Chorioamnionitis - Intermed Mag on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Chorioamnionitis, also known as intra-amniotic infection (IAI), is
 The
The

Overview
at
Cerebral palsy inflammation link
(29 November 2003) at BBC. {{Certain conditions originating in the perinatal period Inflammations Pathology of pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium
inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
of the fetal membrane
The fetal membranes are the four extraembryonic membranes, associated with the developing embryo, and fetus in humans and other mammals.. They are the amnion, chorion, allantois, and yolk sac. The amnion and the chorion are the chorioamniotic ...
s ( amnion and chorion), usually due to bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
l infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable d ...
. In 2015, a National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Workshop expert panel recommended use of the term "triple I" to address the heterogeneity of this disorder. The term triple I refers to intrauterine infection or inflammation or both and is defined by strict diagnostic criteria, but this terminology has not been commonly adopted although the criteria are used.
Chorioamnionitis results from an infection caused by bacteria ascending from the vagina into the uterus and is associated with premature or prolonged labor. It triggers an inflammatory response to release various inflammatory signaling molecules, leading to increased prostaglandin
The prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are der ...
and metalloproteinase release. These substances promote uterine contractions and cervical ripening, causations of premature birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is betwee ...
. The risk of developing chorioamnionitis increases with number of vaginal examination
The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, also known as Pap smear (AE), cervical smear (BE), cervical screening (BE), or smear test (BE)) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes in t ...
s performed in the final month of pregnancy, including labor. Tobacco and alcohol use also puts mothers at risk for chorioamnionitis development.
Chorioamnionitis is caught early by looking at signs and symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain, or abnormal vaginal excretion. Administration of antibiotics if the amniotic sac bursts prematurely can prevent chorioamnionitis occurrence.
Signs and symptoms
The signs and symptoms of clinical chorioamnionitis include fever, leukocytosis (>15,000 cells/mm³), maternal (>100 bpm) or fetal (>160 bpm)tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal ( ...
, uterine tenderness and preterm rupture of membranes.
Causes
Causes of chorioamnionitis stem from bacterial infection as well as obstetric and other related factors.Microorganisms
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
l, viral
Viral means "relating to viruses" (small infectious agents).
Viral may also refer to:
Viral behavior, or virality
Memetic behavior likened that of a virus, for example:
* Viral marketing, the use of existing social networks to spread a marke ...
, and even fungal infections can cause chorioamnionitis. Most commonly from '' Ureaplasma, Fusobacterium'', and '' Streptococcus'' bacteria species. Less commonly, '' Gardnerella, Mycoplasma
''Mycoplasma'' is a genus of bacteria that, like the other members of the class '' Mollicutes'', lack a cell wall around their cell membranes. Peptidoglycan ( murein) is absent. This characteristic makes them naturally resistant to antibiotic ...
,'' and ''Bacteroides'' bacteria species. Sexually transmitted infections, chlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear they may occur only several w ...
and gonorrhea, can cause development of the condition as well. Studies are continuing to identify other microorganism classes and species as infection sources.
Obstetric and other
Birthing-related events, lifestyle, and ethnic background have been linked to an increase in the risk of developing chorioamnionitis apart from bacterial causation. Premature deliveries, ruptures of theamniotic sac
The amniotic sac, also called the bag of waters or the membranes, is the sac in which the embryo and later fetus develops in amniotes. It is a thin but tough transparent pair of membranes that hold a developing embryo (and later fetus) until sh ...
membranes, prolonged labor, and primigravida childbirth are associated with this condition. At term mothers who experience a combination of pre-labor membrane ruptures and multiple invasive vaginal examinations, prolonged labor, or have meconium
Meconium is the earliest stool of a mammalian infant resulting from defecation. Unlike later feces, meconium is composed of materials ingested during the time the infant spends in the uterus: intestinal epithelial cells, lanugo, mucus, amnio ...
appear in the amniotic fluid are at higher risk than at term mothers experiencing just one of those events. In other studies, smoking, alcohol use and drug use are noted as risk factors. Those of African American ethnicity are noted to be at higher risk.
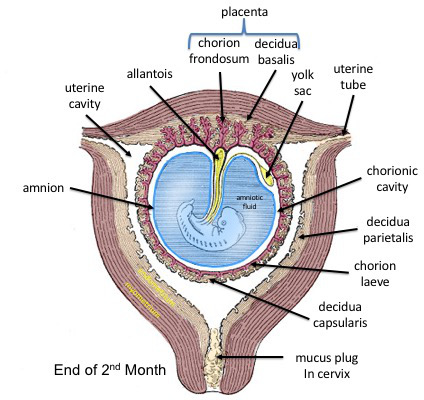
Anatomy
 The
The amniotic sac
The amniotic sac, also called the bag of waters or the membranes, is the sac in which the embryo and later fetus develops in amniotes. It is a thin but tough transparent pair of membranes that hold a developing embryo (and later fetus) until sh ...
consists of two parts:
* The outer membrane is the chorion. It is closest to the mother and physically supports the much thinner amnion.
** The chorion is the last and outermost of the membranes that make up the amniotic sac.
* The inner membrane is the amnion. It is in direct contact with the amniotic fluid, which surrounds the fetus
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal develo ...
.
** The amniotic fluid exists within the amnion, and is where the fetus is able to grow and develop.
** The swelling of the amnion and chorion is characteristic of chorioamnionitis, occurring when bacteria makes its way into the amniotic fluid and creates an infection within the amniotic fluid.
Diagnosis

Pathologic
Chorioamnionitis is diagnosed from ahistologic
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures vis ...
(tissue) examination of the fetal membranes. Confirmed histologic chorioamnionitis without any clinical symptoms is termed subclinical chorioamnionitis and is more common than symptomatic clinical chorioamnionitis.
Infiltration of the chorionic plate by neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in ...
s is diagnostic of (mild) chorioamnionitis. More severe chorioamnionitis involves subamniotic tissue and may have fetal membrane necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated dig ...
and/or abscess formation.
Severe chorioamnionitis may be accompanied by vasculitis of the umbilical blood vessels due to the fetus' inflammatory cells. If very severe, funisitis, inflammation of the umbilical cord connective tissue, occurs.
Suspected clinical diagnosis
The presence of fever between 38.0°C and 39.0°C alone is insufficient to indicate chorioamnionitis and is termed ''isolated maternal fever''. Isolated maternal fever may not have an infectious cause and does not required antibiotic treatment. When intrapartum (during delivery) fever is higher than 39.0°C, suspected diagnosis of chorioamnionitis can be made. Alternatively, if intrapartum fever is between 38.0°C and 39.0°C, an additional risk factor must be present to make a presumptive diagnosis of chorioamnionitis. Additional risk factors include: * Fetal tachycardia * Maternal leukocytosis (>15,000 cells/mm³) * Purulent cervical drainageConfirmed diagnosis
Diagnosis is typically not confirmed until after delivery. However, people with confirmed diagnosis and suspected diagnosis have the same post-delivery treatment regardless of diagnostic status. Diagnosis can be confirmed histologically or through amniotic fluid tests such as gram staining, glucose levels, or other culture results consistent with infection.Prevention
If the amniotic sac breaks early into pregnancy, the potential of introducing bacteria in the amniotic fluid can increase. Administering antibiotics maternally can potentially prevent chorioamnionitis and allow for a longer pregnancy. In addition, it has been shown that it is not necessary to deliver the fetus quickly after chorioamnionitis is diagnosed, so a C-section is not necessary unless maternal health concern is present. However, research has found that beginning labor early at approximately 34 weeks can lessen the likelihood of fetal death, and reduce the potential for excessive infection within the mother. In addition, providers should interview people suspected to have chorioamnionitis about whether they are experiencing signs and symptoms at scheduled obstetrics visits during pregnancy, including whether the individual has experienced excretion vaginally, febrile, or abdominal pain.Treatment
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee Opinion proposes the use of antibiotic treatment in intrapartum mothers with suspected or confirmed chorioamnionitis and maternal fever without an identifiable cause. Intrapartum antibiotic treatment consists of: *Standard **Ampicillin
Ampicillin is an antibiotic used to prevent and treat a number of bacterial infections, such as respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, meningitis, salmonellosis, and endocarditis. It may also be used to prevent group B stre ...
+ gentamicin
Gentamicin is an antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections. This may include bone infections, endocarditis, pelvic inflammatory disease, meningitis, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis among others. It is not ...
*Alternative
** Ampicillin/sulbactam
** Ticarcillin/clavulanate
**Cefoxitine
Cefoxitin is a second-generation cephamycin antibiotic developed by Merck & Co., Inc. from Cephamycin C in the year following its discovery, 1972. It was synthesized in order to create an antibiotic with a broader spectrum. It is often grouped wi ...
** Cefotetan
**Piperacillin/tazobactam
Piperacillin/tazobactam, sold under the brand name Zosyn among others, is a combination medication containing the antibiotic piperacillin and the β-lactamase inhibitor tazobactam. The combination has activity against many Gram-positive and ...
** Ertapenem
* Cesarean delivery
**Ampicillin and gentamicin plus either clindamycin
Clindamycin is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections, including osteomyelitis (bone) or joint infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, strep throat, pneumonia, acute otitis media (middle ear infe ...
or metronidazole
*Penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using ...
-allergy
** Vancomycin + gentamicin
**Gentamicin + clindamycin
However, there is not enough evidence to support the most efficient antimicrobial regimen. Starting the treatment during the intrapartum period is more effective than starting it postpartum; it shortens the hospital stay for the mother and the neonate. There is currently not enough evidence to dictate how long antibiotic therapy should last. Completion of treatment/cure is only considered after delivery.
Supportive measures
Acetaminophen is often used for treating fevers and may be beneficial for fetal tachycardia. There can be increased likelihood for neonatal encephalopathy when mothers have intrapartum fever.Outcomes
Chorioamnionitis has possible associations with numerous neonatal conditions. Intrapartum (during labor) chorioamnionitis may be associated with neonatalpneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severi ...
, meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion ...
, sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is foll ...
, and death. Long-term infant complications like bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD; part of the spectrum of chronic lung disease of infancy) is a chronic lung disease in which premature infants, usually those who were treated with supplemental oxygen, require long-term oxygen. The alveoli that are ...
, cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, spasticity, stiff muscles, Paresis, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be p ...
, and Wilson-Mikity syndrome have been associated to the bacterial infection. Furthermore, histological chorioamnionitis may increase the likelihood of newborn necrotizing enterocolitis, where one or more sections of the bowel die. This occurs when the fetal gut barrier becomes compromised and is more susceptible to conditions like infection and sepsis. In addition, chorioamnionitis can act as a risk factor for premature birth and periventricular leukomalacia.
Complications
For mother and fetus, chorioamnionitis may lead to short-term and long-term issues when microbes move to different areas or trigger inflammatory responses due to infection.Maternal complications
* Higher risk for C-section * Postpartum hemorrhage *Endometritis
Endometritis is inflammation of the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium). Symptoms may include fever, lower abdominal pain, and abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge. It is the most common cause of infection after childbirth. It is also ...
* Bacteremia (often due to '' Group B streptococcus'' and ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Esc ...
'')
* Pelvic abscess
Mothers with chorioamnionitis who undergo a C-section may be more likely to develop pelvic abscesses, septic pelvic thrombophlebitis, and infections at the surgical site.
Fetal complications
* Fetal death * Neonatal sepsisNeonatal complications
* Perinatal death *Asphyxia
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen to the body which arises from abnormal breathing. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which affects primarily the tissues and organs. There are many circumstances that ca ...
* Early onset neonatal sepsis
* Septic shock
Septic shock is a potentially fatal medical condition that occurs when sepsis, which is organ injury or damage in response to infection, leads to dangerously low blood pressure and abnormalities in cellular metabolism. The Third International Co ...
* Neonatal pneumonia
* Infant respiratory distress
In the long-term, infants may be more likely to experience cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, spasticity, stiff muscles, Paresis, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be p ...
or neurodevelopmental disabilities. Disability development is related to the activation of the fetal inflammatory response syndrome (FIRS) when the fetus is exposed to infected amniotic fluid or other foreign entities. This systemic response results in neutrophil and cytokine release that can impair the fetal brain and other vital organs. Compared to infants with clinical chorioamnionitis, it appears cerebral palsy may occur at a higher rate for those with histologic chorioamnionitis. However, more research needs to be done to examine this association. There is also concern about the impact of FIRS on infant immunity as this is a critical time for growth and development. For instance, it may be linked to chronic inflammatory disorders, such as asthma.
Epidemiology
Chorioamnionitis is approximated to occur in about 4% of births in the United States. However, many other factors can increase the risk of chorioamnionitis. For example, in births with premature rupture of membranes (PROM), between 40 and 70% involve chorioamnionitis. Furthermore, clinical chorioamnionitis is implicated in 12% of all cesarean deliveries. Some studies have shown that the risk of chorioamnionitis is higher in those of African American ethnicity, those with immunosuppression, and those who smoke, use alcohol, or abuse drugs.See also
* Chronic deciduitis * Funisitis *Placentitis
Placentitis is an inflammation of the placenta. The main forms of placentitis are:
*Villitis, inflammation of chorionic villi.
*Intervillositis, inflammation of the intervillous space.
It may be caused by vertically transmitted infections.
...
* Wharton's jellyNotes
References
*External links
Overview
at
Cleveland Clinic
Cleveland Clinic is a nonprofit American academic medical center based in Cleveland, Ohio. Owned and operated by the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, an Ohio nonprofit corporation established in 1921, it runs a 170-acre (69 ha) campus in Cleveland, ...
.
Cerebral palsy inflammation link
(29 November 2003) at BBC. {{Certain conditions originating in the perinatal period Inflammations Pathology of pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium