Bulgarian Orthodox Church on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Bulgarian Orthodox Church ( bg, Българска православна църква, translit=Balgarska pravoslavna tsarkva), legally the Patriarchate of Bulgaria ( bg, Българска патриаршия, links=no, translit=Balgarska patriarshiya), is an
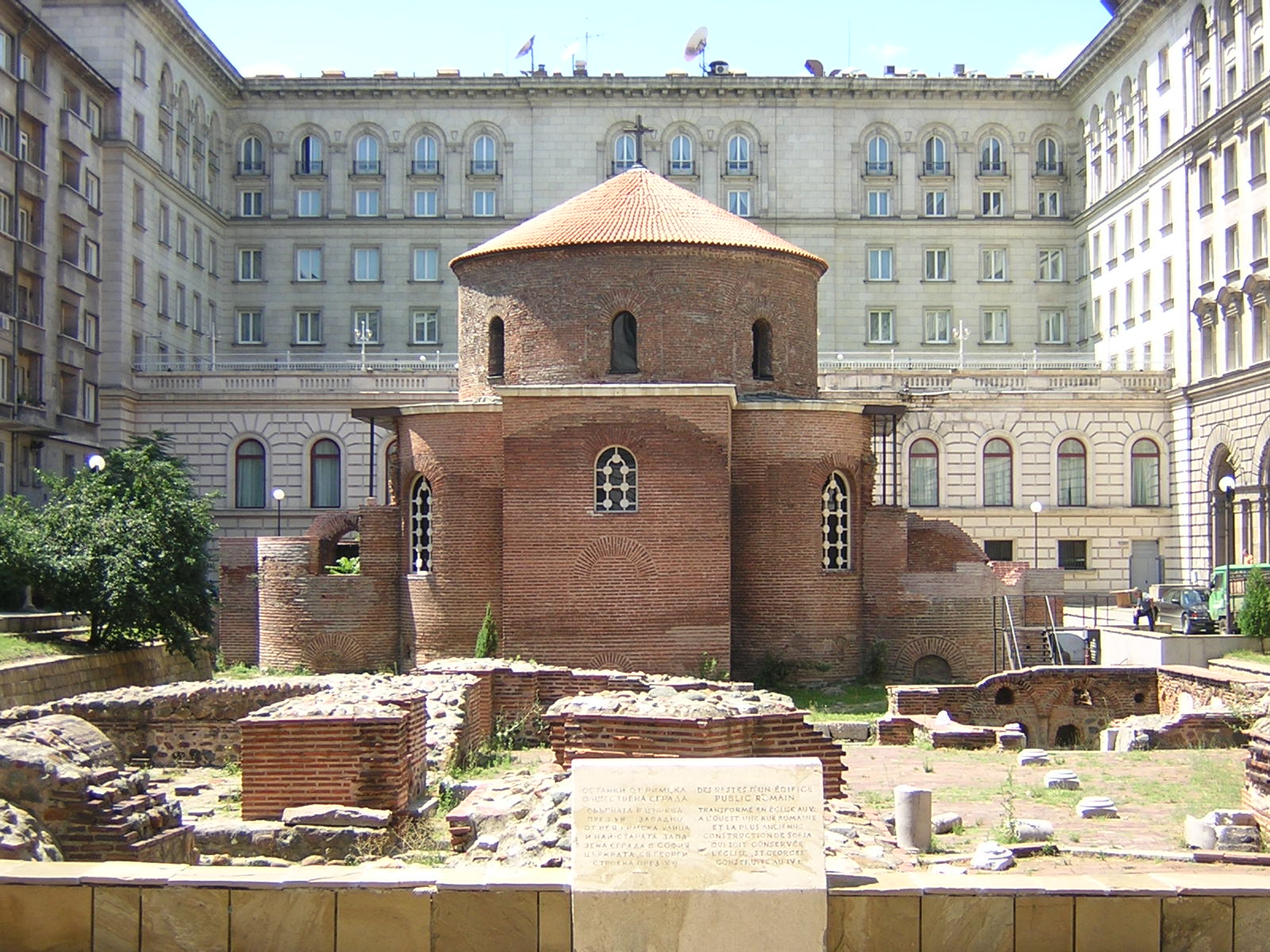


 The Bulgarian Orthodox Church has its origin in the flourishing Christian communities and churches set up in the Balkans as early as the first centuries of the Christian era. Christianity was brought to the Balkans by the apostles
The Bulgarian Orthodox Church has its origin in the flourishing Christian communities and churches set up in the Balkans as early as the first centuries of the Christian era. Christianity was brought to the Balkans by the apostles
 Although the archbishopric enjoyed full internal autonomy, the goals of
Although the archbishopric enjoyed full internal autonomy, the goals of
 Under the reign of
Under the reign of
 Martyrs to the church were made during the forceful conversion to Islam of many districts and almost all larger towns in the Bulgarian provinces of the Ottoman Empire. St. George of Kratovo (d. 1515),
Martyrs to the church were made during the forceful conversion to Islam of many districts and almost all larger towns in the Bulgarian provinces of the Ottoman Empire. St. George of Kratovo (d. 1515),
 In 1762, St.
In 1762, St. 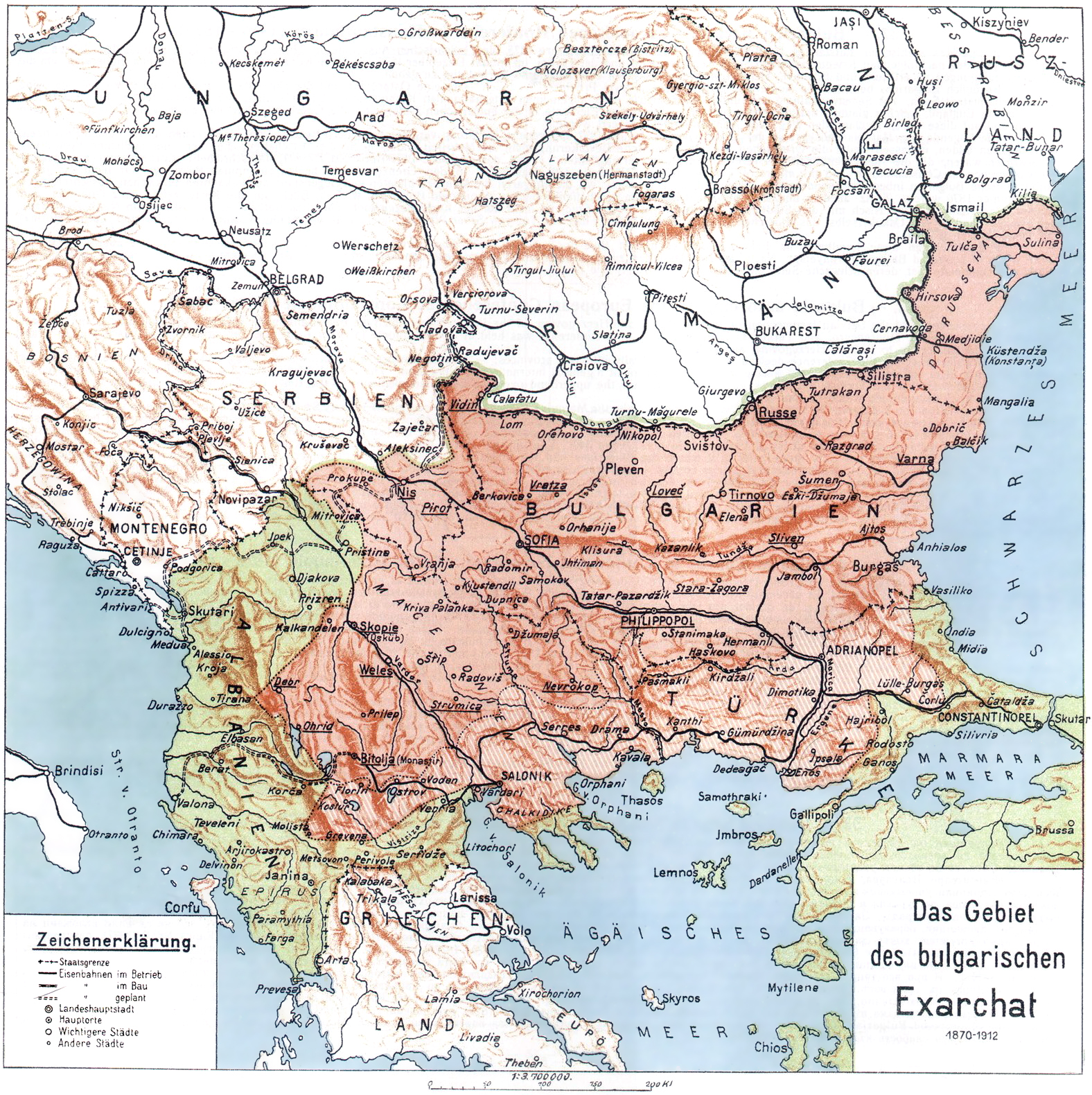 The Patriarchate of Constantinople opposed the change, promptly declaring the
The Patriarchate of Constantinople opposed the change, promptly declaring the
 Conditions for the restoration of the Bulgarian Patriarchate and the election of a head of the Bulgarian Church were created after World War II. In 1945 the schism was lifted and the Patriarch of Constantinople recognised the autocephaly of the Bulgarian Church. In 1950, the Holy Synod adopted a new Statute which paved the way for the restoration of the Patriarchate and in 1953, it elected the Metropolitan of Plovdiv,
Conditions for the restoration of the Bulgarian Patriarchate and the election of a head of the Bulgarian Church were created after World War II. In 1945 the schism was lifted and the Patriarch of Constantinople recognised the autocephaly of the Bulgarian Church. In 1950, the Holy Synod adopted a new Statute which paved the way for the restoration of the Patriarchate and in 1953, it elected the Metropolitan of Plovdiv,  Under Communism (1944–89), Bulgaria's rulers worked to control rather than destroy the church. Still, the early postwar years were unsettling to church hierarchs. During 1944-47 the church was deprived of jurisdiction in marriage, divorce, issuance of birth and death certificates, and other passages that had been sacraments as well as state events. Communists removed study of the catechism and church history from school curricula. They generated anti-religious propaganda and persecuted some priests. From 1947-49 was the height of the campaign to intimidate the church. Bishop Boris was assassinated; Egumenius Kalistrat, administrator of the Rila Monastery, was imprisoned; and various other clergy were murdered or charged with crimes against the state. The communists soon replaced all clergy who refused to endorse the regime's policies. They banished Exarch Stefan, who had co-authored a book in 1948 that was considered anti-Communist.
200px, left, Bulgarian Orthodox priest
From that time until the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the end of Communist rule in 1989, the Bulgarian Orthodox Church and the
Under Communism (1944–89), Bulgaria's rulers worked to control rather than destroy the church. Still, the early postwar years were unsettling to church hierarchs. During 1944-47 the church was deprived of jurisdiction in marriage, divorce, issuance of birth and death certificates, and other passages that had been sacraments as well as state events. Communists removed study of the catechism and church history from school curricula. They generated anti-religious propaganda and persecuted some priests. From 1947-49 was the height of the campaign to intimidate the church. Bishop Boris was assassinated; Egumenius Kalistrat, administrator of the Rila Monastery, was imprisoned; and various other clergy were murdered or charged with crimes against the state. The communists soon replaced all clergy who refused to endorse the regime's policies. They banished Exarch Stefan, who had co-authored a book in 1948 that was considered anti-Communist.
200px, left, Bulgarian Orthodox priest
From that time until the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the end of Communist rule in 1989, the Bulgarian Orthodox Church and the
 The supreme clerical, judicial and administrative power for the whole domain of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church is exercised by the
The supreme clerical, judicial and administrative power for the whole domain of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church is exercised by the 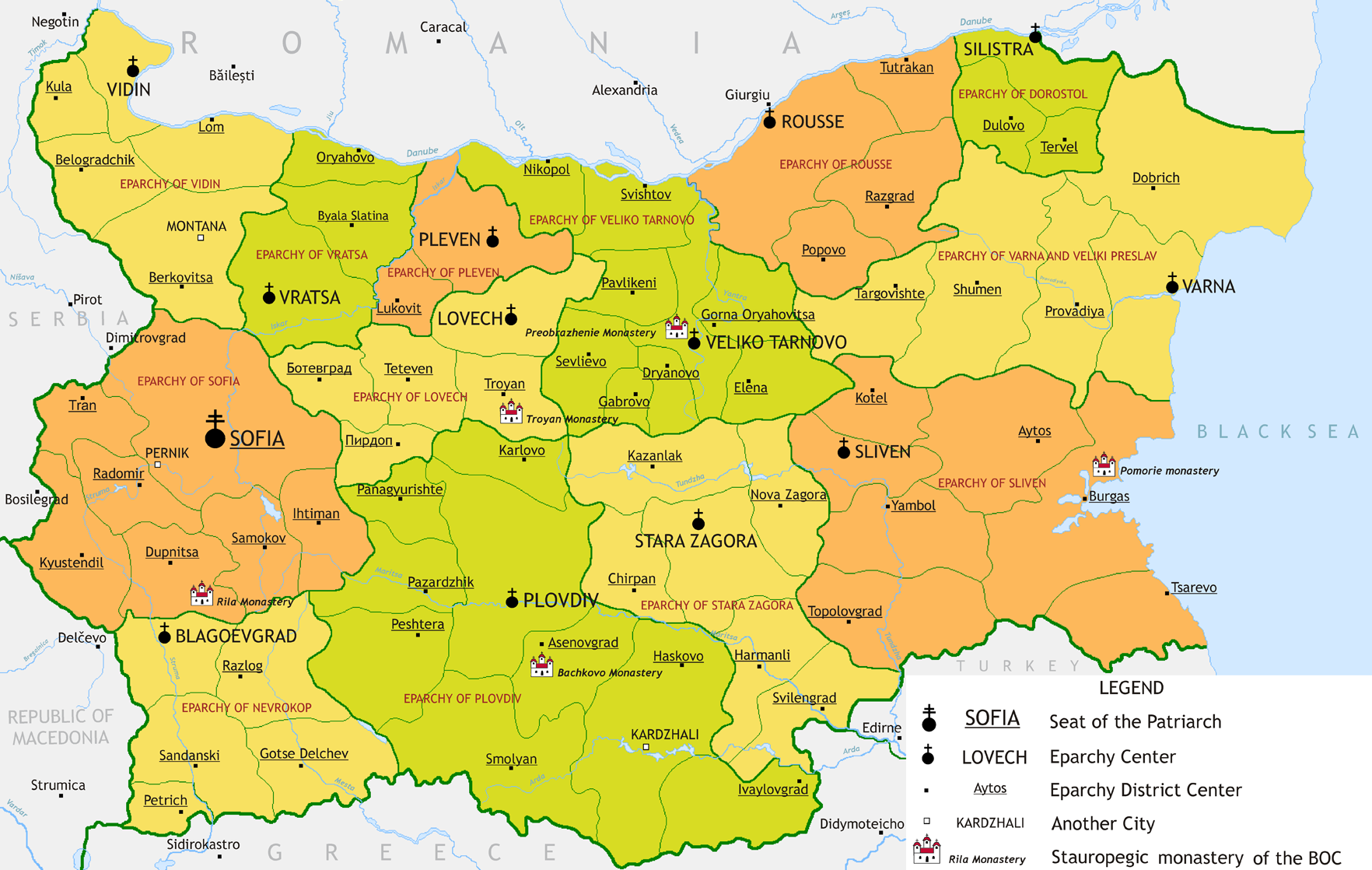 Eparchies in Bulgaria: (with Bulgarian names in brackets)
*Eparchy of Vidin ()
*Eparchy of
Eparchies in Bulgaria: (with Bulgarian names in brackets)
*Eparchy of Vidin ()
*Eparchy of
The official website of the Bulgarian PatriarchateUnofficial web portal of Bulgarian Orthodox Christianity: in Bulgarian language
* History of Bulgaria and the Bulgarian Orthodox Church according to the ''
A short history of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church by CNEWA, the papal agency for humanitarian and pastoral support
* ttp://www.bulgarian-guide.com/about-bulgaria/bulgaria-religion/ Article about the Bulgarian Orthodox Church and Religion in Bulgariabr>Orthodox Life Info Portal
a Bulgarian Orthodox site (in English)
Article on the medieval history of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church in the repository of the Institute for Byzantine Studies of the Austrian Academy of Sciences (in German)
{{Authority control National churches Religious organizations established in the 920s Eastern Orthodox Church bodies in Europe European-Australian culture
autocephalous
Autocephaly (; from el, αὐτοκεφαλία, meaning "property of being self-headed") is the status of a hierarchical Christian church whose head bishop does not report to any higher-ranking bishop. The term is primarily used in Eastern O ...
Orthodox jurisdiction. It is the oldest Slavic Orthodox church, with some 6 million members in Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Maced ...
and between 1.5 and 2 million members in a number of European countries, the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with ...
, Australia, New Zealand and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
. It was recognized as autocephalous in 1945 by the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople.
History
Early Christianity

 The Bulgarian Orthodox Church has its origin in the flourishing Christian communities and churches set up in the Balkans as early as the first centuries of the Christian era. Christianity was brought to the Balkans by the apostles
The Bulgarian Orthodox Church has its origin in the flourishing Christian communities and churches set up in the Balkans as early as the first centuries of the Christian era. Christianity was brought to the Balkans by the apostles Paul
Paul may refer to:
* Paul (given name), a given name (includes a list of people with that name)
* Paul (surname), a list of people
People
Christianity
*Paul the Apostle (AD c.5–c.64/65), also known as Saul of Tarsus or Saint Paul, early Chr ...
and Andrew
Andrew is the English form of a given name common in many countries. In the 1990s, it was among the top ten most popular names given to boys in English-speaking countries. "Andrew" is frequently shortened to "Andy" or "Drew". The word is derive ...
in the 1st century AD, when the first organised Christian communities were formed. By the beginning of the 4th century, Christianity had become the dominant religion in the region. Towns such as Serdica ( Sofia), Philipopolis ( Plovdiv), Odessus ( Varna), Dorostorum ( Silistra) and Adrianople (Edirne
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis (Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, ...
) were significant centres of Christianity in the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
.
The Monastery of Saint Athanasius, the first Christian monastery in Europe, was founded in Thrace in 344 by Athanasius
Athanasius I of Alexandria, ; cop, ⲡⲓⲁⲅⲓⲟⲥ ⲁⲑⲁⲛⲁⲥⲓⲟⲩ ⲡⲓⲁⲡⲟⲥⲧⲟⲗⲓⲕⲟⲥ or Ⲡⲁⲡⲁ ⲁⲑⲁⲛⲁⲥⲓⲟⲩ ⲁ̅; (c. 296–298 – 2 May 373), also called Athanasius the Great, ...
near modern-day Chirpan
Chirpan ( bg, Чирпан, ) is a town on the Tekirska River in Stara Zagora Province of south-central Bulgaria. It is the administrative centre of the homonymous Chirpan Municipality. As of 2021, the town had a population of 13,391 down fro ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Maced ...
, following the Council of Serdica The Council of Serdica, or Synod of Serdica (also Sardica located in modern day Sofia, Bulgaria), was a synod convened in 343 at Serdica in the civil diocese of Dacia, by Emperors Constans I, augustus in the West, and Constantius II, augustus in th ...
and the Edict of Serdica.
The barbarian raids and incursions in the 4th and the 5th centuries, and the settlement of Slavs and Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as nomad ...
in the 6th and the 7th centuries, wrought considerable damage to the ecclesiastical organisation of the Christian Church in the Bulgarian lands, yet did not destroy it. Kubrat and Organa were both baptized together in Constantinople and Christianity started to pave its way from the surviving Christian communities to the surrounding Bulgar-Slavic mass. By the middle of the 9th century, the majority of the Bulgarian Slavs
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe.
Etymology
Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not completely understoo ...
, especially those living in Thrace and Macedonia, were Christianized. The process of conversion also enjoyed some success among the Bulgar nobility. However, it was not until the official adoption of Christianity by Khan
Khan may refer to:
*Khan (inn), from Persian, a caravanserai or resting-place for a travelling caravan
*Khan (surname), including a list of people with the name
*Khan (title), a royal title for a ruler in Mongol and Turkic languages and used by ...
Boris I
Boris I, also known as Boris-Mihail (Michael) and ''Bogoris'' ( cu, Борисъ А҃ / Борисъ-Михаилъ bg, Борис I / Борис-Михаил; died 2 May 907), was the ruler of the First Bulgarian Empire in 852–889. At ...
in 865 that an independent Bulgarian ecclesiastical entity was established.
Establishment
Boris I
Boris I, also known as Boris-Mihail (Michael) and ''Bogoris'' ( cu, Борисъ А҃ / Борисъ-Михаилъ bg, Борис I / Борис-Михаил; died 2 May 907), was the ruler of the First Bulgarian Empire in 852–889. At ...
believed that cultural advancement and the sovereignty and prestige of a Christian Bulgaria could be achieved through an enlightened clergy governed by an autocephalous church. To this end, he manoeuvred between the Patriarch of Constantinople and the Roman Pope for a period of five years until in 870 AD, the Fourth Council of Constantinople granted the Bulgarians an autonomous Bulgarian archbishopric. The archbishopric had its seat in the Bulgarian capital of Pliska, and its diocese covered the whole territory of the Bulgarian state. The tug-of-war between Rome and Constantinople was resolved by putting the Bulgarian archbishopric under the jurisdiction of the Patriarch of Constantinople and the Orthodox Church, from whom it obtained its first primate, its clergy, and theological books.
 Although the archbishopric enjoyed full internal autonomy, the goals of
Although the archbishopric enjoyed full internal autonomy, the goals of Boris I
Boris I, also known as Boris-Mihail (Michael) and ''Bogoris'' ( cu, Борисъ А҃ / Борисъ-Михаилъ bg, Борис I / Борис-Михаил; died 2 May 907), was the ruler of the First Bulgarian Empire in 852–889. At ...
were scarcely fulfilled. A Greek liturgy offered by a Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
clergy furthered neither the cultural development of the Bulgarians, nor the consolidation of the Bulgarian Empire; it would have eventually resulted in the loss of both the identity of the people and the statehood of Bulgaria. Following the Byzantine theory of ''"Imperium sine Patriarcha non staret",'' which said that a close relation should exist between an Empire and Patriarchate, Boris I greeted the arrival of the disciples of the recently deceased Saints Cyril and Methodius in 886 as an opportunity. Boris I gave them the task of instructing the future Bulgarian clergy in the Glagolitic alphabet and the Slavonic liturgy prepared by Cyril
Cyril (also Cyrillus or Cyryl) is a masculine given name. It is derived from the Greek name Κύριλλος (''Kýrillos''), meaning 'lordly, masterful', which in turn derives from Greek κυριος (''kýrios'') 'lord'. There are various varian ...
. The liturgy was based on the vernacular of the Bulgarian Slavs from the region of Thessaloniki. In 893, Boris I expelled the Greek clergy from the country and ordered the Greek language to be replaced with the Slav-Bulgarian vernacular.
Autocephaly and Patriarchate
Following Bulgaria's two decisive victories over the Byzantines at Acheloos (near the present-day city ofPomorie
Pomorie ( bg, Поморие ), historically known as Anchialos (Greek: Αγχίαλος), is a town and seaside resort in southeastern Bulgaria, located on a narrow rocky peninsula in Burgas Bay on the southern Bulgarian Black Sea Coast.
It is ...
) and Katasyrtai (near Constantinople), the government declared the autonomous Bulgarian Archbishopric as autocephalous and elevated it to the rank of Patriarchate at an ecclesiastical and national council held in 919. After Bulgaria and the Byzantine Empire signed a peace treaty in 927 that concluded the 20-year-long war between them, the Patriarchate of Constantinople recognised the autocephalous status of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church and acknowledged its patriarchal dignity.
The Bulgarian Patriarchate was the first autocephalous Slavic Orthodox Church, preceding the autocephaly of the Serbian Orthodox Church (1219) by 300 years and of the Russian Orthodox Church (1596) by some 600 years. It was the sixth Patriarchate after the Pentarchy patriarchates of Rome, Constantinople, Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
, Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
and Jerusalem. The seat of the Patriarchate was the new Bulgarian capital of Preslav. The Patriarch was likely to have resided in the town of Drastar ( Silistra), an old Christian centre noted for its martyrs and Christian traditions.
Ohrid Archbishopric
On April 5, 972, Byzantine EmperorJohn I Tzimisces
John I Tzimiskes (; 925 – 10 January 976) was the senior Byzantine emperor from 969 to 976. An intuitive and successful general, he strengthened the Empire and expanded its borders during his short reign.
Background
John I Tzimiskes ...
conquered and burned down Preslav, and captured Bulgarian Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" i ...
Boris II. Patriarch Damyan managed to escape, initially to Sredetz ( Sofia) in western Bulgaria. In the coming years, the residence of the Bulgarian patriarchs remained closely connected to the developments in the war between the next Bulgarian royal dynasty, the ''Comitopuli
The Kometopuli dynasty ( Bulgarian: ,
Bulgarian; ; Byzantine Greek: , ) was the last royal dynasty in the First Bulgarian Empire, ruling from ca. 976 until the fall of Bulgaria under Byzantine rule in 1018. The most notable member of the dynas ...
'', and the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. Patriarch German resided consecutively in the medieval Bulgarian cities of Maglen (Almopia
Almopia ( el, Αλμωπία), or Enotia, also known in the Middle Ages as Moglena (Greek: Μογλενά, Macedonian and Bulgarian: Меглен or Мъглен), is a municipality and a former province (επαρχία) of the Pella regional un ...
) and Voden ( Edessa) (both in present-day north-western Greece), and Prespa (in present-day southern North Macedonia). Around 990, the next patriarch, Philip, moved to Ohrid (in present-day south-western North Macedonia), which became the permanent seat of the Patriarchate.
After Bulgaria fell under Byzantine domination in 1018, Emperor Basil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus ( gr, Βασίλειος Πορφυρογέννητος ;) and, most often, the Purple-born ( gr, ὁ πορφυρογέννητος, translit=ho porphyrogennetos).. 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar ...
''Bulgaroktonos'' (the “Bulgar-Slayer”) acknowledged the autocephalous status of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church. By special charters (royal decrees), his government set up its boundaries, dioceses, property and other privileges. He deprived the church of its Patriarchal title and reduced it to the rank of an archbishopric. Although the first appointed archbishop (John of Debar John of Debar ( bg, Йоан Дебърски; fl. 1018–1037) was an 11th-century Bulgarian clergyman. He was a bishop under Emperor Samuel of Bulgaria. According to Srđan Pirivatrić he became the last Bulgarian patriarch David in 1016. He r ...
) was a Bulgarian, his successors, as well as the whole higher clergy, were selected from Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
s. The monks and the ordinary priests continued to be predominantly Bulgarian. To a large extent the archbishopric preserved its national character, upheld the Slavonic liturgy, and continued its contribution to the development of Bulgarian literature. The autocephaly of the Ohrid Archbishopric remained respected during the periods of Byzantine, Bulgarian, Serbian, and Ottoman rule. The church continued to exist until it was unlawfully abolished in 1767.
Tarnovo Patriarchate
As a result of the successful uprising of the brothers Peter IV andIvan Asen I
Ivan Asen I, also known as Asen I or John Asen I ( bg, Иван Асен I; died in 1196), was emperor or tsar of Bulgaria from 1187/1188 to 1196 as co-ruler with his elder brother, Peter II. Hailing from the Byzantine theme of Paristrion, hi ...
in 1185/1186, the foundations of the Second Bulgarian Empire were laid with Tarnovo
Veliko Tarnovo ( bg, Велико Търново, Veliko Tărnovo, ; "Great Tarnovo") is a town in north central Bulgaria and the administrative centre of Veliko Tarnovo Province.
Often referred as the "''City of the Tsars''", Veliko Tarnovo ...
as its capital. Following Boris I
Boris I, also known as Boris-Mihail (Michael) and ''Bogoris'' ( cu, Борисъ А҃ / Борисъ-Михаилъ bg, Борис I / Борис-Михаил; died 2 May 907), was the ruler of the First Bulgarian Empire in 852–889. At ...
’s principle that the sovereignty of the state is inextricably linked to the autocephaly of the Church, the two brothers immediately took steps to restore the Bulgarian Patriarchate
The Bulgarian Orthodox Church ( bg, Българска православна църква, translit=Balgarska pravoslavna tsarkva), legally the Patriarchate of Bulgaria ( bg, Българска патриаршия, links=no, translit=Balgarsk ...
. As a start, they established an independent archbishopric in Tarnovo in 1186. The struggle to have the archbishopric recognized according to the canonical order and elevated to the rank of a Patriarchate took almost 50 years. Following the example of Boris I
Boris I, also known as Boris-Mihail (Michael) and ''Bogoris'' ( cu, Борисъ А҃ / Борисъ-Михаилъ bg, Борис I / Борис-Михаил; died 2 May 907), was the ruler of the First Bulgarian Empire in 852–889. At ...
, Bulgarian Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" i ...
Kaloyan manoeuvred for years between the Patriarch of Constantinople and Pope Innocent III. Finally in 1203 the latter proclaimed the Tarnovo Archbishop Vassily " Primate and Archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
of all Bulgaria and Walachia." The union with the Roman Catholic Church continued for well over two decades.
 Under the reign of
Under the reign of Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" i ...
Ivan Asen II (1218–1241), conditions were created for the termination of the union with Rome and for the recognition of the autocephalous status of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church. In 1235 a church council was convened in the town of Lampsakos. Under the presidency of Patriarch Germanus II of Constantinople
Germanus II Nauplius ( el, Γερμανός Β΄ Ναύπλιος; ? – June 1240) was Patriarch of Constantinople (in exile at Nicaea) from 1223 until his death in June 1240.
He was born at Anaplous in the second half of the 12th century. At ...
and with the consent of all Eastern Patriarchs, the council confirmed the Patriarchal dignity of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church and consecrated the Bulgarian archbishop German as Patriarch.
Despite the shrinking of the diocese of the Tarnovo Patriarchate
The Tаrnovo Patriarchate ( bg, Търновска патриаршия) was the name of an independent Bulgarian Orthodox Church in the period of 1235–1393.
History
After the Vlach brothers Ivan Asen I and Peter IV reestablished the Bulgari ...
at the end of the 13th century, its authority in the Eastern Orthodox world remained high. The Patriarch of Tarnovo confirmed the patriarchal dignity of the Serbian Orthodox Church in 1346, despite protests by the Patriarchate of Constantinople. The Tarnovo Literary School
The Tarnovo Literary School ( bg, Търновска книжовна школа) of the late 14th and 15th century was a major medieval Bulgarian cultural academy with important contribution to the Medieval Bulgarian literature established in the ...
developed under the wing of the Patriarchate in the 14th century, with scholars of the rank of Patriarch Evtimiy
Saint Euthymius of Tarnovo (also ''Evtimiy''; , ''Sveti Evtimiy Tarnovski'') was Patriarch of Bulgaria between 1375 and 1393. Regarded as one of the most important figures of medieval Bulgaria, Euthymius was the last head of the Bulgarian Orth ...
, Gregory Tsamblak
Gregory Tsamblak or Grigorij Camblak ( bg, Григорий Цамблак, sr-Cyr, Григорије Цамблак; c. 1365–1420) was a Bulgarian writer and cleric. He was the pretended Metropolitan of Lithuania between 1413 and 1420. A Bulg ...
, and Konstantin of Kostenets. A considerable flowering was noted in the fields of literature, architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings ...
, and painting; the religious and theological literature also flourished.
Tarnovo
Veliko Tarnovo ( bg, Велико Търново, Veliko Tărnovo, ; "Great Tarnovo") is a town in north central Bulgaria and the administrative centre of Veliko Tarnovo Province.
Often referred as the "''City of the Tsars''", Veliko Tarnovo ...
fell under domination by the Ottoman Empire in 1393, whose leaders sent Patriarch Evtimiy
Saint Euthymius of Tarnovo (also ''Evtimiy''; , ''Sveti Evtimiy Tarnovski'') was Patriarch of Bulgaria between 1375 and 1393. Regarded as one of the most important figures of medieval Bulgaria, Euthymius was the last head of the Bulgarian Orth ...
into exile, the autocephalous church organization was destroyed again the next year and integrated into the Ecumenical Patriarchate. In 1394, the Holy Synod
In several of the autocephaly, autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox churches and Eastern Catholic Churches, the patriarch or head bishop is elected by a group of bishops called the Holy Synod. For instance, the Holy Synod is a ...
of the Ecumenical Patriarchate
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople ( el, Οἰκουμενικὸν Πατριαρχεῖον Κωνσταντινουπόλεως, translit=Oikoumenikón Patriarkhíon Konstantinoupóleos, ; la, Patriarchatus Oecumenicus Constanti ...
gave the authorisation to the Metropolitan
Metropolitan may refer to:
* Metropolitan area, a region consisting of a densely populated urban core and its less-populated surrounding territories
* Metropolitan borough, a form of local government district in England
* Metropolitan county, a typ ...
of Moldavia, Jeremiah, "to move with the help of God to the holy Church of Turnovo and to be allowed to perform everything befitting a prelate freely and without restraint." By around 1416, the territory of the Patriarchate of Turnovo was totally subordinated to the Ecumenical Patriarchate. The other Bulgarian religious centrethe Ohrid Archbishopric survived until 1767.
Ottoman rule
As the Ottomans were Muslim, the period of Ottoman rule was the most difficult in the history of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church, to the same extent as it was the hardest in the history of the Bulgarian people. During and immediately after the Ottoman conquest, their forces razed a significant number of Bulgarian churches and monasteries south of the Danube River, including the PatriarchalCathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the ''cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominat ...
church of the Holy Ascension in Tarnovo
Veliko Tarnovo ( bg, Велико Търново, Veliko Tărnovo, ; "Great Tarnovo") is a town in north central Bulgaria and the administrative centre of Veliko Tarnovo Province.
Often referred as the "''City of the Tsars''", Veliko Tarnovo ...
. Some of the surviving structures were converted into mosques. Many of the clergy were killed, while the intelligentsia associated with the Tarnovo Literary School
The Tarnovo Literary School ( bg, Търновска книжовна школа) of the late 14th and 15th century was a major medieval Bulgarian cultural academy with important contribution to the Medieval Bulgarian literature established in the ...
fled north of the Danube.
St. Nicholas of Sofia
St. Nicholas of Sofia the New ( bg, Свети Николай Софийски Нови) is a Christian saint who lived in the 16th century in Sofia, Bulgaria and is considered a martyr in the Bulgarian Orthodox Church. He is referred to as a Ne ...
(d. 1515), St. Damaskin of Gabrovo (d. 1771), St. Zlata of Muglen (d. 1795), St. John the Bulgarian (d. 1814), St. Ignatius of Stara Zagora (d. 1814), St. Onouphry of Gabrovo (d. 1818) and many others died defending their Christian faith.
After many of the leadership of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church were executed, it was fully subordinated to the Patriarch of Constantinople. The millet system in the Ottoman Empire granted a number of important civil and judicial functions to the Patriarch of Constantinople and the diocesan metropolitans. As the higher Bulgarian church clerics were replaced by Greek ones at the beginning of the Ottoman domination, the Bulgarian population was subjected to double oppressionpolitical by the Ottomans and cultural by the Greek clergy. With the rise of Greek nationalism in the second half of the 18th century, the clergy imposed the Greek language and a Greek consciousness on the emerging Bulgarian bourgeoisie. They used the Patriarchate of Constantinople to assimilate other peoples. At the end of the 18th and the beginning of the 19th century, the clergy opened numerous schools with total Greek language curriculum; they nearly banned the Bulgarian-language liturgy. These actions threatened the survival of the Bulgarians as a separate nation and people with its own, distinct national culture.
Throughout the centuries of Ottoman domination, the Orthodox monasteries were instrumental in the preservation of the Bulgarian language and the Bulgarian national consciousness. Especially important were the Zograph and Hilandar monasteries on Mount Athos, as well as the Rila, Troyan
Troyan ( bg, Троян ) is a town remembering the name of Roman Emperor Trajan, in Lovech Province in central Bulgaria with population of 21,997 inhabitants, as of December 2009. It is the administrative centre of the homonymous Troyan Mun ...
, Etropole
Etropole ( bg, Етрополе, ) is a town in western Bulgaria, part of Sofia Province. It is located close to the northern slopes of the Balkan Mountains in the valley of the Iskar River, from Sofia.
History
The area was first settled by the ...
, Dryanovo
Dryanovo ( bg, Дряново, ) is a Bulgarian town situated at the northern foot of the Balkan Mountains in Gabrovo Province; amphitheatrically along the two banks of Dryanovo River, a tributary to the Yantra River. The town is a centre of t ...
, Cherepish and Dragalevtsi monasteries in Bulgaria. The monks managed to preserve their national character in the monasteries, continuing traditions of the Slavonic liturgy and Bulgarian literature. They continued to operate monastery schools and carried out other educational activities, which managed to keep the flame of the Bulgarian culture burning.
Bulgarian Exarchate
 In 1762, St.
In 1762, St. Paisius of Hilendar
Saint Paisius of Hilendar or Paìsiy Hilendàrski ( bg, Свети Паисий Хилендарски) (1722–1773) was a Bulgarian clergyman and a key Bulgarian National Revival figure. He is most famous for being the author of '' Istoriya Sla ...
(1722–1773), a monk from the south-western Bulgarian town of Bansko
Bansko ( bg, Банско ) is a town in southwestern Bulgaria, located at the foot of the Pirin Mountains at an elevation of 1200m above sea level. It is a ski resort.
Legends
There are several legends about who founded Bansko. According to ...
, wrote a short historical work. It was the first work written in the modern Bulgarian vernacular
A vernacular or vernacular language is in contrast with a "standard language". It refers to the language or dialect that is spoken by people that are inhabiting a particular country or region. The vernacular is typically the native language, n ...
and was also the first call for a national awakening. In '' History of Slav-Bulgarians'', Paissiy urged his compatriots to throw off subjugation to the Greek language and culture. The example of Paissiy was followed by a number of other activists
Activism (or Advocacy) consists of efforts to promote, impede, direct or intervene in social, political, economic or environmental reform with the desire to make changes in society toward a perceived greater good. Forms of activism range fro ...
, including St. Sophroniy of Vratsa ( Sofroni Vrachanski) (1739–1813), hieromonk Spiridon of Gabrovo, hieromonk Yoakim Karchovski Yoakim Karchovski ( bg, Йоаким Кърчовски; mk, Јоаким Крчовски c. 1750 - c. 1820), also known as Hadži Joakim, was a cleric, writer and one of the early figures of the Bulgarian National Revival.Becoming Bulgarian: the ...
(d. 1820), hieromonk Kiril Peychinovich
Kiril Peychinovich or Kiril Pejčinoviḱ ( bg, Кирил Пейчинович, sr, Кирил Пејчиновић, mk, Кирил Пејчиновиќ, Church Slavonic: Күриллъ Пейчиновићь (c. 1770 – 7 March 1845)) ...
(d. 1845).
Discontent with the supremacy of the Greek clergy started to flare up in several Bulgarian dioceses as early as the 1820s. It was not until 1850 that the Bulgarians initiated a purposeful struggle against the Greek clerics in a number of bishoprics, demanding their replacement with Bulgarian ones. By that time, most Bulgarian clergy had realised that further struggle for the rights of the Bulgarians
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe.
Etymology
Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not completely understo ...
in the Ottoman Empire could not succeed unless they managed to obtain some degree of autonomy from the Patriarchate of Constantinople. As the Ottomans identified nationality with religion, and the Bulgarians were Eastern Orthodox, the Ottomans considered them part of the ''Roum-Milet'', i.e., the Greeks. To gain Bulgarian schools and liturgy, the Bulgarians needed to achieve an independent ecclesiastical organisation.
The struggle between the Bulgarians, led by Neofit Bozveli
Neofit Bozveli ( bg, Неофит Бозвели) (c. 1785 – 4 June 1848) was a Bulgarian cleric and enlightener and one of the leaders of the Bulgarian Church struggle.
He was born in the lively sub-Balkan town of Kotel. Bozveli completed his ...
and Ilarion Makariopolski
Hilarion of Makariopolis ( ''Ilarion Makariopolski'', el, Ιλαρίων Μακαριουπόλεως, born Stoyan Stoyanov Mihaylovski, bg, Стоян Стоянов Михайловски; 1812–1875) was a 19th-century Bulgarian cleric and ...
, and the Greeks intensified throughout the 1860s. By the end of the decade, Bulgarian bishoprics had expelled most of the Greek clerics, thus the whole of northern Bulgaria, as well as the northern parts of Thrace and Macedonia had effectively seceded from the Patriarchate. The Ottoman government restored the Bulgarian Patriarchate under the name of "Bulgarian Exarchate
The Bulgarian Exarchate ( bg, Българска екзархия, Balgarska ekzarhiya; tr, Bulgar Eksarhlığı) was the official name of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church before its autocephaly was recognized by the Ecumenical See in 1945 and th ...
" by a decree ('' firman'') of the Sultan promulgated on February 28, 1870. The original Exarchate extended over present-day northern Bulgaria ( Moesia), Thrace without the Vilayet of Adrianople
The Vilayet of Adrianople or Vilayet of Edirne ( ota, ولايت ادرنه; ''Vilâyet-i Edirne'') was a first-level administrative division (vilayet) of the Ottoman Empire.
This vilayet was split between Turkey and Greece in 1923, culminating i ...
, as well as over north-eastern Macedonia. After the Christian population of the bishoprics of Skopje and Ohrid voted in 1874 overwhelmingly in favour of joining the Exarchate (Skopje by 91%, Ohrid by 97%), the Bulgarian Exarchate
The Bulgarian Exarchate ( bg, Българска екзархия, Balgarska ekzarhiya; tr, Bulgar Eksarhlığı) was the official name of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church before its autocephaly was recognized by the Ecumenical See in 1945 and th ...
became in control of the whole of Vardar and Pirin Macedonia
Pirin Macedonia or Bulgarian Macedonia ( bg, Пиринска Македония; Българска Македония) (''Pirinska Makedoniya or Bulgarska Makedoniya'') is the third-biggest part of the geographical region Macedonia located on t ...
. The Bulgarian Exarchate was partially represented in southern Macedonia and the Vilayet of Adrianople
The Vilayet of Adrianople or Vilayet of Edirne ( ota, ولايت ادرنه; ''Vilâyet-i Edirne'') was a first-level administrative division (vilayet) of the Ottoman Empire.
This vilayet was split between Turkey and Greece in 1923, culminating i ...
by vicars. Thus, the borders of the Exarchate included all Bulgarian districts in the Ottoman Empire.
 The Patriarchate of Constantinople opposed the change, promptly declaring the
The Patriarchate of Constantinople opposed the change, promptly declaring the Bulgarian Exarchate
The Bulgarian Exarchate ( bg, Българска екзархия, Balgarska ekzarhiya; tr, Bulgar Eksarhlığı) was the official name of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church before its autocephaly was recognized by the Ecumenical See in 1945 and th ...
schismatic and its adherents heretics
Heresy is any belief or theory that is strongly at variance with established beliefs or customs, in particular the accepted beliefs of a church or religious organization. The term is usually used in reference to violations of important religi ...
. Although the status and the guiding principles of the Exarchate reflected the canons, the Patriarchate argued that “surrender of Orthodoxy to ethnic nationalism” was essentially a manifestation of heresy.
The first Bulgarian Exarch was Antim I
Anthim I (, secular name Atanas Mihaylov Chalakov, ; 1816 – 1 December 1888) was a Bulgarian education figure and clergyman, and a participant in the Bulgarian liberation and church-independence movement. He was the first head of the Bulgarian ...
, who was elected by the Holy Synod of the Exarchate in February, 1872. He was discharged by the Ottoman government immediately after the outbreak of the Russo-Turkish War
The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman–Russian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European histor ...
on April 24, 1877, and was sent into exile in Ankara
Ankara ( , ; ), historically known as Ancyra and Angora, is the capital of Turkey. Located in the central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5.1 million in its urban center and over 5.7 million in Ankara Province, mak ...
. His successor, Joseph I Joseph I or Josef I may refer to:
* Joseph I of Constantinople, Ecumenical Patriarch in 1266–1275 and 1282–1283
*Joseph I, Holy Roman Emperor (1678–1711)
* Joseph I (Chaldean Patriarch) (reigned 1681–1696)
*Joseph I of Portugal (1750–1777 ...
, managed to develop and considerably extend its church and school network in the Bulgarian Principality, Eastern Rumelia
Eastern Rumelia ( bg, Източна Румелия, Iztochna Rumeliya; ota, , Rumeli-i Şarkî; el, Ανατολική Ρωμυλία, Anatoliki Romylia) was an autonomous province (''oblast'' in Bulgarian, ''vilayet'' in Turkish) in the Otto ...
, Macedonia and the Adrianople Vilayet
The Vilayet of Adrianople or Vilayet of Edirne ( ota, ولايت ادرنه; ''Vilâyet-i Edirne'') was a first-level administrative division (vilayet) of the Ottoman Empire.
This vilayet was split between Turkey and Greece in 1923, culminating i ...
. In 1895, the Tarnovo Constitution
The Tarnovo Constitution ( bg, Търновска конституция) was the first constitution of Bulgaria.
It was adopted on 16 April 1879 ( O.S.) by the Constituent National Assembly held in Veliko Tarnovo as part of the establishment of ...
formally established the Bulgarian Orthodox Church as the national religion of the nation. On the eve of the Balkan Wars
The Balkan Wars refers to a series of two conflicts that took place in the Balkan States in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan States of Greece, Serbia, Montenegro and Bulgaria declared war upon the Ottoman Empire and def ...
, in Macedonia and the Adrianople Vilayet
The Vilayet of Adrianople or Vilayet of Edirne ( ota, ولايت ادرنه; ''Vilâyet-i Edirne'') was a first-level administrative division (vilayet) of the Ottoman Empire.
This vilayet was split between Turkey and Greece in 1923, culminating i ...
, the Bulgarian Exarchate
The Bulgarian Exarchate ( bg, Българска екзархия, Balgarska ekzarhiya; tr, Bulgar Eksarhlığı) was the official name of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church before its autocephaly was recognized by the Ecumenical See in 1945 and th ...
had seven dioceses with prelates and eight more with acting chairmen in charge and 38 vicariates; 1,218 parishes and 1,212 parish priests; 64 monasteries and 202 chapels; as well as of 1,373 schools with 2,266 teachers and 78,854 pupils.
After World War I, by virtue of the peace treaties, the Bulgarian Exarchate was deprived of its dioceses in Macedonia and Aegean Thrace. Exarch Joseph I transferred his offices from Istanbul to Sofia as early as 1913. After the death of Joseph I Joseph I or Josef I may refer to:
* Joseph I of Constantinople, Ecumenical Patriarch in 1266–1275 and 1282–1283
*Joseph I, Holy Roman Emperor (1678–1711)
* Joseph I (Chaldean Patriarch) (reigned 1681–1696)
*Joseph I of Portugal (1750–1777 ...
in 1915, the Bulgarian Orthodox Church was not in a position to elect its regular head for a total of three decades.
Second restoration of the Bulgarian Patriarchate
Cyril
Cyril (also Cyrillus or Cyryl) is a masculine given name. It is derived from the Greek name Κύριλλος (''Kýrillos''), meaning 'lordly, masterful', which in turn derives from Greek κυριος (''kýrios'') 'lord'. There are various varian ...
, Bulgarian Patriarch. After the death of Patriarch Cyril in 1971, in his place was elected the Metropolitan of Lovech, Maxim
Maxim or Maksim may refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Maxim'' (magazine), an international men's magazine
** ''Maxim'' (Australia), the Australian edition
** ''Maxim'' (India), the Indian edition
* Maxim Radio, ''Maxim'' magazine's radio channel on Si ...
, leading the church until his death in 2012. On 10 November 2012 Metropolitan Cyril of Varna and Veliki Preslav was chosen as interim leader to organize the election of the new Patriarch within four months.
At the church council convened to elect a new Patriarch 24 February 2013, the Metropolitan of Ruse
Ruse may refer to:
Places
*Ruse, Bulgaria, a major city of Bulgaria
**Ruse Municipality
**Ruse Province
** 19th MMC – Ruse, a constituency
*Ruše, a town and municipality in north-eastern Slovenia
* Ruše, Žalec, a small settlement in east-cen ...
, Neophyt was elected Patriarch of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church with 90 votes against 47 for Metropolitan Gabriel of Lovech.
 Under Communism (1944–89), Bulgaria's rulers worked to control rather than destroy the church. Still, the early postwar years were unsettling to church hierarchs. During 1944-47 the church was deprived of jurisdiction in marriage, divorce, issuance of birth and death certificates, and other passages that had been sacraments as well as state events. Communists removed study of the catechism and church history from school curricula. They generated anti-religious propaganda and persecuted some priests. From 1947-49 was the height of the campaign to intimidate the church. Bishop Boris was assassinated; Egumenius Kalistrat, administrator of the Rila Monastery, was imprisoned; and various other clergy were murdered or charged with crimes against the state. The communists soon replaced all clergy who refused to endorse the regime's policies. They banished Exarch Stefan, who had co-authored a book in 1948 that was considered anti-Communist.
200px, left, Bulgarian Orthodox priest
From that time until the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the end of Communist rule in 1989, the Bulgarian Orthodox Church and the
Under Communism (1944–89), Bulgaria's rulers worked to control rather than destroy the church. Still, the early postwar years were unsettling to church hierarchs. During 1944-47 the church was deprived of jurisdiction in marriage, divorce, issuance of birth and death certificates, and other passages that had been sacraments as well as state events. Communists removed study of the catechism and church history from school curricula. They generated anti-religious propaganda and persecuted some priests. From 1947-49 was the height of the campaign to intimidate the church. Bishop Boris was assassinated; Egumenius Kalistrat, administrator of the Rila Monastery, was imprisoned; and various other clergy were murdered or charged with crimes against the state. The communists soon replaced all clergy who refused to endorse the regime's policies. They banished Exarch Stefan, who had co-authored a book in 1948 that was considered anti-Communist.
200px, left, Bulgarian Orthodox priest
From that time until the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the end of Communist rule in 1989, the Bulgarian Orthodox Church and the Bulgarian Communist Party
The Bulgarian Communist Party (BCP; bg, Българска Комунистическа Партия (БКП), Balgarska komunisticheska partiya (BKP)) was the founding and ruling party of the People's Republic of Bulgaria from 1946 until 198 ...
and State Security coexisted in a closely symbiotic partnership, in which each supported the other. 11 (out of 15) members of Bulgarian Orthodox Church's Holy Synod worked for communist State Security. The party supported the elevation of the exarchate to the rank of patriarchate in May 1953. The 1970 commemoration served to recall that the exarchate (which retained its jurisdictional borders until after World War I) included Macedonia and Thrace in addition to present-day Bulgaria. Along with some other autocephalous Orthodox churches, the Bulgarian Orthodox Church does not recognize the autocephaly of the Macedonian Orthodox Church, however it restored communion with it on 22 June 2022.
Canonical status and organization
The Bulgarian Orthodox Church considers itself an inseparable member of the one, holy, synodal and apostolic church and is organized as a self-governing body under the name of Patriarchate. It is divided into thirteen dioceses within the boundaries of the Republic of Bulgaria and has jurisdiction over additional two dioceses for Bulgarians inWestern
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the ar ...
, and the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with t ...
, Canada and Australia. The dioceses of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church are divided into 58 church counties, which, in turn, are subdivided into some 2,600 parishes.
 The supreme clerical, judicial and administrative power for the whole domain of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church is exercised by the
The supreme clerical, judicial and administrative power for the whole domain of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church is exercised by the Holy Synod
In several of the autocephaly, autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox churches and Eastern Catholic Churches, the patriarch or head bishop is elected by a group of bishops called the Holy Synod. For instance, the Holy Synod is a ...
, which includes the Patriarch and the diocesan prelates, who are called metropolitan
Metropolitan may refer to:
* Metropolitan area, a region consisting of a densely populated urban core and its less-populated surrounding territories
* Metropolitan borough, a form of local government district in England
* Metropolitan county, a typ ...
s. Church life in the parishes is guided by the parish priests, numbering some 1,500.
 Eparchies in Bulgaria: (with Bulgarian names in brackets)
*Eparchy of Vidin ()
*Eparchy of
Eparchies in Bulgaria: (with Bulgarian names in brackets)
*Eparchy of Vidin ()
*Eparchy of Vratsa
Vratsa ( bg, Враца ) is the largest city in northwestern Bulgaria and the administrative and economic centre of the municipality of Vratsa and Vratsa district. It is located about 112 km north of Sofia, 40 km southeast of Montana.
...
()
*Eparchy of Lovech ()
*Eparchy of Veliko Tarnovo ()
*Eparchy of Dorostol () (seat in Silistra)
*Eparchy of Varna and Veliki Preslav
The modern Veliki Preslav or Great Preslav ( bg, Велики Преслав, ), former Preslav ( bg, link=no, Преслав; until 1993), is a city and the seat of government of the Veliki Preslav Municipality (Great Preslav Municipality, new B ...
() (seat in Varna)
*Eparchy of Sliven ()
*Eparchy of Stara Zagora ()
*Eparchy of Plovdiv ()
*Eparchy of Sofia ()
*Eparchy of Nevrokop ()
*Eparchy of Pleven ()
*Eparchy of Ruse
Ruse may refer to:
Places
*Ruse, Bulgaria, a major city of Bulgaria
**Ruse Municipality
**Ruse Province
** 19th MMC – Ruse, a constituency
*Ruše, a town and municipality in north-eastern Slovenia
* Ruše, Žalec, a small settlement in east-cen ...
()
Eparchies abroad:
*Eparchy of Central and Western Europe (with seat in Berlin);
* Eparchy of USA, Canada and Australia (with seat in New York City)
The Bulgarian Orthodox Church also has some 120 monasteries in Bulgaria, with about 2,000 monks and nearly as many nuns.
See also
* List of Orthodox Churches * Bulgarian Alternative SynodReferences
External links
The official website of the Bulgarian Patriarchate
* History of Bulgaria and the Bulgarian Orthodox Church according to the ''
Catholic Encyclopedia
The ''Catholic Encyclopedia: An International Work of Reference on the Constitution, Doctrine, Discipline, and History of the Catholic Church'' (also referred to as the ''Old Catholic Encyclopedia'' and the ''Original Catholic Encyclopedia'') i ...
'' (1913).A short history of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church by CNEWA, the papal agency for humanitarian and pastoral support
* ttp://www.bulgarian-guide.com/about-bulgaria/bulgaria-religion/ Article about the Bulgarian Orthodox Church and Religion in Bulgariabr>Orthodox Life Info Portal
a Bulgarian Orthodox site (in English)
Article on the medieval history of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church in the repository of the Institute for Byzantine Studies of the Austrian Academy of Sciences (in German)
{{Authority control National churches Religious organizations established in the 920s Eastern Orthodox Church bodies in Europe European-Australian culture