Bishop of London on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The bishop of London is the ordinary of the
(Accessed 18 December 2017)Diocese of London – Mullally's installation as Bishop of London
(Accessed 26 January 2018) The diocesan bishop of London has had direct episcopal oversight in the Two Cities area (the
 The first mention of Christianity in England comes from
The first mention of Christianity in England comes from 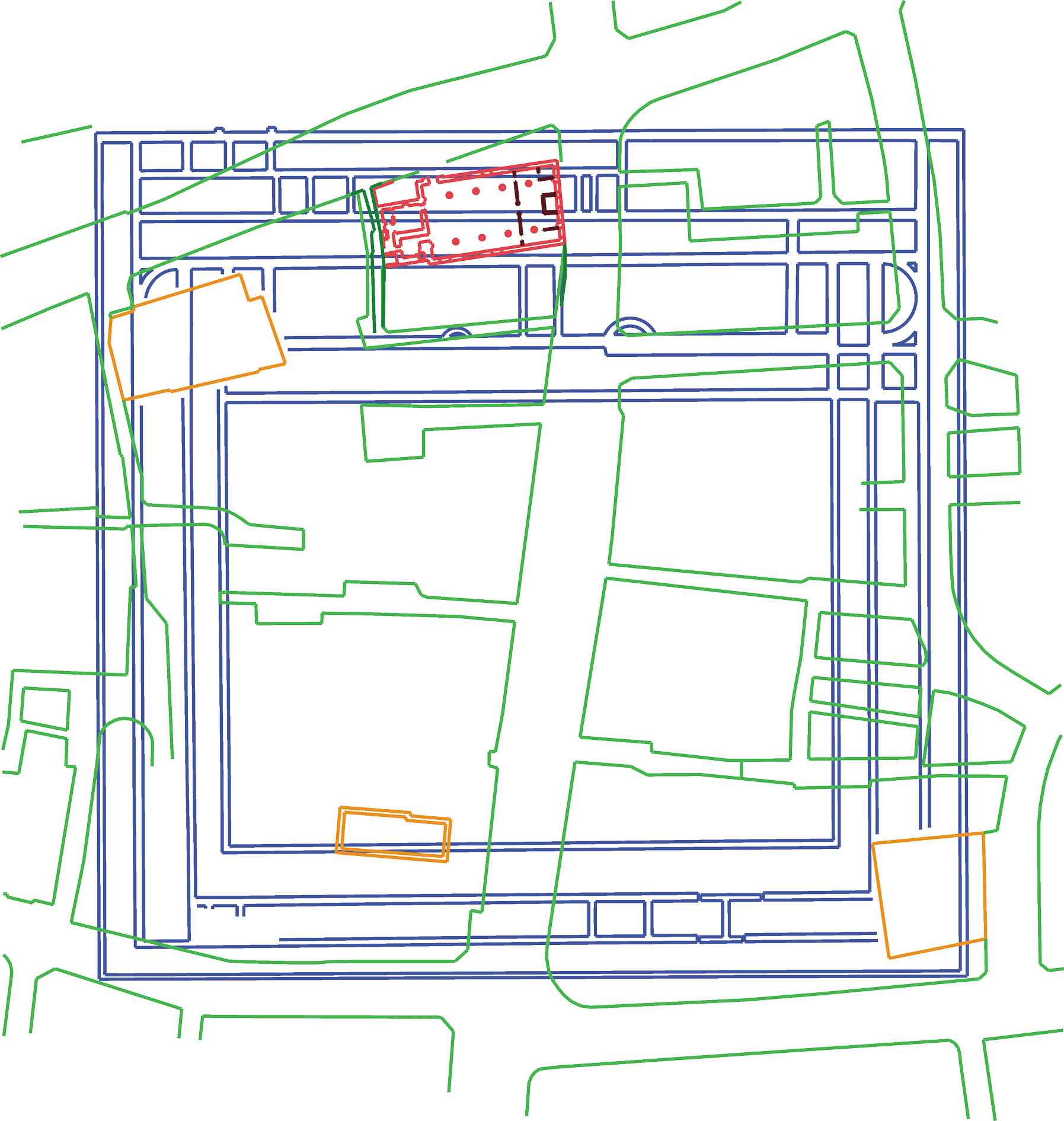 There is a medieval tradition which maintains the church was founded by King Lucius in AD 199. If St Peter's was built in the Roman era, it would make the church contemporaneous to the Romano-British church at Silchester, similarly built adjacent to the Roman Basilica and most likely pre-Constantine in age.
Some caution may be exercised in this respect however, as other research suggests it very rare for early English Christian churches to be founded in pagan temples, and that when temples were turned into churches, this occurred later, in the late sixth century onwards. Historians seem to be more confident that early English Christian churches met in private homes, and that some Roman villas also installed places of Christian worship.
Whether the Lucius story is a fiction, or whether there was actually a church deliberately erected over the shrine room is unclear and could only be settled by archaeological exploration under St Peter's. However, it is interesting that whilst four medieval churches were built around the same time on the foundations of the Roman Basilica and forum, the London city authorities in 1417 determined that St Peter's dated back to Roman times, and indeed was the original seat of English Christianity. This suggests there may have been something extra in St Peter's location and longevity which justifies it predating the others.
In 1995, a large and ornate 4th-century church was discovered on
There is a medieval tradition which maintains the church was founded by King Lucius in AD 199. If St Peter's was built in the Roman era, it would make the church contemporaneous to the Romano-British church at Silchester, similarly built adjacent to the Roman Basilica and most likely pre-Constantine in age.
Some caution may be exercised in this respect however, as other research suggests it very rare for early English Christian churches to be founded in pagan temples, and that when temples were turned into churches, this occurred later, in the late sixth century onwards. Historians seem to be more confident that early English Christian churches met in private homes, and that some Roman villas also installed places of Christian worship.
Whether the Lucius story is a fiction, or whether there was actually a church deliberately erected over the shrine room is unclear and could only be settled by archaeological exploration under St Peter's. However, it is interesting that whilst four medieval churches were built around the same time on the foundations of the Roman Basilica and forum, the London city authorities in 1417 determined that St Peter's dated back to Roman times, and indeed was the original seat of English Christianity. This suggests there may have been something extra in St Peter's location and longevity which justifies it predating the others.
In 1995, a large and ornate 4th-century church was discovered on
Diocese of London website
* ttp://archives.lambethpalacelibrary.org.uk/calmview/Record.aspx?src=CalmView.Catalog&id=fp The papers of the Bishops of London covering 1423–1945 are held at Lambeth Palace Library {{Portal bar, Christianity, England, London London, Bishop of
Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
's Diocese of London
The Diocese of London forms part of the Church of England's Province of Canterbury in England.
It lies directly north of the Thames, covering and all or part of 17 London boroughs. This corresponds almost exactly to the historic county of ...
in the Province of Canterbury
The Province of Canterbury, or less formally the Southern Province, is one of two ecclesiastical provinces which constitute the Church of England. The other is the Province of York (which consists of 12 dioceses).
Overview
The Province consi ...
. By custom the Bishop is also Dean of the Chapel Royal since 1723.
The diocese covers of 17 boroughs of Greater London
Greater London is an administrative area in England, coterminous with the London region, containing most of the continuous urban area of London. It contains 33 local government districts: the 32 London boroughs, which form a Ceremonial count ...
north of the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, s ...
(historically the City of London
The City of London, also known as ''the City'', is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county and Districts of England, local government district with City status in the United Kingdom, city status in England. It is the Old town, his ...
and the County of Middlesex
Middlesex (; abbreviation: Middx) is a Historic counties of England, former county in South East England, now mainly within Greater London. Its boundaries largely followed three rivers: the River Thames, Thames in the south, the River Lea, Le ...
) and a small part of the County of Surrey
Surrey () is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Greater London to the northeast, Kent to the east, East Sussex, East and West Sussex to the south, and Hampshire and Berkshire to the wes ...
(the district of Spelthorne, historically part of Middlesex). The see is in the City of London, where the seat is St Paul's Cathedral
St Paul's Cathedral, formally the Cathedral Church of St Paul the Apostle, is an Anglican cathedral in London, England, the seat of the Bishop of London. The cathedral serves as the mother church of the Diocese of London in the Church of Engl ...
, which was founded as a cathedral in 604 and was rebuilt from 1675 following the Great Fire of London
The Great Fire of London was a major conflagration that swept through central London from Sunday 2 September to Wednesday 5 September 1666, gutting the medieval City of London inside the old London Wall, Roman city wall, while also extendi ...
(1666).
Third in seniority in the Church of England after the archbishops of Canterbury
Canterbury (, ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and UNESCO World Heritage Site, in the county of Kent, England; it was a county borough until 1974. It lies on the River Stour, Kent, River Stour. The city has a mild oceanic climat ...
and York
York is a cathedral city in North Yorkshire, England, with Roman Britain, Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Foss, Foss. It has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a Yor ...
, the bishop is one of five senior bishops who sit as of right as one of the 26 Lords Spiritual
The Lords Spiritual are the bishops of the Church of England who sit in the House of Lords of the United Kingdom. Up to 26 of the 42 diocesan bishops and archbishops of the Church of England serve as Lords Spiritual (not including retired bish ...
in the House of Lords
The House of Lords is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the lower house, the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. One of the oldest ext ...
(for the remaining diocesan bishops of lesser rank, seats are attained upon vacancy, determined by chronological seniority). The other four senior bishops are the archbishop of Canterbury, the archbishop of York, the bishop of Durham
The bishop of Durham is head of the diocese of Durham in the province of York. The diocese is one of the oldest in England and its bishop is a member of the House of Lords. Paul Butler (bishop), Paul Butler was the most recent bishop of Durham u ...
and the bishop of Winchester
The Bishop of Winchester is the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Winchester in the Church of England. The bishop's seat (''cathedra'') is at Winchester Cathedral in Hampshire.
The Bishop of Winchester has always held ''ex officio'' the offic ...
.
The bishop's residence is The Old Deanery, Dean's Court, City of London
The City of London, also known as ''the City'', is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county and Districts of England, local government district with City status in the United Kingdom, city status in England. It is the Old town, his ...
. Previously, until 1973, Fulham Palace
Fulham Palace lies on the north bank of the River Thames in Fulham, London, previously in the former English county of Middlesex. It is the site of the Manor of Fulham dating back to Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Saxon times and in the c ...
in West London was the residence for over 1300 years, and from the 18th century, the bishop also had chambers at London House next to the Bishop's Chapel in Aldersgate Street.
The current (133rd) bishop of London is Sarah Mullally
Dame Sarah Elisabeth Mullally (; born 26 March 1962) is a British Anglican prelate and former nurse. Bishop of London since 2018,
. She was confirmed on 8 March 2018 after acting in post immediately after her canonical election on 25 January 2018.Diocese of London – Next Bishop of London announced(Accessed 18 December 2017)Diocese of London – Mullally's installation as Bishop of London
(Accessed 26 January 2018) The diocesan bishop of London has had direct episcopal oversight in the Two Cities area (the
City of London
The City of London, also known as ''the City'', is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county and Districts of England, local government district with City status in the United Kingdom, city status in England. It is the Old town, his ...
and the City of Westminster
The City of Westminster is a London borough with City status in the United Kingdom, city status in Greater London, England. It is the site of the United Kingdom's Houses of Parliament and much of the British government. It contains a large par ...
) since the institution of the London area scheme in 1979.
History
 The first mention of Christianity in England comes from
The first mention of Christianity in England comes from Tertullian
Tertullian (; ; 155 – 220 AD) was a prolific Early Christianity, early Christian author from Roman Carthage, Carthage in the Africa (Roman province), Roman province of Africa. He was the first Christian author to produce an extensive co ...
, possibly writing in the early 200s, but the first mention of an implied church in London relates to a Bishop of London, either Restitus or Aldephius, attending the Council of Arles in 314 AD.
The location of Londinium's original cathedral is uncertain. The present structure of St Peter upon Cornhill
St Peter upon Cornhill is an Anglican church on the corner of Cornhill and Gracechurch Street in the City of London of medieval, or possibly Roman origin. It was destroyed in the Great Fire of London in 1666 and rebuilt to the designs of Sir C ...
was designed by Christopher Wren
Sir Christopher Wren FRS (; – ) was an English architect, astronomer, mathematician and physicist who was one of the most highly acclaimed architects in the history of England. Known for his work in the English Baroque style, he was ac ...
following the Great Fire in 1666 and stands upon the highest point in the area of old Londinium, but possibly more significantly directly above the location of a pagan shrine room (aedes
''Aedes'' (also known as the tiger mosquito) is a genus of mosquitoes originally found in tropical and subtropical zones, but now found on all continents except Antarctica. Some species have been spread by human activity: ''Aedes albopictus'', ...
) within the great Roman London basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica (Greek Basiliké) was a large public building with multiple functions that was typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek Eas ...
.
 There is a medieval tradition which maintains the church was founded by King Lucius in AD 199. If St Peter's was built in the Roman era, it would make the church contemporaneous to the Romano-British church at Silchester, similarly built adjacent to the Roman Basilica and most likely pre-Constantine in age.
Some caution may be exercised in this respect however, as other research suggests it very rare for early English Christian churches to be founded in pagan temples, and that when temples were turned into churches, this occurred later, in the late sixth century onwards. Historians seem to be more confident that early English Christian churches met in private homes, and that some Roman villas also installed places of Christian worship.
Whether the Lucius story is a fiction, or whether there was actually a church deliberately erected over the shrine room is unclear and could only be settled by archaeological exploration under St Peter's. However, it is interesting that whilst four medieval churches were built around the same time on the foundations of the Roman Basilica and forum, the London city authorities in 1417 determined that St Peter's dated back to Roman times, and indeed was the original seat of English Christianity. This suggests there may have been something extra in St Peter's location and longevity which justifies it predating the others.
In 1995, a large and ornate 4th-century church was discovered on
There is a medieval tradition which maintains the church was founded by King Lucius in AD 199. If St Peter's was built in the Roman era, it would make the church contemporaneous to the Romano-British church at Silchester, similarly built adjacent to the Roman Basilica and most likely pre-Constantine in age.
Some caution may be exercised in this respect however, as other research suggests it very rare for early English Christian churches to be founded in pagan temples, and that when temples were turned into churches, this occurred later, in the late sixth century onwards. Historians seem to be more confident that early English Christian churches met in private homes, and that some Roman villas also installed places of Christian worship.
Whether the Lucius story is a fiction, or whether there was actually a church deliberately erected over the shrine room is unclear and could only be settled by archaeological exploration under St Peter's. However, it is interesting that whilst four medieval churches were built around the same time on the foundations of the Roman Basilica and forum, the London city authorities in 1417 determined that St Peter's dated back to Roman times, and indeed was the original seat of English Christianity. This suggests there may have been something extra in St Peter's location and longevity which justifies it predating the others.
In 1995, a large and ornate 4th-century church was discovered on Tower Hill
Tower Hill is the area surrounding the Tower of London in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. It is infamous for the public execution of high status prisoners from the late 14th to the mid 18th century. The execution site on the higher gro ...
, which seems to have mimicked St Ambrose's cathedral
A cathedral is a church (building), church that contains the of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, Annual conferences within Methodism, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually s ...
in the imperial capital at Milan
Milan ( , , ; ) is a city in northern Italy, regional capital of Lombardy, the largest city in Italy by urban area and the List of cities in Italy, second-most-populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of nea ...
on a still-larger scale. This possible cathedral was built between 350 and 400 out of stone taken from other buildings, including its veneer of black marble. It is perfectly possible that the stone came from the London basilica and forum, which was demolished and levelled around the same time. The 4th-century church was burnt down in the early 5th century.
According to a 12th-century list, which may be recorded by Jocelyne of Furness, there had been 14 "archbishops" of London, claiming London's Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
community was founded in the 2nd century under the legendary King Lucius and his missionary saints Fagan, Deruvian, Elvanus, and Medwin. None of that is considered credible by modern historians.
Following the establishment of the archdiocese of Canterbury
The Province of Canterbury, or less formally the Southern Province, is one of two ecclesiastical provinces which constitute the Church of England. The other is the Province of York (which consists of 12 dioceses).
Overview
The Province consist ...
by the Gregorian mission
The Gregorian missionJones "Gregorian Mission" ''Speculum'' p. 335 or Augustinian missionMcGowan "Introduction to the Corpus" ''Companion to Anglo-Saxon Literature'' p. 17 was a Christian mission sent by Pope Pope Gregory I, Gregory the Great ...
, its leader St Augustine consecrated Mellitus as the first bishop to the Saxon
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
kingdom of Essex
The Kingdom of the East Saxons (; ), referred to as the Kingdom of Essex , was one of the seven traditional kingdoms of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. It was founded in the 6th century and covered the territory later occupied by the counties of Essex ...
in 604. (The first bishop of Rochester
The Bishop of Rochester is the Ordinary (officer), ordinary of the Church of England's Diocese of Rochester in the Province of Canterbury.
The town of Rochester, Kent, Rochester has the bishop's seat, at the Rochester Cathedral, Cathedral Chur ...
was also consecrated the same year.) Bede
Bede (; ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, Bede of Jarrow, the Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable (), was an English monk, author and scholar. He was one of the most known writers during the Early Middle Ages, and his most f ...
records that Augustine's patron, King Æthelberht of Kent
Kent is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Essex across the Thames Estuary to the north, the Strait of Dover to the south-east, East Sussex to the south-west, Surrey to the west, and Gr ...
, built a cathedral for his nephew King Sæberht of Essex as part of this mission. This cathedral was constructed in "London" and dedicated to St Paul. Although it is not clear whether Lundenwic
The Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon period of the history of London dates from the end of the Londinium, Roman period in the 5th century to the beginning of the Norman and medieval London, Norman period in 1066.
Romano-British ''Londinium'' ...
or Lundenburh was intended, it is generally assumed the church was located in the same place occupied by the present St Paul's Cathedral
St Paul's Cathedral, formally the Cathedral Church of St Paul the Apostle, is an Anglican cathedral in London, England, the seat of the Bishop of London. The cathedral serves as the mother church of the Diocese of London in the Church of Engl ...
on Ludgate Hill
Ludgate Hill is a street and surrounding area, on a small hill in the City of London, England. The street passes through the former site of Ludgate, a city gate that was demolished – along with a gaol attached to it – in 1760.
Th ...
in London. Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
rumours that the cathedral had been erected over a Roman temple
Ancient Roman temples were among the most important buildings in culture of ancient Rome, Roman culture, and some of the richest buildings in Architecture of ancient Rome, Roman architecture, though only a few survive in any sort of complete ...
of the goddess Diana are no longer credited: during his rebuilding of the cathedral following the Great Fire of 1666, Christopher Wren
Sir Christopher Wren FRS (; – ) was an English architect, astronomer, mathematician and physicist who was one of the most highly acclaimed architects in the history of England. Known for his work in the English Baroque style, he was ac ...
reported discovering no trace of such a structure. Surrey
Surrey () is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Greater London to the northeast, Kent to the east, East Sussex, East and West Sussex to the south, and Hampshire and Berkshire to the wes ...
was at times a part of the Kingdom of Essex
The Kingdom of the East Saxons (; ), referred to as the Kingdom of Essex , was one of the seven traditional kingdoms of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. It was founded in the 6th century and covered the territory later occupied by the counties of Essex ...
, and with it the Diocese of London, a situation that changed following a synod at Brentford
Brentford is a suburban town in West (London sub region), West London, England and part of the London Borough of Hounslow. It lies at the confluence of the River Brent and the River Thames, Thames, west of Charing Cross.
Its economy has dive ...
around 705, reflecting the growing strength of Mercia
Mercia (, was one of the principal kingdoms founded at the end of Sub-Roman Britain; the area was settled by Anglo-Saxons in an era called the Heptarchy. It was centred on the River Trent and its tributaries, in a region now known as the Midlan ...
at the expense of Essex.
Because the bishop's diocese includes the royal palaces and the seat of government at Westminster
Westminster is the main settlement of the City of Westminster in Central London, Central London, England. It extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street and has many famous landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, Buckingham Palace, ...
, they have been regarded as the "King's bishop" and have historically had considerable influence with members of the Royal Family and leading politicians of the day. Since 1748 it has been customary to appoint the Bishop of London to the post of Dean of His Majesty's Chapels Royal, which has the effect of putting under the bishop's jurisdiction, ''as dean'', several chapels (at the Tower of London
The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic citadel and castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London, England. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamle ...
and St. James's Palace, among others) which are geographically in the Diocese of London but, as royal peculiar
A royal peculiar is a Church of England parish or church exempt from the jurisdiction of the diocese and the province in which it lies, and subject to the direct jurisdiction of the monarch.
Definition
The church parish system dates from the ea ...
s, are officially outside the bishop's jurisdiction ''as bishop''.
The Bishop of London originally had responsibility for the church in the British colonies in North America, although after the American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
of 1776, all that remained under his jurisdiction were the islands of the British West Indies
The British West Indies (BWI) were the territories in the West Indies under British Empire, British rule, including Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, the Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Bermuda, Antigua and Barb ...
. The diocese was further reduced in 1846, when the counties of Essex and Hertfordshire were ceded to the Diocese of Rochester
The Diocese of Rochester is a Church of England diocese in the English county of Kent and the Province of Canterbury. The cathedral church of the diocese is Rochester Cathedral in the former city of Rochester. The bishop's Latin episcopal si ...
.
The ''Report of the Commissioners appointed by his Majesty to inquire into the Ecclesiastical Revenues of England and Wales'' (1835), noted the annual net income for the London see was £13,929.
List of bishops
Romano-British Orthodox Bishops
The dates and names of these early bishops are very uncertain.Post-Augustinian
Post-Conquest
During the Reformation
Post-Reformation
Assistant bishops
Among those who called Assistant Bishop of London, orcoadjutor bishop
A coadjutor bishop (or bishop coadjutor) ("co-assister" in Latin) is a bishop in the Latin Catholic, Anglican and (historically) Eastern Orthodox churches whose main role is to assist the diocesan bishop in administering the diocese.
The coa ...
, were:
*1553–?: Thomas Chetham was consecrated titular bishop
A titular bishop in various churches is a bishop who is not in charge of a diocese.
By definition, a bishop is an "overseer" of a community of the faithful, so when a priest is ordained a bishop, the tradition of the Catholic, Eastern Orthodox an ...
of Sidon
Sidon ( ) or better known as Saida ( ; ) is the third-largest city in Lebanon. It is located on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast in the South Governorate, Lebanon, South Governorate, of which it is the capital. Tyre, Lebanon, Tyre, t ...
on 19 January 1526 to serve as an assistant to the Archbishop of Canterbury and became an assistant to the Bishop of London in 1553
*1554–: John Bird, deposed Bishop of Chester
The Bishop of Chester is the Ordinary of the Church of England Diocese of Chester in the Province of York.
The diocese extends across most of the historic county boundaries of Cheshire, including the Wirral Peninsula and has its see in the ...
was appointed suffragan bishop to the Bishop of London
*Several coadjutor bishops "in Northern and Central Europe", predecessors of the European Bishops of Fulham
*1897–1910 (d.): Alfred Barry, a Canon of Windsor, Rector of St James's Church, Piccadilly and frequently deputised for the Bishop of Marlborough (until 1900), assistant bishop for West London (effectively acting Bishop of Marlborough; 1900–1903), and former Anglican Bishop of Sydney
*1916–1933 (d.): Herbert Bury, Bishop in Northern and Central Europe (1911–1926) and incumbent of City churches (1911–d.); former Bishop of British Honduras
*1962–1966: Ambrose Reeves, former Anglican Bishop of Johannesburg
*1961–1966: Nathaniel Newnham Davis, Warden of United Westminster Almshouses and former Bishop of Antigua
*19781981 (res.): Kenneth Woollcombe, assistant for Westminster and former Bishop of Oxford
The Bishop of Oxford is the diocesan bishop of the Church of England Diocese of Oxford in the Province of Canterbury; his seat is at Christ Church Cathedral, Oxford. The current bishop is Steven Croft (bishop), Steven Croft, following the Confirm ...
*19761979 (ret.): Kenneth Howell, Minister of St John's Downshire Hill, Hampstead and former Bishop in Chile, Bolivia and Peru
*19761987 (ret.): Edward Knapp-Fisher, Canon
Canon or Canons may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Canon (fiction), the material accepted as officially written by an author or an ascribed author
* Literary canon, an accepted body of works considered as high culture
** Western canon, th ...
and Archdeacon of Westminster, Sub- Dean of Westminster (from 1982) and former Bishop of Pretoria
Honorary assistant bishop
An assistant bishop in the Anglican Communion is a bishop appointed to assist a diocesan bishop.
Church of England
In the established Church of England, assistant bishops are usually retired (diocesan or suffragan) bishops – in which case they ...
s – retired bishops taking on occasional duties voluntarily – have included:
*1929–1934 (d.): William Perrin, Rector of St Andrew Undershaft, bishop for Hampstead deanery and retired Bishop of Willesden
*1985–1991 (res.), in Kensington area: Alan Rogers, retired Bishop of Edmonton
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * *External links
Diocese of London website
* ttp://archives.lambethpalacelibrary.org.uk/calmview/Record.aspx?src=CalmView.Catalog&id=fp The papers of the Bishops of London covering 1423–1945 are held at Lambeth Palace Library {{Portal bar, Christianity, England, London London, Bishop of
Bishops
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...