CS23D on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 CS23D is a web server to generate 3D structural models from NMR chemical shifts. CS23D combines maximal fragment assembly with chemical shift threading, ''de novo'' structure generation, chemical shift-based torsion angle prediction, and chemical shift refinement. CS23D makes use of
CS23D is a web server to generate 3D structural models from NMR chemical shifts. CS23D combines maximal fragment assembly with chemical shift threading, ''de novo'' structure generation, chemical shift-based torsion angle prediction, and chemical shift refinement. CS23D makes use of

 CS23D is a web server to generate 3D structural models from NMR chemical shifts. CS23D combines maximal fragment assembly with chemical shift threading, ''de novo'' structure generation, chemical shift-based torsion angle prediction, and chemical shift refinement. CS23D makes use of
CS23D is a web server to generate 3D structural models from NMR chemical shifts. CS23D combines maximal fragment assembly with chemical shift threading, ''de novo'' structure generation, chemical shift-based torsion angle prediction, and chemical shift refinement. CS23D makes use of RefDB
RefDB is a client/server reference database and bibliography tool for markup languages like SGML, XML, and LaTeX. It is suitable for standalone use for the purpose of self-archiving, but can be used as an institutional repository as well. Data s ...
and ShiftX.
CS23D input formats
CS23D accepts chemical shift files in either SHIFTY or BMRB formats.CS23D options
A user can # Exclude a protein from being used as the template # Ignore high-identity homologs in the list of available templates # Change the number of models in the final ensemble # Change the number of model optimization stepsCS23D output
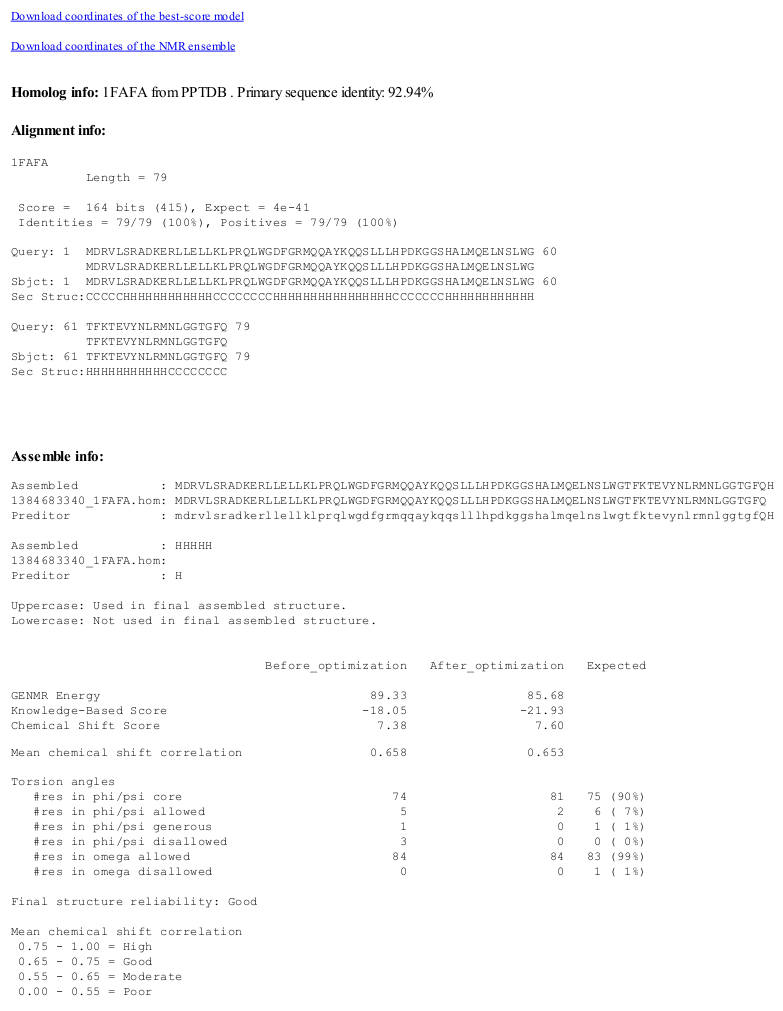
CS23D output consists of a set of 10 best-score PDB coordinates. A hyperlink to the single best score structure is also provided. The overall CS23D score, knowledge-based score, chemical shift score, Ramachandran plot statistics, correlations between the observed and calculated shifts before and after refinement are displayed. A conclusion about structure reliability is given to the user.CS23D protocol
''Homology search:'' The query sequence is used to find homologous proteins or/and protein fragments in a non-redundant database of PDB sequences and secondary structures of PPT-DB usingBLAST
Blast or The Blast may refer to:
*Explosion, a rapid increase in volume and release of energy in an extreme manner
*Detonation, an exothermic front accelerating through a medium that eventually drives a shock front
*A planned explosion in a mine, ...
.
''Homology modelling:'' Homology modelling is done by the Homodeller program, which is a part of the PROTEUS2 program. The proteins that are identified during the homology search step are used as the templates in homology modelling.
''Chemical shift re-referencing:'' Chemical shifts are re-referenced by the RefCor, which is a part of the RCI webserver backend.
''Secondary structure prediction from chemical shifts:'' Secondary structure is predicted from chemical shifts by CSI.
''Torsion angle prediction from chemical shifts:'' Torsion angles are predicted from chemical shifts by PREDITOR.
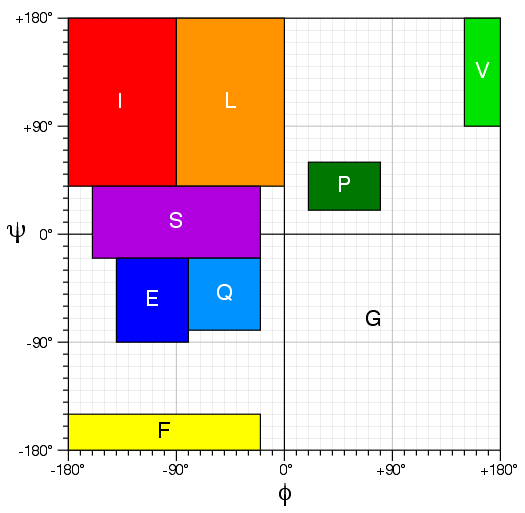
''Chemical shift threading:'' Backbone Phi and Psi torsion angles predicted from chemical shifts by PREDITOR are mapped into nine different regions in Ramachandran space, each of which are assigned specific letters. A protein can be represented by a sequence of these nine "torsion angle letters". Thrifty is using these sequences of torsion angle letters to identify good templates in a database of ~18,500 nonredundant PDB structures that have had their structures converted to the nine-letter Ramachandran "alphabet".
In a similar manner, chemical shift threading is additionally done using three-letter secondary structure alphabet (H for helix, B for beta-strand, C for coil) and secondary structure predicted from chemical shifts by the CSI program.
''Model assembly:''
Subfragments identified by homology modelling and chemical shift threading steps are assembled into initial 3D models using CS23D SFassembler (SubFragment assembler). The initial models are evaluated by the GAFolder scoring function (see below) and the best model is further refined by GAFolder (see more info about GAFolder below).
''Ab initio folding:'' ''Ab initio'' folding is done by Rosetta when no template was identified by the homology modelling and chemical shift threading steps. Rosetta models are evaluated by GAFolder scoring function and the best Rosetta models are refined by GAFolder (see below).
''Model optimization:'' Model optimization in CS23D is done by a torsion-angle-based minimizer GAfolder (Genetic Algorithm folder) that uses a genetic algorithm to sample conformation space. The method is similar to that employed by GENFOLD. GAFolder makes torsion angles moves within the ranges defined by the values and uncertainties of torsion angles predicted by PREDITOR. GAFolder evaluates protein models by the scoring function described below.
''Scoring function:'' Scoring function of GAFolder consists of knowledge based scores and chemical shift scores.
''The knowledge-based scores'' include:
# radius of gyration score,
# hydrogen bond energy,
# number of hydrogen bonds,
# bad contacts score,
# disulfide bond score,
# modified threading energy based on the Bryant and Lawrence potential.
# Ramachandran score that evaluates normality of model torsion angles Phi and Psi
# Omega score that evaluates normality of model torsion omega angles
# Chi score that is based on expected chi angles for different phi and psi combinations.
''The chemical shift component'' of the GAfolder scoring function uses:
# weighted coefficients of correlation between the experimental chemical shifts (CA, CB, CO, N, HA, HN) and chemical shifts calculated by SHIFTX 1.0.
# agreement between model secondary structure and secondary structure predicted by CSI from experimental chemical shifts.
CS23D sub-programs
# CSI - prediction of secondary structure from chemical shifts # BLAST - sequence alignment, homology search #PROTEUS2 - homology modelling #PREDITOR - prediction of torsion angles from chemical shifts # Pepmake - building protein models from torsion angles and sequence # PPT-DB- secondary structure database # Rosetta - ''ab initio'' structure generation # RCI- estimating uncertainty of torsion angles predicted from chemical shifts by PREDITOR # ShiftX 1.0 - is used to generate coefficients of correlation between observed chemical shifts and shifts predicted by ShiftX from protein models # SFAssembler - maximal fragment assembly # GAFolder - chemical shift refinement via a genetic algorithm # Thrifty - chemical shift threading # RefCor - chemical shift re-referencingCS23D dependence on template sequence identity
CS23D is a template-based method. Therefore, its performance depends on sequence identity of the selected template(s), see the adjacent picture. Likewise, Rosetta is a fragment-biased method. Its performance depends on the quality of selected fragments. Fragment quality and, thus, Rosetta performance can be improved by using chemical shifts during the fragment selection step (e.g. in CS-Rosetta protocol). For a structural solution that is not biased by a template structure or fragment structure, one may want to consider obtaining NOE-based distance restraints (8-10 per residue) and using them with the GeNMR program in its ''ab initio'' mode.See also
*Chemical Shift
In nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of an atomic nucleus relative to a standard in a magnetic field. Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure of ...
*NMR
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which atomic nucleus, nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are disturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near and far field, near field) and respond by producing ...
*Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a Spectroscopy, spectroscopic technique based on re-orientation of Atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei with non-zero nuclear sp ...
*Protein nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins (usually abbreviated protein NMR) is a field of structural biology in which NMR spectroscopy is used to obtain information about the structure and dynamics of proteins, and also nucleic acids, and ...
* Protein dynamics#Domains and protein flexibility
*Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
* GeNMR
*Random Coil Index
Random coil index (RCI) predicts protein flexibility by calculating an inverse weighted average of backbone secondary chemical shifts and predicting values of model-free order parameters as well as per-residue RMSD of NMR and molecular dynamics ...
* Protein Chemical Shift Prediction
* Protein Chemical Shift Re-Referencing
*Protein secondary structure
Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occu ...
*Chemical shift index
The chemical shift index or CSI is a widely employed technique in protein nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy that can be used to display and identify the location (i.e. start and end) as well as the type of protein secondary structure (beta ...
*ShiftX
ShiftX (Shifts from X-ray structures) is a freely available web server for rapidly calculating protein chemical shifts from protein X-ray (or NMR) coordinates. Protein chemical shift prediction (also known as protein chemical shift calculation) is ...
*Protein structure prediction
Protein structure prediction is the inference of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence—that is, the prediction of its Protein secondary structure, secondary and Protein tertiary structure, tertiary structure ...
References
{{Reflist Chemistry software