Choroidal Nevus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Choroidal nevus (plural: nevi) is a type of
 Location of the nevi plays a role in determining whether the disease is associated with any symptoms. In unusual circumstances, when the nevus is located below the center of the retina, blurred vision is the result. When a choroidal nevus becomes severe, it can cause leakage of fluid and abnormal development of vascular tissue (
Location of the nevi plays a role in determining whether the disease is associated with any symptoms. In unusual circumstances, when the nevus is located below the center of the retina, blurred vision is the result. When a choroidal nevus becomes severe, it can cause leakage of fluid and abnormal development of vascular tissue (
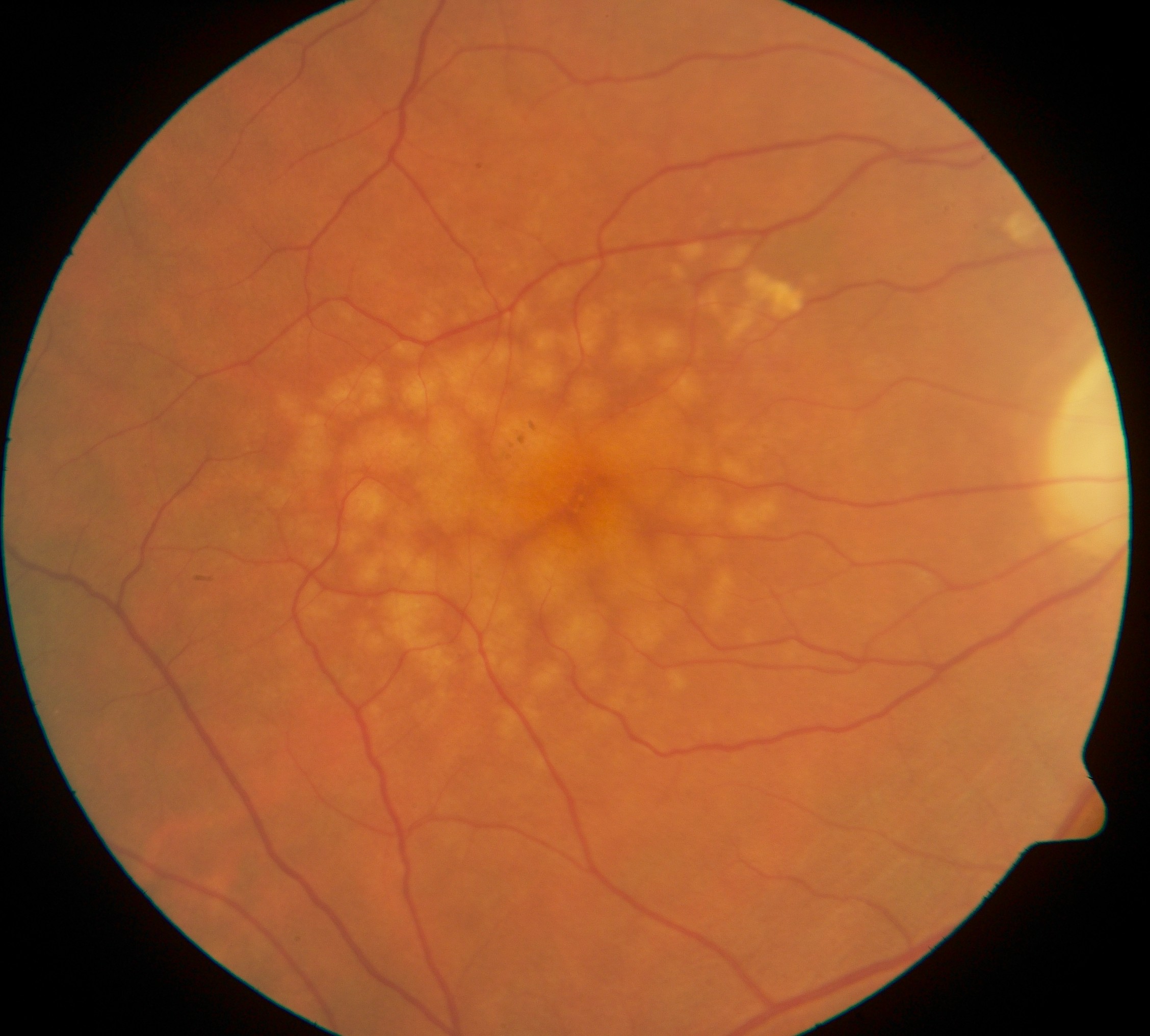 Giant choroidal nevus is described as one that has a basal diameter larger than 10mm. This variant contributes to 8% of all choroidal nevi. Due to its large basal diameter and thickness, it can be easily mistaken and diagnosed as choroidal melanoma. However, it does have the potential to grow into a melanoma. One study reported that over a period of 10 years, 18% of giant nevi grew into melanomas. Some of the most common features observed among these transformed giant nevi are nearness to the
Giant choroidal nevus is described as one that has a basal diameter larger than 10mm. This variant contributes to 8% of all choroidal nevi. Due to its large basal diameter and thickness, it can be easily mistaken and diagnosed as choroidal melanoma. However, it does have the potential to grow into a melanoma. One study reported that over a period of 10 years, 18% of giant nevi grew into melanomas. Some of the most common features observed among these transformed giant nevi are nearness to the
 Naturally, nevi occur more frequently than melanoma. Research shows that only about 1 in 9000 (in the United States population) transform into melanomas. Patients are at particularly high risk if the following is observed:
* A tumor thickness greater than 2mm or a tumor two times or more larger than the optic nerve head.
* Symptoms such as decreased vision (lower acuity), flashing lights and orange pigment on or surrounding the tumor.
* Distance between the margin of the tumor and the optic disk is less than 3mm.
* Subretinal fluid (i.e. the leakage of fluid).
* Ultrasonographic hollowness. In one study, 25% of nevi with hollowness on ultrasonography transformed into melanoma.
* Lack of halo. The presence of a halo is associated with stability of the nevi. This is illustrated by a study which reported that 7% of nevi in the absence of halo, grew into melanoma.
If three or more of the above melanoma risk factors are observed, the risk of the choroidal nevus growing into a melanoma is greater than 50%.
Naturally, nevi occur more frequently than melanoma. Research shows that only about 1 in 9000 (in the United States population) transform into melanomas. Patients are at particularly high risk if the following is observed:
* A tumor thickness greater than 2mm or a tumor two times or more larger than the optic nerve head.
* Symptoms such as decreased vision (lower acuity), flashing lights and orange pigment on or surrounding the tumor.
* Distance between the margin of the tumor and the optic disk is less than 3mm.
* Subretinal fluid (i.e. the leakage of fluid).
* Ultrasonographic hollowness. In one study, 25% of nevi with hollowness on ultrasonography transformed into melanoma.
* Lack of halo. The presence of a halo is associated with stability of the nevi. This is illustrated by a study which reported that 7% of nevi in the absence of halo, grew into melanoma.
If three or more of the above melanoma risk factors are observed, the risk of the choroidal nevus growing into a melanoma is greater than 50%.
eye neoplasm
Eye neoplasms can affect all parts of the eye, and can be a benign tumor or a malignant tumor (cancer). Eye cancers can be primary (starts within the eye) or metastatic cancer (spread to the eye from another organ). The two most common cancers tha ...
that is classified under choroidal tumors as a type of benign (non-cancerous) melanocytic tumor. A choroidal nevus can be described as an unambiguous pigmented blue or green-gray choroidal lesion, found at the front of the eye, around the iris, or the rear end of the eye.
Nevi are usually darkly pigmented tumors because they comprise melanocyte
Melanocytes are melanin-producing neural crest-derived cells located in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin's epidermis, the middle layer of the eye (the uvea),
the inner ear,
vaginal epithelium, meninges,
bones,
and hear ...
s. Dr. Gass, one of the leading specialists on eye diseases, speculates that a choroidal nevus grows from small cells resting as hyperplastic
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of organic tissue that results from cell proliferati ...
lesions, and exhibits growth primarily. In most cases, choroidal nevus is an asymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered as ...
disease, however, in serious conditions, adverse symptoms can be observed.
Choroidal nevus is usually diagnosed through an ophthalmic eye examination, or more specialized technologies such as photographic imaging, ophthalmoscopy
Ophthalmoscopy, also called funduscopy, is a test that allows a health professional to see inside the fundus of the eye and other structures using an ophthalmoscope (or funduscope). It is done as part of an eye examination and may be done as par ...
, ultrasonography
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies f ...
and ocular coherence tomography (OCT). Choroidal nevi can transform into a choroidal or ocular melanoma, becoming cancerous. Therefore, it is crucial to differentiate between a non-cancerous choroidal nevus and lethal melanoma.
Prevalence
The prevalence of choroidal nevus among the United States adult population above 40 years old is 4.7%. In terms of ethnicity, a cohort study done in the United States reported that the prevalence of choroidal nevus was found more in whites (4.1%) than in Chinese (0.4%), blacks (0.7%) and Hispanics (1.2%). However, the difference between Chinese, blacks and Hispanics was not statistically significant. The prevalence of choroidal nevus did not vary between sex, but it did vary with age. The incidence of nevi was discovered to be highest in people between the ages of 55 to 74 and lowest in people aged between 75 and 84. Hence, it is likely that there is a higher prevalence of the disease in people who are comparatively younger. Another study on the prevalence of choroidal nevus among the female population investigated the role of obesity and reproductive factors in the development of the disease. Amongpremenopausal
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often d ...
women, the risk of developing nevus is shown to be four times higher in those who had their first child before 25, compared to those who had their first child after 35. Moreover, among postmenopausal
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often d ...
females, the prevalence in obese females was twice that of non-obese females.
Signs and symptoms
 Location of the nevi plays a role in determining whether the disease is associated with any symptoms. In unusual circumstances, when the nevus is located below the center of the retina, blurred vision is the result. When a choroidal nevus becomes severe, it can cause leakage of fluid and abnormal development of vascular tissue (
Location of the nevi plays a role in determining whether the disease is associated with any symptoms. In unusual circumstances, when the nevus is located below the center of the retina, blurred vision is the result. When a choroidal nevus becomes severe, it can cause leakage of fluid and abnormal development of vascular tissue (neovascularization
Neovascularization is the natural formation of new blood vessels ('' neo-'' + ''vascular'' + '' -ization''), usually in the form of functional microvascular networks, capable of perfusion by red blood cells, that form to serve as collateral circula ...
). This leads to retinal detachment in that part of the eye, which is observed as some loss of vision or flashing lights. Once retinal detachment occurs, the case becomes a surgical emergency. Additionally, if the nevus is present for an extended period of time (years), and hinders the removal of retinal waste products, this can result in the development of yellowish white specks and spots on the surface of the nevi, called drusen
Drusen, from the German word for ''node'' or ''geode'' (singular, "Druse"), are tiny yellow or white accumulations of extracellular material that build up between Bruch's membrane and the retinal pigment epithelium of the eye. The presence of a fe ...
.
Cause
Currently, the cause of choroidal nevus is unknown.Forms of choroidal nevi
There are different ways to describe a choroidal nevus with its specific characteristics, such as halo choroidal nevus, giant choroidal nevus, and choroidal nevus with drusen. It is important to note that these characteristics and forms of nevi can and may overlap and be present at the same time.Halo choroidal nevus
Halo choroidal nevus is described as a yellow halo around the darkly pigmented brown centre, or in other terms, a pigmented centre with a hypo-pigmented periphery. Halo nevi contribute to 5% of all choroidal nevi. The pathogenesis of the halo nevus is not known, but the presence of a halo around the choroidal nevus was statistically proven to have a relatively lower risk of transforming into melanoma and thus is a predictive factor for stability. A few indicators of a halo nevus include an absence of subretinal fluid and orange pigment, thickness level less than 2 mm, as well as the tumor margin being remote from theoptic disk
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviol ...
.
Giant choroidal nevus
 Giant choroidal nevus is described as one that has a basal diameter larger than 10mm. This variant contributes to 8% of all choroidal nevi. Due to its large basal diameter and thickness, it can be easily mistaken and diagnosed as choroidal melanoma. However, it does have the potential to grow into a melanoma. One study reported that over a period of 10 years, 18% of giant nevi grew into melanomas. Some of the most common features observed among these transformed giant nevi are nearness to the
Giant choroidal nevus is described as one that has a basal diameter larger than 10mm. This variant contributes to 8% of all choroidal nevi. Due to its large basal diameter and thickness, it can be easily mistaken and diagnosed as choroidal melanoma. However, it does have the potential to grow into a melanoma. One study reported that over a period of 10 years, 18% of giant nevi grew into melanomas. Some of the most common features observed among these transformed giant nevi are nearness to the foveola
The foveola is located within a region called the macula, a yellowish, cone photoreceptor filled portion of the human retina. Approximately 0.35 mm in diameter, the foveola lies in the center of the fovea and contains only cone cells and a co ...
and ultrasonographic acoustic hollowness, suggesting that these may be the reasons for the transformation into melanomas. Thus, patients with giant nevus require close monitoring.
Choroidal nevus with drusen
Choroidal nevus with drusen can be considered as a sign of chronicity since drusen take years to develop and appear. Drusen are composed of lipids and can actually be an indicator that a tumour is a benign nevus as opposed to a cancerous melanoma. In nevi imaged by OCT, about 41% are found to have drusen.Transformation of a nevus into melanoma
 Naturally, nevi occur more frequently than melanoma. Research shows that only about 1 in 9000 (in the United States population) transform into melanomas. Patients are at particularly high risk if the following is observed:
* A tumor thickness greater than 2mm or a tumor two times or more larger than the optic nerve head.
* Symptoms such as decreased vision (lower acuity), flashing lights and orange pigment on or surrounding the tumor.
* Distance between the margin of the tumor and the optic disk is less than 3mm.
* Subretinal fluid (i.e. the leakage of fluid).
* Ultrasonographic hollowness. In one study, 25% of nevi with hollowness on ultrasonography transformed into melanoma.
* Lack of halo. The presence of a halo is associated with stability of the nevi. This is illustrated by a study which reported that 7% of nevi in the absence of halo, grew into melanoma.
If three or more of the above melanoma risk factors are observed, the risk of the choroidal nevus growing into a melanoma is greater than 50%.
Naturally, nevi occur more frequently than melanoma. Research shows that only about 1 in 9000 (in the United States population) transform into melanomas. Patients are at particularly high risk if the following is observed:
* A tumor thickness greater than 2mm or a tumor two times or more larger than the optic nerve head.
* Symptoms such as decreased vision (lower acuity), flashing lights and orange pigment on or surrounding the tumor.
* Distance between the margin of the tumor and the optic disk is less than 3mm.
* Subretinal fluid (i.e. the leakage of fluid).
* Ultrasonographic hollowness. In one study, 25% of nevi with hollowness on ultrasonography transformed into melanoma.
* Lack of halo. The presence of a halo is associated with stability of the nevi. This is illustrated by a study which reported that 7% of nevi in the absence of halo, grew into melanoma.
If three or more of the above melanoma risk factors are observed, the risk of the choroidal nevus growing into a melanoma is greater than 50%.
Pathophysiology and cytogenetics
The pathophysiology of choroidal melanoma (a type ofuveal melanoma
Uveal melanoma is a type of eye cancer in the uvea of the eye. It is traditionally classed as originating in the iris, choroid, and ciliary body, but can also be divided into class I (low metastatic risk) and class II (high metastatic risk). ...
), is not well understood. However, several molecular mechanisms and cytogenetics
Cytogenetics is essentially a branch of genetics, but is also a part of cell biology/cytology (a subdivision of human anatomy), that is concerned with how the chromosomes relate to cell behaviour, particularly to their behaviour during mitosis ...
may be involved in the process of it becoming malignant. Chromosomal alterations, monosomy
Monosomy is a form of aneuploidy with the presence of only one chromosome from a pair. Partial monosomy occurs when a portion of one chromosome in a pair is missing.
Human monosomy
Human conditions due to monosomy:
* Turner syndrome – People wit ...
3 and chromosome 8 gains have been identified to be associated with metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, ...
in uveal melanomas. Moreover BAP1, GNAQ, GNA11, SF3B1 and EIF1AX gene alterations were shown to be in correlation with uveal melanomas, each with a frequency of 18–45%.
Other risk factors
Although transformation into a melanoma is considered to be sporadic, several general risk factors are identified to be potentially relevant to the malignant transformation. These include light iris color, generally lower levels of melanin (light and untanned skin tones), exposure to arcwelding
Welding is a fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by using high heat to melt the parts together and allowing them to cool, causing fusion. Welding is distinct from lower temperature techniques such as br ...
due to intermittent ultraviolet exposure, as well as diseases such as ocular melanocytosis and dysplastic nevus syndrome
Dysplastic nevus syndrome, also known as familial atypical multiple mole–melanoma (FAMMM) syndrome, is an inherited cutaneous condition described in certain families, and characterized by unusual nevi and multiple inherited melanomas. First des ...
.
Differentiating between choroidal nevi and melanomas
Choroidal nevus has a few features that differentiate it from a choroidal melanoma, its malignant tumor form. ''Speed of growth:'' Nevi with slow growth in terms of size and in the absence of melanoma risk factors, do not show any signs of malignancy. The process of enlargement of the nevus can take up to an average of 15 years. In a long-term follow up study on the growth of choroidal nevi, out of 284 nevi, 31% of the patients only showed slight enlargement of choroidal nevi without any clinical evidence or signs of transformation into melanoma. In contrast, for small melanomas, the speed of growth is much faster, making it easily detectable in a short period of time. In fact, melanomas grow exponentially in thickness during their active growth phase. ''Ability to metastasis:'' Choroidal melanomas are able to undergo distant metastasis, whereas choroidal nevus is unable to do so. ''Risks factors for prediction of growth:'' There is a lack of overlap between the risk factors for the prediction of growth or enlargement of nevus and melanoma. While choroidal melanomas have multiple risk factors including even UV exposure and welding, the only risk factor for choroidal nevus is age. Slow growth and enlargement of choroidal nevi are found to be more common in younger patients, before becoming stable in mid or late adulthood.Diagnosis
Unless the choroidal nevus has progressed to a symptomatic form, it can only be discovered during a normal eye examination. The nevus is identified by its distinctive appearance. With a thickness of approximately 2mm and a color between brown to slate gray, the edge of the nevus blends into the retina. It is entirely possible to have more than one nevus in an eye, or have nevi in both eyes. Diagnostic testing is carried out by ultrasound,fluorescein angiography
Fluorescein angiography (FA), fluorescent angiography (FAG), or fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA) is a technique for examining the circulation of the retina and choroid (parts of the fundus) using a fluorescent dye and a specialized camera. So ...
and OCT. Both OCT and ultrasound fall under ophthalmic diagnostic imaging, allowing practitioners to take direct photographs of eye surfaces. The retinal pigment epithelium
The pigmented layer of retina or retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is the pigmented cell layer just outside the neurosensory retina that nourishes retinal visual cells, and is firmly attached to the underlying choroid and overlying retinal visual ...
(RPE) can be captured as well, using autofluorescence
Autofluorescence is the natural emission of light by biological structures such as mitochondria and lysosomes when they have absorbed light, and is used to distinguish the light originating from artificially added fluorescent markers (fluorophores ...
, because the light waves can detect lipofuscin
Lipofuscin is the name given to fine yellow-brown pigment granules composed of lipid-containing residues of lysosomal digestion. It is considered to be one of the aging or "wear-and-tear" pigments, found in the liver, kidney, heart muscle, reti ...
.
A B-scan ultrasound provides the practitioner with an approximate size of the tumor, in addition to vertical and horizontal measurements, while an A-scan
A-scan ultrasound biometry, commonly referred to as an A-scan (short for Amplitude scan), is a routine type of diagnostic test used in optometry or ophthalmology. The A-scan provides data on the length of the eye, which is a major determinant in ...
determines the amount of internal reflectivity. On the other hand, fluorescein angiography will aid in recognizing whether the tumor has developed its own circulation network.
Optomap
Scanning laser ophthalmoscopy (SLO) is a method of examination of the eye. It uses the technique of confocal laser scanning microscopy for diagnostic imaging of the retina or cornea of the human eye.
As a method used to image the retina with ...
is a common diagnostic tool in recognizing a choroidal nevus from a melanoma. It takes an image of the nevus or melanoma using two different lasers - which are red and green. When using the green laser to view the retina, a nevus would be invisible while a melanoma would be visible. Hence, optomap can distinguish a nevus from a melanoma.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) may have the potential for clinical diagnosis of choroidal nevus or melanoma. This can be achieved through machine learning, whereby a large dataset of imaging photographs of all sizes, shapes and location of nevi are used in training. This would improve detection accuracy as well as the design of treatment for nevi and melanoma.
Treatment
Since typical choroidal nevi do not have adverse effects, treatment is not required. Additionally, there are no safe methods to remove nevi from the eye as of now. Nonetheless, annual evaluations and checkups by ophthalmologists are necessary. The American Academy of Ophthalmology recommends adults aged 40 and above to have full eye examinations, as vision loss and eye diseases are most likely to start around this age.{{Cite web , last=Seltman , first=Whitney , date=7 November 2021 , title=How Often Should I Get My Eyes Checked? , url=https://www.webmd.com/eye-health/what-to-expect-checkup-eye-exam-adults , access-date=2 April 2022 , website=WebMD Most choroidal nevi can be managed and monitored by OCT. However, the abnormal development of vascular tissue as a result of the development of nevi can be treated using anti-VEGF
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF, ), originally known as vascular permeability factor (VPF), is a signal protein produced by many cells that stimulates the formation of blood vessels. To be specific, VEGF is a sub-family of growth factors, ...
agents, injected through the veins. These drugs inactivate the growth factor (VEGF) to reduce neovascularization and swelling. If the choroidal nevus does transform into a melanoma, then it would be treated with cancer therapy.
See also
*Uveal Melanoma
Uveal melanoma is a type of eye cancer in the uvea of the eye. It is traditionally classed as originating in the iris, choroid, and ciliary body, but can also be divided into class I (low metastatic risk) and class II (high metastatic risk). ...
* Prognosis for Choroidal Melanoma
* List of eye diseases
References