Buckingham Palace on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Buckingham Palace () is a royal residence in
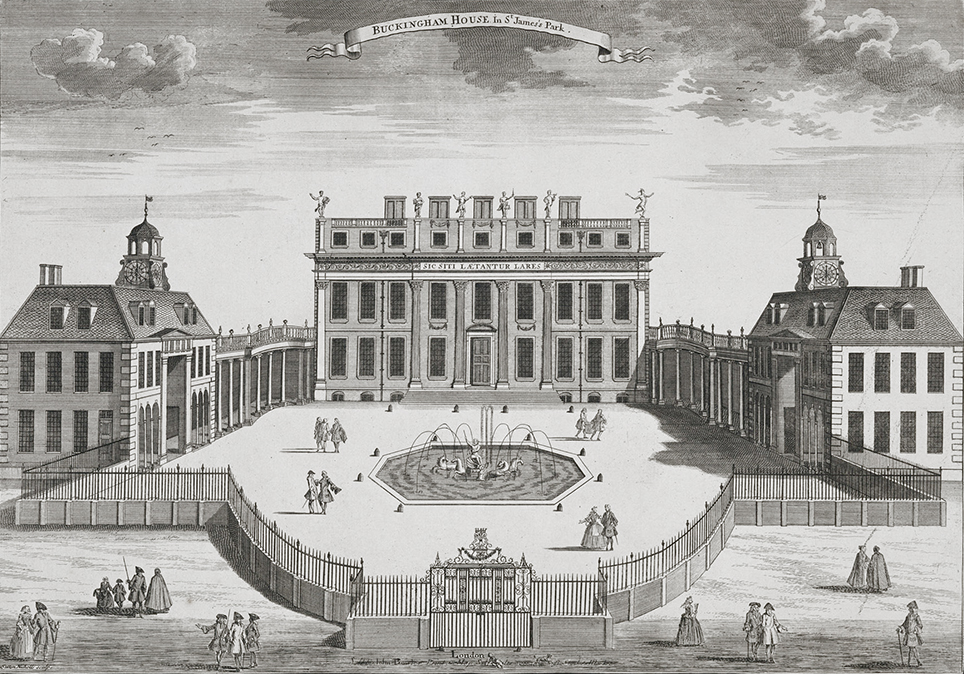 Possibly the first house erected within the site was that of William Blake, around 1624. The next owner was George Goring, 1st Earl of Norwich, who from 1633 extended Blake's house, which came to be known as Goring House, and developed much of today's garden, then known as Goring Great Garden.Harris, p. 21. He did not, however, obtain the freehold interest in the mulberry garden. Unbeknown to Goring, in 1640 the document "failed to pass the Great Seal before Charles I fled London, which it needed to do for legal execution". It was this critical omission that would help the British royal family regain the freehold under
Possibly the first house erected within the site was that of William Blake, around 1624. The next owner was George Goring, 1st Earl of Norwich, who from 1633 extended Blake's house, which came to be known as Goring House, and developed much of today's garden, then known as Goring Great Garden.Harris, p. 21. He did not, however, obtain the freehold interest in the mulberry garden. Unbeknown to Goring, in 1640 the document "failed to pass the Great Seal before Charles I fled London, which it needed to do for legal execution". It was this critical omission that would help the British royal family regain the freehold under
 Many of the palace's contents are part of the
Many of the palace's contents are part of the
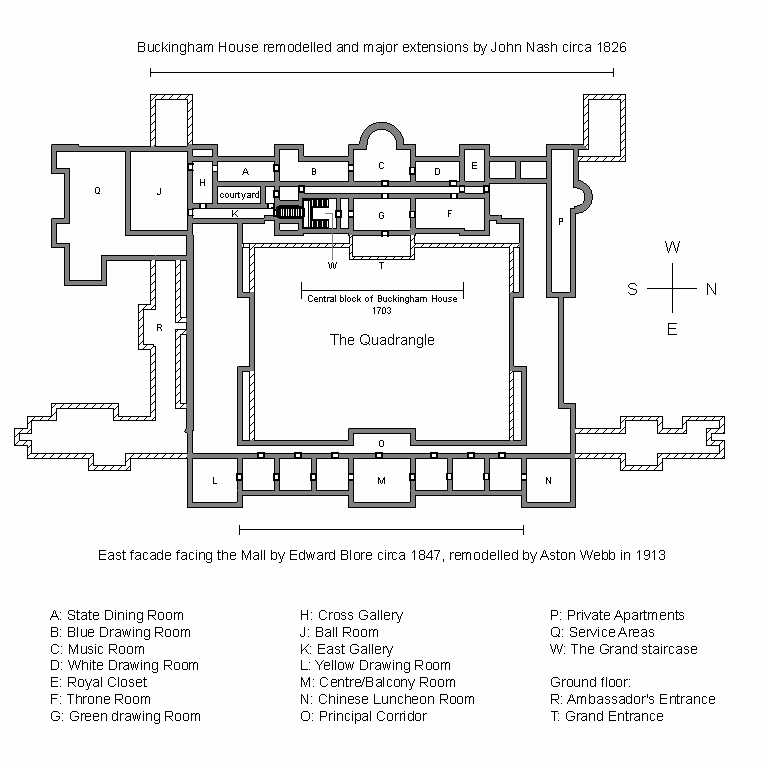 The front of the palace measures across, by deep, by high and contains over of floorspace. There are 775 rooms, including 188 staff bedrooms, 92 offices, 78 bathrooms, 52 principal bedrooms and 19 state rooms. It also has a post office, cinema, swimming pool, doctor's surgery, and jeweller's workshop. The royal family occupy a small suite of private rooms in the north wing.
The front of the palace measures across, by deep, by high and contains over of floorspace. There are 775 rooms, including 188 staff bedrooms, 92 offices, 78 bathrooms, 52 principal bedrooms and 19 state rooms. It also has a post office, cinema, swimming pool, doctor's surgery, and jeweller's workshop. The royal family occupy a small suite of private rooms in the north wing.
 Directly underneath the state apartments are the less grand semi-state apartments. Opening from the Marble Hall, these rooms are used for less formal entertaining, such as luncheon parties and private audiences. At the centre of this floor is the Bow Room, through which thousands of guests pass annually to the monarch's garden parties. When paying a state visit to Britain, foreign
Directly underneath the state apartments are the less grand semi-state apartments. Opening from the Marble Hall, these rooms are used for less formal entertaining, such as luncheon parties and private audiences. At the centre of this floor is the Bow Room, through which thousands of guests pass annually to the monarch's garden parties. When paying a state visit to Britain, foreign
 Between 1847 and 1850, when Blore was building the new east wing, the Brighton Pavilion was once again plundered of its fittings. As a result, many of the rooms in the new wing have a distinctly oriental atmosphere. The red and blue Chinese Luncheon Room is made up of parts of the Brighton Banqueting and Music Rooms with a large oriental chimneypiece designed by Robert Jones and sculpted by Richard Westmacott.Harris, de Bellaigue & Miller, p. 87. It was formerly in the Music Room at the Brighton Pavilion. The ornate clock, known as the Kylin Clock, was made in Jingdezhen, Jiangxi Province, China, in the second half of the 18th century; it has a later movement by Benjamin Vulliamy circa 1820. The Yellow Drawing Room has hand-painted Chinese wallpaper supplied in 1817 for the Brighton Saloon, and a chimneypiece which is a European vision of a Chinese chimneypiece. It has nodding mandarins in niches and fearsome winged
Between 1847 and 1850, when Blore was building the new east wing, the Brighton Pavilion was once again plundered of its fittings. As a result, many of the rooms in the new wing have a distinctly oriental atmosphere. The red and blue Chinese Luncheon Room is made up of parts of the Brighton Banqueting and Music Rooms with a large oriental chimneypiece designed by Robert Jones and sculpted by Richard Westmacott.Harris, de Bellaigue & Miller, p. 87. It was formerly in the Music Room at the Brighton Pavilion. The ornate clock, known as the Kylin Clock, was made in Jingdezhen, Jiangxi Province, China, in the second half of the 18th century; it has a later movement by Benjamin Vulliamy circa 1820. The Yellow Drawing Room has hand-painted Chinese wallpaper supplied in 1817 for the Brighton Saloon, and a chimneypiece which is a European vision of a Chinese chimneypiece. It has nodding mandarins in niches and fearsome winged
 Investitures for the awarding of honours (which include the conferring of
Investitures for the awarding of honours (which include the conferring of
The Royal Encyclopedia
'. London: Macmillan. * Blaikie, Thomas (2002).
You Look Awfully Like the Queen: Wit and Wisdom from the House of Windsor
'. London: HarperCollins. . * Goring, O. G. (1937).
From Goring House to Buckingham Palace
'. London: Ivor Nicholson & Watson. * Harris, John; de Bellaigue, Geoffrey; & Miller, Oliver (1968).
Buckingham Palace
'. London: Nelson. . * Healey, Edma (1997).
The Queen's House: A Social History of Buckingham Palace
'. London: Penguin Group. . * Hedley, Olwen (1971)
The Pictorial History of Buckingham Palace
'. Pitkin, . * * * Mackenzie, Compton (1953).
The Queen's House
'. London: Hutchinson. * . * * * * . * *
Buckingham Palace
at the Royal Family website
Account of Buckingham Palace, with prints of Arlington House and Buckingham House
from ''Old and New London'' (1878)
Account of the acquisition of the Manor of Ebury
from ''Survey of London'' (1977)
The State Rooms, Buckingham Palace
at the
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, and the administrative headquarters of the monarch of the United Kingdom
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the form of government used by the United Kingdom by which a hereditary monarch reigns as the head of state, with their powers Constitutional monarchy, regula ...
. Located in the City of Westminster
The City of Westminster is a London borough with City status in the United Kingdom, city status in Greater London, England. It is the site of the United Kingdom's Houses of Parliament and much of the British government. It contains a large par ...
, the palace is often at the centre of state occasions and royal hospitality. It has been a focal point for the British people
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs modern British citizenship and nationality, w ...
at times of national rejoicing and mourning.
Originally known as Buckingham House, the building at the core of today's palace was a large townhouse
A townhouse, townhome, town house, or town home, is a type of Terraced house, terraced housing. A modern townhouse is often one with a small footprint on multiple floors. In a different British usage, the term originally referred to any type o ...
built for the Duke of Buckingham and Normanby in 1703 on a site that had been in private ownership for at least 150 years. It was acquired by George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland, Ireland from 25 October 1760 until his death in 1820. The Acts of Union 1800 unified Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and ...
in 1761 as a private residence for Queen Charlotte and became known as The Queen's House. During the 19th century it was enlarged by architects John Nash and Edward Blore
Edward Blore (13 September 1787 – 4 September 1879) was a 19th-century English landscape and architectural artist, architect and antiquary.
Early career
Blore was born in Derby, the son of the antiquarian writer Thomas Blore.
Blore's backg ...
, who constructed three wings around a central courtyard. Buckingham Palace became the London residence of the British monarch on the accession of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
in 1837.
The last major structural additions were made in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, including the East Front, which contains the balcony on which the royal family
A royal family is the immediate family of monarchs and sometimes their extended family.
The term imperial family appropriately describes the family of an emperor or empress, and the term papal family describes the family of a pope, while th ...
traditionally appears to greet crowds. A German bomb destroyed the palace chapel during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
; the King's Gallery was built on the site and opened to the public in 1962 to exhibit works of art from the Royal Collection
The Royal Collection of the British royal family is the largest private art collection in the world.
Spread among 13 occupied and historic List of British royal residences, royal residences in the United Kingdom, the collection is owned by King ...
.
The original early-19th-century interior designs, many of which survive, include widespread use of brightly coloured scagliola and blue and pink lapis, on the advice of Charles Long. King Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until Death and state funeral of Edward VII, his death in 1910.
The second child ...
oversaw a partial redecoration in a Belle Époque
The Belle Époque () or La Belle Époque () was a period of French and European history that began after the end of the Franco-Prussian War in 1871 and continued until the outbreak of World War I in 1914. Occurring during the era of the Fr ...
cream and gold colour scheme. Many smaller reception rooms are furnished in the Chinese regency style with furniture and fittings brought from the Royal Pavilion at Brighton
Brighton ( ) is a seaside resort in the city status in the United Kingdom, city of Brighton and Hove, East Sussex, England, south of London.
Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates back to the Bronze Age Britain, Bronze Age, R ...
and from Carlton House. The palace has 775 rooms, and the garden is the largest private garden in London. The state rooms, used for official and state entertaining, are open to the public each year for most of August and September and on some days in winter and spring.
History
Pre-1624
In theMiddle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, the site of the future palace formed part of the Manor of Ebury (also called Eia). The marshy ground was watered by the river Tyburn
Tyburn was a Manorialism, manor (estate) in London, Middlesex, England, one of two which were served by the parish of Marylebone. Tyburn took its name from the Tyburn Brook, a tributary of the River Westbourne. The name Tyburn, from Teo Bourne ...
, which still flows below the courtyard and south wing of the palace. Where the river was fordable (at Cow Ford), the village of Eye Cross grew. Ownership of the site changed hands many times; owners included Edward the Confessor
Edward the Confessor ( 1003 – 5 January 1066) was King of England from 1042 until his death in 1066. He was the last reigning monarch of the House of Wessex.
Edward was the son of Æthelred the Unready and Emma of Normandy. He succeede ...
and Edith of Wessex in late Saxon times, and, after the Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, French people, French, Flemish people, Flemish, and Bretons, Breton troops, all led by the Du ...
, William the Conqueror
William the Conqueror (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), sometimes called William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England (as William I), reigning from 1066 until his death. A descendant of Rollo, he was D ...
. William gave the site to Geoffrey de Mandeville, who bequeathed it to the monks of Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an Anglican church in the City of Westminster, London, England. Since 1066, it has been the location of the coronations of 40 English and British m ...
.
In 1531, Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
acquired the Hospital of St James, which became St James's Palace
St James's Palace is the most senior royal palace in London, England. The palace gives its name to the Court of St James's, which is the monarch's royal court, and is located in the City of Westminster. Although no longer the principal residence ...
, from Eton College
Eton College ( ) is a Public school (United Kingdom), public school providing boarding school, boarding education for boys aged 13–18, in the small town of Eton, Berkshire, Eton, in Berkshire, in the United Kingdom. It has educated Prime Mini ...
, and in 1536 he took the Manor of Ebury from Westminster Abbey. These transfers brought the site of Buckingham Palace back into royal hands for the first time since William the Conqueror had given it away almost 500 years earlier. Various owners leased it from royal landlords, and the freehold was the subject of frenzied speculation during the 17th century. By then, the old village of Eye Cross had long since fallen into decay, and the area was mostly wasteland. Needing money, James VI and I
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and King of Ireland, Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 M ...
sold off part of the Crown freehold but retained part of the site on which he established a mulberry
''Morus'', a genus of flowering plants in the family Moraceae, consists of 19 species of deciduous trees commonly known as mulberries, growing wild and under cultivation in many temperate world regions. Generally, the genus has 64 subordinat ...
garden for the production of silk
Silk is a natural fiber, natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be weaving, woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is most commonly produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoon (silk), c ...
. (This is at the north-west corner of today's palace.) Clement Walker in ''Anarchia Anglicana'' (1649) refers to "new-erected sodoms and spintries at the Mulberry Garden at S. James's"; this suggests it may have been a place of debauchery. Eventually, in the late 17th century, the freehold was inherited from the property tycoon Hugh Audley by the great heiress Mary Davies.
First houses on the site (1624–1761)
 Possibly the first house erected within the site was that of William Blake, around 1624. The next owner was George Goring, 1st Earl of Norwich, who from 1633 extended Blake's house, which came to be known as Goring House, and developed much of today's garden, then known as Goring Great Garden.Harris, p. 21. He did not, however, obtain the freehold interest in the mulberry garden. Unbeknown to Goring, in 1640 the document "failed to pass the Great Seal before Charles I fled London, which it needed to do for legal execution". It was this critical omission that would help the British royal family regain the freehold under
Possibly the first house erected within the site was that of William Blake, around 1624. The next owner was George Goring, 1st Earl of Norwich, who from 1633 extended Blake's house, which came to be known as Goring House, and developed much of today's garden, then known as Goring Great Garden.Harris, p. 21. He did not, however, obtain the freehold interest in the mulberry garden. Unbeknown to Goring, in 1640 the document "failed to pass the Great Seal before Charles I fled London, which it needed to do for legal execution". It was this critical omission that would help the British royal family regain the freehold under George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland, Ireland from 25 October 1760 until his death in 1820. The Acts of Union 1800 unified Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and ...
. When the improvident Goring defaulted on his rents, Henry Bennet, 1st Earl of Arlington was able to purchase the lease of Goring House and he was occupying it when it burned down in 1674, following which he constructed Arlington House on the site – the location of the southern wing of today's palace – the next year. In 1698, John Sheffield acquired the lease. He later became the first Duke of Buckingham and Normanby. Buckingham House was built for Sheffield in 1703 to the design of William Winde. The style chosen was of a large, three-floored central block with two smaller flanking service wings.Harris, p. 22. It was eventually sold by Buckingham's illegitimate son, Charles Sheffield
Charles Sheffield (25 June 1935 – 2 November 2002), was an English-born mathematician, physicist, and science-fiction writer who served as a President of the Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers of America and of the American Astronautical ...
, in 1761Robinson, p. 14. to George III for £21,000. Sheffield's leasehold
A leasehold estate is an ownership of a temporary right to hold land or property in which a Lease, lessee or a tenant has rights of real property by some form of title (property), title from a lessor or landlord. Although a tenant does hold right ...
on the mulberry garden site, the freehold of which was still owned by the royal family, was due to expire in 1774.
From Queen's House to palace (1761–1837)
Under the new royal ownership, the building was originally intended as a private retreat for Queen Charlotte, and was accordingly known as The Queen's House. Remodelling of the structure began in 1762. In 1775, an Act of Parliament settled the property on Queen Charlotte, in exchange for her rights to nearby Old Somerset House, and 14 of her 15 children were born there. Some furnishings were transferred from Carlton House and others had been bought in France after the French Revolution of 1789. WhileSt James's Palace
St James's Palace is the most senior royal palace in London, England. The palace gives its name to the Court of St James's, which is the monarch's royal court, and is located in the City of Westminster. Although no longer the principal residence ...
remained the official and ceremonial royal residence, the name "Buckingham Palace" was used from at least 1791.
After his accession to the throne in 1820, George IV
George IV (George Augustus Frederick; 12 August 1762 – 26 June 1830) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from 29 January 1820 until his death in 1830. At the time of his accession to the throne, h ...
continued the renovation, intending to create a small, comfortable home. However, in 1826, while the work was in progress, the King decided to modify the house into a palace with the help of his architect John Nash. The façade was designed with George IV's preference for French neoclassical architecture in mind. The cost of the renovations grew dramatically, and by 1829 the extravagance of Nash's designs resulted in his removal as the architect. On the death of George IV in 1830, his younger brother William IV hired Edward Blore
Edward Blore (13 September 1787 – 4 September 1879) was a 19th-century English landscape and architectural artist, architect and antiquary.
Early career
Blore was born in Derby, the son of the antiquarian writer Thomas Blore.
Blore's backg ...
to finish the work. William never moved into the palace, preferring Clarence House, which had been built to his specifications and which had been his London home while he was heir presumptive. After the Palace of Westminster
The Palace of Westminster is the meeting place of the Parliament of the United Kingdom and is located in London, England. It is commonly called the Houses of Parliament after the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two legislative ch ...
was destroyed by fire in 1834, he offered to convert Buckingham Palace into a new Houses of Parliament, but his offer was declined.
Queen Victoria (1837–1901)
Buckingham Palace became the principal royal residence in 1837, on the accession of Queen Victoria, who was the first monarch to reside there. While the state rooms were a riot of gilt and colour, the necessities of the new palace were somewhat less luxurious. The chimneys were said to smoke so much that the fires had to be allowed to die down, and consequently the palace was often cold.Woodham-Smith, p. 249. Ventilation was so bad that the interior smelled, and when it was decided to install gas lamps, there was a serious worry about the build-up of gas on the lower floors. It was also said that the staff were lax and lazy and the palace was dirty. Following the Queen's marriage in 1840, her husband, Prince Albert, concerned himself with a reorganisation of thehousehold
A household consists of one or more persons who live in the same dwelling. It may be of a single family or another type of person group. The household is the basic unit of analysis in many social, microeconomic and government models, and is im ...
offices and staff, and with addressing the design faults of the palace.Rappaport, p. 84. By the end of 1840, all the problems had been rectified. However, the builders were to return within a decade.Rappaport, p. 84.
By 1847, the couple found the palace too small for court life and their growing family and a new wing, designed by Edward Blore, was built by Thomas Cubitt, enclosing the central quadrangle. The work, carried out from 1847 to 1849, was paid for by the sale of Brighton Pavilion in 1850. The large East Front, facing The Mall, is today the "public face" of Buckingham Palace and contains the balcony from which the royal family
A royal family is the immediate family of monarchs and sometimes their extended family.
The term imperial family appropriately describes the family of an emperor or empress, and the term papal family describes the family of a pope, while th ...
acknowledge the crowds on momentous occasions and after the annual Trooping the Colour. The ballroom wing and a further suite of state rooms were also built in this period, designed by Nash's student James Pennethorne.King, p. 217. Before Prince Albert's death, in addition to royal ceremonies, investitures and presentations Buckingham Palace was frequently the scene of lavish costume balls and musical entertainments. The most celebrated contemporary musicians entertained there; for example Felix Mendelssohn
Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy (3 February 18094 November 1847), widely known as Felix Mendelssohn, was a German composer, pianist, organist and conductor of the early Romantic music, Romantic period. Mendelssohn's compositions inc ...
is known to have played there on three occasions, and Johann Strauss II
Johann Baptist Strauss II (; ; 25 October 1825 – 3 June 1899), also known as Johann Strauss Jr., the Younger or the Son (), was an List of Austrian composers, Austrian composer of light music, particularly dance music and operettas as well ...
and his orchestra played there when in England.
Widowed in 1861, the grief-stricken Queen withdrew from public life and left Buckingham Palace to live at Windsor Castle
Windsor Castle is a List of British royal residences, royal residence at Windsor, Berkshire, Windsor in the English county of Berkshire, about west of central London. It is strongly associated with the Kingdom of England, English and succee ...
, Balmoral Castle and Osborne House. For many years the palace was seldom used, even neglected. In 1864, a note was found pinned to the fence, saying: "These commanding premises to be let or sold, in consequence of the late occupant's declining business." Eventually, public opinion persuaded the Queen to return to London, though even then she preferred to live elsewhere whenever possible. Court functions were still held at Windsor Castle, presided over by the sombre Queen habitually dressed in mourning black, while Buckingham Palace remained shuttered for most of the year.Robinson, p. 9.
Early 20th century (1901–1945)
In 1901, the new king,Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until Death and state funeral of Edward VII, his death in 1910.
The second child ...
, began redecorating the palace. He and his wife, Queen Alexandra
Alexandra of Denmark (Alexandra Caroline Marie Charlotte Louise Julia; 1 December 1844 – 20 November 1925) was List of British royal consorts, queen-consort of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Empress of India, from 22 Januar ...
, had always been at the forefront of London high society, and their friends, known as "the Marlborough House Set", were considered to be the most eminent and fashionable of the age. Buckingham Palace—the Ballroom, Grand Entrance, Marble Hall, Grand Staircase, vestibules and galleries were redecorated in the Belle Époque
The Belle Époque () or La Belle Époque () was a period of French and European history that began after the end of the Franco-Prussian War in 1871 and continued until the outbreak of World War I in 1914. Occurring during the era of the Fr ...
cream and gold colour scheme they retain today—once again became a setting for entertaining on a majestic scale but leaving some to feel Edward's heavy redecorations were at odds with Nash's original work.
The last major building work took place during the reign of George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until Death and state funeral of George V, his death in 1936.
George w ...
when, in 1913, Aston Webb redesigned Blore's 1850 East Front to resemble in part Giacomo Leoni
Giacomo Leoni (; 1686 – 8 June 1746), also known as James Leoni, was an List of Italian architects, Italian architect, born in Venice. He was a devotee of the work of Florence, Florentine Renaissance architecture, Renaissance architect Leon Ba ...
's Lyme Park
Lyme Park is a large Estate (land), estate south of Disley, Cheshire, England. It is managed by the National Trust and consists of a mansion house surrounded by formal gardens and a Deer park (England), deer park in the Peak District National ...
in Cheshire. This new refaced principal façade (of Portland stone) was designed to be the backdrop to the Victoria Memorial, a large memorial statue of Queen Victoria created by sculptor Thomas Brock, erected outside the main gates on a surround constructed by architect Aston Webb. George V, who had succeeded Edward VII in 1910, had a more serious personality than his father; greater emphasis was now placed on official entertainment and royal duties than on lavish parties. He arranged a series of command performances featuring jazz musicians such as the Original Dixieland Jazz Band (1919; the first jazz performance for a head of state), Sidney Bechet
Sidney Joseph Bechet ( ; May 14, 1897 – May 14, 1959) was an American jazz saxophonist, clarinetist, and composer. He was one of the first important Solo (music), soloists in jazz, and first recorded several months before trumpeter Louis Ar ...
and Louis Armstrong
Louis Daniel Armstrong (August 4, 1901 – July 6, 1971), nicknamed "Satchmo", "Satch", and "Pops", was an American trumpeter and vocalist. He was among the most influential figures in jazz. His career spanned five decades and several era ...
(1932), which earned the palace a nomination in 2009 for a (Kind of) Blue Plaque by the Brecon Jazz Festival as one of the venues making the greatest contribution to jazz music in the United Kingdom.
During the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, which lasted from 1914 until 1918, the palace escaped unscathed. Its more valuable contents were evacuated to Windsor, but the royal family remained in residence. The King imposed rationing at the palace, much to the dismay of his guests and household. To the King's later regret, David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George, 1st Earl Lloyd-George of Dwyfor (17 January 1863 – 26 March 1945) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1922. A Liberal Party (United Kingdom), Liberal Party politician from Wales, he was known for leadi ...
persuaded him to go further and ostentatiously lock the wine cellars and refrain from alcohol, to set a good example to the supposedly inebriated working class. The workers continued to imbibe, and the King was left unhappy at his enforced abstinence.
George V's wife, Queen Mary, was a connoisseur of the arts and took a keen interest in the Royal Collection
The Royal Collection of the British royal family is the largest private art collection in the world.
Spread among 13 occupied and historic List of British royal residences, royal residences in the United Kingdom, the collection is owned by King ...
of furniture and art, both restoring and adding to it. Queen Mary also had many new fixtures and fittings installed, such as the pair of marble Empire style
The Empire style (, ''style Empire'') is an early-nineteenth-century design movement in architecture, furniture, other decorative arts, and the visual arts, representing the second phase of Neoclassicism. It flourished between 1800 and 1815 duri ...
chimneypieces by Benjamin Vulliamy, dating from 1810, in the ground floor Bow Room, the huge low room at the centre of the garden façade. Queen Mary was also responsible for the decoration of the Blue Drawing Room. This room, long, previously known as the South Drawing Room, has a ceiling designed by Nash, coffered with huge gilt console brackets. In 1938, the northwest pavilion, designed by Nash as a conservatory, was converted into a swimming pool.
Second World War
During theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, which broke out in 1939, the palace was bombed nine times. The most serious and publicised incident destroyed the palace chapel in 1940. One bomb fell in the palace quadrangle while George VI
George VI (Albert Frederick Arthur George; 14 December 1895 – 6 February 1952) was King of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Commonwealth from 11 December 1936 until Death and state funeral of George VI, his death in 1952 ...
and Queen Elizabeth (the future Queen Mother) were in the palace, and many windows were blown in and the chapel destroyed. The King and Queen were filmed inspecting their bombed home, and the newsreel footage shown in cinemas throughout the United Kingdom to show the common suffering of rich and poor. As '' The Sunday Graphic'' reported:
It was at this time the Queen famously declared: "I'm glad we have been bombed. Now I can look the East End in the face".
On 15 September 1940, known as Battle of Britain Day, an RAF pilot, Ray Holmes of No. 504 Squadron, rammed a German Dornier Do 17 bomber he believed was going to bomb the palace. Holmes had run out of ammunition to shoot down the bomber and made the quick decision to ram it. He bailed out and the bomber crashed into the forecourt of London Victoria station
Victoria station, also known as London Victoria, is a central London railway terminus and connected London Underground station in Victoria, in the City of Westminster, managed by Network Rail. Named after the nearby Victoria Street, the mai ...
. Its engine was later exhibited at the Imperial War Museum in London. Holmes became a King's Messenger after the war and died at the age of 90 in 2005.
On VE Day—8 May 1945—the palace was the centre of British celebrations. The King, the Queen, Princess Elizabeth (the future queen) and Princess Margaret
Princess Margaret, Countess of Snowdon (Margaret Rose; 21 August 1930 – 9 February 2002) was the younger daughter of King George VI and Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother. She was the younger sister and only sibling of Queen Elizabeth II.
...
appeared on the balcony, with the palace's blacked-out windows behind them, to cheers from a vast crowd in The Mall. The damaged palace was carefully restored after the war by John Mowlem & Co.
Mid-20th century to present day
 Many of the palace's contents are part of the
Many of the palace's contents are part of the Royal Collection
The Royal Collection of the British royal family is the largest private art collection in the world.
Spread among 13 occupied and historic List of British royal residences, royal residences in the United Kingdom, the collection is owned by King ...
; they can, on occasion, be viewed by the public at the King's Gallery, near the Royal Mews. The purpose-built gallery opened in 1962 and displays a changing selection of items from the collection. It occupies the site of the chapel that was destroyed in the Second World War. The palace was designated a Grade I listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a structure of particular architectural or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Hi ...
in 1970. Its state rooms have been open to the public during August and September and on some dates throughout the year since 1993. The money raised in entry fees was originally put towards the rebuilding of Windsor Castle after the 1992 fire devastated many of its staterooms. In the year to 31 March 2017, 580,000 people visited the palace, and 154,000 visited the gallery. In 2004, the palace attempted to claim money from the community energy fund to heat Buckingham Palace, but the claim was rejected due to fear of public backlash.
The palace used to racially segregate staff. In 1968, Charles Tryon, 2nd Baron Tryon, acting as treasurer to Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 19268 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, her death in 2022. ...
, sought to exempt Buckingham Palace from full application of the Race Relations Act 1968. He stated that the palace did not hire people of colour for clerical jobs, only as domestic servants. He arranged with civil servants for an exemption that meant that complaints of racism against the royal household would be sent directly to the Home Secretary
The secretary of state for the Home Department, more commonly known as the home secretary, is a senior minister of the Crown in the Government of the United Kingdom and the head of the Home Office. The position is a Great Office of State, maki ...
and kept out of the legal system.
The palace, like Windsor Castle, is owned by the reigning monarch in right of the Crown
The Crown is a political concept used in Commonwealth realms. Depending on the context used, it generally refers to the entirety of the State (polity), state (or in federal realms, the relevant level of government in that state), the executive ...
. Occupied royal palaces are not part of the Crown Estate, nor are they the monarch's personal property, unlike Sandringham House and Balmoral Castle. The Government of the United Kingdom
His Majesty's Government, abbreviated to HM Government or otherwise UK Government, is the central government, central executive authority of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
is responsible for maintaining the palace in exchange for the profits made by the Crown Estate. In 2015, the State Dining Room was closed for a year and a half because its ceiling had become potentially dangerous. A 10-year schedule of maintenance work, including new plumbing, wiring, boilers and radiators, and the installation of solar panels on the roof, has been estimated to cost £369 million and was approved by the prime minister in November 2016. It will be funded by a temporary increase in the Sovereign Grant paid from the income of the Crown Estate and is intended to extend the building's working life by at least 50 years. In 2017, the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of ...
backed funding for the project by 464 votes to 56.
Buckingham Palace is a symbol and home of the British monarchy, an art gallery and a tourist attraction. Behind the gilded railings and gates that were completed by the Bromsgrove Guild in 1911, lies Webb's famous façade, which was described in a book published by the Royal Collection Trust
The Royal Collection of the British royal family is the largest private art collection in the world.
Spread among 13 occupied and historic royal residences in the United Kingdom, the collection is owned by King Charles III and overseen by the ...
as looking "like everybody's idea of a palace". It has not only been a weekday home of Elizabeth II and Prince Philip but was also the London residence and office of the Duke of York
Duke of York is a title of nobility in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. Since the 15th century, it has, when granted, usually been given to the second son of List of English monarchs, English (later List of British monarchs, British) monarchs ...
until 2023. Prince Edward, Duke of Edinburgh
Prince Edward, Duke of Edinburgh (Edward Antony Richard Louis; born 10 March 1964) is a member of the British royal family. He is the youngest child of Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, and the youngest sibling of King ...
and Sophie, Duchess of Edinburgh continue to have a private apartment in the palace for use when they are in London. The palace also houses their offices, as well as those of the Princess Royal
Princess Royal is a substantive title, title customarily (but not automatically) awarded by British monarchs to their eldest daughters. Although purely honorary, it is the highest honour that may be given to a female member of the royal famil ...
and Princess Alexandra, and is the workplace of more than 800 people. Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms.
Charles was born at Buckingham Palace during the reign of his maternal grandfather, King George VI, and ...
and Queen Camilla
Camilla (born Camilla Rosemary Shand, later Parker Bowles, 17 July 1947) is List of British royal consorts, Queen of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms as the wife of King Charles III.
Camilla was raised in East ...
live at Clarence House while restoration work continues, although they conduct official business at Buckingham Palace, including audiences and receptions. Every year, some 50,000 invited guests are entertained at garden parties, receptions, audiences and banquets. Three garden parties are held in the summer, usually in July. The forecourt of Buckingham Palace is used for the Changing of the Guard, a major ceremony and tourist attraction (daily from April to July; every other day in other months).
Interior
 The front of the palace measures across, by deep, by high and contains over of floorspace. There are 775 rooms, including 188 staff bedrooms, 92 offices, 78 bathrooms, 52 principal bedrooms and 19 state rooms. It also has a post office, cinema, swimming pool, doctor's surgery, and jeweller's workshop. The royal family occupy a small suite of private rooms in the north wing.
The front of the palace measures across, by deep, by high and contains over of floorspace. There are 775 rooms, including 188 staff bedrooms, 92 offices, 78 bathrooms, 52 principal bedrooms and 19 state rooms. It also has a post office, cinema, swimming pool, doctor's surgery, and jeweller's workshop. The royal family occupy a small suite of private rooms in the north wing.
Principal rooms
The principal rooms are contained on the first-floor '' piano nobile'' behind the west-facing garden façade at the rear of the palace. The centre of this ornate suite of state rooms is the Music Room, its large bow the dominant feature of the façade. Flanking the Music Room are the Blue and the White Drawing Rooms. At the centre of the suite, serving as a corridor to link the state rooms, is the Picture Gallery, which is top-lit and long.Harris, p. 41. The Gallery is hung with numerous works including some byRembrandt
Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn (; ; 15 July 1606 – 4 October 1669), mononymously known as Rembrandt was a Dutch Golden Age painter, printmaker, and Drawing, draughtsman. He is generally considered one of the greatest visual artists in ...
, van Dyck, Rubens
Sir Peter Paul Rubens ( ; ; 28 June 1577 – 30 May 1640) was a Flemish artist and diplomat. He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque tradition. Rubens' highly charged compositions reference erudite aspects of clas ...
and Vermeer; other rooms leading from the Picture Gallery are the Throne Room and the Green Drawing Room. The Green Drawing Room serves as a huge anteroom to the Throne Room, and is part of the ceremonial route to the throne from the Guard Room at the top of the Grand Staircase. The Guard Room contains white marble statues of Queen Victoria and Prince Albert, in Roman costume, set in a tribune
Tribune () was the title of various elected officials in ancient Rome. The two most important were the Tribune of the Plebs, tribunes of the plebs and the military tribunes. For most of Roman history, a college of ten tribunes of the plebs ac ...
lined with tapestries. These very formal rooms are used only for ceremonial and official entertaining but are open to the public every summer.
Semi-state apartments
 Directly underneath the state apartments are the less grand semi-state apartments. Opening from the Marble Hall, these rooms are used for less formal entertaining, such as luncheon parties and private audiences. At the centre of this floor is the Bow Room, through which thousands of guests pass annually to the monarch's garden parties. When paying a state visit to Britain, foreign
Directly underneath the state apartments are the less grand semi-state apartments. Opening from the Marble Hall, these rooms are used for less formal entertaining, such as luncheon parties and private audiences. At the centre of this floor is the Bow Room, through which thousands of guests pass annually to the monarch's garden parties. When paying a state visit to Britain, foreign heads of state
A head of state is the public persona of a sovereign state.#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representative of its international persona." The name given to the office of head of sta ...
are usually entertained by the monarch at Buckingham Palace. They are allocated an extensive suite of rooms known as the Belgian Suite, situated at the foot of the Minister's Staircase, on the ground floor of the west-facing Garden Wing. Some of the rooms are named and decorated for particular visitors, such as the 1844 Room, decorated in that year for the state visit of Nicholas I of Russia
Nicholas I, group=pron (Russian language, Russian: Николай I Павлович; – ) was Emperor of Russia, List of rulers of Partitioned Poland#Kings of the Kingdom of Poland, King of Congress Poland, and Grand Duke of Finland from 18 ...
, and the 1855 Room, in honour of the visit of Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles-Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was President of France from 1848 to 1852 and then Emperor of the French from 1852 until his deposition in 1870. He was the first president, second emperor, and last ...
of France. The former is a sitting room that also serves as an audience room and is often used for personal investitures. Narrow corridors link the rooms of the suite; one of them is given extra height and perspective by saucer domes designed by Nash in the style of Soane.Harris, p. 82. A second corridor in the suite has Gothic-influenced cross-over vaulting. The suite was named after Leopold I of Belgium, uncle of Queen Victoria and Prince Albert. In 1936, the suite briefly became the private apartments of the palace when Edward VIII
Edward VIII (Edward Albert Christian George Andrew Patrick David; 23 June 1894 – 28 May 1972), later known as the Duke of Windsor, was King of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Empire, and Emperor of India, from 20 January ...
occupied them. The original early-19th-century interior designs, many of which still survive, included widespread use of brightly coloured scagliola and blue and pink lapis, on the advice of Charles Long. Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until Death and state funeral of Edward VII, his death in 1910.
The second child ...
oversaw a partial redecoration in a Belle Époque
The Belle Époque () or La Belle Époque () was a period of French and European history that began after the end of the Franco-Prussian War in 1871 and continued until the outbreak of World War I in 1914. Occurring during the era of the Fr ...
cream and gold colour scheme.Jones, p. 43.
East wing
 Between 1847 and 1850, when Blore was building the new east wing, the Brighton Pavilion was once again plundered of its fittings. As a result, many of the rooms in the new wing have a distinctly oriental atmosphere. The red and blue Chinese Luncheon Room is made up of parts of the Brighton Banqueting and Music Rooms with a large oriental chimneypiece designed by Robert Jones and sculpted by Richard Westmacott.Harris, de Bellaigue & Miller, p. 87. It was formerly in the Music Room at the Brighton Pavilion. The ornate clock, known as the Kylin Clock, was made in Jingdezhen, Jiangxi Province, China, in the second half of the 18th century; it has a later movement by Benjamin Vulliamy circa 1820. The Yellow Drawing Room has hand-painted Chinese wallpaper supplied in 1817 for the Brighton Saloon, and a chimneypiece which is a European vision of a Chinese chimneypiece. It has nodding mandarins in niches and fearsome winged
Between 1847 and 1850, when Blore was building the new east wing, the Brighton Pavilion was once again plundered of its fittings. As a result, many of the rooms in the new wing have a distinctly oriental atmosphere. The red and blue Chinese Luncheon Room is made up of parts of the Brighton Banqueting and Music Rooms with a large oriental chimneypiece designed by Robert Jones and sculpted by Richard Westmacott.Harris, de Bellaigue & Miller, p. 87. It was formerly in the Music Room at the Brighton Pavilion. The ornate clock, known as the Kylin Clock, was made in Jingdezhen, Jiangxi Province, China, in the second half of the 18th century; it has a later movement by Benjamin Vulliamy circa 1820. The Yellow Drawing Room has hand-painted Chinese wallpaper supplied in 1817 for the Brighton Saloon, and a chimneypiece which is a European vision of a Chinese chimneypiece. It has nodding mandarins in niches and fearsome winged dragons
A dragon is a magical legendary creature that appears in the folklore of multiple cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in Western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depict ...
, designed by Robert Jones.
At the centre of this wing is the famous balcony with the Centre Room behind its glass doors. This is a Chinese-style saloon enhanced by Queen Mary, who, working with the designer Charles Allom, created a more "binding" Chinese theme in the late 1920s, although the lacquer
Lacquer is a type of hard and usually shiny coating or finish applied to materials such as wood or metal. It is most often made from resin extracted from trees and waxes and has been in use since antiquity.
Asian lacquerware, which may be c ...
doors were brought from Brighton in 1873. Running the length of the ''piano nobile'' of the east wing is the Great Gallery, modestly known as the Principal Corridor, which runs the length of the eastern side of the quadrangle. It has mirrored doors and mirrored cross walls reflecting porcelain
Porcelain (), also called china, is a ceramic material made by heating Industrial mineral, raw materials, generally including kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The greater strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to oth ...
pagodas and other oriental furniture from Brighton. The Chinese Luncheon Room and Yellow Drawing Room are situated at each end of this gallery, with the Centre Room in between.
Court ceremonies
 Investitures for the awarding of honours (which include the conferring of
Investitures for the awarding of honours (which include the conferring of knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of a knighthood by a head of state (including the pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church, or the country, especially in a military capacity.
The concept of a knighthood ...
hoods by dubbing with a sword) usually take place in the palace's Throne Room. Investitures are conducted by the King or another senior member of the royal family: a military band plays in the musicians' gallery, as recipients receive their honour
Honour (Commonwealth English) or honor (American English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) is a quality of a person that is of both social teaching and personal ethos, that manifests itself ...
s, watched by their families and friends.Healey, p. 364.
State banquet
A banquet (; ) is a formal large meal where a number of people consume food together. Banquets are traditionally held to enhance the prestige of a host, or reinforce social bonds among joint contributors. Modern examples of these purposes inc ...
s take place in the Ballroom, built in 1854. At long, wide and high, it is the largest room in the palace; at one end of the room is a throne dais (beneath a giant, domed velvet canopy, known as a '' shamiana'' or baldachin, that was used at the Delhi Durbar in 1911). State Banquets are formal dinners held on the first evening of a state visit by a foreign head of state. On these occasions, for up to 170 guests in formal "white tie and decorations", including tiaras, the dining table is laid with the Grand Service, a collection of silver-gilt plate made in 1811 for the Prince of Wales, later George IV.
The largest and most formal reception at Buckingham Palace takes place every November when the King entertains members of the diplomatic corps. On this grand occasion, all the state rooms are in use, as the royal family proceed through them, beginning at the great north doors of the Picture Gallery. As Nash had envisaged, all the large, double-mirrored doors stand open, reflecting the numerous crystal chandeliers and sconces, creating a deliberate optical illusion of space and light.
Smaller ceremonies such as the reception of new ambassadors take place in the "1844 Room". Here too, the King holds small lunch parties, and often meetings of the Privy Council. Larger lunch parties often take place in the curved and domed Music Room or the State Dining Room.Healey, pp. 363–365. Since the bombing of the palace chapel in World War II, royal christenings have sometimes taken place in the Music Room. Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 19268 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, her death in 2022. ...
's first three children were all baptised there. On all formal occasions, the ceremonies are attended by the Yeomen of the Guard, in their historic uniforms, and other officers of the court such as the Lord Chamberlain
The Lord Chamberlain of the Household is the most senior officer of the Royal Households of the United Kingdom, Royal Household of the United Kingdom, supervising the departments which support and provide advice to the Monarchy of the United Ki ...
.
Former ceremonial
Court dress
Formerly, men not wearingmilitary uniform
A military uniform is a standardised clothing, dress worn by members of the armed forces and Paramilitary, paramilitaries of various nations.
Military dress and styles have gone through significant changes over the centuries, from colourful ...
wore knee breeches of 18th-century design. Women's evening dress included trains and tiaras or feathers in their hair (often both). The dress code governing formal court uniform and dress has progressively relaxed. After the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, when Queen Mary wished to follow fashion by raising her skirts a few inches from the ground, she requested a lady-in-waiting
A lady-in-waiting (alternatively written lady in waiting) or court lady is a female personal assistant at a Royal court, court, attending on a royal woman or a high-ranking nobility, noblewoman. Historically, in Europe, a lady-in-waiting was o ...
to shorten her own skirt first to gauge the King's reaction. King George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until Death and state funeral of George V, his death in 1936.
George w ...
disapproved, so the Queen kept her hemline unfashionably low. Following his accession in 1936, King George VI
George VI (Albert Frederick Arthur George; 14 December 1895 – 6 February 1952) was King of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Commonwealth from 11 December 1936 until Death and state funeral of George VI, his death in 1952 ...
and Queen Elizabeth allowed the hemline of daytime skirts to rise. Today, there is no official dress code. Most men invited to Buckingham Palace in the daytime choose to wear service uniform or lounge suits; a minority wear morning coats, and in the evening, depending on the formality of the occasion, black tie or white tie.
Court presentation of débutantes
Débutantes were aristocratic young ladies making their first entrée into society through a presentation to the monarch at court. These occasions, known as "coming out", took place at the palace from the reign of Edward VII. The débutantes entered—wearing full court dress, with three ostrich feathers in their hair—curtsied, performed a backwards walk and a further curtsey, while manoeuvring a dress train of prescribed length. The ceremony, known as an evening court, corresponded to the "courtdrawing room
A drawing room is a room in a house where visitors may be entertained, and an alternative name for a living room. The name is derived from the 16th-century terms withdrawing room and withdrawing chamber, which remained in use through the 17th ce ...
s" of Victoria's reign. After World War II, the ceremony was replaced by less formal afternoon receptions, omitting the requirement of court evening dress. In 1958, Queen Elizabeth II abolished the presentation parties for débutantes, replacing them with Garden Parties, for up to 8,000 invitees in the Garden. They are the largest functions of the year.
Garden and surroundings
At the rear of the palace is the large and park-like garden, which together with its lake is the largest private garden in London. There,Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 19268 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, her death in 2022. ...
hosted her annual garden parties each summer and also held large functions to celebrate royal milestones, such as jubilees. It covers and includes a helicopter landing area, a lake and a tennis court.
Adjacent to the palace is the Royal Mews, also designed by Nash, where the royal carriages, including the Gold State Coach, are housed. This Rococo
Rococo, less commonly Roccoco ( , ; or ), also known as Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and dramatic style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpte ...
styled gilt coach, designed by William Chambers in 1760, has painted panels by Giovanni Battista Cipriani. It was first used for the State Opening of Parliament
The State Opening of Parliament is a ceremonial event which formally marks the beginning of each Legislative session, session of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. At its core is His or Her Majesty's "Speech from the throne, gracious speech ...
by George III in 1762 and has been used by the monarch for every coronation since William IV. It was last used for the coronation of King Charles III and Queen Camilla. Also housed in the mews are the coach horses used at royal ceremonial processions as well as many of the cars used by the royal family.
The Mall, a ceremonial approach route to the palace, was designed by Aston Webb and completed in 1911 as part of a grand memorial to Queen Victoria. It extends from Admiralty Arch
The Admiralty Arch is a historic landmark building in London, providing road and pedestrian access between The Mall, London, The Mall, which extends to the southwest, and Trafalgar Square to the northeast. Commissioned by King Edward VII in mem ...
, across St James's Park to the Victoria Memorial, concluding at the entrance gates into the palace forecourt. This route is used by the cavalcades and motorcades of visiting heads of state, and by the royal family on state occasions—such as the annual Trooping the Colour.
Security breaches
The boy Jones was an intruder who gained entry to the palace on three occasions between 1838 and 1841. At least 12 people have managed to gain unauthorised entry into the palace or its grounds since 1914, including Michael Fagan, who broke into the palace twice in 1982 and entered Queen Elizabeth II's bedroom on the second occasion on 9 July. At the time, news media reported that he had a long conversation with her while she waited for security officers to arrive, but in a 2012 interview with ''The Independent
''The Independent'' is a British online newspaper. It was established in 1986 as a national morning printed paper. Nicknamed the ''Indy'', it began as a broadsheet and changed to tabloid format in 2003. The last printed edition was publis ...
'', Fagan said she ran out of the room, and no conversation took place. It was only in 2007 that trespassing on the palace grounds became a specific criminal offence.
See also
* Flags at Buckingham Palace * List of British royal residences * King's GuardNotes
References
Bibliography
* Allison, Ronald; Riddell, Sarah (1991).The Royal Encyclopedia
'. London: Macmillan. * Blaikie, Thomas (2002).
You Look Awfully Like the Queen: Wit and Wisdom from the House of Windsor
'. London: HarperCollins. . * Goring, O. G. (1937).
From Goring House to Buckingham Palace
'. London: Ivor Nicholson & Watson. * Harris, John; de Bellaigue, Geoffrey; & Miller, Oliver (1968).
Buckingham Palace
'. London: Nelson. . * Healey, Edma (1997).
The Queen's House: A Social History of Buckingham Palace
'. London: Penguin Group. . * Hedley, Olwen (1971)
The Pictorial History of Buckingham Palace
'. Pitkin, . * * * Mackenzie, Compton (1953).
The Queen's House
'. London: Hutchinson. * . * * * * . * *
External links
Buckingham Palace
at the Royal Family website
Account of Buckingham Palace, with prints of Arlington House and Buckingham House
from ''Old and New London'' (1878)
Account of the acquisition of the Manor of Ebury
from ''Survey of London'' (1977)
The State Rooms, Buckingham Palace
at the
Royal Collection Trust
The Royal Collection of the British royal family is the largest private art collection in the world.
Spread among 13 occupied and historic royal residences in the United Kingdom, the collection is owned by King Charles III and overseen by the ...
*
{{Coord, 51, 30, 3, N, 0, 8, 31, W, type:landmark_region:GB, display=title
1837 establishments in England
Buildings and structures on The Mall, London
Edward Blore buildings
Edwardian architecture in London
Georgian architecture in the City of Westminster
Grade I listed buildings in the City of Westminster
Grade I listed palaces
Historic house museums in London
Houses completed in 1703
Houses completed in 1762
John Nash (architect) buildings
Museums in the City of Westminster
Neoclassical architecture in London
Neoclassical palaces
Palaces in London
Regency architecture in Westminster
Royal buildings in London
Royal residences in the City of Westminster
Terminating vistas in the United Kingdom
Tourist attractions in the City of Westminster
Geographical articles missing image alternative text