The effects of climate change on human health are profound because they increase
heat-related illnesses and deaths,
respiratory diseases
Respiratory diseases, or lung diseases, are pathology, pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange difficult in Breathing, air-breathing animals. They include conditions of the respiratory tract including the t ...
, and the spread of
infectious diseases
infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
. There is widespread agreement among researchers, health professionals and organizations that climate change is the biggest global health threat of the 21st century.
Rising temperatures and changes in weather patterns are increasing the severity of
heat waves
"Heat Waves" is a song by British indie rock band Glass Animals released as a single from their third studio album ''Dreamland (Glass Animals album), Dreamland'' on 29 June 2020. A sleeper hit, it is the band's signature song and biggest hit sing ...
,
extreme weather
Extreme weather includes unexpected, unusual, severe weather, severe, or unseasonal weather; weather at the extremes of the historical distribution—the range that has been seen in the past. Extreme events are based on a location's recorded weat ...
and other causes of illness, injury or death. Heat waves and extreme weather events have a big impact on health both directly and indirectly. When people are exposed to higher temperatures for longer time periods they might experience
heat illness
Heat illness is a spectrum of disorders due to increased body temperature. It can be caused by either environmental conditions or by exertion. It includes minor conditions such as heat cramps, heat syncope, and heat exhaustion as well as the ...
and
heat-related death.
In addition to direct impacts, climate change and extreme weather events cause changes in the
biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to mat ...
.
Certain diseases that are carried and spread by living hosts such as
mosquitoes
Mosquitoes, the Culicidae, are a family of small flies consisting of 3,600 species. The word ''mosquito'' (formed by '' mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish and Portuguese for ''little fly''. Mosquitoes have a slender segmented body, ...
and
ticks
Ticks are parasitic arachnids of the order Ixodida. They are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, and species, but can become larger when engorged. Ticks a ...
(known as
vectors) may become more common in some regions. Affected diseases include
dengue fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne disease caused by dengue virus, prevalent in tropical and subtropical areas. Asymptomatic infections are uncommon, mild cases happen frequently; if symptoms appear, they typically begin 3 to 14 days after i ...
and
malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
.
Contracting
waterborne diseases
Waterborne diseases are conditions (meaning adverse effects on human health, such as death, disability, illness or disorders) caused by pathogenic micro-organisms that are transmitted by water. These diseases can be spread while bathing, washing ...
such as
diarrhoeal disease will also be more likely.
Changes in climate can cause
decreasing yields for some crops and regions, resulting in higher
food prices
Food prices refer to the average price level for food across countries, regions and on a global scale. Food prices affect producers and consumers of food. Price levels depend on the food production process, including food marketing and food di ...
, less
available food, and
undernutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a Deficiency (medicine), deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and Vitamin deficiency, other nutrients whic ...
. Climate change can also reduce access to
clean and safe water supply. Extreme weather and its health impact can also threaten the livelihoods and economic stability of people. These factors together can lead to increasing poverty,
human migration
Human migration is the movement of people from one place to another, with intentions of settling, permanently or temporarily, at a new location (geographic region). The movement often occurs over long distances and from one country to another ( ...
, violent conflict, and
mental health
Mental health is often mistakenly equated with the absence of mental illness. However, mental health refers to a person's overall emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It influences how individuals think, feel, and behave, and how t ...
issues.
Climate change affects human health at all ages, from infancy through adolescence, adulthood and old age.
Factors such as age, gender and
socioeconomic status
Socioeconomic status (SES) is a measurement used by economics, economists and sociology, sociologsts. The measurement combines a person's work experience and their or their family's access to economic resources and social position in relation t ...
influence to what extent these effects become wide-spread risks to human health.
Some groups are more
vulnerable than others to the health effects of climate change. These include children, the elderly, outdoor workers and disadvantaged people.
Overview of health effects and pathways
The effects of climate change on human health can be grouped into direct and indirect effects.
Extreme weather, including increased storms, floods, droughts, heat waves and
wildfires
A wildfire, forest fire, or a bushfire is an unplanned and uncontrolled fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a ...
can directly cause injury, illness, or death.
The indirect impact of climate change happens through changes in the environment that alter the
Earth's natural systems on a large-scale. These include worsening
water quality
Water quality refers to the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water based on the standards of its usage. It is most frequently used by reference to a set of standards against which compliance, generally achieved through tr ...
,
air pollution
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the Atmosphere of Earth, air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be Gas, gases like Ground-level ozone, ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles li ...
, reduced food availability, and faster spread of disease-carrying insects.
Both direct and indirect health effects and their impact vary across the world and between different groups of people according to age, gender, mobility and other factors. For example, differences in health service provision or economic development will result in different health risks and outcomes for people in different regions, with less developed countries facing greater health risks. In many places, the combination of lower socioeconomic status and gender roles result in increased health risks to women and girls as a result of climate change, compared to those faced by men and boys (although the converse may apply in other instances).
The various health effects that are related to climate change include
cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
s,
respiratory disease
Respiratory diseases, or lung diseases, are pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange difficult in air-breathing animals. They include conditions of the respiratory tract including the trachea, bronchi, ...
s,
infectious diseases
infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
,
undernutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a Deficiency (medicine), deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and Vitamin deficiency, other nutrients whic ...
,
mental illness
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness, a mental health condition, or a psychiatric disability, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. A mental disorder is ...
,
allergies
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include Allergic rhinitis, hay fever, Food allergy, food al ...
,
injuries
Injury is physiological damage to the living tissue of any organism, whether in humans, in other animals, or in plants.
Injuries can be caused in many ways, including mechanically with penetration by sharp objects such as teeth or with b ...
and
poisoning
Poisoning is the harmful effect which occurs when Toxicity, toxic substances are introduced into the body. The term "poisoning" is a derivative of poison, a term describing any chemical substance that may harm or kill a living organism upon ...
.
The provision of
health care
Health care, or healthcare, is the improvement or maintenance of health via the preventive healthcare, prevention, diagnosis, therapy, treatment, wikt:amelioration, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other disability, physic ...
can also be impacted by the collapse of
health system
A health system, health care system or healthcare system is an organization of people, institutions, and resources that delivers health care services to meet the health needs of target populations.
There is a wide variety of health systems aroun ...
s and damage to infrastructure due to climate-induced events such as flooding. Therefore, building health systems that are
climate resilient is a priority.
Health risks from extreme weather and climate events
Climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
is increasing the frequency and intensity of some
extreme weather
Extreme weather includes unexpected, unusual, severe weather, severe, or unseasonal weather; weather at the extremes of the historical distribution—the range that has been seen in the past. Extreme events are based on a location's recorded weat ...
events. Extreme heat and cold events are the most likely to increase and worsen followed by more frequent heavy rain or snow and increases in the intensity of droughts.
Extreme weather events, such as floods, hurricanes, heatwaves, droughts and wildfires can result in injuries, death and the spread of
infectious diseases
infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
. For example, local
epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example, in meningococcal infection ...
s can occur due to loss of infrastructure, such as hospitals and
sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
services, but also because of climate changes creating a more suitable weather for disease-carrying organisms.
Heat
Since the 1970s, temperature on the surface of Earth has become warmer each decade. This increase happened faster than in any other 50-year period over at least the last 2000 years. Compared to the second half of the 19th century, temperature in the 21st century show a warming of 1.09 °C.
Extreme heat is a direct threat to health, especially for people over 65 years, children, people living in cities and those who have already existing health conditions. Rising
global temperatures impact the health and wellbeing of people in multiple ways. In the last few decades, people all over the world have become more vulnerable to heat and experienced an increasing number of life-threatening
heatwave
A heat wave or heatwave, sometimes described as extreme heat, is a period of abnormally hot weather generally considered to be at least ''five consecutive days''. A heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the area and ...
events.
Extreme heat has negative effects on
mental health
Mental health is often mistakenly equated with the absence of mental illness. However, mental health refers to a person's overall emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It influences how individuals think, feel, and behave, and how t ...
as well, raising the risk of mental health-related hospitalisations and suicidality.
Although heat itself is not a direct threat to health on its own, a combination of factors of rising temperatures can detriment one's health.The effects of heat on an individual's health is influenced by temperatures, humidity, exercise, hydration, age, pre-existing health status and also by occupation, clothing, behavior, autonomy, vulnerability, and sense of obligation.
It is estimated that between 1960 and 1990, climate change has put over 600 million people (9% of the global population) outside the
human climate niche which is the average temperature range in which people have been able to thrive in the past 6,000 years. Unless
greenhouse gas emissions are reduced, regions inhabited by a third of the human population could become as hot as the hottest parts of the
Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
within 50 years. The projected annual average temperature of above 29 °C for these regions would be outside the biologically suitable temperature range for humans.
Heat-related health effects for vulnerable people

Exposure to extreme heat poses an acute health hazard, especially for people deemed as vulnerable.
Vulnerable people with regard to
heat illness
Heat illness is a spectrum of disorders due to increased body temperature. It can be caused by either environmental conditions or by exertion. It includes minor conditions such as heat cramps, heat syncope, and heat exhaustion as well as the ...
es include people with low incomes, minority groups, women (in particular pregnant women), children, older adults (over 65 years old), people with chronic diseases, disabilities and
multiple long-term health conditions.
Other people at risk include those living in urban environments (due to the
urban heat island effect
Urban areas usually experience the urban heat island (UHI) effect; that is, they are significantly warmer than surrounding rural areas. The temperature difference is usually larger at night than during the day, and is most apparent when winds ar ...
), outdoor workers and people who take certain
prescription drug
A prescription drug (also prescription medication, prescription medicine or prescription-only medication) is a pharmaceutical drug that is permitted to be dispensed only to those with a medical prescription. In contrast, over-the-counter drugs c ...
s.
Climate change increases the frequency and severity of heatwaves and thus
heat stress
Hyperthermia, also known as overheating, is a condition in which an individual's body temperature is elevated beyond normal due to failed thermoregulation. The person's body produces or absorbs more heat than it dissipates. When extreme temp ...
for people. A 2022 global study found that heat-related deaths increased significantly between 2000 and 2019, particularly in tropical and low-income countries, underscoring the growing health burden from rising temperatures.
[Zhao, Q., Guo, Y., Ye, T., Gasparrini, A., Tong, S., & Wang, C. (2022). Global, regional, and national burden of mortality associated with non-optimal ambient temperatures from 2000 to 2019: a three-stage modelling study. ''The Lancet Planetary Health'', 6(6), e491–e500]
https://doi.org/10.1016/S2542-5196(22)00091-0
/ref>
Human responses to heat stress can include heat stroke
Heat stroke or heatstroke, also known as sun-stroke, is a severe heat illness that results in a body temperature greater than , along with red skin, headache, dizziness, and confusion. Sweating is generally present in exertional heatstro ...
and overheating (hyperthermia
Hyperthermia, also known as overheating, is a condition in which an individual's body temperature is elevated beyond normal due to failed thermoregulation. The person's body produces or absorbs more heat than it dissipates. When extreme te ...
). Extreme heat is also linked to acute kidney injury
Acute kidney injury (AKI), previously called acute renal failure (ARF), is a sudden decrease in renal function, kidney function that develops within seven days, as shown by an increase in serum creatinine or a decrease in urine output, or both.
...
, low quality sleep
Sleep is a state of reduced mental and physical activity in which consciousness is altered and certain Sensory nervous system, sensory activity is inhibited. During sleep, there is a marked decrease in muscle activity and interactions with th ...
, and complications with pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
.cardiovascular
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart a ...
and respiratory disease
Respiratory diseases, or lung diseases, are pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange difficult in air-breathing animals. They include conditions of the respiratory tract including the trachea, bronchi, ...
.low birth weight
Low birth weight (LBW) is defined by the World Health Organization as a birth weight of an infant of or less, regardless of gestational age. Infants born with LBW have added health risks which require close management, often in a neonatal inten ...
and pre-term birth.chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of long-term kidney disease, defined by the sustained presence of abnormal kidney function and/or abnormal kidney structure. To meet criteria for CKD, the abnormalities must be present for at least three mo ...
(CKD).wet-bulb temperature
The wet-bulb temperature is the lowest temperature that can be reached under current ambient conditions by the evaporation of water only. It is defined as the temperature of a parcel of air cooled to saturation (100% relative humidity) by the ...
of 35 °C is regarded as the limit for humans (called the "physiological threshold for human adaptability" to heat and humidity). As of 2020, only two weather stations had recorded 35 °C wet-bulb temperatures, and only very briefly, but the frequency and duration of these events is expected to rise with ongoing climate change.[
] Global warming above 1.5 degrees risks making parts of the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
uninhabitable because the threshold for the wet bulb temperature may be passed.dementia
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that affects a person's ability to perform activities of daily living, everyday activities. This typically invo ...
, Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
) are more at risk when faced with high temperatures and ought to be extra carefulchronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. GOLD defines COPD as a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory s ...
(COPD) has been estimated for every 1 °C increase in temperatures above 29 °C.
In urban areas
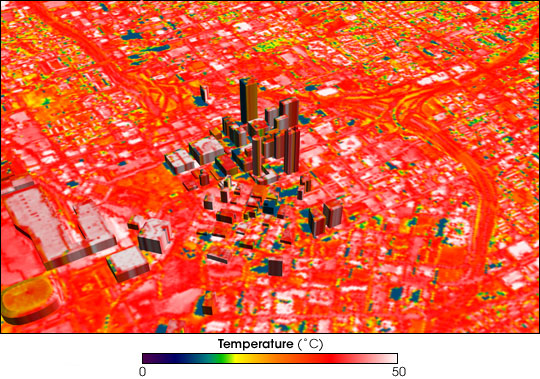 The effects of heatwaves tend to be more pronounced in urban areas because they are typically warmer than surrounding rural areas due to the
The effects of heatwaves tend to be more pronounced in urban areas because they are typically warmer than surrounding rural areas due to the urban heat island
Urban areas usually experience the urban heat island (UHI) effect; that is, they are significantly warmer than surrounding rural areas. The temperature difference is usually larger at night than during the day, and is most apparent when winds ar ...
effect.wet bulb globe temperature
The wet-bulb globe temperature (WBGT) is a measure of environmental heat as it affects humans. Unlike a simple temperature measurement, WBGT accounts for all four major environmental heat factors: air temperature, humidity, radiant heat (fro ...
above 30 °C tripled between 1983 and 2016.
Heat-related mortality
Health experts warn that "exposure to extreme heat increases the risk of death from cardiovascular
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart a ...
, cerebrovascular, and respiratory conditions and all-cause mortality. Heat-related deaths in people older than 65 years reached a record high of an estimated 345 000 deaths in 2019".Karachi
Karachi is the capital city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Sindh, Pakistan. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, largest city in Pakistan and 12th List of largest cities, largest in the world, with a popul ...
, Pakistan in June 2015 due to a severe heat wave with temperatures as high as .air conditioning
Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C (US) or air con (UK), is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior temperature, and in some cases, also controlling the humidity of internal air. Air c ...
) will help prevent heat-related mortality but current air conditioning technology is generally unsustainable as it contributes to greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate chan ...
, air pollution
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the Atmosphere of Earth, air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be Gas, gases like Ground-level ozone, ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles li ...
, peak electricity demand
Energy demand management, also known as demand-side management (DSM) or demand-side response (DSR), is the modification of consumer demand for energy through various methods such as financial incentives and behavioral change through education.
Us ...
, and urban heat islands.
Reduced labour capacity
Heat exposure can affect people's ability to work.The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal, founded in England in 1823. It is one of the world's highest-impact academic journals and also one of the oldest medical journals still in publication.
The journal publishes ...
'' investigated change in labour capacity as an indicator. It found that during 2021, high temperature reduced global potential labour hours by 470 billion – a 37% increase compared to the average annual loss that occurred during the 1990s. Occupational heat exposure especially affects laborers in the agricultural sector of developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed Secondary sector of the economy, industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. ...
. In those countries, the vast majority of these labour hour losses (87%) were in the agricultural sector.
Sports and outdoor exercise
With regards to sporting activities, it has been observed that "hot weather reduces the likelihood of engaging in exercise".
Droughts
Climate change affects multiple factors associated with drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, ...
s, such as how much rain falls and how fast the rain evaporates again. Warming over land increases the severity and frequency of droughts around much of the world.[Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, and O. Zolina, 2021]
Chapter 8: Water Cycle Changes
I
Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1055–1210, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.010. Many of the Drought#Consequences, consequences of droughts have effects on human health.
Floods
Due to an increase in heavy rainfall events, floods
A flood is an overflow of water (list of non-water floods, or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant con ...
are expected to become more severe in the future when they do occur.soil moisture
Soil moisture is the water content of the soil. It can be expressed in terms of volume or weight. Soil moisture measurement can be based on ''in situ'' probes (e.g., capacitance probes, neutron probes) or remote sensing methods.
Water that enters ...
.Floods
A flood is an overflow of water (list of non-water floods, or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant con ...
have short and long-term negative implications to people's health and well-being. Short term implications include mortalities, injuries
Injury is physiological damage to the living tissue of any organism, whether in humans, in other animals, or in plants.
Injuries can be caused in many ways, including mechanically with penetration by sharp objects such as teeth or with b ...
and diseases
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are asso ...
, while long term implications include non-communicable diseases
A non-communicable disease (NCD) is a disease that is not transmissible directly from one person to another. NCDs include Parkinson's disease, autoimmune diseases, strokes, heart diseases, cancers, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, osteoarthriti ...
and psychosocial
The psychosocial approach looks at individuals in the context of the combined influence that psychological factors and the surrounding social environment have on their physical and mental wellness and their ability to function. This approach is ...
health aspects.
Wildfires
Climate change increases wildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, or a bushfire is an unplanned and uncontrolled fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a ...
potential and activity. Climate change leads to a warmer ground temperature and its effects include earlier snowmelt dates, drier than expected vegetation
Vegetation is an assemblage of plants and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular Taxon, taxa, life forms, structure, Spatial ecology, spatial extent, or any other specific Botany, botanic ...
, increased number of potential fire days, increased occurrence of summer droughts
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, ...
, and a prolonged dry season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The t ...
.particulate matter
Particulate matter (PM) or particulates are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. An ''aerosol'' is a mixture of particulates and air, as opposed to the particulate matter alone, though it is sometimes defin ...
that has damaging effects to human health.asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
and chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder; increased risk of lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma, is a malignant tumor that begins in the lung. Lung cancer is caused by genetic damage to the DNA of cells in the airways, often caused by cigarette smoking or inhaling damaging chemicals. Damaged ...
, mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is a type of cancer that develops from the thin layer of tissue that covers many of the internal organs (known as the mesothelium). The area most commonly affected is the lining of the lungs and chest wall. Less commonly the lini ...
and tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
; increased airway hyper-responsiveness; changes in levels of inflammatory mediators and coagulation factors; and respiratory tract infection
Respiratory tract infections (RTIs) are infectious diseases involving the lower or upper respiratory tract. An infection of this type usually is further classified as an upper respiratory tract infection (URI or URTI) or a lower respiratory tract ...
.
Storms
Storms become wetter under climate change. These include tropical cyclones
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its ...
and extratropical cyclones
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable ...
. Both the maximum and mean rainfall rates increase. This more extreme rainfall is also true for thunderstorms
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are som ...
in some regions.
Health risks from climate-sensitive infectious diseases
Health risks from changes in air quality
Indoor air quality
Indoor air pollution is known to affect the health, comfort, and well-being of building occupants. It has also been linked to sick building syndrome
Sick building syndrome (SBS) is a condition in which people develop symptoms of illness or become infected with chronic disease from the building in which they work or reside. In scientific literature, SBS is also known as building-related illn ...
, respiratory issues, reduced productivity, and impaired learning in schools. Indoor air quality is linked inextricably to outdoor air quality. Climate change can affect indoor air quality by increasing the level of outdoor air pollutants such as ozone and particulate matter
Particulate matter (PM) or particulates are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. An ''aerosol'' is a mixture of particulates and air, as opposed to the particulate matter alone, though it is sometimes defin ...
, for example through emissions from wildfires caused by extreme heat and drought. There are numerous predictions for how indoor air pollutants will change in future. Models have attempted to predict how the forecasted scenarios will affect indoor air quality and indoor comfort parameters such as humidity and temperature.
The net-zero challenge requires significant changes in the performance of both new and retrofitted buildings. Increased energy efficient housing (without good ventilation systems) can trap pollutants inside them, whether produced indoors or outdoors, and lead to an increase in human exposure.
Ozone-related health burden
 The relationship between surface ozone (also called
The relationship between surface ozone (also called ground-level ozone
Ground-level ozone (), also known as surface-level ozone and tropospheric ozone, is a trace gas in the troposphere (the lowest level of the atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere), with an average concentration of 20–30 parts per billion by vo ...
) and ambient temperature is complex. Changes in air temperature and water content affect the air's chemistry and the rates of chemical reactions that create and remove ozone. Many chemical reaction rates increase with temperature and lead to increased ozone production. Climate change projections show that rising temperatures and water vapour in the atmosphere will likely increase surface ozone in polluted areas like the eastern United States.[ Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License] Therefore, future surface ozone concentrations depend on the climate change mitigation steps taken (more or less methane emissions) as well as air pollution control steps taken.[Szopa, S., V. Naik, B. Adhikary, P. Artaxo, T. Berntsen, W.D. Collins, S. Fuzzi, L. Gallardo, A. Kiendler-Scharr, Z. Klimont, H. Liao, N. Unger, and P. Zanis, 2021]
Chapter 6: Short-Lived Climate Forcers
I
Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 817–922, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.008.
High surface ozone concentrations often occur during heat waves in the United States.respiratory system
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies grea ...
.[Health Aspects of Air Pollution with Particulate Matter, Ozone and Nitrogen Dioxide](_blank)
. WHO-Europe report 13–15 January 2003 (PDF) Exposure to ozone (and the pollutants that produce it) is linked to premature death
Death is the end of life; the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain a living organism. Death eventually and inevitably occurs in all organisms. The remains of a former organism normally begin to decompose sh ...
, asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
, bronchitis
Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi (large and medium-sized airways) in the lungs that causes coughing. Bronchitis usually begins as an infection in the nose, ears, throat, or sinuses. The infection then makes its way down to the bronchi. ...
, heart attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
, and other cardiopulmonary problems.
Other health risks
Health risks from food and water insecurity
Climate change affects many aspects of food security
Food security is the state of having reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, healthy Human food, food. The availability of food for people of any class, gender, ethnicity, or religion is another element of food protection. Simila ...
through "multiple and interconnected pathways".effects of climate change on agriculture
There are numerous effects of climate change on agriculture, many of which are making it harder for agricultural activities to provide global food security. Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns often result in lower crop yields du ...
, for example failed crops due to more extreme weather events. This comes on top of other coexisting crises that reduce food security in many regions. Less food security means more undernutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a Deficiency (medicine), deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and Vitamin deficiency, other nutrients whic ...
with all its associated health problems. Food insecurity is increasing at the global level (some of the underlying causes are related to climate change, others are not) and about 720–811 million people suffered from hunger in 2020.IPCC Sixth Assessment Report
The Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) of the United Nations (UN) Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is the sixth in a series of reports which assess the available scientific information on climate change. Three Working Groups (WGI, II, ...
does not quantify this number in its chapter on food security.[Bezner Kerr, R., T. Hasegawa, R. Lasco, I. Bhatt, D. Deryng, A. Farrell, H. Gurney-Smith, H. Ju, S. Lluch-Cota, F. Meza, G. Nelson, H. Neufeldt, and P. Thornton, 2022]
Chapter 5: Food, Fibre, and Other Ecosystem Products
In
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.007. A modelling study from 2016 found "a climate change–associated net increase of 529,000 adult deaths worldwide ..from expected reductions in food availability (particularly fruit and vegetables) by 2050, as compared with a reference scenario without climate change."
A headline finding in 2021 regarding marine food security stated that: "In 2018–20, nearly 70% of countries showed increases in average sea surface temperature in their territorial waters compared within 2003–05, reflecting an increasing threat to their marine food productivity and marine food security".
Mental health risks
Pollen allergies
A warming climate can lead to increases of pollen season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's axial tilt, tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperat ...
lengths and concentrations in some regions of the world. For example, in northern mid-latitudes regions, the spring pollen season is now starting earlier.
Reduced nutritional value of crops
Harmful algal blooms in oceans and lakes
 The warming oceans and lakes are leading to more frequent
The warming oceans and lakes are leading to more frequent harmful algal bloom
A harmful algal bloom (HAB), or excessive algae growth, sometimes called a red tide in marine environments, is an algal bloom that causes negative impacts to other organisms by production of natural algae-produced toxins, water deoxygenation, ...
s.blue-green algae
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteria' ...
(cyanobacteria) create neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are toxins that are destructive to nervous tissue, nerve tissue (causing neurotoxicity). Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insult (medical), insultsSpencer 2000 that can adversely affect function ...
s, hepatoxins, cytotoxins or endotoxins that can cause serious and sometimes fatal neurological, liver and digestive diseases in humans. Cyanobacteria grow best in warmer temperatures (especially above 25 degrees Celsius), and so areas of the world that are experiencing general warming as a result of climate change are also experiencing harmful algal blooms more frequently and for longer periods of time.
One of these toxin producing algae is Pseudo-nitzschia fraudulenta. This species produces a substance called domoic acid
Domoic acid (DA) is a kainic acid-type neurotoxin that causes amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP). It is produced by algae and accumulates in shellfish, sardines, and anchovies. When sea lions, otters, cetaceans, humans, and other predators eat cont ...
which is responsible for amnesic shellfish poisoning
Amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP) is an illness caused by consumption of shellfish that contain the marine biotoxin called domoic acid. In mammals, including humans, domoic acid acts as a neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are toxins that are destructive ...
.paralytic shellfish poisoning
Paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) is one of the four recognized syndromes of shellfish poisoning, which share some common features and are primarily associated with bivalve mollusks (such as mussels, clams, oysters and scallops). These shellfi ...
, azaspiracid shellfish poisoning, diarrhetic shellfish poisoning, neurotoxic shellfish poisoning
Neurotoxic shellfish poisoning (NSP) is caused by the consumption of brevetoxins, which are marine toxins produced by the dinoflagellate ''Karenia brevis'' (among several others). These toxins can produce a series of gastrointestinal and neurolo ...
and the above-mentioned amnesic shellfish poisoning.
Potential health benefits
It is possible that a potential health benefit from global warming could result from fewer cold days in winter:
Benefits from climate change mitigation and adaptation
The potential health benefits (also called "co-benefits") from climate change mitigation
Climate change mitigation (or decarbonisation) is action to limit the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that cause climate change. Climate change mitigation actions include energy conservation, conserving energy and Fossil fuel phase-out, repl ...
and adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the p ...
measures are significant, having been described as "the greatest global health opportunity" of the 21st century.air pollution
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the Atmosphere of Earth, air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be Gas, gases like Ground-level ozone, ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles li ...
and associated health benefits) and how it is carried out (in terms of e.g. policymaking) could also determine its effect on living standards (whether and how inequality and poverty are reduced).
There are many health co-benefits associated with climate action. These include those of cleaner air, healthier diets (e.g. less red meat), more active lifestyles, and increased exposure to green urban spaces.[IPCC (2022]
Summary for policy makers
i
Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, United States Biking
Cycling, also known as bicycling or biking, is the activity of riding a bicycle or other types of pedal-driven human-powered vehicles such as balance bikes, unicycles, tricycles, and quadricycles. Cycling is practised around the world fo ...
reduces greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate chan ...
while reducing the effects of a sedentary lifestyle
Sedentary lifestyle is a Lifestyle (social sciences), lifestyle type, in which one is physically inactive and does little or no physical movement and/or exercise. A person living a sedentary lifestyle is often sitting or lying down while enga ...
at the same time According to ''PLoS Medicine'': "obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and cancer, which are in part related to physical inactivity, may be reduced by a switch to low-carbon transport—including walking and cycling."
Future sustainable pathways scenarios may result in an annual reduction of 1.18 million air pollution-related deaths, 5.86 million diet-related deaths, and 1.15 million deaths due to physical inactivity, across nine countries by 2040. These benefits were attributable to the mitigation of direct greenhouse gas emissions and the accompanying actions that reduce exposure to harmful pollutants, as well as improved diets and safe physical activity.well-being
Well-being is what is Intrinsic value (ethics), ultimately good for a person. Also called "welfare" and "quality of life", it is a measure of how well life is going for someone. It is a central goal of many individual and societal endeavors.
...
.
Addressing inequality can assist with climate change mitigation efforts.
Air pollution reduction
Air pollution
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the Atmosphere of Earth, air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be Gas, gases like Ground-level ozone, ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles li ...
generated by fossil fuel combustion is both a major driver of global warming and the cause of a large number of annual deaths with some estimates as high as excess deaths during 2018. Climate change mitigation policies can lead to lower emissions of co-emitted air pollutants, for instance by shifting away from fossil fuel combustion. Gases such as black carbon
Black carbon (BC) is the light-absorbing refractory form of Chemical_element, elemental carbon remaining after pyrolysis (e.g., charcoal) or produced by incomplete combustion (e.g., soot).
Tihomir Novakov originated the term black carbon in ...
and methane contribute both to global warming and to air pollution. Their mitigation can bring benefits in terms of limiting global temperature increases as well as improving air quality. Implementation of the climate pledges made in the run-up to the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (also called the Paris Accords or Paris Climate Accords) is an international treaty on climate change that was signed in 2016. The treaty covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and finance. The Paris Agreement was ...
could therefore have significant benefits for human health by improving air quality.
The replacement of coal-based energy with renewables can lower the number of premature deaths caused by air pollution and decrease health costs associated with coal-related respiratory diseases. This switch to renewable energy is crucial, as air pollution is responsible for over 13 million deaths annually.
Global estimates
 Estimating deaths ( mortality) or DALYs (
Estimating deaths ( mortality) or DALYs (morbidity
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are asso ...
) from the effects of climate change at the global level is very difficult. A 2014 study by the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
estimated the effect of climate change on human health, but not all of the effects of climate change
Effects of climate change are well documented and growing for Earth's natural environment and human societies. Changes to the climate system include an Instrumental temperature record, overall warming trend, Effects of climate change on the ...
were included.diarrhea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
, malaria, dengue, coastal flooding
Coastal flooding occurs when dry and low-lying land is submerged (flooded) by seawater. The range of a coastal Flood, flooding is a result of the elevation of floodwater that penetrates the inland which is controlled by the topography of the coas ...
, and childhood undernutrition. The authors estimated that climate change was projected to cause an additional 250,000 deaths per year between 2030 and 2050 but also stated that "these numbers do not represent a prediction of the overall impacts of climate change on health, since we could not quantify several important causal pathways".diarrhoea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
, 3% of malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
, and 3.8% of dengue fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne disease caused by dengue virus, prevalent in tropical and subtropical areas. Asymptomatic infections are uncommon, mild cases happen frequently; if symptoms appear, they typically begin 3 to 14 days after i ...
deaths worldwide in 2004. Total attributable mortality was about 0.2% of deaths in 2004; of these, 85% were child deaths. The effects of more frequent and extreme storms were excluded from this study.
The health effects of climate change are expected to rise in line with projected ongoing global warming for different climate change scenario
A climate change scenario is a hypothetical future based on a "set of key driving forces".IPCC, 2022Annex I: Glossary an Diemen, R., J.B.R. Matthews, V. Möller, J.S. Fuglestvedt, V. Masson-Delmotte, C. Méndez, A. Reisinger, S. Semenov (eds) In ...
s.
Society and culture
Vulnerability
A 2021 report published in ''The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal, founded in England in 1823. It is one of the world's highest-impact academic journals and also one of the oldest medical journals still in publication.
The journal publishes ...
'' found that climate change does not affect people's health in an equal way. The greatest impact tends to fall on the most vulnerable such as the poor, women, children, the elderly, people with pre-existing health concerns, other minorities and outdoor workers.
Climate justice and climate migrants
Much of the health burden associated with climate change falls on vulnerable people (e.g. indigenous peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
and economically disadvantaged communities). As a result, people of disadvantaged sociodemographic groups experience unequal risks. Often these people will have made a disproportionately low contribution toward man-made global warming, thus leading to concerns over climate justice
Climate justice is a type of environmental justice that focuses on the unequal impacts of climate change on marginalized or otherwise vulnerable populations. Climate justice seeks to achieve an equitable distribution of both the burdens of clima ...
.mental health
Mental health is often mistakenly equated with the absence of mental illness. However, mental health refers to a person's overall emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It influences how individuals think, feel, and behave, and how t ...
. Migration in the context of climate change can be grouped into four types: adaptive migration (see also climate change adaptation
Climate change adaptation is the process of adjusting to the effects of climate change, both current and anticipated.IPCC, 2022Annex II: Glossary[Möller, V., R. van Diemen, J.B.R. Matthews, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, J.S. Fuglestvedt, A. Reisinger ...
), involuntary migration, organised relocation of populations, and immobility (which is when people are unable or unwilling to move even though it is recommended).
Communication strategies
Studies have found that when communicating climate change with the public, it can help encourage engagement if it is framed as a health concern, rather than as an environmental issue. This is especially the case when comparing a health related framing to one that emphasised environmental doom, as was common in the media at least up until 2017.[
] Communicating the ''co-benefits to health'' helps underpin greenhouse gas reduction strategies.climate change adaptation
Climate change adaptation is the process of adjusting to the effects of climate change, both current and anticipated.IPCC, 2022Annex II: Glossary[Möller, V., R. van Diemen, J.B.R. Matthews, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, J.S. Fuglestvedt, A. Reisinger ...
goal.
Connections with public health policies
Due to its significant impact on human health, climate change has become a major concern for public health policy. The United States Environmental Protection Agency had issued a 100-page report on global warming and human health back in 1989.Nairobi
Nairobi is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Kenya. The city lies in the south-central part of Kenya, at an elevation of . The name is derived from the Maasai language, Maasai phrase , which translates to 'place of cool waters', a ...
by UN secretary general
The secretary-general of the United Nations (UNSG or UNSECGEN) is the chief administrative officer of the United Nations and head of the United Nations Secretariat, one of the United Nations System#Six principal organs, six principal organs of ...
Kofi Annan
Kofi Atta Annan (8 April 193818 August 2018) was a Ghanaian diplomat who served as the seventh secretary-general of the United Nations from 1997 to 2006. Annan and the UN were the co-recipients of the 2001 Nobel Peace Prize. He was the founder a ...
. Since 2018, factors such as the 2018 heat wave, the Greta effect and the IPCC's 2018 Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5 °C further increased the urgency for responding to climate change as a global health issue.[ Text was copied from this source, which is available under ]
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
/ref>World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
has suggested a framework that can strengthen health system
A health system, health care system or healthcare system is an organization of people, institutions, and resources that delivers health care services to meet the health needs of target populations.
There is a wide variety of health systems aroun ...
s to make them more resilient and ''climate-sensitive''.
Placing health as a key focus of the Nationally Determined Contributions could present an opportunity to increase ambition and realize health co-benefits.Australian Medical Association
The Australian Medical Association (AMA) is an independent professional association for Australian physician, doctors and medical school#Medical students, medical students. The association is not a government authority and does not regulate or ...
formally declared climate change as a health emergency.
See also
* Effects of climate change on health in the United Kingdom
* Effects of climate change on health in the Philippines
* Effects of climate change
Effects of climate change are well documented and growing for Earth's natural environment and human societies. Changes to the climate system include an Instrumental temperature record, overall warming trend, Effects of climate change on the ...
* Environmental health
Environmental health is the branch of public health concerned with all aspects of the natural environment, natural and built environment affecting human health. To effectively control factors that may affect health, the requirements for a hea ...
* Occupational heat stress
* Water security
The aim of water security is to maximize the benefits of water for humans and ecosystems. The second aim is to limit the risks of destructive impacts of water to an acceptable level. These risks include too much water (flood), too little water (d ...
References
External links
Public health and climate change (''Lancet'')
Climate change and health (World Health Organization)
{{Portal bar, Climate change, Medicine
Effects of climate change
Global health
Climate change and society
Health effects by subject
Environment and health
Health economics
Health education
 Exposure to extreme heat poses an acute health hazard, especially for people deemed as vulnerable. Vulnerable people with regard to
Exposure to extreme heat poses an acute health hazard, especially for people deemed as vulnerable. Vulnerable people with regard to  The effects of heatwaves tend to be more pronounced in urban areas because they are typically warmer than surrounding rural areas due to the
The effects of heatwaves tend to be more pronounced in urban areas because they are typically warmer than surrounding rural areas due to the  The warming oceans and lakes are leading to more frequent
The warming oceans and lakes are leading to more frequent  Estimating deaths ( mortality) or DALYs (
Estimating deaths ( mortality) or DALYs (