Cuon Alpinus Cova Negra on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The dhole ( ; ''Cuon alpinus'') is a
 ''Canis alpinus'' was the
''Canis alpinus'' was the

 The dhole's general tone of the fur is reddish, with the brightest hues occurring in winter. In the winter coat, the back is clothed in a saturated rusty-red to reddish colour with brownish highlights along the top of the head, neck and shoulders. The throat, chest, flanks, and belly and the upper parts of the limbs are less brightly coloured, and are more yellowish in tone. The lower parts of the limbs are whitish, with dark brownish bands on the anterior sides of the forelimbs. The muzzle and forehead are greyish-reddish. The tail is very luxuriant and fluffy, and is mainly of a reddish-ocherous colour, with a dark brown tip. The summer coat is shorter, coarser and darker. The dorsal and lateral
The dhole's general tone of the fur is reddish, with the brightest hues occurring in winter. In the winter coat, the back is clothed in a saturated rusty-red to reddish colour with brownish highlights along the top of the head, neck and shoulders. The throat, chest, flanks, and belly and the upper parts of the limbs are less brightly coloured, and are more yellowish in tone. The lower parts of the limbs are whitish, with dark brownish bands on the anterior sides of the forelimbs. The muzzle and forehead are greyish-reddish. The tail is very luxuriant and fluffy, and is mainly of a reddish-ocherous colour, with a dark brown tip. The summer coat is shorter, coarser and darker. The dorsal and lateral

 Historically, the dhole lived in
Historically, the dhole lived in
 Dholes are far less territory (animal), territorial than wolves, with pups from one clan often joining another without trouble once they mature sexually. Clans typically number 5 to 12 individuals in India, though clans of 40 have been reported. In Thailand, clans rarely exceed three individuals. Unlike other canids, there is no evidence of dholes using urine to mark their territories or travel routes. When urinating, dholes, especially males, may Raised-leg urination, raise one hind leg or both to result in a handstand. Handstand urination is also seen in
Dholes are far less territory (animal), territorial than wolves, with pups from one clan often joining another without trouble once they mature sexually. Clans typically number 5 to 12 individuals in India, though clans of 40 have been reported. In Thailand, clans rarely exceed three individuals. Unlike other canids, there is no evidence of dholes using urine to mark their territories or travel routes. When urinating, dholes, especially males, may Raised-leg urination, raise one hind leg or both to result in a handstand. Handstand urination is also seen in
 In India, the mating season occurs between mid-October and January, while captive dholes in the
In India, the mating season occurs between mid-October and January, while captive dholes in the
 Once large prey is caught, one dhole grabs the prey's nose, while the rest of the pack pulls the animal down by the flanks and hindquarters. They do not use a killing bite to the throat. They occasionally blind their prey by attacking the eyes. Serows are among the only ungulate species capable of effectively defending themselves against dhole attacks, due to their thick, protective coats and short, sharp horns capable of easily impaling dholes. Dholes tear open their prey's flanks and Disembowelment, disembowel it, eating the heart, liver, lungs and some sections of the intestines. The stomach and rumen are usually left untouched. Prey weighing less than is usually killed within two minutes, while large stags may take 15 minutes to die. Once prey is secured, dholes tear off pieces of the carcass and eat in seclusion. They give the pups access to a kill. They are generally tolerant of scavengers at their kills. Both mother and young are provided with regurgitated food by other pack members.
Once large prey is caught, one dhole grabs the prey's nose, while the rest of the pack pulls the animal down by the flanks and hindquarters. They do not use a killing bite to the throat. They occasionally blind their prey by attacking the eyes. Serows are among the only ungulate species capable of effectively defending themselves against dhole attacks, due to their thick, protective coats and short, sharp horns capable of easily impaling dholes. Dholes tear open their prey's flanks and Disembowelment, disembowel it, eating the heart, liver, lungs and some sections of the intestines. The stomach and rumen are usually left untouched. Prey weighing less than is usually killed within two minutes, while large stags may take 15 minutes to die. Once prey is secured, dholes tear off pieces of the carcass and eat in seclusion. They give the pups access to a kill. They are generally tolerant of scavengers at their kills. Both mother and young are provided with regurgitated food by other pack members.

 Like African wild dogs, but unlike wolves, dholes are not known to actively hunt people. They are known to eat insects and lizards. Dholes eat fruit and vegetable matter more readily than other canids. In captivity, they eat various kinds of grasses, herbs and leaves, seemingly for pleasure rather than just when ill. In summertime in the Tian Shan Mountains, dholes eat large quantities of mountain rhubarb. Although opportunistic, dholes have a seeming aversion to hunting cattle and their calves. Livestock predation by dholes has been a problem in Bhutan since the late 1990s, as domestic animals are often left outside to graze in the forest, sometimes for weeks at a time. Livestock stall-fed at night and grazed near homes are never attacked. Oxen are killed more often than cows, probably because they are given less protection.
Like African wild dogs, but unlike wolves, dholes are not known to actively hunt people. They are known to eat insects and lizards. Dholes eat fruit and vegetable matter more readily than other canids. In captivity, they eat various kinds of grasses, herbs and leaves, seemingly for pleasure rather than just when ill. In summertime in the Tian Shan Mountains, dholes eat large quantities of mountain rhubarb. Although opportunistic, dholes have a seeming aversion to hunting cattle and their calves. Livestock predation by dholes has been a problem in Bhutan since the late 1990s, as domestic animals are often left outside to graze in the forest, sometimes for weeks at a time. Livestock stall-fed at night and grazed near homes are never attacked. Oxen are killed more often than cows, probably because they are given less protection.
 In some areas, dholes are wiktionary:sympatric, sympatric to
In some areas, dholes are wiktionary:sympatric, sympatric to
Dhole Home PageArchive
*ARKive ŌĆ
images and movies of the dholeSaving the dhole: The forgotten 'badass' Asian dog more endangered than tigers
''The Guardian'' (25 June 2015)
Photos of dhole in Bandipur
{{Authority control Dhole, Canina (subtribe) Taxa named by Peter Simon Pallas Mammals described in 1811 Carnivorans of Asia Mammals of South Asia Mammals of Southeast Asia Endangered fauna of Asia Pleistocene mammals of Asia Extant Middle Pleistocene first appearances Species that are or were threatened by habitat fragmentation Endangered Fauna of China
canid
Canidae (; from Latin, ''canis'', "dog") is a family (biology), biological family of caniform carnivorans, constituting a clade. A member of this family is also called a canid (). The family includes three subfamily, subfamilies: the Caninae, a ...
native to South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''s┼½├Š'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sun├Ša ...
, East
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that ea ...
and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
. It is anatomically distinguished from members of the genus ''Canis
''Canis'' is a genus of the Caninae which includes multiple extant taxon, extant species, such as Wolf, wolves, dogs, coyotes, and golden jackals. Species of this genus are distinguished by their moderate to large size, their massive, well-develo ...
'' in several aspects: its skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
is convex rather than concave in profile, it lacks a third lower molar, and the upper molars possess only a single cusp
A cusp is the most pointed end of a curve. It often refers to cusp (anatomy), a pointed structure on a tooth.
Cusp or CUSP may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Cusp (singularity), a singular point of a curve
* Cusp catastrophe, a branch of bifu ...
as opposed to between two and four. During the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
, the dhole ranged throughout Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
, with its range also extending into Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
(with a single putative, controversial record also reported from North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
) but became restricted to its historical range 12,000ŌĆō18,000 years ago. It is now extinct in Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
, parts of Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
, and possibly the Korean peninsula
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically divided at or near the 38th parallel between North Korea (Dem ...
and Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
.
Genetic evidence indicates that the dhole was the result of reticulate evolution
Reticulate evolution, or network evolution is the origination of a lineage through the partial merging of two ancestor lineages, leading to relationships better described by a phylogenetic network than a bifurcating tree. Reticulate patterns can ...
, emerging from the hybridization between a species closely related to genus ''Canis'' and one from a lineage closely related to the African wild dog
The African wild dog (''Lycaon pictus''), also called painted dog and Cape hunting dog, is a wild canine native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is the largest wild canine in Africa, and the only extant member of the genus '' Lycaon'', which is disti ...
(''Lycaon pictus'').
The dhole is a highly social animal, living in large clans without rigid dominance hierarchies
In the zoological field of ethology, a dominance hierarchy (formerly and colloquially called a pecking order) is a type of social hierarchy that arises when members of animal social groups interact, creating a ranking system. Different types of ...
and containing multiple breeding females. Such clans usually consist of about 12 individuals, but groups of over 40 are known. It is a diurnal pack hunter which preferentially targets large and medium-sized ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Euungulata ("true ungulates"), which primarily consists of large mammals with Hoof, hooves. Once part of the clade "Ungulata" along with the clade Paenungulata, "Ungulata" has since been determined ...
s. In tropical forests, the dhole competes with the tiger
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is a large Felidae, cat and a member of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Asia. It has a powerful, muscular body with a large head and paws, a long tail and orange fur with black, mostly vertical stripes. It is ...
(''Panthera tigris'') and the leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant cat species in the genus ''Panthera''. It has a pale yellowish to dark golden fur with dark spots grouped in rosettes. Its body is slender and muscular reaching a length of with a ...
(''Panthera pardus''), targeting somewhat different prey species, but still with substantial dietary overlap.
It is listed as Endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
on the IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is an inventory of the global conservation status and extinction risk of biological ...
, as populations are decreasing and estimated to comprise fewer than 2,500 mature individuals. Factors contributing to this decline include habitat loss, loss of prey, competition with other species, persecution due to livestock predation, and disease transfer from domestic dog
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the gray wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it was selectively bred from a population of wolves during the Late Pleistocene by hunter-gatherers ...
s.
Etymology and naming
Theetymology
Etymology ( ) is the study of the origin and evolution of wordsŌĆöincluding their constituent units of sound and meaningŌĆöacross time. In the 21st century a subfield within linguistics, etymology has become a more rigorously scientific study. ...
of "dhole" is unclear. The possible earliest written use of the word in English occurred in 1808 by soldier Thomas Williamson, who encountered the animal in Ramghur district, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
. He stated that ''dhole'' was a common local name for the species. In 1827, Charles Hamilton Smith
Lieutenant-Colonel Charles Hamilton Smith, Royal Guelphic Order, KH, Military Order of William, KW, Royal Society, FRS, Linnean Society of London, FLS (26 December 1776 ŌĆō 21 September 1859) was a British Army officer, artist, naturalist, ant ...
claimed that it was derived from a language spoken in 'various parts of the East'.
Two years later, Smith connected this word with 'mad, crazy', and erroneously compared the Turkish word with and (cfr. also ; ), which are in fact from the Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic languages, Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from ...
*''dwalaz'' 'foolish, stupid'. Richard Lydekker
Richard Lydekker (; 25 July 1849 ŌĆō 16 April 1915) was a British naturalist, geologist and writer of numerous books on natural history. He was known for his contributions to zoology, paleontology, and biogeography. He worked extensively in cata ...
wrote nearly 80 years later that the word was not used by the natives living within the species' range. The Merriam-Webster
Merriam-Webster, Incorporated is an list of companies of the United States by state, American company that publishes reference work, reference books and is mostly known for Webster's Dictionary, its dictionaries. It is the oldest dictionary pub ...
''Dictionary'' theorises that it may have come from the .
Other English names for the species include Asian wild dog, Asiatic wild dog, Indian wild dog, whistling dog, red dog, and red wolf.
Taxonomy and evolution
 ''Canis alpinus'' was the
''Canis alpinus'' was the binomial name
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, altho ...
proposed by Peter Simon Pallas
Peter Simon Pallas Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS FRSE (22 September 1741 ŌĆō 8 September 1811) was a Prussia, Prussian zoologist, botanist, Ethnography, ethnographer, Exploration, explorer, Geography, geographer, Geology, geologist, Natura ...
in 1811, who described its range as encompassing the upper levels of Udskoi Ostrog in Amurland
Outer Manchuria, sometimes called Russian Manchuria, refers to a region in Northeast Asia that is now part of the Russian Far East but historically formed part of Manchuria (until the mid-19th century). While Manchuria now more normatively refer ...
, towards the eastern side and in the region of the upper Lena River
The Lena is a river in the Russian Far East and is the easternmost river of the three great rivers of Siberia which flow into the Arctic Ocean, the others being Ob (river), Ob and Yenisey. The Lena River is long and has a capacious drainage basi ...
, around the Yenisei
The Yenisey or Yenisei ( ; , ) is the fifth-longest river system in the world, and the largest to drain into the Arctic Ocean.
Rising in Mungaragiyn-gol in Mongolia, it follows a northerly course through Lake Baikal and the Krasnoyarsk Dam b ...
River and occasionally crossing into China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
. This northern Russian range reported by Pallas during the 18th and 19th centuries is "considerably north" of where this species occurs today.
''Canis primaevus'' was a name proposed by Brian Houghton Hodgson
Brian Houghton Hodgson (1 February 1801 ŌĆō 23 May 1894) was a pioneer natural history, naturalist and ethnologist working in India and Nepal where he was a British Resident (title), Resident. He described numerous species of birds and mammals fr ...
in 1833 who thought that the dhole was a primitive ''Canis'' form and the progenitor
In genealogy, a progenitor (rarer: primogenitor; or ''Ahnherr'') is the founder (sometimes one that is legendary) of a family, line of descent, gens, clan, tribe, noble house, or ethnic group.. Ebenda''Ahnherr:''"Stammvater eines Geschlec ...
of the domestic dog
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the gray wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it was selectively bred from a population of wolves during the Late Pleistocene by hunter-gatherers ...
. Hodgson later took note of the dhole's physical distinctiveness from the genus ''Canis'' and proposed the genus ''Cuon''.
The first study on the origins of the species was conducted by paleontologist Erich Thenius, who concluded in 1955 that the dhole was a post-Pleistocene descendant of a golden jackal-like ancestor. The paleontologist Bjorn Kurten wrote in his 1968 book ''Pleistocene Mammals of Europe'' that the primitive dhole ''Canis majori'' Del Campana 1913 ŌĆöthe remains of which have been found in Villafranchian
Villafranchian age ( ) is a period of geologic time (3.5ŌĆō1.0 Ma) spanning the Late Pliocene and Early Pleistocene used more specifically with European Land Mammal Ages. Named by Italian geologist Lorenzo Pareto for a sequence of terrestrial se ...
era Valdarno
The Valdarno is the valley of the river Arno, from Florence to the sea. The name applies to the entire river basin, though usage of the term generally excludes Casentino and the valleys formed by major tributaries.
Some towns in the area:
* R ...
, Italy and in ChinaŌĆöwas almost indistinguishable from the genus ''Canis''. In comparison, the modern species has greatly reduced molars and the cusp
A cusp is the most pointed end of a curve. It often refers to cusp (anatomy), a pointed structure on a tooth.
Cusp or CUSP may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Cusp (singularity), a singular point of a curve
* Cusp catastrophe, a branch of bifu ...
s have developed into sharply trenchant points. During the Early Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, more widely known as the Middle Pleistocene (its previous informal name), is an Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale or a Stage (stratigraphy), stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocen ...
there arose both ''Canis majori stehlini'' that was the size of a large wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the grey wolf or gray wolf, is a Canis, canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of Canis lupus, subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, includin ...
, and the early dhole ''Canis alpinus'' Pallas 1811 which first appeared at Hundsheim and Mosbach
Mosbach (; South Franconian: ''Mossbach'') is a town in the north of Baden-W├╝rttemberg, Germany. It is the seat of the Neckar-Odenwald district and has a population of approximately 25,000 distributed in six boroughs: Mosbach Town, Lohrbach, ...
in Germany. In the Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as the Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division ...
era the European dhole
The European dhole (''Cuon alpinus europaeus'') was a paleosubspecies of the dhole, which ranged throughout much of Western and Central Europe during the Middle and Late Pleistocene. Like the modern Asiatic populations, it was a more progressive ...
(''C. a. europaeus'') was modern-looking and the transformation of the lower molar into a single cusped, slicing tooth had been completed; however, its size was comparable with that of a wolf. This subspecies became extinct in Europe at the end of the late W├╝rm
Wurm or W├╝rm may refer to:
Places
* Wurm (Rur), a river in North Rhine-Westphalia in western Germany
* W├╝rm (Amper), a river in Bavaria, southeastern Germany
** W├╝rm glaciation, an Alpine ice age, named after the Bavarian river
* W├╝rm (Nagold ...
period, but the species as a whole still inhabits a large area of Asia. The European dhole may have survived up until the early Holocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
in the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
, and what is believed to be dhole remains have been found at Riparo Fredian in northern Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
dated 10,800 years old.
The vast Pleistocene range of this species also included numerous islands in Asia that this species no longer inhabits, such as Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
, Borneo
Borneo () is the List of islands by area, third-largest island in the world, with an area of , and population of 23,053,723 (2020 national censuses). Situated at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, it is one of the Greater Sunda ...
and possibly Palawan
Palawan (, ), officially the Province of Palawan (; ), is an archipelagic province of the Philippines that is located in the region of Mimaropa. It is the largest province in the country in terms of total area of . The capital and largest c ...
in the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
. Middle Pleistocene dhole fossils have also been found in the Matsukae Cave in northern Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's Japanese archipelago, four main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands (i.e. excluding Okinawa Island, Okinawa and the other Ryukyu Islands, Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Ryukyu Islands, Islands ...
Island in western Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
and in the Lower Kuzuu fauna in Tochigi Prefecture
is a landlocked Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Kant┼Ź region of Honshu. Tochigi Prefecture has a population of 1,897,649 (1 June 2023) and has a geographic area of 6,408 Square kilometre, km2 (2,474 Square mile, sq mi ...
in Honshu
, historically known as , is the largest of the four main islands of Japan. It lies between the Pacific Ocean (east) and the Sea of Japan (west). It is the list of islands by area, seventh-largest island in the world, and the list of islands by ...
Island, east Japan. Dhole fossils from the Late Pleistocene dated to about 10,700 years before present are known from the Luobi Cave or Luobi-Dong cave in Hainan Island
Hainan is an island province and the southernmost province of China. It consists of the eponymous Hainan Island and various smaller islands in the South China Sea under the province's administration. The name literally means "South of the Sea ...
in south China
South China ( zh, s=, p=Hu├Ī'n├Īn, j=jyut6 naam4) is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is ...
where they no longer exist. Additionally, fossils of canidae possibly belonging to dhole have been excavated from Dajia River
Dajia River () is the fifth-longest river in Taiwan located in the north-central of the island. It flows through Taichung City for 142 km.
The sources of the Dajia are: Hsuehshan and Nanhu Mountain in the Central Mountain Range. The Dajia ...
in Taichung County
Taichung County was a County (Taiwan), county in central Taiwan between 1945 and 2010. The county seat was in Yuanlin Township before 1950 and Fengyuan District, Fongyuan City after 1950.
History
Taichung County was established on 26 November ...
, Taiwan.
A single record of the dhole is known from North America. This consists of a jaw fragment and teeth of Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as the Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division ...
age found in San Josecito Cave in northeast Mexico, dating to around 27ŌĆō11,000 years ago. Other researchers have either considered this record as "insufficient" or suggested that further corroboration is required for the definitive taxonomic attribution of these specimens.
Dholes are also known from the Middle and Late Pleistocene fossil record of Europe. In 2021, the analyses of the mitochondrial
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used ...
genomes
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
extracted from the fossil remains of two extinct European dhole specimens from the J├Īchymka cave, Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the south ...
dated 35,000ŌĆō45,000 years old indicate that these were genetically basal to modern dholes and possessed much greater genetic diversity.
The dhole's distinctive morphology has been a source of much confusion in determining the species' systematic position among the Canidae. George Simpson placed the dhole in the subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zo ...
Simocyoninae alongside the African wild dog
The African wild dog (''Lycaon pictus''), also called painted dog and Cape hunting dog, is a wild canine native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is the largest wild canine in Africa, and the only extant member of the genus '' Lycaon'', which is disti ...
and the bush dog
The bush dog (''Speothos venaticus'') is a canine found in Central and South America. In spite of its extensive range, it is very rare in most areas except in Suriname, Guyana and Peru; it was first described by Peter Wilhelm Lund from fossils ...
, on account of all three species' similar dentition. Subsequent authors, including Juliet Clutton-Brock, noted greater morphological similarities to canids of the genera ''Canis'', ''Dusicyon
''Dusicyon'' is an extinct genus of South American canids.
Taxonomy
The type species is ''Dusicyon australis'', the Falkland Islands wolf. In 1914, Oldfield Thomas established this genus, in which he included the culpeo and other South Ame ...
'' and '' Alopex'' than to either '' Speothos'' or '' Lycaon'', with any resemblance to the latter two being due to convergent evolution
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last comm ...
.
Some authors consider the extinct ''Canis'' subgenus
In biology, a subgenus ( subgenera) is a taxonomic rank directly below genus.
In the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, a subgeneric name can be used independently or included in a species name, in parentheses, placed between the ge ...
''Xenocyon
''Xenocyon'' ("strange dog") is an extinct group of canids, either considered a distinct genus or a subgenus of ''Canis''. The group includes ''Canis'' (''Xenocyon'') ''africanus'', ''Canis'' (''Xenocyon'') ''antonii'' and ''Canis'' (''Xenocyon'') ...
'' as ancestral to both the genus ''Lycaon'' and the genus ''Cuon''. Subsequent studies on the canid genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
revealed that the dhole and African wild dog are closely related to members of the genus ''Canis''. This closeness to ''Canis'' may have been confirmed in a menagerie in Madras
Chennai, also known as Madras ( its official name until 1996), is the capital and largest city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost state of India. It is located on the Coromandel Coast of the Bay of Bengal. According to the 2011 Indian ce ...
, where according to zoologist Reginald Innes Pocock
Reginald Innes Pocock, (4 March 1863 ŌĆō 9 August 1947) was a British zoologist.
Pocock was born in Clifton, Bristol, the fourth son of Rev. Nicholas Pocock and Edith Prichard. He began showing interest in natural history at St. Edward's ...
there is a record of a dhole that interbred with a golden jackal. DNA sequencing of the Sardinian dhole
The Sardinian dhole (genus ''Cynotherium'' especially ''C. sardous'') is an extinct insular canid which was endemic to what is now the Mediterranean islands of Sardinia and Corsica during the Middle-Late Pleistocene. It went extinct at the end of ...
(''Cynotherium sardous'') an extinct small canine species formerly native to the island of Sardinia in the Mediterranean, and which has often been suggested to have descended from ''Xenocyon'', has found that it is most closely related to the living dhole among canines.
Admixture with the African wild dog
In 2018,whole genome sequencing
Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing or just genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's ...
was used to compare all members (apart from the black-backed and side-striped jackals) of the genus ''Canis'', along with the dhole and the African wild dog
The African wild dog (''Lycaon pictus''), also called painted dog and Cape hunting dog, is a wild canine native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is the largest wild canine in Africa, and the only extant member of the genus '' Lycaon'', which is disti ...
(''Lycaon pictus''). There was strong evidence of ancient genetic admixture
Genetic admixture occurs when previously isolated populations interbreed resulting in a population that is descended from multiple sources. It can occur between species, such as with hybrids, or within species, such as when geographically dista ...
between the dhole and the African wild dog. Today, their ranges are remote from each other; however, during the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
era the dhole could be found as far west as Europe. The study proposes that the dhole's distribution may have once included the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
, from where it may have admixed with the African wild dog in North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
. However, there is no evidence of the dhole having existed in the Middle East nor North Africa, though the ''Lycaon'' was present in Europe during the Early Pleistocene, with its last record in the region dating to 830,000 years ago. Genetic evidence from the Sardinan dhole suggests that both Sardinian and modern dholes (which are estimated to have split from each other around 900,000 years ago) share ancestry from the ''Lycaon'' lineage, but this ancestry is significantly higher in modern dholes than in the Sardinian dhole.
Subspecies
Historically, up to ten subspecies of dholes have been recognised. , seven subspecies are recognised. However, studies on the dhole'smtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the DNA contained in ...
and microsatellite
A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain Sequence motif, DNA motifs (ranging in length from one to six or more base pairs) are repeated, typically 5ŌĆō50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations within an organ ...
genotype showed no clear subspecific distinctions. Nevertheless, two major phylogeographic groupings were discovered in dholes of the Asian mainland, which likely diverged during a glaciation event. One population extends from South, Central and North India (south of the Ganges) into Myanmar, and the other extends from India north of the Ganges into northeastern India, Myanmar, Thailand and the Malaysian Peninsula. The origin of dholes in Sumatra and Java is, , unclear, as they show greater relatedness to dholes in India, Myanmar and China rather than with those in nearby Malaysia. However, the Canid Specialist Group of the International Union for the Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the status ...
(IUCN) states that further research is needed because all of the samples were from the southern part of this species' range and the Tien Shan
The Tian Shan, also known as the Tengri Tagh or Tengir-Too, meaning the "Mountains of God/Heaven", is a large system of mountain ranges in Central Asia. The highest peak is Jengish Chokusu at high and located in Kyrgyzstan. Its lowest point is ...
subspecies has distinct morphology.
In the absence of further data, the researchers involved in the study speculated that Javan and Sumatran dholes could have been introduced to the islands by humans. Fossils of dhole from the early Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, more widely known as the Middle Pleistocene (its previous informal name), is an Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale or a Stage (stratigraphy), stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocen ...
have been found in Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
.
Characteristics

 The dhole's general tone of the fur is reddish, with the brightest hues occurring in winter. In the winter coat, the back is clothed in a saturated rusty-red to reddish colour with brownish highlights along the top of the head, neck and shoulders. The throat, chest, flanks, and belly and the upper parts of the limbs are less brightly coloured, and are more yellowish in tone. The lower parts of the limbs are whitish, with dark brownish bands on the anterior sides of the forelimbs. The muzzle and forehead are greyish-reddish. The tail is very luxuriant and fluffy, and is mainly of a reddish-ocherous colour, with a dark brown tip. The summer coat is shorter, coarser and darker. The dorsal and lateral
The dhole's general tone of the fur is reddish, with the brightest hues occurring in winter. In the winter coat, the back is clothed in a saturated rusty-red to reddish colour with brownish highlights along the top of the head, neck and shoulders. The throat, chest, flanks, and belly and the upper parts of the limbs are less brightly coloured, and are more yellowish in tone. The lower parts of the limbs are whitish, with dark brownish bands on the anterior sides of the forelimbs. The muzzle and forehead are greyish-reddish. The tail is very luxuriant and fluffy, and is mainly of a reddish-ocherous colour, with a dark brown tip. The summer coat is shorter, coarser and darker. The dorsal and lateral guard hair
Guard hair or overhair is the outer layer of hair of most mammals, which overlay the fur. Guard hairs are long and coarse and protect the rest of the pelage (fur) from abrasion and frequently from moisture. They are visible on the surface of the ...
s in adults measure in length. Dholes in the Moscow Zoo
The Moscow Zoo or Moskovsky Zoopark () is a zoo, the largest in Russia.
History
The Moscow Zoo was founded in 1864 by professor-biologists, K.F. Rulje, S.A. Usov and A.P. Bogdanov, from the Moscow State University. In 1919, the zoo was natio ...
moult once a year from March to May. A melanistic
Melanism is the congenital excess of melanin in an organism resulting in dark pigment.
Pseudomelanism, also called abundism, is another variant of pigmentation, identifiable by dark spots or enlarged stripes, which cover a large part of the bod ...
individual was recorded in the northern Coimbatore
Coimbatore (Tamil: k┼Źyamputt┼½r, ), also known as Kovai (), is one of the major Metropolitan cities of India, metropolitan cities in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is located on the banks of the Noyy ...
Forest Division in Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is the southernmost States and union territories of India, state of India. The List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of Indi ...
.
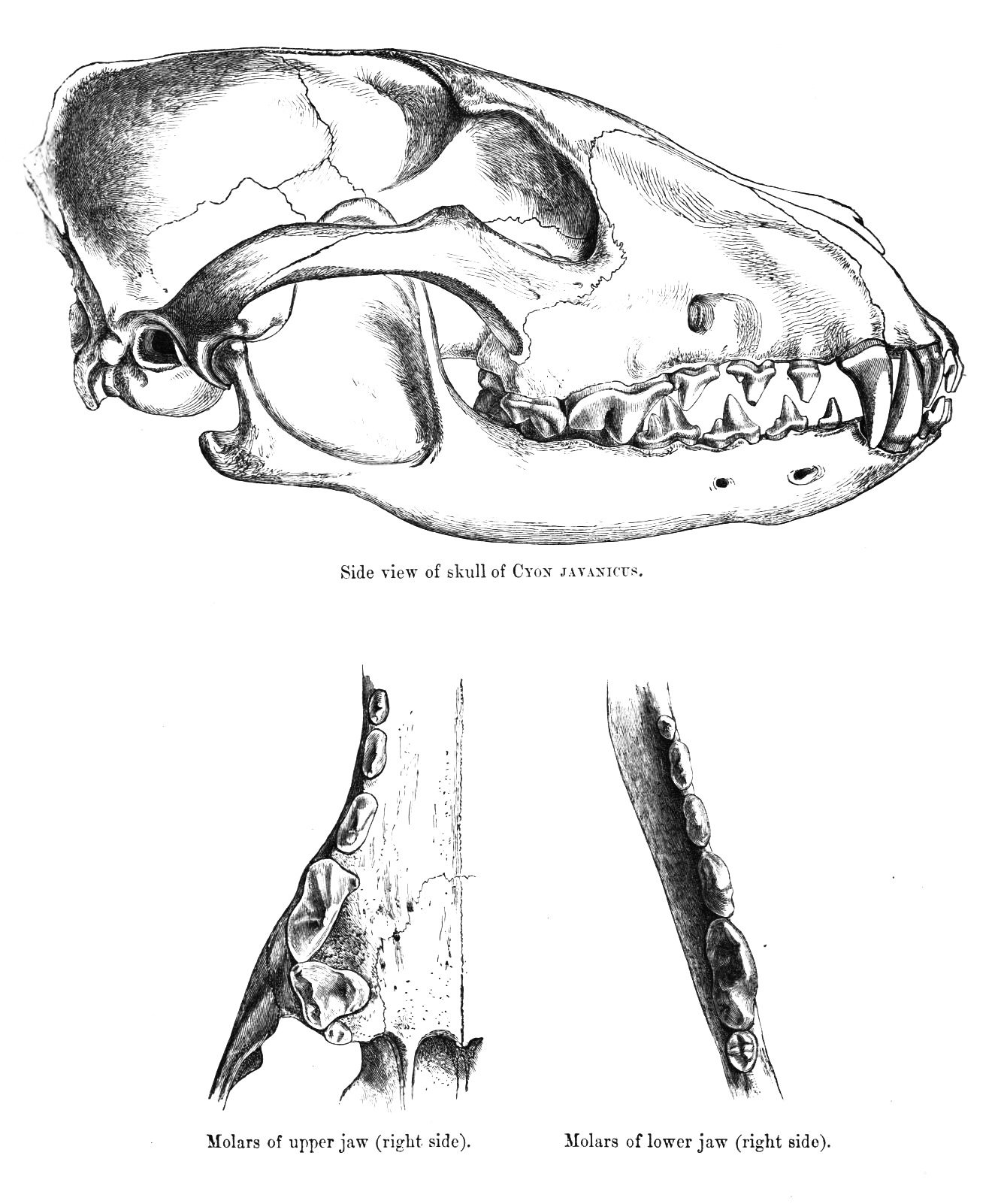
The dhole has a wide and massive skull with a well-developed sagittal crest
A sagittal crest is a ridge of bone running lengthwise along the midline of the top of the skull (at the sagittal suture) of many mammalian and reptilian skulls, among others. The presence of this ridge of bone indicates that there are excepti ...
, and its masseter muscle
In anatomy, the masseter is one of the muscles of mastication. Found only in mammals, it is particularly powerful in herbivores to facilitate chewing of plant matter. The most obvious muscle of mastication is the masseter muscle, since it is the ...
s are highly developed compared to other canid species, giving the face an almost hyena
Hyenas or hyaenas ( ; from Ancient Greek , ) are feliform carnivoran mammals belonging to the family Hyaenidae (). With just four extant species (each in its own genus), it is the fifth-smallest family in the order Carnivora and one of the sma ...
-like appearance. The rostrum
Rostrum may refer to:
* Any kind of a platform for a speaker:
**dais
**pulpit
** podium
* Rostrum (anatomy), a beak, or anatomical structure resembling a beak, as in the mouthparts of many sucking insects
* Rostrum (ship), a form of bow on naval ...
is shorter than that of domestic dogs and most other canids. It has six rather than seven lower molars
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat tooth, teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammal, mammals. They are used primarily to comminution, grind food during mastication, chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, '' ...
.
The upper molars are weak, being one third to one half the size of those of wolves and have only one cusp
A cusp is the most pointed end of a curve. It often refers to cusp (anatomy), a pointed structure on a tooth.
Cusp or CUSP may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Cusp (singularity), a singular point of a curve
* Cusp catastrophe, a branch of bifu ...
as opposed to between two and four, as is usual in canids, an adaptation thought to improve shearing ability and thus speed of prey consumption. This may allow dholes to compete more successfully with kleptoparasite
Kleptoparasitism (originally spelt clepto-parasitism, meaning "parasitism by theft") is a form of feeding in which one animal deliberately takes food from another. The strategy is Evolutionarily stable strategy, evolutionarily stable when stealin ...
s. In terms of size, dholes average about in length (excluding a long tail), and stand around at the shoulders. Adult females can weigh , while the slightly larger male may weigh . The mean weight of adults from three small samples was .
In appearance, the dhole has been variously described as combining the physical characteristics of the gray wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the grey wolf or gray wolf, is a canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, including the dog and dingo, though gr ...
and the red fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe and Asia, plus ...
, and as being "cat-like" on account of its long backbone and slender limbs.
Distribution and habitat

 Historically, the dhole lived in
Historically, the dhole lived in Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
and throughout Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
including Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the AfghanistanŌĆōIran borde ...
, Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan, officially the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia lying in the Tian Shan and Pamir Mountains, Pamir mountain ranges. Bishkek is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Kyrgyzstan, largest city. Kyrgyz ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the KazakhstanŌĆōRussia border, north and west, China to th ...
, Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
, Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the AfghanistanŌĆōTajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
and Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
, though it is now considered to be regionally extinct in these regions. Historical record in South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
from the Veritable Records of the Joseon Dynasty
The ''Veritable Records of the Joseon Dynasty'', sometimes called ''sillok'' () for short, are state-compiled and published records, called Veritable Records, documenting the reigns of the kings of the Joseon dynasty in Korea. Kept from 1392 ...
also indicate that the dhole once inhabited Yangju
Yangju (; ) is a city in Gyeonggi Province, South Korea. Yangju is located south of Dongducheon and north of Uijeongbu, not far from Seoul.
In the past, it was one region with Uijeongbu-si, Guri-si, Namyangju-si, Dongducheon-si, and some parts ...
in Gyeonggi Province
Gyeonggi Province (, ) is the most populous province in South Korea.
Seoul, the nation's largest city and capital, is in the heart of the area but has been separately administered as a provincial-level ''special city'' since 1946. Incheon, ...
, but it is now also extinct in South Korea, with the last known capture reports in 1909 and 1921 from Yeoncheon
Yeoncheon County (''Yeoncheon-gun'') is a county in Gyeonggi Province, South Korea. The county seat is Yeoncheon-eup (ņŚ░ņ▓£ņØŹ) and sits on Gyeongwon Line, the Korail railroad line connecting Seoul, South Korea (ROK), with North Korea (DPRK).
Hi ...
of Gyeonggi Province
Gyeonggi Province (, ) is the most populous province in South Korea.
Seoul, the nation's largest city and capital, is in the heart of the area but has been separately administered as a provincial-level ''special city'' since 1946. Incheon, ...
. The current presence of dholes in North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders China and Russia to the north at the Yalu River, Yalu (Amnok) an ...
and Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
is considered uncertain. The dholes also once inhabited the alpine steppes extending into Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
to the Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory and constitutes an eastern portion of the larger Kashmir region that has been the subject of a Kashmir#Kashmir dispute, dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947 and India an ...
area, though they disappeared from 60% of their historic range in India during the past century. In India, Myanmar, Indochina, Indonesia and China, it prefers forested areas in alpine zone
Alpine tundra is a type of natural region or biome that does not contain trees because it is at high elevation, with an associated alpine climate, harsh climate. As the latitude of a location approaches the poles, the threshold elevation for alp ...
s and is occasionally sighted in plain
In geography, a plain, commonly known as flatland, is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and ...
s regions.
In the Bek-Tosot Conservancy of southern Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan, officially the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia lying in the Tian Shan and Pamir Mountains, Pamir mountain ranges. Bishkek is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Kyrgyzstan, largest city. Kyrgyz ...
, the possible presence of the dholes was considered likely based on genetic samples collected in 2019. This was the first record of dholes from the country in almost three decades.
The dhole might still be present in the Tunkinsky National Park
The Tunka or Tunkinsky National Park (Russian: ąóčāąĮą║ąĖąĮčüą║ąĖą╣) is a national park located in south central Siberia. It covers a mountainous region centered on the Irkut River valley (also referred to as the Tunka Valley) that continues from ...
in extreme southern Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
near Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal is a rift lake and the deepest lake in the world. It is situated in southern Siberia, Russia between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, Irkutsk Oblasts of Russia, Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
. It possibly still lives in the Primorsky Krai
Primorsky Krai, informally known as Primorye, is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject (a krais of Russia, krai) of Russia, part of the Far Eastern Federal District in the Russian Far East. The types of inhabited localities in Russia, ...
province in far eastern Russia, where it was considered a rare and endangered species in 2004, with unconfirmed reports in the Pikthsa-Tigrovy Dom protected forest area; no sighting was reported in other areas since the late 1970s.
Currently, no other recent reports are confirmed of dholes being present in Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
, so the IUCN considered them to be extinct in Russia. However, the dhole might be present in the eastern Sayan Mountains
The Sayan Mountains (, ; ) are a mountain range in southern Siberia spanning southeastern Russia (Buryatia, Irkutsk Oblast, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Tuva and Khakassia) and northern Mongolia. Before the rapid expansion of the Tsardom of Russia, the mou ...
and in the Transbaikal
Transbaikal, Trans-Baikal, Transbaikalia ( rus, ąŚą░ą▒ą░ą╣ą║ą░╠üą╗čīąĄ, r=Zabaykal'ye, p=z╔Öb╔Éj╦łkal╩▓j╔¬), or Dauria (, ''Dauriya'') is a mountainous region to the east of or "beyond" (trans-) Lake Baikal at the south side of the eastern Si ...
region; it has been sighted in Tofalaria in the Irkutsk Oblast
Irkutsk Oblast (; ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located in southeastern Siberia in the basins of the Angara River, Angara, Lena River, Lena, and Nizhnyaya Tunguska Rivers. The administrative center is ...
, the Republic of Buryatia
Buryatia, officially the Republic of Buryatia, is a Republics of Russia, republic of Russia located in the Russian Far East. Formerly part of the Siberian Federal District, it has been administered as part of the Far Eastern Federal District sin ...
and Zabaykalsky Krai
Zabaykalsky Krai is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (a krai), located in the Russian Far East. Its administrative center is Chita, Zabaykalsky Krai, Chita. As of the Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census, the population was ...
.
One pack was sighted in the Qilian Mountains
The Qilian Mountains (), together with the Altyn-Tagh sometimes known as the Nan Shan, as it is to the south of the Hexi Corridor, is a northern outlier of the Kunlun Mountains, forming the border between Qinghai and the Gansu provinces of n ...
in 2006.
In 2011 to 2013, local government officials and herders reported the presence of several dhole packs at elevations of near Taxkorgan Nature Reserve
The Taxkorgan Nature Reserve (officially spelled Taxkorgan Natural Reserve) is a nature reserve in Kashgar Prefecture, Xinjiang, China. It is situated around the Taghdumbash Pamir of Pamir Mountains and Karakorum Mountains. It covers about was e ...
in the Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People' ...
Autonomous Region. Several packs and a female adult with pups were also recorded by camera trap
A camera trap is a camera that is automatically triggered by motion in its vicinity, like the presence of an animal or a human being. It is typically equipped with a motion sensorŌĆöusually a passive infrared (PIR) sensor or an active infrared ...
s at elevations of around in Yanchiwan National Nature Reserve in the northern Gansu Province
Gansu is a provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeastern part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan Plateau, Ti ...
in 2013ŌĆō2014.
Dholes have been also reported in the Altyn-Tagh
Altyn-Tagh (also Altun Mountains or Altun Shan) is a mountain range in Northwestern China that separates the Eastern Tarim Basin from the Tibetan Plateau. The western third is in Xinjiang while the eastern part forms the border between Qinghai t ...
Mountains.
In China's Yunnan
Yunnan; is an inland Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 47.2 million (as of 2020). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces ...
Province, dholes were recorded in Baima Xueshan Nature Reserve in 2010ŌĆō2011. Dhole samples were obtained in Jiangxi
; Gan: )
, translit_lang1_type2 =
, translit_lang1_info2 =
, translit_lang1_type3 =
, translit_lang1_info3 =
, image_map = Jiangxi in China (+all claims hatched).svg
, mapsize = 275px
, map_caption = Location ...
Province in 2013.
Confirmed records by camera-trapping since 2008 have occurred in southern and western Gansu
Gansu is a provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeastern part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan Plateau, Ti ...
province, southern Shaanxi
Shaanxi is a Provinces of China, province in north Northwestern China. It borders the province-level divisions of Inner Mongolia to the north; Shanxi and Henan to the east; Hubei, Chongqing, and Sichuan to the south; and Gansu and Ningxia to t ...
province, southern Qinghai
Qinghai is an inland Provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. It is the largest provinces of China, province of China (excluding autonomous regions) by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xin ...
province, southern and western Yunnan
Yunnan; is an inland Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 47.2 million (as of 2020). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces ...
province, western Sichuan
Sichuan is a province in Southwestern China, occupying the Sichuan Basin and Tibetan PlateauŌĆöbetween the Jinsha River to the west, the Daba Mountains to the north, and the YunnanŌĆōGuizhou Plateau to the south. Its capital city is Cheng ...
province, the southern Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People' ...
Autonomous Region and in the Southeastern Tibet
Tibet (; ''B├Čd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
Autonomoous Region. There are also historical records of dhole dating to 1521ŌĆō1935 in Hainan Island, but the species is no longer present and is estimated to have become extinct around 1942.
The dhole occurs in most of India south of the Ganges, particularly in the Central Indian Highlands and the Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats is a mountain range that stretches along the East Coast of India, eastern coast of the Indian peninsula. Covering an area of , it traverses the states and union territories of India, states of Odisha, Telangana, Andhra Prade ...
. It is also present in Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeast India. It was formed from the North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and India declared it as a state on 20 February 1987. Itanagar is its capital and la ...
, Assam
Assam (, , ) is a state in Northeast India, northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra Valley, Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . It is the second largest state in Northeast India, nor ...
, Meghalaya
Meghalaya (; "the abode of clouds") is a states and union territories of India, state in northeast India. Its capital is Shillong. Meghalaya was formed on 21 January 1972 by carving out two districts from the Assam: the United Khasi Hills an ...
and West Bengal
West Bengal (; Bengali language, Bengali: , , abbr. WB) is a States and union territories of India, state in the East India, eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabi ...
and in the Indo-Gangetic Plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the Northern Plain or North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain spanning across the northern and north-eastern part of the Indian subcontinent. It encompasses North India, northern and East India, easte ...
's Terai
The Terai or Tarai is a lowland region in parts of southern Nepal and northern India that lies to the south of the outer foothills of the Himalayas, the Sivalik Hills and north of the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
This lowland belt is characterised by ...
region. Dhole populations in the Himalaya
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than 100 pea ...
s and northwest India are fragmented.
In 2011, dhole packs were recorded by camera traps in the Chitwan National Park
Chitwan National Park is the first national park of Nepal. It was established in 1973 as the Royal Chitwan National Park and was granted the status of a World Heritage Site in 1984. It covers an area of in the Terai of south-central Nepal. It ra ...
. Its presence was confirmed in the Kanchenjunga Conservation Area
Kanchenjunga Conservation Area is a protected area in the Himalayas of eastern Nepal that was established in 1997. It covers in the Taplejung District and comprises two peaks of Kanchenjunga. In the north it adjoins the Qomolangma National Nat ...
in 2011 by camera traps. In February 2020, dholes were sighted in the Vansda National Park
Vansda National Park, also known as Bansda National Park, is a protected area which represents the thick woodlands of the Dangs and southern Gujarat, and is situated in the Vansda tehsil, Navsari District of Gujarat state, India. Riding on the b ...
, with camera traps confirming the presence of two individuals in May of the same year. This was the first confirmed sighting of dholes in Gujarat since 1970.
In Bhutan, the dhole is present in Jigme Dorji National Park.
In Bangladesh, it inhabits forest reserves in the Sylhet area, as well the Chittagong Hill Tracts in the southeast. Recent camera trap photos in the Chittagong in 2016 showed the continued presence of the dhole. These regions probably do not harbour a viable population, as mostly small groups or solitary individuals were sighted.
In Myanmar, the dhole is present in several protected areas. In 2015, dholes and tigers were recorded by camera-traps for the first time in the hill forests of Karen State.
Its range is highly fragmented in the Malaysian Peninsula, Sumatra, Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
, Vietnam and Thailand, with the Vietnamese population considered to be possibly extinct. In 2014, camera trap videos in the montane tropical forests at in the Kerinci Seblat National Park in Sumatra revealed its continued presence. A camera trapping survey in the Khao Ang Rue Nai Wildlife Sanctuary in Thailand from January 2008 to February 2010 documented one healthy dhole pack. In northern Laos, dholes were studied in Nam Et-Phou Louey National Protected Area. Camera trap surveys from 2012 to 2017 recorded dholes in the same Nam Et-Phou Louey National Protected Area.
In Vietnam, dholes were sighted only in Pu Mat National Park in 1999, in Yok Don National Park in 2003 and 2004; and in Ninh Thuan Province in 2014.
A disjunct dhole population was reported in the area of Trabzon and Rize in northeastern Turkey near the border with Georgia (country), Georgia in the 1990s. This report was not considered to be reliable. One single individual was claimed to have been shot in 2013 in the nearby Kabardino-Balkaria Republic of Russia in the central Caucasus; its remains were analysed in May 2015 by a biologist from the Kabardino-Balkarian State University, who concluded that the skull was indeed that of a dhole. In August 2015, researchers from the National Museum of Natural History (Bulgaria), National Museum of Natural History and the Karadeniz Technical University started an expedition to track and document possible Turkish population of dhole. In October 2015, they concluded that two skins of alleged dholes in Turkey probably belonged to dogs, pending DNA analysis of samples from the skins, and, having analysed photos of the skull of alleged dhole in Kabardino-Balkaria Republic of Russia, they concluded it was a grey wolf.
Ecology and behaviour
Dholes produce whistles resembling the calls of red foxes, sometimes rendered as ''coo-coo''. How this sound is produced is unknown, though it is thought to help in coordinating the pack when travelling through thick brush. When attacking prey, they emit screaming ''KaKaKaKAA'' sounds. Other sounds include whines (food soliciting), growls (warning), screams, chatterings (both of which are alarm calls) and yapping cries. In contrast to wolves, dholes do not Howling, howl or bark. Dholes have a complex body language. Friendly or submissive greetings are accompanied by horizontal lip retraction and the lowering of the tail, as well as licking. Playful dholes open their mouths with their lips retracted and their tails held in a vertical position whilst assuming a play bow. Aggressive or threatening dholes pucker their lips forward in a snarl and raise the hairs on their backs, as well as keep their tails horizontal or vertical. When afraid, they pull their lips back horizontally with their tails tucked and their ears flat against the skull.Social and territorial behaviour
Dholes are more social than gray wolves, and have less of a dominance hierarchy, as seasonal scarcity of food is not a serious concern for them. In this manner, they closely resemble African wild dogs in social structure. They live in clans rather than pack (canine), packs, as the latter term refers to a group of animals that always hunt together. In contrast, dhole clans frequently break into small packs of three to five animals, particularly during the spring season, as this is the optimal number for catching fawns. Dominant dholes are hard to identify, as they do not engage in dominance displays as wolves do, though other clan members will show submissive behaviour toward them. Intragroup fighting is rarely observed. Dholes are far less territory (animal), territorial than wolves, with pups from one clan often joining another without trouble once they mature sexually. Clans typically number 5 to 12 individuals in India, though clans of 40 have been reported. In Thailand, clans rarely exceed three individuals. Unlike other canids, there is no evidence of dholes using urine to mark their territories or travel routes. When urinating, dholes, especially males, may Raised-leg urination, raise one hind leg or both to result in a handstand. Handstand urination is also seen in
Dholes are far less territory (animal), territorial than wolves, with pups from one clan often joining another without trouble once they mature sexually. Clans typically number 5 to 12 individuals in India, though clans of 40 have been reported. In Thailand, clans rarely exceed three individuals. Unlike other canids, there is no evidence of dholes using urine to mark their territories or travel routes. When urinating, dholes, especially males, may Raised-leg urination, raise one hind leg or both to result in a handstand. Handstand urination is also seen in bush dog
The bush dog (''Speothos venaticus'') is a canine found in Central and South America. In spite of its extensive range, it is very rare in most areas except in Suriname, Guyana and Peru; it was first described by Peter Wilhelm Lund from fossils ...
s (''Speothos venaticus'') and domestic dogs. They may defecate in conspicuous places, though a territorial function is unlikely, as faeces are mostly deposited within the clan's territory rather than the periphery. Faeces are often deposited in what appear to be communal Animal latrine, latrines. They do not scrape the earth with their feet, as other canids do, to mark their territories.
Denning
Four kinds of den have been described; simple earth dens with one entrance (usually remodeled striped hyena or porcupine dens); complex cavernous earth dens with more than one entrance; simple cavernous dens excavated under or between rocks; and complex cavernous dens with several other dens in the vicinity, some of which are interconnected. Dens are typically located under dense scrub or on the banks of dry rivers or creeks. The entrance to a dhole den can be almost vertical, with a sharp turn three to four feet down. The tunnel opens into an antechamber, from which extends more than one passage. Some dens may have up to six entrances leading up to of interconnecting tunnels. These "cities" may be developed over many generations of dholes, and are shared by the clan females when raising young together. LikeAfrican wild dog
The African wild dog (''Lycaon pictus''), also called painted dog and Cape hunting dog, is a wild canine native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is the largest wild canine in Africa, and the only extant member of the genus '' Lycaon'', which is disti ...
s and dingoes, dholes will avoid killing prey close to their dens.
Reproduction and development
 In India, the mating season occurs between mid-October and January, while captive dholes in the
In India, the mating season occurs between mid-October and January, while captive dholes in the Moscow Zoo
The Moscow Zoo or Moskovsky Zoopark () is a zoo, the largest in Russia.
History
The Moscow Zoo was founded in 1864 by professor-biologists, K.F. Rulje, S.A. Usov and A.P. Bogdanov, from the Moscow State University. In 1919, the zoo was natio ...
breed mostly in February. Unlike wolf packs, dhole clans may contain more than one breeding female. More than one female dhole may den and rear their litters together in the same den. During mating, the female assumes a crouched, cat-like position. There is no copulatory tie characteristic of other canids when the male dismounts. Instead, the pair lie on their sides facing each other in a semicircular formation. The gestation period lasts 60ŌĆō63 days, with litter sizes averaging four to six pups. Their growth rate is much faster than that of wolves, being similar in rate to that of coyotes.
The hormone metabolites of five males and three females kept in Thai zoos was studied. The breeding males showed an increased level of testosterone from October to January. The oestrogen level of captive females increases for about two weeks in January, followed by an increase of progesterone. They displayed sexual behaviours during the oestrogen peak of the females.
Pups are suckled at least 58 days. During this time, the pack feeds the mother at the den site. Dholes do not use wikt:rendezvous, rendezvous sites to meet their pups as wolves do, though one or more adults will stay with the pups at the den while the rest of the pack hunts. Once weaning begins, the adults of the clan will regurgitate food for the pups until they are old enough to join in hunting. They remain at the den site for 70ŌĆō80 days. By the age of six months, pups accompany the adults on hunts and will assist in killing large prey such as sambar deer, sambar by the age of eight months. Maximum longevity in captivity is 15ŌĆō16 years.
Hunting behaviour
Before embarking on a hunt, clans go through elaborate prehunt social rituals involving nuzzling, body rubbing and mounting. Dholes are primarily Diurnality, diurnal hunters, hunting in the early hours of the morning. They rarely hunt at night, except on moonlit nights, indicating they greatly rely on Visual perception, sight when hunting. They can chase their prey for many hours. During a pursuit, one or more dholes takes over chasing the prey, while the rest of the pack keeps up at a steadier pace behind, taking over once the other group tires. Most chases are short, lasting only . When chasing fleet-footed prey, they run at a pace of . Dholes frequently drive their prey into water bodies, where the targeted animal's movements are hindered. Once large prey is caught, one dhole grabs the prey's nose, while the rest of the pack pulls the animal down by the flanks and hindquarters. They do not use a killing bite to the throat. They occasionally blind their prey by attacking the eyes. Serows are among the only ungulate species capable of effectively defending themselves against dhole attacks, due to their thick, protective coats and short, sharp horns capable of easily impaling dholes. Dholes tear open their prey's flanks and Disembowelment, disembowel it, eating the heart, liver, lungs and some sections of the intestines. The stomach and rumen are usually left untouched. Prey weighing less than is usually killed within two minutes, while large stags may take 15 minutes to die. Once prey is secured, dholes tear off pieces of the carcass and eat in seclusion. They give the pups access to a kill. They are generally tolerant of scavengers at their kills. Both mother and young are provided with regurgitated food by other pack members.
Once large prey is caught, one dhole grabs the prey's nose, while the rest of the pack pulls the animal down by the flanks and hindquarters. They do not use a killing bite to the throat. They occasionally blind their prey by attacking the eyes. Serows are among the only ungulate species capable of effectively defending themselves against dhole attacks, due to their thick, protective coats and short, sharp horns capable of easily impaling dholes. Dholes tear open their prey's flanks and Disembowelment, disembowel it, eating the heart, liver, lungs and some sections of the intestines. The stomach and rumen are usually left untouched. Prey weighing less than is usually killed within two minutes, while large stags may take 15 minutes to die. Once prey is secured, dholes tear off pieces of the carcass and eat in seclusion. They give the pups access to a kill. They are generally tolerant of scavengers at their kills. Both mother and young are provided with regurgitated food by other pack members.
Feeding ecology
Prey animals in India include chital, sambar deer, muntjac, mouse deer, barasingha, wild boar, gaur, water buffaloes, banteng, cattle, nilgai, goats, Indian hares, Himalayan field rats and langurs. There is one record of a pack bringing down an Indian elephant calf inAssam
Assam (, , ) is a state in Northeast India, northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra Valley, Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . It is the second largest state in Northeast India, nor ...
, despite desperate defense of the mother, resulting in numerous losses to the pack. In Kashmir, they prey on markhor, and thamin in Myanmar, Malayan tapir, Sumatran serow in Sumatra and the Malay Peninsula and Javan rusa in Java. In the Tian Shan and Tarbagatai Mountains, dholes prey on Siberian ibexes, arkhar, roe deer, Caspian red deer and wild boar. In the Altai Mountains, Altai and Sayan Mountains
The Sayan Mountains (, ; ) are a mountain range in southern Siberia spanning southeastern Russia (Buryatia, Irkutsk Oblast, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Tuva and Khakassia) and northern Mongolia. Before the rapid expansion of the Tsardom of Russia, the mou ...
, they prey on musk deer and reindeer. In eastern Siberia, they prey on roe deer, Manchurian wapiti, wild pig, musk deer and reindeer, while in Primorye they feed on sika deer and goral. In Mongolia, they prey on argali and rarely Siberian ibex.

 Like African wild dogs, but unlike wolves, dholes are not known to actively hunt people. They are known to eat insects and lizards. Dholes eat fruit and vegetable matter more readily than other canids. In captivity, they eat various kinds of grasses, herbs and leaves, seemingly for pleasure rather than just when ill. In summertime in the Tian Shan Mountains, dholes eat large quantities of mountain rhubarb. Although opportunistic, dholes have a seeming aversion to hunting cattle and their calves. Livestock predation by dholes has been a problem in Bhutan since the late 1990s, as domestic animals are often left outside to graze in the forest, sometimes for weeks at a time. Livestock stall-fed at night and grazed near homes are never attacked. Oxen are killed more often than cows, probably because they are given less protection.
Like African wild dogs, but unlike wolves, dholes are not known to actively hunt people. They are known to eat insects and lizards. Dholes eat fruit and vegetable matter more readily than other canids. In captivity, they eat various kinds of grasses, herbs and leaves, seemingly for pleasure rather than just when ill. In summertime in the Tian Shan Mountains, dholes eat large quantities of mountain rhubarb. Although opportunistic, dholes have a seeming aversion to hunting cattle and their calves. Livestock predation by dholes has been a problem in Bhutan since the late 1990s, as domestic animals are often left outside to graze in the forest, sometimes for weeks at a time. Livestock stall-fed at night and grazed near homes are never attacked. Oxen are killed more often than cows, probably because they are given less protection.
Enemies and competitors
 In some areas, dholes are wiktionary:sympatric, sympatric to
In some areas, dholes are wiktionary:sympatric, sympatric to tiger
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is a large Felidae, cat and a member of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Asia. It has a powerful, muscular body with a large head and paws, a long tail and orange fur with black, mostly vertical stripes. It is ...
s and leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant cat species in the genus ''Panthera''. It has a pale yellowish to dark golden fur with dark spots grouped in rosettes. Its body is slender and muscular reaching a length of with a ...
s. Competition between these species is mostly avoided through differences in prey selection, although there is still substantial dietary overlap. Along with leopards, dholes typically target animals in the range (mean weights of for dhole and for leopard), while tigers selected for prey animals heavier than (but their mean prey weight was ). Also, other characteristics of the prey, such as sex, arboreality and aggressiveness, may play a role in prey selection. For example, dholes preferentially select male chital, whereas leopards kill both sexes more evenly (and tigers prefer larger prey altogether), dholes and tigers kill langurs rarely compared to leopards due to the leopards' greater arboreality, while leopards kill wild boar infrequently due to the inability of this relatively light predator to tackle aggressive prey of comparable weight.
Tigers are dangerous opponents for dholes, as they have sufficient strength to kill a dhole with a single paw strike. Dhole packs are smaller in areas with higher tiger densities due to tigers directly killing dholes and stealing kills they made. The kleptoparasitism causes dholes to prefer hunting smaller animals because they can eat more of a smaller carcass before a tiger arrives to steal it. Direct predation can lead to lower reproductive and recruitment rates, lower hunting success rates and less food for the pups when a helper is killed, and potentially pack destabilization if one member of the breeding pair is killed.
Dhole packs may steal leopard kills, while leopards may kill dholes if they encounter them singly or in pairs. There are numerous records of leopards being treed by dholes. Dholes were once thought to be a major factor in reducing Asiatic cheetah populations, though this is doubtful, as cheetahs live in open areas as opposed to forested areas favoured by dholes. Since leopards are smaller than tigers and are more likely to hunt dholes, dhole packs tend to react more aggressively toward them than they do towards tigers.
Dhole packs occasionally attack Asiatic black bears, snow leopards and sloth bears. When attacking bears, dholes will attempt to prevent them from seeking refuge in caves and lacerate their hindquarters.
Although usually antagonistic toward wolves, they may hunt and feed alongside one another.
The dhole is also sympatric with the Indian wolf (''Canis lupus pallipes'') in parts of its range. There is at least one record of a lone wolf associating with a pair of dholes in Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary, and two observations in Satpura Tiger Reserve. They infrequently associate in mixed groups with golden jackal
The golden jackal (''Canis aureus''), also called the common jackal, is a wolf-like canid that is native to Eurasia. The golden jackal's coat varies in color from a pale creamy yellow in summer to a dark tawny beige in winter. It is smaller a ...
s. Domestic dogs may kill dholes, though they will feed alongside them on occasion.
Diseases and parasites
Dholes are vulnerable to a number of different diseases, particularly in areas where they are wiktionary:Sympatric, sympatric with other canid species. Infectious pathogens such as ''Toxocara canis'' are present in their faeces. They may suffer from rabies, canine distemper, mange, trypanosomiasis, canine parvovirus and endoparasites such as cestodes and roundworms.Threats
Habitat loss is thought to amount to 60% of the dhole's historical range in India. The fragmentation and isolation of dhole populations has resulted in inbreeding and the Allee effect, which threaten its long-term viability. Some ethnic groups like the Kuruba and Mon Khmer-speaking tribes will appropriate dhole kills; some Indian villagers welcome the dhole because of this appropriation of dhole kills. Dholes were persecuted throughout India for bounties until they were given protection by the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972. Methods used for dhole hunting included poisoning, snaring, shooting and clubbing at den sites. Native Indian people killed dholes primarily to protect livestock, while British sporthunters during the British Raj did so under the conviction that dholes were responsible for drops in Game (hunting), game populations. Persecution of dholes still occurs with varying degrees of intensity according to the region. Bounties paid for dholes used to be 25 rupees, though this was reduced to 20 in 1926 after the number of presented dhole carcasses became too numerous to maintain the established reward. The Indochinese dhole population suffers heavily from nonselective hunting techniques such as snaring. The fur trade does not pose a significant threat to the dhole. The people of India do not eat dhole flesh and their fur is not considered overly valuable. Due to their rarity, dholes were never harvested for their skins in large numbers in the Soviet Union and were sometimes accepted as dog or wolf pelts (being labeled as "half wolf" for the latter). The winter fur was prized by the Chinese, who bought dhole pelts in Ussuriysk during the late 1860s for a few silver rubles. In the early 20th century, dhole pelts reached eight rubles in Manchuria. In Jetisu, Semirechye, fur coats made from dhole skin were considered the warmest, but were very costly.Conservation
In India, the dhole is protected under Schedule 2 of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972. The creation of reserves under Project Tiger provided some protection for dhole populations sympatric with tigers. In 2014, the Indian government sanctioned its first dhole conservation breeding centre at the Indira Gandhi Zoological Park (IGZP) in Visakhapatnam. The dhole has been protected in Russia since 1974, though it is vulnerable to poison left out for wolves. In China, the animal is listed as a category II protected species under the Chinese wildlife protection act of 1988. In Cambodia, the dhole is protected from all hunting, while conservation laws in Vietnam limit extraction and utilisation. In 2016, the Korean company Sooam Biotech was reported to be attempting to clone the dhole using dogs as surrogate mothers to help conserve the species.In culture and literature
Three dhole-like animals are featured on the Coping (architecture), coping stone of the Bharhut stupa dating from 100 BC. They are shown waiting by a tree, with a woman or spirit trapped up it, a scene reminiscent of dholes treeing tigers. The animal's fearsome reputation in India is reflected by the number of pejorative names it possesses in Hindi, which variously translate as "red devil", "devil dog", "jungle devil", or "hound of Kali". Leopold von Schrenck had trouble obtaining dhole specimens during his exploration ofAmurland
Outer Manchuria, sometimes called Russian Manchuria, refers to a region in Northeast Asia that is now part of the Russian Far East but historically formed part of Manchuria (until the mid-19th century). While Manchuria now more normatively refer ...
, as the local Gilyaks greatly feared the species. This fear and superstition was not, however, shared by neighbouring Tungusic peoples. It was speculated that this differing attitude towards the dhole was due to the Tungusic peoples' more nomadic, hunter-gatherer lifestyle.
Dholes appear in Rudyard Kipling's ''Red Dog (Kipling short story), Red Dog'', where they are portrayed as aggressive and bloodthirsty animals which descend from the Deccan Plateau into the Seoni, Madhya Pradesh, Seeonee Hills inhabited by Mowgli and his adopted wolf pack to cause carnage among the jungle's denizens. They are described as living in packs numbering hundreds of individuals, and that even Shere Khan and Hathi make way for them when they descend into the jungle. The dholes are despised by the wolves because of their destructiveness, their habit of not living in dens and the hair between their toes. With Mowgli and Kaa's help, the Seeonee wolf pack manages to wipe out the dholes by leading them through bee hives and torrential waters before finishing off the rest in battle.
Japanese author Uchida Roan wrote (; A dog's tale) in 1901 as a Japanese nationalism, nationalistic critique of the declining popularity of indigenous dog breeds, which he asserted were descended from the dhole.
A fictional version of the dhole, imbued with supernatural abilities, appears in a sixth-season episode of TV series ''The X-Files'', titled "Alpha (The X-Files), Alpha".
In China, the dhole were widely known throughout history and mythology. One notable legendary creature is the Nine sons of the dragon, Yazi (), which was believed to be a creature that was part-dhole, part-dragon. In modern times, however, the Chinese word for dhole () is often confused with 'jackal' or 'wolf', resulting in many confusions and mistranslations of dholes as jackals or wolves.
Dholes also appear as enemies in the video game ''Far Cry 4'', alongside other predators such as the Bengal tiger, honey badger, snow leopard, clouded leopard, Tibetan wolf and Asian black bear. They can be found hunting the player and other non-player character, NPCs across the map, but are easily killed, being one of the weakest enemies in the game. They once again appear in the video game ''Far Cry Primal'', where they play similar roles as their counterparts in the previous game, but can now also be tamed and used in combat by Takkar, the main protagonist of the game.
Tameability
Brian Houghton Hodgson kept captured dholes in captivity, and found, with the exception of one animal, they remained shy and vicious even after 10 months. Adult dholes are nearly impossible to tame, though pups are docile and can even be allowed to play with domestic dog pups until they reach early adulthood. A dhole may have been presented as a gift to the Akkadian king Ibbi-Sin as tribute referred to in the inscription as the "red dog of Meluhha" or Indus Valley Civilisation ofPakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
suggesting a once greater range of the dhole.
See also
* ''Wild Dog Diaries''Notes
References
Bibliography
* *External links
Dhole Home Page
*ARKive ŌĆ
images and movies of the dhole
''The Guardian'' (25 June 2015)
Photos of dhole in Bandipur
{{Authority control Dhole, Canina (subtribe) Taxa named by Peter Simon Pallas Mammals described in 1811 Carnivorans of Asia Mammals of South Asia Mammals of Southeast Asia Endangered fauna of Asia Pleistocene mammals of Asia Extant Middle Pleistocene first appearances Species that are or were threatened by habitat fragmentation Endangered Fauna of China