Circuit Schematics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A circuit diagram (or: wiring diagram, electrical diagram, elementary diagram, electronic schematic) is a graphical representation of an
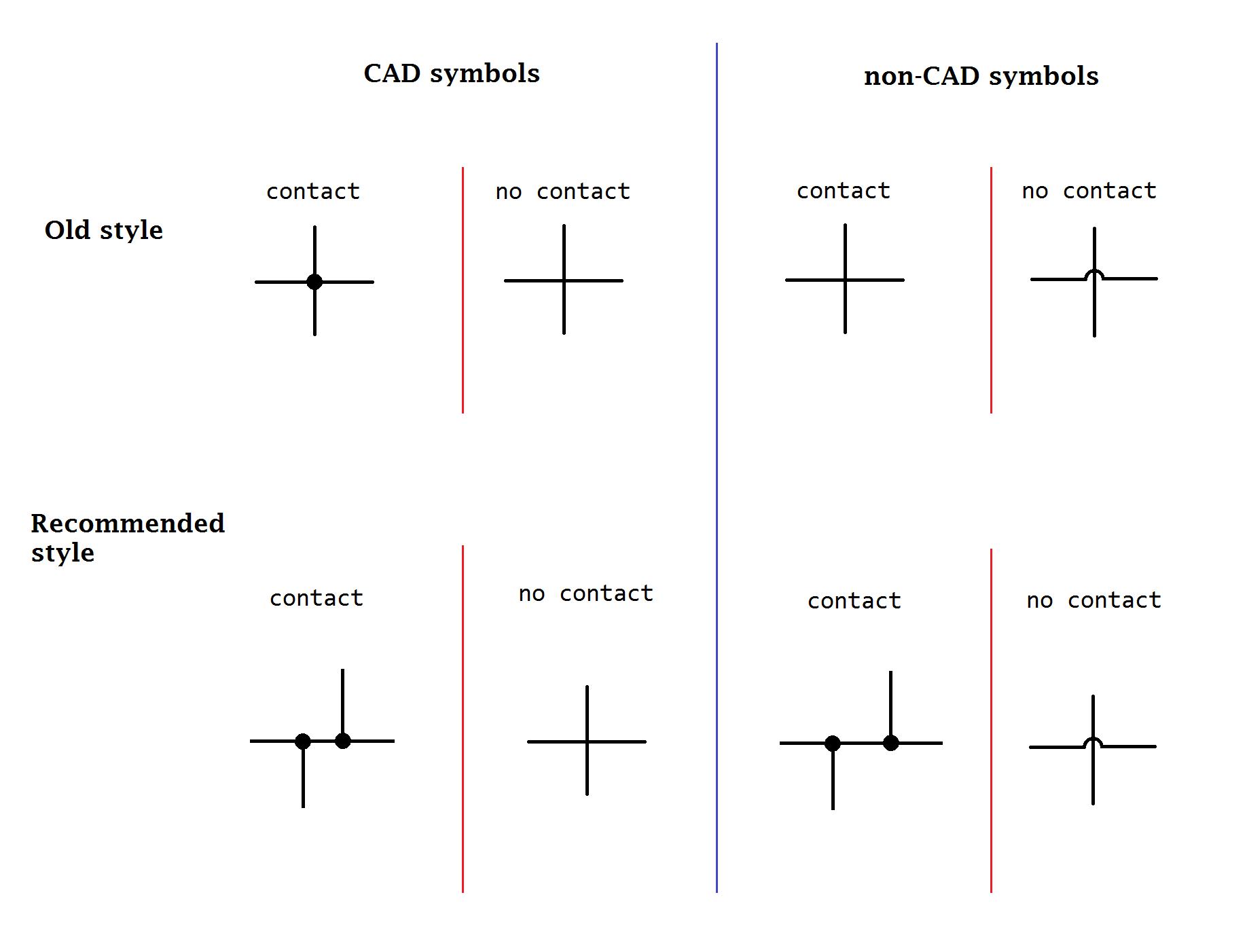 The linkages between leads were once simple crossings of lines. With the arrival of computerized drafting, the connection of two intersecting wires was shown by a crossing of wires with a "dot" or "blob" to indicate a connection. At the same time, the crossover was simplified to be the same crossing, but without a "dot". However, there was a danger of confusing the wires that were connected and not connected in this manner, if the dot was drawn too small or accidentally omitted (e.g. the "dot" could disappear after several passes through a copy machine). As such, the modern practice for representing a 4-way wire connection is to draw a straight wire and then to draw the other wires staggered along it with "dots" as connections (see diagram), so as to form two separate T-junctions that brook no confusion and are clearly not a crossover.
For crossing wires that are insulated from one another, a small semi-circle symbol is commonly used to show one wire "jumping over" the other wire (similar to how jumper wires are used).
A common, hybrid style of drawing combines the T-junction crossovers with "dot" connections and the wire "jump" semi-circle symbols for insulated crossings. In this manner, a "dot" that is too small to see or that has accidentally disappeared can still be clearly differentiated from a "jump".
On a circuit diagram, the
The linkages between leads were once simple crossings of lines. With the arrival of computerized drafting, the connection of two intersecting wires was shown by a crossing of wires with a "dot" or "blob" to indicate a connection. At the same time, the crossover was simplified to be the same crossing, but without a "dot". However, there was a danger of confusing the wires that were connected and not connected in this manner, if the dot was drawn too small or accidentally omitted (e.g. the "dot" could disappear after several passes through a copy machine). As such, the modern practice for representing a 4-way wire connection is to draw a straight wire and then to draw the other wires staggered along it with "dots" as connections (see diagram), so as to form two separate T-junctions that brook no confusion and are clearly not a crossover.
For crossing wires that are insulated from one another, a small semi-circle symbol is commonly used to show one wire "jumping over" the other wire (similar to how jumper wires are used).
A common, hybrid style of drawing combines the T-junction crossovers with "dot" connections and the wire "jump" semi-circle symbols for insulated crossings. In this manner, a "dot" that is too small to see or that has accidentally disappeared can still be clearly differentiated from a "jump".
On a circuit diagram, the
 Once the schematic has been made, it is converted into a layout that can be fabricated onto a printed circuit board (PCB).
Once the schematic has been made, it is converted into a layout that can be fabricated onto a printed circuit board (PCB).
Going with the flow: Using analogies to explain electric circuits
. School science review, 97(361), 51–58.
electrical circuit
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., battery (electricity), batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e. ...
. A pictorial
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be displayed through other media, including a project ...
circuit diagram uses simple images of components, while a schematic diagram
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the sc ...
shows the components and interconnections of the circuit using standardized symbolic representations. The presentation of the interconnections between circuit components in the schematic diagram does not necessarily correspond to the physical arrangements in the finished device.
Unlike a block diagram
A block diagram is a diagram of a system in which the principal parts or functions are represented by blocks connected by lines that show the relationships of the blocks.
or layout diagram, a circuit diagram shows the actual electrical connection
Components of an electrical circuit are electrically connected if an electric current can run between them through an electrical conductor. An electrical connector is an electromechanical device used to create an electrical connection betwee ...
s. A drawing meant to depict the physical arrangement of the wires and the components they connect is called ''artwork'' or ''layout
In general terms, a layout is a structured arrangement of items within certain limits, or a plan for such arrangement.
Specifically, layout may refer to:
* Page layout, the arrangement of visual elements on a page
** Comprehensive layout (comp), ...
'', ''physical design'', or ''wiring diagram
A wiring diagram is a simplified conventional pictorial representation of an electrical circuit. It shows the components of the circuit as simplified shapes, and the power and signal connections between the devices.
A wiring diagram usually ...
''.
Circuit diagrams are used for the design (circuit design
In electrical engineering, the process of circuit design can cover systems ranging from complex electronic systems down to the individual transistors within an integrated circuit. One person can often do the design process without needing a pl ...
), construction (such as PCB
PCB may refer to:
Science and technology
* Polychlorinated biphenyl, an organic chlorine compound, now recognized as an environmental toxin and classified as a persistent organic pollutant
* Printed circuit board, a board used in electronics
* P ...
layout), and maintenance of electrical and electronic equipment.
In computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
, circuit diagrams are useful when visualizing expressions using Boolean algebra
In mathematics and mathematical logic, Boolean algebra is a branch of algebra. It differs from elementary algebra in two ways. First, the values of the variable (mathematics), variables are the truth values ''true'' and ''false'', usually denot ...
.
Symbols
Circuit diagrams are pictures with symbols that have differed from country to country and have changed over time, but are now to a large extent internationally standardized. Simple components often had symbols intended to represent some feature of the physical construction of the device. For example, the symbol for a resistor dates back to the time when that component was made from a long piece of wire wrapped in such a manner as to not produce inductance, which would have made it a coil. These wirewound resistors are now used only in high-power applications, smaller resistors being cast from ''carbon composition'' (a mixture ofcarbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
and filler) or fabricated as an insulating tube or chip coated with a metal film. The internationally standardized symbol for a resistor is therefore now simplified to an oblong, sometimes with the value in ohm
Ohm (symbol Ω) is a unit of electrical resistance named after Georg Ohm.
Ohm or OHM may also refer to:
People
* Georg Ohm (1789–1854), German physicist and namesake of the term ''ohm''
* Germán Ohm (born 1936), Mexican boxer
* Jörg Ohm (1 ...
s written inside, instead of the zig-zag symbol. A less common symbol is simply a series of peaks on one side of the line representing the conductor, rather than back-and-forth.
 The linkages between leads were once simple crossings of lines. With the arrival of computerized drafting, the connection of two intersecting wires was shown by a crossing of wires with a "dot" or "blob" to indicate a connection. At the same time, the crossover was simplified to be the same crossing, but without a "dot". However, there was a danger of confusing the wires that were connected and not connected in this manner, if the dot was drawn too small or accidentally omitted (e.g. the "dot" could disappear after several passes through a copy machine). As such, the modern practice for representing a 4-way wire connection is to draw a straight wire and then to draw the other wires staggered along it with "dots" as connections (see diagram), so as to form two separate T-junctions that brook no confusion and are clearly not a crossover.
For crossing wires that are insulated from one another, a small semi-circle symbol is commonly used to show one wire "jumping over" the other wire (similar to how jumper wires are used).
A common, hybrid style of drawing combines the T-junction crossovers with "dot" connections and the wire "jump" semi-circle symbols for insulated crossings. In this manner, a "dot" that is too small to see or that has accidentally disappeared can still be clearly differentiated from a "jump".
On a circuit diagram, the
The linkages between leads were once simple crossings of lines. With the arrival of computerized drafting, the connection of two intersecting wires was shown by a crossing of wires with a "dot" or "blob" to indicate a connection. At the same time, the crossover was simplified to be the same crossing, but without a "dot". However, there was a danger of confusing the wires that were connected and not connected in this manner, if the dot was drawn too small or accidentally omitted (e.g. the "dot" could disappear after several passes through a copy machine). As such, the modern practice for representing a 4-way wire connection is to draw a straight wire and then to draw the other wires staggered along it with "dots" as connections (see diagram), so as to form two separate T-junctions that brook no confusion and are clearly not a crossover.
For crossing wires that are insulated from one another, a small semi-circle symbol is commonly used to show one wire "jumping over" the other wire (similar to how jumper wires are used).
A common, hybrid style of drawing combines the T-junction crossovers with "dot" connections and the wire "jump" semi-circle symbols for insulated crossings. In this manner, a "dot" that is too small to see or that has accidentally disappeared can still be clearly differentiated from a "jump".
On a circuit diagram, the symbols
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise different concep ...
for components are labelled with a descriptor or reference designator matching that on the list of parts. For example, C1 is the first capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
, L1 is the first inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a Passivity (engineering), passive two-terminal electronic component, electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it. An inductor typic ...
, Q1 is the first transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
, and R1 is the first resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electronic component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active e ...
. Often the value or type designation of the component is given on the diagram beside the part, but detailed specifications would go on the parts list.
Detailed rules for reference designations are provided in the International standard IEC 61346
International Standard IEC/ISO 81346 series "Industrial systems, installations and equipment and industrial products – structuring principles and reference designations" defines the rules for reference designation systems (RDS). It is publis ...
.
Organization
It is a usual (although not universal) convention that schematic drawings are organized on the page from left to right and top to bottom in the same sequence as the flow of the mainsignal
A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of data over some media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processing, information theory and biology.
In ...
or power path. For example, a schematic for a radio receiver might start with the antenna input at the left of the page and end with the loudspeaker at the right. Positive power supply connections for each stage would be shown towards the top of the page, with grounds, negative supplies, or other return paths towards the bottom. Schematic drawings intended for maintenance may have the principal signal paths highlighted to assist in understanding the signal flow through the circuit. More complex devices have multi-page schematics and must rely on cross-reference symbols to show the flow of signals between the different sheets of the drawing.
Detailed rules for the preparation of circuit diagrams, and other document types used in electrotechnology, are provided in the international standard IEC
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; ) is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies. IEC standards cover a vast range of ...
61082-1.
Circuit diagrams are often drawn with the same standardized title block and frame as other engineering drawing
An engineering drawing is a type of technical drawing that is used to convey information about an object. A common use is to specify the geometry necessary for the construction of a component and is called a detail drawing. Usually, a number of ...
s.
Relay logic
Relay logic is a method of implementing combinational logic in electrical control circuits by using several electrical relays wired in a particular configuration.
Ladder logic
The schematic diagrams for relay logic circuits are often called ...
line diagrams, also called ladder logic
Ladder logic was originally a written method to document the design and construction of relay logic, relay racks as used in manufacturing and process control. Each device in the relay rack would be represented by a symbol on the ladder diagram w ...
diagrams, use another common standardized convention for organizing schematic drawings, with a vertical power supply rail on the left and another on the right, and components strung between them like the rungs of a ladder.
Artwork
Schematic-driven layout
Schematic driven layout is the concept in integrated circuit layout or PCB
PCB may refer to:
Science and technology
* Polychlorinated biphenyl, an organic chlorine compound, now recognized as an environmental toxin and classified as a persiste ...
starts with the process of schematic capture
Schematic capture or schematic entry is a step in the design cycle of electronic design automation (EDA) at which the electronic diagram, or electronic schematic of the designed electronic circuit, is created by a designer. This is done interac ...
. The result is what is known as a . The rat's nest is a jumble of wires (lines) criss-crossing each other to their destination nodes. These wires are routed either manually or automatically by the use of electronics design automation (EDA) tools. The EDA tools arrange and rearrange the placement of components and find paths for tracks to connect various nodes. This results in the final layout
In general terms, a layout is a structured arrangement of items within certain limits, or a plan for such arrangement.
Specifically, layout may refer to:
* Page layout, the arrangement of visual elements on a page
** Comprehensive layout (comp), ...
artwork for the integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
or printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes ...
.
A generalized design flow may be as follows:
:Schematic → schematic capture → netlist
In electronic design, a netlist is a description of the connectivity of an electronic circuit. In its simplest form, a netlist consists of a list of the electronic components in a circuit and a list of the nodes they are connected to. A netwo ...
→ rat's nest → routing
Routing is the process of selecting a path for traffic in a Network theory, network or between or across multiple networks. Broadly, routing is performed in many types of networks, including circuit-switched networks, such as the public switched ...
→ artwork → PCB development and etching → component mounting → testing
Education
Teaching about the functioning of electrical circuits is often on primary and secondary school curricula. Students are expected to understand the rudiments of circuit diagrams and their functioning. Use of diagrammatic representations of circuit diagrams can aid understanding of principles of electricity. Principles of the physics of circuit diagrams are often taught with the use of analogies, such as comparing functioning of circuits to other closed systems such aswater heating
Water heating is a heat transfer process that uses an energy source to heat water above its initial temperature. Typical domestic uses of hot water include cooking, cleaning, bathing, and space heating. In industry, hot water and water heated t ...
systems with pumps being the equivalent to batteries.Walker, M. D., & Garlovsky, D. (2016)Going with the flow: Using analogies to explain electric circuits
. School science review, 97(361), 51–58.
See also
* Boxology * Circuit design language *Electronic symbol
An electronic symbol is a pictogram used to represent various electrical and electronic devices or functions, such as wires, batteries, resistors, and transistors, in a schematic diagram of an electrical or electronic circuit. These symbols are ...
* Logic gate
A logic gate is a device that performs a Boolean function, a logical operation performed on one or more binary inputs that produces a single binary output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate, one that has, for ...
* One-line diagram
In power engineering, a single-line diagram (SLD), also sometimes called one-line diagram, is a simplest symbolic representation of an electric power system.
A single line in the diagram typically corresponds to more than one physical conductor ...
* Pinout
In electronics, a pinout (sometimes written "pin-out") is a cross-reference between the contacts, or ''pins'', of an electrical connector or electronic component, and their functions. "Pinout" now supersedes the term "basing diagram" which was the ...
* Schematic capture
Schematic capture or schematic entry is a step in the design cycle of electronic design automation (EDA) at which the electronic diagram, or electronic schematic of the designed electronic circuit, is created by a designer. This is done interac ...
* Schematic editor
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the sc ...
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Circuit Diagram Electrical diagrams Electronic design Diagrams