Converged storage on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
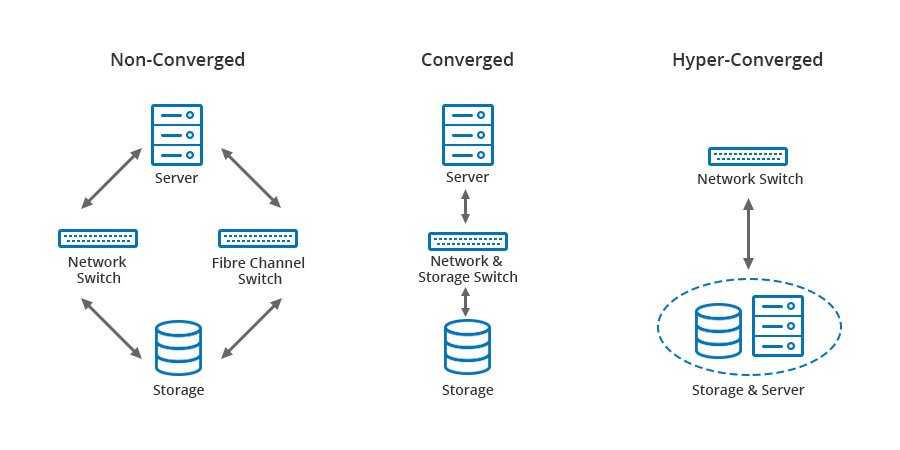 Converged storage is a storage architecture that combines storage and computing resources into a single entity. This can result in the development of platforms for server centric, storage centric or hybrid workloads where applications and data come together to improve application performance and delivery. The combination of storage and compute differs to the traditional IT model in which computation and storage take place in separate or siloed computer equipment. The traditional model requires discrete provisioning changes, such as upgrades and planned migrations, in the face of server load changes, which are increasingly dynamic with
Converged storage is a storage architecture that combines storage and computing resources into a single entity. This can result in the development of platforms for server centric, storage centric or hybrid workloads where applications and data come together to improve application performance and delivery. The combination of storage and compute differs to the traditional IT model in which computation and storage take place in separate or siloed computer equipment. The traditional model requires discrete provisioning changes, such as upgrades and planned migrations, in the face of server load changes, which are increasingly dynamic with
/ref>
 Converged storage is a storage architecture that combines storage and computing resources into a single entity. This can result in the development of platforms for server centric, storage centric or hybrid workloads where applications and data come together to improve application performance and delivery. The combination of storage and compute differs to the traditional IT model in which computation and storage take place in separate or siloed computer equipment. The traditional model requires discrete provisioning changes, such as upgrades and planned migrations, in the face of server load changes, which are increasingly dynamic with
Converged storage is a storage architecture that combines storage and computing resources into a single entity. This can result in the development of platforms for server centric, storage centric or hybrid workloads where applications and data come together to improve application performance and delivery. The combination of storage and compute differs to the traditional IT model in which computation and storage take place in separate or siloed computer equipment. The traditional model requires discrete provisioning changes, such as upgrades and planned migrations, in the face of server load changes, which are increasingly dynamic with virtualization
In computing, virtualization (abbreviated v12n) is a series of technologies that allows dividing of physical computing resources into a series of virtual machines, operating systems, processes or containers.
Virtualization began in the 1960s wit ...
, where converged storage increases the supply of resources along with new VM demands in parallel.
Design considerations
The goal of converged storage is to bring together server and storage and/or application and data to deliver services that are better optimized for target workloads. This can mean server and storage converged within a common hardware platform. For example, ablade server
A blade server is a stripped-down server computer with a modular design optimized to minimize the use of physical space and energy. Blade servers have many components removed to save space, minimize power consumption and other considerations, wh ...
enclosure, applications and storage can be brought together within a server by virtualization
In computing, virtualization (abbreviated v12n) is a series of technologies that allows dividing of physical computing resources into a series of virtual machines, operating systems, processes or containers.
Virtualization began in the 1960s wit ...
. Server and storage can be managed as a resource pool, for example in infrastructure- as-a-service (IaaS).
Common hardware platform
Industry standard servers, such as those using Intel processors (x86
x86 (also known as 80x86 or the 8086 family) is a family of complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set architectures initially developed by Intel, based on the 8086 microprocessor and its 8-bit-external-bus variant, the 8088. Th ...
), form the basis of converged storage. As these servers follow Moore’s Law and increase power and performance they have the capabilities to run storage workloads, in addition to being compute servers. Data centers can further consolidate and minimize the use of physical space and energy by using industry-standard –based blade server
A blade server is a stripped-down server computer with a modular design optimized to minimize the use of physical space and energy. Blade servers have many components removed to save space, minimize power consumption and other considerations, wh ...
for both server and storage.
Common software
In server virtualization, multiple "virtual" servers operate on a single platform usinghypervisor
A hypervisor, also known as a virtual machine monitor (VMM) or virtualizer, is a type of computer software, firmware or hardware that creates and runs virtual machines. A computer on which a hypervisor runs one or more virtual machines is called ...
technology. These virtual servers could be running traditional server tasks, such as applications programming. By using storage controller software, these servers could also be made into data storage systems. This latter architecture is known as virtual machine
In computing, a virtual machine (VM) is the virtualization or emulator, emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide the functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve ...
-based storage. The storage software is often called a VSA−virtual SAN appliance or virtual storage appliance. VSA products from companies such as HP, Nutanix and VMware allow users to build storage-area networks using their existing servers.
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
The goal ofIaaS
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is a cloud computing service model where a cloud services vendor provides computing resources such as storage, network, servers, and virtualization (which emulates computer hardware). This service frees users fro ...
is to provide a pool of resources that can be quickly deployed to deliver new services. This requires a service designer to lay out the required characteristics for a new service or application and an orchestration (computing)
In system administration, orchestration is the automated configuration, coordination, deployment, development, and management of computer systems and software.
Many tools exist to automate server configuration and management.
Usage
Orchestr ...
engine to configure the underlying infrastructure to deliver the new service.
Characteristics
Scale-out architecture
Scale-out architecture is a component of converged storage. Scale-out storage is the combination of modular computers and standardized storage components to create federated storage pools. The result is an increase of computer power, bandwidth and storage capacity that can exceed that of a single traditional storage array or high performance computer. Storage vendors such asNetApp
NetApp, Inc. is an American data infrastructure company that provides unified data storage, integrated data services, and cloud operations (CloudOps) solutions to enterprise customers. The company is based in San Jose, California. It has ranked ...
, Dell
Dell Inc. is an American technology company that develops, sells, repairs, and supports personal computers (PCs), Server (computing), servers, data storage devices, network switches, software, computer peripherals including printers and webcam ...
, Hewlett-Packard
The Hewlett-Packard Company, commonly shortened to Hewlett-Packard ( ) or HP, was an American multinational information technology company. It was founded by Bill Hewlett and David Packard in 1939 in a one-car garage in Palo Alto, California ...
and EMC provide scale-out storage to address both the growth of unstructured data
Unstructured data (or unstructured information) is information that either does not have a pre-defined data model or is not organized in a pre-defined manner. Unstructured information is typically plain text, text-heavy, but may contain data such ...
and the need to simplify data center operations. At the file system level, parallel file systems like BeeGFS are available to provide a single namespace with automatic data distribution for shared network access across the internal storage devices of multiple servers.
Scale-out storage differs from scale-up architectures in traditional storage, which primarily scales by adding many individual disk drives to a single non-clustered storage controller. In a scale-out architecture, management software is used to manage the multiple storage devices, to act like a single system. Storage analyst company, Enterprise Strategy Group, writes that scale-out storage can help to provide timely IT provisioning, improve system availability and provide better resource utilization.
Federation
Storage federation (also known as federated storage) uses distributed volume management to shift workloads from busy arrays to those with available capacity. This is done using native peer-to-peer communication. Multiple autonomous storage systems are combined and managed as a single storage pool. This helps to improve storage utilization, balance workloads and ease storage migration.Multitenant architecture
Converged storage supports the multitenant (multitenancy
Software multitenancy is a software architecture in which a single instance of software runs on a server and serves multiple tenants. Systems designed in such manner are "shared" (rather than
"dedicated" or "isolated"). A tenant is a group of us ...
) architecture of cloud computing
Cloud computing is "a paradigm for enabling network access to a scalable and elastic pool of shareable physical or virtual resources with self-service provisioning and administration on-demand," according to International Organization for ...
, in which multiple machines or users access the virtual and physical resources at the same time. In addition to storage, the other resources accessed in this architecture are processors and networks. A converged storage does this by moving application workloads between disk systems.
Comparisons to traditional storage architectures
Monolithic storage architectures
Monolithic storage architectures share RAM across multiple IO controllers. They have been characterized as large storage arrays that require a large upfront investment and resources. Hitachi Vantara, is quoted as saying such storage requires enterprises to spend $500,000 on customizing their data centers to support the power requirements of monolithic equipment. Monolithic arrays provide failover benefits. The shared cache architecture of monolithic arrays ensures that if one cache module fails, another cache is used to process the user's request. However once you have more than a single system this architecture is complex and requires investment to manage and control the interactions between the different components. Monolithic architectures support both block and file-based architectures, either independently or in a unified storage system that brings together both block and file.Direct-attached storage
Direct-attached storage
Direct-attached storage (DAS) is digital storage directly attached to the computer accessing it, as opposed to storage accessed over a computer network (i.e. network-attached storage). DAS consists of one or more storage units such as hard driv ...
(DAS) provides scaling of storage directly attached to the server. The storage is dedicated to a single server and is not sharable among multiple servers. Data stored on a Storage area network
A storage area network (SAN) or storage network is a computer network which provides access to consolidated, block device, block-level data storage. SANs are primarily used to access Computer data storage, data storage devices, such as disk ...
(SAN) and network-attached storage
Network-attached storage (NAS) is a file-level computer data storage server connected to a computer network providing data access to a Heterogeneous computing, heterogeneous group of clients. In this context, the term "NAS" can refer to both th ...
(NAS) architectures can be shared among several server applications.Mellor, Chris. "Direct-attached storage vs SAN: Clustered DAS model gaining favor in virtualised, solid-state world?," SearchStorage.co.u/ref>
References
{{reflist, colwidth=30em Computer data storage