Celiac plexus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The celiac plexus, also known as the solar plexus because of its radiating nerve fibers, is a complex network of nerves located in the
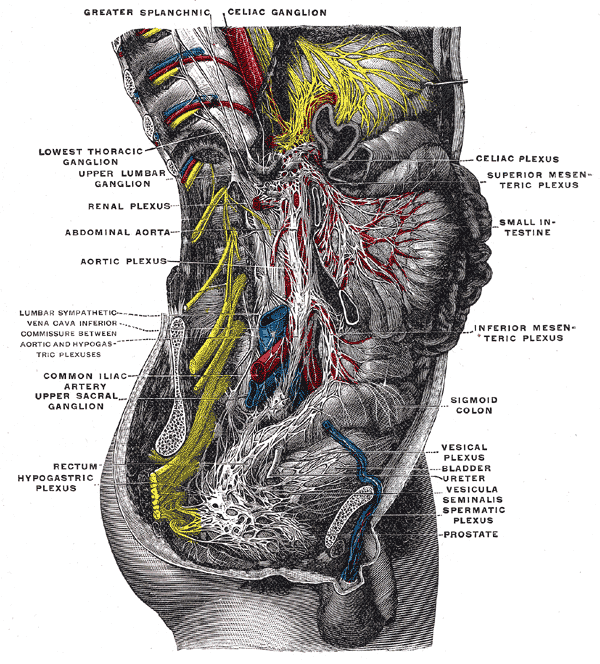
 The celiac plexus includes a number of smaller plexuses:
Other plexuses that are derived from the celiac plexus:
The celiac plexus includes a number of smaller plexuses:
Other plexuses that are derived from the celiac plexus:
 A blunt injury to the celiac plexus normally resolves with rest and deep breathing.
A celiac plexus block by means of fluoroscopically guided injection is sometimes used to treat intractable pain from cancers such as
A blunt injury to the celiac plexus normally resolves with rest and deep breathing.
A celiac plexus block by means of fluoroscopically guided injection is sometimes used to treat intractable pain from cancers such as
The Solar Plexus: Abdominal Brain By Theron Q. Dumont
{{Authority control Nerve plexus Nerves of the torso Vagus nerve
abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal ...
, near where the celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery, and renal arteries branch from the abdominal aorta. It is behind the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
and the omental bursa, and in front of the crura of the diaphragm, on the level of the first lumbar vertebra.
The plexus is formed in part by the greater and lesser splanchnic nerves of both sides, and fibers from the anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
and posterior vagal trunks.
The celiac plexus proper consists of the celiac ganglia with a network of interconnecting fibers. The aorticorenal ganglia are often considered to be part of the celiac ganglia, and thus, part of the plexus.
Structure
 The celiac plexus includes a number of smaller plexuses:
Other plexuses that are derived from the celiac plexus:
The celiac plexus includes a number of smaller plexuses:
Other plexuses that are derived from the celiac plexus:
Terminology
The celiac plexus is often popularly referred to as the solar plexus. In the context of sparring or injury, a strike to the region of the stomach around the celiac plexus is commonly called a blow "to the solar plexus". In this case it is not the celiac plexus itself being referred to, but rather the region around it. A blow to this region may cause the diaphragm to spasm, resulting in difficulty in breathing—a sensation commonly known as " getting the wind knocked out of you". It may also affect the celiac plexus itself, which can cause great pain and interfere with the functioning of theviscera
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to a ...
.
Clinical significance
 A blunt injury to the celiac plexus normally resolves with rest and deep breathing.
A celiac plexus block by means of fluoroscopically guided injection is sometimes used to treat intractable pain from cancers such as
A blunt injury to the celiac plexus normally resolves with rest and deep breathing.
A celiac plexus block by means of fluoroscopically guided injection is sometimes used to treat intractable pain from cancers such as pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer arises when cell (biology), cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a Neoplasm, mass. These cancerous cells have the malignant, ability to invade other parts of ...
. Such a block may be performed by pain management specialists and radiologists, with CT scans for guidance.
Intractable pain related to chronic pancreatitis may be an indication for celiac plexus ablation.
See also
* Cardiac plexus * Celiac ganglia *Superior hypogastric plexus
The superior hypogastric plexus (in older texts, hypogastric plexus or presacral nerve) is a plexus of nerves situated on the vertebral bodies anterior to the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta. It bifurcates to form the left and the right hypog ...
* Manipura
References
External links
* - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: The Celiac Plexus" *The Solar Plexus: Abdominal Brain By Theron Q. Dumont
{{Authority control Nerve plexus Nerves of the torso Vagus nerve