Calcium channel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A calcium channel is an
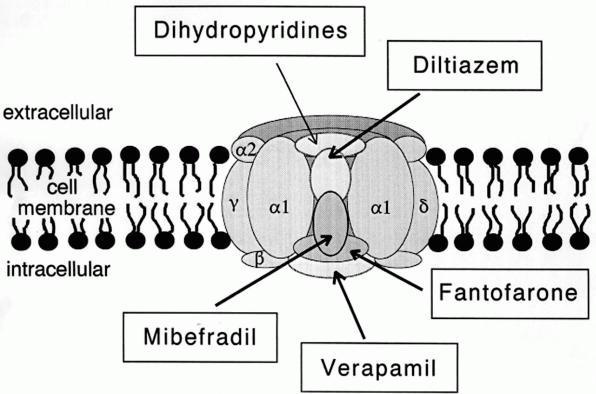 L-type
L-type
ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of io ...
which shows selective permeability to calcium ions. It is sometimes synonymous with voltage-gated calcium channel, although there are also ligand-gated calcium channels.
Comparison tables
The following tables explain gating, gene, location and function of different types of calcium channels, both voltage and ligand-gated.Voltage-gated
Ligand-gated
*the ''receptor-operated calcium channels'' (in vasoconstriction) ** P2X receptors Page 479Pharmacology
 L-type
L-type calcium channel blocker
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium () through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as ...
s are used to treat hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
. In most areas of the body, depolarization is mediated by sodium influx into a cell; changing the calcium permeability has little effect on action potentials. However, in many smooth muscle tissues, depolarization is mediated primarily by calcium influx into the cell. L-type calcium channel blockers selectively inhibit these action potentials in smooth muscle which leads to dilation of blood vessels; this in turn corrects hypertension.
T-type calcium channel blocker
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium () through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as ...
s are used to treat epilepsy. Increased calcium conductance in the neurons leads to increased depolarization and excitability. This leads to a greater predisposition to epileptic episodes. Calcium channel blockers reduce the neuronal calcium conductance and reduce the likelihood of experiencing epileptic attacks.
See also
* .References
External links
* * * * {{Ion channels, g1 Ion channels Electrophysiology Integral membrane proteins Calcium channels