binary cycle power plant on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A binary cycle is a method for generating electrical power from geothermal resources and employs two separate fluid cycles, hence binary cycle. The primary cycle extracts the geothermal energy from the
 In contrast to conventional geothermal power generation methods like dry-steam or
In contrast to conventional geothermal power generation methods like dry-steam or
 The performance of a simple binary cycle and its individual components can be calculated as follows:
The performance of a simple binary cycle and its individual components can be calculated as follows:
reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.
Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including control ...
, and secondary cycle converts the heat
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is al ...
into work
Work may refer to:
* Work (human activity), intentional activity people perform to support themselves, others, or the community
** Manual labour, physical work done by humans
** House work, housework, or homemaking
** Working animal, an animal tr ...
to drive the generator and generate electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
.
Binary cycles permit electricity generation even from low temperature geothermal resources (<180°C) that would otherwise produce insufficient quantities of steam to make flash power plants economically viable. However, due to the lower temperatures binary cycles have low overall efficiencies of about 10-13%.
Introduction
 In contrast to conventional geothermal power generation methods like dry-steam or
In contrast to conventional geothermal power generation methods like dry-steam or flash
Flash, flashes, or FLASH may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Fictional aliases
* Flash (DC Comics character), several DC Comics superheroes with super speed:
** Flash (Barry Allen)
** Flash (Jay Garrick)
** Wally West, the first Kid F ...
, which use a single open cycle, a binary cycle has two separate cycles operating in tandem, hence binary cycle. The primary cycle extracts heat from the geothermal reservoir and provides this to the secondary cycle, which converts heat
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is al ...
into work
Work may refer to:
* Work (human activity), intentional activity people perform to support themselves, others, or the community
** Manual labour, physical work done by humans
** House work, housework, or homemaking
** Working animal, an animal tr ...
(see Heat Engine
In thermodynamics and engineering, a heat engine is a system that converts heat to mechanical energy, which can then be used to do mechanical work. It does this by bringing a working substance from a higher state temperature to a lower state ...
) to drive a generator and produce electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
. Thermodynamically, binary cycle power plants are similar to coal-fired or nuclear power plants
A nuclear power plant (NPP) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power stations, heat is used to generate steam that drives a steam turbine connected to a generator that produces ele ...
in that they employ Rankine Power Cycles, the main difference being the heat source and the choice of cycle working fluid
For fluid power, a working fluid is a gas or liquid that primarily transfers force, motion, or mechanical energy. In hydraulics, water or hydraulic fluid transfers force between hydraulic components such as hydraulic pumps, hydraulic cylinders, a ...
.
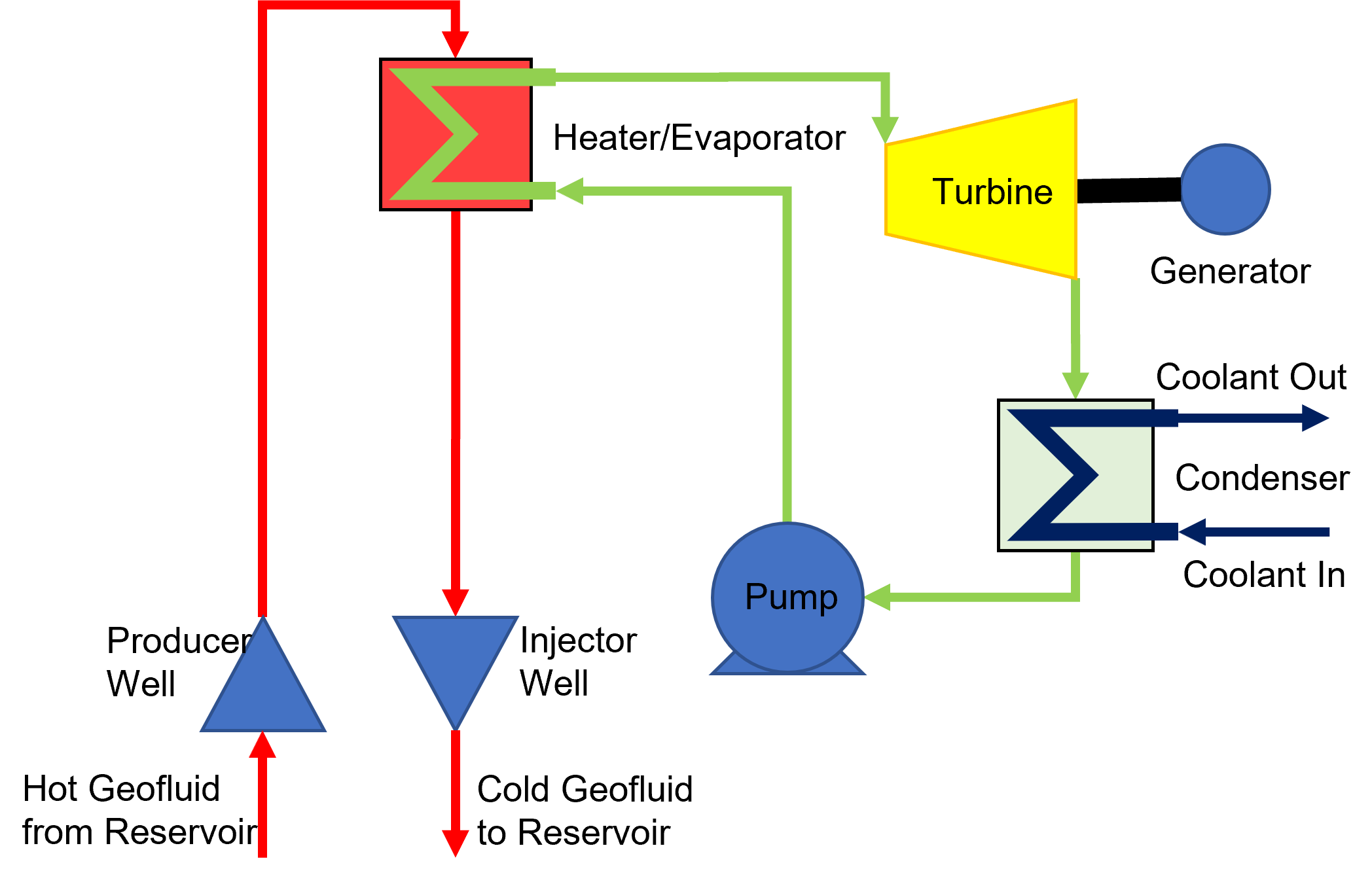
Primary cycle
The geothermal reservoir's hot in-situ fluid (or geofluid) is produced to the surface via a wellbore, if necessary assisted by a pump. On the surface, the hot geofluid transfers some of its heat to the secondary cycle, via aheat exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contac ...
, thus cooling in the process. The cold geofluid is then reinjected into the geothermal reservoir via a separate wellbore, where it is reheated. The primary cycle is considered an "open" cycle.
Secondary cycle
Cold high-pressure working fluid is heated and vapourised in a heat exchanger by the hot geofluid. The hot high-pressure vapour is expanded in aturbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced by a turbine can be used for generating e ...
before being cooled and condensed in a condenser. To close the loop, the cold low-pressure liquid is repressurised via a feed pump
A boiler feedwater pump is a specific type of pump used to pump feedwater into a steam boiler. The water may be freshly supplied or returning condensate produced as a result of the condensation of the steam produced by the boiler. These pumps ar ...
. The secondary cycle is a closed cycle.
The two main secondary cycle configurations are Organic Rankine cycles (ORC) or Kalina cycles, the main difference being the choice of working fluid; an organic fluid (commonly a hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
or refrigerant
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the refrigeration cycle of air conditioning systems and heat pumps where in most cases they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are heavily regulated du ...
) or a water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
-ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous wa ...
mixture respectively.
History
The earliest example of a binary cycle geothermal power plant is thought to have been located onIschia
Ischia ( , , ) is a volcanic island in the Tyrrhenian Sea. It lies at the northern end of the Gulf of Naples, about from Naples. It is the largest of the Phlegrean Islands. Roughly trapezoidal in shape, it measures approximately east to we ...
, Italy, between 1940-1943. The plant is thought to have used Ethyl Chloride
Chloroethane, commonly known as ethyl chloride, is a chemical compound with chemical formula CH3CH2Cl, once widely used in producing tetraethyllead, a gasoline additive. It is a colorless, flammable gas or refrigerated liquid with a faintly s ...
as the working fluid at an effective capacity of 250 kW. However, owing to the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
taking place at the same time, not much is known about this particular installation.
Another binary cycle geothermal power plant was taken into operation in 1967 near Petropavlovsk on the Kamchatka
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: полуостров Камчатка, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and west ...
peninsula, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eight ...
. It was rated at 670 kW and ran for an unknown number of years, proving the concept of binary cycle geothermal power plants.
As of December 2014, there were 203 binary cycle geothermal power plants across 15 countries worldwide, representing 35% of all geothermal power plants, but only generating 10.4% of total geothermal power (about 1250 MW).
Variations
Dual pressure
The working fluid is evaporated at two different pressure levels, and thus temperatures. This improves efficiency by reducing exergetic losses in the primary heat exchanger by maintaining a closer match between the geofluid cooling curve and the working fluid heating curve.Dual fluid
Two secondary cycles are operated in tandem, each with a separate working fluid and boiling point. This improves efficiency by reducing the exergetic losses of the heat introduction process, by ensuring a closer match between the geofluid cooling curve and the working fluids' heating curves.Performance
 The performance of a simple binary cycle and its individual components can be calculated as follows:
The performance of a simple binary cycle and its individual components can be calculated as follows:
Turbine
* is the rate of work done by the turbine, in kW * is the mass flow rate of working fluid, in kg/s * is the turbine efficiency, non-dimensional * is the specificenthalpy
Enthalpy , a property of a thermodynamic system, is the sum of the system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant p ...
of the working fluid at the turbine inlet, in kJ/kg
* is the specific enthalpy of the working fluid at the turbine outlet, assuming isentropic expansion in the turbine, in kJ/kg
Condenser
The equation below can be used to determine the condenser duty and mass flow rate of coolant required. : * is the rate of heat removed from the working fluid in the condenser, in kW * & are the specific enthalpy of the working fluid at the condenser inlet and outlet respectively, in kJ/kg * is the mass flow rate of coolant, in kg/s * & are the specific enthalpy of coolant at the condenser inlet and outlet respectively, in kJ/kgFeed Pump
: * is the rate of work done by the pump to repressurise the working fluid, in kW * is the specific enthalpy of the working fluid at the feed pump outlet, assuming isentropic compression, in kJ/kg * is the specific enthalpy of the working fluid at the feed pump inlet, in kJ/kg * is the pump efficiency, non-dimensionalPrimary Heat Exchanger
The equation below can be used to determine the primary heat exchanger duty and mass flow rate of geofluid required. : * is the rate of heat added to the working fluid within the primary heat exchanger, kW * is the specific enthalpy of the working fluid at the primary heat exchanger inlet, in kJ/kg * is the mass flow rate of geofluid, in kg/s * & are the specific enthalpy of the geofluid at the primary heat exchanger inlet and outlet respectively, in kJ/kgEfficiency
There are a number of different definitions of efficiency that may be considered; these are discussed below.First law efficiency
The first law efficiency (from theFirst law of thermodynamics
The first law of thermodynamics is a formulation of the law of conservation of energy, adapted for thermodynamic processes. It distinguishes in principle two forms of energy transfer, heat and thermodynamic work for a system of a constant amount ...
) is a measure of the conversion of the heat provided to the cycle into useful work. When accounting for real life losses and inefficiencies, real binary cycle geothermal plants have a first law efficiency of between 10-13%.
:
Carnot efficiency
The Carnot effficiency gives the efficiency of an ideal thermodynamic cycle, operating between two reservoirs of different temperatures, as such it provides a theoretical maximum to the efficiency of any heat engine. For this reason, a geothermal power plant producing hot geofluid at 180°C (≈450 K) and rejecting heat at 25°C (≈298 K) has a maximum efficiency of just 34%. : * & are the hot and cold absolute temperature respectively, in KSecond law efficiency
The second law efficiency (from theSecond law of thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on universal experience concerning heat and energy interconversions. One simple statement of the law is that heat always moves from hotter objects to colder objects (or "downhill"), unles ...
) is a measure of the utilisation of the ideally maximum work available and conversion into useful work.
:
:* is the exergy rate of geofluid, in kW.
:* , & are the specific enthalpy, in kJ/kg, the specific entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynam ...
, in kJ/kg/K and the absolute temperature, in K, of the geofluid at the local reference condition. This could be local ambient, wet-bulb or reinjection conditions.
Working fluid selection
The working fluid plays a pivotal role in any binary cycle and must be selected with care. Some criteria for selecting a suitable fluid are given below. #A critical temperature and pressure above the cycle maximum temperature and pressure - most of the heat is transferred at the maximum temperature, increasing efficiency. #A saturation dome that resembles an inverted U - this prevents liquid drop out in the turbine, which reduces efficiency, damages the turbine blades and thus reduces the turbine's lifetime. #High thermal conductivity - improves the heat transfer in the primary heat exchanger and the condenser, reducing the total heat transfer area required and therefore cost of the plant. #Environmental compatibility - non-toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subs ...
, non- carciogenic, low global warming potential
Global warming potential (GWP) is the heat absorbed by any greenhouse gas in the atmosphere, as a multiple of the heat that would be absorbed by the same mass of carbon dioxide (). GWP is 1 for . For other gases it depends on the gas and the time ...
, low ozone depletion potential
The ozone depletion potential (ODP) of a chemical compound is the relative amount of degradation to the ozone layer it can cause, with trichlorofluoromethane (R-11 or CFC-11) being fixed at an ODP of 1.0. Chlorodifluoromethane (R-22), for examp ...
, non-flammable
A combustible material is something that can burn (i.e., ''combust'') in air. A combustible material is flammable if it ignites easily at ambient temperatures. In other words, a combustible material ignites with some effort and a flammable mat ...
, chemically inert.
#Low cost and readily available.
Power plants
There are numerous binary cycle power stations in commercial production.Organic Rankine cycle
* Olkaria III, Kenya * Mammoth Lakes, California, United States * Steamboat Springs (Nevada), United States * Te Huka Power Station, New Zealand *Kirchstockach (Munich), Germany *Traunreut, GermanyKalina cycle
* Husavik Power station * Geothermie UnterhachingSee also
*Geothermal electricity
Geothermal power is electrical power generated from geothermal energy. Technologies in use include dry steam power stations, flash steam power stations and binary cycle power stations. Geothermal electricity generation is currently used in 26 ...
*Working fluid
For fluid power, a working fluid is a gas or liquid that primarily transfers force, motion, or mechanical energy. In hydraulics, water or hydraulic fluid transfers force between hydraulic components such as hydraulic pumps, hydraulic cylinders, a ...
*Organic Rankine cycle
In thermal engineering, the Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) is a type of thermodynamic cycle. It is a variation of the Rankine cycle named for its use of an organic, high- molecular-mass fluid whose vaporization temperature is lower than that of w ...
* Kalina cycleReferences
{{Geothermal power Geothermal energy