Blenheim Palace on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Blenheim Palace (pronounced ) is a country house in
Blenheim Palace (pronounced ) is a country house in
 John Churchill was born in
John Churchill was born in
 The estate given by the nation to Marlborough for the new palace was the manor of Woodstock, sometimes called the Palace of Woodstock, which had been a royal demesne, in reality little more than a deer park. Legend has obscured the manor's origins. King
The estate given by the nation to Marlborough for the new palace was the manor of Woodstock, sometimes called the Palace of Woodstock, which had been a royal demesne, in reality little more than a deer park. Legend has obscured the manor's origins. King
 The architect selected for the ambitious project was a controversial one. The Duchess was known to favour Sir Christopher Wren, famous for St Paul's Cathedral and many other national buildings. The Duke however, following a chance meeting at a playhouse, is said to have commissioned Sir John Vanbrugh there and then. Vanbrugh, a popular dramatist, was an untrained architect, who usually worked in conjunction with the trained and practical
The architect selected for the ambitious project was a controversial one. The Duchess was known to favour Sir Christopher Wren, famous for St Paul's Cathedral and many other national buildings. The Duke however, following a chance meeting at a playhouse, is said to have commissioned Sir John Vanbrugh there and then. Vanbrugh, a popular dramatist, was an untrained architect, who usually worked in conjunction with the trained and practical  Blenheim, however, was not to provide Vanbrugh with the architectural plaudits he imagined it would. The fight over funding led to accusations of extravagance and impracticality of design, many of these charges levelled by the Whig factions in power. He found no defender in the Duchess of Marlborough. Having been foiled in her wish to employ Wren, she levelled criticism at Vanbrugh on every level, from design to taste. In part their problems arose from what was demanded of the architect. The nation (which was then assumed, by both architect and owners, to be paying the bills) wanted a monument, but the Duchess wanted not only a fitting tribute to her husband but also a comfortable home, two requirements that were not compatible in 18th-century architecture. Finally, in the early days of the building the Duke was frequently away on his military campaigns, and it was left to the Duchess to negotiate with Vanbrugh. More aware than her husband of the precarious state of the financial aid they were receiving, she criticised Vanbrugh's grandiose ideas for their extravagance.
Following their final altercation, Vanbrugh was banned from the site. In 1719, whilst the Duchess was away, Vanbrugh viewed the palace in secret. However, when Vanbrugh's wife visited the completed Blenheim as a member of the viewing public in 1725, the Duchess refused to allow her even to enter the park.
Vanbrugh's severe massed Baroque used at Blenheim never truly caught the public imagination, and was quickly superseded by the revival of the
Blenheim, however, was not to provide Vanbrugh with the architectural plaudits he imagined it would. The fight over funding led to accusations of extravagance and impracticality of design, many of these charges levelled by the Whig factions in power. He found no defender in the Duchess of Marlborough. Having been foiled in her wish to employ Wren, she levelled criticism at Vanbrugh on every level, from design to taste. In part their problems arose from what was demanded of the architect. The nation (which was then assumed, by both architect and owners, to be paying the bills) wanted a monument, but the Duchess wanted not only a fitting tribute to her husband but also a comfortable home, two requirements that were not compatible in 18th-century architecture. Finally, in the early days of the building the Duke was frequently away on his military campaigns, and it was left to the Duchess to negotiate with Vanbrugh. More aware than her husband of the precarious state of the financial aid they were receiving, she criticised Vanbrugh's grandiose ideas for their extravagance.
Following their final altercation, Vanbrugh was banned from the site. In 1719, whilst the Duchess was away, Vanbrugh viewed the palace in secret. However, when Vanbrugh's wife visited the completed Blenheim as a member of the viewing public in 1725, the Duchess refused to allow her even to enter the park.
Vanbrugh's severe massed Baroque used at Blenheim never truly caught the public imagination, and was quickly superseded by the revival of the

 The precise responsibility for the funding of the new palace has always been a debatable subject, unresolved to this day. The palace as a reward was mooted within months of the Battle of Blenheim, at a time when Marlborough was still to gain many further victories on behalf of the country. That a grateful nation led by Queen Anne wished and intended to give their national hero a suitable home is beyond doubt, but the exact size and nature of that house is questionable. A warrant dated 1705, signed by the parliamentary treasurer the Earl of Godolphin, appointed Vanbrugh as architect and outlined his remit. Unfortunately for the Churchills, nowhere did this warrant mention Queen or Crown.
The Duke of Marlborough contributed £60,000 to the initial cost when work commenced in 1705, which, supplemented by Parliament, should have built a monumental house. Parliament voted funds for the building of Blenheim, but no exact sum was mentioned nor provision for inflation or over-budget expenses. Almost from the outset, funds were spasmodic. Queen Anne paid some of them, but with growing reluctance and lapses, following her frequent altercations with the Duchess. After their final argument in 1712, all state money ceased and work came to a halt. £220,000 had already been spent and £45,000 was owing to workmen. The Marlboroughs were forced into exile on the continent, and did not return until after the Queen's death in 1714.
The precise responsibility for the funding of the new palace has always been a debatable subject, unresolved to this day. The palace as a reward was mooted within months of the Battle of Blenheim, at a time when Marlborough was still to gain many further victories on behalf of the country. That a grateful nation led by Queen Anne wished and intended to give their national hero a suitable home is beyond doubt, but the exact size and nature of that house is questionable. A warrant dated 1705, signed by the parliamentary treasurer the Earl of Godolphin, appointed Vanbrugh as architect and outlined his remit. Unfortunately for the Churchills, nowhere did this warrant mention Queen or Crown.
The Duke of Marlborough contributed £60,000 to the initial cost when work commenced in 1705, which, supplemented by Parliament, should have built a monumental house. Parliament voted funds for the building of Blenheim, but no exact sum was mentioned nor provision for inflation or over-budget expenses. Almost from the outset, funds were spasmodic. Queen Anne paid some of them, but with growing reluctance and lapses, following her frequent altercations with the Duchess. After their final argument in 1712, all state money ceased and work came to a halt. £220,000 had already been spent and £45,000 was owing to workmen. The Marlboroughs were forced into exile on the continent, and did not return until after the Queen's death in 1714.
 On their return the Duke and Duchess came back into favour at court. The 64-year-old Duke now decided to complete the project at his own expense. In 1716 work resumed, but the project relied completely upon the limited means of the Duke himself. Harmony on the building site was short-lived, as in 1717 the Duke suffered a severe stroke, and the thrifty Duchess took control. The Duchess blamed Vanbrugh entirely for the growing costs and extravagance of the palace, the design of which she had never liked. Following a meeting with the Duchess, Vanbrugh left the building site in a rage, insisting that the new masons, carpenters and craftsmen, brought in by the Duchess, were inferior to those he had employed. The master craftsmen he had patronised, however, such as
On their return the Duke and Duchess came back into favour at court. The 64-year-old Duke now decided to complete the project at his own expense. In 1716 work resumed, but the project relied completely upon the limited means of the Duke himself. Harmony on the building site was short-lived, as in 1717 the Duke suffered a severe stroke, and the thrifty Duchess took control. The Duchess blamed Vanbrugh entirely for the growing costs and extravagance of the palace, the design of which she had never liked. Following a meeting with the Duchess, Vanbrugh left the building site in a rage, insisting that the new masons, carpenters and craftsmen, brought in by the Duchess, were inferior to those he had employed. The master craftsmen he had patronised, however, such as
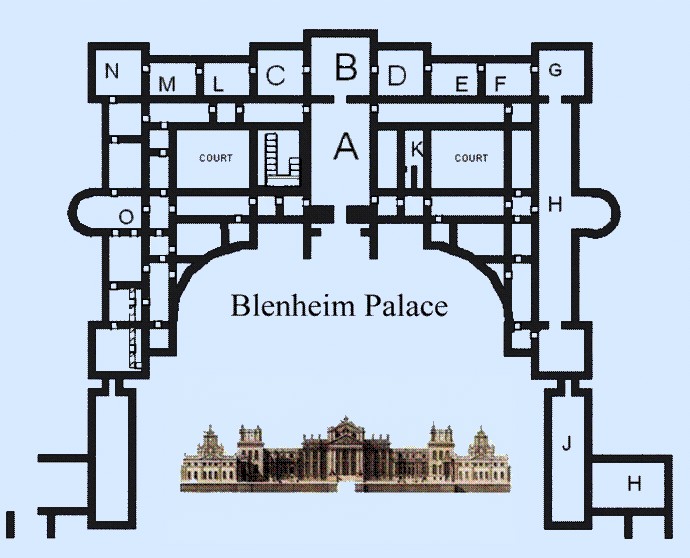 Vanbrugh planned Blenheim in perspective; that is, to be best viewed from a distance. As the site covers some seven acres (28,000 m2) this is also a necessity.
The plan of the palace's principal block (or
Vanbrugh planned Blenheim in perspective; that is, to be best viewed from a distance. As the site covers some seven acres (28,000 m2) this is also a necessity.
The plan of the palace's principal block (or  The solid and huge entrance portico on the north front resembles more the entrance to a
The solid and huge entrance portico on the north front resembles more the entrance to a  This view of the Duke as an
This view of the Duke as an





 The internal layout of the rooms of the central block at Blenheim was defined by the court etiquette of the day. State apartments were designed as an axis of rooms of increasing importance and public use, leading to the chief room. The larger houses, like Blenheim, had two sets of state apartments each mirroring each other. The grandest and most public and important was the central saloon ''("B" in the plan'') which served as the communal state dining room. To either side of the saloon are suites of state apartments, decreasing in importance but increasing in privacy: the first room ''("C")'' would have been an audience chamber for receiving important guests, the next room ''("L")'' a private withdrawing room, the next room ''("M")'' would have been the bedroom of the occupier of the suite, thus the most private. One of the small rooms between the bedroom and the internal courtyard was intended as a dressing room. This arrangement is reflected on the other side of the saloon. The state apartments were intended for use by only the most important guests such as a visiting sovereign. On the left (east) side of the plan on either side of the bow room ''(marked "O")'' can be seen a smaller but nearly identical layout of rooms, which were the suites of the Duke and Duchess themselves. Thus, the bow room corresponds exactly to the saloon in terms of its importance to the two smaller suites.
Blenheim Palace was the birthplace of the 1st Duke's famous descendant,
The internal layout of the rooms of the central block at Blenheim was defined by the court etiquette of the day. State apartments were designed as an axis of rooms of increasing importance and public use, leading to the chief room. The larger houses, like Blenheim, had two sets of state apartments each mirroring each other. The grandest and most public and important was the central saloon ''("B" in the plan'') which served as the communal state dining room. To either side of the saloon are suites of state apartments, decreasing in importance but increasing in privacy: the first room ''("C")'' would have been an audience chamber for receiving important guests, the next room ''("L")'' a private withdrawing room, the next room ''("M")'' would have been the bedroom of the occupier of the suite, thus the most private. One of the small rooms between the bedroom and the internal courtyard was intended as a dressing room. This arrangement is reflected on the other side of the saloon. The state apartments were intended for use by only the most important guests such as a visiting sovereign. On the left (east) side of the plan on either side of the bow room ''(marked "O")'' can be seen a smaller but nearly identical layout of rooms, which were the suites of the Duke and Duchess themselves. Thus, the bow room corresponds exactly to the saloon in terms of its importance to the two smaller suites.
Blenheim Palace was the birthplace of the 1st Duke's famous descendant,
 Blenheim sits in the centre of a large undulating park, a classic example of the
Blenheim sits in the centre of a large undulating park, a classic example of the 

 Following the 1st Duke's death the Duchess concentrated most of her considerable energies on the completion of the palace itself, and the park remained relatively unchanged until the arrival of Capability Brown in 1764. The 4th Duke employed Brown who immediately began an English landscape garden scheme to naturalise and enhance the landscape, with tree planting, and man-made undulations. However, the feature with which he is forever associated is the lake, a huge stretch of water created by damming the River Glyme and ornamented by a series of cascades where the river flows in and out. The lake was narrowed at the point of Vanbrugh's grand bridge, but the three small canal-like streams trickling underneath it were completely absorbed by one river-like stretch. Brown's great achievement at this point was to actually flood and submerge beneath the water level the lower stories and rooms of the bridge itself, thus reducing its incongruous height and achieving what is regarded by many as the epitome of an English landscape. Brown also grassed over the great parterre and the Great Court. The latter was re-paved by Duchêne in the early 20th century. The 5th Duke was responsible for several other garden follies and novelties.
Following the 1st Duke's death the Duchess concentrated most of her considerable energies on the completion of the palace itself, and the park remained relatively unchanged until the arrival of Capability Brown in 1764. The 4th Duke employed Brown who immediately began an English landscape garden scheme to naturalise and enhance the landscape, with tree planting, and man-made undulations. However, the feature with which he is forever associated is the lake, a huge stretch of water created by damming the River Glyme and ornamented by a series of cascades where the river flows in and out. The lake was narrowed at the point of Vanbrugh's grand bridge, but the three small canal-like streams trickling underneath it were completely absorbed by one river-like stretch. Brown's great achievement at this point was to actually flood and submerge beneath the water level the lower stories and rooms of the bridge itself, thus reducing its incongruous height and achieving what is regarded by many as the epitome of an English landscape. Brown also grassed over the great parterre and the Great Court. The latter was re-paved by Duchêne in the early 20th century. The 5th Duke was responsible for several other garden follies and novelties.
 On the death of the 1st Duke in 1722, as both his sons were dead, he was succeeded by his daughter
On the death of the 1st Duke in 1722, as both his sons were dead, he was succeeded by his daughter

 Charles, 9th Duke of Marlborough (1871–1934) can be credited with saving both the palace and the family. Inheriting the near-bankrupt dukedom in 1892, he was forced to find a quick and drastic solution to the problems. Prevented by the strict social dictates of late 19th-century society from earning money, he was left with one solution: he had to marry into money. In November 1896 he coldly and openly without love married the American railroad heiress
Charles, 9th Duke of Marlborough (1871–1934) can be credited with saving both the palace and the family. Inheriting the near-bankrupt dukedom in 1892, he was forced to find a quick and drastic solution to the problems. Prevented by the strict social dictates of late 19th-century society from earning money, he was left with one solution: he had to marry into money. In November 1896 he coldly and openly without love married the American railroad heiress  Blenheim was once again a place of wonder and prestige. However, Consuelo was far from happy; she records many of her problems in her cynical and often less than candid biography ''The Glitter and the Gold''. In 1906 she shocked society and left her husband. They divorced in 1921. She married a Frenchman, Jacques Balsan in 1921. She died in 1964, having lived to see her son become Duke of Marlborough. She frequently returned to Blenheim, the house she had hated and yet saved, albeit as the unwilling sacrifice.
After his divorce the Duke married again, to an American former friend of Consuelo,
Blenheim was once again a place of wonder and prestige. However, Consuelo was far from happy; she records many of her problems in her cynical and often less than candid biography ''The Glitter and the Gold''. In 1906 she shocked society and left her husband. They divorced in 1921. She married a Frenchman, Jacques Balsan in 1921. She died in 1964, having lived to see her son become Duke of Marlborough. She frequently returned to Blenheim, the house she had hated and yet saved, albeit as the unwilling sacrifice.
After his divorce the Duke married again, to an American former friend of Consuelo,

 The palace remains the home of the Dukes of Marlborough, the present incumbent of the title being Charles James (Jamie) Spencer-Churchill, 12th Duke of Marlborough. Charles James succeeded to the Dukedom upon his
The palace remains the home of the Dukes of Marlborough, the present incumbent of the title being Charles James (Jamie) Spencer-Churchill, 12th Duke of Marlborough. Charles James succeeded to the Dukedom upon his
Churchill by Oswald Birley - UK Parliament Living Heritage
Blenheim Art Foundation
Blenheim Palace
at Cotswolds Website * * {{Authority control 1722 establishments in England Baroque palaces Birthplaces of individual people English Baroque architecture English gardens in English Landscape Garden style Gardens by Capability Brown Gardens in Oxfordshire Grade I listed buildings in Oxfordshire Grade I listed houses Grade I listed palaces Grade I listed parks and gardens in Oxfordshire Historic house museums in Oxfordshire Houses completed in 1722 Houses in Oxfordshire John Vanbrugh buildings Mazes Nicholas Hawksmoor buildings Palaces in England Parks and open spaces in Oxfordshire Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Oxfordshire Spencer-Churchill family residences Tourist attractions in Oxfordshire Vanderbilt family residences West Oxfordshire District Winston Churchill World Heritage Sites in England
 Blenheim Palace (pronounced ) is a country house in
Blenheim Palace (pronounced ) is a country house in Woodstock, Oxfordshire
Woodstock is a market town and civil parish, north-west of Oxford in West Oxfordshire in the county of Oxfordshire, England. The 2011 Census recorded a parish population of 3,100.
Blenheim Palace, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is next to W ...
, England. It is the seat of the Dukes of Marlborough
Duke of Marlborough (pronounced ) is a title in the Peerage of England. It was created by Queen Anne in 1702 for John Churchill, 1st Earl of Marlborough (1650–1722), the noted military leader. In historical texts, unqualified use of the ti ...
and the only non-royal
Royal may refer to:
People
* Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name
* A member of a royal family
Places United States
* Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community
* Royal, Illinois, a village
* Royal, Iowa, a ...
, non- episcopal country house in England to hold the title of palace. The palace, one of England's largest houses, was built between 1705 and 1722, and designated a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
in 1987.
The palace is named after the 1704 Battle of Blenheim. It was originally intended to be a reward to John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough
General John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, 1st Prince of Mindelheim, 1st Count of Nellenburg, Prince of the Holy Roman Empire, (26 May 1650 – 16 June 1722 O.S.) was an English soldier and statesman whose career spanned the reign ...
for his military triumphs against the French and Bavarians in the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
, culminating in the Battle of Blenheim. The land was given as a gift, and construction began in 1705, with some financial support from Queen Anne. The project soon became the subject of political infighting, with the Crown cancelling further financial support in 1712, Marlborough's three-year voluntary exile to the Continent, the fall from influence of his duchess, and lasting damage to the reputation of the architect Sir John Vanbrugh
Sir John Vanbrugh (; 24 January 1664 (baptised) – 26 March 1726) was an English architect, dramatist and herald, perhaps best known as the designer of Blenheim Palace and Castle Howard. He wrote two argumentative and outspoken Restora ...
.
Designed in the rare, and short-lived, English Baroque
English Baroque is a term used to refer to modes of English architecture that paralleled Baroque architecture in continental Europe between the Great Fire of London (1666) and roughly 1720, when the flamboyant and dramatic qualities of Baroque ...
style, architectural appreciation of the palace is as divided today as it was in the 1720s. It is unique in its combined use as a family home, mausoleum and national monument
A monument is a type of structure that was explicitly created to commemorate a person or event, or which has become relevant to a social group as a part of their remembrance of historic times or cultural heritage, due to its artistic, hist ...
. The palace is notable as the birthplace and ancestral home of Sir Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from 1 ...
.
Following the palace's completion, it became the home of the Churchill (later Spencer-Churchill) family for the next 300 years, and various members of the family have wrought changes to the interiors, park and gardens. At the end of the 19th century, the palace was saved from ruin by funds gained from the 9th Duke of Marlborough's marriage to American railroad heiress Consuelo Vanderbilt
Consuelo Vanderbilt-Balsan (formerly Consuelo Spencer-Churchill, Duchess of Marlborough; born Consuelo Vanderbilt; March 2, 1877 – December 6, 1964) was a socialite and a member of the prominent American Vanderbilt family. Her first marriage ...
.
Churchills
Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devo ...
. Although his family had aristocratic
Aristocracy (, ) is a form of government that places strength in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocrats. The term derives from the el, αριστοκρατία (), meaning 'rule of the best'.
At the time of the word' ...
relations, it belonged to the minor gentry
Gentry (from Old French ''genterie'', from ''gentil'', "high-born, noble") are "well-born, genteel and well-bred people" of high social class, especially in the past.
Word similar to gentle imple and decentfamilies
''Gentry'', in its widest c ...
rather than the upper echelons of 17th-century society. In 1678, Churchill married Sarah Jennings, and in April that year, he was sent by Charles II to The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital o ...
to negotiate a convention on the deployment of the English army in Flanders. The mission ultimately proved abortive. In May, Churchill was appointed to the temporary rank of Brigadier-General of Foot, but the possibility of a continental campaign was eliminated with the Treaty of Nijmegen
The Treaties of Peace of Nijmegen ('; german: Friede von Nimwegen) were a series of treaties signed in the Dutch city of Nijmegen between August 1678 and October 1679. The treaties ended various interconnected wars among France, the Dutch Repub ...
.
When Churchill returned to England, the Popish Plot resulted in a temporary three-year banishment for James Stuart, Duke of York
James VII and II (14 October 1633 16 September 1701) was King of England and King of Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II of England, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was depo ...
. The Duke obliged Churchill to attend him, first to The Hague, then in Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
. For his services during the crisis, Churchill was made Lord Churchill of Eyemouth in the peerage of Scotland in 1682, and the following year appointed colonel of the King's Own Royal Regiment of Dragoons
The Royal Dragoons (1st Dragoons) was a heavy cavalry regiment of the British Army. The regiment was formed in 1661 as the Tangier Horse. It served for three centuries and was in action during the First and the Second World Wars. It was amalgam ...
.
On the death of Charles II in 1685, his brother, the Duke of York, became King James II
James VII and II (14 October 1633 16 September 1701) was King of England and King of Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was deposed in the Glorious Re ...
. James had been Governor of the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business di ...
(today North America's oldest company, established by royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but s ...
in 1670), and with his succession to the throne, Churchill was appointed the company's third ever governor. He had also been affirmed Gentleman of the Bedchamber in April, and admitted to the English peerage as Baron Churchill of Sandridge in the county of Hertfordshire in May. Following the Monmouth Rebellion, Churchill was promoted to Major General
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of ...
and awarded the lucrative colonelcy of the Third Troop of Life Guards.
When William, Prince of Orange, invaded England in November 1688, Churchill, accompanied by some 400 officers and men, rode to join him in Axminster
Axminster is a market town and civil parish on the eastern border of the county of Devon in England. It is from the county town of Exeter. The town is built on a hill overlooking the River Axe which heads towards the English Channel at Ax ...
. When the King saw he could not even keep Churchill—for so long his loyal and intimate servant—he fled to France. As part of William III's coronation honours, Churchill was created Earl of Marlborough
Earl of Marlborough is a title that has been created twice, both times in the Peerage of England. The first time in 1626 in favour of James Ley, 1st Earl of Marlborough, James Ley, 1st Baron Ley and the second in 1689 for John Churchill, 1st Duke ...
, sworn to the Privy Council, and made a Gentleman of the King's Bedchamber.
During the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
Churchill gained a reputation as a capable military commander, and in 1702 he was elevated to the dukedom of Marlborough. During the war he won a series of victories, including the Battle of Blenheim (1704), the Battle of Ramillies
The Battle of Ramillies (), fought on 23 May 1706, was a battle of the War of the Spanish Succession. For the Grand Alliance – Austria, England, and the Dutch Republic – the battle had followed an indecisive campaign against the Bourbon a ...
(1706), the Battle of Oudenarde (1708), and the Battle of Malplaquet
The Battle of Malplaquet took place on 11 September 1709 during the War of the Spanish Succession and was fought between a French army commanded by the Duke of Villars and a Grand Alliance force under the Duke of Marlborough. In one of the blo ...
(1709). For his victory at Blenheim, the Crown bestowed upon Marlborough the tenancy of the royal manor of Hensington (situated on the site of Woodstock) to site the new palace, and Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
voted a substantial sum of money towards its creation. The rent or ''petit serjeanty'' due to the Crown for the land was set at the peppercorn rent or quit-rent
Quit rent, quit-rent, or quitrent is a tax or land tax imposed on occupants of freehold or leased land in lieu of services to a higher landowning authority, usually a government or its assigns.
Under feudal law, the payment of quit rent (Latin ...
of one copy of the French royal flag to be tendered to the Monarch annually on the anniversary of the Battle of Blenheim. This flag is displayed by the Monarch on a 17th-century French writing table in Windsor Castle
Windsor Castle is a royal residence at Windsor in the English county of Berkshire. It is strongly associated with the English and succeeding British royal family, and embodies almost a millennium of architectural history.
The original c ...
.
Marlborough's wife was by all accounts a cantankerous woman, though capable of great charm. She had befriended the young Princess Anne
Anne, Princess Royal (Anne Elizabeth Alice Louise; born 15 August 1950), is a member of the British royal family. She is the second child and only daughter of Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, and the only sister of K ...
and later, when the princess became Queen, the Duchess of Marlborough, as Her Majesty's Mistress of the Robes
The mistress of the robes was the senior lady in the Royal Household of the United Kingdom.
Formerly responsible for the queen consort's/regnant's clothes and jewellery (as the name implies), the post had the responsibility for arranging the rota ...
, exerted great influence over the Queen on both personal and political levels. The relationship between Queen and Duchess later became strained and fraught, and following their final quarrel in 1711, the money for the construction of Blenheim ceased. For political reasons the Marlboroughs went into exile on the Continent until they returned the day after the Queen's death on 1 August 1714.
Site
 The estate given by the nation to Marlborough for the new palace was the manor of Woodstock, sometimes called the Palace of Woodstock, which had been a royal demesne, in reality little more than a deer park. Legend has obscured the manor's origins. King
The estate given by the nation to Marlborough for the new palace was the manor of Woodstock, sometimes called the Palace of Woodstock, which had been a royal demesne, in reality little more than a deer park. Legend has obscured the manor's origins. King Henry I Henry I may refer to:
876–1366
* Henry I the Fowler, King of Germany (876–936)
* Henry I, Duke of Bavaria (died 955)
* Henry I of Austria, Margrave of Austria (died 1018)
* Henry I of France (1008–1060)
* Henry I the Long, Margrave of the ...
enclosed the park to contain the deer. Henry II housed his mistress Rosamund Clifford (sometimes known as "Fair Rosamund") there in a "bower and labyrinth"; a spring in which she is said to have bathed remains, named after her.
It seems the unostentatious hunting lodge was rebuilt many times, and had an uneventful history until Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is ...
, before her succession, was imprisoned there by her half-sister Mary I
Mary I (18 February 1516 – 17 November 1558), also known as Mary Tudor, and as "Bloody Mary" by her Protestant opponents, was Queen of England and Ireland from July 1553 and Queen of Spain from January 1556 until her death in 1558. She ...
between 1554 and 1555. Elizabeth had been implicated in the Wyatt plot, but her imprisonment at Woodstock was short, and the manor remained in obscurity until bombarded and ruined by Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three K ...
's troops during the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
.
When the park was being re-landscaped as a setting for the Palace, the 1st Duchess wanted the historic ruins demolished, while Vanbrugh, an early conservationist, wanted them restored and made into a landscape feature. The Duchess, as so often in her disputes with her architect, won the day and the remains of the manor were swept away.
Architect
 The architect selected for the ambitious project was a controversial one. The Duchess was known to favour Sir Christopher Wren, famous for St Paul's Cathedral and many other national buildings. The Duke however, following a chance meeting at a playhouse, is said to have commissioned Sir John Vanbrugh there and then. Vanbrugh, a popular dramatist, was an untrained architect, who usually worked in conjunction with the trained and practical
The architect selected for the ambitious project was a controversial one. The Duchess was known to favour Sir Christopher Wren, famous for St Paul's Cathedral and many other national buildings. The Duke however, following a chance meeting at a playhouse, is said to have commissioned Sir John Vanbrugh there and then. Vanbrugh, a popular dramatist, was an untrained architect, who usually worked in conjunction with the trained and practical Nicholas Hawksmoor
Nicholas Hawksmoor (probably 1661 – 25 March 1736) was an English architect. He was a leading figure of the English Baroque style of architecture in the late-seventeenth and early-eighteenth centuries. Hawksmoor worked alongside the principa ...
. The duo had recently completed the first stages of the Baroque Castle Howard
Castle Howard is a stately home in North Yorkshire, England, within the civil parish of Henderskelfe, located north of York. It is a private residence and has been the home of the Carlisle branch of the Howard family for more than 300 years ...
. This huge Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other English counties, functions have ...
mansion was one of England's first houses in the flamboyant European Baroque style. The success of Castle Howard led Marlborough to commission something similar at Woodstock.
 Blenheim, however, was not to provide Vanbrugh with the architectural plaudits he imagined it would. The fight over funding led to accusations of extravagance and impracticality of design, many of these charges levelled by the Whig factions in power. He found no defender in the Duchess of Marlborough. Having been foiled in her wish to employ Wren, she levelled criticism at Vanbrugh on every level, from design to taste. In part their problems arose from what was demanded of the architect. The nation (which was then assumed, by both architect and owners, to be paying the bills) wanted a monument, but the Duchess wanted not only a fitting tribute to her husband but also a comfortable home, two requirements that were not compatible in 18th-century architecture. Finally, in the early days of the building the Duke was frequently away on his military campaigns, and it was left to the Duchess to negotiate with Vanbrugh. More aware than her husband of the precarious state of the financial aid they were receiving, she criticised Vanbrugh's grandiose ideas for their extravagance.
Following their final altercation, Vanbrugh was banned from the site. In 1719, whilst the Duchess was away, Vanbrugh viewed the palace in secret. However, when Vanbrugh's wife visited the completed Blenheim as a member of the viewing public in 1725, the Duchess refused to allow her even to enter the park.
Vanbrugh's severe massed Baroque used at Blenheim never truly caught the public imagination, and was quickly superseded by the revival of the
Blenheim, however, was not to provide Vanbrugh with the architectural plaudits he imagined it would. The fight over funding led to accusations of extravagance and impracticality of design, many of these charges levelled by the Whig factions in power. He found no defender in the Duchess of Marlborough. Having been foiled in her wish to employ Wren, she levelled criticism at Vanbrugh on every level, from design to taste. In part their problems arose from what was demanded of the architect. The nation (which was then assumed, by both architect and owners, to be paying the bills) wanted a monument, but the Duchess wanted not only a fitting tribute to her husband but also a comfortable home, two requirements that were not compatible in 18th-century architecture. Finally, in the early days of the building the Duke was frequently away on his military campaigns, and it was left to the Duchess to negotiate with Vanbrugh. More aware than her husband of the precarious state of the financial aid they were receiving, she criticised Vanbrugh's grandiose ideas for their extravagance.
Following their final altercation, Vanbrugh was banned from the site. In 1719, whilst the Duchess was away, Vanbrugh viewed the palace in secret. However, when Vanbrugh's wife visited the completed Blenheim as a member of the viewing public in 1725, the Duchess refused to allow her even to enter the park.
Vanbrugh's severe massed Baroque used at Blenheim never truly caught the public imagination, and was quickly superseded by the revival of the Palladian
Palladian architecture is a European architectural style derived from the work of the Venetian architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). What is today recognised as Palladian architecture evolved from his concepts of symmetry, perspective and ...
style. Vanbrugh's reputation was irreparably damaged, and he received no further truly great public commissions. For his final design, Seaton Delaval Hall
Seaton Delaval Hall is a Grade I listed country house in Northumberland, England, near the coast just north of Newcastle upon Tyne. Located between Seaton Sluice and Seaton Delaval, it was designed by Sir John Vanbrugh in 1718 for Admiral Geo ...
in Northumberland
Northumberland () is a county in Northern England, one of two counties in England which border with Scotland. Notable landmarks in the county include Alnwick Castle, Bamburgh Castle, Hadrian's Wall and Hexham Abbey.
It is bordered by land ...
, which was hailed as his masterpiece, he used a refined version of the Baroque employed at Blenheim. He died shortly before its completion.
Funding the construction

 The precise responsibility for the funding of the new palace has always been a debatable subject, unresolved to this day. The palace as a reward was mooted within months of the Battle of Blenheim, at a time when Marlborough was still to gain many further victories on behalf of the country. That a grateful nation led by Queen Anne wished and intended to give their national hero a suitable home is beyond doubt, but the exact size and nature of that house is questionable. A warrant dated 1705, signed by the parliamentary treasurer the Earl of Godolphin, appointed Vanbrugh as architect and outlined his remit. Unfortunately for the Churchills, nowhere did this warrant mention Queen or Crown.
The Duke of Marlborough contributed £60,000 to the initial cost when work commenced in 1705, which, supplemented by Parliament, should have built a monumental house. Parliament voted funds for the building of Blenheim, but no exact sum was mentioned nor provision for inflation or over-budget expenses. Almost from the outset, funds were spasmodic. Queen Anne paid some of them, but with growing reluctance and lapses, following her frequent altercations with the Duchess. After their final argument in 1712, all state money ceased and work came to a halt. £220,000 had already been spent and £45,000 was owing to workmen. The Marlboroughs were forced into exile on the continent, and did not return until after the Queen's death in 1714.
The precise responsibility for the funding of the new palace has always been a debatable subject, unresolved to this day. The palace as a reward was mooted within months of the Battle of Blenheim, at a time when Marlborough was still to gain many further victories on behalf of the country. That a grateful nation led by Queen Anne wished and intended to give their national hero a suitable home is beyond doubt, but the exact size and nature of that house is questionable. A warrant dated 1705, signed by the parliamentary treasurer the Earl of Godolphin, appointed Vanbrugh as architect and outlined his remit. Unfortunately for the Churchills, nowhere did this warrant mention Queen or Crown.
The Duke of Marlborough contributed £60,000 to the initial cost when work commenced in 1705, which, supplemented by Parliament, should have built a monumental house. Parliament voted funds for the building of Blenheim, but no exact sum was mentioned nor provision for inflation or over-budget expenses. Almost from the outset, funds were spasmodic. Queen Anne paid some of them, but with growing reluctance and lapses, following her frequent altercations with the Duchess. After their final argument in 1712, all state money ceased and work came to a halt. £220,000 had already been spent and £45,000 was owing to workmen. The Marlboroughs were forced into exile on the continent, and did not return until after the Queen's death in 1714.
 On their return the Duke and Duchess came back into favour at court. The 64-year-old Duke now decided to complete the project at his own expense. In 1716 work resumed, but the project relied completely upon the limited means of the Duke himself. Harmony on the building site was short-lived, as in 1717 the Duke suffered a severe stroke, and the thrifty Duchess took control. The Duchess blamed Vanbrugh entirely for the growing costs and extravagance of the palace, the design of which she had never liked. Following a meeting with the Duchess, Vanbrugh left the building site in a rage, insisting that the new masons, carpenters and craftsmen, brought in by the Duchess, were inferior to those he had employed. The master craftsmen he had patronised, however, such as
On their return the Duke and Duchess came back into favour at court. The 64-year-old Duke now decided to complete the project at his own expense. In 1716 work resumed, but the project relied completely upon the limited means of the Duke himself. Harmony on the building site was short-lived, as in 1717 the Duke suffered a severe stroke, and the thrifty Duchess took control. The Duchess blamed Vanbrugh entirely for the growing costs and extravagance of the palace, the design of which she had never liked. Following a meeting with the Duchess, Vanbrugh left the building site in a rage, insisting that the new masons, carpenters and craftsmen, brought in by the Duchess, were inferior to those he had employed. The master craftsmen he had patronised, however, such as Grinling Gibbons
Grinling Gibbons (4 April 1648 – 3 August 1721) was an Anglo-Dutch sculptor and wood carver known for his work in England, including Windsor Castle and Hampton Court Palace, St Paul's Cathedral and other London churches, Petworth House and othe ...
, refused to work for the lower rates paid by the Marlboroughs. The craftsmen brought in by the Duchess, under the guidance of furniture designer James Moore, and Vanbrugh's assistant architect Hawksmoor, completed the work in perfect imitation of the greater masters.
Following the Duke's death in 1722, completion of the palace and its park became the Duchess's driving ambition. Vanbrugh's assistant Hawksmoor was recalled and in 1723 designed the "Arch of Triumph", based on the Arch of Titus
The Arch of Titus ( it, Arco di Tito; la, Arcus Titi) is a 1st-century AD honorific arch, located on the Via Sacra, Rome, just to the south-east of the Roman Forum. It was constructed in 81 AD by the Emperor Domitian shortly after the death of ...
, at the entrance to the park from Woodstock. Hawksmoor also completed the interior design of the library, the ceilings of many of the state rooms and other details in numerous other minor rooms, and various outbuildings.
Cutting rates of pay to workmen, and using lower-quality materials in unobtrusive places, the widowed Duchess completed the great house as a tribute to her late husband. The final date of completion is not known, but as late as 1735 the Duchess was haggling with Rysbrack over the cost of Queen Anne's statue placed in the library. In 1732 the Duchess wrote "The Chappel is finish'd and more than half the Tomb there ready to set up".
Design and architecture
 Vanbrugh planned Blenheim in perspective; that is, to be best viewed from a distance. As the site covers some seven acres (28,000 m2) this is also a necessity.
The plan of the palace's principal block (or
Vanbrugh planned Blenheim in perspective; that is, to be best viewed from a distance. As the site covers some seven acres (28,000 m2) this is also a necessity.
The plan of the palace's principal block (or corps de logis
In architecture, a ''corps de logis'' () is the principal block of a large, (usually classical), mansion or palace. It contains the principal rooms, state apartments and an entry.Curl, James Stevens (2006). ''Oxford Dictionary of Architecture ...
) is a rectangle (''see plan'') pierced by two courtyards; these serve as little more than light wells. Contained behind the southern facade are the principal state apartments; on the east side are the suites of private apartments of the Duke and Duchess, and on the west along the entire length of the '' piano nobile'' is given a long gallery originally conceived as a picture gallery, but is now the library. The corps de logis is flanked by two further service blocks around square courtyards (''not shown in the plan''). The east court contains the kitchens, laundry, and other domestic offices, the west court adjacent to the chapel the stables and indoor riding school. The three blocks together form the "Great Court" designed to overpower the visitor arriving at the palace. Pilaster
In classical architecture, a pilaster is an architectural element used to give the appearance of a supporting column and to articulate an extent of wall, with only an ornamental function. It consists of a flat surface raised from the main wal ...
s and pillars abound, while from the roofs, themselves resembling those of a small town, great statues in the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
manner of St Peter's in Rome gaze down on the visitor below, who is rendered inconsequential. Other assorted statuary in the guise of martial trophies decorate the roofs, most notably Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great ...
standing atop the entrance pediment
Pediments are gables, usually of a triangular shape.
Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the lintel, or entablature, if supported by columns. Pediments can contain an overdoor and are usually topped by hood moulds.
A pedim ...
in front of two reclining chained French captives sculpted in the style of Michelangelo, and the English lion devouring the French cock, on the lower roofs. Many of these are by such masters as Grinling Gibbons
Grinling Gibbons (4 April 1648 – 3 August 1721) was an Anglo-Dutch sculptor and wood carver known for his work in England, including Windsor Castle and Hampton Court Palace, St Paul's Cathedral and other London churches, Petworth House and othe ...
.
In the design of great 18th-century houses comfort and convenience were subservient to magnificence, and this is certainly the case at Blenheim. This magnificence over creature comfort is heightened as the architect's brief was to create not only a home but also a national monument to reflect the power and civilisation of the nation. To create this monumental effect, Vanbrugh chose to design in a severe Baroque style, using great masses of stone to imitate strength and create shadow as decoration.
pantheon
Pantheon may refer to:
* Pantheon (religion), a set of gods belonging to a particular religion or tradition, and a temple or sacred building
Arts and entertainment Comics
*Pantheon (Marvel Comics), a fictional organization
* ''Pantheon'' (Lone S ...
than a family home. Vanbrugh also liked to employ what he called his "castle air", which he achieved by placing a low tower
A tower is a tall structure, taller than it is wide, often by a significant factor. Towers are distinguished from masts by their lack of guy-wires and are therefore, along with tall buildings, self-supporting structures.
Towers are specifi ...
at each corner of the central block and crowning the towers with vast belvederes of massed stone, decorated with curious finials (disguising the chimneys). Coincidentally these towers, which hint at the pylons of an Egyptian temple
Egyptian temples were built for the official worship of the ancient Egyptian deities, gods and in commemoration of the pharaohs in ancient Egypt and regions under Egyptian control. Temples were seen as houses for the gods or kings to whom they w ...
, further add to the heroic pantheonesque atmosphere of the building.
There are two approaches to the palace's grand entrance, one from the long straight drive through wrought iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.08%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4%). It is a semi-fused mass of iron with fibrous slag inclusions (up to 2% by weight), which give it a wood-like "grain" ...
gates directly into the Great Court; the other, equally if not more impressive, betrays Vanbrugh's true vision: the palace as a bastion or citadel
A citadel is the core fortified area of a town or city. It may be a castle, fortress, or fortified center. The term is a diminutive of "city", meaning "little city", because it is a smaller part of the city of which it is the defensive core.
I ...
, the true monument and home to a great warrior. Piercing the windowless, city-like curtain wall of the east court is the great East Gate, a monumental triumphal arch
A triumphal arch is a free-standing monumental structure in the shape of an archway with one or more arched passageways, often designed to span a road. In its simplest form a triumphal arch consists of two massive piers connected by an arch, cro ...
, more Egyptian in design than Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
. An optical illusion was created by tapering its walls to create an impression of even greater height. Confounding those who accuse Vanbrugh of impracticality, this gate is also the palace's water tower
A water tower is an elevated structure supporting a water tank constructed at a height sufficient to pressurize a distribution system for potable water, and to provide emergency storage for fire protection. Water towers often operate in conju ...
. Through the arch of the gate one views across the courtyard a second equally massive gate, that beneath the clock tower, through which one glimpses the Great Court.
 This view of the Duke as an
This view of the Duke as an omnipotent
Omnipotence is the quality of having unlimited power. Monotheistic religions generally attribute omnipotence only to the deity of their faith. In the monotheistic religious philosophy of Abrahamic religions, omnipotence is often listed as one ...
being is also reflected in the interior design of the palace, and indeed its axis to certain features in the park. It was planned that when the Duke dined in state in his place of honour in the great saloon, he would be the climax of a great procession of architectural mass aggrandising him rather like a proscenium. The line of celebration and honour of his victorious life began with the great column of victory surmounted by his statue and detailing his triumphs, and the next point on the great axis, planted with trees in the position of troops, was the epic Roman style bridge. The approach continues through the great portico into the hall, its ceiling painted by James Thornhill
Sir James Thornhill (25 July 1675 or 1676 – 4 May 1734) was an English painter of historical subjects working in the Italian baroque tradition. He was responsible for some large-scale schemes of murals, including the "Painted Hall" at the Ro ...
with the Duke's apotheosis, then on under a great triumphal arch, through the huge marble door-case with the Duke's marble effigy above it (bearing the ducal plaudit "Nor could Augustus better calm mankind"), and into the painted saloon, the most highly decorated room in the palace, where the Duke was to have sat enthroned.
The Duke was to have sat with his back to the great 30-tonne marble bust of his vanquished foe Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Ver ...
, positioned high above the south portico. Here the defeated King was humiliatingly forced to look down on the great parterre
A ''parterre'' is a part of a formal garden constructed on a level substrate, consisting of symmetrical patterns, made up by plant beds, low hedges or coloured gravels, which are separated and connected by paths. Typically it was the part of ...
and spoils of his conqueror (rather in the same way as severed heads were displayed generations earlier). The Duke did not live long enough to see this majestic tribute realised, and sit enthroned in this architectural vision. The Duke and Duchess moved into their apartments on the eastern side of the palace, but the entirety was not completed until after the Duke's death.
The palace has been Grade I listed on the National Heritage List for England
The National Heritage List for England (NHLE) is England's official database of protected heritage assets. It includes details of all English listed buildings, scheduled monuments, register of historic parks and gardens, protected shipwrecks, a ...
since August 1957.
Palace chapel
The palace chapel, as a consequence of the Duke's death, now obtained even greater importance. The design was altered by the Marlboroughs' friend the Earl of Godolphin, who placed the high altar in defiance of religious convention against the west wall, thus allowing the dominating feature to be the Duke's gargantuan tomb and sarcophagus. Commissioned by the Duchess in 1730, it was designed byWilliam Kent
William Kent (c. 1685 – 12 April 1748) was an English architect, landscape architect, painter and furniture designer of the early 18th century. He began his career as a painter, and became Principal Painter in Ordinary or court painter, bu ...
, and statues of the Duke and Duchess depicted as Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
and Caesarina adorn the great sarcophagus. In bas relief at the base of the tomb, the Duchess ordered to be depicted the surrender of Marshal Tallard
Camille d'Hostun de la Baume, duc de Tallard (14 February 1652 – 20 March 1728) was a French noble, diplomat and military commander, who became Marshal of France.
Military career
Tallard was granted a commission in the French army at the age of ...
. However, the theme throughout the palace of honouring the Duke did not reach its apotheosis until the dowager duchess's death in 1744. Then, the Duke's coffin was returned to Blenheim from its temporary resting place, Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the Unite ...
, and husband and wife were interred together and the tomb erected and completed.Henrietta Spencer-Churchill Now Blenheim had indeed become a pantheon and mausoleum. Successive Dukes and their wives are also interred in the vault beneath the chapel. Other members of family are interred in St. Martin's parish churchyard at Bladon
Bladon is a village and civil parish on the River Glyme about northwest of Oxford, Oxfordshire, England, notable as the burial place of Sir Winston Churchill. The 2011 Census recorded the parish's population as 898.
Places of worship St Mart ...
, a short distance from the palace.
Interior





 The internal layout of the rooms of the central block at Blenheim was defined by the court etiquette of the day. State apartments were designed as an axis of rooms of increasing importance and public use, leading to the chief room. The larger houses, like Blenheim, had two sets of state apartments each mirroring each other. The grandest and most public and important was the central saloon ''("B" in the plan'') which served as the communal state dining room. To either side of the saloon are suites of state apartments, decreasing in importance but increasing in privacy: the first room ''("C")'' would have been an audience chamber for receiving important guests, the next room ''("L")'' a private withdrawing room, the next room ''("M")'' would have been the bedroom of the occupier of the suite, thus the most private. One of the small rooms between the bedroom and the internal courtyard was intended as a dressing room. This arrangement is reflected on the other side of the saloon. The state apartments were intended for use by only the most important guests such as a visiting sovereign. On the left (east) side of the plan on either side of the bow room ''(marked "O")'' can be seen a smaller but nearly identical layout of rooms, which were the suites of the Duke and Duchess themselves. Thus, the bow room corresponds exactly to the saloon in terms of its importance to the two smaller suites.
Blenheim Palace was the birthplace of the 1st Duke's famous descendant,
The internal layout of the rooms of the central block at Blenheim was defined by the court etiquette of the day. State apartments were designed as an axis of rooms of increasing importance and public use, leading to the chief room. The larger houses, like Blenheim, had two sets of state apartments each mirroring each other. The grandest and most public and important was the central saloon ''("B" in the plan'') which served as the communal state dining room. To either side of the saloon are suites of state apartments, decreasing in importance but increasing in privacy: the first room ''("C")'' would have been an audience chamber for receiving important guests, the next room ''("L")'' a private withdrawing room, the next room ''("M")'' would have been the bedroom of the occupier of the suite, thus the most private. One of the small rooms between the bedroom and the internal courtyard was intended as a dressing room. This arrangement is reflected on the other side of the saloon. The state apartments were intended for use by only the most important guests such as a visiting sovereign. On the left (east) side of the plan on either side of the bow room ''(marked "O")'' can be seen a smaller but nearly identical layout of rooms, which were the suites of the Duke and Duchess themselves. Thus, the bow room corresponds exactly to the saloon in terms of its importance to the two smaller suites.
Blenheim Palace was the birthplace of the 1st Duke's famous descendant, Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
, whose life and times are commemorated by a permanent exhibition in the suite of rooms in which he was born ''(marked "K" on the plan)''. Blenheim Palace was designed with all its principal and secondary rooms on the ''piano nobile'', thus there is no great staircase of state: anyone worthy of such state would have no cause to leave the ''piano nobile''. Insofar as Blenheim does have a grand staircase, it is the series of steps in the Great Court which lead to the North Portico. There are staircases of various sizes and grandeur in the central block, but none are designed on the same scale of magnificence as the palace. James Thornhill
Sir James Thornhill (25 July 1675 or 1676 – 4 May 1734) was an English painter of historical subjects working in the Italian baroque tradition. He was responsible for some large-scale schemes of murals, including the "Painted Hall" at the Ro ...
painted the ceiling of the hall in 1716. It depicts Marlborough kneeling to Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great ...
and proffering a map of the Battle of Blenheim. The hall is high, and remarkable chiefly for its size and for its stone carvings by Gibbons, yet in spite of its immense size it is merely a vast anteroom
A vestibule (also anteroom, antechamber, or foyer) is a small room leading into a larger space such as a lobby, entrance hall or passage, for the purpose of waiting, withholding the larger space view, reducing heat loss, providing storage space ...
to the saloon.
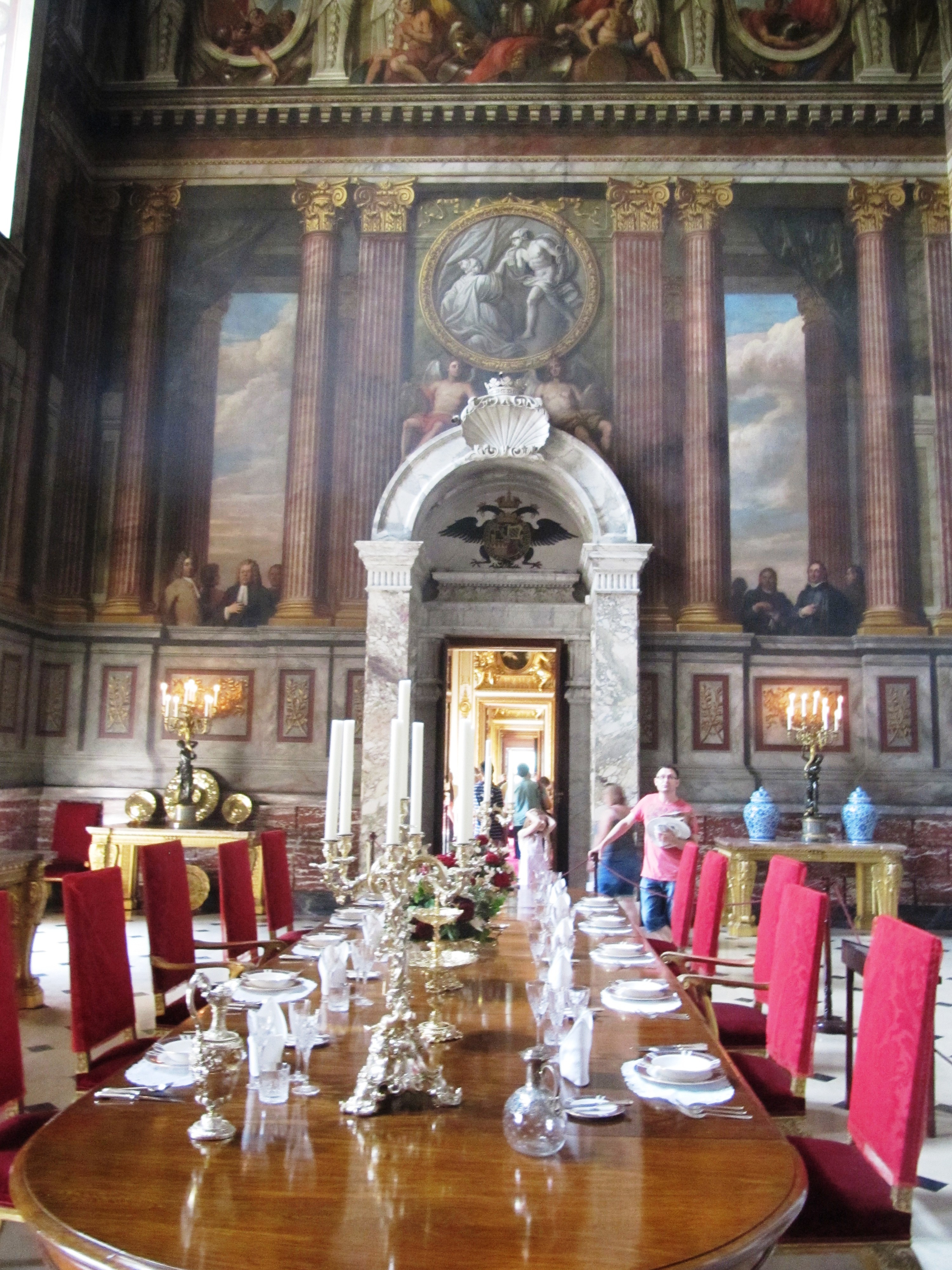
The saloon was also to have been painted by Thornhill, but the Duchess suspected him of overcharging, so the commission was given to Louis Laguerre. This room is an example of three-dimensional painting, or '' trompe l'œil'', "trick-the-eye", a fashionable painting technique at the time. The Peace Treaty of Utrecht was about to be signed, so all the elements in the painting represent the coming of peace. The domed ceiling is an allegorical representation of Peace: John Churchill is in the chariot, he holds a zigzag thunderbolt of war, and the woman who holds back his arm represents Peace. The walls depict all the nations of the world who have come together peacefully. Laguerre also included a self-portrait placing himself next to Dean Jones, chaplain to the 1st Duke, another enemy of the Duchess, although she tolerated him in the household because he could play a good hand at cards. To the right of the doorway leading into the first stateroom, Laguerre included the French spies, said to have big ears and eyes because they may still be spying. Of the four marble door-cases in the room displaying the Duke's crest as a prince of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, only one is by Gibbons, the other three were copied indistinguishably by the Duchess's cheaper craftsmen.
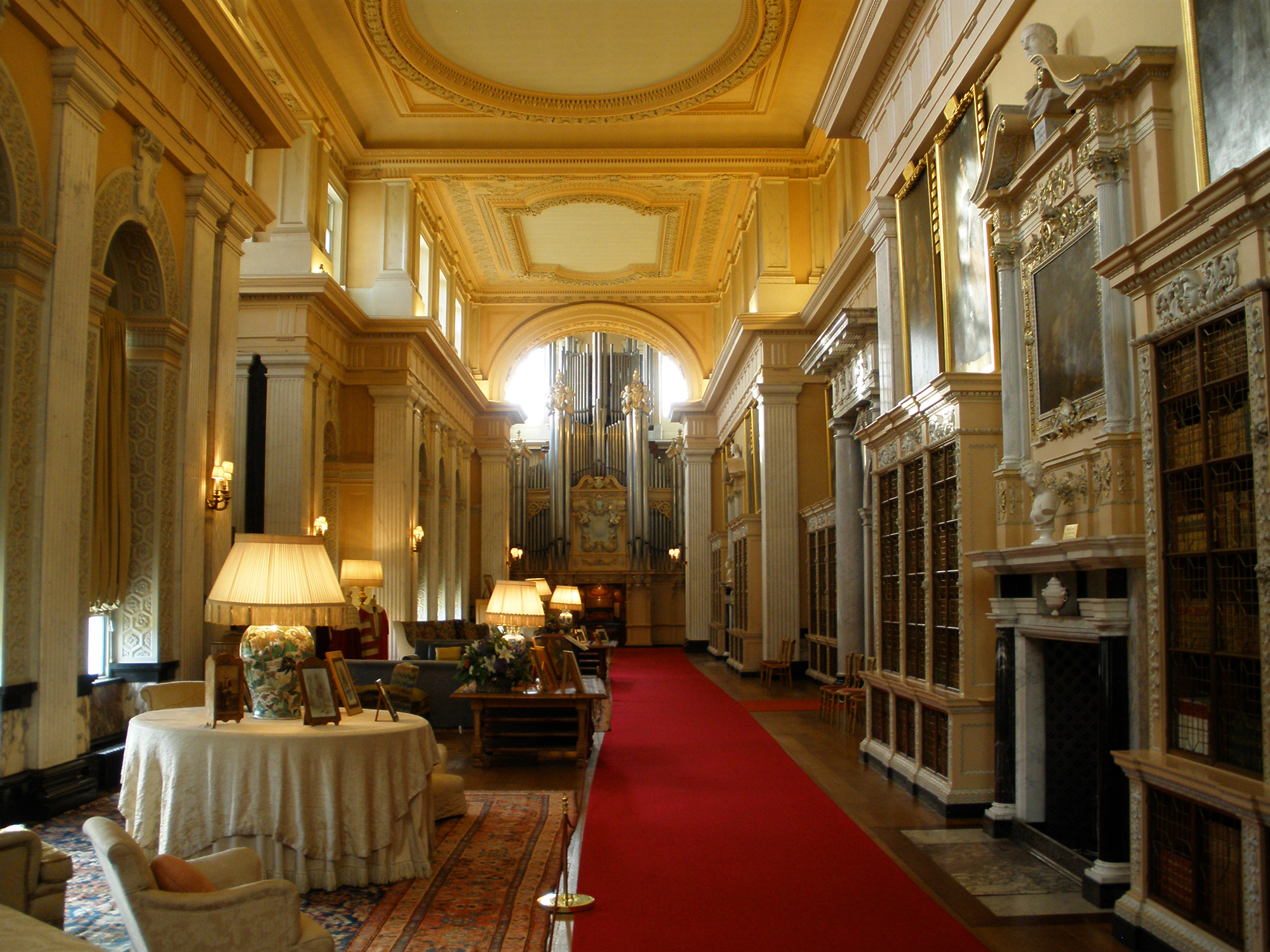
The third remarkable room is the long library designed by Nicholas Hawksmoor
Nicholas Hawksmoor (probably 1661 – 25 March 1736) was an English architect. He was a leading figure of the English Baroque style of architecture in the late-seventeenth and early-eighteenth centuries. Hawksmoor worked alongside the principa ...
in 1722–1725, ''(H)'', long, which was intended as a picture gallery. The ceiling has saucer dome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a m ...
s, which were to have been painted by Thornhill, had the Duchess not upset him. The palace, and in particular this room, was furnished with the many valuable artefacts the Duke had been given, or sequestered as the spoils of war, including a fine art collection. Here in the library, rewriting history in her own indomitable style, the Duchess set up a larger than life statue of Queen Anne, its base recording their friendship.
From the northern end of the library—in which is housed the largest pipe organ in private ownership in Europe, built by England's great organ builder Henry Willis & Sons
Henry Willis & Sons is a British firm of pipe organ builders founded in 1845. Although most of their installations have been in the UK, examples can be found in other countries.
Five generations of the Willis family served as principals of th ...
—access is obtained to the raised colonnade
In classical architecture, a colonnade is a long sequence of columns joined by their entablature, often free-standing, or part of a building. Paired or multiple pairs of columns are normally employed in a colonnade which can be straight or cur ...
which leads to the chapel ''(H)''. The chapel is perfectly balanced on the eastern side of the palace by the vaulted kitchen. This symmetrical balancing and equal weight given to both spiritual and physical nourishment would no doubt have appealed to Vanbrugh's renowned sense of humour, if not the Duchess'. The distance of the kitchen from even the private dining room ''("O" on the plan)'' was obviously of no consideration, hot food being of less importance than to avoid having to inhale the odour of cooking and proximity of servants.
Pipe organs
The Long Library organ was built in 1891 by the famous London firm ofHenry Willis & Sons
Henry Willis & Sons is a British firm of pipe organ builders founded in 1845. Although most of their installations have been in the UK, examples can be found in other countries.
Five generations of the Willis family served as principals of th ...
at a cost of £3,669. It replaced a previous organ built in 1888 by Isaac Abbott of Leeds, which was removed to St Swithun's church, Hither Green
Hither Green is a district in south-east London, England, in the London Borough of Lewisham. It forms the southern part of Lewisham, 6.6 miles (10.6 km) south-east of Charing Cross, and on the Prime Meridian.
Growing extensively with ...
. Originally erected in the central bay, with its back to the water terraces, the Norwich
Norwich () is a cathedral city and district of Norfolk, England, of which it is the county town. Norwich is by the River Wensum, about north-east of London, north of Ipswich and east of Peterborough. As the seat of the See of Norwich, with ...
firm of Norman & Beard moved it to the northwestern end of the library in 1902 and made a few tonal additions and, the following year, cleaned it. No further changes were made until 1930, when the Willis firm lowered the pitch to modern concert pitch
Concert pitch is the pitch reference to which a group of musical instruments are tuned for a performance. Concert pitch may vary from ensemble to ensemble, and has varied widely over music history. The most common modern tuning standard uses ...
: a Welte automatic player was added in 1931, with 70 rolls cut by Marcel Dupré
Marcel Jean-Jules Dupré () (3 May 1886 – 30 May 1971) was a French organist, composer, and pedagogue.
Biography
Born in Rouen into a wealthy musical family, Marcel Dupré was a child prodigy. His father Aimable Albert Dupré was titular o ...
, Joseph Bonnet
Joseph Élie Georges-Marie Bonnet (17 March 1884 – 2 August 1944) was a French composer and organist.
Biography
One of the major French pipe organists, Joseph Bonnet was born in Bordeaux. He first studied with his father, an organist at St ...
, Alfred Hollins, Edwin Lemare
Edwin Henry LemareFrequently misspelled "Lamare" in early publications (9 September 1865 – 24 September 1934) was an English organist and composer who lived the latter part of his life in the United States. He was one of the most highly regard ...
and Harry Goss-Custard also being supplied. This remained in use for some time: the Duke of the time is said to have frequently sat at the organ bench and pretended to play the organ to his guests and they would applaud at the end. This practice is said to have been halted abruptly when the player started before the Duke had reached the organ. This famous instrument is regularly maintained and is played by visiting organists throughout the year, but its condition is declining: a fundraising campaign has been launched for its complete restoration.
The organ in the chapel was built circa 1853 by Robert Postill of York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
: it is notable as a rare unaltered example of this fine builder's work, speaking boldly and clearly into a generous acoustic.
Park and gardens
 Blenheim sits in the centre of a large undulating park, a classic example of the
Blenheim sits in the centre of a large undulating park, a classic example of the English landscape garden
The English landscape garden, also called English landscape park or simply the English garden (french: Jardin à l'anglaise, it, Giardino all'inglese, german: Englischer Landschaftsgarten, pt, Jardim inglês, es, Jardín inglés), is a sty ...
movement and style. When Vanbrugh first cast his eyes over it in 1704 he immediately conceived a typically grandiose plan: through the park trickled the small River Glyme
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wa ...
, and Vanbrugh envisaged this marsh
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found a ...
y brook traversed by the "finest bridge in Europe". Thus, ignoring the second opinion offered by Sir Christopher Wren, the marsh was channelled into three small canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flo ...
-like streams and across it rose a bridge of huge proportions, so huge it was reported to contain some 30-odd rooms. While the bridge was indeed an amazing wonder, in this setting it appeared incongruous, causing Alexander Pope
Alexander Pope (21 May 1688 O.S. – 30 May 1744) was an English poet, translator, and satirist of the Enlightenment era who is considered one of the most prominent English poets of the early 18th century. An exponent of Augustan literature, ...
to comment: "the minnows, as under this vast arch they pass, murmur, 'how like whales we look, thanks to your Grace.'"
Horace Walpole saw it in 1760, shortly before Capability Brown's improvements: "the bridge, like the beggars at the old duchess's gate, begs for a drop of water and is refused." Another of Vanbrugh's schemes was the great parterre
A ''parterre'' is a part of a formal garden constructed on a level substrate, consisting of symmetrical patterns, made up by plant beds, low hedges or coloured gravels, which are separated and connected by paths. Typically it was the part of ...
, nearly half a mile long and as wide as the south front. Also in the park, completed after the 1st Duke's death, is the ''Column of Victory''. It is high and terminates a great avenue of elms leading to the palace, which were planted in the positions of Marlborough's troops
A troop is a military sub-subunit, originally a small formation of cavalry, subordinate to a squadron. In many armies a troop is the equivalent element to the infantry section or platoon. Exceptions are the US Cavalry and the King's Troo ...
at the Battle of Blenheim. Vanbrugh had wanted an obelisk
An obelisk (; from grc, ὀβελίσκος ; diminutive of ''obelos'', " spit, nail, pointed pillar") is a tall, four-sided, narrow tapering monument which ends in a pyramid-like shape or pyramidion at the top. Originally constructed by An ...
to mark the site of the former royal manor, and the trysts of Henry II which had taken place there, causing the 1st Duchess to remark, "If there were obelisks to bee made of all what our Kings have done of that sort, the countrey would bee stuffed with very odd things" (''sic''). The obelisk was never realised.

 Following the 1st Duke's death the Duchess concentrated most of her considerable energies on the completion of the palace itself, and the park remained relatively unchanged until the arrival of Capability Brown in 1764. The 4th Duke employed Brown who immediately began an English landscape garden scheme to naturalise and enhance the landscape, with tree planting, and man-made undulations. However, the feature with which he is forever associated is the lake, a huge stretch of water created by damming the River Glyme and ornamented by a series of cascades where the river flows in and out. The lake was narrowed at the point of Vanbrugh's grand bridge, but the three small canal-like streams trickling underneath it were completely absorbed by one river-like stretch. Brown's great achievement at this point was to actually flood and submerge beneath the water level the lower stories and rooms of the bridge itself, thus reducing its incongruous height and achieving what is regarded by many as the epitome of an English landscape. Brown also grassed over the great parterre and the Great Court. The latter was re-paved by Duchêne in the early 20th century. The 5th Duke was responsible for several other garden follies and novelties.
Following the 1st Duke's death the Duchess concentrated most of her considerable energies on the completion of the palace itself, and the park remained relatively unchanged until the arrival of Capability Brown in 1764. The 4th Duke employed Brown who immediately began an English landscape garden scheme to naturalise and enhance the landscape, with tree planting, and man-made undulations. However, the feature with which he is forever associated is the lake, a huge stretch of water created by damming the River Glyme and ornamented by a series of cascades where the river flows in and out. The lake was narrowed at the point of Vanbrugh's grand bridge, but the three small canal-like streams trickling underneath it were completely absorbed by one river-like stretch. Brown's great achievement at this point was to actually flood and submerge beneath the water level the lower stories and rooms of the bridge itself, thus reducing its incongruous height and achieving what is regarded by many as the epitome of an English landscape. Brown also grassed over the great parterre and the Great Court. The latter was re-paved by Duchêne in the early 20th century. The 5th Duke was responsible for several other garden follies and novelties.
Sir William Chambers
__NOTOC__
Sir William Chambers (23 February 1723 – 10 March 1796) was a Swedish-Scottish architect, based in London. Among his best-known works are Somerset House, and the pagoda at Kew. Chambers was a founder member of the Royal Academy.
Bio ...
, assisted by John Yenn
John Yenn (1750–1821) was a notable 18th-century English architect.
Life
Yenn was born on 8 March 1750. He was a student at the Royal Academy from September 1769. He was elected an associate of the academy in 1774 and a full academician in ...
, was responsible for the small summerhouse known as "The Temple of Diana" down by the lake, where in 1908 Winston Churchill proposed to his future wife.
The extensive landscaped park, woodlands and formal gardens of Blenheim are Grade I listed on the Register of Historic Parks and Gardens. Blenheim Park is a Site of Special Scientific Interest.
Failing fortunes
 On the death of the 1st Duke in 1722, as both his sons were dead, he was succeeded by his daughter
On the death of the 1st Duke in 1722, as both his sons were dead, he was succeeded by his daughter Henrietta Henrietta may refer to:
* Henrietta (given name), a feminine given name, derived from the male name Henry
Places
* Henrietta Island in the Arctic Ocean
* Henrietta, Mauritius
* Henrietta, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
United States
* Henrie ...
. This was an unusual succession and required a special Act of Parliament, as only sons can usually succeed to an English dukedom. When Henrietta died, the title passed to Marlborough's grandson Charles Spencer, Earl of Sunderland, whose mother was Marlborough's second daughter Anne
Anne, alternatively spelled Ann, is a form of the Latin female given name Anna. This in turn is a representation of the Hebrew Hannah, which means 'favour' or 'grace'. Related names include Annie.
Anne is sometimes used as a male name in the ...
.
The 1st Duke, as a soldier, was not a rich man and what fortune he possessed was mostly used for finishing the palace. In comparison with other British ducal families, the Marlboroughs were not very wealthy. Yet they existed quite comfortably until the time of the 5th Duke of Marlborough
George Spencer-Churchill, 5th Duke of Marlborough FSA (6 March 1766 – 5 March 1840), styled Marquess of Blandford until 1817, was a British nobleman, politician, peer, and collector of antiquities and books.
He was the first one to specifi ...
(1766–1840), a spendthrift
A spendthrift (also profligate or prodigal) is someone who is extravagant and recklessly wasteful with money, often to a point where the spending climbs well beyond his or her means. "Spendthrift" derives from an obsolete sense of the word "thrift" ...
who considerably depleted the family's remaining fortune. He was eventually forced to sell other family estates, but Blenheim was safe from him as it was entail
In English common law, fee tail or entail is a form of trust established by deed or settlement which restricts the sale or inheritance of an estate in real property and prevents the property from being sold, devised by will, or otherwise alien ...
ed. This did not prevent him selling the Marlboroughs' Boccaccio
Giovanni Boccaccio (, , ; 16 June 1313 – 21 December 1375) was an Italian writer, poet, correspondent of Petrarch, and an important Renaissance humanist. Born in the town of Certaldo, he became so well known as a writer that he was some ...
for a mere £875 and his own library in over 4000 lots. On his death in 1840, his profligacy left the estate and family with financial problems.
By the 1870s, the Marlboroughs were in severe financial trouble and in 1875 the 7th Duke sold the ''Marriage of Cupid and Psyche
Cupid and Psyche is a story originally from ''Metamorphoses'' (also called '' The Golden Ass''), written in the 2nd century AD by Lucius Apuleius Madaurensis (or Platonicus). The tale concerns the overcoming of obstacles to the love between P ...
'', together with the famed Marlborough gems, at auction for £10,000. However this was not enough to save the family. In 1880, the 7th Duke was forced to petition Parliament to break the protective entail on the Palace and its contents. This was achieved under the Blenheim Settled Estates Act 1880 and the door was now open for wholesale dispersal of Blenheim and its contents. The first victim was the great Sunderland Library which was sold in 1882, including such volumes as ''The Epistles of Horace'', printed at Caen in 1480, and the works of Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
, printed at Verona
Verona ( , ; vec, Verona or ) is a city on the Adige River in Veneto, Italy, with 258,031 inhabitants. It is one of the seven provincial capitals of the region. It is the largest city municipality in the region and the second largest in nor ...
in 1648. The 18,000 volumes raised almost £60,000. The sales continued to denude the palace: Raphael
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino, better known as Raphael (; or ; March 28 or April 6, 1483April 6, 1520), was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. His work is admired for its clarity of form, ease of composition, and visual a ...
's ''Ansidei Madonna
The ''Ansidei Madonna'' (Italian: Pala Ansidei) is a 1505–1507 painting by the Italian High Renaissance artist Raphael, painted during his Florentine period. It shows the Blessed Virgin Mary sitting on a wooden throne, with the child Christ ...
'' was sold for £70,000; Van Dyck
Sir Anthony van Dyck (, many variant spellings; 22 March 1599 – 9 December 1641) was a Brabantian Flemish Baroque artist who became the leading court painter in England after success in the Southern Netherlands and Italy.
The seventh ...
's Equestrian Portrait of Charles I realised £17,500; and finally the "pièce de résistance" of the collection, Peter Paul Rubens
Sir Peter Paul Rubens (; ; 28 June 1577 – 30 May 1640) was a Flemish artist and diplomat from the Duchy of Brabant in the Southern Netherlands (modern-day Belgium). He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque tradi ...
' ''Rubens, His Wife Helena Fourment, and Their Son Peter Paul, and Their Son Frans (1633–1678)'', which had been given by the city of Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
to the 1st Duke in 1704, was also sold, and is now in the Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 ...
in New York City.
These sums of money, vast by the standards of the day, failed to cover the debts and the maintenance of the great palace remained beyond the Marlboroughs' resources. These had always been small in relation to their ducal rank and the size of their house. The British agricultural depression, which started in the 1870s, added to the family's problems. When the 9th Duke inherited in 1892, the land was generating dwindling income.
9th Duke of Marlborough

 Charles, 9th Duke of Marlborough (1871–1934) can be credited with saving both the palace and the family. Inheriting the near-bankrupt dukedom in 1892, he was forced to find a quick and drastic solution to the problems. Prevented by the strict social dictates of late 19th-century society from earning money, he was left with one solution: he had to marry into money. In November 1896 he coldly and openly without love married the American railroad heiress
Charles, 9th Duke of Marlborough (1871–1934) can be credited with saving both the palace and the family. Inheriting the near-bankrupt dukedom in 1892, he was forced to find a quick and drastic solution to the problems. Prevented by the strict social dictates of late 19th-century society from earning money, he was left with one solution: he had to marry into money. In November 1896 he coldly and openly without love married the American railroad heiress Consuelo Vanderbilt
Consuelo Vanderbilt-Balsan (formerly Consuelo Spencer-Churchill, Duchess of Marlborough; born Consuelo Vanderbilt; March 2, 1877 – December 6, 1964) was a socialite and a member of the prominent American Vanderbilt family. Her first marriage ...
.
The marriage was celebrated following lengthy negotiations with her divorced parents: her mother, Alva Vanderbilt
Alva Erskine Belmont (née Smith; January 17, 1853 – January 26, 1933), known as Alva Vanderbilt from 1875 to 1896, was an American multi-millionaire socialite and women's suffrage activist. She was noted for her energy, intelligence, strong ...
, was desperate to see her daughter a duchess, and the bride's father, William Vanderbilt, paid for the privilege. The final price was $2,500,000 ($ million today) in 50,000 shares of the capital stock of the Beech Creek Railway Company with a minimum 4% dividend guaranteed by the New York Central Railroad Company. The couple were given a further annual income each of $100,000 for life.
The teenage Consuelo had been locked in her room by her mother until she agreed to the marriage. The marriage settlement was actually signed in the vestry of St. Thomas Episcopal Church, New York, immediately after the wedding vows had been made. In the carriage leaving the church, Marlborough told Consuelo he loved another woman, and would never return to America, as he "despised anything that was not British".
The replenishing of Blenheim began on the honeymoon itself, with the replacement of the Marlborough gems. Tapestries, paintings and furniture were bought in Europe to fill the depleted palace. On their return the Duke began an exhaustive restoration and redecoration of the palace. The state rooms to the west of the saloon were redecorated with gilt boiseries
Panelling (or paneling in the U.S.) is a millwork wall covering constructed from rigid or semi-rigid components. These are traditionally interlocking wood, but could be plastic or other materials.
Panelling was developed in antiquity to make roo ...
in imitation of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, ...
. Vanbrugh's subtle rivalry to Louis XIV's great palace was now completely undermined, as the interiors became mere pastiches of those of the greater palace.
While this redecoration may not have been without fault (and the Duke later regretted it), other improvements were better received. Another problem caused by the redecoration was that the state and principal bedrooms were now moved upstairs, thus rendering the state rooms an enfilade
Enfilade and defilade are concepts in military tactics used to describe a military formation's exposure to enemy fire. A formation or position is "in enfilade" if weapon fire can be directed along its longest axis. A unit or position is "in de ...
of rather similar and meaningless drawing room
A drawing room is a room in a house where visitors may be entertained, and an alternative name for a living room. The name is derived from the 16th-century terms withdrawing room and withdrawing chamber, which remained in use through the 17th cent ...
s. On the west terrace the French landscape architect Achille Duchêne
Achille Duchêne (1866 — 1947) was a French garden designer who worked in the grand manner established by André Le Nôtre. The son of the landscaper
Henri Duchêne, Achille Duchêne was the garden designer most in demand among high French societ ...
was employed to create a water garden. On a second terrace below this were placed two great fountains in the style of Bernini, scaled models of those in the Piazza Navona
Piazza Navona () is a public open space in Rome, Italy. It is built on the site of the Stadium of Domitian, built in the 1st century AD, and follows the form of the open space of the stadium. The ancient Romans went there to watch the '' agones' ...
which had been presented to the 1st Duke.
Gladys Deacon
Gladys Marie Spencer-Churchill, Duchess of Marlborough (''née'' Deacon; 7 February 1881 – 13 October 1977) was a French American aristocrat and socialite. She was the mistress and later the second wife of Charles Spencer-Churchill, 9th D ...
, who was of an artistic disposition, and a painting of her eyes remains on the ceiling of the great north portico (''see secondary lead image''). A lower terrace was decorated with sphinxes modelled on Gladys and executed by W. Ward Willis in 1930. Before her marriage, while staying with the Marlboroughs, she caused a diplomatic incident by encouraging the young Crown Prince Wilhelm of Germany to form an attachment with her.
The prince had given her an heirloom ring, which the combined diplomatic services of two empires were charged to recover. After her marriage, Gladys was in the habit of dining with the Duke with a revolver by the side of her plate. Tiring of her, the Duke was temporarily forced to close Blenheim, and turn off the utilities to drive her out. They subsequently separated but did not divorce. The Duke died in 1934. His widow died in 1977.
The 9th Duke was succeeded by his and Consuelo Vanderbilt's eldest son, John, 10th Duke of Marlborough (1897–1972), who after eleven years as a widower, remarried at the age of 74, to (Frances) Laura Charteris, formerly the wife of the 2nd Viscount Long
__NOTOC__
Viscount Long, of Wraxall in the County of Wiltshire, is a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom.
It was created in 1921 for the Conservative politician Walter Long, who had previously served as Member of Parliament, Presiden ...
and the 3rd Earl of Dudley
Earl of Dudley, of Dudley Castle in the County of Stafford (now the West Midlands), is a title that has been created twice in the Peerage of the United Kingdom, both times for members of the Ward family.
History
Dudley was first used for a p ...
, and granddaughter of the 11th Earl of Wemyss. The marriage was short-lived, however; the Duke died just six weeks later, on 11 March 1972. The bereaved Duchess complained of "the gloom and inhospitality of Blenheim" after his death, and soon moved out. In her autobiography, ''Laughter from a Cloud'' (1980), she referred to Blenheim Palace as "The Dump". She died in London in 1990.
Second World War
During the war the 10th Duke welcomed the boys from Malvern College as evacuees. In September 1940 Security Service (MI5) was allowed to use the palace as its base until the end of the war.The palace today

 The palace remains the home of the Dukes of Marlborough, the present incumbent of the title being Charles James (Jamie) Spencer-Churchill, 12th Duke of Marlborough. Charles James succeeded to the Dukedom upon his
The palace remains the home of the Dukes of Marlborough, the present incumbent of the title being Charles James (Jamie) Spencer-Churchill, 12th Duke of Marlborough. Charles James succeeded to the Dukedom upon his father
A father is the male parent of a child. Besides the paternal bonds of a father to his children, the father may have a parental, legal, and social relationship with the child that carries with it certain rights and obligations. An adoptive fathe ...
's death on 16 October 2014.
, the Marlboroughs still have to tender a copy of the French royal flag to the Monarch on the anniversary of the Battle of Blenheim as rent for the land that Blenheim Palace stands on.
The palace, park, and gardens are open to the public on payment of an entry fee (maximum , ). Several tourist entertainment attractions separate from the palace are the Formal and Walled Gardens, Marlborough Maze and the Butterfly House. The palace is linked to the Walled Garden by a miniature railway, the Blenheim Park Railway
Blenheim Park Railway is a gauge miniature railway operating in the grounds of Blenheim Palace, in Oxfordshire, England.
History
A portable track for a very small gauge railway was run from 1955, but in 1960 a permanent oval track was built to t ...
.
Lord Edward Spencer-Churchill, the brother of the current Duke, wished to feature a contemporary art programme within the historic setting of the palace where he spent his childhood. He founded Blenheim Art Foundation (BAF), a non-profit organisation, to present large-scale contemporary art exhibitions. BAF launched on 1 October 2014 with the UK's largest ever exhibition by Ai Weiwei
Ai Weiwei (, ; born 28 August 1957) is a Chinese contemporary artist, documentarian, and activist. Ai grew up in the far northwest of China, where he lived under harsh conditions due to his father's exile. As an activist, he has been openly c ...
. The foundation was conceived to give a vast number of people access to innovative contemporary artists working in the context of this historic palace.
In September 2019, on the occasion of the opening of Maurizio Cattelan
Maurizio Cattelan (born 21 September 1960) is an Italian artist. Known primarily for his hyperrealistic sculptures and installations, Cattelan's practice also includes curating and publishing. His satirical approach to art has resulted in him bei ...
's show "Victory is not an option", the palace was the scene of a robbery: unknown thieves entered the palace at night time, just after the opening of the show, and stole a golden toilet, valued at $5 million, which had been installed by the artist in one of the bathrooms.
The public have free access to about five miles (8 km) of public rights of way through the Great Park area of the grounds, which are accessible from Old Woodstock and from the Oxfordshire Way, and which are close to the Column of Victory.See Ordnance Survey maps via map sources:
See also
* Blenheim Palace in film and media *List of Baroque residences
This is a list of Baroque architecture, Baroque palaces and Residenz, residences built in the late 17th and 18th centuries. Baroque architecture is a building style of the Baroque, Baroque era, begun in late 16th-century Italy and spread in Europe ...
* ''Noble Households
''Noble Households: Eighteenth-Century Inventories of Great English Houses'' presents transcripts of inventories of nine great country houses and four London town houses as a tribute to the late historian John Cornforth.
Summary
The inventori ...
'' – book with Blenheim Palace inventory of 1740
Footnotes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * Cornforth, John (2004). ''Early Georgian Interiors''. New Haven, Conn.; London: Yale University Press for the Paul Mellon Centre for Studies in British Art, pp. 275–9 * Murdoch, Tessa (ed.) (2006). ''Noble Households
''Noble Households: Eighteenth-Century Inventories of Great English Houses'' presents transcripts of inventories of nine great country houses and four London town houses as a tribute to the late historian John Cornforth.
Summary
The inventori ...
: Eighteenth-Century Inventories of Great English Houses. A Tribute to John Cornforth
Sir John Warcup Cornforth Jr., (7 September 1917 – 8 December 2013) was an AustralianBritish chemist who won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1975 for his work on the stereochemistry of enzyme-catalysed reactions, becoming the only Nobel l ...
''. Cambridge: John Adamson, pp. 273–83
*
External links
*Churchill by Oswald Birley - UK Parliament Living Heritage
Blenheim Art Foundation
Blenheim Palace
at Cotswolds Website * * {{Authority control 1722 establishments in England Baroque palaces Birthplaces of individual people English Baroque architecture English gardens in English Landscape Garden style Gardens by Capability Brown Gardens in Oxfordshire Grade I listed buildings in Oxfordshire Grade I listed houses Grade I listed palaces Grade I listed parks and gardens in Oxfordshire Historic house museums in Oxfordshire Houses completed in 1722 Houses in Oxfordshire John Vanbrugh buildings Mazes Nicholas Hawksmoor buildings Palaces in England Parks and open spaces in Oxfordshire Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Oxfordshire Spencer-Churchill family residences Tourist attractions in Oxfordshire Vanderbilt family residences West Oxfordshire District Winston Churchill World Heritage Sites in England