Calabria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 =
, demographics1_info2 =
, demographics1_title3 =
, demographics1_info3 =
, timezone1 =
· 20th of 21 , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 = ITF , website
www.regione.calabria.it
, footnotes = , name = Calabria (), is a



 The region is generally known as the "toe" of the "boot" of Italy and is a long and narrow peninsula which stretches from north to south for , with a maximum width of . Some 42% of Calabria's area, corresponding to 15,080 km2, is mountainous, 49% is hilly, while plains occupy only 9% of the region's territory. It is surrounded by the Ionian and Tyrrhenian seas. It is separated from
The region is generally known as the "toe" of the "boot" of Italy and is a long and narrow peninsula which stretches from north to south for , with a maximum width of . Some 42% of Calabria's area, corresponding to 15,080 km2, is mountainous, 49% is hilly, while plains occupy only 9% of the region's territory. It is surrounded by the Ionian and Tyrrhenian seas. It is separated from
 Calabria is commonly considered part of the "Calabrian Arc", an arc-shaped geographic domain extending from the southern part of the Basilicata Region to the northeast of
Calabria is commonly considered part of the "Calabrian Arc", an arc-shaped geographic domain extending from the southern part of the Basilicata Region to the northeast of
 Calabria has one of the oldest records of human presence in Italy, which date back to around 700,000 BC when a type of '' Homo erectus'' evolved leaving traces around coastal areas. During the Paleolithic period Stone Age humans created the "
Calabria has one of the oldest records of human presence in Italy, which date back to around 700,000 BC when a type of '' Homo erectus'' evolved leaving traces around coastal areas. During the Paleolithic period Stone Age humans created the "
 At the end of the 18th century the French took control and in 1808 Napoleon Bonaparte gave the Kingdom of Naples to his brother-in-law
At the end of the 18th century the French took control and in 1808 Napoleon Bonaparte gave the Kingdom of Naples to his brother-in-law
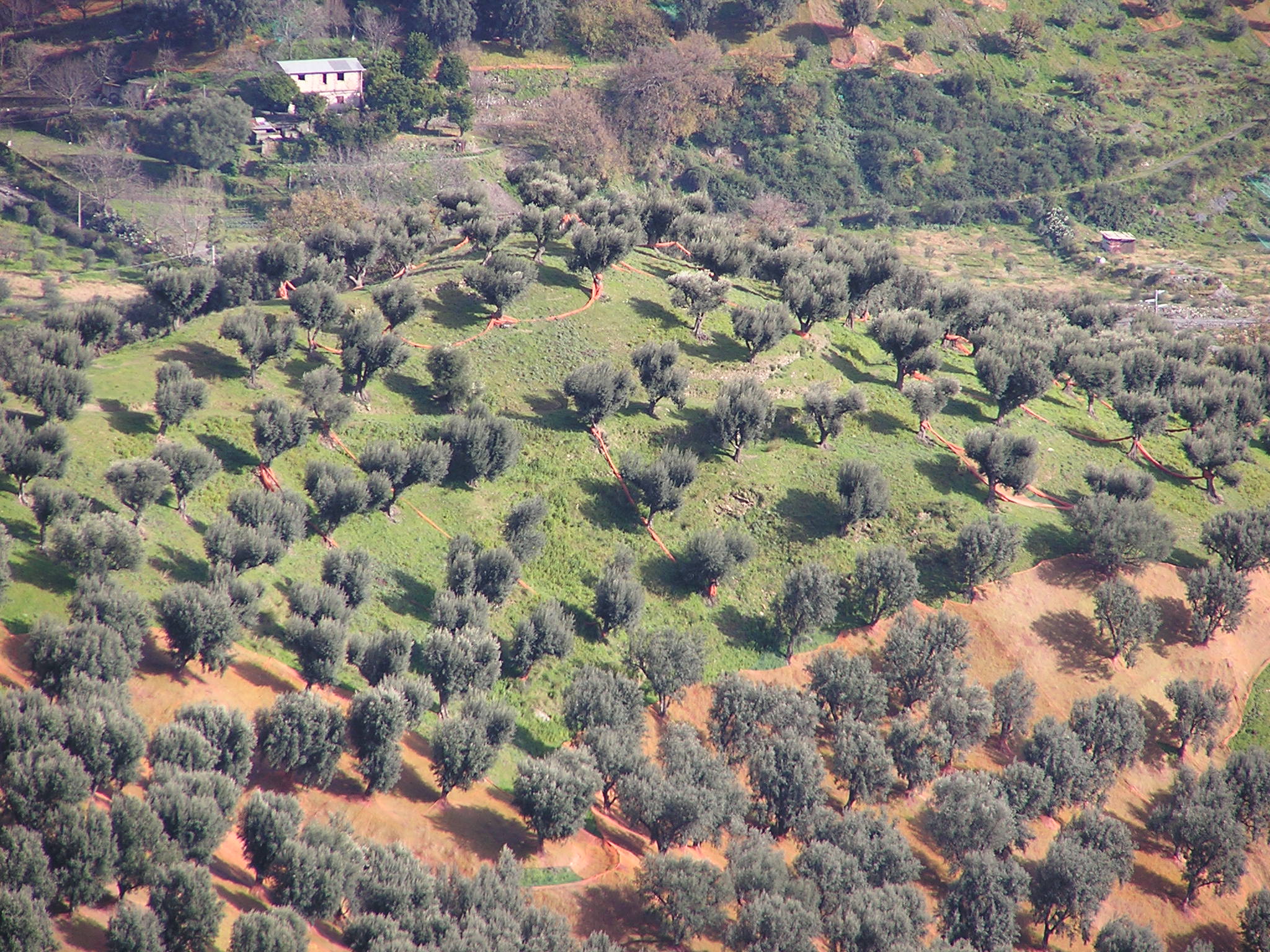 Calabria is agriculturally rich, with the Italy's second highest number of organic farmers after
Calabria is agriculturally rich, with the Italy's second highest number of organic farmers after  Minor fruits such as bergamot and
Minor fruits such as bergamot and 
Bottarga_vom_Thunfisch.jpg, Bottarga di tonno rosso
Sardella.jpg, Sardella calabrese
Xiphias_gladius_stuffed.jpg, Swordfish
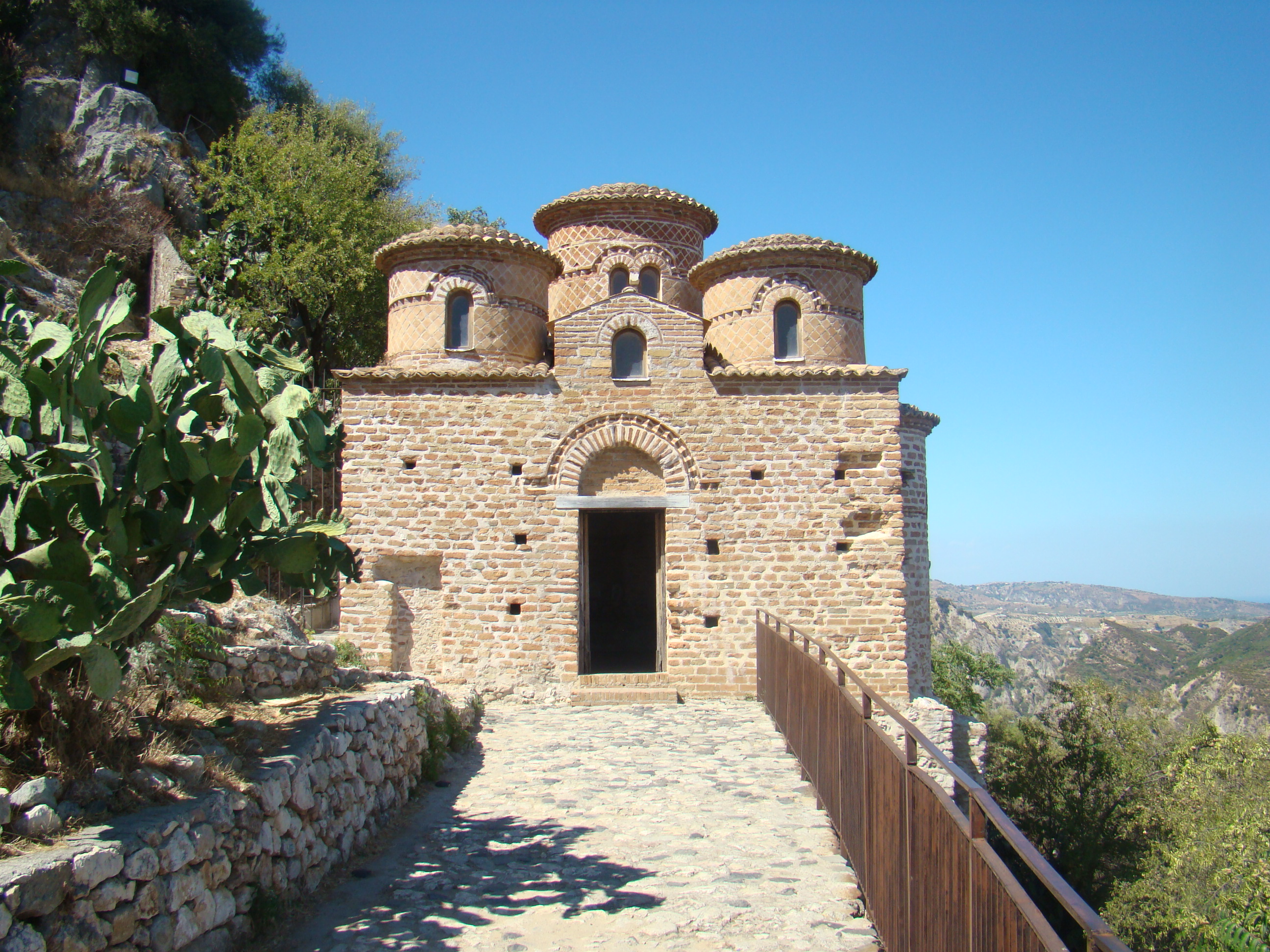

 Tourism in Calabria has increased over the years. The main tourist attractions are the coastline and the mountains. The coastline alternates between rugged cliffs and sandy beaches, and is sparsely interrupted by development when compared to other European seaside destinations. The sea around Calabria is clear, and there is a good level of tourist accommodation. The poet Gabriele D'Annunzio called the coast facing Sicily near Reggio Calabria "... the most beautiful kilometer in Italy" (''il più bel chilometro d'Italia''). The primary mountain tourist draws are Aspromonte and
Tourism in Calabria has increased over the years. The main tourist attractions are the coastline and the mountains. The coastline alternates between rugged cliffs and sandy beaches, and is sparsely interrupted by development when compared to other European seaside destinations. The sea around Calabria is clear, and there is a good level of tourist accommodation. The poet Gabriele D'Annunzio called the coast facing Sicily near Reggio Calabria "... the most beautiful kilometer in Italy" (''il più bel chilometro d'Italia''). The primary mountain tourist draws are Aspromonte and
 The main Calabrian ports are in Reggio Calabria and in
The main Calabrian ports are in Reggio Calabria and in
 Calabria is divided into five provinces:
Calabria is divided into five provinces:
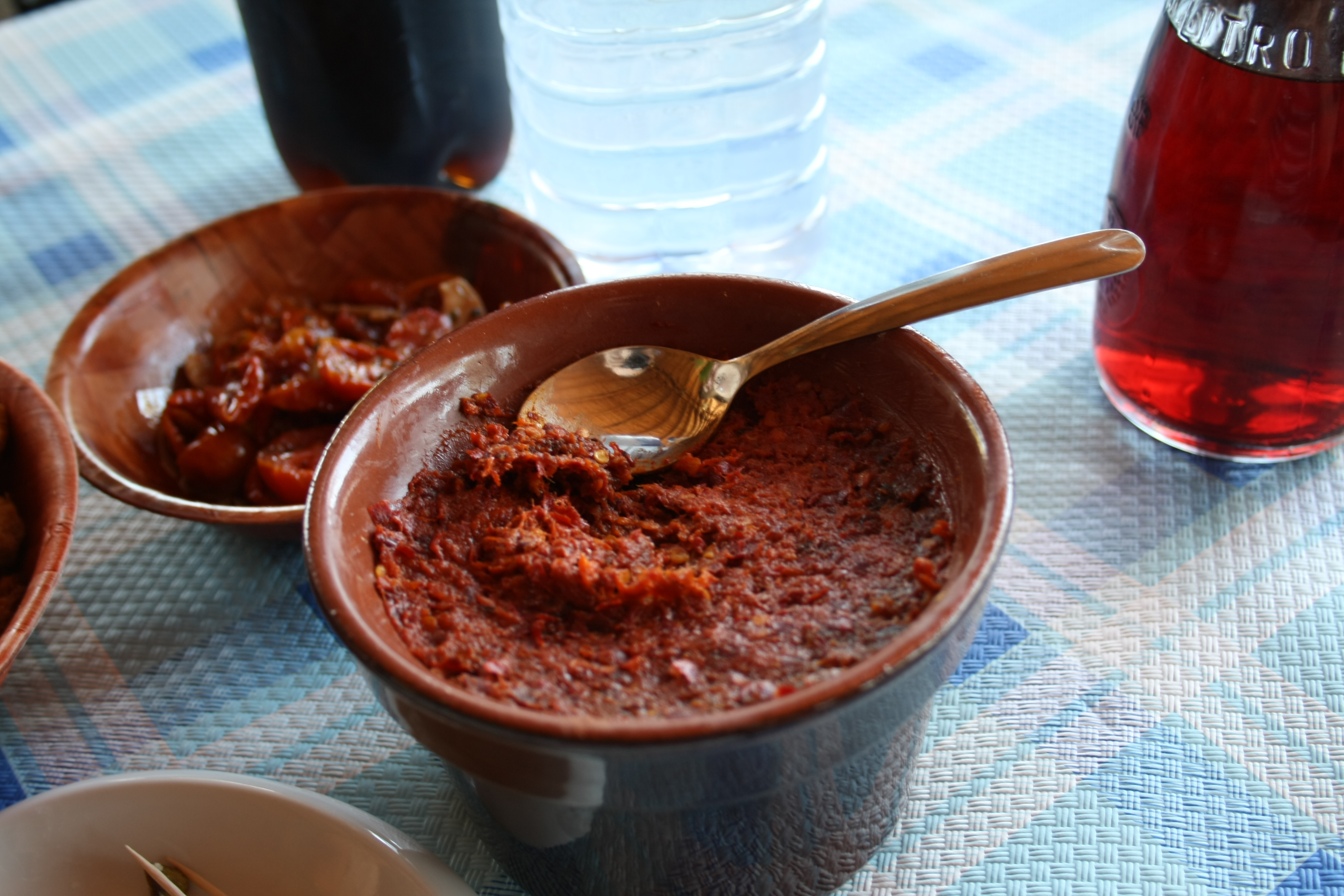 The cuisine is a typical southern Italian
The cuisine is a typical southern Italian
Official website of the region
Official website of tourism
{{coord, 38, 55, N, 16, 36, E, type:adm1st_region:IT-78, display=title Peninsulas of Italy * Regions of Italy NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union Wine regions of Italy
CET
CET or cet may refer to:
Places
* Cet, Albania
* Cet, standard astronomical abbreviation for the constellation Cetus
* Colchester Town railway station (National Rail code CET), in Colchester, England
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Comcast En ...
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = CEST
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal_code_type =
, postal_code =
, area_code_type = ISO 3166 code
, area_code = IT-78
, blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal)
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
, blank_info_sec1 = €33.3 billion (2018)
, blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita
, blank1_info_sec1 = €17,000 (2018)
, blank2_name_sec1 = HDI
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, wh ...
(2018)
, blank2_info_sec1 = 0.845· 20th of 21 , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 = ITF , website
www.regione.calabria.it
, footnotes = , name = Calabria (), is a
region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics ( physical geography), human impact characteristics ( human geography), and the interaction of humanity an ...
in Southern Italy. It is a peninsula bordered by Basilicata to the north, the Ionian Sea to the east, the Strait of Messina
The Strait of Messina ( it, Stretto di Messina, Sicilian: Strittu di Missina) is a narrow strait between the eastern tip of Sicily ( Punta del Faro) and the western tip of Calabria ( Punta Pezzo) in Southern Italy. It connects the Tyrrhenian S ...
to the southwest, which separates it from Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, and the Tyrrhenian Sea to the west. With almost 2 million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the tenth most populous and the tenth largest Italian region by area. Catanzaro
Catanzaro (, or ; scn, label= Catanzarese, Catanzaru ; , or , ''Katastaríoi Lokrói''; ; la, Catacium), also known as the "City of the two Seas", is an Italian city of 86,183 inhabitants (2020), the capital of the Calabria region and of its p ...
is the region's capital, while Reggio Calabria is the most populous city in the region.
Calabria is the birthplace of the term ''Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
'', given to it by the Ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
which settled in this land starting from the 8th century BC
The 8th century BCE started the first day of 800 BC and ended the last day of 701 BC. The 8th century BC is a period of great change for several historically significant civilizations. In Egypt, the 23rd and 24th dynasties lead to rule from ...
. Thanks to its strategic position in the center of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
, the region became the center of Magna Grecia (Greater Greece), with the foundation along its coasts of many Greek city-states ( póleis) that remained for centuries among the richest and most culturally advanced of their time. Calabria is where Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos ( grc, Πυθαγόρας ὁ Σάμιος, Pythagóras ho Sámios, Pythagoras the Samian, or simply ; in Ionian Greek; ) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His politi ...
, one of the fathers of Western philosophy
Western philosophy encompasses the philosophical thought and work of the Western world. Historically, the term refers to the philosophical thinking of Western culture, beginning with the ancient Greek philosophy of the pre-Socratics. The word ' ...
, developed and spread his thought. It's also the birthplace of Milo
Milo may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Milo'' (magazine), a strength sports magazine
*'' Milo: Sticky Notes and Brain Freeze'', a 2011 children's novel by Alan Silberberg
* ''Milo'' (video game), a first-person adventure-puzzle computer ga ...
, the greatest champion of the ancient Olympic Games, and the adoptive homeland of Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
, one of the greatest historians of all time.
In Roman times it was part of the ''Regio III Lucania et Bruttii'', a region of Augustan Italy. After the Gothic War, it became and remained for five centuries a Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
dominion (''Duchy of Calabria'', later promoted to Theme), fully recovering its Hellenic character on a linguistic, religious and artistic level. Cenobitism
Cenobitic (or coenobitic) monasticism is a monastic tradition that stresses community life. Often in the West the community belongs to a religious order, and the life of the cenobitic monk is regulated by a religious rule, a collection of prece ...
flourished, with the rise in the whole peninsula of countless churches, hermitages and monasteries in which multitudes of Basilian monks were dedicated to the transcription of classical and religious texts. The Byzantines introduced the art of silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the ...
in Calabria and made it the main silk production area in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
. In the 11th century, the Norman conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Con ...
started a slow process of Latinization.
It is the birthplace of two of the most influential European philosophers of the 16th century, Bernardino Telesio and Tommaso Campanella
Tommaso Campanella (; 5 September 1568 – 21 May 1639), baptized Giovanni Domenico Campanella, was an Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, theologian, astrologer, and poet.
He was prosecuted by the Roman Inquisition for heresy in 1594 an ...
.
In Calabria there are three historical ethnic minorities: the Griko people
The Griko people ( el, Γκρίκο), also known as Grecanici in Calabria, are an ethnic Greek community of Southern Italy. They are found principally in regions of Calabria and Apulia (peninsula of Salento). The Griko are believed to be remnants ...
, speaking Calabrian Greek (also known as ''Grecanico''), a local variety of the Greek language
Greek ( el, label= Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy ( Calabria and Salento), southe ...
with some unique and archaic features; the Arbëreshë people, descendants of Albanian refugees who fled Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
between the 14th and the 18th centuries following the Ottoman conquest of the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
; the Occitans of Guardia Piemontese
Guardia Piemontese ( Occitan: ''La Gàrdia'') is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Cosenza and the region of Calabria in southern Italy.
Location and language
Guardia Piemontese is located about 55 km northwest of Cosenza on th ...
, a village founded in the 12th century by Waldensians coming from the Western Alps
The Western Alps are the western part of the Alpine Range including the southeastern part of France (e.g. Savoie), the whole of Monaco, the northwestern part of Italy (i.e. Piedmont and the Aosta Valley) and the southwestern part of Switzerland ( ...
. This extraordinary linguistic diversity makes the region an object of study for linguists from all over the world.
Three national parks are found in the Calabria: the Pollino National Park (which is the largest in the country), the Sila National Park and the Aspromonte National Park. This, combined with a large number of beaches, small villages, archaeological parks and ancient castles, makes the region a tourist destination.
Etymology
Starting in the third century BC, the name ''Calabria'' was originally given to the Adriatic coast of theSalento
Salento (Salentino: ''Salentu'', Salentino Griko: ''Σαλέντο'') is a cultural, historical and geographic region at the southern end of the administrative region of Apulia in Southern Italy. It is a sub-peninsula of the Italian Peninsula, ...
peninsula in modern Apulia. In the late first century BC this name came to extend to the entirety of the Salento, when the Roman emperor Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
divided Italy into regions. The whole region of Apulia received the name ''Regio II Apulia et Calabria''. By this time modern Calabria was still known as ''Bruttium'', after the Bruttians who inhabited the region. Later in the seventh century AD, the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
created the Duchy of Calabria from the Salento and the Ionian part of Bruttium. Even though the Calabrian part of the duchy was conquered by the Longobards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 and ...
during the eighth and ninth centuries AD, the Byzantines continued to use the name ''Calabria'' for their remaining territory in Bruttium.
The modern name ''Italy'' derives from ''Italia'', which was first used as a name for the southern part of modern Calabria. Over time the Greeks started to use it for the rest of the southern Italian peninsula as well. After the Roman conquest of the region, the name was used for the entire Italian peninsula and eventually the Alpine region too.
Geography


 The region is generally known as the "toe" of the "boot" of Italy and is a long and narrow peninsula which stretches from north to south for , with a maximum width of . Some 42% of Calabria's area, corresponding to 15,080 km2, is mountainous, 49% is hilly, while plains occupy only 9% of the region's territory. It is surrounded by the Ionian and Tyrrhenian seas. It is separated from
The region is generally known as the "toe" of the "boot" of Italy and is a long and narrow peninsula which stretches from north to south for , with a maximum width of . Some 42% of Calabria's area, corresponding to 15,080 km2, is mountainous, 49% is hilly, while plains occupy only 9% of the region's territory. It is surrounded by the Ionian and Tyrrhenian seas. It is separated from Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
by the Strait of Messina
The Strait of Messina ( it, Stretto di Messina, Sicilian: Strittu di Missina) is a narrow strait between the eastern tip of Sicily ( Punta del Faro) and the western tip of Calabria ( Punta Pezzo) in Southern Italy. It connects the Tyrrhenian S ...
, where the narrowest point between Capo Peloro in Sicily and Punta Pezzo in Calabria is only .
Three mountain ranges are present: Pollino, La Sila
La Sila, also simply Sila, is the name of the mountainous plateau and historic region located in Calabria, southern Italy. The Sila National Park is known to have the purest air in Europe.
Geography
The Sila occupies part of the provinces of Co ...
and Aspromonte, each with its own flora and fauna. The Pollino Mountains in the north of the region are rugged and form a natural barrier separating Calabria from the rest of Italy. Parts of the area are heavily wooded, while others are vast, wind-swept plateaus with little vegetation. These mountains are home to a rare Bosnian Pine variety and are included in the Pollino National Park, which is the largest national park in Italy, covering 1,925.65 square kilometres.
La Sila
La Sila, also simply Sila, is the name of the mountainous plateau and historic region located in Calabria, southern Italy. The Sila National Park is known to have the purest air in Europe.
Geography
The Sila occupies part of the provinces of Co ...
, which has been referred to as the "Great Wood of Italy", is a vast mountainous plateau about above sea level and stretches for nearly along the central part of Calabria. The highest point is Botte Donato, which reaches . The area boasts numerous lakes and dense coniferous forests. La Sila also has some of the tallest trees in Italy which are called the "Giants of the Sila" and can reach up to in height. The Sila National Park is also known to have the purest air in Europe.
The Aspromonte massif forms the southernmost tip of the Italian peninsula bordered by the sea on three sides. This unique mountainous structure reaches its highest point at Montalto, at , and is full of wide, man-made terraces that slope down towards the sea.
Most of the lower terrain in Calabria has been agricultural for centuries, and exhibits indigenous scrubland as well as introduced plants such as the prickly pear cactus
''Opuntia'', commonly called prickly pear or pear cactus, is a genus of flowering plants in the cactus family Cactaceae. Prickly pears are also known as ''tuna'' (fruit), ''sabra'', ''nopal'' (paddle, plural ''nopales'') from the Nahuatl word f ...
. The lowest slopes are rich in vineyards and orchards of citrus fruit, including the Diamante citron
The Diamante citron (''Citrus medica'' var. ''vulgaris'' or cv. ''diamante'' − it, cedro di diamante, he, אתרוג קלבריה or גינובה) is a variety of citron named after the town of Diamante, located in the province of Cosenza, C ...
. Further up, olives and chestnut trees appear while in the higher regions there are often dense forests of oak, pine, beech and fir trees.
Climate
Calabria's climate is influenced by the sea and mountains. TheMediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
is typical of the coastal areas with considerable differences in temperature and rainfall between the seasons, with an average low of during the winter months and an average high of during the summer months. Mountain areas have a typical mountainous climate with frequent snow during winter. The erratic behavior of the Tyrrhenian Sea can bring heavy rainfall on the western slopes of the region, while hot air from Africa makes the east coast of Calabria dry and warm. The mountains that run along the region also influence the climate and temperature of the region. The east coast is much warmer and has wider temperature ranges than the west coast. The geography of the region causes more rain to fall along the west coast than that of the east coast, which occurs mainly during winter and autumn and less during the summer months.
Below are the two extremes of climate in Calabria, the warm mediterranean subtype on the coastline and the highland climate of Monte Scuro.
Geology
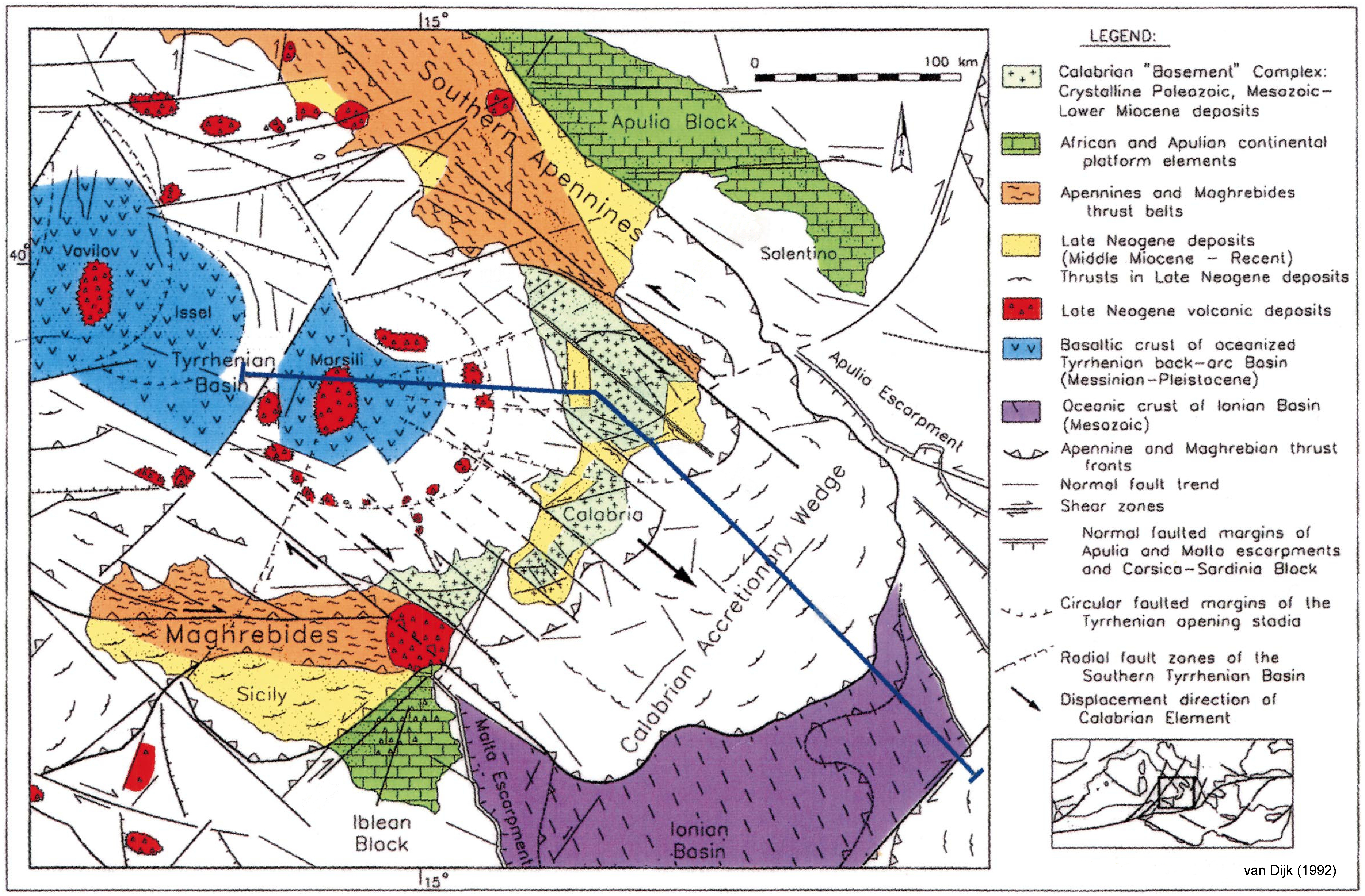
 Calabria is commonly considered part of the "Calabrian Arc", an arc-shaped geographic domain extending from the southern part of the Basilicata Region to the northeast of
Calabria is commonly considered part of the "Calabrian Arc", an arc-shaped geographic domain extending from the southern part of the Basilicata Region to the northeast of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, and including the Peloritano Mountains (although some authors extend this domain from Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
in the north to Palermo in the southwest). The Calabrian area shows basement (crystalline and metamorphic rocks) of Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
and younger ages, covered by (mostly Upper) Neogene sediments. Studies have revealed that these rocks comprise the upper part of a pile of thrust sheets which dominate the Apennines and the Sicilian Maghrebides.van Dijk, J.P., Bello, M., Brancaleoni, G.P., Cantarella, G., Costa, V., Frixa, A., Golfetto, F., Merlini, S., Riva, M., Toricelli, S., Toscano, C., and Zerilli, A. (2000, a); A new structural model for the northern sector of the Calabrian Arc. Tectonophysics, 324, 267–320.
The Neogene evolution of the Central Mediterranean system is dominated by the migration of the Calabrian Arc to the southeast, overriding the African Plate and its promontories.Argand, E. (1922); La tectonique de l'Asie. Comptes Rendus 3rd Int. Geol. Congr., Liège (Be), 1922, 1, 171–372.Boccaletti, M., and Guazzone, G. (1972, b); Evoluzione paleogeografica e geodinamica del Mediterraneo: i bacini marginali. Mem. Soc. geol. It., 13, 162–169.) The main tectonic elements of the Calabrian Arc are the Southern Apennines fold-and-thrust belt, the "Calabria-Peloritani", or simply Calabrian block and the Sicilian Maghrebides fold-and-thrust belt. The foreland area is formed by the Apulia Platform, which is part of the Adriatic Plate, and the Ragusa or Iblean Platform, which is an extension of the African Plate. These platforms are separated by the Ionian Basin
Ionic or Ionian may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Ionic meter, a poetic metre in ancient Greek and Latin poetry
* Ionian mode, a musical mode or a diatonic scale
Places and peoples
* Ionian, of or from Ionia, an ancient region in western ...
. The Tyrrhenian oceanized basin is regarded as the back-arc basin. This subduction system therefore shows the southern plates of African affinity subducting below the northern plates of European affinity.
The geology of Calabria has been studied for more than a century.Ogniben, Leo (1973); Schema geologico della Calabria in base ai dati odierni. Geol. Romana, 12, 243–585.Ippolito, Felice (1959); Bibliografia geologica d'Italia, Vol. 4, Calabria. C.N.R., RomaCortese, E. (1895); Descrizione geologica della Calabria. Mem. Descrit. Carta Geol. It., 9, 310 pp., Roma. The earlier works were mainly dedicated to the evolution of the basement rocks of the area. The Neogene sedimentary successions were merely regarded as "post-orogenic" infill of "neo-tectonic" tensional features. In the course of time, however, a shift can be observed in the temporal significance of these terms, from post-Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " ...
to post-Early Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
to post-middle Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
.
The region is seismically active and is generally ascribed to the re-establishment of an equilibrium after the latest (mid-Pleistocene) deformation phase. Some authors believe that the subduction process is still ongoing, which is a matter of debate.
History
 Calabria has one of the oldest records of human presence in Italy, which date back to around 700,000 BC when a type of '' Homo erectus'' evolved leaving traces around coastal areas. During the Paleolithic period Stone Age humans created the "
Calabria has one of the oldest records of human presence in Italy, which date back to around 700,000 BC when a type of '' Homo erectus'' evolved leaving traces around coastal areas. During the Paleolithic period Stone Age humans created the "Bos Primigenius
The aurochs (''Bos primigenius'') ( or ) is an extinct cattle species, considered to be the wild ancestor of modern domestic cattle. With a shoulder height of up to in bulls and in cows, it was one of the largest herbivores in the Holocene; ...
", a figure of a bull on a cliff which dates back around 12,000 years in the Romito Cave in the town of Papasidero. When the Neolithic period came the first villages were founded around 3,500 BC.
Antiquity
Around 1500 BC a tribe called the Oenotri ("vine-cultivators"), settled in the region. According toGreek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities ...
, they were Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
who were led to the region by their king, Oenotrus. The Greeks used the term 'italoi', which according to some ancient Greek writers was derived from a legendary king of the Oenotri, Italus and according to others from the bull. Originally the Greeks used 'italoi' to indicate Calabrians and later it became synonymous with the rest of the peninsula. Calabria therefore was the first region to be called Italia (Italy).
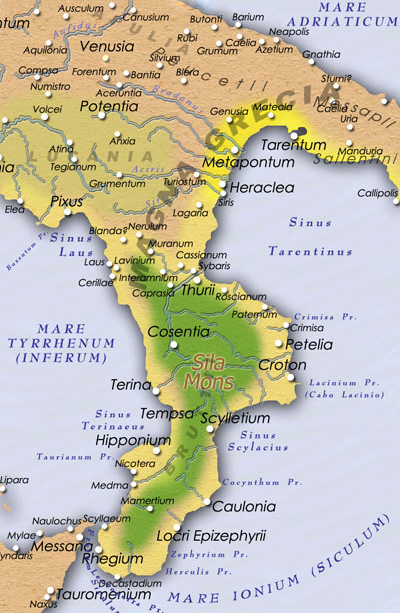
During the eighth and seventh centuries BC, Greek settlers founded many colonies (settlements) on the coast of southern Italy ( Magna Grecia). In Calabria they founded Chone ( Pallagorio), Cosentia ( Cosenza), Clampetia (Amantea Amantea ( Calabrian: ; ) is a town, former bishopric, ''comune'' (municipality) and Latin Catholic titular see in the province of Cosenza in the Calabria region of southern Italy.
It is the twentieth municipality in the region by population, while f ...
), Scyllaeum (Scilla
''Scilla'' () is a genus of about 30 to 80 species of bulb-forming perennial herbaceous plants in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae. Sometimes called the squills in English, they are native to woodlands, subalpine meadows, and sea ...
), Sybaris
Sybaris ( grc, Σύβαρις; it, Sibari) was an important city of Magna Graecia. It was situated in modern Calabria, in southern Italy, between two rivers, the Crathis (Crati) and the Sybaris (Coscile).
The city was founded in 720 BC ...
( Sibari), Hipponion (Vibo Valentia
Vibo Valentia (; Monteleone before 1861; Monteleone di Calabria from 1861 to 1928; scn, label= Calabrian, Vibbu Valenzia or ) is a city and ''comune'' (municipality) in the Calabria region of southern Italy, near the Tyrrhenian Sea. It is the ca ...
), Locri Epizefiri
Locri is a town and ''comune'' (municipality) in the province of Reggio Calabria, Calabria, southern Italy. Its name derives from that of the ancient Greek region of Locris. Today it is an important administrative and cultural centre on the Ioni ...
( Locri), Kaulon
Caulonia or Caulon ( grc, Καυλωνία, Kaulōnía; also spelled Kaulonia or Kaulon) was an ancient city of Magna Graecia on the shore of the Ionian Sea. At some point after the destruction of the city by Rome in 200 BC, the inhabitants moved ...
( Monasterace), Krimisa ( Cirò Marina), Kroton ( Crotone), Laüs (comune of Santa Maria del Cedro), Medma (Rosarno
Rosarno is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Reggio Calabria in the Italian region of Calabria. It is about southwest of Catanzaro and about northeast of Reggio Calabria. Rosarno stands on a natural terrace cloaked in olive ...
), Metauros
Gioia Tauro () is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Reggio Calabria (Italy), on the Tyrrhenian coast. It has an important port, situated along the route connecting Suez to Gibraltar, one of the busiest maritime corridors in t ...
(Gioia Tauro
Gioia Tauro () is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Reggio Calabria (Italy), on the Tyrrhenian coast. It has an important port, situated along the route connecting Suez to Gibraltar, one of the busiest maritime corridors in t ...
), Petelia ( Strongoli), Rhégion ( Reggio Calabria), Scylletium ( Borgia), Temesa (Campora San Giovanni
Campora San Giovanni (''Campura San Giuvanni'' or ''Campura Santu Janni'', in the ancient Camporese dialect) is a ''frazione'' of the ''comune'' (municipality) of Amantea, in the province of Cosenza, Calabria, Italy, located close to the border ...
), Terina (Nocera Terinese
Nocera Terinese is a town and ''comune'' of the province of Catanzaro in the Calabria region of southern Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located ...
), Pandosia (Acri
Acri ( Calabrian: ) is a town of 19.949 inhabitants in the northern part of Calabria region in southern Italy. Since 17 September 2001 Acri has had the "status" of city.
Acri's coat of arms is represented by three mountains surmounted by thre ...
) and Thurii, (Thurio, comune of Corigliano Calabro).
Rhegion was the birthplace of one of the famed nine lyric poets
The Nine Lyric or Melic Poets were a canonical group of ancient Greek poets esteemed by the scholars of Hellenistic Alexandria as worthy of critical study. In the Palatine Anthology it is said that they established lyric song.
They were:
*Alcman o ...
, Ibycus
Ibycus (; grc-gre, Ἴβυκος; ) was an Ancient Greek lyric poet, a citizen of Rhegium in Magna Graecia, probably active at Samos during the reign of the tyrant Polycrates and numbered by the scholars of Hellenistic Alexandria in the cano ...
. Metauros was the birthplace of another of the nine lyric poets
The Nine Lyric or Melic Poets were a canonical group of ancient Greek poets esteemed by the scholars of Hellenistic Alexandria as worthy of critical study. In the Palatine Anthology it is said that they established lyric song.
They were:
*Alcman o ...
, Stesichorus
Stesichorus (; grc-gre, Στησίχορος, ''Stēsichoros''; c. 630 – 555 BC) was a Greek lyric poet native of today's Calabria (Southern Italy). He is best known for telling epic stories in lyric metres, and for some ancient traditions abo ...
, who was the first lyric poet of the western world. Kroton spawned many victors during the ancient Olympics and other Panhellenic Games. Amongst the most famous were Milo of Croton
Milo or Milon of Croton (late 6th century BC) was a famous ancient Greek athlete.
He was most likely a historical person, as he is mentioned by many classical authors, among them Aristotle, Pausanias, Cicero, Herodotus, Vitruvius, Epictetus, an ...
, who won six wrestling events in six Olympics in a row, along with seven events in the Pythian Games, nine events in the Nemean Games and ten events in the Isthmian Games and also Astylos of Croton, who won six running events in three Olympics in a row. Through Alcmaeon of Croton
Alcmaeon of Croton (; el, Ἀλκμαίων ὁ Κροτωνιάτης, ''Alkmaiōn'', ''gen''.: Ἀλκμαίωνος; fl. 5th century BC) was an early Greek medical writer and philosopher-scientist. He has been described as one of the most ...
(a philosopher and medical theorist) and Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos ( grc, Πυθαγόρας ὁ Σάμιος, Pythagóras ho Sámios, Pythagoras the Samian, or simply ; in Ionian Greek; ) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His politi ...
(a mathematician and philosopher), who moved to Kroton in 530 BC, the city became a renowned center of philosophy, science and medicine. The Greeks of Sybaris
Sybaris ( grc, Σύβαρις; it, Sibari) was an important city of Magna Graecia. It was situated in modern Calabria, in southern Italy, between two rivers, the Crathis (Crati) and the Sybaris (Coscile).
The city was founded in 720 BC ...
created "Intellectual Property." Sybaris benefited from "vinoducts" which were a series of pipes that carried wine to the homes of its citizens. The Sybarite founded at least 20 other colonies, including Poseidonia (Paestum
Paestum ( , , ) was a major ancient Greek city on the coast of the Tyrrhenian Sea in Magna Graecia (southern Italy). The ruins of Paestum are famous for their three ancient Greek temples in the Doric order, dating from about 550 to 450 BC, whi ...
in Latin, on the Tyrrhenian coast of Lucania), Laüs (on the border with Lucania) and Scidrus (on the Lucanian coast in the Gulf of Taranto). Locri was renowned for being the town where Zaleucus
Zaleucus ( grc, Ζάλευκος; fl. 7th century BC) was the Greek lawgiver of Epizephyrian Locri, in Italy. According to the Suda, he was previously a slave and a shepherd, and after having been educated he gave laws to his fellow-citizens. Some ...
created the first Western Greek law, the "Locrian Code" and the birthplace of ancient epigrammist and poet Nossis
Nossis ( grc-gre, Νοσσίς) was a Hellenistic Greek poet from Epizephyrian Locris in today's Calabria (Southern Italy). She seems to have been active in the early third century BC, as she wrote an epitaph for the Hellenistic dramatist Rhinth ...
.
The Itali were the first established people of Calabria. Later came the Bruttii from Lucania. These occupied Calabria and called it Bruttium. The Bruttii were very advanced culturally. The Greek cities of Calabria came under the pressure from these Lucanians, an Oscan people who lived in the present day region of Basilicata. They conquered the north of Calabria and pushed further south, taking over part of the interior, probably after they defeated the Thurians near Laus in 390 BC. A few decades later Calabria came under pressure from the Bruttii. They were Lucanian slaves and other fugitives who were seeking refuge on the steep mountains of Calabria. Their name was Lucanian and meant rebels. They took advantage of the weakening of the Greek cites caused by wars between them. They took over Hipponium, Terina and Thurii. They helped the Lucanians to fight Alexander of Epirus
Alexander I of Epirus ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος Α'; c. 371 BC – 331 BC), also known as Alexander Molossus (), was a king of Epirus (343/2–331 BC) of the Aeacid dynasty.Ellis, J. R., ''Philip II and Macedonian Imperialis ...
(334–32 BC), who had come to the aid of Tarentum (in Apulia), which was also pressured by the Lucanians. After this, Agathocles of Syracuse
Agathocles ( grc-gre, Ἀγαθοκλῆς, ''Agathoklḗs''; 361–289 BC) was a Greek tyrant of Syracuse (317–289 BC) and self-styled king of Sicily (304–289 BC).
Biography
Agathocles was born at Thermae Himeraeae (modern na ...
ravaged the coast of Calabria with his fleet, took Hipponium and forced the Bruttii into unfavourable peace terms. However, they soon seized Hipponium again. After Agathloces' death in 289 BC the Lucanians and Bruttii pushed into the territory of Thurii and ravaged it. The city sent envoys to Rome to ask for help in 285 BC and 282 BC. On the second occasion, the Romans sent forces to garrison the city. This was part of the episode which sparked the Pyrrhic war.
During the Pyrrhic War (280–275 BC) the Lucanians and Bruttii sided with Pyrrhus and provided contingents which fought with his army. When Pyrrhus landed in Italy the people of Rhegion were worried about their safety and asked Rome for protection. The Romans sent soldiers from Campania to garrison the city. Coveting the wealth of the city, the soldiers killed its prominent men, sent away the rest and seized their property. The Romans could not do much about it because they were engaged in the war. A few years after the end of the war, in 271 BC, the Romans retook the city, arrested the soldiers and took them to Rome, where they were executed. After Pyrrhus was defeated, to avoid Roman revenge, the Bruttii submitted willingly and gave up half of the Sila, a mountainous plateau which was valuable for its pitch and timber. The timber here was sold all over Italy and the resin of the area was of the highest quality.
During the Second Punic War (218–201 BC) the Bruttii allied with Hannibal, who sent Hanno, one of his commanders, to Calabria. Hanno marched towards Capua
Capua ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in the province of Caserta, in the region of Campania, southern Italy, situated north of Naples, on the northeastern edge of the Campanian plain.
History
Ancient era
The name of Capua comes from the Etrus ...
(in Campania) with Bruttian soldiers to take them to Hannibal's headquarters there twice, but he was defeated on both occasions. When his campaign in Italy came to a dead end, Hannibal took refuge in Calabria, whose steep mountains provided protection against the Roman legions. He set up his headquarters in Kroton and stayed there for four years until he was recalled to Carthage. The Romans fought a battle with him near Kroton, but its details are unknown. Many Calabrian cities surrendered. Calabria was put under a military commander. Nearly a decade after the war, the Romans set up colonies in Calabria: at Tempsa and Kroton (Croto in Latin) in 194 BC, Copiae in the territory of Thurii (Thurium in Latin) in 193 BC, and Vibo Valentia in the territory of Hipponion in 192 BC. The Romans called Calabria Bruttium. Later, during the reign of Augustus it became part of the third region of Italy, the 'Regio III Lucania et Brettium.
Middle Ages
After sacking Rome in 410, Alaric I (King of the Visigoths) went to Calabria with the intention of sailing to Africa. He contracted malaria and died in Cosentia ( Cosenza), probably of fever. Legend has it that he along with the treasure of Rome were buried under the bed of the River Busento. With the fall of the western part of the Roman Empire in 476, Italy was taken over by the Germanic chieftain Odoacer and later became part of theOstrogothic Kingdom
The Ostrogothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of Italy (), existed under the control of the Germanic Ostrogoths in Italy and neighbouring areas from 493 to 553.
In Italy, the Ostrogoths led by Theodoric the Great killed and replaced Odoacer, ...
in 489. The Ostrogothic kings ruled officially as Magistri Militum of the Byzantine Emperors and all government and administrative positions were held by the Romans while all primary laws were legislated by the Byzantine Emperor. Therefore, during the sixth century, under the Ostrogoths' rule, Romans could still be at the center of government and cultural life, such as the Roman Cassiodorus
Magnus Aurelius Cassiodorus Senator (c. 485 – c. 585), commonly known as Cassiodorus (), was a Roman statesman, renowned scholar of antiquity, and writer serving in the administration of Theodoric the Great, king of the Ostrogoths. ''Senator'' ...
who, like Boethius and Symmachus, emerged as one of the most prominent men of his time. He was an administrator, politician, scholar and historian who was born in Scylletium (near Catanzaro). He spent most of his career trying to bridge the divides of East and West, Greek and Latin cultures, Romans and Goths, and official Christianity and Arian Christianity, which was the form of Christianity of the Ostrogoths and which had earlier been banned. He set up his Vivarium (monastery) in Scylletium. He oversaw the collation of three editions of the Bible in Latin. Seeing the practicality of uniting all the books of the Bible in one volume, he was the first who produced Latin Bibles in single volumes. The most well-known of them was the Codex Grandior
The ''Codex Grandior'' ("Larger Codex") was a large single-volume copy of the Bible in an Old Latin translation that was made for or by Cassiodorus. It was one of a number of works held at his monastic foundation Vivarium, near Squillace, Italy.
...
which was the ancestor of all modern western Bibles.
Cassiodorus was at the heart of the administration of the Ostrogothic kingdom. Theodoric made him quaestor sacri palatii (quaestor of the sacred palace, the senior legal authority) in 507, governor of Lucania and Bruttium, consul in 514 and magister officiorum (master of offices, one of the most senior administrative officials) in 523. He was praetorian prefect (chief minister) under the successors of Theodoric: under Athalaric (Theodoric's grandson, reigned 526–34) in 533 and, between 535 and 537, under Theodahad (Theodoric's nephew, reigned 534–36) and Witiges (Theodoric's grandson-in-law, reigned, 536–40). The major works of Cassiodorus, besides the mentioned bibles, were the Historia Gothorum, a history of the Goths, the Variae and account of his administrative career and the Institutiones divinarum et saecularium litterarum, an introduction to the study of the sacred scriptures and the liberal arts which was very influential in the Middle Ages.
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
(Eastern Roman) Emperor Justinian I, retook Italy from the Ostrogoths between 535 and 556. They soon lost much of Italy to the Lombards between 568 and 590, but retained the south for around 500 years until 1059–1071, where they thrived and where the Greek language was the official and vernacular language. In Calabria and towns such as Stilo
, image_skyline = Stilo vecchio 2.jpg
, imagesize =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, image_shield = Stilo-Stemma.png
, shield_alt =
, image_map =
, map_alt =
, m ...
and Rossano and San Demetrio Corone achieved great religious status. From the 7th Century many monasteries were built in the Amendolea and Stilaro Valleys and Stilo was the destination of hermits and Basilian monks. Many Byzantine churches are still seen in the region. The 10th-century church in Rossano, together with the "twin" church of Sant'Adriano in San Demetrio Corone (foundation 955, rebuilt by the Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. ...
on the, still, visible foundations of the previous Byzantine church), are considered between the best preserved Byzantine churches in Italy. They were both built by St. Nilus the Younger
Nilus the Younger, also called Neilos of Rossano ( it, Nilo di Rossano, gr, Όσιος Νείλος, ο εκ Καλαβρίας; 910 – 27 December 1005) was a monk, abbot, and founder of Italo-Byzantine monasticism in southern Italy. He is ven ...
as a retreat for the monks who lived in the tufa grottos underneath. The present name of Calabria comes from the duchy of Calabria.
Around the year 800, Saracens began invading the shores of Calabria, attempting to wrest control of the area from the Byzantines. This group of Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
had already been successful in Sicily and knew that Calabria was another key spot. The people of Calabria retreated into the mountains for safety. Although the Arabs never really got a stronghold on the whole of Calabria, they did control some villages while enhancing trade relations with the eastern world. In 918, Saracens captured Reggio (which was renamed ''Rivà''), holding many of its inhabitants to ransom or keeping them prisoners as slaves. It is during this time of Arab invasions that many staples of today's Calabrian cuisine came into fashion: Citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus ''Citrus'' is native to ...
fruits and eggplants for example. Exotic spices such as cloves and nutmeg were also introduced.
Under the Byzantine dominion, between the end of the 9th and the beginning of the 10th century, Calabria was one of the first regions of Italy to introduce silk production to Europe.
According to André Guillou, mulberry trees
''Morus'', a genus of flowering plants in the family Moraceae, consists of diverse species of deciduous trees commonly known as mulberries, growing wild and under cultivation in many temperate world regions. Generally, the genus has 64 identif ...
for the production of raw silk were introduced to southern Italy by the Byzantines at the end of the ninth century.
Around 1050 the theme of Calabria had 24,000, mulberry trees cultivated for their foliage, and their number tended to expand.
At the beginning of the tenth century (circa 903), the city of Catanzaro was occupied by the Muslim Saracens, who founded an emirate
An emirate is a territory ruled by an emir, a title used by monarchs or high officeholders in the Muslim world. From a historical point of view, an emirate is a political-religious unit smaller than a caliphate. It can be considered equivalen ...
and took the Arab name of قطنصار – QaTanSáar. An Arab presence is evidenced by findings at an eighth-century necropolis which had items with Arabic inscriptions.
Around the year 1050, Catanzaro rebelled against Saracen dominance and returned to a brief period of Byzantine control.
In the 1060s the Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. ...
, under the leadership of Robert Guiscard's brother, Roger I of Sicily
Roger I ( it, Ruggero I, Arabic: ''رُجار'', ''Rujār''; Maltese: ''Ruġġieru'', – 22 June 1101), nicknamed Roger Bosso and The Great, was a Norman nobleman who became the first Count of Sicily from 1071 to 1101. He was a member of the ...
, established a presence in this borderland, and organized a government modeled on the Eastern Roman Empire and was run by the local magnates of Calabria. Of note is that the Normans established their presence here, in southern Italy (namely Calabria), 6 years prior to their conquest of England, (see The Battle of Hastings
The Battle of Hastings nrf, Batâle dé Hastings was fought on 14 October 1066 between the Norman-French army of William, the Duke of Normandy, and an English army under the Anglo-Saxon King Harold Godwinson, beginning the Norman Conquest ...
). The purpose of this strategic presence in Calabria was to lay the foundations for the Crusades 30 years later, and for the creation of two Kingdoms: the Kingship of Jerusalem, and the Kingdom of Sicily. Ships would sail from Calabria to the Holy Land. This made Calabria one of the richest regions in Europe as princes from the noble families of England, France and other regions, constructed secondary residences and palaces here, on their way to the Holy Land. Guiscard's son Bohemond, who was born in San Marco Argentano San Marco Argentano is a town and '' comune'' in the province of Cosenza in the Calabria region of southern Italy.
Main sights include the Norman tower, several churches and the ruins of an abbey, Santa Maria della Matina.
San Marco Argentano w ...
, would be one of the leaders in the first crusade. Of particular note is the Via Francigena, an ancient pilgrim route that goes from Canterbury to Rome and southern Italy, reaching Calabria, Basilicata and Apulia, where the crusaders lived, prayed and trained, respectively.
In 1098, Roger I of Sicily
Roger I ( it, Ruggero I, Arabic: ''رُجار'', ''Rujār''; Maltese: ''Ruġġieru'', – 22 June 1101), nicknamed Roger Bosso and The Great, was a Norman nobleman who became the first Count of Sicily from 1071 to 1101. He was a member of the ...
was named the equivalent of an apostolic legate by Pope Urban II
Pope Urban II ( la, Urbanus II; – 29 July 1099), otherwise known as Odo of Châtillon or Otho de Lagery, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 March 1088 to his death. He is best known for convening th ...
and later his son Roger II of Sicily became the first King of Sicily and formed what would become the Kingdom of Sicily which lasted nearly 700 years. Under the Normans Southern Italy was united as one region and started a feudal system of land ownership in which the Normans were made lords of the land while peasants performed all the work on the land.
In 1147, Roger II of Sicily attacked Corinth and Thebes, two important centres of Byzantine silk production, capturing the weavers and their equipment and establishing his own silkworks in Calabria,Muthesius, Anna, "Silk in the Medieval World". In Jenkins (2003), p. 331. thereby causing the Norman silk industry to flourish.
In 1194, Frederick II, took control of the region, after inheriting the Kingdom from his mother Constance, Queen of Sicily. He created a kingdom that blended cultures, philosophy and customs and would build several castles while fortifying existing ones which the Normans previously constructed. After the death of Frederick II in 1250, Calabria was controlled by the Capetian House of Anjou
The Capetian House of Anjou or House of Anjou-Sicily, was a royal house and cadet branch of the direct French House of Capet, part of the Capetian dynasty. It is one of three separate royal houses referred to as ''Angevin'', meaning "from Anjou" ...
, under the rule of Charles d’Anjou after being granted the crown of the Sicilian Kingdom by Pope Clement IV. In 1282, under Charles d’Anjou, Calabria became a domain of the newly created Kingdom of Naples, and no longer of the Kingdom of Sicily, after he lost Sicily due to the rebellion of the Sicilian Vespers. During the 14th century, would emerge Barlaam of Seminara
Barlaam of Seminara (Bernardo Massari, as a layman), c. 1290–1348, or Barlaam of Calabria ( gr, Βαρλαὰμ Καλαβρός) was an Eastern Orthodox Greek scholar born in southern Italy he was a scholar and clergyman of the 14th century, a ...
who would be Petrarch's Greek teacher and his disciple Leonzio Pilato, who would translate Homer's works for Giovanni Boccaccio.
While the cultivation of mulberry was moving first steps in Northern Italy, silk made in Calabria reached the peak of 50% of the whole Italian/European production. As the cultivation of mulberry was difficult in Northern and Continental Europe, merchants and operators used to purchase in Calabria raw materials to finish the products and resell them for a better price. The Genoese silk artisans used fine Calabrian silk for the production of velvets.
In particular, the silk of Catanzaro
Catanzaro (, or ; scn, label= Catanzarese, Catanzaru ; , or , ''Katastaríoi Lokrói''; ; la, Catacium), also known as the "City of the two Seas", is an Italian city of 86,183 inhabitants (2020), the capital of the Calabria region and of its p ...
supplied almost all of Europe and was sold in a large market fair to Spanish, Venetian, Genoese, Florentine and Dutch merchants.
Catanzaro became the lace capital of Europe with a large silkworm breeding facility that produced all the laces and linens used in the Vatican
Vatican may refer to:
Vatican City, the city-state ruled by the pope in Rome, including St. Peter's Basilica, Sistine Chapel, Vatican Museum
The Holy See
* The Holy See, the governing body of the Catholic Church and sovereign entity recognized ...
. The city was known for its fabrication of silks, velvets, damasks and brocades.
Early modern period
In the XV century,Catanzaro
Catanzaro (, or ; scn, label= Catanzarese, Catanzaru ; , or , ''Katastaríoi Lokrói''; ; la, Catacium), also known as the "City of the two Seas", is an Italian city of 86,183 inhabitants (2020), the capital of the Calabria region and of its p ...
was exporting both its silk cloth and its technical skills to neighbouring Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
. By the middle of the century, silk spinning was taking place in Catanzaro, on a large scale.
In 1442 the Aragonese took control under Alfonso V of Aragon who became ruler under the Crown of Aragon. In 1501 Calabria came under the control of Ferdinand II of Aragon, whose wife Queen Isabella of Castille is famed for sponsoring the first voyage of Christopher Columbus in 1492. Calabria suffered greatly under Aragonese rule with heavy taxes, feuding landlords, starvation and sickness. After a brief period in the early 1700s under the Austrian Habsburgs, Calabria came into the control of the Spanish Bourbons in 1735. It was during the 16th century that Calabria would contribute to modern world history with the creation of the Gregorian calendar
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It was introduced in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years dif ...
by the Calabrian doctor and astronomer Luigi Lilio.
In 1466, King Louis XI
Louis XI (3 July 1423 – 30 August 1483), called "Louis the Prudent" (french: le Prudent), was King of France from 1461 to 1483. He succeeded his father, Charles VII.
Louis entered into open rebellion against his father in a short-lived revol ...
decided to develop a national silk industry in Lyon
Lyon,, ; Occitan language, Occitan: ''Lion'', hist. ''Lionés'' also spelled in English as Lyons, is the List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, third-largest city and Urban area (France), second-largest metropolitan area of F ...
and called a large number of Italian workers, mainly from Calabria. The fame of the master weavers of Catanzaro spread throughout France and they were invited to Lyon to teach the techniques of weaving. In 1470, one of these weavers, known in France as Jean Le Calabrais, invented the first prototype of a Jacquard-type loom. He introduced a new kind of machine which was able to work the yarns faster and more precisely. Over the years, improvements to the loom were ongoing.
Charles V of Spain formally recognized the growth of the silk industry of Catanzaro
Catanzaro (, or ; scn, label= Catanzarese, Catanzaru ; , or , ''Katastaríoi Lokrói''; ; la, Catacium), also known as the "City of the two Seas", is an Italian city of 86,183 inhabitants (2020), the capital of the Calabria region and of its p ...
in 1519 by allowing the city to establish a consulate of the silk craft, charged with regulating and check in the various stages of a production that flourished throughout the sixteenth century. At the moment of the creation of its guild, the city declared that it had over 500 looms. By 1660, when the town had about 16,000 inhabitants, its silk industry kept 1,000 looms, and at least 5,000 people, busy. The silk textiles of Catanzaro
Catanzaro (, or ; scn, label= Catanzarese, Catanzaru ; , or , ''Katastaríoi Lokrói''; ; la, Catacium), also known as the "City of the two Seas", is an Italian city of 86,183 inhabitants (2020), the capital of the Calabria region and of its p ...
were not only sold at the kingdom
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
's markets, they were also exported to Venice, France, Spain and England.
In the 16th century, Calabria was characterized by a strong demographic and economic development, mainly due to the increasing demand of silk products and the simultaneous growth of prices, and became one of the most important Mediterranean markets for silk.
In 1563 philosopher and natural scientist Bernardino Telesio wrote "On the Nature of Things according to their Own Principles" and pioneered early modern empiricism. He would also influence the works of Francis Bacon, René Descartes, Giordano Bruno, Tommaso Campanella and Thomas Hobbes. In 1602 philosopher and poet Tommaso Campanella
Tommaso Campanella (; 5 September 1568 – 21 May 1639), baptized Giovanni Domenico Campanella, was an Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, theologian, astrologer, and poet.
He was prosecuted by the Roman Inquisition for heresy in 1594 an ...
wrote his most famous work, " The City of the Sun" and would later defend Galileo Galilei during his first trial with his work "A Defense of Galileo", which was written in 1616 and published in 1622. In 1613 philosopher and economist Antonio Serra wrote "A Short Treatise on the Wealth and Poverty of Nations" and was a pioneer in the Mercantilist tradition.
During the 17th century silk production in Calabria begin to suffer by the strong competition of new-raising competitors in Italian Peninsula and Europe (France), but also the increasing import from Ottoman Empire and Persia.
Foundation of the historical Italo-Albanian College and Library in 1732 by Pope Clement XII transferred from San Benedetto Ullano to San Demetrio Corone in 1794.
In 1783 a series of earthquakes across Calabria caused around 50,000 deaths and much damage to property, so that many of the buildings in the region were rebuilt after this date.
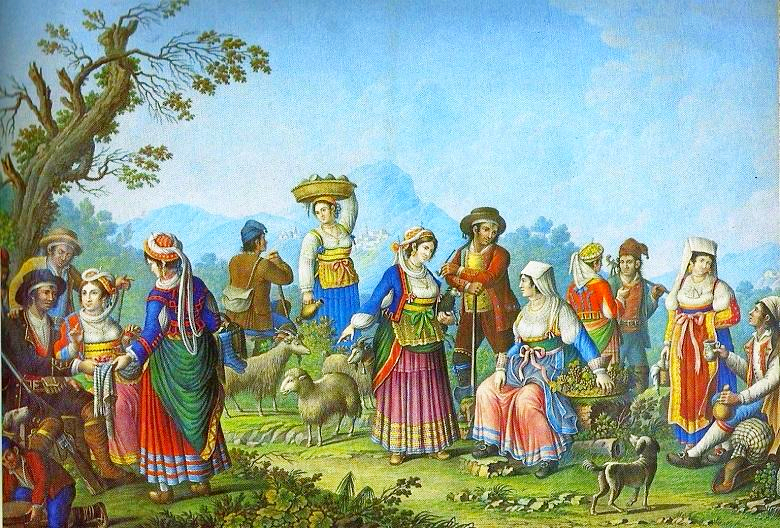
 At the end of the 18th century the French took control and in 1808 Napoleon Bonaparte gave the Kingdom of Naples to his brother-in-law
At the end of the 18th century the French took control and in 1808 Napoleon Bonaparte gave the Kingdom of Naples to his brother-in-law Joachim Murat
Joachim Murat ( , also , ; it, Gioacchino Murati; 25 March 1767 – 13 October 1815) was a French military commander and statesman who served during the French Revolutionary Wars and Napoleonic Wars. Under the French Empire he received the ...
. Murat controlled the kingdom until the return of the Bourbons in 1815. The population of Calabria in 1844 was 1,074,558.
Calabria experienced a series of peasant revolts as part of the European Revolutions of 1848
The Revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the Springtime of the Peoples or the Springtime of Nations, were a series of political upheavals throughout Europe starting in 1848. It remains the most widespread revolutionary wave in Europea ...
. This set the stage for the eventual unification with the rest of Italy in 1861, when the Kingdom of Naples was brought into the union by Giuseppe Garibaldi. The unification was orchestrated by Great Britain in an attempt to nationalize the production of sulfur from the two volcanoes located in Naples and Sicily respectively. The Aspromonte was the scene of a famous battle of the unification of Italy. During the late 19th or early 20th century, pianist and composer Alfonso Rendano
Alfonso Rendano (5 April 1853 – 10 September 1931) was an Italian pianist and composer. He is mostly renowned for inventing the "third pedal", which augmented the interpretative resources of the piano.
Rendano was born in Cosenza. He was pa ...
invented the "Third Pedal", which augmented the interpretative resources of the piano.
The ancient Greek colonies from Naples and to the south, had been completely Latinized, but from the fifth century AD onward Greeks had once again emigrated there when pressed out of their homeland by invasions. This Greek Diaspora allowed the ancient Greek dialects to continue in Southern Italy, much in the same way that the Italian Diaspora allowed long-lost dialects from Italy to thrive in countries where Italians emigrated to. Greek texts were also valued in monasteries and places of learning. However it was Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
in the 8th century, who made Latin the 'official' language of study and communication for Europe. For the sake of uniformity, he supplanted much of the Greek spoken, read or taught in Europe. It was through language (Latin) and education (Latin texts) that Charlemagne united Europe.
During the 13th century a French chronicler who traveled through Calabria stated that "the peasants of Calabria spoke nothing but Greek" given he had traveled to areas where Greek was still available. But the educated classes spoke Italian. Indeed, formal Italian has been taught in schools throughout Italy for nearly two centuries, causing the ancient languages and dialects to continually disappear, much to the chagrin of the cultural community. These lost dialects continue to thrive to this day in North America and Australia, places where Italians emigrated to, on account of the Diaspora.
Modern era
On 19 August 1860, Calabria was invaded from Sicily by Giuseppe Garibaldi and his Redshirts as part of the Expedition of the Thousand. Through King Francesco II of Naples had dispatched 16,000 soldiers to stop the Redshirts, who numbered about 3,500, after a token battle at Reggio Calabria won by the Redshirts, all resistance ceased and Garibaldi was welcomed as a liberator from the oppressive rule of the Bourbons wherever he went in Calabria. Calabria together with the rest of the Kingdom of Naples was incorporated in 1861 into the Kingdom of Italy. Garibaldi planned to complete the ''Risorgimento'' by invading Rome, still ruled by the Pope protected by a French garrison, and began with semi-official encouragement to raise an army. Subsequently, King Victor Emmanuel II decided the possibility of war with France was too dangerous, and on 29 August 1862 Garibaldi's base in the Calabrian town of Aspromonte was attacked by the ''Regio Esercito''. The Battle of Aspromonte ended with the Redshirts defeated with several being executed after surrendering while Garibaldi was badly wounded. In the newly unified Kingdom of Italy, there were significant differences in level of economic development between the ''Nord'' (north) of Italy and the ''Mezzogiorno'' (the south of Italy). Calabria together with the rest of the ''Mezzogiorno'' was neglected under the Kingdom of Italy with the general feeling in Rome being that the region was hopelessly backward and poor. In the late 19th century about 70% of the population of the ''Mezzogiorno'' were illiterate as the government never invested in education for the south. Owing to the Roman Question, until 1903 the Roman Catholic Church had prohibited on the pain of excommunication Catholic men from voting in Italian elections (Italian women were not granted the right to vote until 1946). As the devoutly Catholic population of Calabria tended to boycott elections, the deputies who were elected from the region were the products of the clientistic system, representing the interests of the land-owning aristocracy. In common with the deputies from other regions of the ''Mezzogiorno'', they voted against more money for education under the grounds that an educated population would demand changes that would threaten the power of the traditional elite. Owing to a weak state, society in Calabria came to be dominated in the late 19th century by an organised crime group known as 'Ndrangheta which like the Mafia in Sicily and the Camorra in Campania formed a "parallel state" that co-existed alongside the Italian state. Between 1901 and 1914 Calabrians began emigrating in large numbers, mostly for North America and South America, with the peak year being 1905 with 62,690. On 28 December 1908, Calabria together with Sicily was devastated by an earthquake and then by a tsunami caused by the earthquake, causing about 80, 000 deaths. Within hours of the disaster, ships of the British and Russian navies had arrived on the coast to assist the survivors, but it took the ''Regia Marina'' two days to send a relief expedition from Naples. The bumbling and ineffectual response of the Italian authorities to the disaster caused by feuding officials who did not wish to co-operate with each other contributed to the high death toll as it took weeks for aid to reach some villages and caused much resentment in Calabria. To offset widespread criticism that the northern-dominated government in Rome did not care about the people of Calabria, KingVictor Emmanuel III
The name Victor or Viktor may refer to:
* Victor (name), including a list of people with the given name, mononym, or surname
Arts and entertainment
Film
* ''Victor'' (1951 film), a French drama film
* ''Victor'' (1993 film), a French shor ...
personally took over the relief operation and toured the destroyed villages of Calabria, which won the House of Savoy a measure of popularity in the region. Most notably, after the king took charge of the relief efforts, the feuding between officials ceased and relief aid was delivered with considerably more efficiency, winning Victor Emmanuel the gratitude of the Calabrians.
Fascism was not popular in Calabria. In December 1924 when a false rumor spread in Reggio Calabria that Benito Mussolini had resigned as Prime Minister because of the Matteotti affair, joyous celebrations took place in the city that lasted all night. In the morning, the people of Reggio Calabria learned that Mussolini was still prime minister, but several Fascist officials were dismissed for not suppressing the celebrations. The landed aristocracy and gentry of Calabria, through generally not ideologically committed to Fascism, saw the Fascist regime as a force for order and social stability, and supported the dictatorship. Likewise, the prefects and the policemen of Calabria were conservatives who saw themselves as serving King Victor Emmanuel III first and Mussolini second, but supported Fascism as preferable to Socialism and Communism and persecuted anti-Fascists. Traditional elites in Calabria joined the Fascist Party to pursue their own interests, and local branches of Fascist Party were characterized by much jostling for power and influence between elite families. Under the Fascist regime, several concentration camps were built in Calabria and used to imprison foreigners whose presence in Italy was considered undesirable, such as Chinese immigrants and foreign Jews (though not Italian Jews) together with members of the Roma (Gypsy) minority, whose nomadic lifestyle was viewed as anti-social. The camps which operated from 1938 to 1943 were not death camps, and the majority of those imprisoned survived, but conditions were harsh for the imprisoned.
On 3 September 1943, British and Canadian troops of the British 8th Army landed in Calabria in Operation Baytown
Operation Baytown was an Allied amphibious landing on the mainland of Italy that took place on 3 September 1943, part of the Allied invasion of Italy, itself part of the Italian Campaign, during the Second World War.
Planning
The attack was ...
, marking the first time that the Allies landed on the mainland of Italy. However, the landings in Calabria were a feint and the main Allied blow came on 8 September 1943 with the landing of the American 5th Army at Salerno in Campania that was intended to cut off Axis forces in the ''Mezzogiorno''. The Germans anticipated that the Allies would land at Salerno, and as a consequence, there was relatively little fighting in Calabria. The Italian troops in Calabria mostly surrendered to the advancing 5th British Division and the 1st Canadian Division while there were relatively few German forces in the region to oppose their advance. The main obstacle to the advancing Anglo-Canadian troops turned out to be the trail of destruction left by German combat engineers who systematically blew up bridges and destroyed roads and railroads as the Wehrmacht retreated north. On the same day the Americans landed at Salerno, General Dwight Eisenhower announced on the radio the Armistice of Cassibile that had been signed on 3 September, and with the announcement of the armistice all Italian resistance ceased. The Germans committed most of their forces in the ''Mezzogiorno'' to the Battle of Salerno with the aim of driving the Allies back into the sea and pulled their remaining forces out of Calabria to send them to Salerno. Under the Allied occupation, some Fascists in Calabria waged a terrorist struggle on behalf of the Salo republic, though significantly many of the Fascists tended to be from well-off families concerned about the possibility of social reforms that might weaken their power and only a minority such as Prince Valerio Pignatelli were ideological Fascists. In June 1944, celebrations in Reggio Calabria over the news of the liberation of Rome were disturbed by local Fascists.
The British historian Jonathan Dunnage wrote that there was an "institutional continuity" between the civil servants of the Liberal, Fascist and post-Fascist eras in Calabria as each change of regime saw the bureaucrats of the region adjust to whatever regime was in power in Rome and there was no purge of civil servants either after 1922 or 1943. The "institutional continuity" of the bureaucracy of Calabria were committed to preserving the social structure. On 2 June 1946 referendum, Calabria like the rest of the ''Mezzogiorno'' voted solidly to retain the monarchy. The clientistic political system in Calabria under which elite families handed out patronage to their supporters and used violence against their opponents, which was the prevailing norm in the Liberal and Fascist eras continued after 1945. During the Second World War, the already low living standards of Calabria declined further and the region was notorious as one of the most violent and lawless areas of Italy. Attempts by the peasants of Calabria to take over the land owned by the elite were usually resisted by the authorities. On 28 October 1949 in Melissa the police opened fire on peasants who had seized the land of a local baron, killing three men who were shot in the back as they attempted to flee. Between 1949 and 1966 another wave of migration took place with the peak year of migration being 1957 with some 38, 090 Calabrians leaving that year.
Under the First Republic, starting in the 1960s, investment plans were launched under which Italian state sponsored industrialisation and attempted to improve the infrastructure of Calabria by building modern roads, railroads, ports, etc. The plan was a notable failure with the infrastructure projects going wildly over-budget and taking far longer to complete then scheduled; for an example, construction started on the A3 highway in 1964 intended to link Reggio Calabria to Salerno, which was as of 2016 still unfinished. The failure to complete the A3 highway after 52 years of effort is regarded as a scandal in Italy, and many parts of Calabria were described as an "industrial graveyard" full of the closed down steel mills and chemical plants that all went bankrupt. From July 1970 to February 1971 the Reggio revolt took place as the decision to make Catanzaro instead of Reggio the regional capital prompted massive protests. The compromise decision to make Catanzaro the executive capital and Reggio the administrative capital has led to a bloated and inefficient administration. The high unemployment rate in Calabria has led to extensive migration and Calabria's biggest export has been its own people as Calabrians have moved to either other parts of Italy and abroad, especially to the United States, Canada and Argentina, to seek a better life. In 2016, it was estimated that 18% of the people born in Calabria were living abroad.
Economy
The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of Calabria is subdivided as follows: service industry (28.94%), financial activities and real estate (21.09%), trade, tourism, transportation and communication (19.39%), taxation (11.49%), manufacturing (8.77%), construction (6.19%) and agriculture (4.13%). GDP per capita is 2.34 times less and unemployment is 4 times higher than in Lombardy. Calabria's economy is still based mainly on agriculture. The economy of the region is strongly affected by the presence of the 'Ndrangheta (the localMafia
"Mafia" is an informal term that is used to describe criminal organizations that bear a strong similarity to the original “Mafia”, the Sicilian Mafia and Italian Mafia. The central activity of such an organization would be the arbitration of d ...
syndicate).
Agriculture
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
.
The red onion
Red onions (also known as purple or blue onions in some mainland European countries, though not the UK) are cultivars of the onion ('' Allium cepa''), and have purplish-red skin and white flesh tinged with red. They are most commonly used in c ...
of Tropea
Tropea (; scn, label= Calabrian, Trupìa; la, Tropaea; grc, Τράπεια, Trápeia) is a municipality in the province of Vibo Valentia, in Calabria, Italy.
Tropea is a seaside resort with sandy beaches, located on the Gulf of Saint Euphe ...
is cultivated during summer period on the Tyrrhenian coast of central Calabria. It has been awarded with the protected geographical indication (PGI).
The olive tree represents 29.6% of utilised agricultural area (UAA) and approximately 70% of tree crops. Olive tree cultivation extends from coastal lowland areas to hilly and lower mountainous areas.
The region is the second-highest for olive oil production with Carolea, Ogliarola, and Saracena olives as the main regional varieties.
In Calabria, there are 3 PDO oils: "Bruzio" in the province of Cosenza, "Lametia" in the area of Lamezia Terme and the more recent "Alto Crotonese". In addition to DOP oils there are also PGI oils. The production area of "Olio di Calabria" PGI includes the entire territory of the Calabria region. The production is made exclusively from indigenous olives.
Calabria produces about a quarter of Italy's citrus fruit. The contribution of this region to growing citrus fruit in Italy can be attributed mainly to clementine
A clementine (''Citrus × clementina'') is a tangor, a citrus fruit hybrid between a willowleaf mandarin orange ( ''C.'' × ''deliciosa'') and a sweet orange (''C. × sinensis''), named in honor of Clément Rodier, a French missionary who fir ...
s, oranges, mandarins and lemon
The lemon (''Citrus limon'') is a species of small evergreen trees in the flowering plant family Rutaceae, native to Asia, primarily Northeast India (Assam), Northern Myanmar or China.
The tree's ellipsoidal yellow fruit is used for culin ...
s. Calabria is by far the country's most important clementine-growing region, which account for about 62% (16,164 ha) of the Italian surface dedicated to its cultivation and 69% (437,800 tons) of the total production. Clementina di Calabria is the PGI variety grown in the Calabria region. Also chinotto is cultivated and used to produce carbonated soft drink with the same name.
 Minor fruits such as bergamot and
Minor fruits such as bergamot and citron
The citron (''Citrus medica''), historically cedrate, is a large fragrant citrus fruit with a thick rind. It is said to resemble a 'huge, rough lemon'. It is one of the original citrus fruits from which all other citrus types developed throu ...
and lemon-citron hybrids are found exclusively in Calabria. The south coast of the region produces 90% of the world's bergamots, with a huge industry built around the extraction of bergamot oil. According to Harvard Atlas of Economic Complexity, last year with Italian net export of bergamot oil was 2009 in value of $253,000, after that between 2010 and 2018 was no export of it. The Bergamot orange
''Citrus bergamia'', the bergamot orange (pronounced ), is a fragrant citrus fruit the size of an orange, with a yellow or green color similar to a lime, depending on ripeness.
Genetic research into the ancestral origins of extant citrus cult ...
has been intensively cultivated since the 18th century, but only in the coastal area nearby to Reggio, where geological and weather conditions are optimal. The Chabad
Chabad, also known as Lubavitch, Habad and Chabad-Lubavitch (), is an Orthodox Jewish Hasidic dynasty. Chabad is one of the world's best-known Hasidic movements, particularly for its outreach activities. It is one of the largest Hasidic grou ...
Hasidic dynasty have a preference to take citron
The citron (''Citrus medica''), historically cedrate, is a large fragrant citrus fruit with a thick rind. It is said to resemble a 'huge, rough lemon'. It is one of the original citrus fruits from which all other citrus types developed throu ...
s ("Etrog") from this region for the Sukkot festival.
There is special research Experimental Station for the Industry of the Essential oils and Citrus products in Reggio di Calabria
Reggio di Calabria ( scn, label= Southern Calabrian, Riggiu; el, label=Calabrian Greek, Ρήγι, Rìji), usually referred to as Reggio Calabria, or simply Reggio by its inhabitants, is the largest city in Calabria. It has an estimated popula ...
.
The province of Cosenza represents an important area for figs growing belonging to cultivar "Dottato" that is used to produce the quality-branded dried figs "Fichi di Cosenza" PDO ( Protected Designation of Origin). The anona cherimoya, a plant of tropical origin cultivated in Europe only in Reggio di Calabria
Reggio di Calabria ( scn, label= Southern Calabrian, Riggiu; el, label=Calabrian Greek, Ρήγι, Rìji), usually referred to as Reggio Calabria, or simply Reggio by its inhabitants, is the largest city in Calabria. It has an estimated popula ...
and Spain.
In the province of Catanzaro
The province of Catanzaro ( it, provincia di Catanzaro; Catanzarese: ) is a province of the Calabria region of Italy. The city Catanzaro is both capital of the province and capital of the region of Calabria. The province contains a total of 8 ...
, between San Floro and Cortale, the ancient tradition of sericulture
Sericulture, or silk farming, is the cultivation of silkworms to produce silk. Although there are several commercial species of silkworms, '' Bombyx mori'' (the caterpillar of the domestic silkmoth) is the most widely used and intensively stud ...
is still kept alive, thanks to young generations.
Calabria is the largest producer of porcini mushrooms in Italy, thanks to the heavily wooded forests of the mountains ranges of Pollino, Sila, Serre and Aspromonte. Chestnut production is also widespread in the Calabrian mountains. But not only porcini mushrooms, there is other popular red pine mushroom or rosito.

Peaches
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and cultivated in Zhejiang province of Eastern China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and others (the glossy-skinned, non-fu ...
and nectarines from Calabria have greatly improved in terms of flavour, quality, safety and service. A part of the production is sold on the domestic market, mainly to retailers. The remaining is exported to Northern Europe, mainly Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
and Germany.
The region boasts a very ancient tradition in the cultivation and production of liquorice. The eighty percent of the national production is concentrated in this region.
Calabria has long coast and produce some distinctive fish products:
Manufacturing
Food and textile industries are the most developed and vibrant. Within the industrial sector, manufacturing contributes to a gross value added of 7.2%. In the manufacturing sector the main branches are foodstuff, beverage and tobacco with a contribution to the sector very close to the national average. Over the recent decades some petrochemical, engineering and chemical industries have emerged, within the areas of Crotone,Vibo Valentia
Vibo Valentia (; Monteleone before 1861; Monteleone di Calabria from 1861 to 1928; scn, label= Calabrian, Vibbu Valenzia or ) is a city and ''comune'' (municipality) in the Calabria region of southern Italy, near the Tyrrhenian Sea. It is the ca ...
and Reggio Calabria.
The province of Catanzaro boasts a great tradition in the textile manufacturing, especially silk. Recently, several young people have given new life to this activity, developing green and sustainable economy projects. In fact, among the municipalities of Girifalco, San Floro and Cortale, sericulture
Sericulture, or silk farming, is the cultivation of silkworms to produce silk. Although there are several commercial species of silkworms, '' Bombyx mori'' (the caterpillar of the domestic silkmoth) is the most widely used and intensively stud ...
is still practiced, the breeding of silkworms combined with the cultivation of mulberry trees
''Morus'', a genus of flowering plants in the family Moraceae, consists of diverse species of deciduous trees commonly known as mulberries, growing wild and under cultivation in many temperate world regions. Generally, the genus has 64 identif ...
.
Tiriolo and Badolato are known above all for the manufacturing of the "vancale", the typical Calabrian shawl, made of wool or silk, worn by women in ancient times on traditional costumes during the dance of tarantella
() is a group of various southern Italian folk dances originating in the regions of Calabria, Campania and Puglia. It is characterized by a fast upbeat tempo, usually in time (sometimes or ), accompanied by tambourines. It is among the mo ...
, or as an ornamental decoration of the houses.
Typical in Tiriolo is also the manufacturing of carpets, linen and broom
A broom (also known in some forms as a broomstick) is a cleaning tool consisting of usually stiff fibers (often made of materials such as plastic, hair, or corn husks) attached to, and roughly parallel to, a cylindrical handle, the broomstick. I ...
fibers, bobbin lace making, embroidery, precious ceramics
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
, furnishing objects and artistic sculptures. The artistic production of weaving is also active in other centers such as in Platania
Platania is a ''comune'' and town in the province of Catanzaro in the western part of the Calabria region of Italy.
Bounding communes
* Conflenti
* Decollatura
* Lamezia Terme
Lamezia Terme (), commonly called Lamezia, is an Italian city and ...
and Petrizzi
Petrizzi is a ''comune'' and town in the province of Catanzaro in the Calabria region of Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle o ...
where once hemp fibers were also produced.
In Soveria Mannelli
Soveria Mannelli ( scn, Suverìa Mannielli) is a town and '' comune'' in the province of Catanzaro, in the Calabria region of southern Italy.
The town is bordered by Bianchi, Carlopoli, Colosimi, Decollatura, Gimigliano
Gimigliano ( Calabri ...
, Lanificio Leo, the oldest textile factory in Calabria founded in 1873, is still active. The factory still retains majestic and evocative tools dating back to the late nineteenth century.
The traditional production of artistic ceramics dating back to the Magna Graecia period is handed down in the ancient towns of Squillace and Seminara.
The small town of Serrastretta
Serrastretta is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Catanzaro in the Calabria region of southern Italy.
The town is bordered by Amato, Decollatura, Feroleto Antico, Lamezia Terme, Miglierina, Pianopoli, Platania and San Pietro Apostolo. ...
, a green village in the woods of Presila, is known for its wood production, in particular for its chairs characterized by a very original straw.
There is a plant of Hitachi Rail Italy in Reggio di Calabria
Reggio di Calabria ( scn, label= Southern Calabrian, Riggiu; el, label=Calabrian Greek, Ρήγι, Rìji), usually referred to as Reggio Calabria, or simply Reggio by its inhabitants, is the largest city in Calabria. It has an estimated popula ...
, which manufactures railcars
A railcar (not to be confused with a railway car) is a self-propelled railway vehicle designed to transport passengers. The term "railcar" is usually used in reference to a train consisting of a single coach (carriage, car), with a drive ...
of regional trains like Vivalto.
Tourism


 Tourism in Calabria has increased over the years. The main tourist attractions are the coastline and the mountains. The coastline alternates between rugged cliffs and sandy beaches, and is sparsely interrupted by development when compared to other European seaside destinations. The sea around Calabria is clear, and there is a good level of tourist accommodation. The poet Gabriele D'Annunzio called the coast facing Sicily near Reggio Calabria "... the most beautiful kilometer in Italy" (''il più bel chilometro d'Italia''). The primary mountain tourist draws are Aspromonte and
Tourism in Calabria has increased over the years. The main tourist attractions are the coastline and the mountains. The coastline alternates between rugged cliffs and sandy beaches, and is sparsely interrupted by development when compared to other European seaside destinations. The sea around Calabria is clear, and there is a good level of tourist accommodation. The poet Gabriele D'Annunzio called the coast facing Sicily near Reggio Calabria "... the most beautiful kilometer in Italy" (''il più bel chilometro d'Italia''). The primary mountain tourist draws are Aspromonte and La Sila
La Sila, also simply Sila, is the name of the mountainous plateau and historic region located in Calabria, southern Italy. The Sila National Park is known to have the purest air in Europe.
Geography
The Sila occupies part of the provinces of Co ...
, with its national park and lakes. Some other prominent destinations include:
* Reggio Calabria is on the strait between the mainland and Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, the largest and oldest city in Calabria dating from the 8th century BC, known for its panoramic seaside with botanical gardens between the art nouveau buildings and the beaches, and its 3,000 years of history with its Aragonese Castle and the Museo Nazionale della Magna Grecia
The Museo Nazionale della Magna Grecia (''National Museum of Magna Græcia''), Museo Archeologico Nazionale di Reggio Calabria (''National Archaeological Museum of Reggio Calabria'') or Palazzo Piacentini is a museum in Reggio Calabria, souther ...
where the Riace bronzes (''Bronzi di Riace'') are located.
* Cosenza, birthplace of scientist and philosopher Bernardino Telesio and seat of the Cosentian Academy, known for its cultural institutions, the old quarter, a Hohenstaufen Castle, an open-air museum and an 11th-century Romanesque-Gothic Cathedral. On 12 October 2011, the Cathedral of Cosenza received UNESCO World Heritage status for being "Heritage Witness to a Culture of Peace". This is the first award given by UNESCO to the region of Calabria.
* Scilla
''Scilla'' () is a genus of about 30 to 80 species of bulb-forming perennial herbaceous plants in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae. Sometimes called the squills in English, they are native to woodlands, subalpine meadows, and sea ...
, on the Tyrrhenian Sea, "pearl" of the "Violet Coast", has a delightful panorama and is the site of some of Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
's tales.
* Tropea
Tropea (; scn, label= Calabrian, Trupìa; la, Tropaea; grc, Τράπεια, Trápeia) is a municipality in the province of Vibo Valentia, in Calabria, Italy.
Tropea is a seaside resort with sandy beaches, located on the Gulf of Saint Euphe ...
, on the Tyrrhenian Sea coast, is home to a dramatic seaside beach, and the Santa Maria dell'Isola sanctuary. It is also renowned for its sweet red onions (mainly produced in Ricadi).
* Capo Vaticano, on the Tyrrhenian Sea, is a wide bathing place near Tropea.
* Gerace, near Locri, is a medieval city with a Norman Castle and Norman Cathedral.
* Squillace, a seaside resort and important archaeological site. Nearby is the birthplace of Cassiodorus
Magnus Aurelius Cassiodorus Senator (c. 485 – c. 585), commonly known as Cassiodorus (), was a Roman statesman, renowned scholar of antiquity, and writer serving in the administration of Theodoric the Great, king of the Ostrogoths. ''Senator'' ...
.
* Stilo
, image_skyline = Stilo vecchio 2.jpg
, imagesize =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, image_shield = Stilo-Stemma.png
, shield_alt =
, image_map =
, map_alt =
, m ...
, the birthplace of philosopher Tommaso Campanella
Tommaso Campanella (; 5 September 1568 – 21 May 1639), baptized Giovanni Domenico Campanella, was an Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, theologian, astrologer, and poet.
He was prosecuted by the Roman Inquisition for heresy in 1594 an ...
, with its Norman Castle and Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
church, the ''Cattolica
Cattolica (; rgn, Catòlga) is a town and ''comune'' in the Province of Rimini, Italy, with 16,233 inhabitants as of 2007.
History
Archaeological excavations show that the area was already settled in Roman times.
Cattolica rose as a resting pl ...
''.
* Pizzo Calabro
Pizzo ( scn, label= Calabrian, U Pizzu), also called Pizzo Calabro, is a seaport and in the province of Vibo Valentia (Calabria, southern Italy), situated on a steep cliff overlooking the Gulf of Saint Euphemia.
Fishing is one of the main acti ...
, on the Tyrrhenian Sea coast, known for its ice cream called "Tartufo". Interesting places in Pizzo are Piazza Repubblica and the Aragonese castle where Murat was shot.
* Paola, a town situated on the Tyrrhenian Sea coast, renowned for being the birthplace of St. Francis of Paola, patron saint of Calabria and Italian sailors, and for the old Franciscan sanctuary built during the last hundred years of the Middle Ages by the will of St. Francis.
* Sibari, on the Ionian coast, a village situated near the archaeological site of the ancient city of ''Sybaris
Sybaris ( grc, Σύβαρις; it, Sibari) was an important city of Magna Graecia. It was situated in modern Calabria, in southern Italy, between two rivers, the Crathis (Crati) and the Sybaris (Coscile).
The city was founded in 720 BC ...
'', a Greek colony of the 8th century BC.
* Lamezia Terme, the main transportation hub of the region with its international airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surfa ...
which links it to many destinations in Europe plus Canada and Israel and the train station
A train station, railway station, railroad station or depot is a railway facility where trains stop to load or unload passengers, freight or both. It generally consists of at least one platform, one track and a station building providing s ...
. Several are the historical sights of the city, like the Norman-Swabian castle, the Jewish historical quarter and the Casa del Libro Antico (House of the Ancient Book) where books from the 16th to the 19th centuries, as well as old globes and ancient maps reproduction are well preserved and available to be seen by the public.
* Catanzaro
Catanzaro (, or ; scn, label= Catanzarese, Catanzaru ; , or , ''Katastaríoi Lokrói''; ; la, Catacium), also known as the "City of the two Seas", is an Italian city of 86,183 inhabitants (2020), the capital of the Calabria region and of its p ...
, an important silk center since the time of the Byzantines, is located at the centre of the narrowest point of Italy, from where the Ionian Sea and Tyrrhenian Sea are both visible, but not from Catanzaro. Of note are the well-known one-arch bridge (Viaduct Morandi-Bisantis, one of the tallest in Europe), the cathedral (rebuilt after World War II bombing), the castle, the promenade on the Ionian sea, the park of biodiversity and the archaeological park.
* Soverato on the Ionian Sea, also known as the "Pearl" of the Ionian Sea. Especially renowned for its beaches, boardwalk and nightlife.
* Badolato near Soverato is a well-preserved medieval hilltop village with 13 churches. It was selected as one of the 1000 marvels of Italy to mark the anniversary of the unification of Italy.
* Nicotera on the Tyrrhenian Sea, is a small medieval town with an ancient Ruffo's castle.
* Ancient temples of the Roman gods on the sun-kissed hills of Catanzaro
Catanzaro (, or ; scn, label= Catanzarese, Catanzaru ; , or , ''Katastaríoi Lokrói''; ; la, Catacium), also known as the "City of the two Seas", is an Italian city of 86,183 inhabitants (2020), the capital of the Calabria region and of its p ...
still stand as others are swept beneath the earth. Many excavations are going on along the east coast, digging up what seems to be an ancient burial ground.
* Samo
Samo (–) founded the first recorded political union of Slavic tribes, known as Samo's Empire (''realm'', ''kingdom'', or ''tribal union''), stretching from Silesia to present-day Slovakia, ruling from 623 until his death in 658. According to ...
, a village on the foot of the Aspromonte, is well known for its spring water and ruins of the old village destroyed in the 1908 Messina earthquake
The 1908 Messina earthquake (also known as the 1908 Messina and Reggio earthquake) occurred on 28 December in Sicily and Calabria, southern Italy with a moment magnitude of 7.1 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). The epice ...
.
* Mammola, art center, tourist and gastronomic, has an ancient history. The old town, with its small houses attached to each other, the ancient churches and noble palaces. Of particular interest is the Museum Park Santa Barbara, a place of art and cultural events of many international artists and the Shrine of St. Nicodemo of the 10th century, in the highlands of Limina. Its gastronomy with the "Stocco" typical of Mammola, cooked in various ways, other typical products are smoked ricotta and goat cheese, salami pepper and wild fennel, bread "pizza" (corn bread) and wheat bread baked in a wood oven.
* Praia a Mare on the Tyrrhenian Sea, is a well-known tourist city, thanks to the Isola di Dino and the seaside beach.
* Spilinga is known for its spicy pork pâté, 'Nduja
'Nduja () is a spicy, spreadable pork sausage from the region of Calabria in Southern Italy. It is similar to sobrassada from the Balearic Islands in Spain, and is loosely based on the French andouille. It is Calabria's contribution to the many ...
.
Calabria attracts year-round tourism, offering both summer and winter activities, in addition to its cultural, historical, artistic heritage, it has an abundance of protected natural habitats and 'green' zones. The of its coast make Calabria a tourist destination during the summer. The low industrial development and the lack of major cities in much of its territory have allowed the maintenance of indigenous marine life.
The most sought-after seaside destinations are: Tropea
Tropea (; scn, label= Calabrian, Trupìa; la, Tropaea; grc, Τράπεια, Trápeia) is a municipality in the province of Vibo Valentia, in Calabria, Italy.
Tropea is a seaside resort with sandy beaches, located on the Gulf of Saint Euphe ...
, Pizzo Calabro
Pizzo ( scn, label= Calabrian, U Pizzu), also called Pizzo Calabro, is a seaport and in the province of Vibo Valentia (Calabria, southern Italy), situated on a steep cliff overlooking the Gulf of Saint Euphemia.
Fishing is one of the main acti ...
, Capo Vaticano, Reggio Calabria, Soverato, Scilla
''Scilla'' () is a genus of about 30 to 80 species of bulb-forming perennial herbaceous plants in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae. Sometimes called the squills in English, they are native to woodlands, subalpine meadows, and sea ...
, Scalea, Sellia Marina, Montepaone, Montauro
Montauro ( Calabrian: ) is a ''comune'' and town in the province of Catanzaro in the Calabria region of Italy.
The municipalities of Gasperina, Montepaone, Palermiti
Palermiti () is a village and ''comune'' of the province of Catanzaro in the Cala ...
, Copanello (comune of Staletti), Tonnara di Palmi, Diamante
A diamanté (also spelled diamante) is a glittering ornament, such as an artificial jewel (e.g. a rhinestone) or a sequin.
Diamante may also refer to:
Places
Argentina
* Diamante, Entre Ríos, a ''municipio'' in Diamante Department
* Diamante ...
, Paola, Fiumefreddo Bruzio
Fiumefreddo Bruzio ( Calabrian: ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Cosenza in the Calabria region of southern Italy. In 2005, Fiumefreddo Bruzio was awarded as one of the ''Borghi più belli d'italia'' (lit. one of the most beautiful vil ...
, Amantea Amantea ( Calabrian: ; ) is a town, former bishopric, ''comune'' (municipality) and Latin Catholic titular see in the province of Cosenza in the Calabria region of southern Italy.
It is the twentieth municipality in the region by population, while f ...
, Praia a Mare, Belvedere Marittimo, Roseto Capo Spulico, Corigliano Calabro, Cirò Marina, Amendolara
Amendolara ( Lucano: ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Cosenza in the Calabria region of southern Italy.
The city is at an altitude of 200 meters above sea level and overlooks the Ionian Sea.
History
The name probably derives fr ...
, Roccella Ionica, Bagnara Calabra
Bagnara Calabra (or simply Bagnara) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Reggio Calabria in Calabria, southern Italy. It is located in the hills facing the Tyrrhenian Sea on the southern tip of the region, about southwest of Catanz ...
, Nicotera, Cariati
Cariati () is a town and '' comune'' in the province of Cosenza in the Calabria region of southern Italy. Cariati is divided into two parts: Cariati Superiore, situated on top of a hill, and Cariati Marina, which is stretched along the Ionian c ...
, Zambrone, Isola di Capo Rizzuto, Caminia (comune of Staletti), Siderno, Parghelia
Parghelia is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Vibo Valentia in the Italian region Calabria, located about southwest of Catanzaro and about west of Vibo Valentia. As of 31 December 2004, it had a population of 1,383 and an area of . ...
, Ricadi and San Nicola Arcella.
In addition to the coastal tourist destinations, the interior of Calabria is rich in history, traditions, art and culture. Cosenza is among the most important cultural cities of Calabria, with a rich historical and artistic patrimony. Medieval castles, towers, churches, monasteries and other French castles and structures from the Norman to the Aragonese periods are common elements in both the interior and coastline of Calabria.
The mountains offer skiing and other winter activities: Sila, Pollino and Aspromonte are three national parks that offer facilities for winter sports, especially in the towns of Camigliatello (comune of Spezzano della Sila), Lorica (comune of San Giovanni in Fiore
San Giovanni in Fiore (; nap, label= Calabrian, Sangiuvanni ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Cosenza in the Calabria region of southern Italy.
The town originates from the Florense Abbey, built here by the Calabrian monk Joachim of ...
), Gambarie
Santo Stefano in Aspromonte is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Reggio Calabria in the Italian region Calabria, located about southwest of Catanzaro and about northeast of Reggio Calabria. As of 31 December 2004, it had a populat ...
and Monte Sant'Elia (''comune
The (; plural: ) is a local administrative division of Italy, roughly equivalent to a township or municipality. It is the third-level administrative division of Italy, after regions ('' regioni'') and provinces (''province''). The can also ...
'' of Palmi).
Unemployment rate
The unemployment rate stood at 20.1% in 2020 and was the highest in Italy and one of the highest inside the European Union.Infrastructure and transport
Shipping and ports
 The main Calabrian ports are in Reggio Calabria and in
The main Calabrian ports are in Reggio Calabria and in Gioia Tauro
Gioia Tauro () is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Reggio Calabria (Italy), on the Tyrrhenian coast. It has an important port, situated along the route connecting Suez to Gibraltar, one of the busiest maritime corridors in t ...
. The port of Reggio is equipped with five loading docks of a length of .
The port of Gioia Tauro has seven loading docks with an extension of ; it is the largest in Italy and the eighth largest container port
A container port or container terminal is a facility where cargo containers are transshipped between different transport vehicles, for onward transportation. The transshipment may be between container ships and land vehicles, for example train ...
in Europe, with a 2018 throughput of s from more than 3,000 ships. In a 2006 report, Italian investigators estimated that 80% of Europe's cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly used recreationally for its euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South Ameri ...
arrived from Colombia via Gioia Tauro's docks. The port is also involved in the illegal arms trafficking
Arms trafficking or gunrunning is the illicit trade of contraband small arms and ammunition, which constitutes part of a broad range of illegal activities often associated with transnational criminal organizations. The illegal trade of small arm ...
. These activities are controlled by the Ndrangheta'' criminal syndicate.Bitter harvestThe Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers ''The Observer'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Gu ...
, 19 December 2006
Motorways and rail
The region is served by three heavily used roads: two national highways along the coasts (the SS18 betweenNaples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
and Reggio Calabria and the SS106 between Reggio Calabria and Taranto) and the A2 motorway, which links Salerno to Reggio Calabria, passing by Cosenza along the old inland route. Building this motorway took 55 years and was extremely over budget due to organized crime infiltration.
There is high-speed rail on Calabria's Tyrrhenian Coast with the Frecciargento
''Frecciargento'' is a high-speed train of the Italian national train operator, Trenitalia, and a member of the train category Le Frecce. The name, which means "Silver Arrow", was introduced in 2012 after it had previously been known as Eu ...
(Silver Arrow) offering a route from Rome to Reggio Calabria. There are also many ferries connecting Calabria with Sicily through the Strait of Sicily with the main one being from Villa San Giovanni to Messina.
Air travel
In Calabria there are two main airports: the Reggio Calabria Airport, a few kilometres from Reggio Calabria's city centre, built in 1939 was Calabria's first airport; the Lamezia Terme Airport is currently the first airport in Calabria for number of passengers per year.Demographics
The following is a list of Calabrian municipalities with a population of over 20,000: # Reggio Calabria – 186,013 #Catanzaro
Catanzaro (, or ; scn, label= Catanzarese, Catanzaru ; , or , ''Katastaríoi Lokrói''; ; la, Catacium), also known as the "City of the two Seas", is an Italian city of 86,183 inhabitants (2020), the capital of the Calabria region and of its p ...
– 93,265
# Corigliano-Rossano – 77,220
# Lamezia Terme – 71,123
# Cosenza – 69,827
# Crotone – 61,529
# Rende
Rende is a city and ''comune'' in the province of Cosenza, Calabria, southern Italy, home to the headquarters of the University of Calabria. It has a population of about 35,000, or more than 60,000 if the university students living there are tak ...
– 35,352
# Vibo Valentia
Vibo Valentia (; Monteleone before 1861; Monteleone di Calabria from 1861 to 1928; scn, label= Calabrian, Vibbu Valenzia or ) is a city and ''comune'' (municipality) in the Calabria region of southern Italy, near the Tyrrhenian Sea. It is the ca ...
– 33,857
# Castrovillari – 22,518
# Acri
Acri ( Calabrian: ) is a town of 19.949 inhabitants in the northern part of Calabria region in southern Italy. Since 17 September 2001 Acri has had the "status" of city.
Acri's coat of arms is represented by three mountains surmounted by thre ...
– 21,263
# Montalto Uffugo – 20,553
Government and politics
Sister jurisdictions
* Burwood, Australia. * State ofWest Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the B ...
, United States.
Administrative divisions
 Calabria is divided into five provinces:
Calabria is divided into five provinces:
Healthcare system
Because of their debts, since 2009 they were administered by an extraordinary commissioner appointed by the central Italian government. In 2012, the Calabria Region unified 11 ''Azienda Sanitaria Locale'' into 5 provincial units, when came into force a regional law approved on 11 May 2007. In July 2021, theConstitutional Court of Italy
The Constitutional Court of the Italian Republic ( it, Corte costituzionale della Repubblica Italiana) is the highest court of Italy in matters of constitutional law. Sometimes, the name ''Consulta'' is used as a metonym for it, because its sessi ...
censored the decree of law with the appointing of a new commissioner, because it didn't provide a new administrative structure to solve the long-time crisis of the Calabria's regional healthcare system. It has been seen as an unavoidable step to return to an ordinary and cost-effective administration at a regional level, as it is provided by the Italian Constitution.
Language
Although the official national language of Calabria has been Standard Italian since before unification in 1861, Calabria has dialects that have been spoken in the region for centuries. The Calabrian language is a direct derivative of Latin. Most linguists divide the variousdialects
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a ...
into two different language groups. In the northern area of the region, the Calabrian dialects are considered part of the Neapolitan language and are grouped as Northern Calabrian. In the rest of the region, the Calabrian dialects are often grouped as Central and Southern Calabrian, and are considered part of the Sicilian language
Sicilian ( scn, sicilianu, link=no, ; it, siciliano) is a Romance language that is spoken on the island of Sicily and its satellite islands. A variant, ''Calabro-Sicilian'', is spoken in southern Calabria, where it is called Southern Calabro ...
. However, in Guardia Piemontese
Guardia Piemontese ( Occitan: ''La Gàrdia'') is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Cosenza and the region of Calabria in southern Italy.
Location and language
Guardia Piemontese is located about 55 km northwest of Cosenza on th ...
, as well as some quarters of Reggio Calabria, a variety of Occitan called Gardiol can also be found. In addition, since Calabria was once ruled by the French and Spanish, some Calabrian dialects exhibit Spanish and French influences.
Another important linguistic minority, in the nine towns of Bovesìa in the province of Reggio Calabria, speaks a derivative of ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
called Griko
Griko, sometimes spelled Grico, is the dialect of Italiot Greek spoken by Griko people in Salento (province of Lecce) and (also called Grecanic) in Calabria. Some Greek linguists consider it to be a Modern Greek dialect and often call it ( el, ...
, a remnant of Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
rule and ancient Magna Graecia.
Religion
The majority of Calabrians areRoman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
. Historically, Calabrians were Greek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church ( Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also cal ...
, and in 732 the dioceses of Southern Italy were even moved to the jurisdiction of the Patriarch of Constantinople. There are also communities of Evangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being " born again", in which an individual expe ...
s in the region. Calabria has also been called "The Land of Saints" as the region was the birthplace of many saints spanning nearly 2,000 years. The most famous saint in Calabria and also the patron saint of the region is St. Francis of Paola. Calabria also has another patron saint called Saint Bruno of Cologne who was the founder of the Carthusian Order. Saint Bruno would build the charterhouse of Serra San Bruno
Serra San Bruno ( Calabrian: ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Vibo Valentia in the Italian region Calabria, located about southwest of Catanzaro and about southeast of Vibo Valentia. As of 31 December 2004, it had a populat ...
, a town which bears his name, in 1095 and later die there in 1101.
Even though it is currently a very small community, there has been a long history of the presence of Jews in Calabria. The Jews have had a presence in the region for at least 1600 years and possibly as much as 2300 years. Calabrian Jews have had notably influence on many areas of Jewish life and culture. Although virtually identical to the Jews of Sicily, the Jews of Calabria are considered a distinct Jewish population due to historical and geographic considerations. There is a small community of Italian Anusim
Anusim ( he, אֲנוּסִים, ; singular male, anús, he, אָנוּס ; singular female, anusáh, , meaning "coerced") is a legal category of Jews in ''halakha'' (Jewish law) who were forced to abandon Judaism against their will, typically ...
who have resumed the Jewish faith.
It is important to highlight the presence of Calabrians in Renaissance humanism and in the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
. Indeed, the Hellenistics in this period frequently came from Calabria maybe because of the Greek influence. The rediscovery of Ancient Greek was very difficult because this language had been almost forgotten. In this period the presence of Calabrian humanists or refugees from Constantinople was fundamental. The study of Ancient Greek, in this period, was mainly a work of two monks of the monastery of Seminara: Barlaam, bishop of Gerace, and his disciple, Leonzio Pilato. Leonzio Pilato, in particular, was a Calabrian born near Reggio Calabria. He was an important teacher of Ancient Greek and translator, and he helped Giovanni Boccaccio in the translations of Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
's works.
Cuisine
Mediterranean cuisine
Mediterranean cuisine is the food and methods of preparation used by the people of the Mediterranean Basin. The idea of a Mediterranean cuisine originates with the cookery writer Elizabeth David's book, '' A Book of Mediterranean Food'' (1950 ...
with a balance between meat-based dishes (pork, lamb, goat), vegetables (especially eggplant), and fish. Pasta (as in Central Italy and the rest of Southern Italy) is also very important in Calabria. In contrast to most other Italian regions, Calabrians have traditionally placed an emphasis on the preservation of their food and packing vegetables and meats in olive oil, and on making sausages and cold cuts ( soppressata, 'nduja
'Nduja () is a spicy, spreadable pork sausage from the region of Calabria in Southern Italy. It is similar to sobrassada from the Balearic Islands in Spain, and is loosely based on the French andouille. It is Calabria's contribution to the many ...
, capocollo
Capocollo () or coppa () is a traditional Italian and Corsican pork cold cut ('' salume'') made from the dry-cured muscle running from the neck to the fourth or fifth rib of the pork shoulder or neck. It is a whole-muscle salume, dry cured, an ...
). Along the coast fish is cured, especially swordfish, sardine
"Sardine" and "pilchard" are common names for various species of small, oily forage fish in the herring family Clupeidae. The term "sardine" was first used in English during the early 15th century, a folk etymology says it comes from the It ...
s (''sardelle rosamarina'') and cod ('' baccalà''). Local desserts are typically fried, honey-sweetened pastries such as ''cudduraci'', nacatole, ''scalille'' or ''scalidde'', or baked biscotti-type treats such as ''nzudda''.
Some local specialties include Caciocavallo
Caciocavallo is a type of stretched-curd cheese made out of sheep's or cow's milk. It is produced throughout Southern Italy, particularly in the Apennine Mountains and in the Gargano peninsula. Shaped like a teardrop, it is similar in taste to ...
cheese, ''cipolla rossa di Tropea
Red onions (also known as purple or blue onions in some mainland European countries, though not the UK) are cultivars of the onion (''Allium cepa''), and have purplish-red skin and white flesh tinged with red. They are most commonly used in co ...
'' (red onion), '' frìttuli'' and '' curcùci'' (fried pork), liquorice (''liquirizia''), '' lagane e cicciari'' (a pasta dish with chickpeas),'' pecorino crotonese'' (sheep cheese), and pignolata.
In ancient times Calabria was referred to as ''Enotria'' (from Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
, ', "land of wine"). According to ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
tradition, ('), the youngest of the sons of Lycaon, was the eponym of Oenotria. Some vineyards have origins dating back to the ancient Greek colonists. The best known DOC
DOC, Doc, doc or DoC may refer to:
In film and television
* ''Doc'' (2001 TV series), a 2001–2004 PAX series
* ''Doc'' (1975 TV series), a 1975–1976 CBS sitcom
* "D.O.C." (''Lost''), a television episode
* ''Doc'' (film), a 1971 Wester ...
wines are Cirò (Province of Crotone
The province of Crotone ( it, provincia di Crotone) is a province in the Calabria region of southern Italy. It was formed in 1992 out of a section of the province of Catanzaro. The provincial capital is the city of Crotone. It borders the province ...
) and Donnici ( Province of Cosenza). 3% of the total annual production qualifies as DOC. Important grape varieties are the red Gaglioppo and white Greco. Many producers are resurrecting local, ancient grape varieties which have been around for as long as 3000 years.
Transportation
Airports
* Lamezia Terme International Airport * Reggio Calabria Airport * Crotone Airport (summer only)Seaports
* Port of Gioia Tauro (the busiest container port in Italy and 9th-busiest in Europe) * Port of Reggio Calabria * Port of Vibo Valentia * Port of Villa San Giovanni * Port of Corigliano Calabro * Port of CrotoneBridges
Calabria has the two highest bridges in Italy: *Italia Viaduct
Italia Viaduct is a viaduct near Laino Borgo, Calabria, Italy. It is the highest bridge in Italy, and was the second highest bridge in the world when it opened in 1974. , it is among the forty highest bridges in the world. The bridge is locate ...
* Sfalassa Viaduct (also the highest and longest span frame bridge in the world)
Universities
There are 3 public universities in the region of Calabria *University of Calabria
The University of Calabria ( it, Università della Calabria, UNICAL) is a state-run university in Italy. Located in Arcavacata, a hamlet of Rende and a suburb of Cosenza, the university was founded in 1972. Among its founders there were Beniamino ...
(Cosenza)
* Magna Graecia University (Catanzaro)
* Mediterranea University of Reggio Calabria
Mediterranea University of Reggio Calabria ( it, Università degli Studi Mediterranea di Reggio Calabria), also referred to as Mediterranea University or University of Reggio Calabria, or simply UNIRC, is an Italian public research university, lo ...
There is also the private University for Foreigners "Dante Alighieri" in Reggio Calabria.
Notable people
See also
*1783 Calabrian earthquakes
The 1783 Calabrian earthquakes were a sequence of five strong earthquakes that hit the region of Calabria in southern Italy (then part of the Kingdom of Naples), the first two of which produced significant tsunamis. The epicenters form a clear a ...
* 1905 Calabria earthquake
* 1908 Messina earthquake
The 1908 Messina earthquake (also known as the 1908 Messina and Reggio earthquake) occurred on 28 December in Sicily and Calabria, southern Italy with a moment magnitude of 7.1 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). The epice ...
* Arbëreshë people
* Duke of Calabria
Duke of Calabria was the traditional title of the heir apparent of the Kingdom of Naples after the accession of Robert of Naples. It was also adopted by the heads of certain Houses that had once claimed the Kingdom of Naples in lieu of the royal ...
* Bruttians
* Griko people
The Griko people ( el, Γκρίκο), also known as Grecanici in Calabria, are an ethnic Greek community of Southern Italy. They are found principally in regions of Calabria and Apulia (peninsula of Salento). The Griko are believed to be remnants ...
* Magna Graecia
* Oenotrians
* Strait of Messina Bridge
* Theme of Sicily
References
Further reading
* Dal Lago, Enrico, and Rick Halpern, eds. ''The American South and the Italian Mezzogiorno: Essays in Comparative History'' (2002) * Dunston, Lara, and Terry Carter. ''Travellers Calabria'' (Travellers – Thomas Cook) (2009), guidebook * Moe, Nelson. ''The View from Vesuvius: Italian Culture and the Southern Question'' (2002) * Schneider, Jane. ''Italy's 'Southern Question': Orientalism in One Country'' (1998)External links
Official website of the region
Official website of tourism
{{coord, 38, 55, N, 16, 36, E, type:adm1st_region:IT-78, display=title Peninsulas of Italy * Regions of Italy NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union Wine regions of Italy