Carpometacarpi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
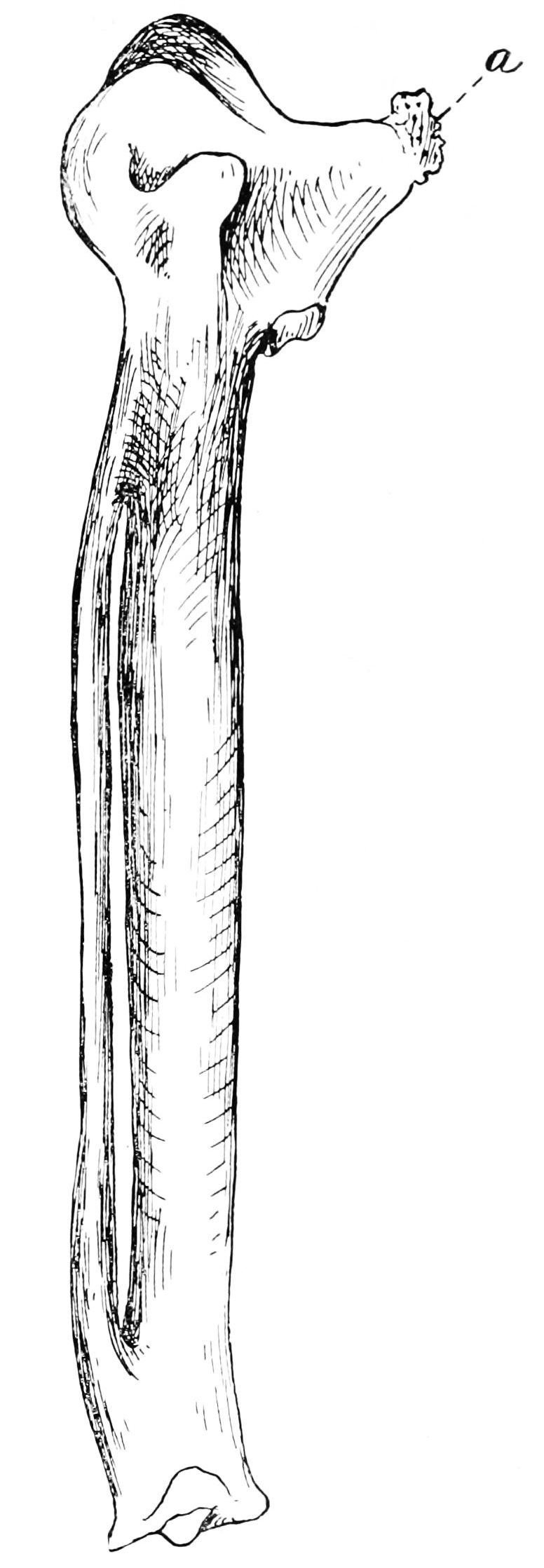 The carpometacarpus is a bone found in the hands of
The carpometacarpus is a bone found in the hands of  To non-
To non-
 The carpometacarpus is a bone found in the hands of
The carpometacarpus is a bone found in the hands of birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
. It results from the fusion of the carpal
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The terms "carpus" and "carpal" are derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In huma ...
and metacarpal
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, also known as the "palm bones", are the appendicular bones that form the intermediate part of the hand between the phalanges (fingers) and the carpal bones ( wrist bones), which articulate ...
bone, and is essentially a single fused bone between the wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal ...
and the knuckle
The knuckles are the joints of the fingers. The word is cognate to similar words in other Germanic languages, such as the Dutch "knokkel" (knuckle) or German "Knöchel" (ankle), i.e., ''Knöchlein'', the diminutive of the German word for bone ( ...
s. It is a smallish bone in most birds, generally flattened and with a large hole in the middle. In flightless bird
Flightless birds are birds that cannot Bird flight, fly, as they have, through evolution, lost the ability to. There are over 60 extant species, including the well-known ratites (ostriches, emus, cassowary, cassowaries, Rhea (bird), rheas, an ...
s, however, its shape may be slightly different, or it might be absent entirely.
It forms the tip of the wing
A wing is a type of fin that produces both Lift (force), lift and drag while moving through air. Wings are defined by two shape characteristics, an airfoil section and a planform (aeronautics), planform. Wing efficiency is expressed as lift-to-d ...
skeleton in birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
. To it, most of the primary remiges
Flight feathers (''Pennae volatus'') are the long, stiff, asymmetrically shaped, but symmetrically paired pennaceous feathers on the wings or tail of a bird; those on the wings are called remiges (), singular remex (), while those on the ta ...
attach. The alula
The alula , or bastard wing, (plural ''alulae'') is a small projection on the anterior edge of the wing of modern birds and a few non-avian dinosaurs. The word is Latin and means "winglet"; it is the diminutive of ''ala'', meaning "wing". The a ...
, by contrast, is formed by the thumb
The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the index finger. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position (where the palm is facing to the front), the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thumb ...
, which does not completely fuse with the other hand-bones. Likewise, the tipmost primaries attach to the phalanx bone
The phalanges (: phalanx ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones.
Structu ...
s.
 To non-
To non-biologists
A biologist is a scientist who conducts research in biology. Biologists are interested in studying life on Earth, whether it is an individual cell, a multicellular organism, or a community of interacting populations. They usually specialize in ...
the carpometacarpus may be best known from buffalo wings. Buffalo wings come in two basic sizes, a large angled one containing three major bones, and a smaller flat one containing only two. The bone missing in the latter is the carpometacarpus.
See also
*Carpometacarpal joint
The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are five joints in the wrist that articulate the distal row of carpal bones and the proximal bases of the five metacarpal bones.
The CMC joint of the thumb or the first CMC joint, also known as the trapeziometaca ...
, a joint (not a bone) in the human wrist
References
* Bird anatomy {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub