Calcitonin has short absorption and elimination half-lives of 10–15 minutes and 50–80 minutes, respectively. Salmon calcitonin is primarily and almost exclusively degraded in the kidneys, forming pharmacologically inactive fragments of the molecule. Therefore, the metabolic clearance is much lower in patients with end-stage kidney failure than in healthy subjects. However, the clinical relevance of this finding is not known. Plasma protein binding is 30% to 40%.
Characteristics in patients
There is a relationship between the subcutaneous dose of calcitonin and peak plasma concentrations. Following parenteral administration of 100 IU calcitonin, peak plasma concentration lies between about 200 and 400 pg/ml. Higher blood levels may be associated with increased incidence of nausea, vomiting, and secretory diarrhea.Preclinical safety data
Conventional long-term toxicity, reproduction, mutagenicity, and carcinogenicity studies have been performed in laboratory animals. Salmon calcitonin is devoid of embryotoxic, teratogenic, and mutagenic potential. An increased incidence of pituitary adenomas has been reported in rats given synthetic salmon calcitonin for 1 year. This is considered a species-specific effect and of no clinical relevance. Salmon calcitonin does not cross the placental barrier. In lactating animals given calcitonin, suppression of milk production has been observed. Calcitonin is secreted into the milk.Pharmaceutical manufacture
Calcitonin was extracted from the ultimobranchial glands (thyroid-like glands) of fish, particularly salmon. Salmon calcitonin resembles human calcitonin, but is more active. At present, it is produced either byrecombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be f ...
technology or by chemical peptide synthesis
In organic chemistry, peptide synthesis is the production of peptides, compounds where multiple amino acids are linked via amide bonds, also known as peptide bonds. Peptides are chemically synthesized by the condensation reaction of the carboxyl ...
. The pharmacological properties of the synthetic and recombinant peptides have been demonstrated to be qualitatively and quantitatively equivalent.
Uses of calcitonin
Treatments
 Calcitonin can be used therapeutically for the treatment of
Calcitonin can be used therapeutically for the treatment of hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia, also spelled hypercalcaemia, is a high calcium (Ca2+) level in the blood serum. The normal range is 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L), with levels greater than 2.6 mmol/L defined as hypercalcem ...
or osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone a ...
.
In a recent clinical study, subcutaneous injections of calcitonin have reduced the incidence of fractures and reduced the decrease in bone mass in women with type 2 diabetes complicated with osteoporosis.
Subcutaneous injections of calcitonin in patients with mania
Mania, also known as manic syndrome, is a mental and behavioral disorder defined as a state of abnormally elevated arousal, affect, and energy level, or "a state of heightened overall activation with enhanced affective expression together wi ...
resulted in significant decreases in irritability, euphoria and hyperactivity and hence calcitonin holds promise for treating bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevat ...
. However no further work on this potential application of calcitonin has been reported.
Diagnostics
It may be used diagnostically as a tumor marker formedullary thyroid cancer
Medullary thyroid cancer is a form of thyroid carcinoma which originates from the parafollicular cells (C cells), which produce the hormone calcitonin.Hu MI, Vassilopoulou-Sellin R, Lustig R, Lamont JP"Thyroid and Parathyroid Cancers"in Pazdur R, ...
, in which high calcitonin levels may be present and elevated levels after surgery may indicate recurrence. It may even be used on biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a dise ...
samples from suspicious lesions (e.g., lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
s that are swollen) to establish whether they are metastases
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, the ...
of the original cancer.
Cutoffs for calcitonin to distinguish cases with medullary thyroid cancer have been suggested to be as follows, with a higher value increasing the suspicion of medullary thyroid cancer:
*females: 5 ng/L or pg/mL
*males: 12 ng/L or pg/mL
*children under 6 months of age: 40 ng/L or pg/mL
*children between 6 months and 3 years of age: 15 ng/L or pg/mL
When over 3 years of age, adult cutoffs may be used
A Cochrane Cochrane may refer to:
Places Australia
*Cochrane railway station, Sydney, a railway station on the closed Ropes Creek railway line
Canada
* Cochrane, Alberta
* Cochrane Lake, Alberta
* Cochrane District, Ontario
** Cochrane, Ontario, a town wit ...
rystematic review assessed the diagnostic accuracy of basal and stimulated calcitonin
Calcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone secreted by parafollicular cells (also known as C cells) of the thyroid (or endostyle) in humans and other chordates. in the ultimopharyngeal body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing the ...
for Medullary Thyroid cancer. Although both basal and combined basal and stimulated calcitonin testing presented high accuracy ( sensitivity: between 82% and 100%; specificity: between 97.2% and 100%), these results had a high risk of bias due to design flaws of included studies. Overall, the value of routine testing of calcitonin for diagnosis and prognosis of Medullary Thyroid Cancer remains uncertain and questionable.
Increased levels of calcitonin have also been reported for various other conditions. They include: C-cell hyperplasia, nonthyroidal oat cell carcinoma, nonthyroidal carcinoma and other nonthyroidal malignancies, acute kidney injury
Acute kidney injury (AKI), previously called acute renal failure (ARF), is a sudden decrease in kidney function that develops within 7 days, as shown by an increase in serum creatinine or a decrease in urine output, or both.
Causes of AKI are c ...
and chronic kidney failure
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of kidney disease in which a gradual loss of kidney function occurs over a period of months to years. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, v ...
, hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia, also spelled hypercalcaemia, is a high calcium (Ca2+) level in the blood serum. The normal range is 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L), with levels greater than 2.6 mmol/L defined as hypercalcem ...
, hypergastrinemia, and other gastrointestinal disorders, and pulmonary disease.
Structure
Calcitonin is a polypeptide hormone of 32 amino acids, with a molecular weight of 3454.93 daltons. Its structure comprises a single alpha helix. Alternative splicing of the gene coding for calcitonin produces a distantly related peptide of 37 amino acids, calledcalcitonin gene-related peptide
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is a member of the calcitonin family of peptides consisting of calcitonin, amylin, adrenomedullin, adrenomedullin 2 ( intermedin) and calcitonin‑receptor‑stimulating peptide. Calcitonin is mainly produ ...
(CGRP), beta type.
The following are the amino acid sequences of salmon and human calcitonin:
* salmon:
Cys-Ser-Asn-Leu-Ser-Thr-Cys-Val-Leu-Gly-Lys-Leu-Ser-Gln-Glu-Leu-His-Lys-Leu-Gln-Thr-Tyr-Pro-Arg-Thr-Asn-Thr-Gly-Ser-Gly-Thr-Pro
* human:
Cys-Gly-Asn-Leu-Ser-Thr-Cys-Met-Leu-Gly-Thr-Tyr-Thr-Gln-Asp-Phe-Asn-Lys-Phe-His-Thr-Phe-Pro-Gln-Thr-Ala-Ile-Gly-Val-Gly-Ala-Pro
Compared to salmon calcitonin, human calcitonin differs at 16 residues.
Research
In addition to the injectable and nasal spray dosage forms of the salmon calcitonin, noninvasive oral formulations of the peptide are currently under clinical development. The short-half-life of this peptide in serum triggered several attempts to enhance plasma concentrations. The peptide is complexed with a macromolecule that acts as an absorption enhancer through the transcellular pathway and, additionally, protects the peptide from the harsh pH and enzymatic conditions of the GI tract. This complexation is weak, noncovalent and reversible and the drug remains chemically unmodified. After passage through the intestine, the delivery agent dissociates from the peptide. One of the extensively studied oral formulations is the disodium salts of 5-CNAC oral calcitonin. This novel oral platform in a number of clinical trials at different phases has demonstrated promising enhanced pharmacokinetic profile, high bioavailability, well-established safety and comparable efficacy to that of nasal calcitonin especially for treatment of postmenopausal bone loss.See also
*Procalcitonin
Procalcitonin (PCT) is a peptide precursor of the hormone calcitonin, the latter being involved with calcium homeostasis. It arises once preprocalcitonin is cleaved by endopeptidase. It was first identified by Leonard J. Deftos and Bernard A. Ro ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * *External links
The Calcitonin Protein
* {{Amyloidosis Peptide hormones Hormones of the thyroid gland Human hormones Hormones of calcium metabolism Tumor markers Thyroid