Chechen Republic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Chechnya ( rus, Чечня́, Chechnyá, p=tɕɪtɕˈnʲa; ce, Нохчийчоь, Noxçiyçö), officially the Chechen Republic,; ce, Нохчийн Республика, Noxçiyn Respublika is a republic of
 Traces of human settlement dating back to 40,000 BC were found near Lake Kezanoi. Cave paintings, artifacts, and other archaeological evidence indicate continuous habitation for some 8,000 years. People living in these settlements used tools, fire, and clothing made of animal skins.
The
Traces of human settlement dating back to 40,000 BC were found near Lake Kezanoi. Cave paintings, artifacts, and other archaeological evidence indicate continuous habitation for some 8,000 years. People living in these settlements used tools, fire, and clothing made of animal skins.
The
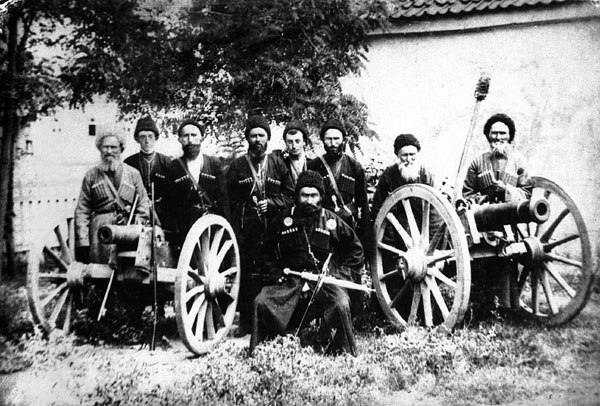
 Under intermittent Persian rule since 1555, in 1783 the eastern Georgians of Kartl-Kakheti led by Erekle II and Russia signed the Treaty of Georgievsk. According to this treaty, Kartl-Kakheti received protection from Russia, and Georgia abjured any dependence on
Under intermittent Persian rule since 1555, in 1783 the eastern Georgians of Kartl-Kakheti led by Erekle II and Russia signed the Treaty of Georgievsk. According to this treaty, Kartl-Kakheti received protection from Russia, and Georgia abjured any dependence on
 The First Chechen War took place from 1994 to 1996, when Russian forces attempted to regain control over Chechnya, which had declared independence in November 1991. Despite overwhelming numerical superiority in men, weaponry, and air support, the Russian forces were unable to establish effective permanent control over the mountainous area due to numerous successful full-scale battles and
The First Chechen War took place from 1994 to 1996, when Russian forces attempted to regain control over Chechnya, which had declared independence in November 1991. Despite overwhelming numerical superiority in men, weaponry, and air support, the Russian forces were unable to establish effective permanent control over the mountainous area due to numerous successful full-scale battles and

 Chechen rebels continued to fight Russian troops and conduct terrorist attacks. In October 2002, 40–50 Chechen rebels seized a Moscow theater and took about 900 civilians hostage. The crisis ended with 117 hostages and up to 50 rebels dead, mostly due to an unknown aerosol pumped into the building by Russian special forces to incapacitate the people inside.
In response to the increasing terrorism, Russia tightened its grip on Chechnya and expanded its anti-terrorist operations throughout the region. Russia installed a pro-Russian Chechen regime. In 2003, a referendum was held on a constitution that reintegrated Chechnya within Russia but provided limited autonomy. According to the Chechen government, the referendum passed with 95.5% of the votes and almost 80% turnout. ''
Chechen rebels continued to fight Russian troops and conduct terrorist attacks. In October 2002, 40–50 Chechen rebels seized a Moscow theater and took about 900 civilians hostage. The crisis ended with 117 hostages and up to 50 rebels dead, mostly due to an unknown aerosol pumped into the building by Russian special forces to incapacitate the people inside.
In response to the increasing terrorism, Russia tightened its grip on Chechnya and expanded its anti-terrorist operations throughout the region. Russia installed a pro-Russian Chechen regime. In 2003, a referendum was held on a constitution that reintegrated Chechnya within Russia but provided limited autonomy. According to the Chechen government, the referendum passed with 95.5% of the votes and almost 80% turnout. ''
 * Grozny (capital)
* Shali
*
* Grozny (capital)
* Shali
*
 According to the 2021 Census, the population of the republic is 1,510,824, up from 1,268,989 in the 2010 Census.
As of the 2010 Census,
According to the 2021 Census, the population of the republic is 1,510,824, up from 1,268,989 in the 2010 Census.
As of the 2010 Census,
File:Life expectancy in Russian subject -Chechnya.png, Life expectancy at birth in Chechnya
File:Life expectancy in Russian subject -Chechnya -diff.png, Life expectancy with calculated differences
File:Life expectancy in Russia -Chechnya.png, Life expectancy in Chechnya in comparison with neighboring regions of the country
File:Comparison gender life expectancy -Russia.svg, Interactive chart of comparison of male and female life expectancy for 2021. Open th
original svg-file
in a separate window and hover over a bubble to highlight it. File:Comparison gender life expectancy -Russia -urban vs rural.svg, Analogious interactive chart of comparison of urban and rural life expectancy.Original interactive file
 :Source
:Source
Fedstat (Суммарный коэффициент рождаемости)

 The former separatist religious leader (mufti) Akhmad Kadyrov, looked upon as a traitor by many separatists, was elected president with 83% of the vote in an internationally monitored election on 5 October 2003. Incidents of ballot stuffing and voter intimidation by Russian soldiers and the exclusion of separatist parties from the polls were subsequently reported by
The former separatist religious leader (mufti) Akhmad Kadyrov, looked upon as a traitor by many separatists, was elected president with 83% of the vote in an internationally monitored election on 5 October 2003. Incidents of ballot stuffing and voter intimidation by Russian soldiers and the exclusion of separatist parties from the polls were subsequently reported by

 Ichkeria was a member of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organisation between 1991 and 2010. Former president of
Ichkeria was a member of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organisation between 1991 and 2010. Former president of
Diplomatic relations with Ichkeria were also established by the partially recognised Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan under the
 On 10 March 2011,
On 10 March 2011,
Roy Conrad. Grozny. A few days...
*Dunlop, John B. ''Russia Confronts Chechnya: Roots of a Separatist Conflict'' *Evangelista, Mathew. ''The Chechen Wars: Will Russia Go the Way of the Soviet Union?''. . *Gall, Charlotta & de Waal, Thomas. ''Chechnya: A Small Victorious War''. *Gall, Carlotta, and de Waal, Thomas ''Chechnya: Calamity in the Caucasus'' * Goltz, Thomas. ''Chechnya Diary : A War Correspondent's Story of Surviving the War in Chechnya''. M E Sharpe (2003). *Hasanov, Zaur. The Man of the Mountains. (facts based novel on growing influence of the radical Islam during 1st and 2nd Chechnya wars) *Khan, Ali
The Chechen Terror: The Play within the Play
* Khlebnikov, Paul. ''Razgovor s varvarom'' (Interview with a barbarian). . * Lieven, Anatol. ''Chechnya : Tombstone of Russian Power'' * Mironov, Vyacheslav. ''Ya byl na etoy voyne.'' (I was in this war) Biblion – Russkaya Kniga, 2001. Partial translation available online. * Mironov, Vyacheslav
Vyacheslav Mironov. Assault on Grozny Downtown
* Mironov, Vyacheslav
Vyacheslav Mironov. ''I was in that war''.
*Oliker, Olga ''Russia's Chechen Wars 1994–2000: Lessons from Urban Combat''. . (A strategic and tactical analysis of the Chechen Wars.) *Pelton, Robert Young. ''Hunter Hammer and Heaven, Journeys to Three World's Gone Mad'' () * Politkovskaya, Anna. ''A Small Corner of Hell: Dispatches from Chechnya'' *Rasizade, Alec. Chechnya: the Achilles heel of Russia. = Contemporary Review (Oxford) in three parts: 1
April 2005 issue, volume 286, number 1671, pages 193–197
2
3
*Seirstad, Asne. The Angel of Grozny. *Wood, Tony
Book review in
Islamist Extremism in Chechnya: A Threat to U.S. Homeland?: Joint Hearing before the Subcommittee on Europe, Eurasia, and Emerging Threats and the Subcommittee on Terrorism, Nonproliferation, and Trade of the Committee on Foreign Affairs, House of Representatives, One Hundred Thirteenth Congress, First Session, April 26, 2013
*
Chechnya Guide
{{Authority control 1993 establishments in Russia Chechen-speaking countries and territories North Caucasian Federal District North Caucasus Regions of Europe with multiple official languages States and territories established in 1993
Russia
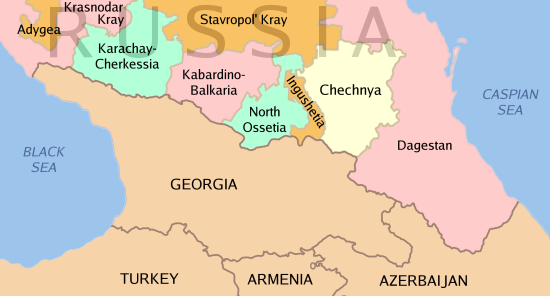
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
. It is situated in the North Caucasus
The North Caucasus, ( ady, Темыр Къафкъас, Temır Qafqas; kbd, Ишхъэрэ Къаукъаз, İṩxhərə Qauqaz; ce, Къилбаседа Кавказ, Q̇ilbaseda Kavkaz; , os, Цӕгат Кавказ, Cægat Kavkaz, inh, ...
of Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, wh ...
, close to the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad s ...
. The republic forms a part of the North Caucasian Federal District
North Caucasian Federal District (russian: Се́веро-Кавка́зский федера́льный о́круг, ''Severo-Kavkazsky federalny okrug'') is one of the eight federal districts of Russia. It is located in extreme southern Ru ...
, and shares land borders with the country of Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
to its south; with the Russian republics of Dagestan
Dagestan ( ; rus, Дагеста́н, , dəɡʲɪˈstan, links=yes), officially the Republic of Dagestan (russian: Респу́блика Дагеста́н, Respúblika Dagestán, links=no), is a republic of Russia situated in the North ...
, Ingushetia, and North Ossetia-Alania to its east, north, and west; and with Stavropol Krai to its northwest.
After the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, the Checheno-Ingush ASSR
The Checheno-Ingush Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic; inh, Нохч-ГӀалгӀай Автономе Советий Социализма Республика, Noxç-Ġalġay Avtonome Sovetiy Socializma Respublika; russian: Чече́но-И ...
split into two parts: the Republic of Ingushetia and the Chechen Republic. The latter proclaimed the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria
The Chechen Republic of Ichkeria (; ce, Нохчийн Республик Ичкери, Nóxçiyn Respublik Içkeri; russian: Чеченская Республика Ичкерия; abbreviated as "ChRI" or "CRI") was a ''de facto'' state tha ...
, which sought independence. Following the First Chechen War of 1994–1996 with Russia, Chechnya gained ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with '' de jure'' ("by l ...
'' independence as the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria, although ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legall ...
'' it remained a part of Russia. Russian federal control was restored in the Second Chechen War of 1999–2009, with Chechen politics being dominated by Akhmad Kadyrov, and later his son Ramzan Kadyrov.
The republic covers an area of , with a population of over 1.4 million residents .
It is home to the indigenous Chechens
The Chechens (; ce, Нохчий, , Old Chechen: Нахчой, ''Naxçoy''), historically also known as ''Kisti'' and '' Durdzuks'', are a Northeast Caucasian ethnic group of the Nakh peoples native to the North Caucasus in Eastern Europe. "E ...
, part of the Nakh peoples
The Nakh peoples, also known as ''Vainakh peoples'' (Chechen/Ingush: , apparently derived from Chechen , Ingush "our people"; also Chechen-Ingush), are a group of Caucasian peoples identified by their use of the Nakh languages and other cultu ...
, and of primarily Muslim faith. Grozny is the capital and largest city.
History
Origin of Chechnya's population
According to Leonti Mroveli, the 11th-century Georgian chronicler, the word Caucasian is derived from theNakh
Nakh may refer to:
* Nach (Bible acronym) (NaKh), an acronym for ''Nevi'im'' ''Ksuvim''/''Ktuvim'' (the Prophets and (Holy) Writings of ''Tanach'')
* Nakh languages, a group of languages within Northeast Caucasian, spoken chiefly by the Chechens ...
ancestor Kavkas.
According to George Anchabadze of Ilia State University: American linguist Johanna Nichols "has used language to connect the modern people of the Caucasus region to the ancient farmers of the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent ( ar, الهلال الخصيب) is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, State of Palestine, Palestine and Jordan, together with the northern region of Kuwait, sou ...
" and her research suggests that "farmers of the region were proto-Nakh-Daghestanians." Nichols stated: "The Nakh–Dagestanian languages
The Northeast Caucasian languages, also called East Caucasian, Nakh-Daghestani or ''Vainakh-Daghestani'', is a family of languages spoken in the Russian republics of Dagestan, Chechnya and Ingushetia and in Northern Azerbaijan as well as i ...
are the closest thing we have to a direct continuation of the cultural and linguistic community that gave rise to Western civilisation."
Prehistory
 Traces of human settlement dating back to 40,000 BC were found near Lake Kezanoi. Cave paintings, artifacts, and other archaeological evidence indicate continuous habitation for some 8,000 years. People living in these settlements used tools, fire, and clothing made of animal skins.
The
Traces of human settlement dating back to 40,000 BC were found near Lake Kezanoi. Cave paintings, artifacts, and other archaeological evidence indicate continuous habitation for some 8,000 years. People living in these settlements used tools, fire, and clothing made of animal skins.
The Caucasian Epipaleolithic
Trialetian is the name for an Upper Paleolithic-Epipaleolithic stone tool industry from the South Caucasus. It is tentatively dated to the period between 16,000 / 13,000 BP and 8,000 BP.
Archaeology
The name of the archaeological culture deriv ...
and early Caucasian Neolithic era saw the introduction of agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peop ...
, irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been dev ...
, and the domestication of animals in the region. Settlements near Ali-Yurt and Magas, discovered in modern times, revealed tools made out of stone: stone axes, polished stones, stone knives, stones with holes drilled in them, clay dishes etc. Settlements made out of clay bricks were discovered in the plains. In the mountains there were settlements made from stone and surrounded by walls; some of them dated back to 8000 BC. This period also saw the appearance of the wheel (3000 BC), horseback riding, metal works (copper, gold, silver, iron), dishes, armor, daggers, knives and arrow tips in the region. The artifacts were found near Nasare-Cort, Muzhichi, Ja-E-Bortz (alternatively known as Surkha-khi), Abbey-Gove (also known as Nazran or Nasare).
Pre-imperial era
The German scientistPeter Simon Pallas
Peter Simon Pallas Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS FRSE (22 September 1741 – 8 September 1811) was a Prussian zoologist and botanist who worked in Russia between 1767 and 1810.
Life and work
Peter Simon Pallas was born in Berlin, the son ...
believed that the Vainakh people (Chechens and Ingush) were the direct descendants from Alania. In 1239, the Alania capital of Maghas and the Alan confederacy of the Northern Caucasian
Caucasian may refer to:
Anthropology
*Anything from the Caucasus region
**
**
** ''Caucasian Exarchate'' (1917–1920), an ecclesiastical exarchate of the Russian Orthodox Church in the Caucasus region
*
*
*
Languages
* Northwest Caucasian l ...
highlanders, nations, and tribes was destroyed by Batu Khan (a Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
leader and a grandson of Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr /> Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent) Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin ...
).
According to the missionary Pian de Carpine, a part of the Alans had successfully resisted a Mongol siege on a mountain for 12 years:
This twelve year old siege is not found in any other report, however the Russian historian A.I. Krasnov connected this battle with two Chechen folktales he recorded in 1967 that spoke of an old hunter named Idig who with his companions defended the Dakuoh mountain for 12 years against Tatar-Mongols. He also reported to have found several arrowheads and spears from the 13th century near the very mountain at which the battle took place:
In the 14th and 15th centuries, there was frequent warfare between the Chechens, Tamerlan
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617–19 February 1405), later Timūr Gurkānī ( chg, ''Temür Kür ...
and Tokhtamysh, culminating in the Battle of the Terek River
The Battle of the Terek River was the last major battle of Tokhtamysh–Timur war. It took place on April 14, 1395, at the Terek River, North Caucasus. The result was a victory for Timur.
Battle
Tokhtamysh's cavalry attacked the right flank a ...
. The Chechen tribes built fortresses, castles, and defensive walls, protecting the mountains from the invaders. Part of the lowland tribes were occupied by Mongols. However, during the mid-14th century a strong Chechen kingdom called Simsir emerged under Khour Ela, a Chechen king that led the Chechen politics and wars. He was in charge of an army of Chechens against the rogue warlord Mamai and defeated him in the Battle of Tatar-tup in 1362. The kingdom of Simsir met its end during the Timurid invasion of the Caucasus, when Khour Ela allied himself with the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragment ...
Khan Tokhtamysh in the Battle of the Terek River. Timur sought to punish the highlanders for their allegiance to Tokhtamysh and as a consequence invaded Simsir in 1395.
The 16th century saw the first Russian involvement in the Caucasus. In 1558, Temryuk of Kabarda sent his emissaries to Moscow requesting help from Ivan the Terrible
Ivan IV Vasilyevich (russian: Ива́н Васи́льевич; 25 August 1530 – ), commonly known in English as Ivan the Terrible, was the grand prince of Moscow from 1533 to 1547 and the first Tsar of all Russia from 1547 to 1584.
Iv ...
against the Vainakh tribes. Ivan the Terrible married Temryuk's daughter Maria Temryukovna. An alliance was formed to gain the ground in the central Caucasus for the expanding Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I ...
against stubborn Vainakh defenders. Chechnya was a nation in the Northern Caucasus that fought against foreign rule continually since the 15th century. Several Chechen leaders such as the 17th century Mehk-Da Aldaman Gheza led the Chechen politics and fought off encroachments of foreign powers. He defended the borders of Chechnya from invasions of Kabardinians and Avars during the Battle of Khachara in 1667.
The Chechens converted over the next few centuries to Sunni Islam, as Islam was associated with resistance to Russian encroachment.
Imperial rule

Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
first sought to increase Russia's political influence in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
and the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad s ...
at the expense of Safavid Persia when he launched the Russo-Persian War of 1722–1723. Notable in Chechen history, this particular Russo-Persian War marked the first military encounter between Imperial Russia
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. T ...
and the Vainakh. Russian forces succeeded in taking much of the Caucasian territories from Iran for several years.
As the Russians took control of the Caspian corridor and moved into Persian-ruled Dagestan
Dagestan ( ; rus, Дагеста́н, , dəɡʲɪˈstan, links=yes), officially the Republic of Dagestan (russian: Респу́блика Дагеста́н, Respúblika Dagestán, links=no), is a republic of Russia situated in the North ...
, Peter's forces ran into mountain tribes. Peter sent a cavalry force to subdue them, but the Chechens routed them. In 1732, after Russia already ceded back most of the Caucasus to Persia, now led by Nader Shah
Nader Shah Afshar ( fa, نادر شاه افشار; also known as ''Nader Qoli Beyg'' or ''Tahmāsp Qoli Khan'' ) (August 1688 – 19 June 1747) was the founder of the Afsharid dynasty of Iran and one of the most powerful rulers in Iranian ...
, following the Treaty of Resht, Russian troops clashed again with Chechens in a village called Chechen-aul along the Argun River. The Russians were defeated again and withdrew, but this battle is responsible for the apocryphal story about how the Nokchi came to be known as "Chechens"-the people ostensibly named for the place the battle had taken place. The name Chechen was however already used since as early as 1692.
 Under intermittent Persian rule since 1555, in 1783 the eastern Georgians of Kartl-Kakheti led by Erekle II and Russia signed the Treaty of Georgievsk. According to this treaty, Kartl-Kakheti received protection from Russia, and Georgia abjured any dependence on
Under intermittent Persian rule since 1555, in 1783 the eastern Georgians of Kartl-Kakheti led by Erekle II and Russia signed the Treaty of Georgievsk. According to this treaty, Kartl-Kakheti received protection from Russia, and Georgia abjured any dependence on Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
. In order to increase its influence in the Caucasus and to secure communications with Kartli and other Christian regions of the Transcaucasia which it considered useful in its wars against Persia and Turkey, the Russian Empire began conquering the Northern Caucasus mountains. The Russian Empire used Christianity to justify its conquests, allowing Islam to spread widely because it positioned itself as the religion of liberation from tsardom, which viewed Nakh tribes as "bandits". The rebellion was led by Mansur Ushurma
Sheikh Mansur ("The-Victorious"; born Mansur Ushurma, Mansur Ucherman; 2 June 1762 – 13 April 1794) was a Chechen military commander and Islamic leader who fought for Chechnya and Circassia. He was influential in the resistance against Cather ...
, a Chechen Naqshbandi ( Sufi) sheikh—with wavering military support from other North Caucasian tribes. Mansur hoped to establish a Transcaucasus Islamic state under sharia law. He was unable to fully achieve this because in the course of the war he was betrayed by the Ottomans, handed over to Russians, and executed in 1794.
Following the forced ceding of the current territories of Dagestan, most of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
, and Georgia by Persia to Russia, following the Russo-Persian War of 1804–1813 and its resultant Treaty of Gulistan
The Treaty of Gulistan (russian: Гюлистанский договор; fa, عهدنامه گلستان) was a peace treaty concluded between the Russian Empire and Iran on 24 October 1813 in the village of Gulistan (now in the Goranboy Distr ...
, Russia significantly widened its foothold in the Caucasus at the expense of Persia. Another successful Caucasus war against Persia several years later, starting in 1826 and ending in 1828 with the Treaty of Turkmenchay
The Treaty of Turkmenchay ( fa, عهدنامه ترکمنچای; russian: Туркманчайский договор) was an agreement between Qajar Iran and the Russian Empire, which concluded the Russo-Persian War (1826–28). It was second o ...
, and a successful war against Ottoman Turkey in 1828 and 1829, enabled Russia to use a much larger portion of its army in subduing the natives of the North Caucasus
The North Caucasus, ( ady, Темыр Къафкъас, Temır Qafqas; kbd, Ишхъэрэ Къаукъаз, İṩxhərə Qauqaz; ce, Къилбаседа Кавказ, Q̇ilbaseda Kavkaz; , os, Цӕгат Кавказ, Cægat Kavkaz, inh, ...
.
The resistance of the Nakh tribes never ended and was a fertile ground for a new Muslim- Avar commander, Imam Shamil, who fought against the Russians from 1834 to 1859 (see Murid War). In 1859, Shamil was captured by Russians at aul Gunib. Shamil left Baysangur of Benoa, a Chechen with one arm, one eye, and one leg, in charge of command at Gunib. Baysangur broke through the siege and continued to fight Russia for another two years until he was captured and killed by Russians. The Russian tsar hoped that by sparing the life of Shamil, the resistance in the North Caucasus would stop, but it did not. Russia began to use a colonization tactic by destroying Nakh settlements and building Cossack defense lines in the lowlands. The Cossacks suffered defeat after defeat and were constantly attacked by mountaineers, who were robbing them of food and weaponry.
The tsarists' regime used a different approach at the end of the 1860s. They offered Chechens and Ingush to leave the Caucasus for the Ottoman Empire (see Muhajir (Caucasus)). It is estimated that about 80% of Chechens and Ingush left the Caucasus during the deportation. It weakened the resistance which went from open warfare to insurgent warfare. One of the notable Chechen resistance fighters at the end of the 19th century was a Chechen abrek Zelimkhan Gushmazukaev and his comrade-in-arms Ingush abrek Sulom-Beck Sagopshinski. Together they built up small units which constantly harassed Russian military convoys, government mints, and government post-service, mainly in Ingushetia and Chechnya. Ingush aul Kek was completely burned when the Ingush refused to hand over Zelimkhan. Zelimkhan was killed at the beginning of the 20th century. The war between Nakh tribes and Russia resurfaced during the times of the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
, which saw the Nakh struggle against Anton Denikin and later against the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
.
On 21 December 1917, Ingushetia, Chechnya, and Dagestan declared independence from Russia and formed a single state: "United Mountain Dwellers of the North Caucasus" (also known as the Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus) which was recognized by major world powers. The capital of the new state was moved to Temir-Khan-Shura (Dagestan). Tapa Tchermoeff, a prominent Chechen statesman, was elected the first prime minister of the state. The second prime minister elected was Vassan-Girey Dzhabagiev, an Ingush statesman, who also was the author of the constitution of the republic in 1917, and in 1920 he was re-elected for the third term. In 1921 the Russians attacked and occupied the country and forcefully absorbed it into the Soviet state. The Caucasian war for independence restarted, and the government went into exile.
Soviet rule
During Soviet rule, Chechnya and Ingushetia were combined to form theChecheno-Ingush Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
The Checheno-Ingush Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic; inh, Нохч-ГӀалгӀай Автономе Советий Социализма Республика, Noxç-Ġalġay Avtonome Sovetiy Socializma Respublika; russian: Чече́но-И ...
. In the 1930s, Chechnya was flooded with many Ukrainians fleeing from a famine. As a result, many of the Ukrainians settled in Chechen-Ingush ASSR permanently and survived the famine.
Although over 50,000 Chechens and over 12,000 Ingush were fighting against Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
on the front line (including Heroes of the USSR: Abukhadzhi Idrisov, Khanpasha Nuradilov russian: Ханпаша Нурадилович Нурадилов
, image = Khanpasha Nuradilov 140-190 for collage.jpg
, birth_date =
, death_date =
, birth_place = Yaryksu-Aukh village, Khasav-Yurt District, Dagestan, Mounta ...
, Movlid Visaitov
Movlid Visaitov (; 13 May 1914 23 May 1986) was a Chechen Red Army colonel and a Hero of the Soviet Union. Visaitov was commander of 255th Separate Chechen–Ingush cavalry regiment during World War II.
He was the first Soviet officer to radio- ...
), and although Nazi German troops advanced as far as the Ossetian ASSR city of Ordzhonikidze and the Chechen-Ingush ASSR city of Malgobek after capturing half of the Caucasus in less than a month, Chechens and Ingush were falsely accused as Nazi supporters and entire nations were deported during Operation Lentil to the Kazakh SSR
; kk, Қазақ Советтік Социалистік Республикасы)
*1991: Republic of Kazakhstan (russian: Республика Казахстан; kk, Қазақстан Республикасы)
, linking_name = the ...
(later Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
) in 1944 near the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
where over 60% of Chechen and Ingush populations perished.Lieven, Dominic. Russia: Chechnya. Microsoft Encarta 2008. Microsoft Corporation. American historian Norman Naimark
Norman M. Naimark (; born 1944, New York City) is an American historian. He is the Robert and Florence McDonnell Professor of Eastern European Studies at Stanford University, and a senior fellow at the Hoover Institution. He writes on modern Easte ...
writes: The deportation was justified by the materials prepared by NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (russian: Наро́дный комиссариа́т вну́тренних дел, Naródnyy komissariát vnútrennikh del, ), abbreviated NKVD ( ), was the interior ministry of the Soviet Union.
...
officer Bogdan Kobulov accusing Chechens and Ingush in a mass conspiracy preparing rebellion and providing assistance to the German forces. Many of the materials were later proven to be fabricated. Alexander Nikolaevich Yakovlev ''Time of darkness'', Moscow, 2003, , pages 205–206 (russian: Яковлев А. Сумерки. Москва: Материк 2003 г.) Even distinguished Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
officers who fought bravely against Germans (e.g. the commander of 255th Separate Chechen-Ingush regiment Movlid Visaitov
Movlid Visaitov (; 13 May 1914 23 May 1986) was a Chechen Red Army colonel and a Hero of the Soviet Union. Visaitov was commander of 255th Separate Chechen–Ingush cavalry regiment during World War II.
He was the first Soviet officer to radio- ...
, the first to contact American forces at Elbe river) were deported. There is a theory that the real reason why Chechens and Ingush were deported was the desire of Russia to attack Turkey, an anti-communist country, as Chechens and Ingush could impede such plans. In 2004, the European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it adop ...
recognized the deportation of Chechens and Ingush as an act of genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the L ...
.
The territory of the Chechen-Ingush Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic was divided between Stavropol Krai (where Grozny Okrug
Grozny Oblast (russian: Гро́зненская о́бласть) was an administrative entity (an ''oblast'') of the Russian SFSR that was established as Grozny Okrug () on 7 March 1944 and abolished on 9 January 1957.
Formation
After the 1940 ...
was formed), the Dagestan ASSR, the North Ossetian ASSR, and the Georgian SSR
The Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic (Georgian SSR; ka, საქართველოს საბჭოთა სოციალისტური რესპუბლიკა, tr; russian: Грузинская Советская Соц� ...
.
The Chechens and Ingush were allowed to return to their land after 1956 during de-Stalinisation under Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and chairman of the country's Council of Ministers from 1958 to 1964. During his rule, Khrushchev ...
when the Chechen-Ingush ASSR was restored but with both the boundaries and ethnic composition of the territory significantly changed. There were many (predominantly Russian) migrants from other parts of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, who often settled in the abandoned family homes of Chechens and Ingushes. The republic lost its Prigorodny District which transferred to North Ossetian ASSR but gained predominantly Russian Naursky District and Shelkovskoy District that is considered the homeland for Terek Cossacks.
The Russification
Russification (russian: русификация, rusifikatsiya), or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians, whether involuntarily or voluntarily, give up their culture and language in favor of the Russian cultur ...
policies towards Chechens continued after 1956, with Russian language proficiency required in many aspects of life to provide Chechens better opportunities for advancement in the Soviet system.
On 26 November 1990, the Supreme Council of Chechen-Ingush ASSR adopted the "Declaration of State Sovereignty of the Chechen-Ingush Republic". This declaration was part of the reorganisation of the Soviet Union. This new treaty was to be signed 22 August 1991, which would have transformed 15 republic states into more than 80. The 19–21 August 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt led to the abandonment of this reorganisation.
With the impending dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, an independence movement, the Chechen National Congress, was formed, led by ex-Soviet Air Force
The Soviet Air Forces ( rus, Военно-воздушные силы, r=Voyenno-vozdushnyye sily, VVS; literally "Military Air Forces") were one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Soviet Air Defence Forces. The Air Forces ...
general and new Chechen President Dzhokhar Dudayev
Dzhokhar Musayevich Dudayev (, ; russian: Джохар Мусаевич Дудаев; ; 15 February 1944 – 21 April 1996) was a Soviet Air Force general and Chechen separatist leader who was the first president of the Chechen Republic of Ich ...
. It campaigned for the recognition of Chechnya as a separate nation. This movement was opposed by Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin ( rus, Борис Николаевич Ельцин, p=bɐˈrʲis nʲɪkɐˈla(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈjelʲtsɨn, a=Ru-Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin.ogg; 1 February 1931 – 23 April 2007) was a Soviet and Russian politician wh ...
's Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia
North Asia or Northern Asia, also referred to as Siberia, is the northern region of Asia, which is defined in geographic ...
, which argued that Chechnya had not been an independent entity within the Soviet Union—as the Baltic, Central Asian, and other Caucasian States had—but was part of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
and hence did not have a right under the Soviet constitution to secede. It also argued that other republics of Russia
The republics of Russia are 22 territories in the Russia, Russian Federation that each constitute a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject, the highest-level administrative division of Russian territory. They are one of several types of fe ...
, such as Tatarstan
The Republic of Tatarstan (russian: Республика Татарстан, Respublika Tatarstan, p=rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə tətɐrˈstan; tt-Cyrl, Татарстан Республикасы), or simply Tatarstan (russian: Татарстан, tt ...
, would consider seceding from the Russian Federation if Chechnya were granted that right. Finally, it argued that Chechnya was a major hub in the oil infrastructure of Russia and hence its secession would hurt the country's economy and energy access.
In the ensuing decade, the territory was locked in an ongoing struggle between various factions, usually fighting unconventionally.
Chechen Wars
 The First Chechen War took place from 1994 to 1996, when Russian forces attempted to regain control over Chechnya, which had declared independence in November 1991. Despite overwhelming numerical superiority in men, weaponry, and air support, the Russian forces were unable to establish effective permanent control over the mountainous area due to numerous successful full-scale battles and
The First Chechen War took place from 1994 to 1996, when Russian forces attempted to regain control over Chechnya, which had declared independence in November 1991. Despite overwhelming numerical superiority in men, weaponry, and air support, the Russian forces were unable to establish effective permanent control over the mountainous area due to numerous successful full-scale battles and insurgency
An insurgency is a violent, armed rebellion against authority waged by small, lightly armed bands who practice guerrilla warfare from primarily rural base areas. The key descriptive feature of insurgency is its asymmetric nature: small irregu ...
raids. The Budyonnovsk hospital hostage crisis in 1995 shocked the Russian public.
In April 1996 the first democratically elected president of Chechnya, Dzhokhar Dudayev
Dzhokhar Musayevich Dudayev (, ; russian: Джохар Мусаевич Дудаев; ; 15 February 1944 – 21 April 1996) was a Soviet Air Force general and Chechen separatist leader who was the first president of the Chechen Republic of Ich ...
, was killed by Russian forces using a booby trap bomb and a missile fired from a warplane after he was located by triangulating the position of a satellite phone
A satellite telephone, satellite phone or satphone is a type of mobile phone that connects to other phones or the telephone network by radio through orbiting satellites instead of terrestrial cell sites, as cellphones do. The advantage of a ...
he was using.
The widespread demoralisation of the Russian forces in the area and a successful offensive to re-take Grozny by Chechen rebel forces led by Aslan Maskhadov prompted Russian President Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin ( rus, Борис Николаевич Ельцин, p=bɐˈrʲis nʲɪkɐˈla(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈjelʲtsɨn, a=Ru-Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin.ogg; 1 February 1931 – 23 April 2007) was a Soviet and Russian politician wh ...
to declare a ceasefire in 1996, and sign a peace treaty
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an agreement to stop hostilities; a surr ...
a year later that saw a withdrawal of Russian forces.
After the war, parliamentary and presidential elections took place in January 1997 in Chechnya and brought to power new President Aslan Maskhadov, chief of staff and prime minister in the Chechen coalition government, for a five-year term. Maskhadov sought to maintain Chechen sovereignty while pressing the Russian government to help rebuild the republic, whose formal economy and infrastructure were virtually destroyed. Russia continued to send money for the rehabilitation of the republic; it also provided pensions and funds for schools and hospitals. Nearly half a million people (40% of Chechnya's prewar population) had been internally displaced and lived in refugee camps or overcrowded villages. Alex Goldfarb and Marina Litvinenko. "Death of a Dissident: The Poisoning of Alexander Litvinenko and the Return of the KGB." Free Press, New York, 2007. . There was an economic downturn. Two Russian brigades were permanently stationed in Chechnya.
In lieu of the devastated economic structure, kidnapping emerged as the principal source of income countrywide, procuring over US$200 million during the three-year independence of the chaotic fledgling state, although victims were rarely killed. In 1998, 176 people were kidnapped, 90 of whom were released, according to official accounts. President Maskhadov started a major campaign against hostage-takers, and on 25 October 1998, Shadid Bargishev, Chechnya's top anti-kidnapping official, was killed in a remote-controlled car bombing. Bargishev's colleagues then insisted they would not be intimidated by the attack and would go ahead with their offensive. Political violence and religious extremism, blamed on "Wahhabism
Wahhabism ( ar, ٱلْوَهَّابِيَةُ, translit=al-Wahhābiyyah) is a Sunni Islamic Islamic revival, revivalist and Islamic fundamentalism, fundamentalist movement associated with the reformist doctrines of the 18th-century Arabians, ...
", was rife. In 1998, Grozny authorities declared a state of emergency
A state of emergency is a situation in which a government is empowered to be able to put through policies that it would normally not be permitted to do, for the safety and protection of its citizens. A government can declare such a state du ...
. Tensions led to open clashes between the Chechen National Guard and Islamist militants, such as the July 1998 confrontation in Gudermes.
The War of Dagestan began on 7 August 1999, during which the Islamic International Peacekeeping Brigade (IIPB) began an unsuccessful incursion into the neighboring Russian republic of Dagestan
Dagestan ( ; rus, Дагеста́н, , dəɡʲɪˈstan, links=yes), officially the Republic of Dagestan (russian: Респу́блика Дагеста́н, Respúblika Dagestán, links=no), is a republic of Russia situated in the North ...
in favor of the Shura of Dagestan which sought independence from Russia. In September, a series of apartment bombs that killed around 300 people in several Russian cities, including Moscow, were blamed on the Chechen separatists. Some journalists contested the official explanation, instead blaming the Russian Secret Service for blowing up the buildings to initiate a new military campaign against Chechnya. In response to the bombings, a prolonged air campaign of retaliatory strikes against the Ichkerian regime and a ground offensive that began in October 1999 marked the beginning of the Second Chechen War. Much better organized and planned than in the first Chechen War, the Russian armed forces took control of most regions. The Russian forces used brutal force, killing 60 Chechen civilians during a mop-up operation in Aldy, Chechnya on 5 February 2000. After the re-capture of Grozny in February 2000, the Ichkerian regime fell apart.
Post-war reconstruction and insurgency

 Chechen rebels continued to fight Russian troops and conduct terrorist attacks. In October 2002, 40–50 Chechen rebels seized a Moscow theater and took about 900 civilians hostage. The crisis ended with 117 hostages and up to 50 rebels dead, mostly due to an unknown aerosol pumped into the building by Russian special forces to incapacitate the people inside.
In response to the increasing terrorism, Russia tightened its grip on Chechnya and expanded its anti-terrorist operations throughout the region. Russia installed a pro-Russian Chechen regime. In 2003, a referendum was held on a constitution that reintegrated Chechnya within Russia but provided limited autonomy. According to the Chechen government, the referendum passed with 95.5% of the votes and almost 80% turnout. ''
Chechen rebels continued to fight Russian troops and conduct terrorist attacks. In October 2002, 40–50 Chechen rebels seized a Moscow theater and took about 900 civilians hostage. The crisis ended with 117 hostages and up to 50 rebels dead, mostly due to an unknown aerosol pumped into the building by Russian special forces to incapacitate the people inside.
In response to the increasing terrorism, Russia tightened its grip on Chechnya and expanded its anti-terrorist operations throughout the region. Russia installed a pro-Russian Chechen regime. In 2003, a referendum was held on a constitution that reintegrated Chechnya within Russia but provided limited autonomy. According to the Chechen government, the referendum passed with 95.5% of the votes and almost 80% turnout. ''The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Econ ...
'' was skeptical of the results, arguing that "few outside the Kremlin regard the referendum as fair".
In September 2004, separatist rebels occupied a school in the town of Beslan, North Ossetia
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north' ...
, demanding recognition of the independence of Chechnya and a Russian withdrawal. 1,100 people (including 777 children) were taken hostage. The attack lasted three days, resulting in the deaths of over 331 people, including 186 children. After the 2004 school siege, Russian president Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin; (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who holds the office of president of Russia. Putin has served continuously as president or prime minister since 1999: as prime m ...
announced sweeping security and political reforms, sealing borders in the Caucasus region and revealing plans to give the central government more power. He also vowed to take tougher action against domestic terrorism, including preemptive strikes against Chechen separatists. In 2005 and 2006, separatist leaders Aslan Maskhadov and Shamil Basayev were killed.
Since 2007, Chechnya has been governed by Ramzan Kadyrov. Kadyrov's rule has been characterized by high-level corruption, a poor human rights record, widespread use of torture
Torture is the deliberate infliction of severe pain or suffering on a person for reasons such as punishment, extracting a confession, interrogation for information, or intimidating third parties. Some definitions are restricted to acts ...
, and a growing cult of personality. Allegations of anti-gay purges in Chechnya were initially reported on 1 April 2017.
In April 2009, Russia ended its counter-terrorism operation and pulled out the bulk of its army. The insurgency in the North Caucasus continued even after this date. The Caucasus Emirate had fully adopted the tenets of a Salafist jihadist group through its strict adherence to the Sunni Hanbali obedience to the literal interpretation of the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing.: ...
and the Sunnah
In Islam, , also spelled ( ar, سنة), are the traditions and practices of the Islamic prophet Muhammad that constitute a model for Muslims to follow. The sunnah is what all the Muslims of Muhammad's time evidently saw and followed and pass ...
.
In June 2022, the US State Department advised citizens not to travel to Chechnya, due to terrorism, kidnapping, and risk of civil unrest.
Geography
Situated in the eastern part of theNorth Caucasus
The North Caucasus, ( ady, Темыр Къафкъас, Temır Qafqas; kbd, Ишхъэрэ Къаукъаз, İṩxhərə Qauqaz; ce, Къилбаседа Кавказ, Q̇ilbaseda Kavkaz; , os, Цӕгат Кавказ, Cægat Kavkaz, inh, ...
in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, wh ...
, Chechnya is surrounded on nearly all sides by Russian Federal territory. In the west, it borders North Ossetia
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north' ...
and Ingushetia, in the north, Stavropol Krai, in the east, Dagestan, and to the south, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
. Its capital is Grozny. Chechnya is well known for being mountainous, but it is in fact split between the more flat areas north of the Terek, and the highlands south of the Terek.
*Area: 17,300 km2 (6680 sq mi)
*Borders:
**''Internal'':
***Dagestan
Dagestan ( ; rus, Дагеста́н, , dəɡʲɪˈstan, links=yes), officially the Republic of Dagestan (russian: Респу́блика Дагеста́н, Respúblika Dagestán, links=no), is a republic of Russia situated in the North ...
(NE)
*** Ingushetia (W)
*** North Ossetia–Alania (W)
*** Stavropol Krai (NW)
**''Foreign'':
***Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
(Kakheti
Kakheti ( ka, კახეთი ''K’akheti''; ) is a region ( mkhare) formed in the 1990s in eastern Georgia from the historical province of Kakheti and the small, mountainous province of Tusheti. Telavi is its capital. The region comprises e ...
and Mtskheta-Mtianeti) (S)
Rivers:
*Terek Terek may refer to:
Places China
* (), a list of township-level divisions of Xinjiang, town in Xinjiang, China
Kyrgyzstan
*Terek, Alay, a village in Alay District, Osh Region
*Terek, Kara-Kulja, a village in Kara-Kulja District, Osh Region
*Terek ...
*Sunzha
Sunzha (russian: Сунжа, Sunzha; inh, Шолжа-Пхье, Šolža-Pꜧe; is a town and the administrative center of the Sunzhensky District of the Republic of Ingushetia Russia. Before 2016 it was called Ordzhonikidzevskaya ( inh, Ордж ...
* Argun
Climate
Despite a relatively small territory, Chechnya is characterized by a significant variety of climate conditions. The average temperature in Grozny is 11.2 °C (52.1 °F).Cities and towns with over 20,000 people
 * Grozny (capital)
* Shali
*
* Grozny (capital)
* Shali
*Urus-Martan
Urus-Martan (russian: Уру́с-Марта́н; ce, Хьалха-Марта, ''Ẋalxa-Marta'' or , ''Martanthi'') is a town and the administrative center of Urus-Martanovsky District of the Chechen Republic, Russia, located on the Martan River. ...
* Gudermes
* Argun
Administrative divisions
The Chechen Republic is divided into 15 districts and 3 cities of republican significance.Informal divisions
There are no true districts of Chechnya, but the different dialects of the Chechen language informally define different districts. The main dialects are: Grozny, also known as the Dzhokhar dialect, is the dialect of people who live in and in some towns around Grozny. Naskhish, a dialect spoken to the northeast of Chechnya. The most notable difference in this dialect is the addition of the letters "ȯ", "ј" and "є" Day, pronounced like the word 'die' is spoken in a small section of the south, around and in the town of Day. There are other dialects which are believed to define districts, but because these areas are so isolated, not much research has been done on these areas.Demographics
 According to the 2021 Census, the population of the republic is 1,510,824, up from 1,268,989 in the 2010 Census.
As of the 2010 Census,
According to the 2021 Census, the population of the republic is 1,510,824, up from 1,268,989 in the 2010 Census.
As of the 2010 Census, Chechens
The Chechens (; ce, Нохчий, , Old Chechen: Нахчой, ''Naxçoy''), historically also known as ''Kisti'' and '' Durdzuks'', are a Northeast Caucasian ethnic group of the Nakh peoples native to the North Caucasus in Eastern Europe. "E ...
at 1,206,551 make up 95.3% of the republic's population. Other groups include Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
(24,382, or 1.9%), Kumyks
, image = Abdul-Wahab son of Mustafa — a prominent Kumyk architect of the 19th century.
, population = near 600,000
, region1 =
, pop1 = 503,060
, ref1 =
, region2 =
, pop2 ...
(12,221, or 1%), Ingush Ingush may refer to:
* Ingush language
* Ingush people
The Ingush (, inh, ГIалгIай, translit=Ghalghaj, pronounced ) per Oxford dictionary "a member of a people living mainly in Ingushetia in the central Caucasus." Ingushetia is a federa ...
(1,296 or 0.1%) and a host of other small groups, each accounting for less than 0.5% of the total population. The Armenian community, which used to number around 15,000 in Grozny alone, has dwindled to a few families. The Armenian church of Grozny was demolished in 1930. The birth rate was 25.41 in 2004. (25.7 in Achkhoi Martan, 19.8 in Groznyy, 17.5 in Kurchaloi, 28.3 in Urus Martan and 11.1 in Vedeno).
At the end of the Soviet era, ethnic Russians (including Cossacks) comprised about 23% of the population (269,000 in 1989), but now Russians number only about 16,400 people (about 1.2% of the population) and still some emigration is happening.
The languages used in the Republic are Chechen and Russian. Chechen belongs to the Vaynakh or North-central Caucasian language family, which also includes Ingush Ingush may refer to:
* Ingush language
* Ingush people
The Ingush (, inh, ГIалгIай, translit=Ghalghaj, pronounced ) per Oxford dictionary "a member of a people living mainly in Ingushetia in the central Caucasus." Ingushetia is a federa ...
and Batsb. Some scholars place it in a wider North Caucasian languages.
Life expectancy
Despite its difficult past, Chechnya has a highlife expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
, one of the highest in Russia. But the pattern of life expectancy is unusual, and in according to numerous statistics, Chechnya stands out from the overall picture. In 2020 Chechnya had the deepest fall in life expectancy, but in 2021 it had the biggest rise. Chechnya has the highest excess of life expectancy in rural areas over cities.
original svg-file
in a separate window and hover over a bubble to highlight it. File:Comparison gender life expectancy -Russia -urban vs rural.svg, Analogious interactive chart of comparison of urban and rural life expectancy.
Settlements
Vital statistics
Fedstat (Суммарный коэффициент рождаемости)
Ethnic groups
(in the territory of modern Chechnya)Religion

Islam
Islam is the predominant religion in Chechnya, practiced by 95% of those polled in Grozny in 2010. Most of the population follows either the Shafi'i or theHanafi
The Hanafi school ( ar, حَنَفِية, translit=Ḥanafiyah; also called Hanafite in English), Hanafism, or the Hanafi fiqh, is the oldest and one of the four traditional major Sunni schools ( maddhab) of Islamic Law (Fiqh). It is named ...
schools of fiqh
''Fiqh'' (; ar, فقه ) is Islamic jurisprudence. Muhammad-> Companions-> Followers-> Fiqh.
The commands and prohibitions chosen by God were revealed through the agency of the Prophet in both the Quran and the Sunnah (words, deeds, and ...
(Islamic jurisprudence
Jurisprudence, or legal theory, is the theoretical study of the propriety of law. Scholars of jurisprudence seek to explain the nature of law in its most general form and they also seek to achieve a deeper understanding of legal reasoning ...
). The Shafi'i school of jurisprudence has a long tradition among the Chechens, and thus it remains the most practiced. Many Chechens are also Sufis, of either the Qadiri or Naqshbandi orders.
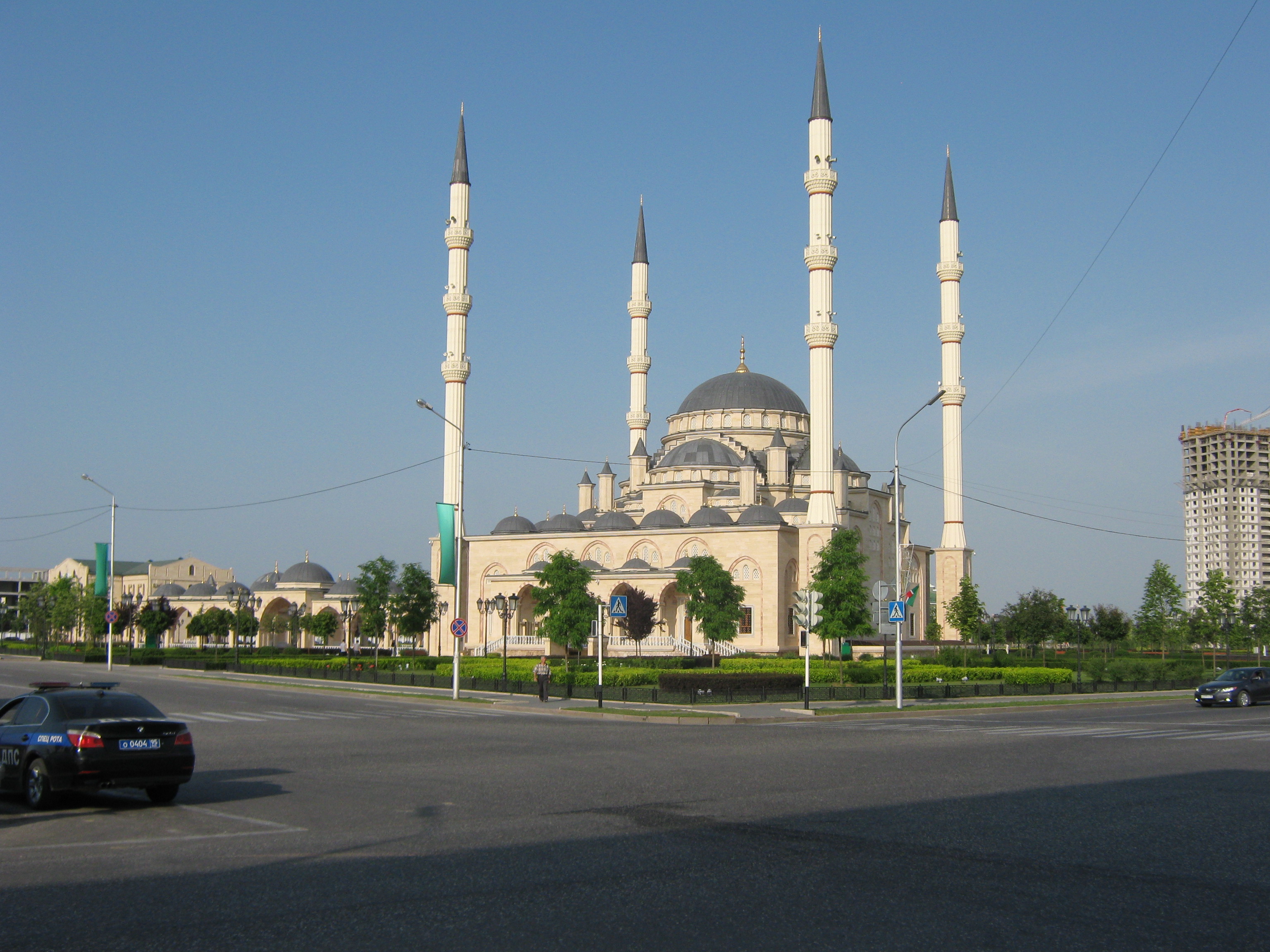
Following the end of the Soviet Union, there has been an Islamic revival in Chechnya, and in 2011 it was estimated that there were 465 mosques, including the Akhmad Kadyrov Mosque in Grozny accommodating 10,000 worshippers, as well 31 madrasas, including an Islamic university named Kunta-haji and a Center of Islamic Medicine in Grozny which is the largest such institution in Europe.
Christianity
From the 11th to 13th centuries (i.e. before Mongol invasions of Durdzuketia), there was a mission of Georgian Orthodox missionaries to the Nakh peoples. Their success was limited, though a couple of highland teips did convert (conversion was largely byteip
Teips (also taip, teyp; Nakh тайпа ''taypa'' : ''family, kin, clan, tribe''Нохчийн-Оьрсийн словарь (Chechen-Russian Dictionary, A.G. Matsiyev, Moscow, 1961), ''also available online:'Чеченско-Русский сл� ...
). However, during the Mongol invasions, these Christianized teip
Teips (also taip, teyp; Nakh тайпа ''taypa'' : ''family, kin, clan, tribe''Нохчийн-Оьрсийн словарь (Chechen-Russian Dictionary, A.G. Matsiyev, Moscow, 1961), ''also available online:'Чеченско-Русский сл� ...
s gradually reverted to paganism, perhaps due to the loss of trans-Caucasian contacts as the Georgians fought the Mongols and briefly fell under their dominion.
The once-strong Russian minority in Chechnya, mostly Terek Cossacks and estimated as numbering approximately 25,000 in 2012, are predominantly Russian Orthodox, although currently only one church exists in Grozny. In August 2011, Archbishop Zosima of Vladikavkaz
Vladikavkaz (russian: Владикавка́з, , os, Дзæуджыхъæу, translit=Dzæwdžyqæw, ;), formerly known as Ordzhonikidze () and Dzaudzhikau (), is the capital city of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania, Russia. It is located in ...
and Makhachkala
Makhachkala ( rus, Махачкала, , məxətɕkɐˈla, links=yes),; av, Махӏачхъала, Maħaçqala; ce, ХӀинжа-ГӀала, Hinƶa-Ġala; az, Маһачгала, Mahaçqala; nog, Махачкала; lbe, Махачкъала; ...
performed the first mass baptism
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost inv ...
ceremony in the history of the Chechen Republic in the Terek River of Naursky District in which 35 citizens of Naursky and Shelkovsky districts were converted to Orthodoxy. As of 2020, there are eight Orthodox churches in Chechnya, the largest is the temple of the Archangel Michael in Grozny.
Politics
Since 1990, the Chechen Republic has had many legal, military, and civil conflicts involving separatist movements and pro-Russian authorities. Today, Chechnya is a relatively stablefederal republic
A federal republic is a federation of Federated state, states with a republican form of government. At its core, the literal meaning of the word republic when used to reference a form of government means: "a country that is governed by elected r ...
, although there is still some separatist movement activity. Its regional constitution entered into effect on 2 April 2003, after an all-Chechen referendum was held on 23 March 2003. Some Chechens were controlled by regional teip
Teips (also taip, teyp; Nakh тайпа ''taypa'' : ''family, kin, clan, tribe''Нохчийн-Оьрсийн словарь (Chechen-Russian Dictionary, A.G. Matsiyev, Moscow, 1961), ''also available online:'Чеченско-Русский сл� ...
s, or clans, despite the existence of pro- and anti-Russian political structures.
Regional government
 The former separatist religious leader (mufti) Akhmad Kadyrov, looked upon as a traitor by many separatists, was elected president with 83% of the vote in an internationally monitored election on 5 October 2003. Incidents of ballot stuffing and voter intimidation by Russian soldiers and the exclusion of separatist parties from the polls were subsequently reported by
The former separatist religious leader (mufti) Akhmad Kadyrov, looked upon as a traitor by many separatists, was elected president with 83% of the vote in an internationally monitored election on 5 October 2003. Incidents of ballot stuffing and voter intimidation by Russian soldiers and the exclusion of separatist parties from the polls were subsequently reported by Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, prom ...
(OSCE) monitors. On 9 May 2004, Kadyrov was assassinated in Grozny football stadium by a landmine
A land mine is an explosive device concealed under or on the ground and designed to destroy or disable enemy targets, ranging from combatants to vehicles and tanks, as they pass over or near it. Such a device is typically detonated automati ...
explosion that was planted beneath a VIP stage and detonated during a parade, and Sergey Abramov was appointed acting prime minister after the incident. However, since 2005 Ramzan Kadyrov (son of Akhmad Kadyrov) has been the caretaker prime minister, and in 2007 was appointed as the new president. Many allege he is the wealthiest and most powerful man in the republic, with control over a large private militia (the Kadyrovites). The militia, which began as his father's security force, has been accused of killings and kidnappings by human rights organisations such as Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human ...
.
Separatist government

 Ichkeria was a member of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organisation between 1991 and 2010. Former president of
Ichkeria was a member of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organisation between 1991 and 2010. Former president of Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
Zviad Gamsakhurdia deposed in a military coup of 1991 and a participant of the Georgian Civil War, recognized the independence of the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria in 1993.in 1993, ex –President of Georgia Zviad Gamsakhurdia recognized Chechnya's independence..Diplomatic relations with Ichkeria were also established by the partially recognised Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan under the
Taliban
The Taliban (; ps, طالبان, ṭālibān, lit=students or 'seekers'), which also refers to itself by its state name, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a Deobandi Islamic fundamentalist, militant Islamist, jihadist, and Pas ...
government on 16 January 2000. This recognition ceased with the fall of the Taliban in 2001. However, despite Taliban recognition, there were no friendly relations between the Taliban and Ichkeria—Maskhadov rejected their recognition, stating that the Taliban were illegitimate.Kullberg, Anssi. "The Background of Chechen Independence Movement III: The Secular Movement". ''The Eurasian politician''. 1 October 2003 Ichkeria also received vocal support from the Baltic countries, a group of Ukrainian nationalists, and Poland; Estonia once voted to recognize, but the act never was followed through due to pressure applied by both Russia and the EU.Kuzio, Taras. "The Chechen crisis and the 'near abroad. ''Central Asian Survey'', Volume 14, Issue 4 1995, pages 553–572
The president of this government was Aslan Maskhadov, the foreign minister was Ilyas Akhmadov, who was the spokesman for Maskhadov. Aslan Maskhadov had been elected in an internationally monitored election in 1997 for four years, which took place after signing a peace agreement with Russia. In 2001 he issued a decree prolonging his office for one additional year; he was unable to participate in the 2003 presidential election since separatist parties were barred by the Russian government, and Maskhadov faced accusations of terrorist offenses in Russia. Maskhadov left Grozny and moved to the separatist-controlled areas of the south at the onset of the Second Chechen War. Maskhadov was unable to influence a number of warlords who retain effective control over Chechen territory, and his power was diminished as a result. Russian forces killed Maskhadov on 8 March 2005, and the assassination of Maskhadov was widely criticized since it left no legitimate Chechen separatist leader with whom to conduct peace talks. Akhmed Zakayev, deputy prime minister and a foreign minister under Maskhadov, was appointed shortly after the 1997 election and is currently living under asylum in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
. He and others chose Abdul Khalim Saidullayev
Abdul-Halim Abusalamovich Sadulayev ( ; Chechen: Сайд-Iелийн Абусаламин кІант Iабдул-Хьалим, ''Sadulin Abusalamin-Kant Abdulhalim''; Russian: Абдул-Халим Αбусаламович Сайдулае ...
, a relatively unknown Islamic judge who was previously the host of an Islamic program on Chechen television, to replace Maskhadov following his death. On 17 June 2006, it was reported that Russian special forces killed Abdul Khalim Saidullayev in a raid in the Chechen town of Argun.
The successor of Saidullayev became Doku Umarov. On 31 October 2007, Umarov abolished the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria
The Chechen Republic of Ichkeria (; ce, Нохчийн Республик Ичкери, Nóxçiyn Respublik Içkeri; russian: Чеченская Республика Ичкерия; abbreviated as "ChRI" or "CRI") was a ''de facto'' state tha ...
and its presidency and in its place proclaimed the Caucasus Emirate with himself as its Emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
. This change of status has been rejected by many Chechen politicians and military leaders who continue to support the existence of the republic.
During the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, the Ukrainian parliament
The Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine ( uk, Верхо́вна Ра́да Украї́ни, translit=, Verkhovna Rada Ukrainy, translation=Supreme Council of Ukraine, Ukrainian abbreviation ''ВРУ''), often simply Verkhovna Rada or just Rada, is the ...
voted to recognize the "Chechen republic of Ichkeria as territory temporarily occupied by the Russian Federation".
Human rights
The Internal Displacement Monitoring Center reports that after hundreds of thousands of ethnic Russians and Chechens fled their homes following inter-ethnic and separatist conflicts in Chechnya in 1994 and 1999, more than 150,000 people still remain displaced in Russia today. Human rights groups criticized the conduct of the 2005 parliamentary elections as unfairly influenced by the central Russian government and military. In 2006Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human ...
reported that pro-Russian Chechen forces under the command of Ramzan Kadyrov, as well as federal police personnel, used torture to get information about separatist forces. "If you are detained in Chechnya, you face a real and immediate risk of torture. And there is little chance that your torturer will be held accountable", said Holly Cartner, Director of the Europe and Central Asia division of the Human Rights Watch.
In 2009, the US government financed American organization Freedom House
Freedom House is a non-profit, majority U.S. government funded organization in Washington, D.C., that conducts research and advocacy on democracy, political freedom, and human rights. Freedom House was founded in October 1941, and Wendell Wi ...
included Chechnya in the "Worst of the Worst" list of most repressive societies in the world, together with Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, Joh ...
, North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and ...
, Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
, and others.
On 1 February 2009, ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' released extensive evidence to support allegations of consistent torture and executions under the Kadyrov government. The accusations were sparked by the assassination in Austria of a former Chechen rebel who had gained access to Kadyrov's inner circle, 27-year-old Umar Israilov Umar S. Israilov (russian: Умар Шарпуддиевич Исраилов; c. 1982 – January 13, 2009) was a former bodyguard of Chechen President Ramzan Kadyrov who became a critic of the Chechen government. He was shot and killed in exi ...
.
On 1 July 2009, Amnesty International released a detailed report covering the human rights violations committed by the Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia
North Asia or Northern Asia, also referred to as Siberia, is the northern region of Asia, which is defined in geographic ...
against Chechen citizens. Among the most prominent features was that those abused had no method of redress against assaults, ranging from kidnapping to torture, while those responsible were never held accountable. This led to the conclusion that Chechnya was being ruled without law, being run into further devastating destabilization.
 On 10 March 2011,
On 10 March 2011, Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human ...
reported that since Chechenization, the government has pushed for enforced Islamic dress code. The president Ramzan Kadyrov is quoted as saying "I have the right to criticize my wife. She doesn't ave the right to criticize me
''Alta Velocidad Española'' (''AVE'') is a service of high-speed rail in Spain operated by Renfe, the Spanish national railway company, at speeds of up to . As of December 2021, the Spanish high-speed rail network, on part of which the AVE s ...
With us n Chechen society a wife is a housewife
A housewife (also known as a homemaker or a stay-at-home mother/mom/mum) is a woman whose role is running or managing her family's home— housekeeping, which includes caring for her children; cleaning and maintaining the home; making, buyin ...
. A woman should know her place. A woman should give her love to us en.. She would be an'sproperty. And the man is the owner. Here, if a woman does not behave properly, her husband, father, and brother are responsible. According to our tradition, if a woman fools around, her family members kill her... That's how it happens, a brother kills his sister or a husband kills his wife... As a president, I cannot allow for them to kill. So, let women not wear shorts...". He has also openly defended honor killings on several occasions.
On 9 July 2017, Russian newspaper '' Novaya Gazeta'' reported that a number of people were subject to an extrajudicial execution on the night of 26 January 2017. It published 27 names of the people known to be dead, but stressed that the list is "not all f those killed
F, or f, is the sixth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ef'' (pronounced ), and the plural is ''efs''.
Hist ...
; the newspaper asserted that 50 people may have been killed in the execution. Some of the dead were gay, but not all; the deaths appeared to have been triggered by the death of a policeman, and according to the author of the report, Elena Milashina, were executed for alleged terrorism.
In December 2021, up to 50 family members of critics of the Kadyrov government were abducted in a wave of mass kidnappings beginning on 22 December.
LGBT rights
On 1 September 1997, Criminal Code reportedly being implemented in the Chechen Republic-Ichkeriya, Article 148 punishes "anal sexual intercourse between a man and a woman or a man and a man". For first- and second-time offenders, the punishment is caning. A third conviction leads to the death penalty, which can be carried out in a number of ways including stoning orbeheading
Decapitation or beheading is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and most other animals, since it deprives the brain of oxygenated blood, while all other organs are deprived of the i ...
.
In 2017, it was reported by '' Novaya Gazeta'' and human rights groups that Chechen authorities had set up concentration camp
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simp ...
s, one of which is in Argun, where gay men are interrogated and subjected to physical violence. On 27 June 2018, the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe noted "cases of abduction, arbitrary detention and torture ... with the direct involvement of Chechen law enforcement officials and on the orders of top-level Chechen authorities" and expressed dismay "at the statements of Chechen and Russian public officials denying the existence of LGBTI people in the Chechen Republic". Kadyrov's spokesman Alvi Karimov told Interfax
Interfax (russian: Интерфакс) is a Russian news agency. The agency is owned by Interfax News Agency joint-stock company and is headquartered in Moscow.
History
As the first non-governmental channel of political and economic informati ...
that gay people "simply do not exist in the republic" and made an approving reference to honor killings by family members "if there were such people in Chechnya". In a 2021 Council of Europe report into anti-LGBTI hate crimes, rapporteur Foura ben Chikha described the "state-sponsored attacks carried out against LGBTI people in Chechnya in 2017" as "the single most egregious example of violence against LGBTI people in Europe that has occurred in decades".
On 11 January 2019, it was reported that another 'gay purge' had begun in the country in December 2018, with several gay men and women being detained. The Russian LGBT Network
The Russian LGBT Network (russian: Российская ЛГБТ-сеть) is a non-governmental LGBT rights organization working for the social acceptance of and protection of the rights of LGBT people in Russia. Founded in 2006, it was reformed ...
believes that around 40 people were detained and two killed.
Economy
During the war, the Chechen economy fell apart. In 1994, the separatists planned to introduce a new currency, but the change did not occur due to the re-taking of Chechnya by Russian troops in the Second Chechen War. The economic situation in Chechnya has improved considerably since 2000. According to the ''New York Times'', major efforts to rebuild Grozny have been made, and improvements in the political situation have led some officials to consider setting up a tourism industry, though there are claims that construction workers are being irregularly paid and that poor people have been displaced. Chechnya's unemployment was 67% in 2006 and fell to 21.5% in 2014. Total revenue of the budget of Chechnya for 2017 was 59.2 billion rubles. Of these, 48.5 billion rubles were grants from the federal budget of the Russian Federation. In late 1970s, Chechnya produced up to 20 million tons of oil annually, production declined sharply to approximately 3 million tons in the late 1980s, and to below 2 million tons before 1994, first (1994–1996) second Russian invasion of Chechnya (1999) inflicted material damage on the oil-sector infrastructure, oil production decreased to 750,000 tons in 2001 only to increase to 2 million tons in 2006, by 2012 production was 1 million tons. Gazprom, the Russian national oil company, has control of Chechen oil and gas currently.References
Notes
Sources
* * *Further reading
*Anderson, Scott. The Man Who Tried to Save the World. * Babchenko, Arkady. ''One Soldier's War in Chechnya''. Portobello, London *Baiev, Khassan. ''The Oath: A Surgeon Under Fire''. * Bennigsen-Broxup, Marie. ''The North Caucasus Barrier: The Russian Advance Towards the Muslim World''. *Bird, Chris. ''To Catch a Tartar: Notes from the Caucasus''. *Bornstein, Yvonne and Ribowsky, Mark. "Eleven Days of Hell: My True Story of Kidnapping, Terror, Torture And Historic FBI & KGB Rescue" AuthorHouse, 2004. . *Conrad, RoyRoy Conrad. Grozny. A few days...
*Dunlop, John B. ''Russia Confronts Chechnya: Roots of a Separatist Conflict'' *Evangelista, Mathew. ''The Chechen Wars: Will Russia Go the Way of the Soviet Union?''. . *Gall, Charlotta & de Waal, Thomas. ''Chechnya: A Small Victorious War''. *Gall, Carlotta, and de Waal, Thomas ''Chechnya: Calamity in the Caucasus'' * Goltz, Thomas. ''Chechnya Diary : A War Correspondent's Story of Surviving the War in Chechnya''. M E Sharpe (2003). *Hasanov, Zaur. The Man of the Mountains. (facts based novel on growing influence of the radical Islam during 1st and 2nd Chechnya wars) *Khan, Ali
The Chechen Terror: The Play within the Play
* Khlebnikov, Paul. ''Razgovor s varvarom'' (Interview with a barbarian). . * Lieven, Anatol. ''Chechnya : Tombstone of Russian Power'' * Mironov, Vyacheslav. ''Ya byl na etoy voyne.'' (I was in this war) Biblion – Russkaya Kniga, 2001. Partial translation available online. * Mironov, Vyacheslav
Vyacheslav Mironov. Assault on Grozny Downtown
* Mironov, Vyacheslav
Vyacheslav Mironov. ''I was in that war''.
*Oliker, Olga ''Russia's Chechen Wars 1994–2000: Lessons from Urban Combat''. . (A strategic and tactical analysis of the Chechen Wars.) *Pelton, Robert Young. ''Hunter Hammer and Heaven, Journeys to Three World's Gone Mad'' () * Politkovskaya, Anna. ''A Small Corner of Hell: Dispatches from Chechnya'' *Rasizade, Alec. Chechnya: the Achilles heel of Russia. = Contemporary Review (Oxford) in three parts: 1
April 2005 issue, volume 286, number 1671, pages 193–197
2
3
*Seirstad, Asne. The Angel of Grozny. *Wood, Tony
Book review in
The Independent
''The Independent'' is a British online newspaper. It was established in 1986 as a national morning printed paper. Nicknamed the ''Indy'', it began as a broadsheet and changed to tabloid format in 2003. The last printed edition was publishe ...
, 2007
External links
* of the Republic of Chechnya * * * (video)Islamist Extremism in Chechnya: A Threat to U.S. Homeland?: Joint Hearing before the Subcommittee on Europe, Eurasia, and Emerging Threats and the Subcommittee on Terrorism, Nonproliferation, and Trade of the Committee on Foreign Affairs, House of Representatives, One Hundred Thirteenth Congress, First Session, April 26, 2013
*
Chechnya Guide
{{Authority control 1993 establishments in Russia Chechen-speaking countries and territories North Caucasian Federal District North Caucasus Regions of Europe with multiple official languages States and territories established in 1993