Bob Fitzsimmons on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Robert James Fitzsimmons (26 May 1863 – 22 October 1917) was a British
 Robert James Fitzsimmons was born on 26 May 1863 in
Robert James Fitzsimmons was born on 26 May 1863 in
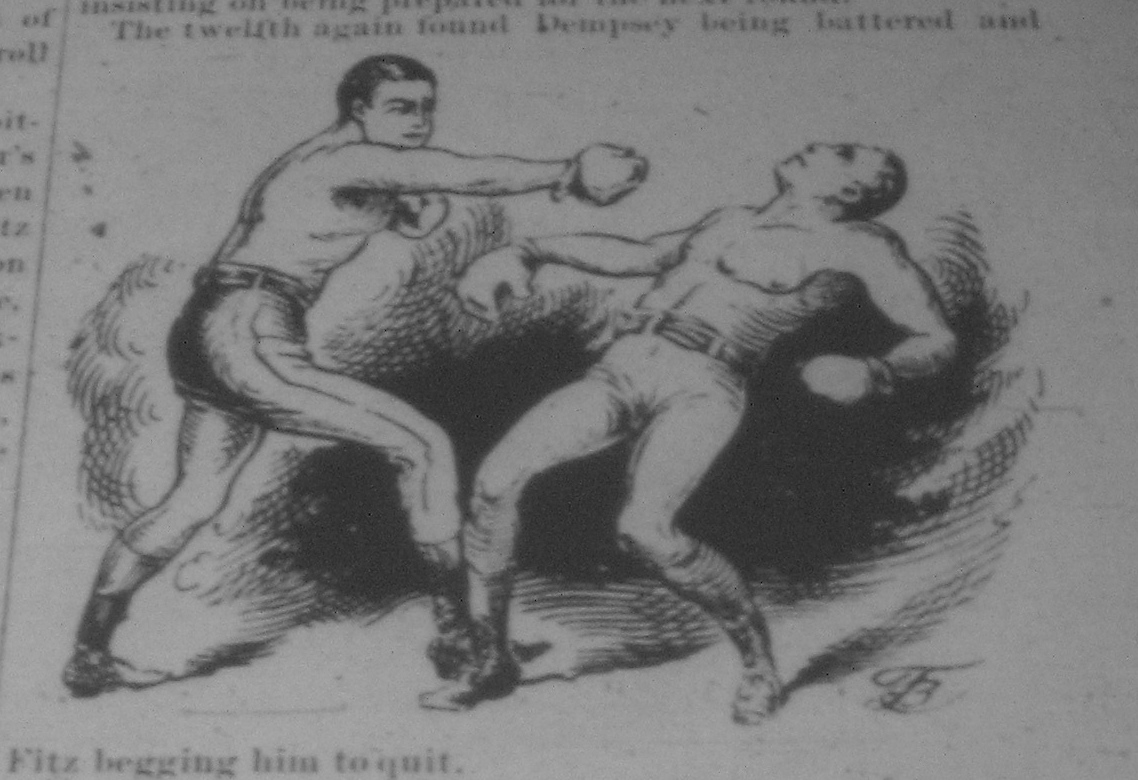 Then, on 14 January 1891, in , he won his first world title from
Then, on 14 January 1891, in , he won his first world title from
 In 1896, Fitzsimmons won a disputed version of the World Heavyweight Championship in a fight in Langtry, Texas, against the Irish fighter Peter Maher. On 17 March 1897, in Carson City, Nevada, he knocked out American
In 1896, Fitzsimmons won a disputed version of the World Heavyweight Championship in a fight in Langtry, Texas, against the Irish fighter Peter Maher. On 17 March 1897, in Carson City, Nevada, he knocked out American
 Fitzsimmons died of
Fitzsimmons died of
Boxing Hall of Fame
ESPN.com
* in the ''
Biography in the 1966 ''Encyclopaedia of New Zealand'' (birth year wrong)
* * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Fitzsimmons, Bob 1863 births 1917 deaths 19th-century British people Bare-knuckle boxers Burials at Graceland Cemetery (Chicago) British emigrants to New Zealand New Zealand people of Cornish descent American people of Cornish descent British emigrants to the United States English male boxers English people of Irish descent Heavyweight boxers International Boxing Hall of Fame inductees Light-heavyweight boxers Middleweight boxers New Zealand male boxers New Zealand emigrants to the United States New Zealand people of English descent People associated with physical culture People from Helston World boxing champions World heavyweight boxing champions New Zealand world boxing champions World middleweight boxing champions Deaths from pneumonia in Illinois
professional boxer
Professional boxing, or prizefighting, is regulated, sanctioned boxing. Professional boxing bouts are fought for a purse that is divided between the boxers as determined by contract. Most professional bouts are supervised by a regulatory autho ...
who was the sport's first three-division world champion. He also achieved fame for beating Gentleman Jim Corbett (the man who beat John L. Sullivan), and he is in ''The Guinness Book of World Records
''Guinness World Records'', known from its inception in 1955 until 1999 as ''The Guinness Book of Records'' and in previous United States editions as ''The Guinness Book of World Records'', is a reference book published annually, listing world ...
'' as the lightest heavyweight champion, weighing just 165 pounds when he won the title. Nicknamed Ruby Robert and The Freckled Wonder, he took pride in his lack of scars and appeared in the ring wearing heavy woollen underwear to conceal the disparity between his trunk and leg-development.
Considered one of the hardest punchers in boxing history, Fitzsimmons is ranked as No. 8 on '' The Ring'' magazine's list of 100 greatest punchers of all time.
Early life
 Robert James Fitzsimmons was born on 26 May 1863 in
Robert James Fitzsimmons was born on 26 May 1863 in Helston
Helston ( kw, Hellys) is a town and civil parish in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is situated at the northern end of the Lizard Peninsula approximately east of Penzance and south-west of Falmouth.Ordnance Survey: Landranger map she ...
, Cornwall, England, the youngest of seven boys and five girls born to James and Jane () Fitzsimmons. Not long before his birth, his parents had moved from his father's native Ireland to Cornwall, where his mother came from, in order for his father to find work as a policeman.Ingram 2012, p. 37. Fitzsimmons received his early education at the National school in Helston. In 1873, the family moved again; James, Jane and their youngest five children sailed on the ''Adamant'' for the 93-day journey to Lyttelton, New Zealand
Lyttelton (Māori: ''Ōhinehou'') is a port town on the north shore of Lyttelton Harbour / Whakaraupō, at the northwestern end of Banks Peninsula and close to Christchurch, on the eastern coast of the South Island of New Zealand.
As a landing ...
.
They settled in Timaru
Timaru (; mi, Te Tihi-o-Maru) is a port city in the southern Canterbury Region of New Zealand, located southwest of Christchurch and about northeast of Dunedin on the eastern Pacific coast of the South Island. The Timaru urban area is home to ...
, a town 147 km (91 miles) south-west of Lyttelton populated mainly by Cornish immigrants, and James Fitzsimmons established a blacksmith's forge in the town. Once Fitzsimmons had completed his education at the Timaru Main School, he took on a range of jobs. He wanted to join the crew of the ''Isabella Ridley'', and do some service as a sailor, hoping that it would toughen him up for a career in boxing, but the ship was badly damaged in storms while still docked in Timaru. Instead, he took on a range of jobs; as a butcher's delivery boy, a carriage painter, striker at an iron foundry, and a decorator, before becoming an apprentice at his family's blacksmith's forge with his brother Jarrett. His time working in the blacksmith's forge helped to develop his upper body, particularly his arms and shoulders. During his time working in the blacksmith's forge, there are stories that Fitzsimmons was not averse to fighting quarrelsome, often drunk, customers, and it was suggested that this even boosted business, as customers returned to the forge, hoping to see a fight.
Amateur career
In the early 1880sJem Mace
James "Jem" Mace (8 April 1831 – 30 November 1910) was an English boxing champion, primarily during the bare-knuckle era. He was born at Beeston, Norfolk. Although nicknamed "The Gypsy", he denied Romani ethnicity in his autobiography. Fi ...
, an English bare-knuckle boxer, travelled to New Zealand, and Timaru hosted both his boxing school, and the first boxing championships held in New Zealand. Fitzsimmons entered the tournament and knocked out four opponents on his way to winning the competition. He successfully defended his title in the subsequent competition. During one of these tournaments, it is often suggested that Fitzsimmons defeated Herbert Slade
Herbert Augustus Slade (10 January 1851 – 6 April 1913), also known as "Maori" Slade, the Big Maori, the Maori Mauler or the Australian Giant, was a New Zealand boxer of Irish and Māori descent, who fought John L. Sullivan for the heavyweig ...
, a professional heavyweight boxer who was touring with Mace, but Slade was touted as being undefeated in 1883, and it is possible that it was Slade's brother that Fitzsimmons beat. After these tournaments, Fitzsimmons boxed at least six times in New Zealand, including some bare knuckle bouts, but it is unclear if he received payment for his fights during this time.
Professional career
Move to Australia
Boxing record books show Fitzsimmons officially began boxing professionally in 1883, in Australia. He beat Jim Crawford there by getting a knockout in three rounds. Fitzsimmons had his first 28 definite professional fights in Australia, where he lost the Australian middleweight title to Mick Dooley (rumours spoke of a fixed bout) and where he also won a fight by knockout while on the floor: when Edward Starlight Robins dropped Fitzsimmons to the canvas in round nine of their fight, he also broke his hand and could not continue, therefore the referee declared Fitzsimmons the winner by a knockout. By this stage, Fitzsimmons had established his own style. He developed a certain movement and caginess from one of the greatest bare-knuckle fighters,Jem Mace
James "Jem" Mace (8 April 1831 – 30 November 1910) was an English boxing champion, primarily during the bare-knuckle era. He was born at Beeston, Norfolk. Although nicknamed "The Gypsy", he denied Romani ethnicity in his autobiography. Fi ...
. Mace encouraged Fitzsimmons to develop his punching technique, drawing on the enormous power he had gained from blacksmithing. Fitzsimmons delivered short, accurate and occasionally conclusive punches. He soon built up a reputation as by far the hardest puncher in boxing.
Winning the Middleweight title
Moving on to the United States, Fitzsimmons fought four more times in 1890, winning three and drawing one.Jack (Nonpareil) Dempsey
John Edward Kelly (December 15, 1862 – November 1, 1895) was an Irish-American boxer, better known as Nonpareil Jack Dempsey, who was the first holder of the World Middleweight Championship (1884–1891). He was nicknamed "Nonpareil" because ...
. Fitzsimmons knocked out Dempsey (from whom the later Jack Dempsey
William Harrison "Jack" Dempsey (June 24, 1895 – May 31, 1983), nicknamed Kid Blackie and The Manassa Mauler, was an American professional boxer who competed from 1914 to 1927, and reigned as the world heavyweight champion from 1919 to 1926 ...
took his name) in the 13th round to become the World Middleweight Champion. Fitzsimmons knocked Dempsey down at least 13 times and by the finish left him in such a pitiable condition that he begged him to quit. Since Dempsey would not do so, Fitzsimmons knocked him out and then carried him to his corner. On 22 July, police broke off his fight with Jim Hall after he had knocked Hall down several times.
Fitzsimmons spent the next two years fighting non-title bouts and exhibitions until giving Hall a chance at the title in 1893. He retained the crown by a knockout in round four. He spent the rest of that year doing exhibitions, and on 2 June, he had scheduled a two-way exhibition where he would demonstrate in public how to hit the boxing bag and then how to box against a real opponent. Reportedly, two freak accidents happened that day: Fitzsimmons hit the bag so hard that it broke, and then his opponent of that day allegedly slipped, getting hit in the head and the boxing exhibition was cancelled.
At a public sparring performance on 16 November 1894 at Jacob's Opera House, Syracuse, New York, Fitzsimmons knocked out sparring partner Con Riordan, who was carried off unconscious and died several hours later. Two months later Fitzsimmons was charged with manslaughter but was acquitted.
Fitzsimmons vs. Sharkey
After vacating the Middleweight title, Fitzsimmons began campaigning at heavyweight (the light heavyweight division did not exist at that time). On 2 December 1896, the San Francisco Athletic Club sponsored a fight at the Mechanics' Pavilion in San Francisco between Fitzsimmons andTom Sharkey
Thomas "Sailor Tom" Sharkey (November 26, 1873 – April 17, 1953) was a boxer who fought two fights with heavyweight champion James J. Jeffries. Sharkey's recorded ring career spanned from 1893 to 1904. He is credited with having won 40 fi ...
. Unable to find a referee, they called on former lawman Wyatt Earp
Wyatt Berry Stapp Earp (March 19, 1848 – January 13, 1929) was an American lawman and gambler in the American West, including Dodge City, Deadwood, and Tombstone. Earp took part in the famous gunfight at the O.K. Corral, during which l ...
. He had officiated 30 or so matches in earlier days, though not under the Marquess of Queensberry rules. The fight may have been the most anticipated fight on American soil that year. Fitzsimmons was favoured to win, and bets flowed heavily his way. Earp entered the ring still armed with his customary Colt .45 and drew a lot of attention when he had to be disarmed. He later said he forgot he was wearing it. Fitzsimmons was taller and quicker than Sharkey and dominated the fight from the opening bell. In the eighth round, Fitzsimmons hit Sharkey with his famed "solar plexus punch," an uppercut under the heart that could render a man temporarily helpless. The punch caught Sharkey, Earp, and most of the crowd by surprise, and Sharkey dropped, clutched his groin, and rolled on the canvas, screaming foul.
Earp stopped the bout, ruling that Fitzsimmons had hit Sharkey with a low blow. His ruling was greeted with loud boos and catcalls. Very few witnessed the foul Earp ruled on. He awarded the decision to Sharkey, who attendants carried out as "...limp as a rag."
Winning the heavyweight title
 In 1896, Fitzsimmons won a disputed version of the World Heavyweight Championship in a fight in Langtry, Texas, against the Irish fighter Peter Maher. On 17 March 1897, in Carson City, Nevada, he knocked out American
In 1896, Fitzsimmons won a disputed version of the World Heavyweight Championship in a fight in Langtry, Texas, against the Irish fighter Peter Maher. On 17 March 1897, in Carson City, Nevada, he knocked out American Jim Corbett
Edward James Corbett (25 July 1875 – 19 April 1955) was a British hunter, tracker, naturalist, and author who hunted a number of man-eating tigers and leopards in the Indian subcontinent.
He held the rank of colonel in the British Indian ...
, generally recognised as the legitimate World Heavyweight Champion (having won the title from John L. Sullivan in 1892) in round 14. This constituted a remarkable achievement, as Jim Corbett, a skilled boxer, weighed one stone 3 pounds (17 lb) more than Fitzsimmons. He out-boxed Fitzsimmons for several rounds, knocked him down in the sixth round and badly damaged his face with his jab, left hook and right hand, but Fitzsimmons kept coming and Corbett began to tire. In the 14th round, Fitzsimmons won the title with his "solar plexus" punch. Corbett collapsed in agony. Fitzsimmons' "solar plexus" punch became legendary, although he himself may never have used the phrase. The entire fight was filmed by Enoch J. Rector and released to cinemas as ''The Corbett-Fitzsimmons Fight
''The Corbett-Fitzsimmons Fight'' is an 1897 documentary film directed by Enoch J. Rector depicting the 1897 boxing match between James J. Corbett and Bob Fitzsimmons in Carson City, Nevada on St. Patrick's Day. Originally running for more t ...
'', the longest film ever released at the time. Using her maiden name, it was covered by Nellie Verrill Mighels Davis, the first woman to report a prize fight.
Fitzsimmons spent the rest of 1897 and 1898 doing stage tours. In 1899, Fitzsimmons fought James J. Jeffries
James Jackson "Jim" Jeffries (April 15, 1875 – March 3, 1953) was an American professional boxer and World Heavyweight Champion.
He was known for his enormous strength and stamina. Using a technique taught to him by his trainer, former Welte ...
at the Coney Island Athletic Club near Brooklyn, New York. Most people gave Jeffries little chance, even though at over 15 stones (95 kg) he massively outweighed his opponent and was far younger, but Jeffries lifted the World Heavyweight Championship from Fitzsimmons with an 11th-round knockout.
In June 1901 Fitzsimmons took part in a wrestling
Wrestling is a series of combat sports involving grappling-type techniques such as clinch fighting, throws and takedowns, joint locks, pins and other grappling holds. Wrestling techniques have been incorporated into martial arts, combat ...
match against Gus Ruhlin. He lost and went back to boxing. He then enjoyed legitimate boxing knockouts of leading contenders Ruhlin and Tom Sharkey
Thomas "Sailor Tom" Sharkey (November 26, 1873 – April 17, 1953) was a boxer who fought two fights with heavyweight champion James J. Jeffries. Sharkey's recorded ring career spanned from 1893 to 1904. He is credited with having won 40 fi ...
.
In 1901 he published a book ''Physical Culture and Self-Defense'' (Philadelphia: D. Biddle). In 1902, he and Jeffries had a rematch, once again with the World Heavyweight Champion at stake. Fitzsimmons battered Jeffries, who suffered horrible punishment. With his nose and cheek bones broken, most would have sympathized with Jeffries had he quit, but he kept going until his enormous strength and youth wore down Bob and he knocked him out cold in round eight.
Winning the Light Heavyweight title
In November 1903, Fitzsimmons made history by defeating World Light Heavyweight Champion George Gardiner (also known as Gardner) by a decision in 20 rounds, becoming the first boxer to win titles in three weight-divisions. Soon afterward, he went back to the Heavyweights, where he kept fighting until 1914, with mixed results. In 1907 at age 44, Fitzsimmons fought much younger Jack Johnson, during the time period in which reigning championJames J. Jeffries
James Jackson "Jim" Jeffries (April 15, 1875 – March 3, 1953) was an American professional boxer and World Heavyweight Champion.
He was known for his enormous strength and stamina. Using a technique taught to him by his trainer, former Welte ...
refused to fight Johnson. The bout between Johnson and Fitzsimmons ended in victory for Johnson with a second round knockout.Ken Burns, ''Unforgivable Blackness''
Retirement
Although Fitzsimmons became a world champion in each of the Middleweight, Light Heavyweight and Heavyweight divisions, historians do ''not'' consider him the first world Light Heavyweight Champion to become World Heavyweight Champion, because he won the Heavyweight title before winning the Light Heavyweight belt.Michael Spinks
Michael Spinks (born July 13, 1956) is an American former professional boxer who competed from 1977 to 1988. He held world championships in two weight classes, including the undisputed light heavyweight title from 1983 to 1985, and the lineal ...
counts as the first Light Heavyweight World Champion to win the Heavyweight belt as well. However, Fitzsimmons was the first Middleweight Champion to win the Heavyweight title and the only Heavyweight Champion to drop down and win the Light Heavyweight title. Fitzsimmons and later Henry Armstrong
Henry Jackson Jr. (December 12, 1912 – October 24, 1988) was an American professional boxer and a world boxing champion who fought under the name Henry Armstrong.
Armstrong was one of the few fighters to win in three or more different divisi ...
were the only men to win undisputed world championships in three different weight classes.
Fitzsimmons had a final professional record of 66 wins with 59 by knockout, 8 losses, 4 draws, 19 no contests and 2 no decisions (Newspaper Decisions: 2–0–0).
Fitzsimmons's exact record remains unknown, as the boxing world often kept records poorly during his era.
Death and legacy
 Fitzsimmons died of
Fitzsimmons died of pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severi ...
on 22 October 1917 in Chicago, survived by his fourth wife. His grave lies in the Graceland Cemetery
Graceland Cemetery is a large historic garden cemetery located in the north side community area of Uptown, in the city of Chicago, Illinois, United States. Established in 1860, its main entrance is at the intersection of Clark Street and Ir ...
, Uptown. Having four wives, a gambling habit and a susceptibility to confidence tricksters, he did not hold on to the money he made.
The statue ''Peace'' on the Dewey Arch was modelled on Fitzsimmons by the sculptor Daniel Chester French. A statue of Fitzsimmons has also stood in the city centre of Timaru, New Zealand, since 1987. It was commissioned by New Zealand millionaire boxing fan Bob Jones and sculpted by Margriet Windhausen.
The International Boxing Hall of Fame
The modern International Boxing Hall of Fame (IBHOF), located in Canastota, New York, honors boxers, trainers and other contributors to the sport worldwide. Inductees are selected by members of the Boxing Writers Association of America. The I ...
has made Fitzsimmons a member in its "Old Timer" category.
In 2003 '' The Ring'' named Fitzsimmons number eight of all time among boxing's best punchers.
Works
*Personal life
Fitzsimmons married four times and had six children, four of whom survived infancy.Professional boxing record
All information in this section is derived from BoxRec, unless otherwise stated.Official record
Allnewspaper decision A newspaper decision was a type of decision in professional boxing. It was rendered by a consensus of sportswriters attending a bout after it had ended inconclusively with a "no decision", as many regions had not adopted the National Sporting Club ...
s are officially regarded as “no decision” bouts and are not counted in the win/loss/draw column.
Unofficial record
Record with the inclusion ofnewspaper decision A newspaper decision was a type of decision in professional boxing. It was rendered by a consensus of sportswriters attending a bout after it had ended inconclusively with a "no decision", as many regions had not adopted the National Sporting Club ...
s in the win/loss/draw column.
See also
* List of heavyweight boxing champions *List of light heavyweight boxing champions
This is a chronological list of world light heavyweight boxing champions, as recognized by four of the better-known sanctioning organizations:
Championship recognition
1903–1910
The light-heavyweight division was created in 1903, the brainc ...
* List of middleweight boxing champions
* List of boxing triple champions
In boxing, a triple champion is a boxer who has won world titles in three weight classes. For most of the 20th century it was a remarkable and rare achievement accomplished by only a handful of fighters. Beginning in the 1970s, triple champions hav ...
Notes and references
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * *Further reading
*''Kiwis With Gloves On'' by Brian F O'Brien, published 1960, Reed.External links
*Boxing Hall of Fame
ESPN.com
* in the ''
Dictionary of New Zealand Biography
The ''Dictionary of New Zealand Biography'' (DNZB) is an encyclopedia or biographical dictionary containing biographies of over 3,000 deceased New Zealanders. It was first published as a series of print volumes from 1990 to 2000, went online ...
''
Biography in the 1966 ''Encyclopaedia of New Zealand'' (birth year wrong)
* * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Fitzsimmons, Bob 1863 births 1917 deaths 19th-century British people Bare-knuckle boxers Burials at Graceland Cemetery (Chicago) British emigrants to New Zealand New Zealand people of Cornish descent American people of Cornish descent British emigrants to the United States English male boxers English people of Irish descent Heavyweight boxers International Boxing Hall of Fame inductees Light-heavyweight boxers Middleweight boxers New Zealand male boxers New Zealand emigrants to the United States New Zealand people of English descent People associated with physical culture People from Helston World boxing champions World heavyweight boxing champions New Zealand world boxing champions World middleweight boxing champions Deaths from pneumonia in Illinois