artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
and signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as audio signal processing, sound, image processing, images, Scalar potential, potential fields, Seismic tomograph ...
. These platforms encompass machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task ( ...
, reasoning
Reason is the capacity of consciously applying logic by drawing valid conclusions from new or existing information, with the aim of seeking the truth. It is associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, religion, scien ...
, natural language processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related ...
, speech recognition
Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers. It is also ...
and vision
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to:
Perception Optical perception
* Visual perception, the sense of sight
* Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight
* Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain und ...
(object recognition
Object recognition – technology in the field of computer vision for finding and identifying objects in an image or video sequence. Humans recognize a multitude of objects in images with little effort, despite the fact that the image of the ...
), human–computer interaction
Human–computer interaction (HCI) is the process through which people operate and engage with computer systems. Research in HCI covers the design and the use of computer technology, which focuses on the interfaces between people (users) and comp ...
, dialog and narrative generation, among other technologies.
Definition
At present, there is no widely agreed upon definition for cognitive computing in eitheracademia
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of tertiary education. The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 386 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the go ...
or industry.
In general, the term cognitive computing has been used to refer to new hardware and/or software that mimics the functioning of the human brain
The human brain is the central organ (anatomy), organ of the nervous system, and with the spinal cord, comprises the central nervous system. It consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. The brain controls most of the activi ...
(2004). In this sense, cognitive computing is a new type of computing with the goal of more accurate models of how the human brain/mind
The mind is that which thinks, feels, perceives, imagines, remembers, and wills. It covers the totality of mental phenomena, including both conscious processes, through which an individual is aware of external and internal circumstances ...
senses, reasons, and responds to stimulus. Cognitive computing applications link data analysis
Data analysis is the process of inspecting, Data cleansing, cleansing, Data transformation, transforming, and Data modeling, modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, informing conclusions, and supporting decision-making. Da ...
and adaptive page displays ( AUI) to adjust content for a particular type of audience. As such, cognitive computing hardware and applications strive to be more affective
Affect, in psychology, is the underlying experience of feeling, emotion, attachment, or mood. It encompasses a wide range of emotional states and can be positive (e.g., happiness, joy, excitement) or negative (e.g., sadness, anger, fear, dis ...
and more influential by design.
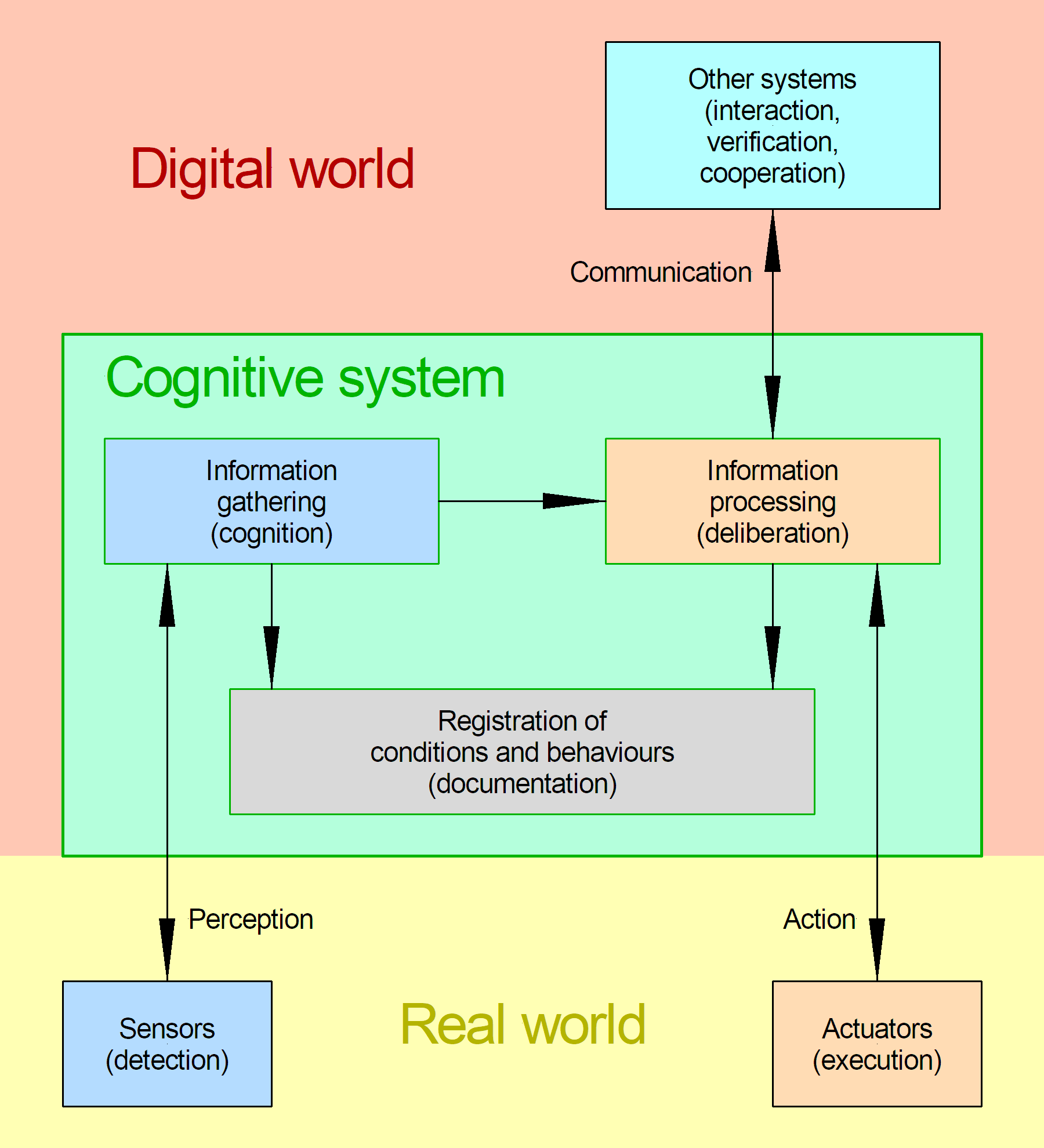 The term "cognitive system" also applies to any artificial construct able to perform a cognitive process where a cognitive process is the transformation of data, information, knowledge, or wisdom to a new level in the DIKW Pyramid. While many cognitive systems employ techniques having their origination in
The term "cognitive system" also applies to any artificial construct able to perform a cognitive process where a cognitive process is the transformation of data, information, knowledge, or wisdom to a new level in the DIKW Pyramid. While many cognitive systems employ techniques having their origination in artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
research, cognitive systems, themselves, may not be artificially intelligent. For example, a neural network
A neural network is a group of interconnected units called neurons that send signals to one another. Neurons can be either biological cells or signal pathways. While individual neurons are simple, many of them together in a network can perfor ...
trained to recognize cancer on an MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
scan may achieve a higher success rate than a human doctor. This system is certainly a cognitive system but is not artificially intelligent.
Cognitive systems may be engineered to feed on dynamic data in real-time, or near real-time, and may draw on multiple sources of information, including both structured and unstructured digital information, as well as sensory inputs (visual, gestural, auditory, or sensor-provided).
Cognitive analytics
Cognitive computing-branded technology platforms typically specialize in the processing and analysis of large,unstructured data
Unstructured data (or unstructured information) is information that either does not have a pre-defined data model or is not organized in a pre-defined manner. Unstructured information is typically plain text, text-heavy, but may contain data such ...
sets.
Applications
;Education: Even if cognitive computing can not take the place of teachers, it can still be a heavy driving force in the education of students. Cognitive computing being used in the classroom is applied by essentially having an assistant that is personalized for each individual student. This cognitive assistant can relieve the stress that teachers face while teaching students, while also enhancing the student's learning experience over all. Teachers may not be able to pay each and every student individual attention, this being the place that cognitive computers fill the gap. Some students may need a little more help with a particular subject. For many students, Human interaction between student and teacher can causeanxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response ...
and can be uncomfortable. With the help of Cognitive Computer tutor
Tutoring is private academic help, usually provided by an expert teacher; someone with deep knowledge or defined expertise in a particular subject or set of subjects.
A tutor, formally also called an academic tutor, is a person who provides assis ...
s, students will not have to face their uneasiness and can gain the confidence to learn and do well in the classroom. While a student is in class with their personalized assistant, this assistant can develop various techniques, like creating lesson plans, to tailor and aid the student and their needs.
;Healthcare: Numerous tech companies are in the process of developing technology that involves cognitive computing that can be used in the medical field. The ability to classify and identify is one of the main goals of these cognitive devices. This trait can be very helpful in the study of identifying carcinogen
A carcinogen () is any agent that promotes the development of cancer. Carcinogens can include synthetic chemicals, naturally occurring substances, physical agents such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, and biologic agents such as viruse ...
s. This cognitive system that can detect would be able to assist the examiner in interpreting countless numbers of documents in a lesser amount of time than if they did not use Cognitive Computer technology. This technology can also evaluate information about the patient, looking through every medical record in depth, searching for indications that can be the source of their problems.
;Commerce: Together with Artificial Intelligence, it has been used in warehouse management systems to collect, store, organize and analyze all related supplier data. All these aims at improving efficiency, enabling faster decision-making, monitoring inventory and fraud detection
;Human Cognitive Augmentation: In situations where humans are using or working collaboratively with cognitive systems, called a human/cog ensemble, results achieved by the ensemble are superior to results obtainable by the human working alone. Therefore, the human is cognitively augmented. In cases where the human/cog ensemble achieves results at, or superior to, the level of a human expert then the ensemble has achieved synthetic expertise. In a human/cog ensemble, the "cog" is a cognitive system employing virtually any kind of cognitive computing technology.
;Other use cases
* Speech recognition
Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers. It is also ...
* Sentiment analysis
Sentiment analysis (also known as opinion mining or emotion AI) is the use of natural language processing, text analysis, computational linguistics, and biometrics to systematically identify, extract, quantify, and study affective states and subje ...
* Face detection
Face detection is a computer technology being used in a variety of applications that identifies human faces in digital images. Face detection also refers to the psychological process by which humans locate and attend to faces in a visual scene ...
* Risk assessment
Risk assessment is a process for identifying hazards, potential (future) events which may negatively impact on individuals, assets, and/or the environment because of those hazards, their likelihood and consequences, and actions which can mitigate ...
* Fraud detection
* Behavioral recommendations
Industry work
Cognitive computing in conjunction withbig data
Big data primarily refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data processing, data-processing application software, software. Data with many entries (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with ...
and algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algo ...
s that comprehend customer needs, can be a major advantage in economic decision making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be either ra ...
.
The powers of cognitive computing and artificial intelligence hold the potential to affect almost every task that humans are capable of performing. This can negatively affect employment for humans, as there would be no such need for human labor anymore. It would also increase the inequality of wealth; the people at the head of the cognitive computing industry would grow significantly richer, while workers without ongoing, reliable employment would become less well off.
The more industries start to use cognitive computing, the more difficult it will be for humans to compete. Increased use of the technology will also increase the amount of work that AI-driven robot
A robot is a machine—especially one Computer program, programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions Automation, automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the robot control, co ...
s and machines can perform. Only extraordinarily talented, capable and motivated humans would be able to keep up with the machines. The influence of competitive individuals in conjunction with artificial intelligence/cognitive computing with has the potential to change the course of humankind.
See also
*Automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machine ...
* Affective computing
Affective computing is the study and development of systems and devices that can recognize, interpret, process, and simulate human affects. It is an interdisciplinary field spanning computer science, psychology, and cognitive science. While som ...
* Analytics
Analytics is the systematic computational analysis of data or statistics. It is used for the discovery, interpretation, and communication of meaningful patterns in data, which also falls under and directly relates to the umbrella term, data sc ...
* Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
* Artificial neural network
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks.
A neural network consists of connected ...
* Brain computer interface
The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head ( cephalization), usually near organs for special sen ...
* Cognitive computer
* Cognitive reasoning
* Cognitive science
Cognitive science is the interdisciplinary, scientific study of the mind and its processes. It examines the nature, the tasks, and the functions of cognition (in a broad sense). Mental faculties of concern to cognitive scientists include percep ...
* Enterprise cognitive system
* Semantic Web
The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable.
To enable the encoding o ...
* Social neuroscience
Social neuroscience is an interdisciplinary field devoted to understanding the relationship between social experiences and biological systems. Humans are fundamentally a social species, and studies indicate that various social influences, includi ...
* Synthetic intelligence
Synthetic intelligence (SI) is an alternative/opposite term for artificial intelligence emphasizing that the intelligence of machines need not be an imitation or in any way artificial; it can be a genuine form of intelligence. John Haugeland prop ...
* Usability
Usability can be described as the capacity of a system to provide a condition for its users to perform the tasks safely, effectively, and efficiently while enjoying the experience. In software engineering, usability is the degree to which a softw ...
* Neuromorphic engineering
* AI accelerator
A neural processing unit (NPU), also known as AI accelerator or deep learning processor, is a class of specialized hardware accelerator or computer system designed to accelerate artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning applications, inc ...
References
Further reading
* {{Cite web, url=http://www.hpcwire.com/2016/02/25/25170/, title=Mapping Out a New Role for Cognitive Computing in Science, last=Russell, first=John, date=2016-02-15, website=HPCwire, access-date=2016-04-21 Artificial intelligence Branches of cognitive science