Church Governance on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Ecclesiastical polity is the government of a church. There are local (
Ecclesiastical polity is the government of a church. There are local (
 Churches having episcopal polity are governed by
Churches having episcopal polity are governed by  Episcopal polity is the predominant pattern in
Episcopal polity is the predominant pattern in
 Many
Many
 Many
Many  Presbyterian ''polity'' and the Presbyterian ''tradition'' are not identical. Continental reformed churches (e.g. Dutch) can also be described as presbyterian, with a few key differences. Continental churches that historically follow the
Presbyterian ''polity'' and the Presbyterian ''tradition'' are not identical. Continental reformed churches (e.g. Dutch) can also be described as presbyterian, with a few key differences. Continental churches that historically follow the
Church Order of Dordrecht
' (1618/1619) will, in general, consider their levels of government "broader" rather than "higher" courts. Additionally, the reformed classis is a temporary, delegated body, so the minister is firstly a member of his congregation as opposed to the standing presbytery. The
 Congregational polity is historically
Congregational polity is historically  Churches with congregational polity include
Churches with congregational polity include
 Other religious organizations, for example
Other religious organizations, for example
A study of religious authority (especially pp. 97–218) as well as the secular authority of the state. *
A study of the conflict and prestige of episcopal church authority with other forms of church polity as they affect inter-Christian relations and ecumenism.
Ecclesiastical polity
at the ''
 Ecclesiastical polity is the government of a church. There are local (
Ecclesiastical polity is the government of a church. There are local (congregational
Congregationalism (also Congregational Churches or Congregationalist Churches) is a Reformed Christianity, Reformed Christian (Calvinist) tradition of Protestant Christianity in which churches practice Congregationalist polity, congregational ...
) forms of organization as well as denominational. A church's polity may describe its ministerial offices or an authority structure between churches. Polity relates closely to ecclesiology
In Christian theology, ecclesiology is the study of the Church, the origins of Christianity, its relationship to Jesus, its role in salvation, its polity, its discipline, its eschatology, and its leadership.
In its early history, one of th ...
, the theological
Theology is the study of religious belief from a religious perspective, with a focus on the nature of divinity. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of an ...
study of the church.
History
Questions of church government were documented early on in the first chapters of theActs of the Apostles
The Acts of the Apostles (, ''Práxeis Apostólōn''; ) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of The gospel, its message to the Roman Empire.
Acts and the Gospel of Luke make u ...
and "theological debate about the nature, location, and exercise of authority, in the church" has been ongoing ever since. The first act recorded after the Ascension of Jesus Christ
The Ascension of Jesus (anglicized from the Vulgate ) is the Christian and Islamic belief that Jesus ascended to Heaven. Christian doctrine, as reflected in the major Christian creeds and confessional statements, holds that Jesus ascended afte ...
was the election of Saint Matthias
Matthias (; Koine Greek: , , from Hebrew ; ; died ) was, according to the Acts of the Apostles, chosen by God through the apostles to replace Judas Iscariot following the latter's betrayal of Jesus and his subsequent death. His calling as ...
as one of the Twelve Apostles
In Christian theology and ecclesiology, the apostles, particularly the Twelve Apostles (also known as the Twelve Disciples or simply the Twelve), were the primary disciples of Jesus according to the New Testament. During the life and minist ...
, to replace Judas Iscariot
Judas Iscariot (; ; died AD) was, according to Christianity's four canonical gospels, one of the original Twelve Apostles of Jesus Christ. Judas betrayed Jesus to the Sanhedrin in the Garden of Gethsemane, in exchange for thirty pieces of sil ...
.
During the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the papacy and ...
, reformers asserted that the New Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianit ...
prescribed an ecclesiastical government different from the episcopal polity maintained by the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, and consequently different Protestant bodies organized into different types of polities. During this period Richard Hooker
Richard Hooker (25 March 1554 – 2 November 1600) was an English priest in the Church of England and an influential theologian.''The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church'' by F. L. Cross (Editor), E. A. Livingstone (Editor) Oxford Univer ...
wrote ''Of the Laws of Ecclesiastical Polity
Richard Hooker (25 March 1554 – 2 November 1600) was an English priest in the Church of England and an influential theologian.''The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church'' by F. L. Cross (Editor), E. A. Livingstone (Editor) Oxford Univer ...
'', the first volumes of which were published in 1594, to defend the polity of the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
against Puritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to rid the Church of England of what they considered to be Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should b ...
objections. It is from the title of this work that the term ''ecclesiastical polity'' may have originated. With respect to ecclesiology
In Christian theology, ecclesiology is the study of the Church, the origins of Christianity, its relationship to Jesus, its role in salvation, its polity, its discipline, its eschatology, and its leadership.
In its early history, one of th ...
, Hooker preferred the term ''polity'' to ''government'' as the former term "containeth both hegovernment and also whatsoever besides belongeth to the ordering of the Church in public."
Types
There are four general types of polity: episcopal, connexional,presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a historically Reformed Protestant tradition named for its form of church government by representative assemblies of elders, known as "presbyters". Though other Reformed churches are structurally similar, the word ''Pr ...
, and congregational
Congregationalism (also Congregational Churches or Congregationalist Churches) is a Reformed Christianity, Reformed Christian (Calvinist) tradition of Protestant Christianity in which churches practice Congregationalist polity, congregational ...
.
Episcopal polity
 Churches having episcopal polity are governed by
Churches having episcopal polity are governed by bishop
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...
s. The title bishop comes from the Greek word , which translates as ''overseer''. In the Catholic Church, bishops have authority over the diocese
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, prov ...
, which is both sacramental and political; as well as performing ordination
Ordination is the process by which individuals are Consecration in Christianity, consecrated, that is, set apart and elevated from the laity class to the clergy, who are thus then authorized (usually by the religious denomination, denominationa ...
s, confirmation
In Christian denominations that practice infant baptism, confirmation is seen as the sealing of the covenant (religion), covenant created in baptism. Those being confirmed are known as confirmands. The ceremony typically involves laying on o ...
s, and consecration
Sacred describes something that is dedicated or set apart for the service or worship of a deity; is considered worthy of spiritual respect or devotion; or inspires awe or reverence among believers. The property is often ascribed to objects ( ...
s, the bishop supervises the clergy
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
of the diocese and represents the diocese both secularly and in the hierarchy of church governance.
Bishops may be subject to higher ranking bishops (variously called archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
s, metropolitans or patriarch
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Roman Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholic Churches are termed patriarchs (and ...
s, depending upon the tradition; ''see article Bishop
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...
'') They also meet in councils or synod
A synod () is a council of a Christian denomination, usually convened to decide an issue of doctrine, administration or application. The word '' synod'' comes from the Ancient Greek () ; the term is analogous with the Latin word . Originally, ...
s. These synods, subject to precedency by higher ranking bishops, may govern the dioceses which are represented in the council, though the synod
A synod () is a council of a Christian denomination, usually convened to decide an issue of doctrine, administration or application. The word '' synod'' comes from the Ancient Greek () ; the term is analogous with the Latin word . Originally, ...
may also be purely advisory. In episcopal polity, ''presbyter
Presbyter () is an honorific title for Christian clergy. The word derives from the Greek ''presbyteros'', which means elder or senior, although many in Christian antiquity understood ''presbyteros'' to refer to the bishop functioning as overseer ...
'' (elder) refers to a priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deity, deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in parti ...
.
Churches governed by episcopacy do not simply adhere to a chain of command
A command hierarchy is a group of people who carry out orders based on others' authority within the group.
Military chain of command
In a military context, the chain of command is the line of authority and responsibility along which orders ...
. Instead, some authority may be held by synods and colleges of bishops, and other authority by lay and clerical
Clerical may refer to:
* Pertaining to the clergy
* Pertaining to a clerical worker
* Clerical script, a style of Chinese calligraphy
* Clerical People's Party
See also
* Cleric (disambiguation)
* Clerk (disambiguation)
{{disambiguation ...
councils. Patterns of authority are subject to a wide variety of historical rights and honours which may cut across simple lines of authority.
 Episcopal polity is the predominant pattern in
Episcopal polity is the predominant pattern in Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
, Oriental Orthodox
The Oriental Orthodox Churches are Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christian churches adhering to Miaphysitism, Miaphysite Christology, with approximately 50 million members worldwide. The Oriental Orthodox Churches adhere to the Nicene Christian ...
, and Anglican
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
churches. It is common in some Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a Protestant Christianity, Christian Christian tradition, tradition whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's brother ...
and Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
churches, as well as amongst some of the African-American Pentecostal
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a movement within the broader Evangelical wing of Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes direct personal experience of God in Christianity, God through Baptism with the Holy Spirit#Cl ...
traditions such as the Church of God in Christ
The Church of God in Christ (COGIC) is an international Christian perfection#Holiness Pentecostalism, Holiness–Pentecostal Christian denomination, and a large Pentecostal denomination in the United States. Although an international and multi ...
and the Full Gospel Baptist Church Fellowship.Connexional polity
 Many
Many Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a Protestant Christianity, Christian Christian tradition, tradition whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's brother ...
and Wesleyan
Wesleyan theology, otherwise known as Wesleyan–Arminian theology, or Methodist theology, is a theological tradition in Protestant Christianity based upon the ministry of the 18th-century evangelical reformer brothers John Wesley and Charle ...
churches use a derivative of episcopalianism known as connexional polity. It emphasizes essential interdependence through fellowship, consultation, government and oversight. Some Methodist churches have bishops
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...
, but those individuals are not nearly as powerful as in episcopal churches.
Connexionalism is sometimes identified as an organization, while other times as relationship or theological principle. The United Methodist Church
The United Methodist Church (UMC) is a worldwide mainline Protestant Christian denomination, denomination based in the United States, and a major part of Methodism. In the 19th century, its main predecessor, the Methodist Episcopal Church, was ...
defines ''connection'' as the principle that "all leaders and congregations are connected in a network of loyalties and commitments that support, yet supersede, local concerns."
A minority of Methodist denominations use another non-connexional form of government, such as the Congregational Methodist Church.
Presbyterian polity
 Many
Many Reformed church
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Christian, Presbyterian, ...
es are governed by a hierarchy of councils (or ''courts''). The lowest level council governs a single local church and is called the '' session'' or ''consistory
Consistory is the anglicized form of the consistorium, a council of the closest advisors of the Roman emperors. It can also refer to:
*A papal consistory, a formal meeting of the Sacred College of Cardinals of the Roman Catholic Church
*Consistor ...
''; its members are called '' elders''. The minister of the church (sometimes referred to as a ''teaching elder'') is a member of and presides over the session; lay representatives (''ruling elders'' or, informally, just elders) are elected by the congregation. The session sends representatives to the next level higher council, called the '' presbytery'' or ''classis''. In some Presbyterian churches there are higher level councils (synod
A synod () is a council of a Christian denomination, usually convened to decide an issue of doctrine, administration or application. The word '' synod'' comes from the Ancient Greek () ; the term is analogous with the Latin word . Originally, ...
s or general assemblies). Each council has authority over its constituents, and the representatives at each level are expected to use their own judgment. For example, each session approves and installs its own elders, and each presbytery approves the ministers serving within its territory and the connections between those ministers and particular congregations. Hence higher level councils act as courts of appeal for church trials and disputes, and it is not uncommon to see rulings and decisions overturned.
 Presbyterian ''polity'' and the Presbyterian ''tradition'' are not identical. Continental reformed churches (e.g. Dutch) can also be described as presbyterian, with a few key differences. Continental churches that historically follow the
Presbyterian ''polity'' and the Presbyterian ''tradition'' are not identical. Continental reformed churches (e.g. Dutch) can also be described as presbyterian, with a few key differences. Continental churches that historically follow the Church Order of Dordrecht
' (1618/1619) will, in general, consider their levels of government "broader" rather than "higher" courts. Additionally, the reformed classis is a temporary, delegated body, so the minister is firstly a member of his congregation as opposed to the standing presbytery. The
Episcopal Church in the United States of America
The Episcopal Church (TEC), also known as the Protestant Episcopal Church in the United States of America (PECUSA), is a member of the worldwide Anglican Communion, based in the United States. It is a mainline Protestant denomination and is ...
arguably contains a kind of lay presbyterian polity. Governance by bishops is paralleled by a system of deputies, who are lay and clerical representatives elected by parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christianity, Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest#Christianity, priest, often termed a parish pries ...
es and, at the national level, by the dioceses. Legislation in the general convention requires the separate consent of the bishops and of the deputies.
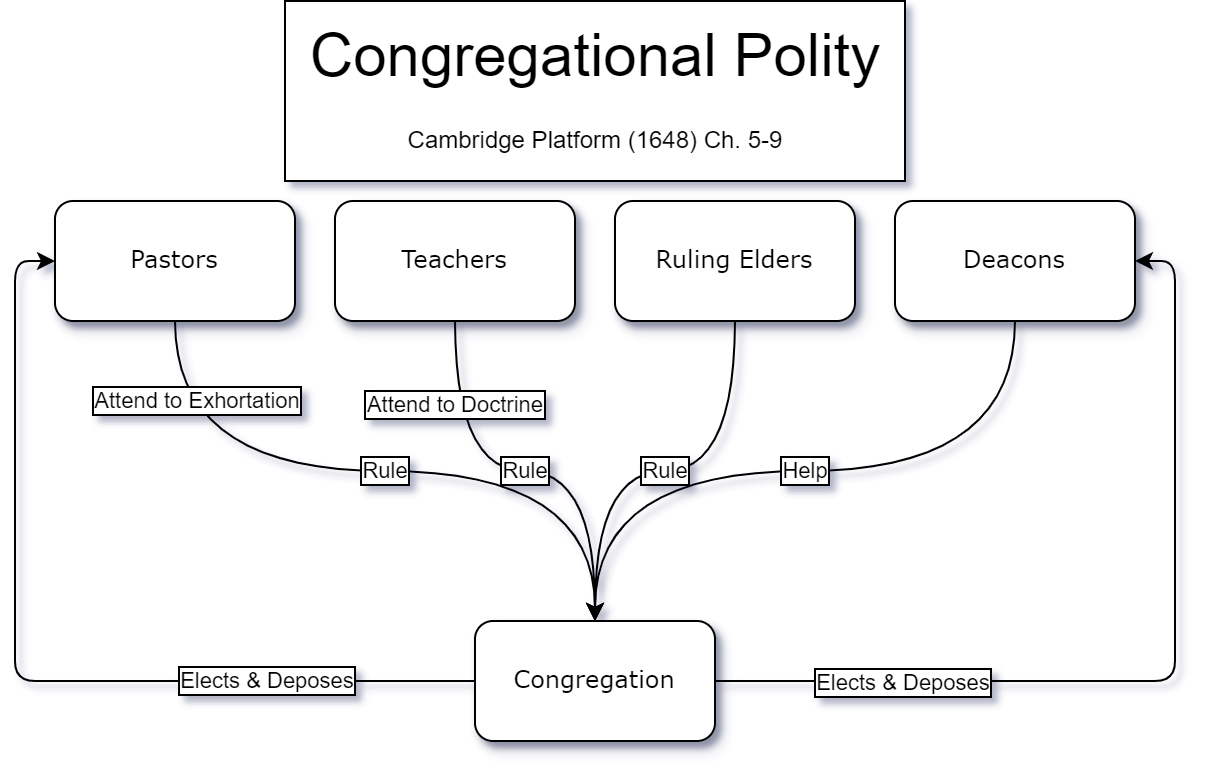
Congregational polity
 Congregational polity is historically
Congregational polity is historically reformed
Reform is beneficial change.
Reform, reformed or reforming may also refer to:
Media
* ''Reform'' (album), a 2011 album by Jane Zhang
* Reform (band), a Swedish jazz fusion group
* ''Reform'' (magazine), a Christian magazine
Places
* Reform, Al ...
, like presbyterianism, but retains the autonomy (lit. self-rule) of the local church. Congregational churches
Congregationalism (also Congregational Churches or Congregationalist Churches) is a Reformed Christianity, Reformed Christian (Calvinist) tradition of Protestant Christianity in which churches practice Congregationalist polity, congregational ...
dispense titles such as "Popes, Patriarchs, Cardinals, Arch-Bishops, Lord-Bishops, Arch-Deacons, Officials, Commissaries, and the like". The congregation has its being without any ministers and is enabled to elect and install its own officers. Ordination
Ordination is the process by which individuals are Consecration in Christianity, consecrated, that is, set apart and elevated from the laity class to the clergy, who are thus then authorized (usually by the religious denomination, denominationa ...
may involve officers of other churches, especially when the church participates in a local vicinage, association, or convention. Broader assemblies formed by delegates from congregationally governed churches (e.g. the Southern Baptist Convention
The Southern Baptist Convention (SBC), alternatively the Great Commission Baptists (GCB), is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is the world's largest Baptist organization, the largest Protestant, and the second-largest Chr ...
) do not have power to rule their constituents.
The number of offices in the church generally ranges from two (elder & deacon) to four (pastor, teacher, ruling elder & deacon) in congregational churches.
 Churches with congregational polity include
Churches with congregational polity include Congregationalists
Congregationalism (also Congregational Churches or Congregationalist Churches) is a Reformed Christian (Calvinist) tradition of Protestant Christianity in which churches practice congregational government. Each congregation independently a ...
, Baptists
Baptists are a Christian denomination, denomination within Protestant Christianity distinguished by baptizing only professing Christian believers (believer's baptism) and doing so by complete Immersion baptism, immersion. Baptist churches ge ...
, Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to the Religious Society of Friends, a historically Protestantism, Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations. Members refer to each other as Friends after in the Bible, and originally ...
and much of Non-denominational Christianity
Non-denominational Christianity (or nondenominational Christianity) consists of churches, and individual Christians, which typically distance themselves from the confessionalism or creedalism of other Christian communities by not formally align ...
. Congregational polity is sometimes called ''Baptist polity'' because of the relative prevalence of Baptists.
Historic statements of congregational polity include the Cambridge Platform
The Cambridge Platform is a statement of congregational church government for the churches of colonial New England. It was written in 1648 in response to Presbyterian criticism and served as the religious constitution of Massachusetts until 1780 ...
, Savoy Declaration
The Savoy Declaration is a Congregationalist confession of faith. Its full title is ''A Declaration of the Faith and Order owned and practised in the Congregational Churches in England.'' It was drawn up in October 1658 by English Independents a ...
, Saybrook Platform
The Saybrook Platform was a constitution for the Congregational church in Connecticut in the 18th century.
Historical context
Religious and civic leaders in Connecticut around 1700 were distressed by the colony-wide decline in personal religiou ...
and Second London Confession.
As a "self-governed voluntary institution", it could be considered a type of religious anarchism
Anarchism is a political philosophy and Political movement, movement that seeks to abolish all institutions that perpetuate authority, coercion, or Social hierarchy, hierarchy, primarily targeting the state (polity), state and capitalism. A ...
.
Other forms
 Other religious organizations, for example
Other religious organizations, for example Seventh-day Adventist
The Seventh-day Adventist Church (SDA) is an Adventist Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the seventh day of the week in the Christian (Gregorian) and the Hebrew calendar, as the Sabbat ...
, Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a Christian denomination that is an outgrowth of the Bible Student movement founded by Charles Taze Russell in the nineteenth century. The denomination is nontrinitarian, millenarian, and restorationist. Russell co-fou ...
, the Salvation Army
The Salvation Army (TSA) is a Protestantism, Protestant Christian church and an international charitable organisation headquartered in London, England. It is aligned with the Wesleyan-Holiness movement. The organisation reports a worldwide m ...
, and the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Restorationism, restorationist Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, denomination and the ...
(LDS Church), are unique. Some have hierarchies similar to an episcopal polity, but may be more complex, with additional levels. Leaders are not always called ''bishops'', in some cases they have secular-like titles such as ''president'' or ''overseer''. The term ''bishop'' may be used to describe functionaries in minor leadership roles, such as a leader of an individual congregation; it may also be used as an honorific, particularly within the Holiness movement
The Holiness movement is a Christianity, Christian movement that emerged chiefly within 19th-century Methodism, and to a lesser extent influenced other traditions such as Quakers, Quakerism, Anabaptism, and Restorationism. Churches aligned with ...
.
Polity, autonomy, and ecumenism
Although a church's polity determines its ministers and discipline, it need not affect relations with other Christian organizations. The unity of a church is an essentialdoctrine
Doctrine (from , meaning 'teaching, instruction') is a codification (law), codification of beliefs or a body of teacher, teachings or instructions, taught principles or positions, as the essence of teachings in a given branch of knowledge or in a ...
of ecclesiology
In Christian theology, ecclesiology is the study of the Church, the origins of Christianity, its relationship to Jesus, its role in salvation, its polity, its discipline, its eschatology, and its leadership.
In its early history, one of th ...
, but because the divisions between churches presuppose the absence of mutual authority, internal polity does not directly answer how these divisions are treated.
For example, among churches of episcopal polity, different theories are expressed:
* In Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
, the various churches retain autonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy is the capacity to make an informed, uncoerced decision. Autonomous organizations or institutions are independent or self-governing. Autonomy can also be ...
but are held to be unified by common doctrine and conciliarity
Conciliarity is the adherence of various Christian communities to the authority of ecumenical councils and to synodal church governance. It is not to be confused with conciliarism, which is a particular historical movement within the Catholi ...
, i. e., subjection to the authority of councils, such as ecumenical council
An ecumenical council, also called general council, is a meeting of bishops and other church authorities to consider and rule on questions of Christian doctrine, administration, discipline, and other matters in which those entitled to vote are ...
s, Holy Synod
In several of the autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Churches and Eastern Catholic Churches, the patriarch or head bishop is elected by a group of bishops called the Holy Synod. For instance, the Holy Synod is a ruling body of the Georgian Orthodox ...
s, and the former standing council, the Endemusa Synod.
* The Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
understands herself as a single polity whose supreme earthly authority is the Supreme Pontiff
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the pope was the sovereign or head of sta ...
(Pope).
* In Anglicanism
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
, the churches are autonomous, though the majority of members are organizationally united in the Anglican Communion
The Anglican Communion is a Christian Full communion, communion consisting of the Church of England and other autocephalous national and regional churches in full communion. The archbishop of Canterbury in England acts as a focus of unity, ...
, which has no governmental authority.
Plurality and singularity
A ''plurality of elders'' is considered desirable in some (esp. reformed) traditions, preferring two or more officers in the local church. This contrasts with singular models often found in Roman Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, and Anglican churches, or the "pastor/president" system of someProtestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
churches. This is commonly encouraged among Presbyterians
Presbyterianism is a historically Reformed Protestant tradition named for its form of church government by representative assemblies of elders, known as "presbyters". Though other Reformed churches are structurally similar, the word ''Pr ...
, some Pentecostal
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a movement within the broader Evangelical wing of Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes direct personal experience of God in Christianity, God through Baptism with the Holy Spirit#Cl ...
churches, Churches of Christ
The Churches of Christ, also commonly known as the Church of Christ, is a loose association of autonomous Christian congregations located around the world. Typically, their distinguishing beliefs are that of the necessity of baptism for salvation ...
, the Disciples of Christ
The Christian Church (Disciples of Christ) is a mainline Protestant Christian denomination in the United States and Canada. The denomination started with the Restoration Movement during the Second Great Awakening, first existing during the 19th ...
, Baptists
Baptists are a Christian denomination, denomination within Protestant Christianity distinguished by baptizing only professing Christian believers (believer's baptism) and doing so by complete Immersion baptism, immersion. Baptist churches ge ...
and the Plymouth Brethren
The Plymouth Brethren or Assemblies of Brethren are a low church and Nonconformist (Protestantism), Nonconformist Christian movement whose history can be traced back to Dublin, Ireland, in the mid to late 1820s, where it originated from Anglica ...
. Advocates claim biblical precedent, citing that New Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianit ...
churches appear to all have had multiple elders.
Conversely, one minister may serve in two roles. A pastor with two churches may be said to have a "dual charge". In the Church of England, two or more otherwise independent benefice
A benefice () or living is a reward received in exchange for services rendered and as a retainer for future services. The Roman Empire used the Latin term as a benefit to an individual from the Empire for services rendered. Its use was adopted by ...
s may be 'held in ''plurality by a single priest.
See also
*Hierarchy of the Catholic Church
The hierarchy of the Catholic Church consists of its bishops, priests, and deacons. In the ecclesiological sense of the term, "hierarchy" strictly means the "holy ordering" of the church, the Body of Christ, so to respect the diversity of gif ...
* Organizational structure of Jehovah's Witnesses
* Polity of the Seventh-day Adventist Church
References
Footnotes
Bibliography
* * * * * * *Further reading
*A study of religious authority (especially pp. 97–218) as well as the secular authority of the state. *
A study of the conflict and prestige of episcopal church authority with other forms of church polity as they affect inter-Christian relations and ecumenism.
External links
Ecclesiastical polity
at the ''
Encyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, ...
''
{{Authority control
Christian terminology
Ecclesiastical polities