Bird feet and legs on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The anatomy of bird legs and feet is diverse, encompassing many accommodations to perform a wide variety of functions.
Most birds are classified as
The anatomy of bird legs and feet is diverse, encompassing many accommodations to perform a wide variety of functions.
Most birds are classified as 
 The bird
The bird
 Most birds have four toes, typically three facing forward and one pointing backward. In a typical perching bird, they consist respectively of 3,4, 5 and 2
Most birds have four toes, typically three facing forward and one pointing backward. In a typical perching bird, they consist respectively of 3,4, 5 and 2
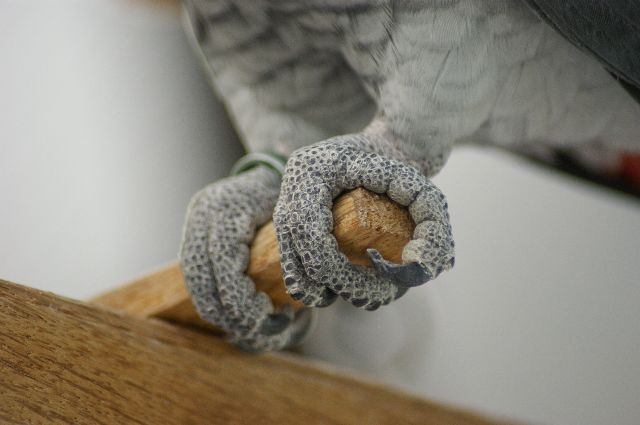





 Because avian
Because avian
 Typical toe arrangements in
Typical toe arrangements in
 Palmations and lobes enable swimming or help walking on loose ground such as mud. The webbed or palmated feet of birds can be categorized into several types:
* Palmate: only the anterior digits (2–4) are joined by webbing. Found in
Palmations and lobes enable swimming or help walking on loose ground such as mud. The webbed or palmated feet of birds can be categorized into several types:
* Palmate: only the anterior digits (2–4) are joined by webbing. Found in
/nowiki>Small zoological dictionary /nowiki>leg
{{cite book , ref=none , last=Kowalska-Dyrcz , first=Alina , editor-last=Busse , editor-first=Przemysław , series=Mały słownik zoologiczny /nowiki>Small zoological dictionary /nowiki>synsacrum
{{cite book , last1=Dobrowolski , first1=Kazimierz A. , last2=Klimaszewski , first2=Sędzimir M. , last3=Szelęgiewicz , first3=Henryk , publisher=Wydawnictwo Szkolne i Pedagogiczne , location=Warsaw , year=1981 , pages= 462–464, 469 , chapter=Chapters: Gromada: Ptaki - Aves: Układ kostny; Pas miednicowy i kończyna tylna /nowiki>Class: Birds: The skeletal system; The pelvic girdle and the hindlimb
{{cite journal , last=Earls , first=Kathleen D. , date=Feb 2000 , title=Kinematics and mechanics of ground take-off in the starling Sturnis vulgaris and the quail ''Coturnix coturnix'' , journal=The Journal of Experimental Biology , volume=203 , issue=Pt 4 , pages=725–739 , doi=10.1242/jeb.203.4.725 , url=http://jeb.biologists.org/content/jexbio/203/4/725.full.pdf , pmid=10648214
{{cite book , last1=Fastovsky , first1=David E. , last2=Weishampel , first2=David B. , publisher=Cambridge University Press , location=Cambridge, UK , year=2005 , title=The Evolution and Extinction of the Dinosaurs , edition=2nd , url=https://books.google.com/books?id=M8nt10bkovIC&pg=PA304, isbn=978-0-521-81172-9
{{cite journal , last=Gier , first=H. T. , year=1952 , title=The air sacs of the loon , journal= The Auk , volume=69 , issue = 1 , pages=40–49 , url=https://sora.unm.edu/sites/default/files/journals/auk/v069n01/p0040-p0049.pdf , doi=10.2307/4081291, jstor=4081291
{{cite book , last=Gill , first=Frank B. , publisher=W.H. Freeman and Company , location=New York , year=2001 , title=Ornithology , edition=2md , isbn=978-0-7167-2415-5
{{cite book , last=Kalbe , first=Lothar , publisher=Urania-Verlag , location=Leipzig-Jena-Berlin , year=1983 , pages= 72–77 , chapter=Besondere Formen für spezielle Aufgaben der Wassertiere /nowiki>Special adaptations of aquatic animals to specific lifestyles
{{cite book , last=Kochan , first=Jack B. , series=Birds , title=Feet & Legs , publisher=Stackpole Books , location=Mechanicsburg , year=1994 , isbn=978-0-8117-2515-6
{{cite book , last1=Proctor , first1=Noble S. , last2=Lynch , first2=Patrick J. , title=Manual of Ornithology. Avian Structure & Function , publisher=
 The anatomy of bird legs and feet is diverse, encompassing many accommodations to perform a wide variety of functions.
Most birds are classified as
The anatomy of bird legs and feet is diverse, encompassing many accommodations to perform a wide variety of functions.
Most birds are classified as digitigrade
In terrestrial vertebrates, digitigrade () locomotion is walking or running on the toes (from the Latin ''digitus'', 'finger', and ''gradior'', 'walk'). A digitigrade animal is one that stands or walks with its toes (metatarsals) touching the groun ...
animals, meaning they walk on their toes rather than the entire foot. Some of the lower bones of the foot (the distals and most of the metatarsal
The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the me ...
) are fused to form the tarsometatarsus
The tarsometatarsus is a bone that is only found in the lower leg of birds and some non-avian dinosaurs. It is formed from the fusion of several bones found in other types of animals, and homologous to the mammalian tarsus (ankle bones) and me ...
– a third segment of the leg, specific to birds. The upper bones of the foot ( proximals), in turn, are fused with the tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it conn ...
to form the tibiotarsus, as over time the centralia
Centralia may refer to:
Places Australia
*Central Australia, sometimes called "Centralia"
Canada
* Centralia, Ontario
** RCAF Station Centralia, a former Royal Canadian Air Force training base
** Centralia (Essery Field) Aerodrome
United State ...
disappeared. The fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity ...
also reduced.; ;
The legs are attached to a strong assembly consisting of the pelvic girdle
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The p ...
extensively fused with the uniform spinal bone (also specific to birds) called the '' synsacrum'', built from some of the fused bones.

Hindlimbs
Birds are generallydigitigrade
In terrestrial vertebrates, digitigrade () locomotion is walking or running on the toes (from the Latin ''digitus'', 'finger', and ''gradior'', 'walk'). A digitigrade animal is one that stands or walks with its toes (metatarsals) touching the groun ...
animals ( toe-walkers), which affects the structure of their leg skeleton. They use only their hindlimb
A hindlimb or back limb is one of the paired articulated appendages (limbs) attached on the caudal ( posterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso.http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/hind%20limb, Merriam Webster Dictionary-Hin ...
s to walk (bipedalism
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' ...
). Their forelimb
A forelimb or front limb is one of the paired articulated appendages (limbs) attached on the cranial ( anterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso. With reference to quadrupeds, the term foreleg or front leg is often used inste ...
s evolved to become wing
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is e ...
s. Most bones of the avian foot (excluding toes) are fused together or with other bones, having changed their function over time.
Tarsometatarsus
Some lower bones of the foot are fused to form thetarsometatarsus
The tarsometatarsus is a bone that is only found in the lower leg of birds and some non-avian dinosaurs. It is formed from the fusion of several bones found in other types of animals, and homologous to the mammalian tarsus (ankle bones) and me ...
– a third segment of the leg specific to birds. It consists of merged distals and metatarsal
The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the me ...
s II, III and IV. Metatarsus I remains separated as a base of the first toe. The tarsometatarsus is the extended foot area, which gives the leg extra lever length.
Tibiotarsus
The foot's upper bones ( proximals) are fused with thetibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it conn ...
to form the tibiotarsus, while the centralia
Centralia may refer to:
Places Australia
*Central Australia, sometimes called "Centralia"
Canada
* Centralia, Ontario
** RCAF Station Centralia, a former Royal Canadian Air Force training base
** Centralia (Essery Field) Aerodrome
United State ...
are absent. The anterior (frontal) side of the dorsal end of the tibiotarsus (at the knee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the ...
) contains a protruding enlargement called the cnemial crest The cnemial crest is a crestlike prominence located at the front side of the head of the tibiotarsus or tibia in the legs of many mammals and reptiles (including birds and other dinosaurs). The main extensor muscle of the thigh
In human anat ...
.
Patella
At the knee above thecnemial crest The cnemial crest is a crestlike prominence located at the front side of the head of the tibiotarsus or tibia in the legs of many mammals and reptiles (including birds and other dinosaurs). The main extensor muscle of the thigh
In human anat ...
is the patella
The patella, also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur (thigh bone) and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in many tetrapods, such as ...
(kneecap). Some species do not have patellas, sometimes only a cnemial crest. In grebes
Grebes () are aquatic diving birds in the order Podicipediformes . Grebes are widely distributed freshwater birds, with some species also found in marine habitats during migration and winter. Some flightless species exist as well, most notably i ...
both a normal patella and an extension of the cnemial crest are found.
Fibula
Thefibula
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity ...
is reduced and adheres extensively to the tibia, usually reaching two-thirds of its length. Only penguins
Penguins (order Sphenisciformes , family Spheniscidae ) are a group of aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere: only one species, the Galápagos penguin, is found north of the Equator. Highly adapt ...
have full-length fibulae.
Knee and ankle – confusions
 The bird
The bird knee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the ...
joint between the femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates ...
and tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it conn ...
(or rather tibiotarsus) points forwards, but is hidden within the feather
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premie ...
s. The backward-pointing "heel
The heel is the prominence at the posterior end of the foot. It is based on the projection of one bone, the calcaneus or heel bone, behind the articulation of the bones of the lower leg.
Structure
To distribute the compressive forces exer ...
" (ankle
The ankle, or the talocrural region, or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joi ...
) that is easily visible is a joint between the tibiotarsus and tarsometatarsus
The tarsometatarsus is a bone that is only found in the lower leg of birds and some non-avian dinosaurs. It is formed from the fusion of several bones found in other types of animals, and homologous to the mammalian tarsus (ankle bones) and me ...
. The joint inside the tarsus occurs also in some reptiles. It is worth noting here that the name "thick knee" of the members of the family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
Burhinidae is a misnomer because their heels are large.
The chicks in the orders Coraciiformes
The Coraciiformes are a group of usually colourful birds including the kingfishers, the bee-eaters, the rollers, the motmots, and the todies. They generally have syndactyly, with three forward-pointing toes (and toes 3 & 4 fused at their bas ...
and Piciformes
Nine families of largely arboreal birds make up the order Piciformes , the best-known of them being the Picidae, which includes the woodpeckers and close relatives. The Piciformes contain about 71 living genera with a little over 450 species, of ...
have ankles covered by a patch of tough skins with tubercles known as the ''heel-pad''. They use the heel-pad to shuffle inside the nest cavities or holes.
Toes and unfused metatarsals
 Most birds have four toes, typically three facing forward and one pointing backward. In a typical perching bird, they consist respectively of 3,4, 5 and 2
Most birds have four toes, typically three facing forward and one pointing backward. In a typical perching bird, they consist respectively of 3,4, 5 and 2 phalanges
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones. ...
. Some birds, like the sanderling
The sanderling (''Calidris alba'') is a small wading bird. The name derives from Old English ''sand-yrðling'', "sand-ploughman". The genus name is from Ancient Greek ''kalidris'' or ''skalidris'', a term used by Aristotle for some grey-colou ...
, have only the forward-facing toes; these are called tridactyl feet while the ostrich
Ostriches are large flightless birds of the genus ''Struthio'' in the order Struthioniformes, part of the infra-class Palaeognathae, a diverse group of flightless birds also known as ratites that includes the emus, rheas, and kiwis. There ...
have only two toes (didactyl feet). The first digit, called the hallux
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being ''digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being ''plan ...
, is homologous to the human big toe
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being ''digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being ''plan ...
.
The claw
A claw is a curved, pointed appendage found at the end of a toe or finger in most amniotes (mammals, reptiles, birds). Some invertebrates such as beetles and spiders have somewhat similar fine, hooked structures at the end of the leg or tarsus ...
s are located on the extreme phalanx of each toe. They consist of a horny keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up Scale (anatomy), scales, hair, Nail ...
ous podotheca, or sheath, and are not part of the skeleton.
The bird foot also contains one or two metatarsals not fused in the tarsometatarsus
The tarsometatarsus is a bone that is only found in the lower leg of birds and some non-avian dinosaurs. It is formed from the fusion of several bones found in other types of animals, and homologous to the mammalian tarsus (ankle bones) and me ...
.
Pelvic girdle and synsacrum
The legs are attached to a very strong, lightweight assembly consisting of thepelvic girdle
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The p ...
extensively fused with the uniform spinal bone called the synsacrum, which is specific to birds. The synsacrum is built from the lumbar
In tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids ( pelycosa ...
fused with the sacral, some of the first sections of the caudal
Caudal may refer to:
Anatomy
* Caudal (anatomical term) (from Latin ''cauda''; tail), used to describe how close something is to the trailing end of an organism
* Caudal artery, the portion of the dorsal aorta of a vertebrate that passes into the ...
, and sometimes the last one or two sections of the thoracic
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the crea ...
vertebrae
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
, depending on species (birds have altogether between 10 and 22 vertebrae). Except for those of ostrich
Ostriches are large flightless birds of the genus ''Struthio'' in the order Struthioniformes, part of the infra-class Palaeognathae, a diverse group of flightless birds also known as ratites that includes the emus, rheas, and kiwis. There ...
es and rheas
The rheas ( ), also known as ñandus ( ) or South American ostriches, are large ratites (flightless birds without a keel on their sternum bone) in the order Rheiformes, native to South America, distantly related to the ostrich and emu. Most tax ...
, pubic bones
In vertebrates, the pubic region ( la, pubis) is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three main regions making up the coxal bone. The left and right pubic regions are each made up of three sections, a superior ramus, inferior r ...
do not connect to each other, easing egg-laying.
Rigidity and reduction of mass
Fusions of individual bones into strong, rigid structures are characteristic. Most major bird bones are extensively pneumatized. They contain many air pockets connected to the pulmonaryair sacs
Air sacs are spaces within an organism where there is the constant presence of air. Among modern animals, birds possess the most air sacs (9–11), with their extinct dinosaurian relatives showing a great increase in the pneumatization (presence o ...
of the respiratory system
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies g ...
. Their spongy interior makes them strong relative to their mass. The number of pneumatic bones depends on the species; pneumaticity is slight or absent in diving bird
Diving birds are birds which plunge into the water to catch fish or other prey. Such birds may enter the water from flight, such as pelicans, gannets and tropicbirds; or they may dive from the surface of the water, such as the diving ducks, cormora ...
s. For example, in the long-tailed duck
The long-tailed duck (''Clangula hyemalis''), formerly known as oldsquaw, is a medium-sized sea duck that breeds in the tundra and taiga regions of the arctic and winters along the northern coastlines of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. It is th ...
, the leg and wing bones are not pneumatic, in contrast with some of the other bones, while loon
Loons ( North American English) or divers ( British / Irish English) are a group of aquatic birds found in much of North America and northern Eurasia. All living species of loons are members of the genus ''Gavia'', family Gaviidae and order ...
s and puffin
Puffins are any of three species of small alcids (auks) in the bird genus ''Fratercula''. These are pelagic seabirds that feed primarily by diving in the water. They breed in large colonies on coastal cliffs or offshore islands, nesting in crev ...
s have even more massive skeletons with no aired bones. The flightless ostrich
Ostriches are large flightless birds of the genus ''Struthio'' in the order Struthioniformes, part of the infra-class Palaeognathae, a diverse group of flightless birds also known as ratites that includes the emus, rheas, and kiwis. There ...
and emu have pneumatic femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates ...
s, and so far this is the only known pneumatic bone in these birds except for the ostrich's cervical vertebrae.
Fusions (leading to rigidity) and pneumatic bones (leading to reduced mass) are some of the many adaptations of birds for flight.
Plantigrade locomotion
Most birds, exceptloon
Loons ( North American English) or divers ( British / Irish English) are a group of aquatic birds found in much of North America and northern Eurasia. All living species of loons are members of the genus ''Gavia'', family Gaviidae and order ...
s and grebe
Grebes () are aquatic diving birds in the order Podicipediformes . Grebes are widely distributed freshwater birds, with some species also found in marine habitats during migration and winter. Some flightless species exist as well, most notably ...
s, are digitigrade
In terrestrial vertebrates, digitigrade () locomotion is walking or running on the toes (from the Latin ''digitus'', 'finger', and ''gradior'', 'walk'). A digitigrade animal is one that stands or walks with its toes (metatarsals) touching the groun ...
, not plantigrade
151px, Portion of a human skeleton, showing plantigrade habit
In terrestrial animals, plantigrade locomotion means walking with the toes and metatarsals flat on the ground. It is one of three forms of locomotion adopted by terrestrial mammals. ...
. Also, chicks in the nest
A nest is a structure built for certain animals to hold eggs or young. Although nests are most closely associated with birds, members of all classes of vertebrates and some invertebrates construct nests. They may be composed of organic materi ...
can use the entire foot
The foot ( : feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg mad ...
(toes and tarsometatarsus
The tarsometatarsus is a bone that is only found in the lower leg of birds and some non-avian dinosaurs. It is formed from the fusion of several bones found in other types of animals, and homologous to the mammalian tarsus (ankle bones) and me ...
) with the heel on the ground.
Loons tend to walk this way because their legs and pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
are highly specialized for swimming. They have a narrow pelvis, which moves the attachment point of the femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates ...
to the rear, and their tibiotarsus is much longer than the femur. This shifts the feet (toes) behind the center of mass
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the balance point) is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. This is the point to which a force may ...
of the loon body. They walk usually by pushing themselves on their breasts; larger loons cannot take off from land. This position, however, is highly suitable for swimming because their feet are located at the rear like the propeller
A propeller (colloquially often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon ...
on a motorboat
A motorboat, speedboat or powerboat is a boat that is exclusively powered by an engine.
Some motorboats are fitted with inboard engines, others have an outboard motor installed on the rear, containing the internal combustion engine, the gea ...
.
Grebe
Grebes () are aquatic diving birds in the order Podicipediformes . Grebes are widely distributed freshwater birds, with some species also found in marine habitats during migration and winter. Some flightless species exist as well, most notably ...
s and many other waterfowl have shorter femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates ...
and a more or less narrow pelvis, too, which gives the impression that their legs are attached to the rear as in loon
Loons ( North American English) or divers ( British / Irish English) are a group of aquatic birds found in much of North America and northern Eurasia. All living species of loons are members of the genus ''Gavia'', family Gaviidae and order ...
s.
Functions




forelimb
A forelimb or front limb is one of the paired articulated appendages (limbs) attached on the cranial ( anterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso. With reference to quadrupeds, the term foreleg or front leg is often used inste ...
s are wings
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is expre ...
, many forelimb functions are performed by the bill
Bill(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
* Banknote, paper cash (especially in the United States)
* Bill (law), a proposed law put before a legislature
* Invoice, commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer
* Bill, a bird or animal's beak
Pla ...
and hindlimb
A hindlimb or back limb is one of the paired articulated appendages (limbs) attached on the caudal ( posterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso.http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/hind%20limb, Merriam Webster Dictionary-Hin ...
s. It has been proposed that the hindlimbs are important in flight
Flight or flying is the process by which an object moves through a space without contacting any planetary surface, either within an atmosphere (i.e. air flight or aviation) or through the vacuum of outer space (i.e. spaceflight). This can be a ...
as accelerators when taking-off. Some leg and foot functions, including conventional ones and those specific to birds, are:
* Locomotion
** Walking, running (ostrich
Ostriches are large flightless birds of the genus ''Struthio'' in the order Struthioniformes, part of the infra-class Palaeognathae, a diverse group of flightless birds also known as ratites that includes the emus, rheas, and kiwis. There ...
es, grouse
Grouse are a group of birds from the order Galliformes, in the family Phasianidae. Grouse are presently assigned to the tribe Tetraonini (formerly the subfamily Tetraoninae and the family Tetraonidae), a classification supported by mitochondria ...
, wild turkey
The wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') is an upland ground bird native to North America, one of two extant species of turkey and the heaviest member of the order Galliformes. It is the ancestor to the domestic turkey, which was originally d ...
s) hopping, climbing (woodpecker
Woodpeckers are part of the bird family Picidae, which also includes the piculets, wrynecks, and sapsuckers. Members of this family are found worldwide, except for Australia, New Guinea, New Zealand, Madagascar, and the extreme polar regions ...
s, nuthatch
The nuthatches () constitute a genus, ''Sitta'', of small passerine birds belonging to the family Sittidae. Characterised by large heads, short tails, and powerful bills and feet, nuthatches advertise their territory using loud, simple songs. M ...
es, treecreeper
The treecreepers are a family, Certhiidae, of small passerine birds, widespread in wooded regions of the Northern Hemisphere and sub-Saharan Africa. The family contains eleven species in two genera, '' Certhia'' and '' Salpornis''. Their plumage ...
s)
** Swimming and steering underwater (duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form ...
s, grebe
Grebes () are aquatic diving birds in the order Podicipediformes . Grebes are widely distributed freshwater birds, with some species also found in marine habitats during migration and winter. Some flightless species exist as well, most notably ...
s, loon
Loons ( North American English) or divers ( British / Irish English) are a group of aquatic birds found in much of North America and northern Eurasia. All living species of loons are members of the genus ''Gavia'', family Gaviidae and order ...
s)
* Perching (as on a branch) or clinging
* Carrying (like osprey
The osprey (''Pandion haliaetus''), , also called sea hawk, river hawk, and fish hawk, is a diurnal, fish-eating bird of prey with a cosmopolitan range. It is a large raptor reaching more than in length and across the wings. It is brown o ...
s holding fish
Fish are Aquatic animal, aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack Limb (anatomy), limbs with Digit (anatomy), digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous and bony fish as we ...
)
* Flight
Flight or flying is the process by which an object moves through a space without contacting any planetary surface, either within an atmosphere (i.e. air flight or aviation) or through the vacuum of outer space (i.e. spaceflight). This can be a ...
-related
** Serving probably as the primary take-off accelerator. In the common vampire bat
The common vampire bat (''Desmodus rotundus'') is a small, leaf-nosed bat native to Latin America. It is one of three extant species of vampire bat, the other two being the hairy-legged and the white-winged vampire bats. The common vampire bat ...
, by contrast, the required force is generated by the wing
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is e ...
.
** Absorbing the shock of landing on a perch and on the water, becoming " water skis"
* Feeding and related
** Catching and killing prey in raptors (hawk
Hawks are birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. They are widely distributed and are found on all continents except Antarctica.
* The subfamily Accipitrinae includes goshawks, sparrowhawks, sharp-shinned hawks and others. This subfa ...
s, owl
Owls are birds from the order Strigiformes (), which includes over 200 species of mostly solitary and nocturnal birds of prey typified by an upright stance, a large, broad head, binocular vision, binaural hearing, sharp talons, and feathers a ...
s)
** Holding (used like hands in parrot
Parrots, also known as psittacines (), are birds of the roughly 398 species in 92 genera comprising the order Psittaciformes (), found mostly in tropical and subtropical regions. The order is subdivided into three superfamilies: the Psittacoide ...
s) and pulling apart food (with help from the bill
Bill(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
* Banknote, paper cash (especially in the United States)
* Bill (law), a proposed law put before a legislature
* Invoice, commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer
* Bill, a bird or animal's beak
Pla ...
)
** Scratching the ground in search of food
*** Double scratch: hopping forward and then backward using both feet to scratch (often towhees, sparrow
Sparrow may refer to:
Birds
* Old World sparrows, family Passeridae
* New World sparrows, family Passerellidae
* two species in the Passerine family Estrildidae:
** Java sparrow
** Timor sparrow
* Hedge sparrow, also known as the dunnock or hed ...
s, junco
A junco , genus ''Junco'', is a small North American bird in the New World sparrow family Passerellidae. Junco systematics are still confusing after decades of research, with various authors accepting between three and twelve species. Despite ...
s)
*** One-footed scratch (grouse
Grouse are a group of birds from the order Galliformes, in the family Phasianidae. Grouse are presently assigned to the tribe Tetraonini (formerly the subfamily Tetraoninae and the family Tetraonidae), a classification supported by mitochondria ...
, quail
Quail is a collective name for several genera of mid-sized birds generally placed in the order Galliformes. The collective noun for a group of quail is a flock, covey, or bevy.
Old World quail are placed in the family Phasianidae, and New ...
s, wild turkey
The wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') is an upland ground bird native to North America, one of two extant species of turkey and the heaviest member of the order Galliformes. It is the ancestor to the domestic turkey, which was originally d ...
s, domestic chicken
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domestication, domesticated junglefowl species, with attributes of wild species such as the grey junglefowl, grey and the Ceylon junglefowl that are originally from Southeastern Asia. Rooster ...
)
*Reproduction and related
** Cradling and turning eggs during incubation. Birds lacking a brood patch
A brood patch is a patch of featherless skin on the underside of birds during the nesting season. Feathers act as inherent insulators, and prevent efficient incubation. Birds have solved this evolutionary dilemma by developing dedicated brood patc ...
incubate the eggs with their feet – grasping one or even two of them (gannet
Gannets are seabirds comprising the genus ''Morus'' in the family Sulidae, closely related to boobies.
Gannets are large white birds with yellowish heads; black-tipped wings; and long bills. Northern gannets are the largest seabirds in the ...
s, boobies
A booby is a seabird in the genus ''Sula'', part of the family Sulidae. Boobies are closely related to the gannets (''Morus''), which were formerly included in ''Sula''.
Systematics and evolution
The genus ''Sula'' was introduced by the Fren ...
) or keeping them on the top surfaces of their feet (penguin
Penguins (order Sphenisciformes , family Spheniscidae ) are a group of aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere: only one species, the Galápagos penguin, is found north of the Equator. Highly adap ...
s under a pouch of belly skin, murres).
** Courtship (sage grouse
Sage-grouse are grouse belonging to the bird genus ''Centrocercus.'' The genus includes two species: the Gunnison grouse (''Centrocercus minimus'') and the greater sage-grouse (''Centrocercus urophasianus''). These birds are distributed throug ...
), including aerial courtship (bald eagle
The bald eagle (''Haliaeetus leucocephalus'') is a bird of prey found in North America. A sea eagle, it has two known subspecies and forms a species pair with the white-tailed eagle (''Haliaeetus albicilla''), which occupies the same niche as ...
s)
** Building nests (with help from the bill
Bill(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
* Banknote, paper cash (especially in the United States)
* Bill (law), a proposed law put before a legislature
* Invoice, commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer
* Bill, a bird or animal's beak
Pla ...
)
* Preening and cleaning. Sometimes birds use a special claw
A claw is a curved, pointed appendage found at the end of a toe or finger in most amniotes (mammals, reptiles, birds). Some invertebrates such as beetles and spiders have somewhat similar fine, hooked structures at the end of the leg or tarsus ...
(for example, barn owl
The barn owl (''Tyto alba'') is the most widely distributed species of owl in the world and one of the most widespread of all species of birds, being found almost everywhere except for the polar and desert regions, Asia north of the Himala ...
s have a so-called "feather comb"). Some heron
The herons are long-legged, long-necked, freshwater and coastal birds in the family Ardeidae, with 72 recognised species, some of which are referred to as egrets or bitterns rather than herons. Members of the genera ''Botaurus'' and ''Ixobrychu ...
s and nightjars
Nightjars are medium-sized nocturnal or crepuscular birds in the family Caprimulgidae and order Caprimulgiformes, characterised by long wings, short legs, and very short bills. They are sometimes called goatsuckers, due to the ancient folk ta ...
use the claw for cleaning the head.
* Heat loss regulation (heron
The herons are long-legged, long-necked, freshwater and coastal birds in the family Ardeidae, with 72 recognised species, some of which are referred to as egrets or bitterns rather than herons. Members of the genera ''Botaurus'' and ''Ixobrychu ...
s, gull
Gulls, or colloquially seagulls, are seabirds of the family Laridae in the suborder Lari. They are most closely related to the terns and skimmers and only distantly related to auks, and even more distantly to waders. Until the 21st century ...
s, giant petrel
Giant petrels form a genus, ''Macronectes'', from the family Procellariidae, which consists of two species. They are the largest birds of this family. Both species are restricted to the Southern Hemisphere, and though their distributions overla ...
s, stork
Storks are large, long-legged, long-necked wading birds with long, stout bills. They belong to the family called Ciconiidae, and make up the order Ciconiiformes . Ciconiiformes previously included a number of other families, such as herons an ...
s, New World vulture
The New World vulture or condor family, Cathartidae, contains seven extant species in five genera. It includes five extant vultures and two extant condors found in warm and temperate areas of the Americas. The "New World" vultures were widespr ...
s, duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form ...
s, geese
A goose ( : geese) is a bird of any of several waterfowl species in the family Anatidae. This group comprises the genera '' Anser'' (the grey geese and white geese) and ''Branta'' (the black geese). Some other birds, mostly related to the she ...
)
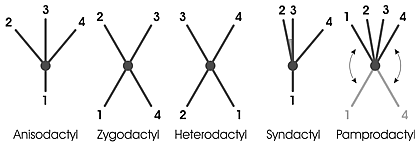
Toe arrangements
 Typical toe arrangements in
Typical toe arrangements in bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s are:
* Anisodactyl: three toes in front (2, 3, 4), and one in back (1); in nearly all songbird
A songbird is a bird belonging to the suborder Passeri of the perching birds (Passeriformes). Another name that is sometimes seen as the scientific or vernacular name is Oscines, from Latin ''oscen'', "songbird". The Passeriformes contains 5000 ...
s and most other perching birds.; ; ;
* Zygodactyl: two toes in front (2, 3) and two in back (1, 4) – the outermost front toe (4) is reversed. The zygodactyl arrangement is a case of convergence
Convergence may refer to:
Arts and media Literature
*''Convergence'' (book series), edited by Ruth Nanda Anshen
*Convergence (comics), "Convergence" (comics), two separate story lines published by DC Comics:
**A four-part crossover storyline that ...
, because it evolved in birds in different ways nine times.
** In many perching birds – most woodpecker
Woodpeckers are part of the bird family Picidae, which also includes the piculets, wrynecks, and sapsuckers. Members of this family are found worldwide, except for Australia, New Guinea, New Zealand, Madagascar, and the extreme polar regions ...
s and their allies, osprey
The osprey (''Pandion haliaetus''), , also called sea hawk, river hawk, and fish hawk, is a diurnal, fish-eating bird of prey with a cosmopolitan range. It is a large raptor reaching more than in length and across the wings. It is brown o ...
s, owl
Owls are birds from the order Strigiformes (), which includes over 200 species of mostly solitary and nocturnal birds of prey typified by an upright stance, a large, broad head, binocular vision, binaural hearing, sharp talons, and feathers a ...
s, cuckoo
Cuckoos are birds in the Cuculidae family, the sole taxon in the order Cuculiformes . The cuckoo family includes the common or European cuckoo, roadrunners, koels, malkohas, couas, coucals and anis. The coucals and anis are sometimes separ ...
s, most parrot
Parrots, also known as psittacines (), are birds of the roughly 398 species in 92 genera comprising the order Psittaciformes (), found mostly in tropical and subtropical regions. The order is subdivided into three superfamilies: the Psittacoide ...
s, mousebird
The mousebirds are birds in the order Coliiformes. They are the sister group to the clade Eucavitaves, which includes the Leptosomiformes (the cuckoo roller), Trogoniformes (trogons), Bucerotiformes (hornbills and hoopoes), Piciformes (wood ...
s, some swift
Swift or SWIFT most commonly refers to:
* SWIFT, an international organization facilitating transactions between banks
** SWIFT code
* Swift (programming language)
* Swift (bird), a family of birds
It may also refer to:
Organizations
* SWIFT, ...
s and cuckoo roller
The cuckoo-roller or courol (''Leptosomus discolor'')del Hoyo, J. Elliott, A. & Sargatal, J. (2001) is the only bird in the family Leptosomidae , which was previously often placed in the order Coraciiformes but is now placed in its own order Lept ...
s.
*** Woodpeckers, when climbing, can rotate the outer rear digit (4) to the side in an ectropodactyl arrangement. Black-backed woodpecker
The black-backed woodpecker (''Picoides arcticus''), also known as the Arctic three-toed woodpecker, is a medium-sized woodpecker ( long) inhabiting the forests of North America.
Taxonomy
The black-backed woodpecker was described and illustrat ...
s, Eurasian three-toed woodpecker
The Eurasian three-toed woodpecker (''Picoides tridactylus'') is a medium-sized woodpecker that is found from northern Europe across northern Asia to Japan.
Taxonomy
The Eurasian three-toed woodpecker was formally described in 1758 by the Swedi ...
s and American three-toed woodpecker
The American three-toed woodpecker (''Picoides dorsalis'') is a medium-sized woodpecker ( family Picidae), which is native to North America.
Description
This woodpecker has a length of , a wingspan of , and an average weight of ; its maximum l ...
s have three toes – the inner rear (1) is missing and the outer rear (4) points always backward and never rotates.
*** Owl
Owls are birds from the order Strigiformes (), which includes over 200 species of mostly solitary and nocturnal birds of prey typified by an upright stance, a large, broad head, binocular vision, binaural hearing, sharp talons, and feathers a ...
s, osprey
The osprey (''Pandion haliaetus''), , also called sea hawk, river hawk, and fish hawk, is a diurnal, fish-eating bird of prey with a cosmopolitan range. It is a large raptor reaching more than in length and across the wings. It is brown o ...
s and turaco
The turacos make up the bird family Musophagidae ( "banana-eaters"), which includes plantain-eaters and go-away-birds. In southern Africa both turacos and go-away-birds are commonly known as loeries. They are semi-zygodactylous: the fourth ( ...
s can rotate the outer toe (4) back and forth.
* Heterodactyl: two toes in front (3, 4) and two in back (2, 1) – the inner front toe (2) is reversed; heterodactyl arrangement only exists in trogon
The trogons and quetzals are birds in the order Trogoniformes which contains only one family, the Trogonidae. The family Trogonidae contains 46 species in seven genera. The fossil record of the trogons dates back 49 million years to the Early E ...
s.
* Syndactyl: three toes in front (2, 3, 4), one in back (1); the inner and middle (2, 3) are joined for much of their length. Common in Coraciiformes
The Coraciiformes are a group of usually colourful birds including the kingfishers, the bee-eaters, the rollers, the motmots, and the todies. They generally have syndactyly, with three forward-pointing toes (and toes 3 & 4 fused at their bas ...
, including kingfisher
Kingfishers are a family, the Alcedinidae, of small to medium-sized, brightly colored birds in the order Coraciiformes. They have a cosmopolitan distribution, with most species found in the tropical regions of Africa, Asia, and Oceania, ...
s and hornbill
Hornbills (Bucerotidae) are a family of bird found in tropical and subtropical Africa, Asia and Melanesia. They are characterized by a long, down-curved bill which is frequently brightly coloured and sometimes has a casque on the upper mandibl ...
s.
* Pamprodactyl: two inner toes in front (2, 3), the two outer (1, 4) can rotate freely forward and backward. In mousebird
The mousebirds are birds in the order Coliiformes. They are the sister group to the clade Eucavitaves, which includes the Leptosomiformes (the cuckoo roller), Trogoniformes (trogons), Bucerotiformes (hornbills and hoopoes), Piciformes (wood ...
s and some swift
Swift or SWIFT most commonly refers to:
* SWIFT, an international organization facilitating transactions between banks
** SWIFT code
* Swift (programming language)
* Swift (bird), a family of birds
It may also refer to:
Organizations
* SWIFT, ...
s. Some swift
Swift or SWIFT most commonly refers to:
* SWIFT, an international organization facilitating transactions between banks
** SWIFT code
* Swift (programming language)
* Swift (bird), a family of birds
It may also refer to:
Organizations
* SWIFT, ...
s move all four digits forward to use them as hooks to hang.
The most common arrangement is the anisodactyl foot, and second among perching birds is the zygodactyl arrangement.
Claws
All birds have claws at the end of the toes. The claws are typically curved and the radius of curvature tends to be greater as the bird is larger although they tend to be straighter in large ground dwelling birds such as ratites. Some species (includingnightjar
Nightjars are medium-sized nocturnal or crepuscular birds in the family Caprimulgidae and order Caprimulgiformes, characterised by long wings, short legs, and very short bills. They are sometimes called goatsuckers, due to the ancient folk tal ...
s, heron
The herons are long-legged, long-necked, freshwater and coastal birds in the family Ardeidae, with 72 recognised species, some of which are referred to as egrets or bitterns rather than herons. Members of the genera ''Botaurus'' and ''Ixobrychu ...
s, frigatebird
Frigatebirds are a family of seabirds called Fregatidae which are found across all tropical and subtropical oceans. The five extant species are classified in a single genus, ''Fregata''. All have predominantly black plumage, long, deeply forke ...
s, owls and pratincoles) have comb-like serrations on the claw of the middle toe that may aid in scratch preening
Preening is a found in birds that involves the use of the beak to position feathers, interlock feather that have become separated, clean plumage, and keep ectoparasites in check. Feathers contribute significantly to a bird's insulation, waterp ...
.
Webbing and lobation
 Palmations and lobes enable swimming or help walking on loose ground such as mud. The webbed or palmated feet of birds can be categorized into several types:
* Palmate: only the anterior digits (2–4) are joined by webbing. Found in
Palmations and lobes enable swimming or help walking on loose ground such as mud. The webbed or palmated feet of birds can be categorized into several types:
* Palmate: only the anterior digits (2–4) are joined by webbing. Found in duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form ...
s, geese
A goose ( : geese) is a bird of any of several waterfowl species in the family Anatidae. This group comprises the genera '' Anser'' (the grey geese and white geese) and ''Branta'' (the black geese). Some other birds, mostly related to the she ...
and swan
Swans are birds of the family Anatidae within the genus ''Cygnus''. The swans' closest relatives include the geese and ducks. Swans are grouped with the closely related geese in the subfamily Anserinae where they form the tribe Cygnini. Som ...
s, gull
Gulls, or colloquially seagulls, are seabirds of the family Laridae in the suborder Lari. They are most closely related to the terns and skimmers and only distantly related to auks, and even more distantly to waders. Until the 21st century ...
s and tern
Terns are seabirds in the family Laridae that have a worldwide distribution and are normally found near the sea, rivers, or wetlands. Terns are treated as a subgroup of the family Laridae which includes gulls and skimmers and consists of e ...
s, and other aquatic birds (auk
An auk or alcid is a bird of the family Alcidae in the order Charadriiformes. The alcid family includes the murres, guillemots, auklets, puffins, and murrelets. The word "auk" is derived from Icelandic ''álka'', from Old Norse ''alka'' (a ...
s, flamingo
Flamingos or flamingoes are a type of wading bird in the family Phoenicopteridae, which is the only extant family in the order Phoenicopteriformes. There are four flamingo species distributed throughout the Americas (including the Caribbea ...
s, fulmar
The fulmars are tubenosed seabirds of the family Procellariidae. The family consists of two extant species and two extinct fossil species from the Miocene.
Fulmars superficially resemble gulls, but are readily distinguished by their flight on ...
s, jaegers, loon
Loons ( North American English) or divers ( British / Irish English) are a group of aquatic birds found in much of North America and northern Eurasia. All living species of loons are members of the genus ''Gavia'', family Gaviidae and order ...
s, petrel
Petrels are tube-nosed seabirds in the bird order Procellariiformes.
Description
The common name does not indicate relationship beyond that point, as "petrels" occur in three of the four families within that group (all except the albatross f ...
s, shearwater
Shearwaters are medium-sized long-winged seabirds in the petrel family Procellariidae. They have a global marine distribution, but are most common in temperate and cold waters, and are pelagic outside the breeding season.
Description
These tub ...
s and skimmer
Skimmer may refer to: Animals
*Skimmer (bird), a common name for birds in the genus ''Rynchops''
*Skimmer (dragonfly), a common name for dragonflies in the family Libellulidae
*Water strider or skimmer, a common name for insects in the family Ge ...
s). Diving duck
The diving ducks, commonly called pochards or scaups, are a category of duck which feed by diving beneath the surface of the water. They are part of Anatidae, the diverse and very large family that includes ducks, geese, and swans.
The diving d ...
s also have a lobed hind toe (1), and gulls, terns and allies have a reduced hind toe.;
* Totipalmate: all four digits (1–4) are joined by webbing. Found in gannet
Gannets are seabirds comprising the genus ''Morus'' in the family Sulidae, closely related to boobies.
Gannets are large white birds with yellowish heads; black-tipped wings; and long bills. Northern gannets are the largest seabirds in the ...
s and boobies
A booby is a seabird in the genus ''Sula'', part of the family Sulidae. Boobies are closely related to the gannets (''Morus''), which were formerly included in ''Sula''.
Systematics and evolution
The genus ''Sula'' was introduced by the Fren ...
, pelican
Pelicans (genus ''Pelecanus'') are a genus of large water birds that make up the family Pelecanidae. They are characterized by a long beak and a large throat pouch used for catching prey and draining water from the scooped-up contents before ...
s, cormorant
Phalacrocoracidae is a family of approximately 40 species of aquatic birds commonly known as cormorants and shags. Several different classifications of the family have been proposed, but in 2021 the IOC adopted a consensus taxonomy of seven ge ...
s, anhinga
The anhinga (; ''Anhinga anhinga''), sometimes called snakebird, darter, American darter, or water turkey, is a water bird of the warmer parts of the Americas. The word ''anhinga'' comes from ''a'ñinga'' in the Brazilian Tupi language and means ...
s and frigatebird
Frigatebirds are a family of seabirds called Fregatidae which are found across all tropical and subtropical oceans. The five extant species are classified in a single genus, ''Fregata''. All have predominantly black plumage, long, deeply forke ...
s. Some gannets have brightly colored feet used in display.
* Semipalmate: a small web between the anterior digits (2–4). Found in some plover
Plovers ( , ) are a widely distributed group of wading birds belonging to the subfamily Charadriinae.
Description
There are about 66 species in the subfamily, most of them called "plover" or "dotterel". The closely related lapwing subf ...
s (Eurasian dotterel
The Eurasian dotterel (''Charadrius morinellus''), also known in Europe as just dotterel, is a small wader in the plover family of birds.
The dotterel is a brown and black streaked bird with a broad white eye-stripe and an orange-red chest ba ...
s) and sandpiper
Sandpipers are a large family, Scolopacidae, of waders. They include many species called sandpipers, as well as those called by names such as curlew and snipe. The majority of these species eat small invertebrates picked out of the mud or soil ...
s (semipalmated sandpiper
The semipalmated sandpiper (''Calidris pusilla'') is a very small shorebird. The genus name is from Ancient Greek ''kalidris'' or ''skalidris'', a term used by Aristotle for some grey-coloured waterside birds. The specific ''pusilla'' is Lati ...
s, stilt sandpiper
The stilt sandpiper (''Calidris himantopus'') is a small shorebird. The scientific name is from Ancient Greek. The genus name ''kalidris'' or ''skalidris'' is a term used by Aristotle for some grey-coloured waterside birds. The specific ''himanto ...
s, upland sandpipers, greater yellowlegs
The greater yellowlegs (''Tringa melanoleuca'') is a large shorebird in the family Scolopacidae. It breeds in central Canada and southern Alaska and winters in southern North America, Central America, the West Indies and South America.
Taxonomy
...
and willet
The willet (''Tringa semipalmata'') is a large shorebird in the family Scolopacidae. It is a relatively large and robust sandpiper, and is the largest of the species called "shanks" in the genus ''Tringa''. Its closest relative is the lesser yel ...
), avocet
The four species of avocets are a genus, ''Recurvirostra'', of waders in the same avian family as the stilts. The genus name comes from Latin , 'curved backwards' and , 'bill'. The common name is thought to derive from the Italian ( Ferrarese) ...
, heron
The herons are long-legged, long-necked, freshwater and coastal birds in the family Ardeidae, with 72 recognised species, some of which are referred to as egrets or bitterns rather than herons. Members of the genera ''Botaurus'' and ''Ixobrychu ...
s (only two toes), all grouse
Grouse are a group of birds from the order Galliformes, in the family Phasianidae. Grouse are presently assigned to the tribe Tetraonini (formerly the subfamily Tetraoninae and the family Tetraonidae), a classification supported by mitochondria ...
, and some domesticated breeds of chicken
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domesticated junglefowl species, with attributes of wild species such as the grey and the Ceylon junglefowl that are originally from Southeastern Asia. Rooster or cock is a term for an adu ...
. Plovers and lapwing
Lapwings (subfamily Vanellinae) are any of various ground-nesting birds (family Charadriidae) akin to plovers and dotterels. They range from in length, and are noted for their slow, irregular wingbeats in flight and a shrill, wailing cry. A gro ...
s have a vestigial hind toe (1), and sandpipers and their allies have a reduced and raised hind toe barely touching the ground. The sanderling
The sanderling (''Calidris alba'') is a small wading bird. The name derives from Old English ''sand-yrðling'', "sand-ploughman". The genus name is from Ancient Greek ''kalidris'' or ''skalidris'', a term used by Aristotle for some grey-colou ...
is the only sandpiper having 3 toes (tridactyl foot).; ;
* Lobate: the anterior digits (2–4) are edged with lobes of skin. Lobes expand or contract when a bird swims. In grebe
Grebes () are aquatic diving birds in the order Podicipediformes . Grebes are widely distributed freshwater birds, with some species also found in marine habitats during migration and winter. Some flightless species exist as well, most notably ...
s, coot
Coots are medium-sized water birds that are members of the rail family, Rallidae. They constitute the genus ''Fulica'', the name being the Latin term for "coot". Coots have predominantly black plumage, and—unlike many rails—they are usually ...
s, phalarope
__NOTOC__
A phalarope is any of three living species of slender-necked shorebirds in the genus ''Phalaropus'' of the bird family Scolopacidae.
Phalaropes are close relatives of the shanks and tattlers, the '' Actitis'' and Terek sandpipers ...
s, finfoots and some palmate-footed duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form ...
s on the hallux (1). Grebes have more webbing between the toes than coots and phalaropes.
The palmate foot is most common.
Thermal regulation
Some birds likegull
Gulls, or colloquially seagulls, are seabirds of the family Laridae in the suborder Lari. They are most closely related to the terns and skimmers and only distantly related to auks, and even more distantly to waders. Until the 21st century ...
s, heron
The herons are long-legged, long-necked, freshwater and coastal birds in the family Ardeidae, with 72 recognised species, some of which are referred to as egrets or bitterns rather than herons. Members of the genera ''Botaurus'' and ''Ixobrychu ...
s, duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form ...
s or geese
A goose ( : geese) is a bird of any of several waterfowl species in the family Anatidae. This group comprises the genera '' Anser'' (the grey geese and white geese) and ''Branta'' (the black geese). Some other birds, mostly related to the she ...
can regulate their temperature through their feet.
The arteries
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pu ...
and vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated ...
s intertwine in the legs, so heat can be transferred from arteries back to veins before reaching the feet. Such a mechanism is called countercurrent exchange
Countercurrent exchange is a mechanism occurring in nature and mimicked in industry and engineering, in which there is a crossover of some property, usually heat or some chemical, between two flowing bodies flowing in opposite directions to each ...
. Gull
Gulls, or colloquially seagulls, are seabirds of the family Laridae in the suborder Lari. They are most closely related to the terns and skimmers and only distantly related to auks, and even more distantly to waders. Until the 21st century ...
s can open a shunt between these vessels, turning back the bloodstream above the foot, and constrict the vessels in the foot. This reduces heat loss by more than 90 percent. In gulls, the temperature of the base of the leg is 32 °C (89 °F), while that of the foot may be close to 0 °C (32 °F).
However, for cooling, this heat-exchange network can be bypassed and blood-flow through the foot significantly increased (giant petrel
Giant petrels form a genus, ''Macronectes'', from the family Procellariidae, which consists of two species. They are the largest birds of this family. Both species are restricted to the Southern Hemisphere, and though their distributions overla ...
s). Some birds also excrete onto their feet, increasing heat loss via evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when h ...
(stork
Storks are large, long-legged, long-necked wading birds with long, stout bills. They belong to the family called Ciconiidae, and make up the order Ciconiiformes . Ciconiiformes previously included a number of other families, such as herons an ...
s, New World vulture
The New World vulture or condor family, Cathartidae, contains seven extant species in five genera. It includes five extant vultures and two extant condors found in warm and temperate areas of the Americas. The "New World" vultures were widespr ...
s).
See also
*Bird anatomy
Bird anatomy, or the physiological structure of birds' bodies, shows many unique adaptations, mostly aiding flight. Birds have a light skeletal system and light but powerful musculature which, along with circulatory and respiratory systems cap ...
* Dactyly
In biology, dactyly is the arrangement of digits (fingers and toes) on the hands, feet, or sometimes wings of a tetrapod animal. It comes from the Greek word δακτυλος (''dáktylos'') = "finger".
Sometimes the ending "-dactylia" is us ...
* Synsacrum
* Tarsometatarsus
The tarsometatarsus is a bone that is only found in the lower leg of birds and some non-avian dinosaurs. It is formed from the fusion of several bones found in other types of animals, and homologous to the mammalian tarsus (ankle bones) and me ...
* Tibiotarsus
References
{{Reflist, 2, refs= {{cite journal , last1=Bezuidenhout , first1=A.J. , last2=Groenewald , first2=H.B. , last3=Soley , first3=J.T. , year=1999 , title=An anatomical study of the respiratory air sacs in ostriches , journal=Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research , volume=66 , issue=4 , pages=317–325 , url=http://repository.up.ac.za/bitstream/handle/2263/20155/39bezuidenhout1999.pdf , pmid=10689704 {{cite book , last=Kowalska-Dyrcz , first=Alina , editor-last=Busse , editor-first=Przemysław , series=Mały słownik zoologicznyYale University Press
Yale University Press is the university press of Yale University. It was founded in 1908 by George Parmly Day, and became an official department of Yale University in 1961, but it remains financially and operationally autonomous.
, Yale Univers ...
, location=New Haven and London , year=1993 , pages=70–75, 140–141, 142–144 , chapter=Chapters: 6. Topography of the foot, 11. The pelvic girdle, and 12. The bones of the leg and foot Family , isbn=978-0-300-07619-6
{{cite book , last1=Romer , first1=Alfred Sherwood , last2=Parsons , first2=Thomas S. , year=1977 , title=The Vertebrate Body , publisher=Holt-Saunders International , location= Philadelphia, PA , pages= 205–208 , isbn= 978-0-03-910284-5
{{cite journal , last=Schorger , first=A. W. , date=September 1947 , title=The deep diving of the loon and old-squaw and its mechanism , journal=The Wilson Bulletin , volume=59 , issue=3 , pages=151–159 , url=https://sora.unm.edu/sites/default/files/journals/wilson/v059n03/p0151-p0159.pdf
{{cite book , last1=Elphick , first1=John B. , last2=Dunning , first2=Jack B. Jr., last3=Sibley , first3=David Allen , title=National Audubon Society: The Sibley Guide to Bird Life & Behavior , publisher=Alfred A. Knopf , location=New York , year=2001 , isbn=978-0-679-45123-5 , ref={{harvid, Elphick et al, 2001 , url-access=registration , url=https://archive.org/details/sibleyguidetobir00sibl_1
{{cite journal , last=Wedel , first=Mathew J. , year=2003 , title=Vertebral pneumaticity, air sacs, and the physiology of sauropod dinosaurs , journal=Paleobiology , volume=29 , issue=2 , pages=243–255 , url=http://sauroposeidon.files.wordpress.com/2010/04/wedel-2003-sauropod-pneumaticity.pdf , doi=10.1666/0094-8373(2003)029<0243:vpasat>2.0.co;2
{{Cite journal , url=http://www.nature.com/news/2000/000310/full/news000316-1.html , title=Off to a flying jump-start : Nature News , journal=Nature , last=Whitfield , first=John , date=10 March 2000 , publisher=Nature Publishing Group , accessdate=17 January 2014 , doi=10.1038/news000316-1
Bird anatomy
Lower limb anatomy