Coal In Columbia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Mineral industry of Colombia refers to the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials in
Mineral industry of Colombia refers to the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials in
''Colombia: A Country Study''
(Rex A. Hudson, ed.).
 Mining of
Mining of
 The discovery of of high-quality oil at the Cusiana and Cupiagua fields, about east of
The discovery of of high-quality oil at the Cusiana and Cupiagua fields, about east of
 While Colombia has vast hydroelectric potential, a prolonged drought in 1992 forced severe electricity rationing throughout the country until mid-1993. The consequences of the drought on electricity-generating capacity caused the government to commission the construction or upgrading of 10
While Colombia has vast hydroelectric potential, a prolonged drought in 1992 forced severe electricity rationing throughout the country until mid-1993. The consequences of the drought on electricity-generating capacity caused the government to commission the construction or upgrading of 10

 Colombia's
Colombia's
/ref> As of 2009, La Colosa mining project (to be exploited by

 Colombia is the main producer of finer quality emeralds worldwide. Colombia produced 2.7 Mcarats (540 kg) of emeralds during 2008. Emerald mines are located both in the Boyacá and Cundinamarca Departments. Colombian emeralds constitute 50-95% of the world production, the numbers depending on the year, source and emeralds grade.
Colombia is the main producer of finer quality emeralds worldwide. Colombia produced 2.7 Mcarats (540 kg) of emeralds during 2008. Emerald mines are located both in the Boyacá and Cundinamarca Departments. Colombian emeralds constitute 50-95% of the world production, the numbers depending on the year, source and emeralds grade.

Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
. Colombia is well-endowed with mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Mi ...
s and energy resources. It has the largest coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
reserves in Latin America, and is second to Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
in hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ...
potential. Estimates of petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil or simply oil, is a naturally occurring, yellowish-black liquid chemical mixture found in geological formations, consisting mainly of hydrocarbons. The term ''petroleum'' refers both to naturally occurring un ...
reserves in 1995 were . Colombia also possesses significant amounts of nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
and gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
. Other important metals included platinum
Platinum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a density, dense, malleable, ductility, ductile, highly unreactive, precious metal, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name origina ...
and silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
, which were extracted in much smaller quantities. Colombia also produces copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, small amounts of iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the f ...
, and bauxite
Bauxite () is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)), and diaspore (α-AlO(OH) ...
. Nonmetallic mined minerals include salt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as r ...
, limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
, sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
, gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate Hydrate, dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, drywall and blackboard or sidewalk ...
, dolomite, barite
Baryte, barite or barytes ( or ) is a mineral consisting of barium sulfate (Ba S O4). Baryte is generally white or colorless, and is the main source of the element barium. The ''baryte group'' consists of baryte, celestine (strontium sulfate), ...
, feldspar
Feldspar ( ; sometimes spelled felspar) is a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagiocl ...
, clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
, magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula . It is one of the iron oxide, oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetism, ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetization, magnetized to become a ...
, mica
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into fragile elastic plates. This characteristic is described as ''perfect basal cleavage''. Mica is co ...
, talcum, and marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is ty ...
. Colombia also produces most of the world's emeralds
Emerald is a gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6) colored green by trace amounts of chromium or sometimes vanadium.Hurlbut, Cornelius S. Jr., and Kammerling, Robert C. (1991). ''Gemology'', John Wiley & Sons, New York, ...
. Despite the variety of minerals available for exploitation, Colombia still had to import substances such as iron, copper, and aluminum to meet its industrial needs.
Materials recovered by mining in the country include oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) and lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturate ...
, with proved reserves of (2006 estimate) and natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
, with annual production of 6.18 billion m3 (2004 estimate) and reserves of 114.4 billion m3 (1 January 2005 estimate).
Minerals—in particular coal, oil, and natural gas, but also emeralds, gold, and nickel—have played an important role in Colombia's GDP and foreign trade in the last 20 years. Accounting for only 1.4 percent of GDP and 13 percent of total exports between 1980 and 1984, minerals represented about 5 percent of GDP and 42 percent of total exports in 2006. The minerals industry has compensated to a certain extent for the decreasing role of agriculture and has expanded the importance of commodities for the economy as a whole. Colombia is the world's leading source of emeralds, and illegal mining
Illegal mining is mining activity that is undertaken without state permission. Illegal mining is the extraction of precious metals/rocks without following the proper procedures to participate in legal mining activity. These procedures include pe ...
is commonplace. Illegal mining, especially of gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
, has grown due to Colombia's aggressive counter narcotics policies, which increase the risks associated with the drug economy. However, production of precious minerals is small scale despite high international prices for minerals such as gold.Roberto Steiner and Hernán Vallejo. "Mining and energy". I''Colombia: A Country Study''
(Rex A. Hudson, ed.).
Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is a research library in Washington, D.C., serving as the library and research service for the United States Congress and the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It also administers Copyright law o ...
Federal Research Division
The Federal Research Division (FRD) is the research and analysis unit of the United States Library of Congress.
The Federal Research Division provides directed research and analysis on domestic and international subjects to agencies of the Unite ...
(2010).
History
 Mining of
Mining of kaolinite
Kaolinite ( ; also called kaolin) is a clay mineral, with the chemical composition Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedral sheet of silica () linked through oxygen atoms to one octahedral sheet of alumina () ...
and hematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of . ...
for pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other raw materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is al ...
pigments started in what is today Colombia since the mid-late neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
, with archaeological evidence of ceramic production and sedentary groups living in El Abra
El Abra is the name given to an extensive archeological site, located in the valley of the same name. El Abra is situated in the east of the municipality Zipaquirá extending to the westernmost part of Tocancipá in the department of Cundinama ...
settlements and the Colombian Caribbean coast (near the towns of San Jacinto, Monsú, Puerto Chacho, and Puerto Hormiga archaeological site) beginning around the year 5940 BCE around the town of San Jacinto. This would place these pottery shards among the oldest ever recovered anywhere. The earliest examples of gold mining and goldwork have been attributed to the Tumaco
Tumaco is a port city and municipality in the Nariño Department, Colombia, by the Pacific Ocean. It is located on the southwestern corner of Colombia, near the border with Ecuador, and experiences a hot tropical climate. Tumaco is inhabited main ...
people of the Pacific coast and date to around 325 BCE. Gold would play a pivotal role in luring the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
conquistador
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (; ; ) were Spanish Empire, Spanish and Portuguese Empire, Portuguese colonizers who explored, traded with and colonized parts of the Americas, Africa, Oceania and Asia during the Age of Discovery. Sailing ...
es to the area during the 16th century.
Gold was considered sacred by most of the Precolumbian
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era, also known as the pre-contact era, or as the pre-Cabraline era specifically in Brazil, spans from the initial peopling of the Americas in the Upper Paleolithic to the onset of European c ...
civilizations of the area. In Muisca mythology, Gold (Chiminigagua) was considered itself a deity, and the force of creation. Copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
mining was very important for the classic Quimbaya civilization, which developed the tumbaga
''Tumbaga'' is the name given by Spanish Conquistadors for a non-specific alloy of gold and copper, and metals composed of these elements. Pieces made of tumbaga were widely found in pre-Columbian Mesoamerica in North America and South America.
...
alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
.
Although significant in the colonial economy, it never commanded a large portion of Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
's GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performance o ...
in modern times. With the discovery and exploitation of large coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
reserves, however, the role of mining in the national economy expanded in the late 1980s.
Mineral resources of Colombia
Oil
 The discovery of of high-quality oil at the Cusiana and Cupiagua fields, about east of
The discovery of of high-quality oil at the Cusiana and Cupiagua fields, about east of Bogotá
Bogotá (, also , , ), officially Bogotá, Distrito Capital, abbreviated Bogotá, D.C., and formerly known as Santa Fe de Bogotá (; ) during the Spanish Imperial period and between 1991 and 2000, is the capital city, capital and largest city ...
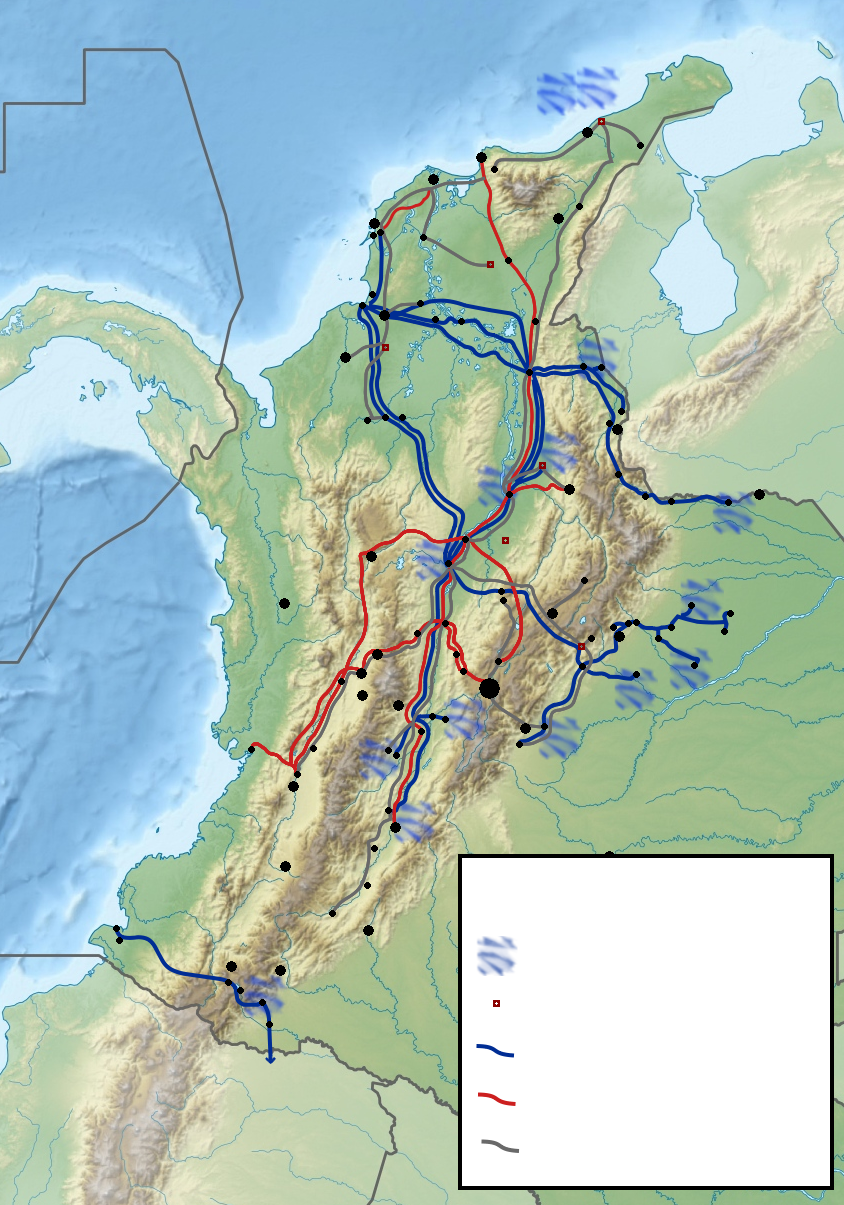
, has enabled Colombia to become a net oil exporter since 1986. The Transandino pipeline transports oil from Orito in the Department of Putumayo to the Pacific port of Tumaco
Tumaco is a port city and municipality in the Nariño Department, Colombia, by the Pacific Ocean. It is located on the southwestern corner of Colombia, near the border with Ecuador, and experiences a hot tropical climate. Tumaco is inhabited main ...
in the Department of Nariño. Total crude oil production averages ; about is exported.
The Pastrana government liberalized the petroleum investment policies, leading to an increase in exploration activity. Refining capacity cannot satisfy domestic demand, so some refined products, especially gasoline
Gasoline ( North American English) or petrol ( Commonwealth English) is a petrochemical product characterized as a transparent, yellowish, and flammable liquid normally used as a fuel for spark-ignited internal combustion engines. When for ...
, must be imported. Plans for the construction of new refineries are under development.
Natural gas
 While Colombia has vast hydroelectric potential, a prolonged drought in 1992 forced severe electricity rationing throughout the country until mid-1993. The consequences of the drought on electricity-generating capacity caused the government to commission the construction or upgrading of 10
While Colombia has vast hydroelectric potential, a prolonged drought in 1992 forced severe electricity rationing throughout the country until mid-1993. The consequences of the drought on electricity-generating capacity caused the government to commission the construction or upgrading of 10 thermoelectric
The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice versa via a thermocouple. A thermoelectric device creates a voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. Conversely, when ...
power plants. Half will be coal-fired, and half will be fired by natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
. The government also has begun awarding bids for the construction of a natural gas pipeline system that will extend from the country's extensive gas fields to its major population centers. Plans call for this project to make natural gas available to millions of Colombian households by the middle of the next decade.
Starting in 2004, Colombia became a net energy exporter, exporting electricity to Ecuador
Ecuador, officially the Republic of Ecuador, is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. It also includes the Galápagos Province which contain ...
and developing connections to Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
, Venezuela
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It com ...
and Panama
Panama, officially the Republic of Panama, is a country in Latin America at the southern end of Central America, bordering South America. It is bordered by Costa Rica to the west, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north, and ...
to export to those markets as well. The Trans-Caribbean pipeline connecting western Venezuela to Panama through Colombia was inaugurated by October, 2007, thanks to cooperation between presidents Álvaro Uribe
Álvaro Uribe Vélez (born 4 July 1952) is a Colombian politician who served as the 31st President of Colombia from 7 August 2002 to 7 August 2010.
Uribe started his political career in his home department of Antioquia Department, Antioquia. H ...
of Colombia, Martín Torrijos
Martín Erasto Torrijos Espino (; born July 18, 1963) is a Panamanian politician who was President of Panama from 2004 to 2009.
He was fathered out of wedlock by Panamanian military ruler Omar Torrijos, the '' de facto'' head of Panama from 19 ...
of Panama and Hugo Chávez
Hugo Rafael Chávez Frías (; ; 28 July 1954 – 5 March 2013) was a Venezuelan politician, Bolivarian Revolution, revolutionary, and Officer (armed forces), military officer who served as the 52nd president of Venezuela from 1999 until De ...
of Venezuela.
Since 2022, Colombia has encountered new challenges in its energy sector. President Gustavo Petro
Gustavo Francisco Petro Urrego (; born 19 April 1960) is a Colombian politician who is the 34th and current president of Colombia since 2022. Upon inauguration, he became the Pink tide, first left-wing president in the History of Colombia, recen ...
, with a strong focus on combating climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
, has declined to issue licenses for new natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
exploration, despite dwindling reserves. This policy has led to expectations of increased energy costs, compelling the country to import liquefied natural gas
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volume o ...
(LNG), which is substantially more expensive than domestic sources. The state oil company, Ecopetrol
Ecopetrol, formerly known as Empresa Colombiana de Petróleo S.A. () is the largest and primary petroleum company in Colombia. As a result of its continuous growth, Ecopetrol forms part of the Fortune Global 500 and was ranked 346. In the 2020 ...
, is attempting to address this shortfall by restarting previously suspended projects and increasing output from smaller fields. Nonetheless, projections indicate a widening gap between gas supply and demand, potentially impacting the competitiveness of Colombian industries.
Coal

 Colombia's
Colombia's coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
output has increased consistently from 4 million tons in 1981 to 65.6 million tons in 2006, when it contributed 1.4 percent of the world's coal production. In 2006 Colombia accounted for 81 percent of the total coal production in Central and South America. Furthermore, 94 percent of Colombia's coal is of very good quality and is classified as hard, with high heat-generating capacity. Coal has been Colombia's second-largest export since 2001.
The largest coal mines—and the ones that generate the most exports—are located in the north of the country, in the departments of La Guajira
La Guajira () is a departments of Colombia, department of Colombia. It occupies most of the Guajira Peninsula in the northeast region of the country, on the Caribbean Sea and bordering Venezuela, at the northernmost tip of South America. The ca ...
and Cesar Cesar or César may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''César'' (film), a 1936 French romantic drama
* ''César'' (play), a play by Marcel Pagnolt
Places
* Cesar, Portugal
* Cesar Department, Colombia
* Cesar River, in Colombia
* Cesar ...
. Cerrejón
Cerrejón is a large Coal mining, open-pit coal mine in Northern Colombia owned by Glencore. At Cerrejón, low-ash, low-sulphur bituminous coal from the Cerrejón Formation is excavated. At over the mine is one of the largest of its type, the la ...
is considered to be one of the largest open-pit
Open-pit mining, also known as open-cast or open-cut mining and in larger contexts mega-mining, is a surface mining technique that extracts rock (geology), rock or minerals from the earth.
Open-pit mines are used when deposits of commercially ...
coal mines in the world. The 2008 coal production in Cerrejon was calculated in 31.2 million tons. There are also smaller coal mines scattered throughout the rest of the nation.
Since 2000 government participation in the production of coal has been decreasing, and there has been a shift to private domestic and foreign investors. Major changes have occurred in the institutional framework of the coal industry in recent years. In particular, in 2000 the government sold the stakes that Colombia Coal ( Carbocol), a state-owned company, had in Cerrejón, and the new mining code introduced in 2001 led the government to concentrate on its role as regulator through the Ministry of Mines and Energy.
In 2020, Colombia had 5 trillion short tons of proved coal reserves, mostly bituminous coal
Bituminous coal, or black coal, is a type of coal containing a tar-like substance called bitumen or asphalt. Its coloration can be black or sometimes dark brown; often there are well-defined bands of bright and dull material within the coal seam, ...
, making it the second-largest amount in South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
behind Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
. Colombia produced 54 million short tons (MMst) of coal in 2020, with 9 MMst consumed domestically. However, coal production fell by 42% in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
and a 91-day strike at a major mine in the north of the country. Most of the coal produced in Colombia is exported, making it the fourth-largest coal exporter in the world in 2020, after Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
, and Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
. Coal was the country's second-largest export commodity by value, after oil and petroleum products
Petroleum products are materials derived from crude oil (petroleum) as it is processed in oil refineries. Unlike petrochemicals, which are a collection of well-defined usually pure organic compounds, petroleum products are complex mixtures. Most ...
. Colombia exported 75 MMst of coal in 2020, primarily to Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
and Latin America
Latin America is the cultural region of the Americas where Romance languages are predominantly spoken, primarily Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Latin America is defined according to cultural identity, not geogr ...
. In the same year, Colombia was the largest source of U.S. coal imports, accounting for 71% of total U.S. coal imports, or about 6.1 MMst.
In 2021, Colombia was South America’s largest coal producer and the second-largest producer of petroleum and other liquids, after Brazil. The country is also a significant oil exporter; in 2021, it was the fifth-largest crude oil exporter to the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
. Despite being a major coal producer, Colombia uses very little coal domestically, relying mainly on hydropower
Hydropower (from Ancient Greek -, "water"), also known as water power or water energy, is the use of falling or fast-running water to Electricity generation, produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by energy transformation, ...
for its electricity needs and exporting most of its coal production.
Gold
The production ofgold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
during 2008 was calculated at , with an increase of 34.2% with respect to the previous year.Investment opportunities in Colombian mining industry/ref> As of 2009, La Colosa mining project (to be exploited by
AngloGold Ashanti
AngloGold Ashanti Limited is a South African gold mining company, with global operations. With a diverse portfolio of cooperation, projects, and exploration activities, AngloGold Ashanti was formed in 2004 by the merger of AngloGold and the ...
) near Cajamarca, Tolima
Cajamarca is a town and municipality in the Tolima Department of Colombia. The population of the municipality was 17,309 as of the 2018 census. The municipality has two populated centres, the town centre of Cajamarca and the locality of Anaime. ...
is in planning phase, with calculated reserves of 12.9 million ounces. However, there is controversy about the possible environmental damage. In the Colombian economy, Gold is the most important metal in terms of short-term revenues.
Silver
Platinum
Copper
Copper is a growingmining industry
Mining is the extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agricultural processes, or feasibly created artificially in a la ...
in Colombia. There are many new projects that aim to give Colombia the ability to mine more copper. Currently, there is only one company in Colombia that mines for copper.
Nickel
The Cerro Matoso nickel mine, located in Montelíbano, Córdoba in northern Colombia, combines a lateritic nickelore
Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals, typically including metals, concentrated above background levels, and that is economically viable to mine and process. The grade of ore refers to the concentration ...
deposit with a low cost ferronickel
Ferroalloy refers to various alloys of iron with a high proportion of one or more other elements such as manganese (Mn), aluminium (Al), or silicon (Si). They are used in the production of steels and alloys. The alloys impart distinctive qualitie ...
smelter. It produces an average of 52,000 tons of nickel/year, which places this mine in the second place of nickel producers worldwide. Cerromatoso is currently owned by BHP
BHP Group Limited, founded as the Broken Hill Proprietary Company, is an Australian multinational mining and metals corporation. BHP was established in August 1885 and is headquartered in Melbourne, Victoria.
As of 2024, BHP was the world� ...
. Disagreement among the direction and the trade union
A trade union (British English) or labor union (American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers whose purpose is to maintain or improve the conditions of their employment, such as attaining better wages ...
workers, with frequent strike
Strike may refer to:
People
*Strike (surname)
* Hobart Huson, author of several drug related books
Physical confrontation or removal
*Strike (attack), attack with an inanimate object or a part of the human body intended to cause harm
* Airstrike, ...
s produced heavy losses during 2008
Halite
Halite
Halite ( ), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, pi ...
was explored by the Precolumbian
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era, also known as the pre-contact era, or as the pre-Cabraline era specifically in Brazil, spans from the initial peopling of the Americas in the Upper Paleolithic to the onset of European c ...
cultures such as the Muisca
The Muisca (also called the Chibcha) are indigenous peoples in Colombia and were a Pre-Columbian culture of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense that formed the Muisca Confederation before the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The Muisca spe ...
, as an important trade product. Early halite mining is dated about 5th century BC. The traditional halite mining was described by Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 1769 – 6 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, natural history, naturalist, List of explorers, explorer, and proponent of Romanticism, Romantic philosophy and Romanticism ...
during his visit to Zipaquira in 1801.
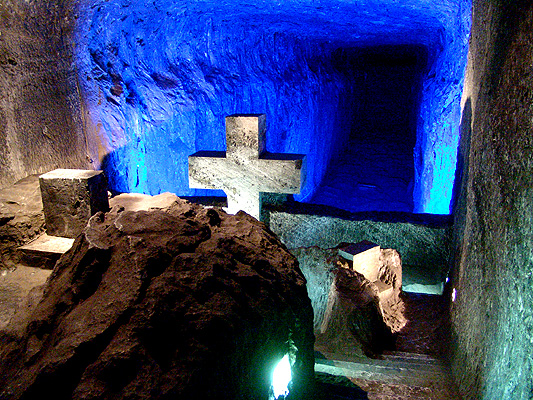
Nowadays, the Zipaquirá halite mine contains the Salt Cathedral of Zipaquirá
The Salt Cathedral of Zipaquirá () is an underground Roman Catholic church built within the tunnels of a salt mine underground in a halite mountain near the city of Zipaquirá, in Cundinamarca Department, Cundinamarca, Colombia. It is a touris ...
, entirely hand-carved in halite, including the religious icon
An icon () is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, in the cultures of the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, Catholic, and Lutheran churches. The most common subjects include Jesus, Mary, saints, and angels. Although especially ...
s, ornaments and architectural details; the Salt Park and the national mineralogy
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical mineralogy, optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifact (archaeology), artifacts. Specific s ...
museum
A museum is an institution dedicated to displaying or Preservation (library and archive), preserving culturally or scientifically significant objects. Many museums have exhibitions of these objects on public display, and some have private colle ...
.
Gemstones
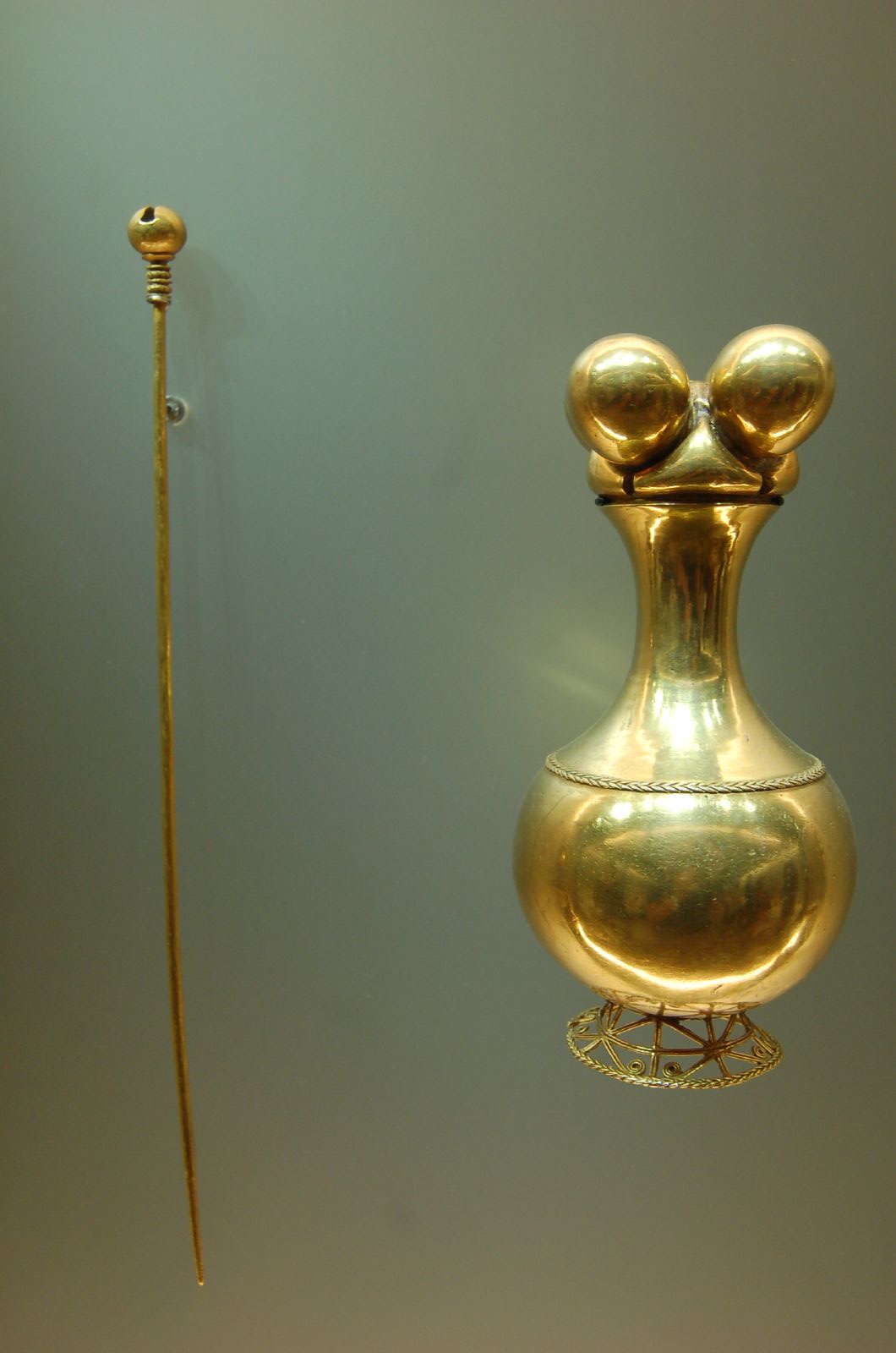
 Colombia is the main producer of finer quality emeralds worldwide. Colombia produced 2.7 Mcarats (540 kg) of emeralds during 2008. Emerald mines are located both in the Boyacá and Cundinamarca Departments. Colombian emeralds constitute 50-95% of the world production, the numbers depending on the year, source and emeralds grade.
Colombia is the main producer of finer quality emeralds worldwide. Colombia produced 2.7 Mcarats (540 kg) of emeralds during 2008. Emerald mines are located both in the Boyacá and Cundinamarca Departments. Colombian emeralds constitute 50-95% of the world production, the numbers depending on the year, source and emeralds grade.
Relevance
The Colombian mining industry remains as one of the most dynamic and promising sectors of the Colombian economy, in just one year the investment has reached record figures in excess of two billion dollars and the trend in the short term is not reversed. The mining industry contributes with the economic growth and social development and the development of the regions where the activity is legally established. In addition this demonstrates that the contribution in the social and environmental component is higher than the industry average. Government efforts to expand mining in Colombia were needed to encourage private sector investment. In the late 1980s, much of Colombia remained inadequately charted, and reserve estimates were considered only marginally reliable. The government set a policy of developing infrastructure (roads, electricity, and communications), providing technical assistance, and encouraging sound credit and legal policies to minimize problems with land titling. Through joint ventures and the promotion of small mining companies, government officials believed that the mining sector could contribute more to national employment, income, and wealth.Human rights and crime
According to a 2013U.S. Department of Labor
The United States Department of Labor (DOL) is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government. It is responsible for the administration of federal laws governing occupational safety and health, wage and hour standards, unem ...
report on the worst forms of child labor
Child labour is the exploitation of children through any form of work that interferes with their ability to attend regular school, or is mentally, physically, socially and morally harmful. Such exploitation is prohibited by legislation w ...
and labor conditions around the world, the Colombian mining industry employs underage children. The report indicated that Colombia's industrial sector employed 20% of the working children who were aged 5 to 14 years old. However, and despite the government's participation in a "4-year, $9 million project to combat child labor and improve workplace health and safety in mining", children continue to engage in child labor. In fact, the Bureau of International Labor Affairs
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) is an operating unit of the United States Department of Labor which manages the department's international responsibilities. According to its mission statement:
''“The Bureau of International La ...
issued a List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in December 2014 where Colombia was mentioned for its use of underage children in brick, coal, gold and emerald mining.
Mining infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and pri ...
is a common target of terrorist attack
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of violence against non-combatants to achieve political or ideological aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violence during peacetime or in the context of war a ...
s, specially the oil and gas pipelines
A pipeline is a system of pipes for long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas, typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than of pipeline in 120 countries around the world. The Un ...
, mainly by the Farc
The Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia – People's Army (, FARC–EP or FARC) was a Marxist–Leninist guerrilla group involved in the continuing Colombian conflict starting in 1964. The FARC-EP was officially founded in 1966 from peasan ...
and ELN guerrilla
Guerrilla warfare is a form of unconventional warfare in which small groups of irregular military, such as rebels, Partisan (military), partisans, paramilitary personnel or armed civilians, which may include Children in the military, recruite ...
s. The mining companies have been implicated in extortion
Extortion is the practice of obtaining benefit (e.g., money or goods) through coercion. In most jurisdictions it is likely to constitute a criminal offence. Robbery is the simplest and most common form of extortion, although making unfounded ...
payments to guerrillas
Guerrilla warfare is a form of unconventional warfare in which small groups of irregular military, such as rebels, Partisan (military), partisans, paramilitary personnel or armed civilians, which may include Children in the military, recruite ...
in exchange for access to mining locations. The Caño Limón– Coveñas pipeline, which stretches 780 km from the Caño Limón to the Atlantic port of Coveñas, has come under heavy attack, including 170 attacks in 2002 alone, The pipeline remained out of operation for 266 days of that year and the government estimates that these bombings reduced the GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performance o ...
of Colombia by 0.5%. The bombings, which have occurred on average once every 5 days, have caused substantial environmental damage, often in fragile rainforests
Rainforests are forests characterized by a closed and continuous tree Canopy (biology), canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforests can be generally classified as tropi ...
and jungles.
On October 14, 1998, a pipeline exploded because of bombs placed by ELN guerrillas. The burning oil spread fire across the Machuca village near Segovia, Antioquia. 85 peasants died and over 30 were injured.
On the morning of December 13, 1998, after two days of combat between the army protecting the pipelines and the FARC, a Colombian Air Force helicopter carried out an air attack against guerrillas near the village of Santo Domingo, including the use of cluster-bombs. After the bombing was over, the bodies of seventeen civilians were found in Santo Domingo, including seven children. The case was subsequently handed over to a Colombian military court, with convictions of 31 years of prison for the accused. The decision called for the case to be judged in civil court and for comprehensive reparations to the victims.
References
{{Colombian emeralds Industry in Colombia Illegal mining