Berlin Offensive on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of Berlin, designated as the Berlin Strategic Offensive Operation by the

 On 12 January 1945, the Red Army began the Vistula–Oder Offensive across the
On 12 January 1945, the Red Army began the Vistula–Oder Offensive across the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
, and also known as the Fall of Berlin, was one of the last major offensives of the European theatre of World War II
The European theatre of World War II was one of the two main theatres of combat during World War II. It saw heavy fighting across Europe for almost six years, starting with Germany's invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939 and ending with the ...
.
After the Vistula–Oder Offensive of January–February 1945, the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
had temporarily halted on a line east of Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitu ...
. On 9 March, Germany established its defence plan for the city with Operation Clausewitz
Operation Clausewitz (''Fall Clausewitz'') was the code word initiating the defence of Berlin by Nazi Germany during the final stage of the European Theatre of World War II. Clausewitz was established in the 9 March 1945 document, ''Basic Order ...
. The first defensive preparations at the outskirts of Berlin were made on 20 March, under the newly appointed commander of Army Group Vistula
Army Group Vistula () was an Army Group of the '' Wehrmacht'', formed on 24 January 1945. It lasted for 105 days, having been put together from elements of Army Group A (shattered in the Soviet Vistula-Oder Offensive), Army Group Centre (similarl ...
, General Gotthard Heinrici
Gotthard Fedor August Heinrici (25 December 1886 – 10 December 1971) was a German general during World War II. Heinrici is considered as the premier defensive expert of the ''Wehrmacht''. His final command was Army Group Vistula, formed from t ...
.
When the Soviet offensive resumed on 16 April, two Soviet fronts (army group
An army group is a military organization consisting of several field armies, which is self-sufficient for indefinite periods. It is usually responsible for a particular geographic area. An army group is the largest field organization handled ...
s) attacked Berlin from the east and south, while a third overran German forces positioned north of Berlin. Before the main battle in Berlin commenced, the Red Army encircled the city after successful battles of the Seelow Heights
The Seelow Heights are situated around the town of Seelow, about east of Berlin, and overlook the Oderbruch, the western flood plain of the River Oder, which is a further to the east.
They are sometimes known as the "Gates to Berlin", because ...
and Halbe. On 20 April 1945, Hitler's
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
birthday, the 1st Belorussian Front
The 1st Belorussian Front ( Russian: Пéрвый Белорусский фронт, ''Perviy Belorusskiy front'', also romanized " Byelorussian") was a major formation of the Soviet Army during World War II, being equivalent to a Western army ...
led by Marshal
Marshal is a term used in several official titles in various branches of society. As marshals became trusted members of the courts of Medieval Europe, the title grew in reputation. During the last few centuries, it has been used for elevated o ...
Georgy Zhukov
Georgy Konstantinovich Zhukov ( rus, Георгий Константинович Жуков, p=ɡʲɪˈorɡʲɪj kənstɐnʲˈtʲinəvʲɪtɕ ˈʐukəf, a=Ru-Георгий_Константинович_Жуков.ogg; 1 December 1896 – ...
, advancing from the east and north, started shelling Berlin's city centre, while Marshal Ivan Konev
Ivan Stepanovich Konev ( rus, link=no, Ива́н Степа́нович Ко́нев, p=ɪˈvan sʲtʲɪˈpanəvʲɪtɕ ˈkonʲɪf; – 21 May 1973) was a Soviet general and Marshal of the Soviet Union who led Red Army forces on the ...
's 1st Ukrainian Front
The 1st Ukrainian Front (Russian: Пéрвый Украи́нский фронт), previously the Voronezh Front (Russian: Воронежский Фронт) was a major formation of the Soviet Army during World War II, being equivalent to a ...
broke through Army Group Centre
Army Group Centre (german: Heeresgruppe Mitte) was the name of two distinct strategic German Army Groups that fought on the Eastern Front in World War II. The first Army Group Centre was created on 22 June 1941, as one of three German Army for ...
and advanced towards the southern suburbs of Berlin. On 23 April General Helmuth Weidling
Helmuth Otto Ludwig Weidling (2 November 1891 – 17 November 1955) was a German general during World War II. He was the last commander of the Berlin Defence Area during the Battle of Berlin, and led the defence of the city against Soviet forc ...
assumed command of the forces within Berlin. The garrison
A garrison (from the French ''garnison'', itself from the verb ''garnir'', "to equip") is any body of troops stationed in a particular location, originally to guard it. The term now often applies to certain facilities that constitute a mili ...
consisted of several depleted and disorganised Army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
and Waffen-SS
The (, "Armed SS") was the combat branch of the Nazi Party's ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with Waffen-SS foreign volunteers and conscripts, volunteers and conscripts from both occup ...
divisions, along with poorly trained ''Volkssturm
The (; "people's storm") was a levée en masse national militia established by Nazi Germany during the last months of World War II. It was not set up by the German Army, the ground component of the combined German ''Wehrmacht'' armed forces, ...
'' and Hitler Youth
The Hitler Youth (german: Hitlerjugend , often abbreviated as HJ, ) was the youth organisation of the Nazi Party in Germany. Its origins date back to 1922 and it received the name ("Hitler Youth, League of German Worker Youth") in July 1926. ...
members. Over the course of the next week, the Red Army gradually took the entire city.
On 30 April, Hitler and several of his officials committed suicide. The city's garrison surrendered on 2 May but fighting continued to the north-west, west, and south-west of the city until the end of the war in Europe on 8 May (9 May in the Soviet Union) as some German units fought westward so that they could surrender to the Western Allies rather than to the Soviets.
Background

 On 12 January 1945, the Red Army began the Vistula–Oder Offensive across the
On 12 January 1945, the Red Army began the Vistula–Oder Offensive across the Narew
The Narew (; be, Нараў, translit=Naraŭ; or ; Sudovian: ''Naura''; Old German: ''Nare''; uk, Нарва, translit=Narva) is a 499-kilometre (310 mi) river primarily in north-eastern Poland, which is also a tributary of the river Vi ...
River; and, from Warsaw, a three-day operation on a broad front, which incorporated four army Fronts. On the fourth day, the Red Army broke out and started moving west, up to per day, taking East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label= Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
, Danzig, and Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint Joh ...
, drawing up on a line east of Berlin along the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
River.
The newly created Army Group Vistula
Army Group Vistula () was an Army Group of the '' Wehrmacht'', formed on 24 January 1945. It lasted for 105 days, having been put together from elements of Army Group A (shattered in the Soviet Vistula-Oder Offensive), Army Group Centre (similarl ...
, under the command of ''Reichsführer-SS
(, ) was a special title and rank that existed between the years of 1925 and 1945 for the commander of the (SS). ''Reichsführer-SS'' was a title from 1925 to 1933, and from 1934 to 1945 it was the highest rank of the SS. The longest-servi ...
'' Heinrich Himmler
Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was of the (Protection Squadron; SS), and a leading member of the Nazi Party of Germany. Himmler was one of the most powerful men in Nazi Germany and a main architect of th ...
, attempted a counter-attack, but this had failed by 24 February. The Red Army then drove on to Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
, clearing the right bank of the Oder River, thereby reaching into Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
.
In the south the Siege of Budapest took place. Three German divisions' attempts to relieve the encircled Hungarian capital city failed, and Budapest fell to the Soviets on 13 February. Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and the ...
insisted on a counter-attack to recapture the Drau-Danube triangle. The goal was to secure the oil region of Nagykanizsa
Nagykanizsa (; hr, Velika Kaniža/Velika Kanjiža, or just ''Kaniža/Kanjiža''; german: Großkirchen, Groß-Kanizsa; it, Canissa; sl, Velika Kaniža; tr, Kanije), known colloquially as Kanizsa, is a medium-sized city in Zala County in south ...
and regain the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
River for future operations, but the depleted German forces had been given an impossible task. By 16 March, the German Lake Balaton Offensive had failed, and a counter-attack by the Red Army took back in 24 hours everything the Germans had taken ten days to gain. On 30 March, the Soviets entered Austria; and in the Vienna Offensive
The Vienna offensive was an offensive launched by the Soviet 2nd and 3rd Ukrainian Fronts in order to capture Vienna, Austria, during World War II. The offensive lasted from 16 March to 15 April 1945.
After several days of street-to-street f ...
they captured Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
on 13 April.
Between June and September 1944, the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
had lost more than a million men, and it lacked the fuel and armaments needed to operate effectively. On 12 April 1945, Hitler, who had earlier decided to remain in the city against the wishes of his advisers, heard the news that the American President Franklin D. Roosevelt had died. This briefly raised false hopes in the ''Führerbunker
The ''Führerbunker'' () was an air raid shelter located near the Reich Chancellery in Berlin, Germany. It was part of a subterranean bunker complex constructed in two phases in 1936 and 1944. It was the last of the Führer Headquarters ...
'' that there might yet be a falling out among the Allies and that Berlin would be saved at the last moment, as had happened once before when Berlin was threatened (see the Miracle of the House of Brandenburg).
No plans were made by the Western Allies to seize the city by a ground operation. The Supreme Commander [Western] Allied Expeditionary Force, General Eisenhower lost interest in the race to Berlin
The Race to Berlin was a competition between Soviet Marshals Georgy Zhukov and Ivan Konev to be the first to enter Berlin during the final months of World War II in Europe.
In early 1945, with Germany's defeat inevitable, Soviet Premier Joseph ...
and saw no further need to suffer casualties by attacking a city that would be in the Soviet sphere of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence (SOI) is a spatial region or concept division over which a state or organization has a level of cultural, economic, military or political exclusivity.
While there may be a formal a ...
after the war, envisioning excessive friendly fire
In military terminology, friendly fire or fratricide is an attack by belligerent or neutral forces on friendly troops while attempting to attack enemy/hostile targets. Examples include misidentifying the target as hostile, cross-fire while en ...
if both armies attempted to occupy the city at once. The major Western Allied contribution to the battle was the bombing of Berlin
A bomb is an explosive weapon that uses the exothermic reaction of an explosive material to provide an extremely sudden and violent release of energy. Detonations inflict damage principally through ground- and atmosphere-transmitted mechanica ...
during 1945. During 1945 the United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
launched very large daytime raids on Berlin and for 36 nights in succession, scores of RAF Mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "li ...
s bombed the German capital, ending on the night of 20/21 April 1945 just before the Soviets entered the city.
Preparations
The Soviet offensive into central Germany, what later becameEast Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In t ...
, had two objectives. Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretar ...
did not believe the Western Allies would hand over territory occupied by them in the post-war Soviet zone, so he began the offensive on a broad front and moved rapidly to meet the Western Allies as far west as possible. But the overriding objective was to capture Berlin. The two goals were complementary because possession of the zone could not be won quickly unless Berlin were taken. Another consideration was that Berlin itself held useful post-war strategic assets, including Adolf Hitler and the German nuclear weapons program. On 6 March, Hitler appointed Lieutenant General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on th ...
Helmuth Reymann
Hellmuth Reymann (24 November 1892 – 8 December 1988) was an officer in the German Army ('' Heer'') during World War II. He was one of the last commanders of the Berlin Defence Area during the final assault by Soviet forces on Berlin.
World ...
commander of the Berlin Defence Area, replacing Lieutenant General Bruno Ritter von Hauenschild
__NOTOC__
Bruno Ritter von Hauenschild (9 June 1896 – 10 March 1953), born Bruno Hauenschild, was a general in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany during World War II
Hauenschild served in World War I; at the beginning of World War II, he rejoin ...
.
On 20 March, General Gotthard Heinrici
Gotthard Fedor August Heinrici (25 December 1886 – 10 December 1971) was a German general during World War II. Heinrici is considered as the premier defensive expert of the ''Wehrmacht''. His final command was Army Group Vistula, formed from t ...
was appointed Commander-in-Chief of Army Group Vistula replacing Himmler. Heinrici was one of the best defensive tacticians in the German army, and he immediately started to lay defensive plans. Heinrici correctly assessed that the main Soviet thrust would be made over the Oder River and along the main east-west Autobahn. He decided not to try to defend the banks of the Oder with anything more than a light skirmishing screen. Instead, Heinrici arranged for engineers
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who invent, design, analyze, build and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considering the li ...
to fortify the Seelow Heights
The Seelow Heights are situated around the town of Seelow, about east of Berlin, and overlook the Oderbruch, the western flood plain of the River Oder, which is a further to the east.
They are sometimes known as the "Gates to Berlin", because ...
, which overlooked the Oder River at the point where the Autobahn crossed them. This was some west of the Oder and east of Berlin. Heinrici thinned out the line in other areas to increase the manpower available to defend the heights. German engineers turned the Oder's flood plain, already saturated by the spring thaw, into a swamp
A swamp is a forested wetland.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in ...
by releasing the water from a reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.
Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including contr ...
upstream. Behind the plain on the plateau, the engineers built three belts of defensive emplacements reaching back towards the outskirts of Berlin (the lines nearer to Berlin were called the ''Wotan'' position). These lines consisted of anti-tank
Anti-tank warfare originated from the need to develop technology and tactics to destroy tanks during World War I. Since the Triple Entente deployed the first tanks in 1916, the German Empire developed the first anti-tank weapons. The first dev ...
ditches, anti-tank gun emplacements, and an extensive network of trenches
A trench is a type of excavation or in the ground that is generally deeper than it is wide (as opposed to a wider gully, or ditch), and narrow compared with its length (as opposed to a simple hole or pit).
In geology, trenches result from erosi ...
and bunkers
A bunker is a defensive military fortification designed to protect people and valued materials from falling bombs, artillery, or other attacks. Bunkers are almost always underground, in contrast to blockhouses which are mostly above ground. T ...
.
On 9 April, after a long resistance, Königsberg
Königsberg (, ) was the historic Prussian city that is now Kaliningrad, Russia. Königsberg was founded in 1255 on the site of the ancient Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades, and was ...
in East Prussia fell to the Red Army. This freed up Marshal Rokossovsky
Konstantin Konstantinovich (Xaverevich) Rokossovsky (Russian: Константин Константинович Рокоссовский; pl, Konstanty Rokossowski; 21 December 1896 – 3 August 1968) was a Soviet and Polish officer who becam ...
's 2nd Belorussian Front
The 2nd Belorussian Front ( Russian: Второй Белорусский фронт, alternative spellings are 2nd Byelorussian Front) was a military formation, of Army group size, of the Soviet Army during the Second World War. Soviet army g ...
to move west to the east bank of the Oder river. Marshal Georgy Zhukov
Georgy Konstantinovich Zhukov ( rus, Георгий Константинович Жуков, p=ɡʲɪˈorɡʲɪj kənstɐnʲˈtʲinəvʲɪtɕ ˈʐukəf, a=Ru-Георгий_Константинович_Жуков.ogg; 1 December 1896 – ...
concentrated his 1st Belorussian Front
The 1st Belorussian Front ( Russian: Пéрвый Белорусский фронт, ''Perviy Belorusskiy front'', also romanized " Byelorussian") was a major formation of the Soviet Army during World War II, being equivalent to a Western army ...
, which had been deployed along the Oder river from Frankfurt (Oder)
Frankfurt (Oder), also known as Frankfurt an der Oder (), is a city in the German state of Brandenburg. It has around 57,000 inhabitants, is one of the easternmost cities in Germany, the fourth-largest city in Brandenburg, and the largest German ...
in the south to the Baltic, into an area in front of the Seelow Heights. The 2nd Belorussian Front moved into the positions being vacated by the 1st Belorussian Front north of the Seelow Heights. While this redeployment was in progress, gaps were left in the lines; and the remnants of General Dietrich von Saucken
Dietrich Friedrich Eduard Kasimir von Saucken (16 May 1892 – 27 September 1980) was a German general during World War II who commanded the 2nd Army and the Army East Prussia. Turning down an offer to escape by air, he surrendered to the Re ...
's German II Army, which had been bottled up in a pocket near Danzig, managed to escape into the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
delta. To the south, Marshal Konev Konev (russian: Конев and Bulgarian, ua, Конєв from ''конь'' or ''кон'' meaning ''horse'') is a Russian, Bulgarian or Ukrainian masculine surname, its feminine counterpart is Koneva. It may refer to:
*Anatoly Konev (1921–1965), ...
shifted the main weight of the 1st Ukrainian Front
The 1st Ukrainian Front (Russian: Пéрвый Украи́нский фронт), previously the Voronezh Front (Russian: Воронежский Фронт) was a major formation of the Soviet Army during World War II, being equivalent to a ...
out of Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( pl, Górny Śląsk; szl, Gůrny Ślůnsk, Gōrny Ślōnsk; cs, Horní Slezsko; german: Oberschlesien; Silesian German: ; la, Silesia Superior) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, locate ...
and north-west to the Neisse
The Lusatian Neisse (german: Lausitzer Neiße; pl, Nysa Łużycka; cs, Lužická Nisa; Upper Sorbian: ''Łužiska Nysa''; Lower Sorbian: ''Łužyska Nysa''), or Western Neisse, is a river in northern Central Europe.1st Polish Army), 6,250 tanks, 7,500 aircraft, 41,600

 German
:
German
:
 The command of the German V Corps, trapped with the IX Army north of Forst, passed from the IV Panzer Army to the IX Army. The corps was still holding on to the Berlin-
The command of the German V Corps, trapped with the IX Army north of Forst, passed from the IV Panzer Army to the IX Army. The corps was still holding on to the Berlin- On 23 April 1945, the Soviet 1st Belorussian Front and 1st Ukrainian Front continued to tighten the encirclement, severing the last link between the German IX Army and the city. Elements of the 1st Ukrainian Front continued to move westward and started to engage the German XII Army moving towards Berlin. On this same day, Hitler appointed General
On 23 April 1945, the Soviet 1st Belorussian Front and 1st Ukrainian Front continued to tighten the encirclement, severing the last link between the German IX Army and the city. Elements of the 1st Ukrainian Front continued to move westward and started to engage the German XII Army moving towards Berlin. On this same day, Hitler appointed General
 The forces available to General Weidling for the city's defence included roughly 45,000 soldiers in several severely depleted
The forces available to General Weidling for the city's defence included roughly 45,000 soldiers in several severely depleted
 In the early hours of 29 April the Soviet
In the early hours of 29 April the Soviet
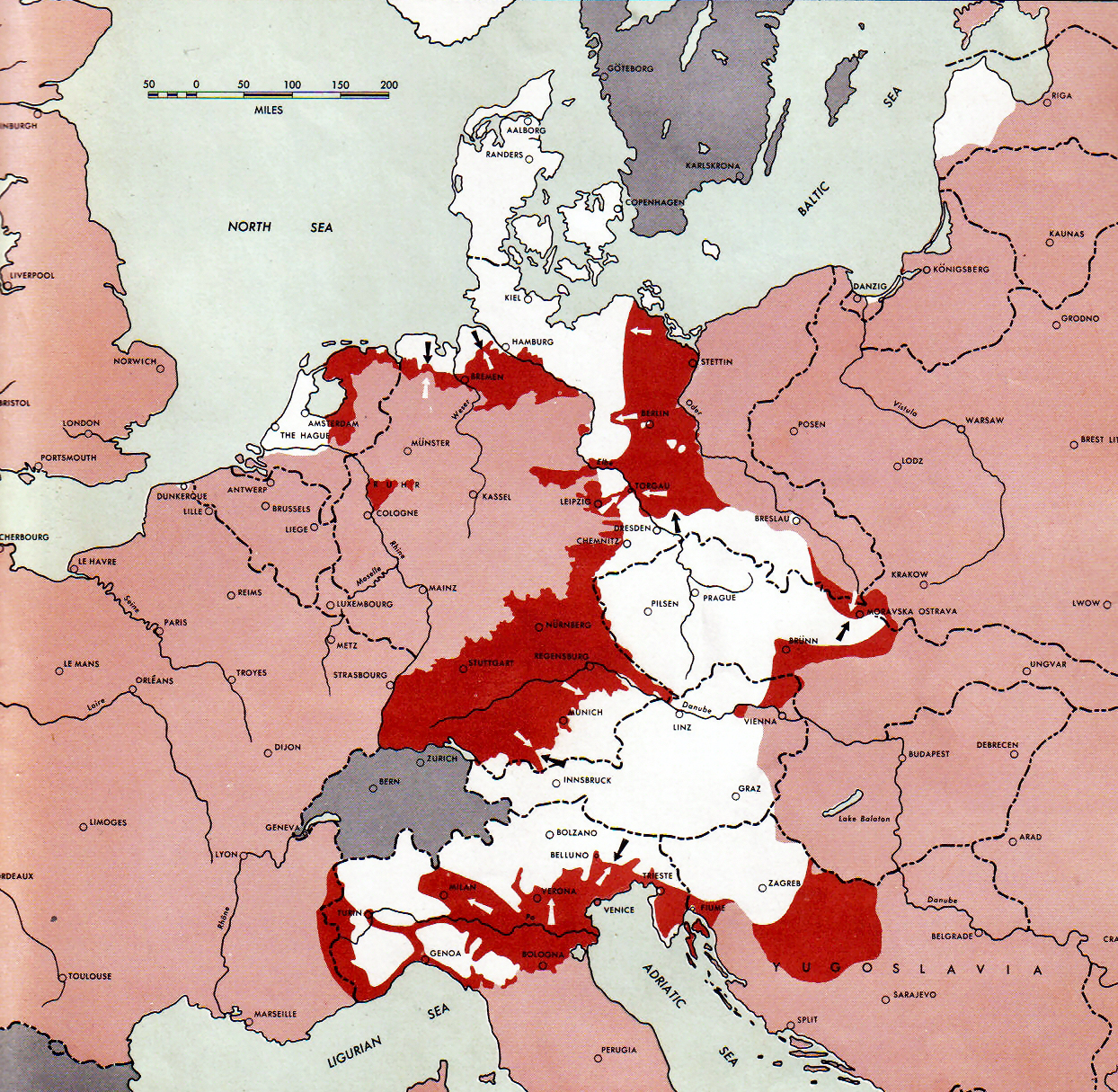 During the early hours of 30 April, Weidling informed Hitler in person that the defenders would probably exhaust their ammunition during the night. Hitler granted him permission to attempt a breakout through the encircling Red Army lines. That afternoon, Hitler and Braun committed
During the early hours of 30 April, Weidling informed Hitler in person that the defenders would probably exhaust their ammunition during the night. Hitler granted him permission to attempt a breakout through the encircling Red Army lines. That afternoon, Hitler and Braun committed
 The successes of the 1st Ukrainian Front during the first nine days of the battle meant that by 25 April, they were occupying large swathes of the area south and south-west of Berlin. Their spearheads had met elements of the 1st Belorussian Front west of Berlin, completing the investment of the city. Meanwhile, the
The successes of the 1st Ukrainian Front during the first nine days of the battle meant that by 25 April, they were occupying large swathes of the area south and south-west of Berlin. Their spearheads had met elements of the 1st Belorussian Front west of Berlin, completing the investment of the city. Meanwhile, the 
 According to Grigoriy Krivosheev, declassified archival data gives 81,116 Soviet dead for the operation, including the battles of Seelow Heights and the Halbe. Another 280,251 were reported wounded or sick. The operation also cost the Soviets about 1,997 tanks and self-propelled guns. All losses were considered irrecoverable - i.e. beyond economic repair or no longer serviceable. The Soviets claimed to have captured nearly 480,000 German soldiers, while German research put the number of dead between 92,000 and 100,000. Some 125,000 civilians are estimated to have died during the entire operation.
According to Grigoriy Krivosheev, declassified archival data gives 81,116 Soviet dead for the operation, including the battles of Seelow Heights and the Halbe. Another 280,251 were reported wounded or sick. The operation also cost the Soviets about 1,997 tanks and self-propelled guns. All losses were considered irrecoverable - i.e. beyond economic repair or no longer serviceable. The Soviets claimed to have captured nearly 480,000 German soldiers, while German research put the number of dead between 92,000 and 100,000. Some 125,000 civilians are estimated to have died during the entire operation.
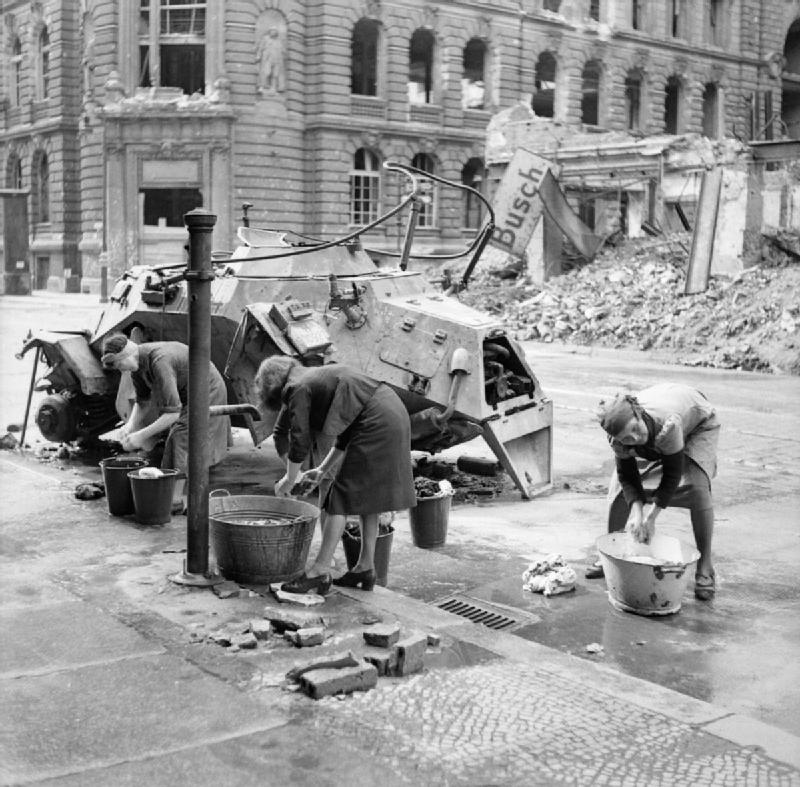 In those areas that the Red Army had captured and before the fighting in the centre of the city had stopped, the Soviet authorities took measures to start restoring essential services. Almost all transport in and out of the city had been rendered inoperative, and bombed-out sewers had contaminated the city's water supplies. The Soviet authorities appointed local Germans to head each city block, and organised the cleaning-up. The Red Army made a major effort to feed the residents of the city. Most Germans, both soldiers and civilians, were grateful to receive food issued at Red Army
In those areas that the Red Army had captured and before the fighting in the centre of the city had stopped, the Soviet authorities took measures to start restoring essential services. Almost all transport in and out of the city had been rendered inoperative, and bombed-out sewers had contaminated the city's water supplies. The Soviet authorities appointed local Germans to head each city block, and organised the cleaning-up. The Red Army made a major effort to feed the residents of the city. Most Germans, both soldiers and civilians, were grateful to receive food issued at Red Army  During and immediately following the assault, in many areas of the city, vengeful Soviet troops (often rear echelon units) engaged in
During and immediately following the assault, in many areas of the city, vengeful Soviet troops (often rear echelon units) engaged in


 All told, 402 Red Army personnel were bestowed the USSR's highest degree of distinction, the title
All told, 402 Red Army personnel were bestowed the USSR's highest degree of distinction, the title
OnWar.com
on 1 July 2003.
artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during si ...
pieces and mortars, 3,255 truck-mounted Katyusha rocket launchers (nicknamed 'Stalin's Pipe Organs'), and 95,383 motor vehicles, many manufactured in the US.
Opposing forces
Northern Sector German : Third Panzer Army : General of PanzerHasso von Manteuffel
Freiherr Hasso Eccard von Manteuffel (14 January 1897 – 24 September 1978) was a German baron born to the Prussian noble von Manteuffel family and was a general during World War II who commanded the 5th Panzer Army. He was a recipient of th ...
:*4 infantry divisions
:*3 naval divisions
:*2 volksgrenadier divisions
Soviet
: Second Belorussian Front
The 2nd Belorussian Front (Russian: Второй Белорусский фронт, alternative spellings are 2nd Byelorussian Front) was a military formation, of Army group size, of the Soviet Army during the Second World War. Soviet army gr ...
: Marshal Konstantin Rokossovsky
Konstantin Konstantinovich (Xaverevich) Rokossovsky ( Russian: Константин Константинович Рокоссовский; pl, Konstanty Rokossowski; 21 December 1896 – 3 August 1968) was a Soviet and Polish officer who bec ...
:*31 rifle divisions
:* 7 guards rifle divisions
:* 1 motorized rifle battalion
:* 3 tank battalions
Middle Sector

 German
:
German
: Army Group Vistula
Army Group Vistula () was an Army Group of the '' Wehrmacht'', formed on 24 January 1945. It lasted for 105 days, having been put together from elements of Army Group A (shattered in the Soviet Vistula-Oder Offensive), Army Group Centre (similarl ...
: Colonel General Gotthard Heinrici
Gotthard Fedor August Heinrici (25 December 1886 – 10 December 1971) was a German general during World War II. Heinrici is considered as the premier defensive expert of the ''Wehrmacht''. His final command was Army Group Vistula, formed from t ...
:*15 infantry divisions
:* 6 panzer divisions
:* 2 motorized infantry divisions
: Ninth Army
: General of Infantry Theodor Busse
Ernst Hermann August Theodor Busse (15 December 1897 – 21 October 1986) was a German officer during World War I and World War II.
Early life and career
Busse, a native of Frankfurt (Oder), joined the Imperial German Army as an officer cad ...
:* 5 infantry divisions
:* 4 panzergrenadier divisions
:* 1 panzer division
:* 1 SS grenadier division
:* 1 security division
:* 1 Jäger division
:* 1 parachute division
:* 1 Kampfgruppe
Soviet
: First Belorussian Front
: Marshal Georgy Zhukov
Georgy Konstantinovich Zhukov ( rus, Георгий Константинович Жуков, p=ɡʲɪˈorɡʲɪj kənstɐnʲˈtʲinəvʲɪtɕ ˈʐukəf, a=Ru-Георгий_Константинович_Жуков.ogg; 1 December 1896 – ...
:*54 rifle divisions
:*16 guards rifle divisions
:* 5 infantry divisions (Polish)
:* 3 guards cavalry divisions
:* 3 mechanized brigades
:* 6 guards mechanized brigades
:* 7 tank brigades
:*10 guards tank brigades
:* 1 armored brigade (Polish)
:* 2 motorized rifle brigades
Southern Sector
German
: Army Group Centre
Army Group Centre (german: Heeresgruppe Mitte) was the name of two distinct strategic German Army Groups that fought on the Eastern Front in World War II. The first Army Group Centre was created on 22 June 1941, as one of three German Army for ...
: Feldmarshal Ferdinand Schörner
:*13 infantry divisions
:* 3 panzer divisions
:* 1 Reichsarbeitsdienst division
:* 1 SS police division
:* 1 SS grenadier division
:* 1 anti-aircraft division
:* 2 Kampfgruppen
Soviet
* First Ukrainian Front
: Marshal Ivan Konev
Ivan Stepanovich Konev ( rus, link=no, Ива́н Степа́нович Ко́нев, p=ɪˈvan sʲtʲɪˈpanəvʲɪtɕ ˈkonʲɪf; – 21 May 1973) was a Soviet general and Marshal of the Soviet Union who led Red Army forces on the ...
:*26 rifle divisions
:*15 guards rifle divisions
:* 5 infantry divisions (Polish)
:* 3 guards cavalry divisions
:* 1 guards airborne division
:* 9 guards mechanized brigades
:* 3 mechanized brigades
:* 4 guards motorized rifle brigades
:* 1 armored corps (Polish)
:* 4 tank brigades
:*10 guards tank brigades
:* 1 motorized rifle brigade
Battle of the Oder–Neisse
The sector in which most of the fighting in the overall offensive took place was the Seelow Heights, the last major defensive line outside Berlin. TheBattle of the Seelow Heights
The Battle of the Seelow Heights (german: Schlacht um die Seelower Höhen) was part of the Berlin Offensive, Berlin Strategic Offensive Operation (16 April–2 May 1945). A pitched battle, it was one of the last assaults on large Field entrenchm ...
, fought over four days from 16 until 19 April, was one of the last pitched battle
A pitched battle or set-piece battle is a battle in which opposing forces each anticipate the setting of the battle, and each chooses to commit to it. Either side may have the option to disengage before the battle starts or shortly thereafter. A ...
s of World War II: almost one million Red Army soldiers and more than 20,000 tanks and artillery pieces were deployed to break through the "Gates to Berlin", which were defended by about 100,000 German soldiers and 1,200 tanks and guns. The Soviet forces led by Zhukov broke through the defensive positions, having suffered about 30,000 dead, while 12,000 German personnel were killed.
On 19 April, the fourth day, the 1st Belorussian Front broke through the final line of the Seelow Heights and nothing but broken German formations lay between them and Berlin. The 1st Ukrainian Front, having captured Forst the day before, fanned out into open country. One powerful thrust by Gordov's 3rd Guards Army and Rybalko's 3rd
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* 1⁄60 of a ''second'', or 1⁄3600 of a ''minute''
Places
* 3rd Street (disambiguation)
* Third Avenue (disambiguation)
* H ...
and Lelyushenko's 4th Guards Tank Armies were heading north-east towards Berlin while other armies headed west towards a section of the United States Army's front line south-west of Berlin on the Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Re ...
. With these advances, the Soviet forces drove a wedge between Army Group Vistula in the north and Army Group Centre
Army Group Centre (german: Heeresgruppe Mitte) was the name of two distinct strategic German Army Groups that fought on the Eastern Front in World War II. The first Army Group Centre was created on 22 June 1941, as one of three German Army for ...
in the south. By the end of the day, the German eastern front line north of Frankfurt around Seelow and to the south around Forst had ceased to exist. These breakthroughs allowed the two Soviet Fronts to envelop
Envelopment is the military tactic of seizing objectives in the enemy's rear with the goal of destroying specific enemy forces and denying them the ability to withdraw. Rather than attacking an enemy head-on as in a frontal assault an envelopment ...
the German 9th Army in a large pocket west of Frankfurt. Attempts by the 9th Army to break out to the west resulted in the Battle of Halbe
The Battle of Halbe (german: Kesselschlacht von Halbe, russian: Хальбский котёл, Halbe pocket) was a battle lasting from April 24 – May 1, 1945 in which the German Ninth Army—under the command of General Theodor Busse—was dest ...
. The cost to the Soviet forces had been very high, with over 2,807 tanks lost between 1 and 19 April, including at least 727 at the Seelow Heights.
In the meantime, RAF Mosquitos conducted tactical air raids against German positions inside Berlin on the nights of 15 April (105 bombers), 17 April (61 bombers), 18 April (57 bombers), 19 April (79 bombers), and 20 April (78 bombers).
Encirclement of Berlin
On 20 April 1945, Hitler's 56th birthday, Soviet artillery of the 1st Belorussian Front began shelling Berlin and did not stop until the city surrendered. The weight of ordnance delivered by Soviet artillery during the battle was greater than the total tonnage dropped by Western Allied bombers on the city. While the 1st Belorussian Front advanced towards the east and north-east of the city, the 1st Ukrainian Front pushed through the last formations of the northern wing of Army Group Centre and passed north of Juterbog, well over halfway to the American front line on the river Elbe atMagdeburg
Magdeburg (; nds, label=Low Saxon, Meideborg ) is the capital and second-largest city of the German state Saxony-Anhalt. The city is situated at the Elbe river.
Otto I, the first Holy Roman Emperor and founder of the Archdiocese of Magdebu ...
. To the north between Stettin
Szczecin (, , german: Stettin ; sv, Stettin ; Latin: ''Sedinum'' or ''Stetinum'') is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major s ...
and Schwedt
Schwedt (or Schwedt/Oder; ) is a town in Brandenburg, in northeastern Germany. With the official status of a ''Große Kreisstadt, Große kreisangehörige Stadt'' (major district town), it is the largest town of the Uckermark (district), Uckermark ...
, the 2nd Belorussian Front attacked the northern flank of Army Group Vistula, held by Hasso von Manteuffel
Freiherr Hasso Eccard von Manteuffel (14 January 1897 – 24 September 1978) was a German baron born to the Prussian noble von Manteuffel family and was a general during World War II who commanded the 5th Panzer Army. He was a recipient of th ...
's III Panzer Army. The next day, Bogdanov Bogdanov (Богданов) or Bogdanova (Богданова; feminine) is a common Russian surname that derives from the given name Bogdan and literally means ''Bogdan's''. Translated: Bogu dan = God gave. Notable people with the surname include:
...
's 2nd Guards Tank Army
The 2nd Guards Tank Army () was a large military formation of the Red Army and later the Soviet Army, now part of the Russian Ground Forces of the Russian Federation.
The army was originally formed in early 1943 as the 2nd Tank Army. It was the ...
advanced nearly north of Berlin and then attacked south-west of Werneuchen
Werneuchen () is a town in Brandenburg, Germany, in the district of Barnim northeast of Berlin within the metropolitan area. Most of the population of Werneuchen commutes to Berlin.
Demography
File:Bevölkerungsentwicklung Werneuchen.pdf, D ...
. The Soviet plan was to encircle Berlin first and then envelop the IX Army.
 The command of the German V Corps, trapped with the IX Army north of Forst, passed from the IV Panzer Army to the IX Army. The corps was still holding on to the Berlin-
The command of the German V Corps, trapped with the IX Army north of Forst, passed from the IV Panzer Army to the IX Army. The corps was still holding on to the Berlin-Cottbus
Cottbus (; Lower Sorbian: ''Chóśebuz'' ; Polish: Chociebuż) is a university city and the second-largest city in Brandenburg, Germany. Situated around southeast of Berlin, on the River Spree, Cottbus is also a major railway junction with exte ...
highway front line. Field Marshal Ferdinand Schörner's Army Group Centre launched a counter-offensive aimed at breaking through to Berlin from the south and entering (the Battle of Bautzen) in the 1st Ukrainian Front region, engaging the 2nd Polish Army and elements of the Red Army's 52nd Army and 5th Guards Army. When the old southern flank of the IV Panzer Army had some local successes counter-attacking north against the 1st Ukrainian Front, Hitler unrealistically ordered the IX Army to hold Cottbus and set up a front facing west. Next, they were to attack the Soviet columns advancing north to form a pincer that would meet the IV Panzer Army coming from the south and envelop the 1st Ukrainian Front before destroying it. They were to anticipate a southward attack by the III Panzer Army and be ready to be the southern arm of a pincer attack that would envelop 1st Belorussian Front, which would be destroyed by SS-General Felix Steiner
Felix Martin Julius Steiner (23 May 1896 – 12 May 1966) was a German SS commander during the Nazi era. During World War II, he served in the Waffen-SS, the combat branch of the SS, and commanded several SS divisions and corps. He was awarded t ...
's Army Detachment advancing from north of Berlin. Later in the day, when Steiner explained that he did not have the divisions to achieve this, Heinrici made it clear to Hitler's staff that unless the IX Army retreated immediately, it would be enveloped by the Soviets. He stressed that it was already too late for it to move north-west to Berlin and would have to retreat west. Heinrici went on to say that if Hitler did not allow it to move west, he would ask to be relieved of his command.
On 22 April 1945, at his afternoon situation conference, Hitler fell into a tearful rage when he realised that his plans, prepared the previous day, could not be achieved. He declared that the war was lost, blaming the generals for the defeat and that he would remain in Berlin until the end and then kill himself.
In an attempt to coax Hitler out of his rage, General Alfred Jodl
Alfred Josef Ferdinand Jodl (; 10 May 1890 – 16 October 1946) was a German '' Generaloberst'' who served as the chief of the Operations Staff of the '' Oberkommando der Wehrmacht'' – the German Armed Forces High Command – throughout Worl ...
speculated that General Walther Wenck
Walther Wenck () (18 September 1900 – 1 May 1982) was a German officer and industrialist. He was the youngest General of the branch (''General der Truppengattung'') in the German Army and a staff officer during World War II. At the end of the w ...
's XII Army, which was facing the Americans, could move to Berlin because the Americans, already on the Elbe River, were unlikely to move further east. This assumption was based on his viewing of the captured Eclipse documents, which organised the partition of Germany among the Allies. Hitler immediately grasped the idea, and within hours Wenck was ordered to disengage from the Americans and move the XII Army north-east to support Berlin. It was then realised that if the IX Army moved west, it could link up with the XII Army. In the evening Heinrici was given permission to make the link-up.
Elsewhere, the 2nd Belorussian Front had established a bridgehead deep on the west bank of the Oder and was heavily engaged with the III Panzer Army. The IX Army had lost Cottbus and was being pressed from the east. A Soviet tank spearhead was on the Havel
The Havel () is a river in northeastern Germany, flowing through the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Berlin and Saxony-Anhalt. It is a right tributary of the Elbe and long. However, the direct distance from its source to its mo ...
River to the east of Berlin, and another had at one point penetrated the inner defensive ring of Berlin.
The capital was now within range of field artillery. A Soviet war correspondent, in the style of World War II Soviet journalism, gave the following account of an important event which took place on 22 April 1945 at 08:30 local time:
 On 23 April 1945, the Soviet 1st Belorussian Front and 1st Ukrainian Front continued to tighten the encirclement, severing the last link between the German IX Army and the city. Elements of the 1st Ukrainian Front continued to move westward and started to engage the German XII Army moving towards Berlin. On this same day, Hitler appointed General
On 23 April 1945, the Soviet 1st Belorussian Front and 1st Ukrainian Front continued to tighten the encirclement, severing the last link between the German IX Army and the city. Elements of the 1st Ukrainian Front continued to move westward and started to engage the German XII Army moving towards Berlin. On this same day, Hitler appointed General Helmuth Weidling
Helmuth Otto Ludwig Weidling (2 November 1891 – 17 November 1955) was a German general during World War II. He was the last commander of the Berlin Defence Area during the Battle of Berlin, and led the defence of the city against Soviet forc ...
as the commander of the Berlin Defence Area, replacing Lieutenant General Reymann. Meanwhile, by 24 April 1945 elements of 1st Belorussian Front and 1st Ukrainian Front had completed the encirclement of the city. Within the next day, 25 April 1945, the Soviet investment
Investment is the dedication of money to purchase of an asset to attain an increase in value over a period of time. Investment requires a sacrifice of some present asset, such as time, money, or effort.
In finance, the purpose of investing is ...
of Berlin was consolidated, with leading Soviet units probing and penetrating the S-Bahn defensive ring. By the end of the day, it was clear that the German defence of the city could not do anything but temporarily delay the capture of the city by the Soviets, since the decisive stages of the battle had already been fought and lost by the Germans outside the city. By that time, Schörner's offensive, initially successful, had mostly been thwarted, although he did manage to inflict significant casualties on the opposing Polish and Soviet units, slowing down their progress.
Battle in Berlin
 The forces available to General Weidling for the city's defence included roughly 45,000 soldiers in several severely depleted
The forces available to General Weidling for the city's defence included roughly 45,000 soldiers in several severely depleted German Army
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the ''Luftwaf ...
and Waffen-SS
The (, "Armed SS") was the combat branch of the Nazi Party's ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with Waffen-SS foreign volunteers and conscripts, volunteers and conscripts from both occup ...
divisions. These divisions were supplemented by the police
The police are a Law enforcement organization, constituted body of Law enforcement officer, persons empowered by a State (polity), state, with the aim to law enforcement, enforce the law, to ensure the safety, health and possessions of citize ...
force, boys
A boy is a young male human. The term is commonly used for a child or an adolescent. When a male human reaches adulthood, he is described as a man.
Definition, etymology, and use
According to the ''Merriam-Webster Dictionary'', a boy is "a ...
in the compulsory Hitler Youth
The Hitler Youth (german: Hitlerjugend , often abbreviated as HJ, ) was the youth organisation of the Nazi Party in Germany. Its origins date back to 1922 and it received the name ("Hitler Youth, League of German Worker Youth") in July 1926. ...
, and the ''Volkssturm
The (; "people's storm") was a levée en masse national militia established by Nazi Germany during the last months of World War II. It was not set up by the German Army, the ground component of the combined German ''Wehrmacht'' armed forces, ...
''. Many of the 40,000 elderly men of the ''Volkssturm'' had been in the army as young men and some were veterans of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
. Hitler appointed ''SS Brigadeführer
SS is an abbreviation for ''Schutzstaffel'', a paramilitary organisation in Nazi Germany.
SS, Ss, or similar may also refer to:
Places
*Guangdong Experimental High School (''Sheng Shi'' or ''Saang Sat''), China
*Province of Sassari, Italy (vehi ...
'' Wilhelm Mohnke the Battle Commander for the central government district that included the Reich Chancellery
The Reich Chancellery (german: Reichskanzlei) was the traditional name of the office of the Chancellor of Germany (then called ''Reichskanzler'') in the period of the German Reich from 1878 to 1945. The Chancellery's seat, selected and prepared ...
and ''Führerbunker''. He had over 2,000 men under his command. Weidling organised the defences into eight sectors designated 'A' through to 'H' each one commanded by a colonel or a general, but most had no combat experience. To the west of the city was the 20th Infantry Division. To the north of the city was the 9th Parachute Division. To the north-east of the city was the Panzer Division ''Müncheberg''. To the south-east of the city and to the east of Tempelhof Airport
Berlin Tempelhof Airport (german: Flughafen Berlin-Tempelhof) was one of the first airports in Berlin, Germany. Situated in the south-central Berlin borough of Tempelhof-Schöneberg, the airport ceased operating in 2008 amid controversy, leav ...
was the 11th SS Panzergrenadier Division ''Nordland''. The reserve, 18th Panzergrenadier Division
18 (eighteen) is the natural number following 17 and preceding 19.
In mathematics
* Eighteen is a composite number, its divisors being 1, 2, 3, 6 and 9. Three of these divisors (3, 6 and 9) add up to 18, hence 18 is a semiperfect number. ...
, was in Berlin's central district.
On 23 April, Berzarin's 5th Shock Army and Katukov's 1st Guards Tank Army assaulted Berlin from the south-east and, after overcoming a counter-attack by the German LVI Panzer Corps, reached the Berlin S-Bahn
The Berlin S-Bahn () is a rapid transit railway system in and around Berlin, the capital city of Germany. It has been in operation under this name since December 1930, having been previously called the special tariff area ''Berliner Stadt-, Ri ...
ring railway on the north side of the Teltow
Teltow [] is a town in the Potsdam-Mittelmark district, in Brandenburg, Germany.
Geography
Teltow is part of the agglomeration of Berlin. The distance to the Berlin city centre is , while the distance to Potsdam is .
The Teltow Canal links th ...
Canal by the evening of 24 April. During the same period, of all the German forces ordered to reinforce the inner defences of the city by Hitler, only a small contingent of French SS volunteers under the command of ''SS Brigadeführer'' Gustav Krukenberg
Gustav Krukenberg (8 March 1888 – 23 October 1980) was a high-ranking member of the Waffen-SS and commander of the SS Charlemagne Division and the remains of the SS Division Nordland during the Battle of Berlin in April 1945. After Krukenberg s ...
arrived in Berlin. During 25 April, Krukenberg was appointed as the commander of Defence Sector C, the sector under the most pressure from the Soviet assault on the city.
On 26 April, Chuikov's 8th Guards Army
The 8th Guards Order of Lenin Combined Arms Army (abbreviated 8th CAA) is an army of the Russian Ground Forces, headquartered in Novocherkassk, Rostov Oblast, within Russia′s Southern Military District, that was reinstated in 2017 as a success ...
and the 1st Guards Tank Army fought their way through the southern suburbs and attacked Tempelhof Airport, just inside the S-Bahn defensive ring, where they met stiff resistance from the ''Müncheberg'' Division. But by 27 April, the two understrength divisions (''Müncheberg'' and ''Nordland'') that were defending the south-east, now facing five Soviet armies—from east to west, the 5th Shock Army, the 8th Guards Army, the 1st Guards Tank Army and Rybalko's 3rd Guards Tank Army (part of the 1st Ukrainian Front)—were forced back towards the centre, taking up new defensive positions around Hermannplatz. Krukenberg informed General Hans Krebs, Chief
Chief may refer to:
Title or rank
Military and law enforcement
* Chief master sergeant, the ninth, and highest, enlisted rank in the U.S. Air Force and U.S. Space Force
* Chief of police, the head of a police department
* Chief of the bo ...
of the General Staff
A military staff or general staff (also referred to as army staff, navy staff, or air staff within the individual services) is a group of officers, enlisted and civilian staff who serve the commander of a division or other large military ...
of (OKH
The (; abbreviated OKH) was the high command of the Army of Nazi Germany. It was founded in 1935 as part of Adolf Hitler's rearmament of Germany. OKH was ''de facto'' the most important unit within the German war planning until the defeat at ...
) that within 24 hours the ''Nordland'' would have to fall back to the centre sector Z (for ''Zentrum''). The Soviet advance to the city centre was along these main axes: from the south-east, along the Frankfurter Allee (ending and stopped at the Alexanderplatz
() ( en, Alexander Square) is a large public square and transport hub in the central Mitte district of Berlin. The square is named after the Russian Tsar Alexander I, which also denotes the larger neighbourhood stretching from in the no ...
); from the south along Sonnenallee
''Sonnenallee'' (''Sun Avenue'' or ''Sun Alley'') is a 1999 German comedy film about life in East Berlin in the late 1970s. The movie was directed by Leander Haußmann. The film was released shortly before the corresponding novel, ''Am kürzere ...
ending north of the Belle-Alliance-Platz, from the south ending near the Potsdamer Platz
Potsdamer Platz (, ''Potsdam Square'') is a public square and traffic intersection in the center of Berlin, Germany, lying about south of the Brandenburg Gate and the Reichstag (German Parliament Building), and close to the southeast corn ...
and from the north ending near the Reichstag. The Reichstag, the Moltke bridge, Alexanderplatz, and the Havel bridges at Spandau saw the heaviest fighting, with house-to-house and hand-to-hand combat
Hand-to-hand combat (sometimes abbreviated as HTH or H2H) is a physical confrontation between two or more persons at short range (grappling distance or within the physical reach of a handheld weapon) that does not involve the use of weapons.Hun ...
. The foreign contingents of the SS fought particularly hard, because they were ideologically motivated and they believed that they would not live if captured.
Battle for the Reichstag
 In the early hours of 29 April the Soviet
In the early hours of 29 April the Soviet 3rd Shock Army
The 3rd Shock Army (russian: Третья ударная армия) was a field army of the Red Army formed during the Second World War. The "Shock" armies were created with the specific structure to engage and destroy significant enemy forces ...
crossed the Moltke Bridge and started to fan out into the surrounding streets and buildings. The initial assaults on buildings, including the Ministry of the Interior, were hampered by the lack of supporting artillery. It was not until the damaged bridges were repaired that artillery could be moved up in support. At 04:00 hours, in the ''Führerbunker'', Hitler signed his last will and testament
A will or testament is a legal document that expresses a person's (testator) wishes as to how their property ( estate) is to be distributed after their death and as to which person (executor) is to manage the property until its final distributio ...
and, shortly afterwards, married Eva Braun
Eva Anna Paula Hitler (; 6 February 1912 – 30 April 1945) was a German photographer who was the longtime companion and briefly the wife of Adolf Hitler. Braun met Hitler in Munich when she was a 17-year-old assistant and model for his ...
. At dawn the Soviets pressed on with their assault in the south-east. After very heavy fighting they managed to capture Gestapo
The (), abbreviated Gestapo (; ), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe.
The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Prussia into one orga ...
headquarters on Prinz-Albrechtstrasse, but a Waffen-SS counter-attack forced the Soviets to withdraw from the building. To the south-west the 8th Guards Army attacked north across the Landwehr canal into the Tiergarten.
By the next day, 30 April, the Soviets had solved their bridging problems and with artillery support at 06:00 they launched an attack on the Reichstag, but because of German entrenchments and support from 12.8 cm guns away on the roof of the Zoo flak tower, close by Berlin Zoo
The Berlin Zoological Garden (german: link=no, Zoologischer Garten Berlin) is the oldest surviving and best-known zoo in Germany. Opened in 1844, it covers and is located in Berlin's Tiergarten. With about 1,380 different species and over 20,2 ...
, it was not until that evening that the Soviets were able to enter the building. The Reichstag had not been in use since it had burned
Burned or burnt may refer to:
* Anything which has undergone combustion
* Burned (image), quality of an image transformed with loss of detail in all portions lighter than some limit, and/or those darker than some limit
* ''Burnt'' (film), a 2015 ...
in February 1933 and its interior resembled a rubble heap more than a government building. The German troops inside made excellent use of this and were heavily entrenched. Fierce room-to-room fighting ensued. At that point there was still a large contingent of German soldiers in the basement who launched counter-attacks against the Red Army. By 2 May 1945 the Red Army controlled the building entirely. The famous photo of the two soldiers planting the flag on the roof of the building is a re-enactment photo taken the day after the building was taken. To the Soviets the event as represented by the photo became symbolic of their victory demonstrating that the Battle of Berlin, as well as the Eastern Front hostilities as a whole, ended with the total Soviet victory. As the 756th Regiment's commander Zinchenko had stated in his order to Battalion Commander Neustroev "... the Supreme High Command ... and the entire Soviet People order you to erect the victory banner on the roof above Berlin".
Battle for the centre
 During the early hours of 30 April, Weidling informed Hitler in person that the defenders would probably exhaust their ammunition during the night. Hitler granted him permission to attempt a breakout through the encircling Red Army lines. That afternoon, Hitler and Braun committed
During the early hours of 30 April, Weidling informed Hitler in person that the defenders would probably exhaust their ammunition during the night. Hitler granted him permission to attempt a breakout through the encircling Red Army lines. That afternoon, Hitler and Braun committed suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and ...
and their bodies were cremated not far from the bunker. In accordance with Hitler's last will and testament, Admiral Karl Dönitz
Karl Dönitz (sometimes spelled Doenitz; ; 16 September 1891 24 December 1980) was a German admiral who briefly succeeded Adolf Hitler as head of state in May 1945, holding the position until the dissolution of the Flensburg Government fo ...
became the " President of the Reich" (''Reichspräsident'') and Joseph Goebbels became the new Chancellor of the Reich (''Reichskanzler
The chancellor of Germany, officially the federal chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany,; often shortened to ''Bundeskanzler''/''Bundeskanzlerin'', / is the head of the federal government of Germany and the commander in chief of the Ge ...
'').
As the perimeter shrank and the surviving defenders fell back, they became concentrated into a small area in the city centre. By now there were about 10,000 German soldiers in the city centre, which was being assaulted from all sides. One of the other main thrusts was along Wilhelmstrasse on which the Air Ministry, built of reinforced concrete
Reinforced concrete (RC), also called reinforced cement concrete (RCC) and ferroconcrete, is a composite material in which concrete's relatively low ultimate tensile strength, tensile strength and ductility are compensated for by the inclusion ...
, was pounded by large concentrations of Soviet artillery. The remaining German Tiger tanks of the Hermann von Salza
Hermann von Salza (or Herman of Salza; c. 1165 – 20 March 1239) was the fourth Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights, serving from 1210 to 1239. A skilled diplomat with ties to the Holy Roman Emperor and the Pope, Hermann oversaw the expansio ...
battalion took up positions in the east of the Tiergarten to defend the centre against Kuznetsov's 3rd Shock Army (which although heavily engaged around the Reichstag was also flanking the area by advancing through the northern Tiergarten) and the 8th Guards Army advancing through the south of the Tiergarten. These Soviet forces had effectively cut the sausage-shaped area held by the Germans in half and made any escape attempt to the west for German troops in the centre much more difficult.
During the early hours of 1 May, Krebs talked to General Chuikov, commander of the Soviet 8th Guards Army,, states 3 am, and , 4 am, for Krebs' meeting with Chuikov informing him of Hitler's death and a willingness to negotiate a citywide surrender. They could not agree on terms because of Soviet insistence on unconditional surrender and Krebs' claim that he lacked authorisation to agree to that. Goebbels was against surrender. In the afternoon, Goebbels and his wife killed their children and then themselves. Goebbels's death removed the last impediment which prevented Weidling from accepting the terms of unconditional surrender of his garrison, but he chose to delay the surrender until the next morning to allow the planned breakout to take place under the cover of darkness.
Breakout and surrender
On the night of 1/2 May, most of the remnants of the Berlin garrison attempted to break out of the city centre in three different directions. Only those that went west through the Tiergarten and crossed theCharlottenbrücke
Charlotten Bridge (German ''Charlottenbrücke'') in Spandau links the old town of Spandau on the west bank of the Havel with the east bank.
It was one of the few bridges over which some of the German garrison of Berlin were able to escape during ...
(a bridge over the Havel) into Spandau
Spandau () is the westernmost of the 12 boroughs () of Berlin, situated at the confluence of the Havel and Spree rivers and extending along the western bank of the Havel. It is the smallest borough by population, but the fourth largest by land ...
succeeded in breaching Soviet lines. Only a handful of those who survived the initial breakout made it to the lines of the Western Allies—most were either killed or captured by the Red Army's outer encirclement forces west of the city. Early in the morning of 2 May, the Soviets captured the Reich Chancellery. General Weidling surrendered with his staff at 06:00 hours. He was taken to see General Vasily Chuikov at 08:23, where Weidling ordered the city's defenders to surrender to the Soviets.
The 350-strong garrison of the Zoo flak tower left the building. There was sporadic fighting in a few isolated buildings where some SS troops still refused to surrender, but the Soviets reduced such buildings to rubble.
Hitler's Nero Decree
The city's food supplies had been largely destroyed on Hitler's orders. 128 of the 226 bridges had been blown up and 87 pumps rendered inoperative. "A quarter of the subway stations were under water, flooded on Hitler's orders. Thousands and thousands who had sought shelter in them had drowned when the SS had carried out the blowing up of the protective devices on the Landwehr Canal." A number of workers, on their own initiative, resisted or sabotaged the SS's plan to destroy the city's infrastructure; they successfully prevented the blowing up of the Klingenberg power station, the Johannisthal waterworks, and other pumping stations, railroad facilities, and bridges.Battle outside Berlin
At some point on 28 April or 29 April, General Heinrici, Commander-in-Chief of Army Group Vistula, was relieved of his command after disobeying Hitler's direct orders to hold Berlin at all costs and never order a retreat, and was replaced by GeneralKurt Student
Kurt Arthur Benno Student (12 May 1890 – 1 July 1978) was a German general in the Luftwaffe during World War II. An early pioneer of airborne forces, Student was in overall command of developing a paratrooper force to be known as the '' Fallsch ...
. General Kurt von Tippelskirch
__NOTOC__
Kurt Oskar Heinrich Ludwig Wilhelm von Tippelskirch (9 October 1891 – 10 May 1957) was a general in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany during World War II who commanded several armies and Army Group Vistula. He surrendered to the United S ...
was named as Heinrici's interim replacement until Student could arrive and assume control. There remains some confusion as to who was in command, as some references say that Student was captured by the British and never arrived. Regardless of whether von Tippelskirch or Student was in command of Army Group Vistula, the rapidly deteriorating situation that the Germans faced meant that Army Group Vistula's coordination of the armies under its nominal command during the last few days of the war was of little significance.
On the evening of 29 April, Krebs contacted General Alfred Jodl (Supreme Army Command) by radio:
In the early morning of 30 April, Jodl replied to Krebs:
North
While the 1st Belorussian Front and the 1st Ukrainian Front encircled Berlin, and started the battle for the city itself, Rokossovsky's 2nd Belorussian Front started his offensive to the north of Berlin. On 20 April between Stettin and Schwedt, Rokossovsky's 2nd Belorussian Front attacked the northern flank of Army Group Vistula, held by the III Panzer Army. By 22 April, the 2nd Belorussian Front had established a bridgehead on the east bank of the Oder that was over deep and was heavily engaged with the III Panzer Army. On 25 April, the 2nd Belorussian Front broke through III Panzer Army's line around the bridgehead south of Stettin, crossed the ''Randowbruch'' Swamp, and were now free to move west towards Montgomery'sBritish 21st Army Group
The 21st Army Group was a British headquarters formation formed during the Second World War. It controlled two field armies and other supporting units, consisting primarily of the British Second Army and the First Canadian Army. Established in ...
and north towards the Baltic port of Stralsund
Stralsund (; Swedish: ''Strålsund''), officially the Hanseatic City of Stralsund (German: ''Hansestadt Stralsund''), is the fifth-largest city in the northeastern German federal state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania after Rostock, Schwerin, N ...
.
The German III Panzer Army and the German XXI Army situated to the north of Berlin retreated westwards under relentless pressure from Rokossovsky's 2nd Belorussian Front, and was eventually pushed into a pocket wide that stretched from the Elbe to the coast. To their west was the British 21st Army Group (which on 1 May broke out of its Elbe bridgehead and had raced to the coast capturing Wismar
Wismar (; Low German: ''Wismer''), officially the Hanseatic City of Wismar (''Hansestadt Wismar'') is, with around 43,000 inhabitants, the sixth-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, and the fourth-largest cit ...
and Lübeck
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the state ...
), to their east Rokossovsky's 2nd Belorussian Front and to the south was the United States Ninth Army
The Ninth Army is a field army of the United States Army, garrisoned at Caserma Ederle, Vicenza, Italy. It is the United States Army Service Component Command of United States Africa Command (USAFRICOM or AFRICOM).
Activated just eight weeks b ...
which had penetrated as far east as Ludwigslust and Schwerin
Schwerin (; Mecklenburgian Low German: ''Swerin''; Latin: ''Suerina'', ''Suerinum'') is the capital and second-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern as well as of the region of Mecklenburg, after Rostock. It ...
.
South
 The successes of the 1st Ukrainian Front during the first nine days of the battle meant that by 25 April, they were occupying large swathes of the area south and south-west of Berlin. Their spearheads had met elements of the 1st Belorussian Front west of Berlin, completing the investment of the city. Meanwhile, the
The successes of the 1st Ukrainian Front during the first nine days of the battle meant that by 25 April, they were occupying large swathes of the area south and south-west of Berlin. Their spearheads had met elements of the 1st Belorussian Front west of Berlin, completing the investment of the city. Meanwhile, the 58th Guards Rifle Division
The 58th Guards Rifle Division () was an elite Guards infantry division of the Red Army during World War II.
It was formed in June 1942 as the 1st Rifle Division (1st formation) and was converted into the 58th Guards Rifle Division at the end o ...
of the 5th Guards Army in 1st Ukrainian Front made contact with the 69th Infantry Division (United States)
The 69th Infantry Division, nicknamed the "fighting 69th," was a Division of the United States Army formed during World War II. It is distinct from the 69th Infantry Regiment (New York) (the "Fighting 69th").
The shoulder sleeve insignia of the ...
of the United States First Army
First Army is the oldest and longest-established field army of the United States Army. It served as a theater army, having seen service in both World War I and World War II, and supplied the US army with soldiers and equipment during the Korea ...
near Torgau
Torgau () is a town on the banks of the Elbe in northwestern Saxony, Germany. It is the capital of the district Nordsachsen.
Outside Germany, the town is best known as where on 25 April 1945, the United States and Soviet Armies forces fi ...
, on the Elbe River. These manoeuvres had broken the German forces south of Berlin into three parts. The German IX Army was surrounded in the Halbe pocket
The Battle of Halbe (german: Kesselschlacht von Halbe, russian: Хальбский котёл, Halbe pocket) was a battle lasting from April 24 – May 1, 1945 in which the German Ninth Army—under the command of General Theodor Busse—was dest ...
. Wenck's XII Army, obeying Hitler's command of 22 April, was attempting to force its way into Berlin from the south-west but met stiff resistance from 1st Ukrainian Front around Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and, with around 183,000 inhabitants, largest city of the German state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of ...
. Schörner's Army Group Centre was forced to withdraw from the Battle of Berlin, along its lines of communications towards Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
.
Between 24 April and 1 May, the IX Army fought a desperate action to break out of the pocket in an attempt to link up with the XII Army. Hitler assumed that after a successful breakout from the pocket, the IX Army could combine forces with the XII Army and would be able to relieve Berlin. There is no evidence to suggest that Generals Heinrici, Busse, or Wenck thought that this was even remotely strategically feasible, but Hitler's agreement to allow the IX Army to break through Soviet lines allowed many German soldiers to escape to the west and surrender to the United States Army.
At dawn on 28 April, the youth divisions ''Clausewitz
Carl Philipp Gottfried (or Gottlieb) von Clausewitz (; 1 June 1780 – 16 November 1831) was a Prussian general and military theorist who stressed the "moral", in modern terms meaning psychological, and political aspects of waging war. His m ...
'', '' Scharnhorst'', and '' Theodor Körner'' attacked from the south-west toward the direction of Berlin. They were part of Wenck's XX Corps and were made up of men from the officer training schools, making them some of the best units the Germans had in reserve. They covered a distance of about , before being halted at the tip of Lake Schwielow, south-west of Potsdam and still from Berlin. During the night, General Wenck reported to the German Supreme Army Command in Fuerstenberg that his XII Army had been forced back along the entire front. According to Wenck, no attack on Berlin was possible. At that point, support from the IX Army could no longer be expected. In the meantime, about 25,000 German soldiers of the IX Army, along with several thousand civilians, succeeded in reaching the lines of the XII Army after breaking out of the Halbe pocket. The casualties on both sides were very high. Nearly 30,000 Germans were buried after the battle in the cemetery at Halbe. About 20,000 soldiers of the Red Army also died trying to stop the breakout; most are buried at a cemetery next to the Baruth-Zossen road. These are the known dead, but the remains of more who died in the battle are found every year, so the total of those who died will never be known. Nobody knows how many civilians died but it could have been as high as 10,000.
Having failed to break through to Berlin, Wenck's XII Army made a fighting retreat back towards the Elbe and American lines after providing the IX Army survivors with surplus transport. By 6 May many German Army units and individuals had crossed the Elbe and surrendered to the US Ninth Army. Meanwhile, the XII Army's bridgehead, with its headquarters in the park of Schönhausen
Schönhausen ( Low Saxon: ''Schöönhusen'') is a municipality in the district of Stendal in Saxony-Anhalt in Germany. It is the seat of the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' ("collective municipality") Elbe-Havel-Land.
Geography
The village is situated on ...
, came under heavy Soviet artillery bombardment and was compressed into an area eight by two kilometres (five by one and a quarter miles).

Surrender
On the night of 2–3 May, General von Manteuffel, commander of the III Panzer Army along with General von Tippelskirch, commander of the XXI Army, surrendered to the US Army. Von Saucken's II Army, that had been fighting north-east of Berlin in the Vistula Delta, surrendered to the Soviets on 9 May. On the morning of 7 May, the perimeter of the XII Army's bridgehead began to collapse. Wenck crossed the Elbe under small arms fire that afternoon and surrendered to the American Ninth Army.Aftermath
 According to Grigoriy Krivosheev, declassified archival data gives 81,116 Soviet dead for the operation, including the battles of Seelow Heights and the Halbe. Another 280,251 were reported wounded or sick. The operation also cost the Soviets about 1,997 tanks and self-propelled guns. All losses were considered irrecoverable - i.e. beyond economic repair or no longer serviceable. The Soviets claimed to have captured nearly 480,000 German soldiers, while German research put the number of dead between 92,000 and 100,000. Some 125,000 civilians are estimated to have died during the entire operation.
According to Grigoriy Krivosheev, declassified archival data gives 81,116 Soviet dead for the operation, including the battles of Seelow Heights and the Halbe. Another 280,251 were reported wounded or sick. The operation also cost the Soviets about 1,997 tanks and self-propelled guns. All losses were considered irrecoverable - i.e. beyond economic repair or no longer serviceable. The Soviets claimed to have captured nearly 480,000 German soldiers, while German research put the number of dead between 92,000 and 100,000. Some 125,000 civilians are estimated to have died during the entire operation.
 In those areas that the Red Army had captured and before the fighting in the centre of the city had stopped, the Soviet authorities took measures to start restoring essential services. Almost all transport in and out of the city had been rendered inoperative, and bombed-out sewers had contaminated the city's water supplies. The Soviet authorities appointed local Germans to head each city block, and organised the cleaning-up. The Red Army made a major effort to feed the residents of the city. Most Germans, both soldiers and civilians, were grateful to receive food issued at Red Army
In those areas that the Red Army had captured and before the fighting in the centre of the city had stopped, the Soviet authorities took measures to start restoring essential services. Almost all transport in and out of the city had been rendered inoperative, and bombed-out sewers had contaminated the city's water supplies. The Soviet authorities appointed local Germans to head each city block, and organised the cleaning-up. The Red Army made a major effort to feed the residents of the city. Most Germans, both soldiers and civilians, were grateful to receive food issued at Red Army soup kitchen
A soup kitchen, food kitchen, or meal center, is a place where food is offered to the hungry usually for free or sometimes at a below-market price (such as via coin donations upon visiting). Frequently located in lower-income neighborhoods, soup ...
s, which began on Colonel-General Berzarin's orders. After the capitulation the Soviets went house to house, arresting and imprisoning anyone in a uniform including firemen and railwaymen.
 During and immediately following the assault, in many areas of the city, vengeful Soviet troops (often rear echelon units) engaged in
During and immediately following the assault, in many areas of the city, vengeful Soviet troops (often rear echelon units) engaged in mass rape
Mass sexual assault is the collective sexual assault of individuals in public by a group. Typically acting under the protective cover of large gatherings, victims have reported being groped, stripped, beaten, bitten, penetrated and raped.
Egy ...
, pillage
Looting is the act of stealing, or the taking of goods by force, typically in the midst of a military, political, or other social crisis, such as war, natural disasters (where law and civil enforcement are temporarily ineffective), or rioting. ...
and murder. Oleg Budnitskii, historian at the Higher School of Economics in Moscow, told a BBC Radio programme that Red Army soldiers were astounded when they reached Germany. "For the first time in their lives, eight million Soviet people came abroad, the Soviet Union was a closed country. All they knew about foreign countries was there was unemployment, starvation and exploitation. And when they came to Europe they saw something very different from Stalinist Russia ... especially Germany. They were really furious, they could not understand why being so rich, Germans came to Russia". Other authors question the narrative of sexual violence by Red Army soldiers being more than what was a sad normality from all sides during the war, including the Western Allies. Nikolai Berzarin, commander of the Red Army in Berlin, quickly introduced penalties up to the death penalty for looting and rape.
Despite Soviet efforts to supply food and rebuild the city, starvation remained a problem. In June 1945, one month after the surrender, the average Berliner was getting only 64 percent of a daily ration of . Across the city over a million people were without homes.
Commemoration

 All told, 402 Red Army personnel were bestowed the USSR's highest degree of distinction, the title
All told, 402 Red Army personnel were bestowed the USSR's highest degree of distinction, the title Hero of the Soviet Union
The title Hero of the Soviet Union (russian: Герой Советского Союза, translit=Geroy Sovietskogo Soyuza) was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded together with the Order of Lenin personally or collectively for ...
(HSU), for their valor in Berlin's immediate suburbs and in the city itself. Marshals of the Soviet Union Zhukov and Konev received their third and second HSU awards respectively, for their roles in the battle's outcome. Combat medic Guards Senior Sergeant Lyudmila S. Kravets, was the Battle of Berlin's only female HSU recipient for her valorous actions while serving in 1st Rifle Battalion, 63rd Guards Rifle Regiment, 23rd Guards Rifle Division (subordinate to 3rd Shock Army). Additionally, 280 Red Army enlisted personnel earned the Soviet Order of Glory First Class and attained status as Full Cavaliers of the Order of Glory for their heroism during the Battle of Berlin. In Soviet society, Full Cavaliers of the Order of Glory were accorded the same rights and privileges as Heroes of the Soviet Union.
Some 1.1 million Soviet personnel who took part in the capture of Berlin from 22 April to 2 May 1945 were awarded the Medal "For the Capture of Berlin"
The Medal "For the Capture of Berlin" (russian: Медаль «За взятие Берлина») was a World War II campaign medal of the Soviet Union established on June 9, 1945 by decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR to ...
.
The design of the Victory Banner
The Soviet Banner of Victory (russian: Знамя Победы, translit=Znamya Pobedy) was the banner raised by the Red Army soldiers on the Reichstag building in Berlin on 1 May 1945, the day after Adolf Hitler committed suicide. It was r ...
for celebrations of the Soviet Victory Day was defined by a federal law of Russia on 7 May 2007.
Poland's official Flag Day is held each year on 2 May, the last day of the battle in Berlin, when the Polish Army hoisted its flag on the Berlin Victory Column.
See also
* Medal for Participation in the Battle of Berlin *Soviet Union in World War II
The United Kingdom, France, and Italy signed the Munich Agreement with Nazi Germany on 30 September 1938, an agreement which provided "cession to Germany of the Sudeten German territory" of Czechoslovakia. Almost a year later the Sovi ...
* Siege of Breslau
*German Instrument of Surrender
The German Instrument of Surrender (german: Bedingungslose Kapitulation der Wehrmacht, lit=Unconditional Capitulation of the " Wehrmacht"; russian: Акт о капитуляции Германии, Akt o kapitulyatsii Germanii, lit=Act of capi ...
and Berlin Declaration (1945)
The Berlin Declaration (german: Berliner Erklärung/Deklaration) of 5 June 1945 or the Declaration regarding the defeat of Germany,Officially, the "Declaration regarding the defeat of Germany and the assumption of supreme authority with respect to ...
* German World War II strongholds
*Mikhail Minin
Mikhail Petrovich Minin (russian: Михаил Петрович Минин; July 29, 1922 – January 10, 2008) was a Russian Soviet soldier who was the first to enter the Reichstag building on April 30, 1945, during the Battle of Berlin, and ...
* Panzerbär
*Prague Offensive
The Prague offensive (russian: Пражская стратегическая наступательная операция, Prazhskaya strategicheskaya nastupatel'naya operatsiya, lit=Prague strategic offensive) was the last major military ...
*Soviet war crimes
The war crimes and crimes against humanity which were perpetrated by the Soviet Union and its armed forces from 1919 to 1991 include acts which were committed by the Red Army (later called the Soviet Army) as well as acts which were committ ...
* Stunde Null
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Originally published in "World War II" at Suite101.com on 1 May 1999. Revised edition published in "Articles On War" aOnWar.com
on 1 July 2003.
Further reading
* — Includes the Order of Battle for the Battle for Berlin () * * *Anonymous
Anonymous may refer to:
* Anonymity, the state of an individual's identity, or personally identifiable information, being publicly unknown
** Anonymous work, a work of art or literature that has an unnamed or unknown creator or author
* Anony ...
; ''A Woman in Berlin
''A Woman in Berlin'' (german: Eine Frau in Berlin) is a memoir by German journalist Marta Hillers, originally released anonymously in 1954. The identity of Hillers as the author was not revealed until 2003, after her death. The memoir covers th ...
: Six Weeks in the Conquered City'' Translated by Anthes Bell,
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* — Alternative account of crimes against civilians
*RT (TV network)
RT (formerly Russia Today or Rossiya Segodnya (russian: Россия Сегодня) is a Russian state-controlled international news television network funded by the Russian government. It operates pay television and free-to-air channe ...
, (official channel on YouTube). . 27 June 2010. 26-minute video.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Berlin
Conflicts in 1945
1945 in Germany
1945 in military history
1940s in Berlin
Military history of Berlin
Encirclements in World War II
Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitu ...
Battles of World War II involving Germany
Battles of World War II involving the Soviet Union
April 1945 events
May 1945 events