Chip-scale atomic clock on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
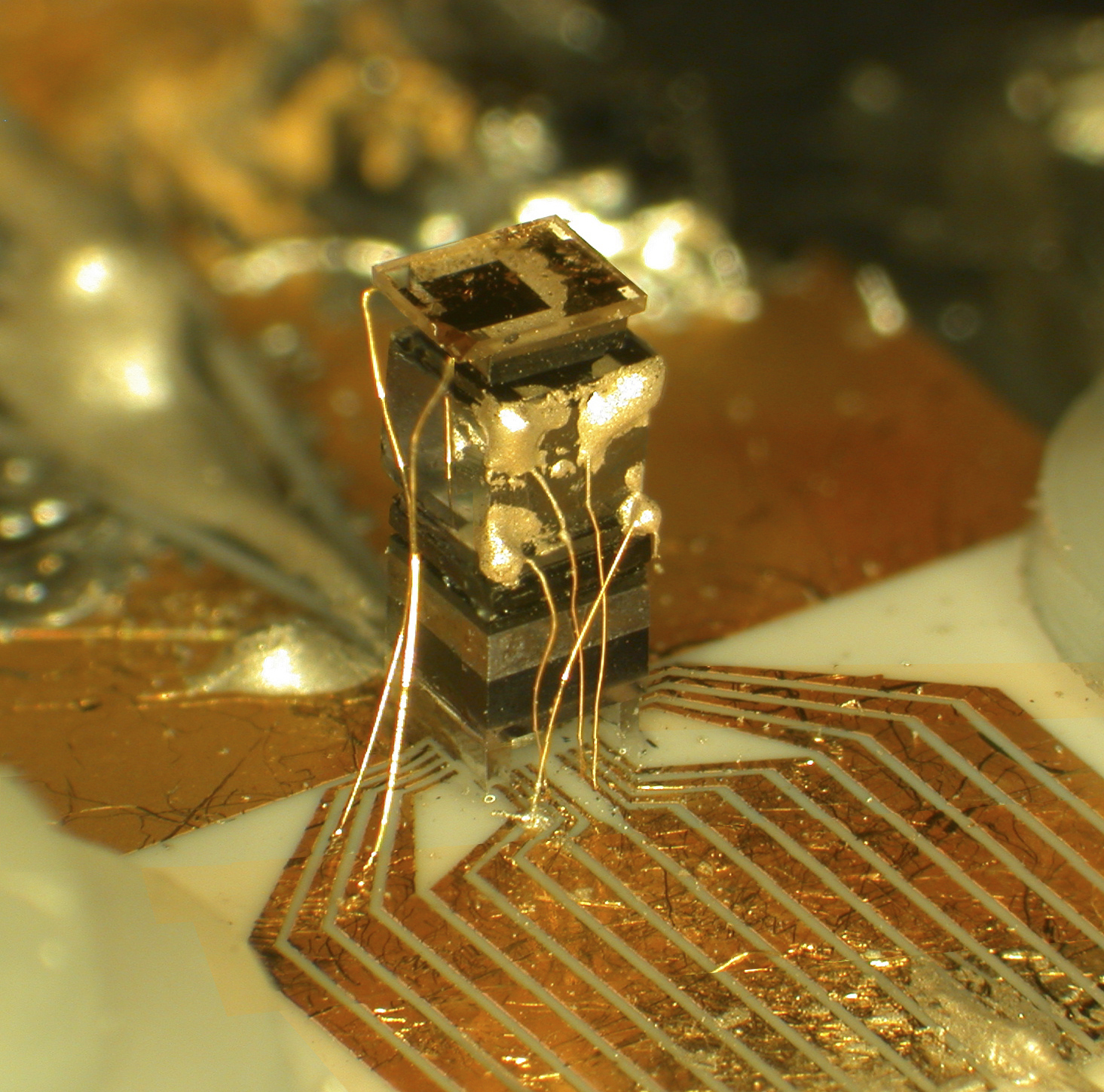 A chip scale atomic clock (CSAC) is a compact, low-power atomic clock fabricated using techniques of
A chip scale atomic clock (CSAC) is a compact, low-power atomic clock fabricated using techniques of
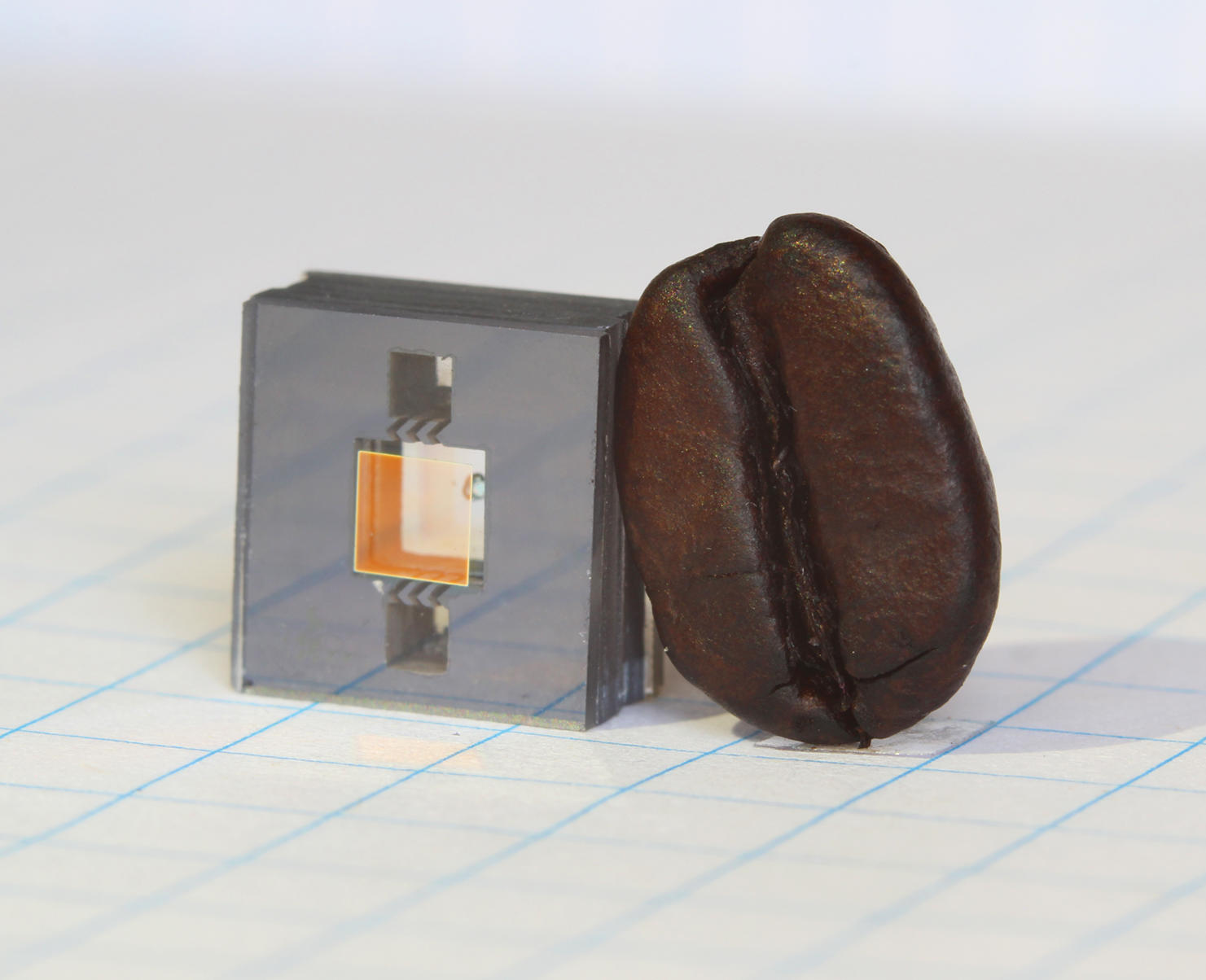 Conventional vapor cell atomic clocks are about the size of a deck of cards, consume about 10 W of electrical power and cost about $3,000. Shrinking these to the size of a semiconductor chip required extensive development and several breakthroughs. An important part of development was designing the device so it could be manufactured using standard semiconductor fabrication techniques where possible, to keep its cost low enough that it could become a mass market device. Conventional caesium clocks use a glass tube containing caesium, which are challenging to make smaller than 1 cm. In the CSAC,
Conventional vapor cell atomic clocks are about the size of a deck of cards, consume about 10 W of electrical power and cost about $3,000. Shrinking these to the size of a semiconductor chip required extensive development and several breakthroughs. An important part of development was designing the device so it could be manufactured using standard semiconductor fabrication techniques where possible, to keep its cost low enough that it could become a mass market device. Conventional caesium clocks use a glass tube containing caesium, which are challenging to make smaller than 1 cm. In the CSAC,
AccuBeat
 A chip scale atomic clock (CSAC) is a compact, low-power atomic clock fabricated using techniques of
A chip scale atomic clock (CSAC) is a compact, low-power atomic clock fabricated using techniques of microelectromechanical systems
MEMS (micro-electromechanical systems) is the technology of microscopic devices incorporating both electronic and moving parts. MEMS are made up of components between 1 and 100 micrometres in size (i.e., 0.001 to 0.1 mm), and MEMS devices ...
(MEMS) and incorporating a low-power semiconductor laser as the light source. The first CSAC physics package was demonstrated at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical s ...
) in 2003, based on an invention made in 2001. The work was funded by the US Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the Army, Navy, Marines, Air Force, Space Force, ...
's Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military. Originally known as the Adva ...
(DARPA) with the goal of developing a microchip-sized atomic clock
An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated with different energy levels, and in transitions betwee ...
for use in portable equipment. In military equipment it is expected to provide improved location and battlespace
Battlespace or battle-space is a term used to signify a military strategy which integrates multiple armed forces for the military theater (warfare), theatre of operations, including aerial warfare, air, information warfare, information, ground w ...
situational awareness
Situational awareness or situation awareness, often abbreviated as SA is the understanding of an environment, its elements, and how it changes with respect to time or other factors. It is also defined as the perception of the elements in the envi ...
for dismounted soldier
A soldier is a person who is a member of an army. A soldier can be a Conscription, conscripted or volunteer Enlisted rank, enlisted person, a non-commissioned officer, a warrant officer, or an Officer (armed forces), officer.
Etymology
The wo ...
s when the global positioning system
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based hyperbolic navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission Delta 31. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provide ge ...
is not available, but many civilian applications are also envisioned. Commercial manufacturing of these atomic clocks began in 2011. The CSAC, the world's smallest atomic clock, is 4 x 3.5 x 1 cm (1.5 x 1.4 x 0.4 inches) in size, weighs 35 grams, consumes only 115 mW of power, and can keep time to within 100 microseconds per day after several years of operation.
A more stable design based on the vibration of rubidium
Rubidium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Rb and atomic number 37. It is a very soft, whitish-grey solid in the alkali metal group, similar to potassium and caesium. Rubidium is the first alkali metal in the group to have ...
atoms was demonstrated by NIST in 2019.
How it works
Like other caesium atomic clocks, the clock keeps time by a precise 9.192631770 GHzmicrowave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
signal emitted by electron spin transitions between two hyperfine energy level
A quantum mechanics, quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound state, bound—that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy, called energy levels. This contrasts with classical mechanics, classical pa ...
s in atoms of caesium-133. A feedback mechanism keeps a quartz crystal oscillator on the chip locked to this frequency, which is divided down by digital counters to give 10 MHz and 1 Hz clock signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and ...
s provided to output pins. On the chip, liquid metal caesium in a tiny 2 mm capsule, fabricated using silicon micromachining techniques, is heated to vaporize the alkali metal. A semiconductor laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
shines a beam of infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
light modulated by the microwave oscillator
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
through the capsule onto a photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are devices that detect light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation and convert it into an electrical signal. They are essential in a wide range of applications, from digital imaging and optical ...
. When the oscillator is at the precise frequency of the transition, the optical absorption of the caesium atoms is reduced, increasing the output of the photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are devices that detect light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation and convert it into an electrical signal. They are essential in a wide range of applications, from digital imaging and optical ...
. The output of the photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are devices that detect light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation and convert it into an electrical signal. They are essential in a wide range of applications, from digital imaging and optical ...
is used as feedback in a frequency locked loop circuit to keep the oscillator at the correct frequency.
Development
 Conventional vapor cell atomic clocks are about the size of a deck of cards, consume about 10 W of electrical power and cost about $3,000. Shrinking these to the size of a semiconductor chip required extensive development and several breakthroughs. An important part of development was designing the device so it could be manufactured using standard semiconductor fabrication techniques where possible, to keep its cost low enough that it could become a mass market device. Conventional caesium clocks use a glass tube containing caesium, which are challenging to make smaller than 1 cm. In the CSAC,
Conventional vapor cell atomic clocks are about the size of a deck of cards, consume about 10 W of electrical power and cost about $3,000. Shrinking these to the size of a semiconductor chip required extensive development and several breakthroughs. An important part of development was designing the device so it could be manufactured using standard semiconductor fabrication techniques where possible, to keep its cost low enough that it could become a mass market device. Conventional caesium clocks use a glass tube containing caesium, which are challenging to make smaller than 1 cm. In the CSAC, MEMS
MEMS (micro-electromechanical systems) is the technology of microscopic devices incorporating both electronic and moving parts. MEMS are made up of components between 1 and 100 micrometres in size (i.e., 0.001 to 0.1 mm), and MEMS devices ...
techniques were used to create a caesium capsule only 2 cubic millimeters in size. The light source in conventional atomic clocks is a rubidium
Rubidium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Rb and atomic number 37. It is a very soft, whitish-grey solid in the alkali metal group, similar to potassium and caesium. Rubidium is the first alkali metal in the group to have ...
atomic-vapor discharge lamp, which was bulky and consumed large amounts of power. In the CSAC this was replaced by an infrared vertical cavity surface emitting laser
The vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL ) is a type of semiconductor laser diode with laser beam emission perpendicular from the top surface, contrary to conventional edge-emitting semiconductor lasers (also called ''in-plane'' lasers ...
(VCSEL) fabricated on the chip, with its beam radiating upward into the caesium capsule above it. Another advance was the elimination of the microwave cavity
A microwave cavity or radio frequency cavity (RF cavity) is a special type of resonator, consisting of a closed (or largely closed) metal structure that confines electromagnetic fields in the microwave or radio frequency, RF region of the spect ...
used in conventional clocks, whose size, equal to a wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
of the microwave frequency, about 3 cm, formed the fundamental lower limit to the size of the clock. The cavity was made unnecessary by the use of a quantum technique, coherent population trapping.
Commercialization
The CSAC program achieved a hundredfold size reduction while using 50 times less power than traditional atomic clocks, which led to extensive CSAC use in military and commercial applications. According to an October 2023 report, the CSAC market is expected to grow at a "remarkable" compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2023 to 2030. Major commercial players includeMicrosemi
Microsemi Corporation was an Aliso Viejo, California-based provider of semiconductor and system solutions for aerospace & defense, communications, data center and industrial markets.
In February 2018, it was announced that Chandler, Arizona-ba ...
(Microchip Technology
Microchip Technology Incorporated is a publicly listed American semiconductor corporation that manufactures microcontroller, mixed-signal, analog, and Flash-IP integrated circuits.
Its corporate headquarters is located in Chandler, Arizona. ...
), Teledyne, Chengdu Spaceon Electronics, anAccuBeat
External links NIST on a chip
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Chip-scale atomic clock Atomic clocks Electronic test equipment