conceptions of God on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Conceptions of God in classical theist, monotheist, pantheist, and panentheist traditions – or of the supreme deity in
 Within
Within
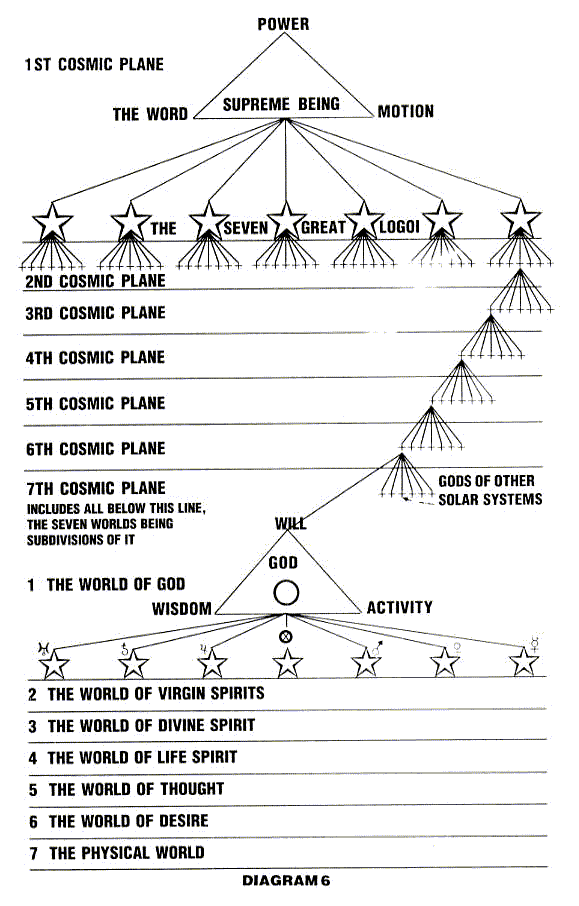 The esoteric Christian teachings of the Rosicrucian Fellowship, promulgated to the western world in the early 20th century as '' Western Wisdom Teachings'', present the conception of The Absolute -- unmanifested and unlimited "Boundless Being" or "Root of Existence", beyond the whole universe and beyond comprehension -- from whom proceeds the Supreme Being at the dawn of manifestation: The One, the " Great Architect of the Universe". From the threefold Supreme Being proceed the "seven Great Logoi" who contain within themselves all the great hierarchies that differentiate more and more as they diffuse through the six lower Cosmic Planes.
The esoteric Christian teachings of the Rosicrucian Fellowship, promulgated to the western world in the early 20th century as '' Western Wisdom Teachings'', present the conception of The Absolute -- unmanifested and unlimited "Boundless Being" or "Root of Existence", beyond the whole universe and beyond comprehension -- from whom proceeds the Supreme Being at the dawn of manifestation: The One, the " Great Architect of the Universe". From the threefold Supreme Being proceed the "seven Great Logoi" who contain within themselves all the great hierarchies that differentiate more and more as they diffuse through the six lower Cosmic Planes.
 In the Highest World of the seventh (lowest) Cosmic Plane dwells the God of the solar systems in the universe. These great beings are also threefold in manifestation, like the Supreme Being; their three aspects are ''Will'', ''Wisdom'' and ''Activity''.
According to these teachings, in the beginning of a ''Day of Manifestation'' a certain collective Great Being, God, limits himself to a certain portion of space, in which he elects to create the
In the Highest World of the seventh (lowest) Cosmic Plane dwells the God of the solar systems in the universe. These great beings are also threefold in manifestation, like the Supreme Being; their three aspects are ''Will'', ''Wisdom'' and ''Activity''.
According to these teachings, in the beginning of a ''Day of Manifestation'' a certain collective Great Being, God, limits himself to a certain portion of space, in which he elects to create the
Concepts of God.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Conceptions Of God
henotheistic
Henotheism is the worship of a single, supreme god that does not deny the existence or possible existence of other deities that may be worshipped. Friedrich Schelling (1775–1854) coined the word, and Friedrich Welcker (1784–1868) ...
religions – can extend to various levels of abstraction
Abstraction is a process where general rules and concepts are derived from the use and classifying of specific examples, literal (reality, real or Abstract and concrete, concrete) signifiers, first principles, or other methods.
"An abstraction" ...
:
* as a powerful, personal, supernatural
Supernatural phenomena or entities are those beyond the Scientific law, laws of nature. The term is derived from Medieval Latin , from Latin 'above, beyond, outside of' + 'nature'. Although the corollary term "nature" has had multiple meanin ...
being, or as the deification of an esoteric
Western esotericism, also known as the Western mystery tradition, is a wide range of loosely related ideas and movements that developed within Western society. These ideas and currents are united since they are largely distinct both from orthod ...
, mystical
Mysticism is popularly known as becoming one with God or the Absolute, but may refer to any kind of ecstasy or altered state of consciousness which is given a religious or spiritual meaning. It may also refer to the attainment of insight ...
or philosophical
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
entity or category;
* as the " Ultimate", the ''summum bonum
''Summum bonum'' is a Latin expression meaning the highest or ultimate good, which was introduced by the Roman philosopher Cicero to denote the fundamental principle on which some system of ethics is based—that is, the aim of actions, which, ...
'', the "Absolute Infinite", the " Transcendent", or Existence
Existence is the state of having being or reality in contrast to nonexistence and nonbeing. Existence is often contrasted with essence: the essence of an entity is its essential features or qualities, which can be understood even if one does ...
or Being
Existence is the state of having being or reality in contrast to nonexistence and nonbeing. Existence is often contrasted with essence: the essence of an entity is its essential features or qualities, which can be understood even if one do ...
itself;
* as the ground of being, the monistic substrate, that which we cannot understand; and so on.
The first recordings that survive of monotheistic conceptions of God
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
, borne out of henotheism and (mostly in Eastern religions) monism
Monism attributes oneness or singleness () to a concept, such as to existence. Various kinds of monism can be distinguished:
* Priority monism states that all existing things go back to a source that is distinct from them; e.g., in Neoplatonis ...
, are from the Hellenistic period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
. Of the many objects and entities that religions and other belief systems across the ages have labeled as divine, the one criterion they share is their acknowledgment as divine by a group or groups of human beings.
Hellenistic philosophy and religion
Aristotelianism
In his ''Metaphysics
Metaphysics is the branch of philosophy that examines the basic structure of reality. It is traditionally seen as the study of mind-independent features of the world, but some theorists view it as an inquiry into the conceptual framework of ...
'', Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
discusses the meaning of "being as being". Aristotle holds that "being" primarily refers to the Unmoved Mover
The unmoved mover () or prime mover () is a concept advanced by Aristotle as a primary cause (or first uncaused cause) or " mover" of all the motion in the universe. As is implicit in the name, the moves other things, but is not itself moved by ...
s, and assigned one of these to each movement in the heavens. Each Unmoved mover continuously contemplates its own contemplation, and everything that fits the second meaning of "being" by having its source of motion in itself, i.e., moves because the knowledge of its Mover causes it to emulate this Mover (or should).
Aristotle's definition of God attributes perfection to this being, and, as a perfect being, it can only contemplate upon perfection and not on imperfection; otherwise perfection would not be one of his attributes. God, according to Aristotle, is in a state of "stasis" untouched by change and imperfection. The "unmoved mover" is very unlike the conception of God that one sees in most religions. It has been likened to a person who is playing domino
Dominoes is a family of tile-based games played with gaming pieces. Each domino is a rectangular tile, usually with a line dividing its face into two square ''ends''. Each end is marked with a number of spots (also called '' pips'' or ''dots'' ...
s and pushes one of them over, so that every other domino in the set is pushed over as well, without the being having to do anything about it. Although, in the 18th century, the French educator Allan Kardec brought a very similar conception of God during his work of codifying Spiritism
Spiritism may refer to:
Religion
* Espiritismo, a Latin American and Caribbean belief that evolved and less evolved spirits can affect health, luck and other aspects of human life
* Kardecist spiritism, a new religious movement established in ...
, this differs from the interpretation of God in most religions, where he is seen to be personally involved in his creation.
Hermeticism
In the ancient Greek philosophical ''Hermetica
The ''Hermetica'' are texts attributed to the legendary Hellenistic figure Hermes Trismegistus, a syncretic combination of the Greek god Hermes and the Egyptian god Thoth. These texts may vary widely in content and purpose, but by modern con ...
'', the ultimate reality is called by many names, such as God, Lord, Father, Mind (''Nous
''Nous'' (, ), from , is a concept from classical philosophy, sometimes equated to intellect or intelligence, for the cognitive skill, faculty of the human mind necessary for understanding what is truth, true or reality, real.
Alternative Eng ...
''), the Creator, the All, the One, etc. However, peculiar to the Hermetic view of the divinity is that it is both the all ( Greek: ''to pan'') and the creator of the all: all created things pre-exist in God, and God is the nature of the cosmos (being both the substance from which it proceeds and the governing principle which orders it), yet the things themselves and the cosmos were all created by God. Thus, God creates itself, and is both transcendent (as the creator of the cosmos) and immanent (as the created cosmos). These ideas are closely related to the cosmo-theological views of the Stoics.
Abrahamic religions
The term "Abrahamic God", in this sense, refers to the conception of God that remains a foundational point of belief and doctrine in all three of the largest and best-known Abrahamic religious traditions:Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
, Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
, and Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
. (While similar views also predominate among those Abrahamic faiths to which there are far fewer adherents, such as Samaritanism
Samaritanism (; ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic ethnic religion. It comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Samaritan people, who originate from the Hebrews and Israelites and began to emerge as a relative ...
and Babism, the quintessentially-Abrahamic conception of deity is most well-attested in the aforementioned three overarching faiths.)
In this view, God is conceived of as eternal, omnipotent
Omnipotence is the property of possessing maximal power. Monotheistic religions generally attribute omnipotence only to the deity of their faith. In the monotheistic religious philosophy of Abrahamic religions, omnipotence is often listed as ...
, omniscient and as the creator of the universe. God is further held to have the properties of holiness, justice, jealousy, omnibenevolence
Omnibenevolence is the property of possessing maximal goodness. Some philosophers, such as Epicurus, have argued that it is impossible, or at least improbable, for a deity to exhibit such a property alongside omniscience and omnipotence, as a r ...
and omnipresence
Omnipresence or ubiquity is the property of being present anywhere and everywhere. The term omnipresence is most often used in a religious context as an attribute of a deity or supreme being, while the term ubiquity is generally used to describ ...
. Proponents of Abrahamic faiths believe that God is also transcendent, meaning that he is outside space and outside time and therefore not subject to anything within his creation, but at the same time a personal God, involved, listening to prayer
File:Prayers-collage.png, 300px, alt=Collage of various religionists praying – Clickable Image, Collage of various religionists praying ''(Clickable image – use cursor to identify.)''
rect 0 0 1000 1000 Shinto festivalgoer praying in front ...
and reacting to the actions of his creatures.
Baháʼí Faith
TheBaháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the Baháʼí Faith and the unity of religion, essential worth of all religions and Baháʼí Faith and the unity of humanity, the unity of all people. Established by ...
believes in a single, imperishable God
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
, the creator of all things, including all the creatures and forces in the universe. In Baháʼí belief, God is beyond space and time but is also described as "a personal God, unknowable, inaccessible, the source of all Revelation, eternal, omniscient, omnipresent and almighty." Though inaccessible directly, God is nevertheless seen as conscious of creation, possessing a mind, will and purpose. Baháʼís believe that God expresses this will at all times and in many ways, including Manifestations, a series of divine "messengers" or "educators". In expressing God's intent, these manifestations are seen to establish religion in the world. Baháʼí teachings
The teachings of the Baháʼí Faith are derived from the writings of Baháʼu'lláh, its founder. A corpus of Baháʼí literature include books and writings of the Báb and Baháʼu'lláh, along with the public talks and writings of ‘Abdu� ...
state that God is too great for humans to fully comprehend, nor to create a complete and accurate image. Bahá'u'lláh often refers to God by titles, such as the "All-Powerful" or the "All-Loving".
Gnosticism
In manyGnostic
Gnosticism (from Ancient Greek: , romanized: ''gnōstikós'', Koine Greek: �nostiˈkos 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems that coalesced in the late 1st century AD among early Christian sects. These diverse g ...
systems, God is known as the '' Monad'', or the One.
Christianity
As sustainer
"Creator, Sustainer, Redeemer" is reportedly a "common phrase" in Protestantism in the United States, specifically inBaptist
Baptists are a Christian denomination, denomination within Protestant Christianity distinguished by baptizing only professing Christian believers (believer's baptism) and doing so by complete Immersion baptism, immersion. Baptist churches ge ...
liturgy.
Trinitarianism
 Within
Within Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
, the doctrine
Doctrine (from , meaning 'teaching, instruction') is a codification (law), codification of beliefs or a body of teacher, teachings or instructions, taught principles or positions, as the essence of teachings in a given branch of knowledge or in a ...
of the Trinity
The Trinity (, from 'threefold') is the Christian doctrine concerning the nature of God, which defines one God existing in three, , consubstantial divine persons: God the Father, God the Son (Jesus Christ) and God the Holy Spirit, thr ...
states that God
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
is a single being that exists, simultaneously and eternally, as a perichoresis of three hypostases (i.e. persons; ''personae'', ''prosopa''): the Father (the Source, the Eternal Majesty); the Son (the eternal ''Logos
''Logos'' (, ; ) is a term used in Western philosophy, psychology and rhetoric, as well as religion (notably Logos (Christianity), Christianity); among its connotations is that of a rationality, rational form of discourse that relies on inducti ...
'' ("Word"), manifest in human form as Jesus
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
and thereafter as Christ
Jesus ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Christianity, central figure of Christianity, the M ...
); and the Holy Spirit
The Holy Spirit, otherwise known as the Holy Ghost, is a concept within the Abrahamic religions. In Judaism, the Holy Spirit is understood as the divine quality or force of God manifesting in the world, particularly in acts of prophecy, creati ...
(the Paraclete or advocate). Since the 4th Century AD, in both Eastern and Western Christianity, this doctrine has been stated as "One God in Three Persons", all three of whom, as distinct and co-eternal "persons" or " hypostases", share a single divine essence
Essence () has various meanings and uses for different thinkers and in different contexts. It is used in philosophy and theology as a designation for the property (philosophy), property or set of properties or attributes that make an entity the ...
, being, or nature.
Following the First Council of Constantinople
The First Council of Constantinople (; ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in Constantinople (now Istanbul, Turkey) in AD 381 by the Roman Emperor Theodosius I. This second ecumenical council, an effort to attain consensus in the ...
, the Son is described as eternally begotten by the Father ("begotten of his Father before all worlds"). This generation does not imply a beginning for the Son or an inferior relationship with the Father. The Son is the perfect image of his Father, and is consubstantial with him. The Son returns that love, and that union between the two is the third person of the Trinity, the Holy Spirit. The Holy Spirit is consubstantial and co-equal with the Father and the Son. Thus, God contemplates and loves himself, enjoying infinite and perfect beatitude within himself. This relationship between the other two persons is called procession
A procession is an organized body of people walking in a formal or ceremonial manner.
History
Processions have in all peoples and at all times been a natural form of public celebration, as forming an orderly and impressive ceremony. Religious ...
. Although the theology of the Trinity is accepted in most Christian churches, there are theological differences, notably between Catholic and Orthodox thought on the procession of the Holy Spirit (see filioque
( ; ), a Latin term meaning "and from the Son", was added to the original Nicene Creed, and has been the subject of great controversy between Eastern and Western Christianity. The term refers to the Son, Jesus Christ, with the Father, as th ...
). Some Christian communions do not accept the Trinitarian doctrine, at least not in its traditional form. Notable groups include the Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a Christian denomination that is an outgrowth of the Bible Student movement founded by Charles Taze Russell in the nineteenth century. The denomination is nontrinitarian, millenarian, and restorationist. Russell co-fou ...
, Mormons
Mormons are a Religious denomination, religious and ethnocultural group, cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's d ...
, Christadelphians
The Christadelphians () are a Restorationism, restorationist and Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Biblical unitarianism, (Biblical Unitarian) Christian denomination. The name means 'brothers and sisters in Christ',"The Christadelphians, or breth ...
, Unitarians, Arians, and Adoptionists.
Unitarianism
Within Christianity,Unitarianism
Unitarianism () is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian sect of Christianity. Unitarian Christians affirm the wikt:unitary, unitary God in Christianity, nature of God as the singular and unique Creator deity, creator of the universe, believe that ...
is the view that God consists of only one person, the Father
A father is the male parent of a child. Besides the paternal bonds of a father to his children, the father may have a parental, legal, and social relationship with the child that carries with it certain rights and obligations. A biological fat ...
, instead of three persons as Trinitarianism states. Unitarians believe that mainstream Christianity has been corrupted over history, and that it is not strictly monotheistic
Monotheism is the belief that one God is the only, or at least the dominant deity.F. L. Cross, Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. A ...
. There are different Unitarian views on Jesus, ranging from seeing him purely as a man who was chosen by God, to seeing him as a divine being, as the Son of God who had pre-existence. Thus, Unitarianism is typically divided into two principal groups:
* Arianism
Arianism (, ) is a Christology, Christological doctrine which rejects the traditional notion of the Trinity and considers Jesus to be a creation of God, and therefore distinct from God. It is named after its major proponent, Arius (). It is co ...
, which believes in the pre-existence of the Logos
''Logos'' (, ; ) is a term used in Western philosophy, psychology and rhetoric, as well as religion (notably Logos (Christianity), Christianity); among its connotations is that of a rationality, rational form of discourse that relies on inducti ...
, and holds that the Son was God's first creation.
* Socinianism, the view that Jesus was a mere man, and had no existence before his birth.
Even though the term "unitarian" did not first appear until the 17th century in reference to the Polish Brethren, the basic tenets of Unitarianism go back to the time of Arius
Arius (; ; 250 or 256 – 336) was a Cyrenaica, Cyrenaic presbyter and asceticism, ascetic. He has been regarded as the founder of Arianism, which holds that Jesus Christ was not Eternity, coeternal with God the Father, but was rather created b ...
in the 4th century, an Alexandrian priest that taught the doctrine that only the Father was God, and that the Son had been created by the Father. Arians rejected the term " homoousios''"'' (consubstantial) as a term describing the Father and Son, viewing such term as compromising the uniqueness and primacy of God, and accused it of dividing the indivisible unit of the divine essence. Unitarians trace their history back to the Apostolic Age, arguing, as do Trinitarians and Binitarians, that their Christology
In Christianity, Christology is a branch of Christian theology, theology that concerns Jesus. Different denominations have different opinions on questions such as whether Jesus was human, divine, or both, and as a messiah what his role would b ...
most closely reflects that of the early Christian community and Church Fathers
The Church Fathers, Early Church Fathers, Christian Fathers, or Fathers of the Church were ancient and influential Christian theologians and writers who established the intellectual and doctrinal foundations of Christianity. The historical peri ...
.
Binitarianism
Binitarianism is the view that there exist two equal co-ruling powers in heaven. Within Christianity, it is the belief that there were originally two beings in the Godheadthe Father and the Wordthat became the Son (Jesus the Christ). Binitarians normally believe that God is a family, currently consisting of the Father and the Son. Some binitarians believe that others will ultimately be born into that divine family. Hence, binitarians are nontrinitarian, but they are also not unitarian. Binitarians, like most unitarians and trinitarians, claim their views were held by the original New Testament Church. Unlike most unitarians and trinitarians who tend to identify themselves by those terms, binitarians normally do not refer to their belief in the duality of the Godhead, with the Son subordinate to the Father; they simply teach the Godhead in a manner that has been termed as binitarianism. The word "binitarian" is typically used by scholars and theologians as a contrast to a trinitarian theology: a theology of "two" in God rather than a theology of "three", and although some critics prefer to use the term ditheist or dualist instead of binitarian, those terms suggests that God is not one, yet binitarians believe that God is one family. It is accurate to offer the judgment that most commonly when someone speaks of a Christian "binitarian" theology the "two" in God are the Father and the Son... A substantial amount of recent scholarship has been devoted to exploring the implications of the fact that Jesus was ''worshipped'' by those first Jewish Christians, since in Judaism "worship" was limited to the worship of God" (Barnes M. Early Christian Binitarianism: the Father and the Holy Spirit. Early Christian Binitarianism - as read at NAPS 2001). Much of this recent scholarship has been the result of the translations of the ''Nag Hammadi
Nag Hammadi ( ; ) is a city and Markaz (administrative division), markaz in Upper Egypt.
It is located on the west bank of the Nile in the Qena Governorate, about north-west of Luxor. The city had a population of close to 61,737 .
History
...
'' and other ancient manuscripts that were not available when older scholarly texts (such as Wilhelm Bousset's ''Kyrios Christos'', 1913) were written.
Mormonism
In the Mormonism represented by most of Mormon communities, includingthe Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Restorationism, restorationist Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, denomination and the ...
, "God" means Elohim
''Elohim'' ( ) is a Hebrew word meaning "gods" or "godhood". Although the word is plural in form, in the Hebrew Bible it most often takes singular verbal or pronominal agreement and refers to a single deity, particularly but not always the Go ...
(the Father), whereas "Godhead" means a council of three distinct entities; Elohim, Jehovah
Jehovah () is a Romanization, Latinization of the Hebrew language, Hebrew , one Tiberian vocalization, vocalization of the Tetragrammaton (YHWH), the proper name of the God in Judaism, God of Israel in the Hebrew BibleOld Testament. The Tetr ...
(the Son, or Jesus), and the Holy Spirit
The Holy Spirit, otherwise known as the Holy Ghost, is a concept within the Abrahamic religions. In Judaism, the Holy Spirit is understood as the divine quality or force of God manifesting in the world, particularly in acts of prophecy, creati ...
. The Father and Son have perfected, material bodies, while the Holy Spirit is a spirit and does not have a body. This conception differs from the traditional Christian Trinity
The Trinity (, from 'threefold') is the Christian doctrine concerning the nature of God, which defines one God existing in three, , consubstantial divine persons: God the Father, God the Son (Jesus Christ) and God the Holy Spirit, thr ...
; in Mormonism, the three persons are considered to be physically separate beings, or personages, but indistinguishable in will and purpose. As such, the term " Godhead" differs from how it is used in traditional Christianity. This description of God represents the orthodoxy
Orthodoxy () is adherence to a purported "correct" or otherwise mainstream- or classically-accepted creed, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical co ...
of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Restorationism, restorationist Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, denomination and the ...
(LDS Church), established early in the 19th century. However, the Mormon concept of God has expanded since the faith's founding in the late 1820s.
Islam
''Allāh'', withoutplural
In many languages, a plural (sometimes list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated as pl., pl, , or ), is one of the values of the grammatical number, grammatical category of number. The plural of a noun typically denotes a quantity greater than ...
or gender
Gender is the range of social, psychological, cultural, and behavioral aspects of being a man (or boy), woman (or girl), or third gender. Although gender often corresponds to sex, a transgender person may identify with a gender other tha ...
, is the divine name of God mentioned in the Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
, while " ʾilāh" is the term used for a deity or a god in general.
Islam's most fundamental concept is a strict monotheism called '' tawḥīd''. God is described in the surah
A ''surah'' (; ; ) is an Arabic word meaning 'chapter' in the Quran. There are 114 ''suwar'' in the Quran, each divided into ayah, verses (). The ''suwar'' are of unequal length; the shortest ''surah'' (al-Kawthar) has only three verses, while ...
Al-Ikhlas as: "Say: He is God, the One; God, the Eternal, the Absolute; He begot no one, nor is He begotten; Nor is there to Him equivalent anyone." Muslims deny the Christian doctrine of the Trinity
The Trinity (, from 'threefold') is the Christian doctrine concerning the nature of God, which defines one God existing in three, , consubstantial divine persons: God the Father, God the Son (Jesus Christ) and God the Holy Spirit, thr ...
and divinity of Jesus
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
, comparing it to polytheism. In Islam, God is beyond all comprehension or equal and does not resemble any of his creations in any way. Thus, Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
s are not iconodules and are not expected to visualize God. The message of God is carried by angels to 124,000 messengers starting with Adam and concluding with Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
. God is described and referred in the Quran by certain names or attributes, the most common being '' Al-Rahman'', meaning "Most Compassionate" and ''Al-Rahim'', meaning "Most Merciful" (see Names of God in Islam
Names of God in Islam () are 99 names that each contain Attributes of God in Islam, which are implied by the respective names.
These names usually denote his praise, gratitude, commendation, glorification, magnification, perfect attributes, ...
). ''Al Qayyum'', sometimes rendered "the Sustainer", is one of the 99 Names of God in Islam.
Muslims believe that creation of everything in the universe is brought into being by God's sheer command “‘ Be, and it is.” and that the purpose of existence is to please God, both by worship
Worship is an act of religious devotion usually directed towards a deity or God. For many, worship is not about an emotion, it is more about a recognition of a God. An act of worship may be performed individually, in an informal or formal group, ...
and by good deeds. There are no intermediaries, such as clergy
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
, to contact God: “He is nearer to his creation than the jugular vein”
Judaism
InJudaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
, God
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
has been conceived in a variety of ways. Traditionally, Judaism holds that Yahweh
Yahweh was an Ancient Semitic religion, ancient Semitic deity of Weather god, weather and List of war deities, war in the History of the ancient Levant, ancient Levant, the national god of the kingdoms of Kingdom of Judah, Judah and Kingdom ...
, the God of Abraham
Abraham (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father who began the Covenant (biblical), covenanta ...
, Isaac
Isaac ( ; ; ; ; ; ) is one of the three patriarchs (Bible), patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, Islam, and the Baháʼí Faith. Isaac first appears in the Torah, in wh ...
, and Jacob
Jacob, later known as Israel, is a Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions. He first appears in the Torah, where he is described in the Book of Genesis as a son of Isaac and Rebecca. Accordingly, alongside his older fraternal twin brother E ...
and the national god of the Israelites
Israelites were a Hebrew language, Hebrew-speaking ethnoreligious group, consisting of tribes that lived in Canaan during the Iron Age.
Modern scholarship describes the Israelites as emerging from indigenous Canaanites, Canaanite populations ...
, delivered the Israelites from slavery in Egypt, and gave them the Law of Moses
The Law of Moses ( ), also called the Mosaic Law, is the law said to have been revealed to Moses by God. The term primarily refers to the Torah or the first five books of the Hebrew Bible.
Terminology
The Law of Moses or Torah of Moses (Heb ...
at biblical Mount Sinai
Mount Sinai (, ''Har Sīnay'') is the mountain at which the Ten Commandments were given to the Prophets in Judaism, Hebrew prophet Moses by God in Judaism, God, according to the Book of Exodus in the Hebrew Bible/Old Testament. In the Book of ...
as described in the Torah
The Torah ( , "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. The Torah is also known as the Pentateuch () ...
. According to the rationalist stream of Judaism articulated by Maimonides
Moses ben Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (, ) and also referred to by the Hebrew acronym Rambam (), was a Sephardic rabbi and Jewish philosophy, philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Torah schola ...
, which later came to dominate much of official traditional Jewish thought, God is understood as the absolute one, indivisible, and incomparable being
Existence is the state of having being or reality in contrast to nonexistence and nonbeing. Existence is often contrasted with essence: the essence of an entity is its essential features or qualities, which can be understood even if one do ...
who is the ultimate cause of all existence. Traditional interpretations of Judaism generally emphasize that God is personal yet also transcendent, while some modern interpretations of Judaism emphasize that God is a force or ideal.
Jewish monotheism is a continuation of earlier Hebrew henotheism, the exclusive worship of the God of Israel as prescribed in the Torah and practiced at the Temple of Jerusalem. Strict monotheism emerges in Hellenistic Judaism
Hellenistic Judaism was a form of Judaism in classical antiquity that combined Jewish religious tradition with elements of Hellenistic culture and religion. Until the early Muslim conquests of the eastern Mediterranean, the main centers of Hellen ...
and Rabbinical Judaism. Pronunciation of the proper name of the God of Israel came to be avoided in the Hellenistic era (Second Temple Judaism
Second Temple Judaism is the Judaism, Jewish religion as it developed during the Second Temple period, which began with the construction of the Second Temple around 516 BCE and ended with the Siege of Jerusalem (70 CE), destruction of Jerusalem in ...
) and instead Jews refer to God as '' HaShem'', meaning "the Name". In prayer and reading of scripture, the Tetragrammaton
The TetragrammatonPronounced ; ; also known as the Tetragram. is the four-letter Hebrew-language theonym (transliteration, transliterated as YHWH or YHVH), the name of God in the Hebrew Bible. The four Hebrew letters, written and read from ...
is substituted with Adonai
Judaism has different names given to God in Judaism, God, which are considered sacred: (), (''Adonai'' ), (''El (deity), El'' ), ( ), (''El Shaddai, Shaddai'' ), and ( ); some also include I Am that I Am.This is the formulation of Josep ...
("my Lord").
Some Kabbalistic thinkers have held the belief that all of existence is itself a part of God, and that we as humanity are unaware of our own inherent godliness and are grappling to come to terms with it. The standing view in Hasidism
Hasidism () or Hasidic Judaism is a religious movement within Judaism that arose in the 18th century as a Spirituality, spiritual revival movement in contemporary Western Ukraine before spreading rapidly throughout Eastern Europe. Today, most ...
currently, is that there is nothing in existence outside of God – all being is within God, and yet all of existence cannot contain him. Regarding this, Solomon
Solomon (), also called Jedidiah, was the fourth monarch of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), Kingdom of Israel and Judah, according to the Hebrew Bible. The successor of his father David, he is described as having been the penultimate ...
stated while dedicating the Temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a place of worship, a building used for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. By convention, the specially built places of worship of some religions are commonly called "temples" in Engli ...
, "But will God in truth dwell with mankind on the earth? Behold, the heaven and the heaven of heavens cannot contain You."
Modern Jewish thinkers have constructed a wide variety of other ideas about God. Hermann Cohen believed that God should be identified with the "archetype of morality," an idea reminiscent of Plato's idea of the Good. Mordecai Kaplan believed that God is the sum of all natural processes that allow man to become self-fulfilled, and Humanistic Judaism
Humanistic Judaism () is a Jewish movement that offers a nontheistic alternative to contemporary branches of Judaism. It defines Judaism as the cultural and historical experience of the Jewish people rather than a religion, and encourages Jews ...
fully rejects the notion of the existence of a God.
Mandaeism
InMandaeism
Mandaeism (Mandaic language, Classical Mandaic: ),https://qadaha.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/nhura-dictionary-mandaic-english-mandaic.pdf sometimes also known as Nasoraeanism or Sabianism, is a Gnosticism, Gnostic, Monotheism, ...
, '' Hayyi Rabbi'' (), or 'The Great Living God' is the Supreme God from which all things emanate. He is also known as 'The First Life', since during the creation of the material world, Yushamin emanated from Hayyi Rabbi as the "Second Life." According to Qais Al-Saadi, "the principles of the Mandaean doctrine: the belief of the only one great God, Hayyi Rabbi, to whom all absolute properties belong; He created all the worlds, formed the soul through his power, and placed it by means of angels into the human body. So He created Adam and Eve
Adam and Eve, according to the creation myth of the Abrahamic religions, were the first man and woman. They are central to the belief that humanity is in essence a single family, with everyone descended from a single pair of original ancestors. ...
, the first man and woman." Mandaeans recognize God to be the eternal, creator of all, the one and only in domination who has no partner.Hanish, Shak (2019). The Mandaeans In Iraq. In
Indian religions
Buddhism
The non-adherence to the notion of a supreme God or a prime mover is seen as a key distinction betweenBuddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
and other religious views. In Buddhism, the sole aim of the spiritual practice is the complete alleviation of distress (''dukkha'') in '' samsara'', called ''nirvana
Nirvana, in the Indian religions (Jainism, Hinduism, Buddhism, and Sikhism), is the concept of an individual's passions being extinguished as the ultimate state of salvation, release, or liberation from suffering ('' duḥkha'') and from the ...
''. The Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha (),*
*
*
was a śramaṇa, wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist lege ...
neither denies nor accepts a creator, denies endorsing any views on creation and states that questions on the origin of the world are worthless. Some teachers instruct students beginning Buddhist meditation
Buddhist meditation is the practice of meditation in Buddhism. The closest words for meditation in the classical languages of Buddhism are ''bhavana, bhāvanā'' ("mental development") and ''Dhyāna in Buddhism, jhāna/dhyāna'' (a state of me ...
that the notion of divinity is not incompatible with Buddhism, but dogmatic beliefs in a supreme personal creator are considered a hindrance to the attainment of ''nirvana'', the highest goal of Buddhist practice.
Despite this apparent non-theism
Theism is broadly defined as the belief in the existence of at least one deity. In common parlance, or when contrasted with '' deism'', the term often describes the philosophical conception of God that is found in classical theism—or the co ...
, Buddhists consider veneration of the Noble Ones very important although the two main schools of Buddhism differ mildly in their reverential attitudes. While Theravada Buddhists view the Buddha as a human being who attained ''nirvana'' or arahanthood through human efforts, Mahayana Buddhists consider him an embodiment of the cosmic '' dharmakaya'' (a notion of transcendent divinity), who was born for the benefit of others and not merely a human being. In addition, some Mahayana Buddhists worship their chief Bodhisattva
In Buddhism, a bodhisattva is a person who has attained, or is striving towards, '' bodhi'' ('awakening', 'enlightenment') or Buddhahood. Often, the term specifically refers to a person who forgoes or delays personal nirvana or ''bodhi'' in ...
, Avalokiteshvara and hope to embody him.
Buddhists accept the existence of beings known as '' devas'' in higher realms, but they, like humans, are said to be suffering in ''samsara'', and not necessarily wiser than us. In fact, the Buddha is often portrayed as a teacher of the gods, and superior to them. Despite this, there are believed to be enlightened ''deva''s on the path of Buddhahood.
In Buddhism, the idea of the metaphysical absolute is deconstructed in the same way as of the idea of an enduring "self", but it is not necessarily denied. Reality is considered as dynamic, interactive and non-substantial, which implies rejection of ''Brahman'' or of a divine substratum. A cosmic principle can be embodied in concepts such as the '' dharmakaya''. Though there is a primordial Buddha (or, in Vajrayana
''Vajrayāna'' (; 'vajra vehicle'), also known as Mantrayāna ('mantra vehicle'), Guhyamantrayāna ('secret mantra vehicle'), Tantrayāna ('tantra vehicle'), Tantric Buddhism, and Esoteric Buddhism, is a Mahāyāna Buddhism, Mahāyāna Buddhis ...
, the Adi-Buddha, a representation of immanent enlightenment in nature), its representation as a creator is a symbol of the presence of a universal cyclical creation and dissolution of the cosmos and not of an actual personal being. An intelligent, metaphysical underlying basis, however, is not ruled out by Buddhism, although Buddhists are generally very careful to distinguish this idea from that of an independent creator God.
Hinduism
InHinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
, the concept of god is complex and depends on the particular tradition. The concept spans conceptions from absolute monism
Monism attributes oneness or singleness () to a concept, such as to existence. Various kinds of monism can be distinguished:
* Priority monism states that all existing things go back to a source that is distinct from them; e.g., in Neoplatonis ...
to henotheism, monotheism
Monotheism is the belief that one God is the only, or at least the dominant deity.F. L. Cross, Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. A ...
and polytheism. In the Vedic period monotheistic god concept culminated in the semi-abstract semi-personified form of creative soul dwelling in all god such as Vishvakarman, Purusha, and Prajapati
Prajapati (, ) is a Vedas, Vedic deity of Hinduism. He is later identified with Brahma, the creator god.
Prajapati is a form of the creator-god Brahma, but the name is also the name of many different gods, in many Hindu scriptures, ranging f ...
. In the majority of Vaishnavism
Vaishnavism () ), also called Vishnuism, is one of the major Hindu denominations, Hindu traditions, that considers Vishnu as the sole Para Brahman, supreme being leading all other Hindu deities, that is, ''Mahavishnu''. It is one of the majo ...
traditions, he is Vishnu
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation ( ...
, and the text identifies this being as Krishna
Krishna (; Sanskrit language, Sanskrit: कृष्ण, ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme God (Hinduism), Supreme God in his own right. He is the god of protection, c ...
, sometimes referred as '' svayam bhagavan''. The term ''isvara'' - from the root is, to have extraordinary power. Some traditional '' sankhya'' systems contrast '' purusha'' (divine, or souls) to '' prakriti'' (nature or energy), however the term for sovereign god, ishvara is mentioned six times in the Atharva Veda
The Atharvaveda or Atharva Veda (, , from ''wikt:अथर्वन्, अथर्वन्'', "priest" and ''wikt:वेद, वेद'', "knowledge") or is the "knowledge storehouse of ''wikt:अथर्वन्, atharvans'', the proced ...
, and is central to many traditions. As per Advaita Vedanta school of Hindu philosophy the notion of ''Brahman
In Hinduism, ''Brahman'' (; IAST: ''Brahman'') connotes the highest universal principle, the ultimate reality of the universe.P. T. Raju (2006), ''Idealistic Thought of India'', Routledge, , page 426 and Conclusion chapter part XII In the ...
'' (the highest Universal Principle) is akin to that of god; except that unlike most other philosophies Advaita likens Brahman to '' atman'' (the true Self of an individual). For Sindhi Hindus, who are deeply influenced by Sikhism
Sikhism is an Indian religion and Indian philosophy, philosophy that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent around the end of the 15th century CE. It is one of the most recently founded major religious groups, major religio ...
, God
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
is seen as the omnipotent cultivation of all Hindu gods and goddesses. In short, the soul '' paramatma'' of all gods and goddesses are the omnipresent Brahman and are enlightened beings.
The conception of a deity in a sustaining/conserving/preserving mode is also used in Hindu theology where the Godhead, or Trimūrti in Sanskrit, consists of Brahma
Brahma (, ) is a Hindu god, referred to as "the Creator" within the Trimurti, the triple deity, trinity of Para Brahman, supreme divinity that includes Vishnu and Shiva.Jan Gonda (1969)The Hindu Trinity, Anthropos, Bd 63/64, H 1/2, pp. 212– ...
the Creator, Vishnu
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation ( ...
the Preserver/Sustainer, and Shiva
Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions w ...
the Destroyer.
Brahman
Brahman
In Hinduism, ''Brahman'' (; IAST: ''Brahman'') connotes the highest universal principle, the ultimate reality of the universe.P. T. Raju (2006), ''Idealistic Thought of India'', Routledge, , page 426 and Conclusion chapter part XII In the ...
is the eternal, unchanging, infinite, immanent, and transcendent reality which is the divine ground of all matter, energy, time, space, being and everything beyond in this Universe. The nature of Brahman is described as transpersonal, personal and impersonal by different philosophical schools. The word ''Brahman'' is derived from the verb ''brh'' (Sanskrit: to grow), and connotes greatness and infinity.
Brahman is talked of at two levels (''apara'' and ''para''). He is the fountainhead of all concepts but he himself cannot be conceived. He is the universal conceiver, universal concept and all the means of concept. Apara-Brahman is the same Para Brahma but for human understanding thought of as universal mind '' cum'' universal intellect from which all human beings derive an iota as their mind, intellect etc.
Ishvara
Ishvara is a philosophical concept in Hinduism, meaning controller or the Supreme controller (i.e. God) in a monotheistic or the Supreme Being or as an ''Ishta-deva'' of monistic thought. Ishvara is a transcendent and immanent entity best described in the last chapter of the Shukla Yajur Veda Samhita, known as the Ishavasya Upanishad. It states "''ishavasyam idam sarvam''" which means whatever there is in this world is covered and filled with Ishvara. Ishvara not only creates the world, but then also enters into everything there is. In Saivite traditions, the term is used as part of the compound "''Maheshvara''" ("great lord") later as a name for Siva.Bhagavan
Bhagavan literally means "possessing fortune, blessed, prosperous" (from the noun ''bhaga'', meaning "fortune, wealth", cognate to Slavic bog "god"), and hence "illustrious, divine, venerable, holy", etc. In some traditions of Hinduism it is used to indicate the Supreme Being or Absolute Truth, but with specific reference to that Supreme Being as possessing a personality (a personal God). This personal feature indicated in Bhagavan differentiates its usage from other similar terms such as Brahman, the "Supreme Spirit" or "spirit", and thus, in this usage, Bhagavan is in many ways analogous to the general Christian and Islamic conception of God.Jainism
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion whose three main pillars are nonviolence (), asceticism (), and a rejection of all simplistic and one-sided views of truth and reality (). Jainism traces its s ...
does not support belief in a creator deity
A creator deity or creator god is a deity responsible for the creation of the Earth, world, and universe in human religion and mythology. In monotheism, the single God is often also the creator. A number of monolatristic traditions separate a ...
. According to Jain doctrine, the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents. It comprises all of existence, any fundamental interaction, physical process and physical constant, and therefore all forms of matter and energy, and the structures they form, from s ...
and its constituents—soul, matter, space, time, and principles of motion—have always existed. All the constituents and actions are governed by universal natural laws. It is not possible to create matter out of nothing and hence the sum total of matter in the universe remains the same (similar to law of conservation of mass
In physics and chemistry, the law of conservation of mass or principle of mass conservation states that for any system closed to all transfers of matter the mass of the system must remain constant over time.
The law implies that mass can neith ...
). Jain text claims that the universe consists of Jiva
''Jiva'' (, IAST: ), also referred as ''Jivātman,'' is a living being or any entity imbued with a life force in Hinduism and Jīva (Jainism), Jainism. The word itself originates from the Sanskrit verb-root ''jīv'', which translates as 'to br ...
(life force or souls) and Ajiva (lifeless objects). Similarly, the soul
The soul is the purported Mind–body dualism, immaterial aspect or essence of a Outline of life forms, living being. It is typically believed to be Immortality, immortal and to exist apart from the material world. The three main theories that ...
of each living being is unique and uncreated and has existed since beginningless time.
The Jain theory of causation holds that a cause and its effect are always identical in nature and hence a conscious and immaterial entity like God cannot create a material entity like the universe. Furthermore, according to the Jain concept of divinity, any soul who destroys its karmas and desires, achieves liberation/Nirvana. A soul who destroys all its passions and desires has no desire to interfere in the working of the universe. Moral rewards and sufferings are not the work of a divine being, but a result of an innate moral order in the cosmos
The cosmos (, ; ) is an alternative name for the universe or its nature or order. Usage of the word ''cosmos'' implies viewing the universe as a complex and orderly system or entity.
The cosmos is studied in cosmologya broad discipline covering ...
; a self-regulating mechanism whereby the individual reaps the fruits of his own actions through the workings of the karmas.
Through the ages, Jain philosophers have adamantly rejected and opposed the concept of creator and omnipotent God. This has resulted in Jainism being labeled as '' nastika darsana'' ( atheist philosophy) by rival religious philosophies. The theme of non-creationism and absence of omnipotent God and divine grace runs strongly in all the philosophical dimensions of Jainism, including its cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe, the cosmos. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', with the meaning of "a speaking of the wo ...
, concepts of ''karma
Karma (, from , ; ) is an ancient Indian concept that refers to an action, work, or deed, and its effect or consequences. In Indian religions, the term more specifically refers to a principle of cause and effect, often descriptively called ...
'' and '' moksa'' and its moral code of conduct. Jainism asserts a religious and virtuous life is possible without the idea of a creator god.
Sikhism
The term for God inSikhism
Sikhism is an Indian religion and Indian philosophy, philosophy that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent around the end of the 15th century CE. It is one of the most recently founded major religious groups, major religio ...
is '' Waheguru''. Guru Nanak
Gurū Nānak (15 April 1469 – 22 September 1539; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ; pronunciation: , ), also known as ('Father Nanak'), was an Indian spiritual teacher, mystic and poet, who is regarded as the founder of Sikhism and is t ...
describes God as '' nirankar'' (from the Sanskrit ''nirākārā'', meaning "formless"), ''akal'' (meaning "eternal") and '' alakh'' (from the Sanskrit ''alakśya'', meaning "invisible" or "unobserved"). Sikhism's principal scripture, the Guru Granth Sahib
The Guru Granth Sahib (, ) is the central holy religious scripture of Sikhism, regarded by Sikhs as the final, sovereign and eternal Guru following the lineage of the ten human gurus of the religion. The Adi Granth (), its first rendition, w ...
, starts with the figure " 1", signifying the unity of God. Nanak's interpretation of God is that of a single, personal and transcendental creator with whom the devotee must develop a most intimate faith and relationship to achieve salvation
Salvation (from Latin: ''salvatio'', from ''salva'', 'safe, saved') is the state of being saved or protected from harm or a dire situation. In religion and theology, ''salvation'' generally refers to the deliverance of the soul from sin and its c ...
. Sikhism advocates the belief in one god who is omnipresent ('' sarav vi'āpak''), whose qualities are infinite and who is without gender, a nature represented (especially in the Guru Granth Sahib) by the term '' Ek Onkar''.
Nanak further emphasizes that a full understanding of God is beyond human beings, but that God is also not wholly unknowable. God is considered omnipresent in all creation and visible everywhere to the spiritually awakened. Nanak stresses that God must be seen by human beings from "the inward eye" or "heart" and that meditation
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique to train attention and awareness and detach from reflexive, "discursive thinking", achieving a mentally clear and emotionally calm and stable state, while not judging the meditat ...
must take place inwardly to achieve this enlightenment progressively; its rigorous application is what enables communication between God and human beings.
Sikh
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Si ...
s believe in a single God that has existed from the beginning of time and will survive forever. God is genderless, fearless, formless, immutable, ineffable, self-sufficient, omnipotent and not subject to the cycle of birth and death.
God in Sikhism is depicted in three distinct aspects: God as deity; God in relation to creation; and God in relation to man. During a discourse with ''siddha
''Siddha'' (Sanskrit: '; "perfected one") is a term that is used widely in Indian religions and culture. It means "one who is accomplished." It refers to perfected masters who have achieved a high degree of perfection of the intellect as we ...
s'' (wandering Hindu adept
An adept is an individual identified as having attained a specific level of knowledge, skill, or aptitude in doctrines relevant to a particular occult discipline, such as alchemy or magic.
According to magical tradition, adepts stand out from ...
s), Nanak is asked where "the Transcendent God" was before creation. He replies: "To think of the Transcendent Lord in that state is to enter the realm of wonder. Even at that stage of sunn, he permeated all that void" (GG, 940).
Early Modern and new religious movements
Rosicrucian Fellowship
 The esoteric Christian teachings of the Rosicrucian Fellowship, promulgated to the western world in the early 20th century as '' Western Wisdom Teachings'', present the conception of The Absolute -- unmanifested and unlimited "Boundless Being" or "Root of Existence", beyond the whole universe and beyond comprehension -- from whom proceeds the Supreme Being at the dawn of manifestation: The One, the " Great Architect of the Universe". From the threefold Supreme Being proceed the "seven Great Logoi" who contain within themselves all the great hierarchies that differentiate more and more as they diffuse through the six lower Cosmic Planes.
The esoteric Christian teachings of the Rosicrucian Fellowship, promulgated to the western world in the early 20th century as '' Western Wisdom Teachings'', present the conception of The Absolute -- unmanifested and unlimited "Boundless Being" or "Root of Existence", beyond the whole universe and beyond comprehension -- from whom proceeds the Supreme Being at the dawn of manifestation: The One, the " Great Architect of the Universe". From the threefold Supreme Being proceed the "seven Great Logoi" who contain within themselves all the great hierarchies that differentiate more and more as they diffuse through the six lower Cosmic Planes.
 In the Highest World of the seventh (lowest) Cosmic Plane dwells the God of the solar systems in the universe. These great beings are also threefold in manifestation, like the Supreme Being; their three aspects are ''Will'', ''Wisdom'' and ''Activity''.
According to these teachings, in the beginning of a ''Day of Manifestation'' a certain collective Great Being, God, limits himself to a certain portion of space, in which he elects to create the
In the Highest World of the seventh (lowest) Cosmic Plane dwells the God of the solar systems in the universe. These great beings are also threefold in manifestation, like the Supreme Being; their three aspects are ''Will'', ''Wisdom'' and ''Activity''.
According to these teachings, in the beginning of a ''Day of Manifestation'' a certain collective Great Being, God, limits himself to a certain portion of space, in which he elects to create the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
for the evolution of added self-consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is awareness of a state or object, either internal to oneself or in one's external environment. However, its nature has led to millennia of analyses, explanations, and debate among philosophers, scientists, an ...
. In God there are contained hosts of glorious hierarchies and lesser beings of every grade of intelligence and stage of consciousness, from omniscience
Omniscience is the property of possessing maximal knowledge. In Hinduism, Sikhism and the Abrahamic religions, it is often attributed to a divine being or an all-knowing spirit, entity or person. In Jainism, omniscience is an attribute that any ...
to an unconsciousness
Unconsciousness is a state in which a living individual exhibits a complete, or near-complete, inability to maintain an awareness of self and environment or to respond to any human or environmental stimulus. Unconsciousness may occur as the r ...
deeper than that of the deepest trance condition.
During the current period of manifestation, these various grades of beings are working to acquire more experience than they possessed at the beginning of this period of existence. Those who, in previous manifestations, have attained to the highest degree of development work on those who have not yet evolved any consciousness. In the Solar system, God's Habitation, there are seven Worlds differentiated by God, within Himself, one after another. Mankind's evolutionary scheme is slowly carried through five of these Worlds in seven great Periods ("Days") of manifestation -- the pilgrimage through a succession of Solar systems throughout the ''Cosmic Day'' of the Universe; ''billions and billions'' of years during which the evolving virgin Spirit becomes first human and, then, a God.
Unitarian Universalism (UU)
Concepts about deity are diverse among UUs. Some have no belief in any gods (atheism); others believe in many gods (polytheism). Some believe the question of the existence of any god is most likely unascertainable or unknowable (agnosticism). Some believe God is a metaphor for a transcendent reality. Some believe in a female god (goddess), a passive god (Deism), an Abrahamic god, or a god manifested in nature or the universe (pantheism). Many UUs reject the idea of deities and instead speak of the "spirit of life" that binds all life on Earth. UUs support each person's search for truth and meaning in concepts of spirituality. Historically, unitarianism and universalism were denominations within Christianity.Unitarianism
Unitarianism () is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian sect of Christianity. Unitarian Christians affirm the wikt:unitary, unitary God in Christianity, nature of God as the singular and unique Creator deity, creator of the universe, believe that ...
referred to a belief about the nature of Jesus Christ that affirmed God as a singular entity and rejected the doctrine of the Trinity. Universalism
Universalism is the philosophical and theological concept within Christianity that some ideas have universal application or applicability.
A belief in one fundamental truth is another important tenet in universalism. The living truth is se ...
referred to a theological belief that all persons will be reconciled to God because of divine love and mercy (Universal Salvation).
Brahma Kumaris
According to Brahma Kumaris, God is the incorporeal soul with the maximum degree of spiritual qualities such as peace and love.Extraterrestrial
Some comparatively new belief systems and books portray God asextraterrestrial life
Extraterrestrial life, or alien life (colloquially, aliens), is life that originates from another world rather than on Earth. No extraterrestrial life has yet been scientifically conclusively detected. Such life might range from simple forms ...
. Many of these theories hold that intelligent beings from another world have been visiting Earth for many thousands of years and have influenced the development of our religions. Some of these books posit that prophets or messiahs were sent to the human race in order to teach morality and encourage the development of civilization (see, for example, Rael and Zecharia Sitchin).
Meher Baba
The spiritual teacher Meher Baba described God as infinite love: "God is not understood in His essence until He is also understood as Infinite Love. Divine Love is unlimited in essence and expression, because it is experienced by the soul through the soul itself. The sojourn of the soul is a thrilling divine romance in which the lover, who in the beginning is conscious of nothing but emptiness, frustration, superficiality and the gnawing chains of bondage, gradually attains an increasingly fuller and freer expression of love and ultimately disappears and merges in the Divine Beloved to realize the unity of the Lover and the Beloved in the supreme and eternal fact of God as Infinite Love."Satanism
Anton LaVey, founder of the Church of Satan, espoused the view that "god" is a creation of man, rather than man being a creation of "god". In his book, '' The Satanic Bible'', the Satanist's view of god is described as the Satanist's true "self"—a projection of his or her own personality—not an external deity. Satan is used as a representation of personal liberty and individualism. LaVey discusses this extensively in ''The Book of Lucifer'', explaining that the gods worshipped by other religions are also projections of man's true self. He argues that man's unwillingness to accept his own ego has caused him to externalize these gods so as to avoid the feeling ofnarcissism
Narcissism is a self-centered personality style characterized as having an excessive preoccupation with oneself and one's own needs, often at the expense of others. Narcissism, named after the Greek mythological figure ''Narcissus'', has evolv ...
that would accompany self-worship.
Modern philosophy
Process philosophy and open theism
Process theology
Process theology is a type of theology developed from Alfred North Whitehead's (1861–1947) process philosophy, but most notably by Charles Hartshorne (1897–2000), John B. Cobb (1925–2024), and Eugene H. Peters (1929–1983). Process ...
is a school of thought influenced by the metaphysical process philosophy
Process philosophy (also ontology of becoming or processism) is an approach in philosophy that identifies processes, changes, or shifting relationships as the only real experience of everyday living. In opposition to the classical view of change ...
of Alfred North Whitehead
Alfred North Whitehead (15 February 1861 – 30 December 1947) was an English mathematician and philosopher. He created the philosophical school known as process philosophy, which has been applied in a wide variety of disciplines, inclu ...
(1861–1947), while open theism is a similar theological movement that began in the 1990s.
In both views, God is not omnipotent in the classical sense of a coercive being. Reality is not made up of material substances that endure through time, but serially-ordered events, which are experiential in nature. The universe is characterized by process and change carried out by the agents of free will
Free will is generally understood as the capacity or ability of people to (a) choice, choose between different possible courses of Action (philosophy), action, (b) exercise control over their actions in a way that is necessary for moral respon ...
. Self-determination
Self-determination refers to a people's right to form its own political entity, and internal self-determination is the right to representative government with full suffrage.
Self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international la ...
characterizes everything in the universe, not just human beings. God and creatures co-create. God cannot force anything to happen, but rather only influence the exercise of this universal free will by offering possibilities. Process theology is compatible with panentheism
Panentheism (; "all in God", from the Greek , and ) is the belief that the divine intersects every part of the universe and also extends beyond space and time. The term was coined by the German philosopher Karl Krause in 1828 (after reviewin ...
, the concept that God contains the universe (pantheism
Pantheism can refer to a number of philosophical and religious beliefs, such as the belief that the universe is God, or panentheism, the belief in a non-corporeal divine intelligence or God out of which the universe arisesAnn Thomson; Bodies ...
) but also transcends it. God as the ultimate logician - God may be defined as the only entity, by definition, possessing the ability to reduce an infinite number of logical equations having an infinite number of variables and an infinite number of states to minimum form instantaneously.
Posthuman
A posthuman God is a hypothetical future entity descended from or created by humans, but possessing capabilities so radically exceeding those of present humans as to appear godlike. One common variation of this idea is the belief or aspiration that humans will create a God entity emerging from anartificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
. Another variant is that humanity itself will evolve into a posthuman God.
The concept of a posthuman god has become common in science fiction
Science fiction (often shortened to sci-fi or abbreviated SF) is a genre of speculative fiction that deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts. These concepts may include information technology and robotics, biological manipulations, space ...
. Science fiction author Arthur C. Clarke said in an interview, "It may be that our role on this planet is not to worship God, but to create him." Clarke's friend and colleague, the late Isaac Asimov
Isaac Asimov ( ; – April 6, 1992) was an Russian-born American writer and professor of biochemistry at Boston University. During his lifetime, Asimov was considered one of the "Big Three" science fiction writers, along with Robert A. H ...
, postulated in his story "The Last Question
"The Last Question" is a science fiction short story by American writer Isaac Asimov. It first appeared in the November 1956 issue of ''Science Fiction Quarterly'' and in the anthologies in the collections ''Nine Tomorrows'' (1959), ''The Best ...
" a merger between humanity and machine intelligence that ultimately produces a deity capable of reversing entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, most commonly associated with states of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the micros ...
and subsequently initiates a new Creation trillions of years from the present era when the Universe is in the last stage of heat death. In Frank Herbert
Franklin Patrick Herbert Jr. (October 8, 1920February 11, 1986) was an American science-fiction author, best known for his 1965 novel Dune (novel), ''Dune'' and its five sequels. He also wrote short stories and worked as a newspaper journalist, ...
's science-fiction series Dune
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, flat ...
, a messianic figure is created after thousands of years of controlled breeding. The Culture series, by Iain M. Banks, represents a blend in which a transhuman
Transhuman, or trans-human, is the concept of an intermediary form between human and Posthuman#Transhumanism, posthuman. In other words, a transhuman is a being that resembles a human in most respects but who has powers and abilities beyond those ...
society is guarded by godlike machine intelligences. A stronger example is posited in the novel '' Singularity Sky'' by Charles Stross, in which a future artificial intelligence is capable of changing events even in its own past, and takes strong measures to prevent any other entity from taking advantage of similar capabilities. Another example appears in the popular online novella '' The Metamorphosis of Prime Intellect'' in which an advanced artificial intelligence uses its own advanced quantum brain to resolve discrepancies in physics theories and develop a unified field theory which gives it absolute control over reality, in a take on philosophical digitalism.
Phenomenological definition
The philosopher Michel Henry defines God from a phenomenological point of view. He says: "God is Life, he is the essence of Life, or, if we prefer, the essence of Life is God. Saying this we already know what is God the father the almighty, creator of heaven and earth, we know it not by the effect of a learning or of some knowledge, we don't know it by the thought, on the background of the truth of the world; we know it and we can know it only in and by the Life itself. We can know it only in God."''I Am the Truth. Toward a Philosophy of Christianity''. This Life is not biological life defined by objective and exterior properties, nor an abstract and empty philosophical concept, but the absolute phenomenological life, a radically immanent life that possesses in it the power of showing itself in itself without distance, a life that reveals permanently itself.See also
* Ceremonial pole *Existence of God
The existence of God is a subject of debate in the philosophy of religion and theology. A wide variety of arguments for and against the existence of God (with the same or similar arguments also generally being used when talking about the exis ...
* Monolatry
* Names of God
There are various names of God, many of which enumerate the various Quality (philosophy), qualities of a Supreme Being. The English word ''God (word), god'' (and its equivalent in other languages) is used by multiple religions as a noun to ref ...
* Theism
Theism is broadly defined as the belief in the existence of at least one deity. In common parlance, or when contrasted with '' deism'', the term often describes the philosophical conception of God that is found in classical theism—or the co ...
* Theological noncognitivism
References
External links
*Concepts of God.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Conceptions Of God