Celecoxib Structure on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Celecoxib, sold under the brand name Celebrex among others, is a
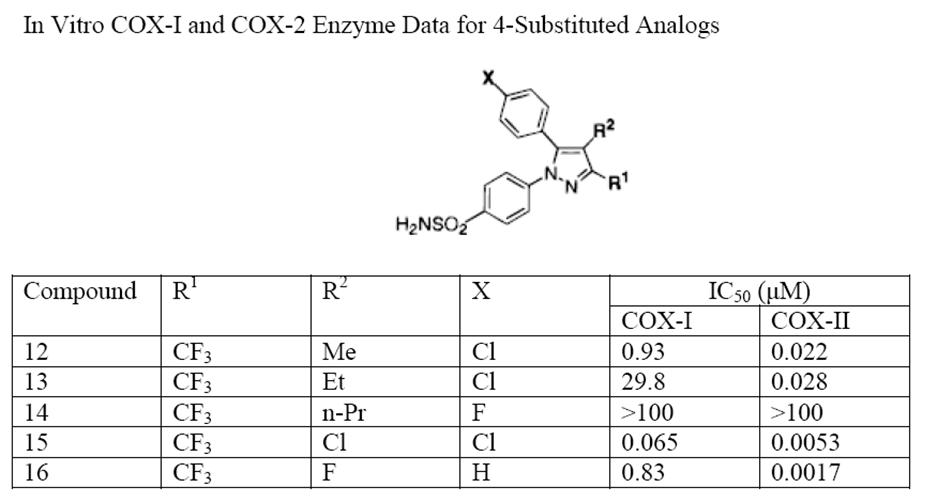
 The Searle research group found the two appropriately substituted aromatic rings must reside on adjacent positions about the central ring for adequate COX-2 inhibition. Various modifications can be made to the 1,5-diarylpyrazole moiety to deduce the structure-activity relationship of celecoxib. A para-sulfamoylphenyl at position 1 of the pyrazole was found to have a higher potency for COX-2 selective inhibition than a para-methoxyphenyl (see structures 1 and 2, below). In addition, a 4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl or 4-sulfamoylphenyl is known to be necessary for COX-2 inhibition. For instance, replacing either of these entities with a –SO2NHCH3 substituent diminishes COX-2 inhibitory activity as noted with a very high inhibitory concentration-50 (see structures 3 – 5). At the 3-position of the pyrazole, a trifluoromethyl or difluoromethyl provides superior selectivity and potency compared to a fluoromethyl or methyl substitution (see structures 6 – 9).
Celecoxib is compound 22; the 4-sulfamoylphenyl on the 1-pyrazol substituent is required for COX-2 inhibition and the 4-methyl on the 5-pyrazol system has low steric hindrance to maximising potency, while the 3-trifluoromethyl group provides superior selectivity and potency. To explain the selectivity of celecoxib, it is necessary to analyze the free energy of binding difference between the drug molecule and COX-1 compared to COX-2 enzymes. The structural modifications highlight the importance of binding to residue 523 in the side binding pocket of the cyclooxygenase enzyme, which is an isoleucine in COX-1 and a valine in COX-2. This mutation appears to contribute to COX-2 selectivity by creating steric hindrance between the sulfonamide oxygen and the methyl group of Ile523 that effectively destabilizes the celecoxib-COX-1 complex.
The Searle research group found the two appropriately substituted aromatic rings must reside on adjacent positions about the central ring for adequate COX-2 inhibition. Various modifications can be made to the 1,5-diarylpyrazole moiety to deduce the structure-activity relationship of celecoxib. A para-sulfamoylphenyl at position 1 of the pyrazole was found to have a higher potency for COX-2 selective inhibition than a para-methoxyphenyl (see structures 1 and 2, below). In addition, a 4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl or 4-sulfamoylphenyl is known to be necessary for COX-2 inhibition. For instance, replacing either of these entities with a –SO2NHCH3 substituent diminishes COX-2 inhibitory activity as noted with a very high inhibitory concentration-50 (see structures 3 – 5). At the 3-position of the pyrazole, a trifluoromethyl or difluoromethyl provides superior selectivity and potency compared to a fluoromethyl or methyl substitution (see structures 6 – 9).
Celecoxib is compound 22; the 4-sulfamoylphenyl on the 1-pyrazol substituent is required for COX-2 inhibition and the 4-methyl on the 5-pyrazol system has low steric hindrance to maximising potency, while the 3-trifluoromethyl group provides superior selectivity and potency. To explain the selectivity of celecoxib, it is necessary to analyze the free energy of binding difference between the drug molecule and COX-1 compared to COX-2 enzymes. The structural modifications highlight the importance of binding to residue 523 in the side binding pocket of the cyclooxygenase enzyme, which is an isoleucine in COX-1 and a valine in COX-2. This mutation appears to contribute to COX-2 selectivity by creating steric hindrance between the sulfonamide oxygen and the methyl group of Ile523 that effectively destabilizes the celecoxib-COX-1 complex.
CAFC Court Decision Reach-Through Claims Declared Invalid
/ref> According to the
COX-2 inhibitor
Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors (COX-2 inhibitors), also known as coxibs, are a type of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that directly target cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), an enzyme responsible for inflammation and pain. Targeting selectivity ...
and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a Indication (medicine), therapeutic drug class which Analgesic, reduces pain, Anti-inflammatory, decreases inflammation, Antipyretic, decreases fever, and Antithrombotic, prevents bl ...
(NSAID). It is used to treat the pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or res ...
and inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
in osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of articular cartilage, joint cartilage and underlying bone. A form of arthritis, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affect ...
, acute pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or res ...
in adults, rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
, psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a long-term inflammatory arthritis that may occur in some people affected by the autoimmune disease psoriasis. The classic features of psoriatic arthritis include dactylitis (sausage-like swelling of the fingers ...
, ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis from the disease spectrum of axial spondyloarthritis. It is characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine, typically where the spine joins the pelvis. With AS, eye and bow ...
, painful menstruation, and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
Juvenile may refer to:
In general
*Juvenile status, or minor (law), prior to adulthood
*Juvenile (organism)
Music
*Juvenile (rapper) (born 1975), stage name of American rapper Terius Gray
*''Juveniles'', a 2020 studio album by the band Kingswoo ...
. It may also be used to decrease the risk of colorectal adenomas in people with familial adenomatous polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an autosomal dominant inherited condition in which numerous adenomatous polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colon ...
. It is taken by mouth
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications.
Oral administ ...
. Benefits are typically seen within an hour.
Common side effects include abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues. Since the abdomen contains most of the body's vital organs, it can be an indicator of a wide variety of diseases. Given th ...
, nausea, and diarrhea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
. Serious side effects may include heart attacks
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is retr ...
, stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
s, gastrointestinal perforation
Gastrointestinal perforation, also known as gastrointestinal rupture, is a hole in the wall of the gastrointestinal tract. The gastrointestinal tract is composed of hollow digestive organs leading from the mouth to the anus. Symptoms of gastroi ...
, gastrointestinal bleeding
Gastrointestinal bleeding (GI bleed), also called gastrointestinal hemorrhage (GIB), is all forms of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the rectum. When there is significant blood loss over a short time, symptoms may includ ...
, kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as renal failure or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney fa ...
, and anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis (Greek: 'up' + 'guarding') is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of the use of emergency medication on site. It typicall ...
. Use is not recommended in people at high risk for heart disease. The risks are similar to other NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes dysmenorrhea, painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It can be taken oral administration, ...
and naproxen
Naproxen, sold under the brand name Aleve among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain, menstrual cramps, and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout and fever. It is taken orally. It ...
. Use in the later part of pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
or during breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, also known as nursing, is the process where breast milk is fed to a child. Infants may suck the milk directly from the breast, or milk may be extracted with a Breast pump, pump and then fed to the infant. The World Health Orga ...
is not recommended.
Celecoxib has demonstrated adjunctive
In linguistics, an adjunct is an optional, or ''structurally dispensable'', part of a sentence, clause, or phrase that, if removed or discarded, will not structurally affect the remainder of the sentence. Example: In the sentence ''John helped Bill ...
benefits in major depression
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Intro ...
and efficacy in reducing polyp recurrence in familial adenomatous polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an autosomal dominant inherited condition in which numerous adenomatous polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colon ...
, while also being investigated for broader psychiatric, anticancer, and chemopreventive applications.
Celecoxib was patented in 1993 and came into medical use in 1999. It is available as a generic medication
A generic drug is a pharmaceutical drug that contains the same chemical substance as a drug that was originally protected by chemical patents. Generic drugs are allowed for sale after the patents on the original drugs expire. Because the active ch ...
. In 2022, it was the 93rd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 7million prescriptions.
Medical uses
Celecoxib is indicated for the treatment ofosteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of articular cartilage, joint cartilage and underlying bone. A form of arthritis, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affect ...
, rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
, psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a long-term inflammatory arthritis that may occur in some people affected by the autoimmune disease psoriasis. The classic features of psoriatic arthritis include dactylitis (sausage-like swelling of the fingers ...
, acute pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or res ...
, musculoskeletal pain, painful menstruation
Menstruation (also known as a period, among other colloquial terms) is the regular discharge of blood and Mucous membrane, mucosal tissue from the endometrium, inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. The menstrual cycle is characterized ...
, ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis from the disease spectrum of axial spondyloarthritis. It is characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine, typically where the spine joins the pelvis. With AS, eye and bow ...
, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
Juvenile may refer to:
In general
*Juvenile status, or minor (law), prior to adulthood
*Juvenile (organism)
Music
*Juvenile (rapper) (born 1975), stage name of American rapper Terius Gray
*''Juveniles'', a 2020 studio album by the band Kingswoo ...
, and to reduce the number of colon and rectal polyps in people with familial adenomatous polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an autosomal dominant inherited condition in which numerous adenomatous polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colon ...
. It may be used in children with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
Juvenile may refer to:
In general
*Juvenile status, or minor (law), prior to adulthood
*Juvenile (organism)
Music
*Juvenile (rapper) (born 1975), stage name of American rapper Terius Gray
*''Juveniles'', a 2020 studio album by the band Kingswoo ...
who are older than two years of age and weigh more than 10 kg (22 lb).
For postoperative pain, it is more or less equal to ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes dysmenorrhea, painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It can be taken oral administration, ...
. For pain relief, it is similar to paracetamol
Paracetamol, or acetaminophen, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic agent used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. It is a widely available over-the-counter drug sold under various brand names, including Tylenol and Panadol.
Parac ...
(acetaminophen) at 3990 mg per day, which is the first line treatment for osteoarthritis.
Evidence of effects is not clear as several studies done by the manufacturer have not been released for independent analysis.
Familial adenomatous polyposis
It has been used to reduce colon and rectal polyps in people with familial adenomatous polyposis, but it is not known if it decreases rates ofcancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, so it is not a good choice for this reason.
Adverse effects
* Cardiovascular events: NSAIDs are associated with an increased risk of serious (and potentially fatal) adverse cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke. Risk may be increased with duration of use or pre-existing cardiovascular risk factors or disease. Individual cardiovascular risk profiles should be evaluated before prescribing. New-onsethypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
or exacerbation of hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
may occur (NSAIDs may impair response to thiazide or loop diuretics), and may contribute to cardiovascular events; monitor blood pressure and use with caution in patients with hypertension. Celecoxib may cause sodium and fluid retention, so its use in patients with edema or heart failure warrants caution. Long-term cardiovascular risk in children has not been evaluated. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration of time, consistent with individual patient goals, to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events; alternative therapies should be considered for patients at high risk. The increased risk is about 37%.
* Gastrointestinal events: NSAIDs may increase the risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) ulceration, bleeding, and perforation (may be fatal). These events may occur at any time during therapy and without warning. Use caution with a history of GI disease (bleeding or ulcers), concurrent therapy with aspirin, anticoagulants and/or corticosteroids, smoking, use of alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
, and the elderly or debilitated patients. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration of time, consistent with individual patient goals, to reduce the risk of GI adverse events; alternate therapies should be considered for patients at high risk. When used concomitantly with ≤325 mg of aspirin, a substantial increase in the risk of gastrointestinal complications (e.g., ulcer) occurs; concomitant gastroprotective therapy (e.g., proton pump inhibitors) is recommended. The increased risk is about 81%.
* Hematologic effects: Anemia may occur; monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit in people on long-term treatment. Celecoxib does not usually affect prothrombin time
The prothrombin time (PT) – along with its derived measures of prothrombin ratio (PR) and international normalized ratio (INR) – is an assay for evaluating the Coagulation#Extrinsic pathway, extrinsic pathway and Coagulation#Common pathway, ...
, partial thromboplastin time, or platelet
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation#Coagulation factors, coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a thrombus, blood clot. Platelets have no ...
counts; it does not inhibit platelet aggregation at approved doses.
People with a prior history of ulcer disease or GI bleeding require special precautions. Moderate to severe liver impairment or GI toxicity can occur with or without warning symptoms in people treated with NSAIDs.
In October 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
(FDA) required the drug label to be updated for all nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications to describe the risk of kidney problems in unborn babies that result in low amniotic fluid. They recommend avoiding NSAIDs in pregnant women at 20 weeks or later in pregnancy.
Allergy
Celecoxib contains asulfonamide
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the Chemical structure, structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this gro ...
moiety and may cause allergic reactions in those allergic to other sulfonamide-containing drugs. This is in addition to the contraindication in people with severe allergies to other NSAIDs. However, it has a low (reportedly 4%) chance of inducing cutaneous reactions among persons who have a history of such reactions to aspirin or nonselective NSAIDs. NSAIDs may cause serious skin adverse events, including exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), also known as Lyell's syndrome, is a type of severe skin reaction. Together with Stevens–Johnson syndrome (SJS) it forms a spectrum of disease, with TEN being more severe. Early symptoms include fever and f ...
; events may occur without warning and in patients without prior known sulfa allergy. Use should be discontinued at the first sign of rash (or any other hypersensitivity).
Heart attack and stroke
A 2013 meta-analysis of hundreds of clinical trials found that coxibs (the class of drugs that includes celecoxib) increase the risk of major cardiovascular problems by about 37% over placebo. In 2016, a randomized trial provided strong evidence that treatment with celecoxib is not more likely to result in poor cardiovascular outcomes than treatment with naproxen or ibuprofen. As a result, in 2018 an FDA advisory panel concluded that celecoxib poses no greater risk for causing heart attacks and strokes than the commonly-used NSAIDs ibuprofen or naproxen and recommended that the FDA consider changing its advice to physicians regarding celecoxib's safety. The COX-2 inhibitor rofecoxib (Vioxx) was removed from the market in 2004 due to its risk. Like all NSAIDs on the US market, celecoxib carries an FDA-mandated "black box warning" for cardiovascular and gastrointestinal risk. In February 2007, theAmerican Heart Association
The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate Heart, cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability ...
warned that with respect to "patients with a prior history of or at high risk for cardiovascular disease... use of COX-2 inhibitors for pain relief should be limited to patients for whom there are no appropriate alternatives, and then, only in the lowest dose and for the shortest duration necessary."
In 2005, a study published in the ''Annals of Internal Medicine
''Annals of Internal Medicine'' is an academic medical journal published by the American College of Physicians (ACP). It is one of the most widely cited and influential specialty medical journals in the world. ''Annals'' publishes content releva ...
'' found that cardiovascular effects of COX-2 inhibitors differ, depending on the drug. Other COX-2-selective inhibitors, such as rofecoxib, have significantly higher myocardial infarction rates than celecoxib. In April 2005, after an extensive review of data, the FDA concluded it was likely "that there is a 'class effect' for increased CV risk for all NSAIDs". In a 2006 meta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, th ...
of randomized control studies, the cerebrovascular events associated with COX-2 inhibitors were examined, but no significant risks were found when compared to nonselective NSAIDs or placebos.
Drug interactions
Celecoxib undergoes metabolism primarily by the enzymesCYP2C9
Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily C member 9 (abbreviated CYP2C9) is an enzyme protein. The enzyme is involved in the metabolism, by oxidation, of both xenobiotics, including drugs, and endogenous compounds, including fatty acids. In humans, t ...
and CYP3A4
Cytochrome P450 3A4 (abbreviated CYP3A4) () is an important enzyme in the body, mainly found in the liver and in the intestine, which in humans is encoded by ''CYP3A4'' gene. It organic redox reaction, oxidizes small foreign organic molecules ( ...
, but it also interacts with CYP2D6
Cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CYP2D6'' gene. ''CYP2D6'' is primarily expressed in the liver. It is also highly expressed in areas of the central nervous system, including the substantia nigra.
CYP2 ...
, inhibiting its activity without being metabolized by it. The CYP2C9 gene exhibits considerable genetic variability, with common polymorphisms, such as rs1799853 and rs1057910, linked to reduced enzyme activity and altered pharmacokinetics of celecoxib. Additionally, the influence of CYP2D6 on celecoxib metabolism is inconsistent, with its effect varying depending on the individual’s CYP2C9 genetic profile.
Caution must be exercised with concomitant use of 2C9 inhibitors, such as fluconazole
Fluconazole is an antifungal medication used for a number of fungal infections. These include candidiasis, blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, dermatophytosis, and tinea versicolor. It is also used to pr ...
, which can greatly elevate celecoxib serum levels. If used concomitantly with lithium, celecoxib increases lithium plasma levels. If used concomitantly with warfarin, celecoxib may result in an increased risk of bleeding complications. The risk of bleeding and gastric ulcers also increases further when selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions.
SSRIs primarily work by blo ...
s (SSRI) are used in combination with celecoxib. The drug may increase the risk of kidney failure with angiotensin
Angiotensin is a peptide hormone that causes vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure. It is part of the renin–angiotensin system, which regulates blood pressure. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adr ...
-converting enzyme-inhibitors, such as lisinopril, and diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics ...
s, such as hydrochlorothiazide
Hydrochlorothiazide, sold under the brand name Hydrodiuril among others, is a diuretic medication used to treat hypertension and swelling due to fluid build-up. Other uses include treating diabetes insipidus and renal tubular acidosis and t ...
.
Mechanism of action
Anti-inflammatory
A highly selective reversible inhibitor of the COX-2 isoform ofcyclooxygenase
Cyclooxygenase (COX), officially known as prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase (PTGS), is an enzyme (specifically, a family of isozymes, ) that is responsible for biosynthesis of prostanoids, including thromboxane and prostaglandins such a ...
, celecoxib inhibits the transformation of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin precursors. Therefore, it has analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. Nonselective NSAIDs (such as aspirin, naproxen, and ibuprofen) inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2. Inhibition of COX-1 (which celecoxib does not inhibit at therapeutic concentrations) inhibits the production of prostaglandins and the production of thromboxane A2, a platelet activator. COX-1 is traditionally defined as a constitutively expressed "housekeeping" enzyme and plays a role in the protection of the gastrointestinal mucosa, kidney hemodynamics, and platelet thrombogenesis. COX-2, on the contrary, is extensively expressed in cells involved in inflammation and is upregulated by bacterial lipopolysaccharides, cytokines, growth factors, and tumor promoters. Celecoxib is approximately 10-20 times more selective for COX-2 inhibition over COX-1. It binds with its polar sulfonamide side chain to a hydrophilic side pocket region close to the active COX-2 binding site. In theory, this selectivity allows celecoxib and other COX-2 inhibitors to reduce inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
(and pain) while minimizing gastrointestinal adverse drug reaction
An adverse drug reaction (ADR) is a harmful, unintended result caused by taking medication. ADRs may occur following a single dose or prolonged administration of a drug or may result from the combination of two or more drugs. The meaning of this ...
s (e.g. stomach ulcers) that are common with nonselective NSAIDs.
Anti-cancer
For its use in reducing colon polyps, celecoxib affects genes and pathways involved in inflammation and malignant transformation in tumors, but not normal tissues. Celecoxib binds to Cadherin-11 (which may explain the reduction in cancer progression).Structure-activity relationship

 The Searle research group found the two appropriately substituted aromatic rings must reside on adjacent positions about the central ring for adequate COX-2 inhibition. Various modifications can be made to the 1,5-diarylpyrazole moiety to deduce the structure-activity relationship of celecoxib. A para-sulfamoylphenyl at position 1 of the pyrazole was found to have a higher potency for COX-2 selective inhibition than a para-methoxyphenyl (see structures 1 and 2, below). In addition, a 4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl or 4-sulfamoylphenyl is known to be necessary for COX-2 inhibition. For instance, replacing either of these entities with a –SO2NHCH3 substituent diminishes COX-2 inhibitory activity as noted with a very high inhibitory concentration-50 (see structures 3 – 5). At the 3-position of the pyrazole, a trifluoromethyl or difluoromethyl provides superior selectivity and potency compared to a fluoromethyl or methyl substitution (see structures 6 – 9).
Celecoxib is compound 22; the 4-sulfamoylphenyl on the 1-pyrazol substituent is required for COX-2 inhibition and the 4-methyl on the 5-pyrazol system has low steric hindrance to maximising potency, while the 3-trifluoromethyl group provides superior selectivity and potency. To explain the selectivity of celecoxib, it is necessary to analyze the free energy of binding difference between the drug molecule and COX-1 compared to COX-2 enzymes. The structural modifications highlight the importance of binding to residue 523 in the side binding pocket of the cyclooxygenase enzyme, which is an isoleucine in COX-1 and a valine in COX-2. This mutation appears to contribute to COX-2 selectivity by creating steric hindrance between the sulfonamide oxygen and the methyl group of Ile523 that effectively destabilizes the celecoxib-COX-1 complex.
The Searle research group found the two appropriately substituted aromatic rings must reside on adjacent positions about the central ring for adequate COX-2 inhibition. Various modifications can be made to the 1,5-diarylpyrazole moiety to deduce the structure-activity relationship of celecoxib. A para-sulfamoylphenyl at position 1 of the pyrazole was found to have a higher potency for COX-2 selective inhibition than a para-methoxyphenyl (see structures 1 and 2, below). In addition, a 4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl or 4-sulfamoylphenyl is known to be necessary for COX-2 inhibition. For instance, replacing either of these entities with a –SO2NHCH3 substituent diminishes COX-2 inhibitory activity as noted with a very high inhibitory concentration-50 (see structures 3 – 5). At the 3-position of the pyrazole, a trifluoromethyl or difluoromethyl provides superior selectivity and potency compared to a fluoromethyl or methyl substitution (see structures 6 – 9).
Celecoxib is compound 22; the 4-sulfamoylphenyl on the 1-pyrazol substituent is required for COX-2 inhibition and the 4-methyl on the 5-pyrazol system has low steric hindrance to maximising potency, while the 3-trifluoromethyl group provides superior selectivity and potency. To explain the selectivity of celecoxib, it is necessary to analyze the free energy of binding difference between the drug molecule and COX-1 compared to COX-2 enzymes. The structural modifications highlight the importance of binding to residue 523 in the side binding pocket of the cyclooxygenase enzyme, which is an isoleucine in COX-1 and a valine in COX-2. This mutation appears to contribute to COX-2 selectivity by creating steric hindrance between the sulfonamide oxygen and the methyl group of Ile523 that effectively destabilizes the celecoxib-COX-1 complex.
History
It was initially marketed byPfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered at The Spiral (New York City), The Spiral in Manhattan, New York City. Founded in 184 ...
for arthritis. Celecoxib and other COX-2 selective inhibitors, valdecoxib, parecoxib, and mavacoxib, were discovered by a team at the Searle division of Monsanto
The Monsanto Company () was an American agrochemical and agricultural biotechnology corporation founded in 1901 and headquartered in Creve Coeur, Missouri. Monsanto's best-known product is Roundup, a glyphosate-based herbicide, developed ...
led by John Talley.
Two lawsuits arose over the discovery of celecoxib. Daniel L. Simmons of Brigham Young University
Brigham Young University (BYU) is a Private education, private research university in Provo, Utah, United States. It was founded in 1875 by religious leader Brigham Young and is the flagship university of the Church Educational System sponsore ...
(BYU) discovered the COX-2 enzyme in 1988, and in 1991, BYU entered into a collaboration with Monsanto
The Monsanto Company () was an American agrochemical and agricultural biotechnology corporation founded in 1901 and headquartered in Creve Coeur, Missouri. Monsanto's best-known product is Roundup, a glyphosate-based herbicide, developed ...
to develop drugs to inhibit it. Monsanto's pharmaceutical division was later purchased by Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered at The Spiral (New York City), The Spiral in Manhattan, New York City. Founded in 184 ...
, and in 2006, BYU sued Pfizer for breach of contract, claiming Pfizer did not properly pay contractual royalties back to BYU. A settlement was reached in April 2012, in which Pfizer agreed to pay $450 million. Other important discoveries in COX-2 were made at University of Rochester
The University of Rochester is a private university, private research university in Rochester, New York, United States. It was founded in 1850 and moved into its current campus, next to the Genesee River in 1930. With approximately 30,000 full ...
, which patented the discoveries. When the patent was issued, the university sued Searle (later Pfizer) in a case called, ''University of Rochester v. G.D. Searle & Co.'', 358 F.3d 916 (Fed. Cir. 2004). The court ruled in favor of Searle in 2004, holding in essence that the university had claimed a method requiring, yet provided no written description of, a compound that could inhibit COX-2, and therefore the patent was invalid.Ranjana Kadle (2004CAFC Court Decision Reach-Through Claims Declared Invalid
/ref> According to the
National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, NGO, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the ...
, Philip Needleman, who was vice president of Monsanto
The Monsanto Company () was an American agrochemical and agricultural biotechnology corporation founded in 1901 and headquartered in Creve Coeur, Missouri. Monsanto's best-known product is Roundup, a glyphosate-based herbicide, developed ...
in 1989 and president of Searle in 1993 oversaw research into COX-2 that led to the development of the anti-inflammatory drug celecoxib (Celebrex). He became senior executive vice president and chief scientist of Pharmacia
Pharmacia was a pharmaceutical and biotechnological company in Sweden that merged with the American pharmaceutical company Upjohn in 1995.
History
Pharmacia company was founded in 1911 in Stockholm, Sweden by pharmacist Gustav Felix Grönfel ...
from 2000 to 2003. Celecoxib was discovered and developed by G. D. Searle & Company and was approved by the FDA on 31 December 1998. It was co-promoted by Monsanto Company (parent company of Searle) and Pfizer under the brand name Celebrex. Monsanto merged with Pharmacia
Pharmacia was a pharmaceutical and biotechnological company in Sweden that merged with the American pharmaceutical company Upjohn in 1995.
History
Pharmacia company was founded in 1911 in Stockholm, Sweden by pharmacist Gustav Felix Grönfel ...
, from which the Medical Research Division was acquired by Pfizer, giving Pfizer ownership of Celebrex. The drug was at the core of a major patent dispute that was resolved in Searle's favor (later Pfizer) in 2004. In ''University of Rochester v. G.D. Searle & Co.'', 358 F.3d 916 (Fed. Cir. 2004), the University of Rochester
The University of Rochester is a private university, private research university in Rochester, New York, United States. It was founded in 1850 and moved into its current campus, next to the Genesee River in 1930. With approximately 30,000 full ...
claimed that United States Pat. No. 6,048,850 (which claimed a method of inhibiting COX-2 in humans using a compound, without actually disclosing what that compound might be) covered drugs such as celecoxib. The court ruled in favor of Searle, holding in essence that the university had claimed a method requiring, yet provided no written description of, a compound that could inhibit COX-2, and therefore the patent was invalid.
After the withdrawal of rofecoxib from the market in September 2004, celecoxib enjoyed a robust increase in sales. However, the results of the APC trial in December of that year raised concerns that Celebrex might carry risks similar to those of rofecoxib, and Pfizer announced a moratorium on direct-to-consumer advertising
Direct-to-consumer advertising (DTCA) refers to the pharmaceutical marketing, marketing and advertising of medication, pharmaceutical products directly to consumers as patients, as opposed to specifically targeting health professionals. The term ...
of Celebrex soon afterward. Sales reached $2 billion in 2006. Before its availability in generic form, it was one of Pfizer's "best-selling drugs, amounting to more than $2.5 billion in sales y 2012 and was prescribed to 2.4 million" people in 2011. By 2012, 33 million Americans had taken celecoxib.
Pfizer resumed advertising Celebrex in magazines in 2006, and resumed television advertising in April 2007 with an unorthodox, -minute advertisement which extensively discussed the adverse effects of Celebrex in comparison with other anti-inflammatory drugs. The ad drew criticism from the consumer advocacy group Public Citizen
Public Citizen is an American non-profit, Progressivism in the United States, progressive consumer rights advocacy group, and think tank based in Washington, D.C. It was founded in 1971 by the American activist and lawyer Ralph Nader.
Lobbying e ...
, which called the ad's comparisons misleading. Pfizer responded to Public Citizen's concerns with assurances that they are truthfully advertising the risk and benefits of Celebrex as set forth by the FDA.
In 2025, Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration decided to include celecoxib 200mg as the first Schedule 3 (Pharmacist Only Medicine) selective COX-2 inhibitor in a primary pack containing not more than 10 dosage units for the short-term treatment of acute pain due to primary dysmenorrhoea or musculoskeletal or soft tissue injury in adults.
Society and culture
Fabricated efficacy studies
Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered at The Spiral (New York City), The Spiral in Manhattan, New York City. Founded in 184 ...
and its partner, Pharmacia
Pharmacia was a pharmaceutical and biotechnological company in Sweden that merged with the American pharmaceutical company Upjohn in 1995.
History
Pharmacia company was founded in 1911 in Stockholm, Sweden by pharmacist Gustav Felix Grönfel ...
presented findings from their study that Celebrex was "better in protecting the stomach from serious complications than other drugs." This became Celebrex's main selling point. However, following federal investigations it was revealed that Pfizer and Pharmacia "only presented the results from the first six months of a year-long study rather than the whole thing." These partial results were then published in The Journal of the American Medical Association. In 2001, the US Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
(FDA) released the full results of the Pfizer and Pharmacia study which showed that they had withheld crucial data. By 2012, a federal judge unsealed "thousands of pages of internal documents and depositions" in a "long-running securities fraud case against Pfizer."
In March 2009, Scott S. Reuben, former chief of acute pain at Baystate Medical Center, Springfield, Massachusetts, revealed that the data for 21 studies he had authored for the efficacy of the drug (along with others such as Vioxx) had been fabricated. The analgesic effects of the drugs had been exaggerated. Reuben was also a former paid spokesperson for Pfizer. Although from 2002 to 2007 Pfizer underwrote much of Dr. Reuben's research and "many of his trials found that Celebrex and Lyrica, Pfizer drugs, were effective against postoperative pain," Pfizer was not aware of the fraudulent data. None of the retracted studies were submitted to either the US Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
or the European Union's regulatory agencies before the drug's approval. Although Pfizer issued a public statement declaring, "It is very disappointing to learn about Dr. Scott Reuben's alleged actions. When we decided to support Dr. Reuben's research, he worked for a credible academic medical center and appeared to be a reputable investigator", the documents unsealed in 2012, revealed that by February 2000, Pharmacia employees had devised a strategy to present the findings.
Brand names
Pfizer markets celecoxib under the brand name Celebrex, and it is available as oral capsules containing 50, 100, 200, or 400 mg of celecoxib. It is legally available in many jurisdictions as a generic under several brand names. In the US, celecoxib was covered by three patents, two of which expired on 30 May 2014, and one of which (US RE44048) was due to expire 2 December 2015. On 13 March 2014, that patent was found to be invalid fordouble patenting
Double patenting is the granting of two patents for a single invention, to the same proprietor and in the same country or countries. According to the European Patent Office, it is an accepted principle in most patent systems that two patents canno ...
. Upon the patent expiry on 30 May 2014, the FDA approved the first versions of generic celecoxib.
In the US, Celebrex is marketed by Viatris after Upjohn was spun off from Pfizer.
Research
Psychiatry
On the theory that inflammation plays a role in the pathogenesis of major mental disorders, celecoxib has been trialed for a number of psychiatric disorders, includingmajor depression
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Intro ...
, bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in ...
, and schizophrenia
Schizophrenia () is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations (typically, Auditory hallucination#Schizophrenia, hearing voices), delusions, thought disorder, disorganized thinking and behavior, and Reduced affect display, f ...
. A 2014 meta-analysis concluded that adjunctive
In linguistics, an adjunct is an optional, or ''structurally dispensable'', part of a sentence, clause, or phrase that, if removed or discarded, will not structurally affect the remainder of the sentence. Example: In the sentence ''John helped Bill ...
treatment with celecoxib improved depressive symptoms, response, and remission rates compared to placebo.
Bipolar disorder
A meta-analysis considering trials of celecoxib as an adjunctive treatment inbipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in ...
was inconclusive citing low evidence quality.
Familial adenomatous polyposis
It has been used to reduce colon and rectal polyps in people with familial adenomatous polyposis, but it is not known if it decreases rates ofcancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, so it is not a good choice for this reason.
Cancer prevention
The use of celecoxib to reduce the risk ofcolorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the Colon (anatomy), colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include Lower gastrointestinal ...
has been investigated, but neither celecoxib nor any other drug is indicated for this use. Small-scale clinical trials in very high-risk people (belonging to FAP families) showed celecoxib can prevent polyp growth. Hence, large-scale randomized clinical trials were undertaken. Results show a 33 to 45% polyp recurrence reduction in people treated with celecoxib each day. However, serious cardiovascular events were significantly more frequent in the celecoxib-treated groups. Aspirin shows a similar (and possibly larger) protective effect, has demonstrated cardioprotective effects and is significantly cheaper, but no head-to-head clinical trials have compared the two drugs.
Cancer treatment
Different from cancer prevention, cancer treatment is focused on the therapy of tumors that have already formed and have established themselves inside the patient. Many studies are going on to determine whether celecoxib might be useful for this latter condition. However, during molecular studies in the laboratory, it became apparent that celecoxib could interact with other intracellular components besides its most famous target, COX-2. The discovery of these additional targets has generated much controversy, and the initial assumption that celecoxib reduces tumor growth primarily by the inhibition of COX-2 became contentious. Certainly, the inhibition of COX-2 is paramount for the anti-inflammatory and analgesic function of celecoxib. However, whether inhibition of COX-2 also plays a dominant role in this drug's anticancer effects is unclear. For example, a recent study withmalignant tumor
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal ...
cells showed celecoxib could inhibit the growth of these cells ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in ...
'', but COX-2 played no role in this outcome; even more strikingly, the anticancer effects of celecoxib were also obtained with the use of cancer cell types that do not even contain COX-2. Karen Seibert and colleagues have published research showing antiangiogenic and antitumor activity of celecoxib in animal models.
Additional support for the idea that other targets besides COX-2 are important for celecoxib's anticancer effects has come from studies with chemically modified versions of celecoxib. Several dozen analogs of celecoxib were generated with small alterations in their chemical structure
A chemical structure of a molecule is a spatial arrangement of its atoms and their chemical bonds. Its determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target m ...
s. Some of these analogs retained COX-2 inhibitory activity, whereas many others did not. However, when the ability of all these compounds to kill tumor cells in cell culture
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cell (biology), cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. After cells of interest have been Cell isolation, isolated from living tissue, ...
was investigated, the antitumor potency did not at all depend on whether or not the respective compound could inhibit COX-2, showing the inhibition of COX-2 was not required for the anticancer effects. One of these compounds, 2,5-dimethyl-celecoxib, which entirely lacks the ability to inhibit COX-2, actually displayed stronger anticancer activity than celecoxib.
References
Further reading
* *External links
* * {{Authority control Antineoplastic drugs COX-2 inhibitors CYP2D6 inhibitors Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Drugs developed by Pfizer Pyrazoles Sulfonamides Trifluoromethyl compounds Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate 4-Tolyl compounds