Battle of Perryville on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of Perryville, also known as the Battle of Chaplin Hills, was fought on October 8, 1862, in the Chaplin Hills west of Perryville, Kentucky, as the culmination of the Confederate Heartland Offensive (Kentucky Campaign) during the
Buell, several miles behind the action, was unaware that a major battle was taking place and did not send any reserves to the front until late in the afternoon. The Union troops on the left flank, reinforced by two brigades, stabilized their line, and the Confederate attack sputtered to a halt. Later, three Confederate regiments assaulted the Union division on the Springfield Pike but were repulsed and fell back into Perryville. Union troops pursued, and skirmishing occurred in the streets until dark. By that time, Union reinforcements were threatening the Confederate left flank. Bragg, short of men and supplies, withdrew during the night, and continued the Confederate retreat by way of

 Situated between the Southern states of
Situated between the Southern states of
File:KENTUCKY CAMPAIGN MAP1.jpg, Western Theater: Movements April–August 1862
File:KENTUCKY CAMPAIGN MAP3.jpg, Western Theater: Confederate invasion of Kentucky (August–October 1862)
 Hardee had selected Perryville for a few reasons. The village of approximately 300 residents had an excellent road network with connections to nearby towns in six directions, allowing for strategic flexibility. It was located to prevent the Federals from reaching the Confederate supply depot in Bryantsville. Finally, it was a potential source of water. An extremely wet winter and spring of 1862, believed caused by the eruption of Mt. Dubbi in East Africa in May 1861, gave way to dry conditions during June which stayed that way throughout the summer and into early fall. The Southern states remained locked under a stagnant high pressure ridge that sent daytime temperatures soaring with little rain to cool things down.The heat was oppressive for both men and horses, and the few sources of drinking water provided by the rivers and creeks west of town—most reduced to isolated stagnant puddles—were desperately sought after.
Hardee had selected Perryville for a few reasons. The village of approximately 300 residents had an excellent road network with connections to nearby towns in six directions, allowing for strategic flexibility. It was located to prevent the Federals from reaching the Confederate supply depot in Bryantsville. Finally, it was a potential source of water. An extremely wet winter and spring of 1862, believed caused by the eruption of Mt. Dubbi in East Africa in May 1861, gave way to dry conditions during June which stayed that way throughout the summer and into early fall. The Southern states remained locked under a stagnant high pressure ridge that sent daytime temperatures soaring with little rain to cool things down.The heat was oppressive for both men and horses, and the few sources of drinking water provided by the rivers and creeks west of town—most reduced to isolated stagnant puddles—were desperately sought after.
 Cheatham's artillery bombardment began at 12:30 p.m., but he did not immediately order his infantry forward. Union troops continued to file into line, extending their flank to the north, beyond the intended avenue of attack. Bragg moved Cheatham's division into Walker's Bend, assuming the redirected attack would now strike the Union's open flank. Unfortunately for the Confederates, their cavalry reconnaissance withdrew before McCook placed an artillery battery under Lt. Charles Parsons and the brigade of Brig. Gen. William R. Terrill onto the Open Knob, a prominent hill on the northern end of the battlefield.
The brigade of Brig. Gen. Daniel S. Donelson was the first to cross the Chaplin River, climb the bluffs on the west bank, and began its attack around 2 p.m. Two of the brigade's regiments had been detached, leaving only three for the attack. Cheatham shouted, "Give 'em hell, boys!" One of the enduring legends of the Civil War is that Gen. Polk, who was also an Episcopal
Cheatham's artillery bombardment began at 12:30 p.m., but he did not immediately order his infantry forward. Union troops continued to file into line, extending their flank to the north, beyond the intended avenue of attack. Bragg moved Cheatham's division into Walker's Bend, assuming the redirected attack would now strike the Union's open flank. Unfortunately for the Confederates, their cavalry reconnaissance withdrew before McCook placed an artillery battery under Lt. Charles Parsons and the brigade of Brig. Gen. William R. Terrill onto the Open Knob, a prominent hill on the northern end of the battlefield.
The brigade of Brig. Gen. Daniel S. Donelson was the first to cross the Chaplin River, climb the bluffs on the west bank, and began its attack around 2 p.m. Two of the brigade's regiments had been detached, leaving only three for the attack. Cheatham shouted, "Give 'em hell, boys!" One of the enduring legends of the Civil War is that Gen. Polk, who was also an Episcopal  Parsons' eight guns on the Open Knob were manned by inexperienced soldiers, some of whom were infantry recruits from the
Parsons' eight guns on the Open Knob were manned by inexperienced soldiers, some of whom were infantry recruits from the 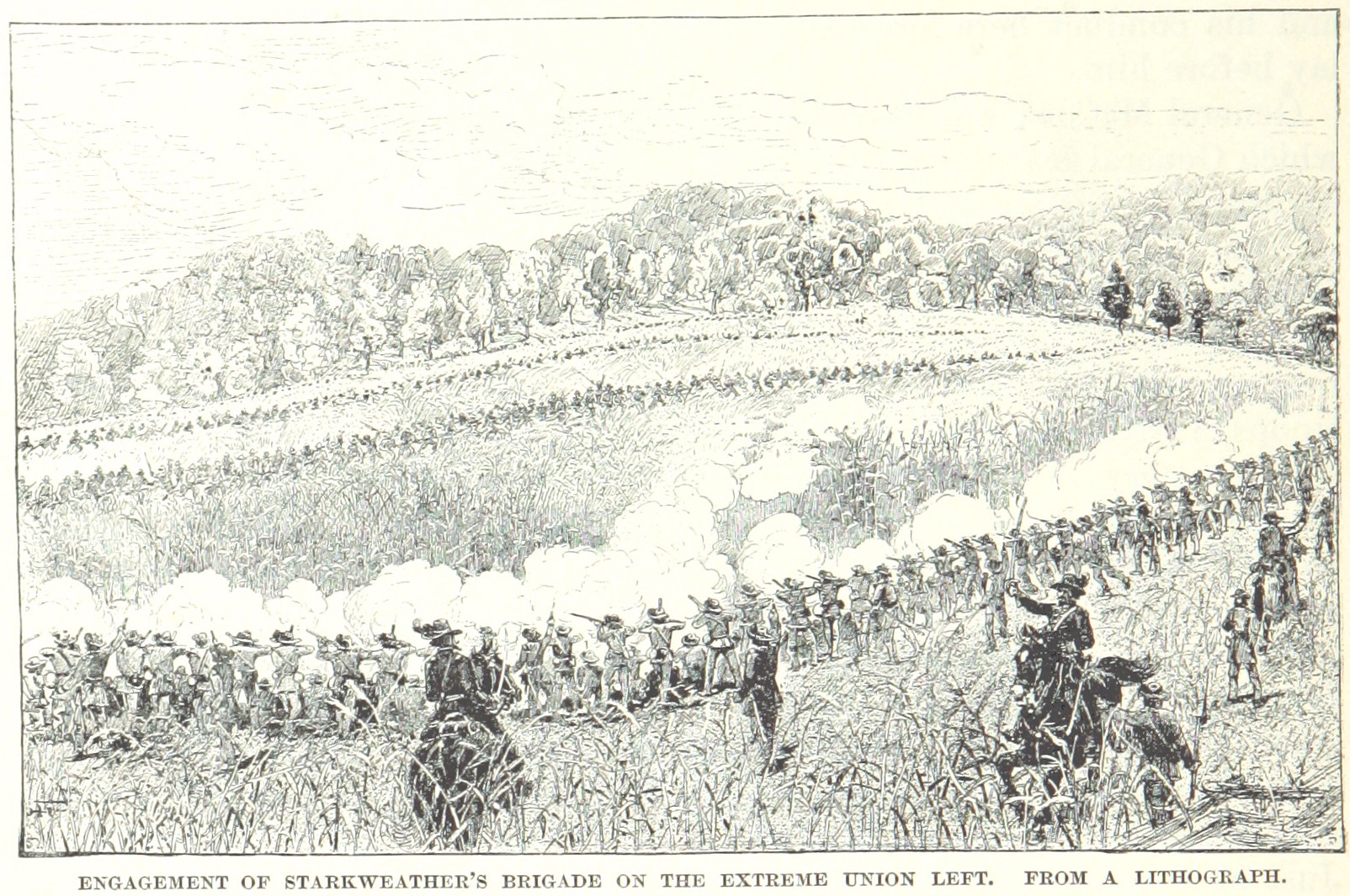 Maney's attack continued to the west, down the reverse slope of the Open Knob, through a cornfield, and across the Benton Road, after which was another steep ridge, occupied by the 2,200 men in the Union 28th Brigade of Col. John C. Starkweather (Rousseau's division), and twelve guns. Those guns made the Open Knob an untenable position. Starkweather had placed his 21st Wisconsin in the cornfield about the time that Maney was attacking Parsons' position. The inexperienced men of the 21st—some of whom had never fired their weapons before, the regiment having been formed less than a month earlier—could see little through the 10- to high cornstalks of the cornfield. They were surprised as the remnants of Terrill's brigade retreated through their position. As Terrill himself retreated, he shouted, "The Rebels are advancing in terrible force!" Terrill convinced the regimental adjutant to order yet another bayonet charge; 200 men advanced and were quickly smashed by the oncoming Confederates. While the Union men had to hold their fire to keep from shooting their retreating comrades, artillery fire from Starkweather's batteries caused numerous
Maney's attack continued to the west, down the reverse slope of the Open Knob, through a cornfield, and across the Benton Road, after which was another steep ridge, occupied by the 2,200 men in the Union 28th Brigade of Col. John C. Starkweather (Rousseau's division), and twelve guns. Those guns made the Open Knob an untenable position. Starkweather had placed his 21st Wisconsin in the cornfield about the time that Maney was attacking Parsons' position. The inexperienced men of the 21st—some of whom had never fired their weapons before, the regiment having been formed less than a month earlier—could see little through the 10- to high cornstalks of the cornfield. They were surprised as the remnants of Terrill's brigade retreated through their position. As Terrill himself retreated, he shouted, "The Rebels are advancing in terrible force!" Terrill convinced the regimental adjutant to order yet another bayonet charge; 200 men advanced and were quickly smashed by the oncoming Confederates. While the Union men had to hold their fire to keep from shooting their retreating comrades, artillery fire from Starkweather's batteries caused numerous  To fill a gap in the Confederate line where Donelson's brigade had fought, Cheatham deployed the Tennessee brigade of Brig. Gen.
To fill a gap in the Confederate line where Donelson's brigade had fought, Cheatham deployed the Tennessee brigade of Brig. Gen.  At that time Brig. Gen. Terrill returned to the fight, leading his troops up the reverse slope of the hill. He was mortally wounded by an artillery shell exploding overhead and died at 2 a.m. the following day. Starkweather, meanwhile, was able to salvage six of his twelve guns and move them west to the next ridge. Col. Albert S. Hall began the day as regimental commander of the 105th Ohio, and with the deaths of Jackson, Terrill, and Col. George Webster, advanced all the way to command of the 10th Division by the end of the day.
Once again the Federals had a strong defensive position, with good artillery support and a stone wall at the top of a steep slope. Maney's and Stewart's men attempted three assaults, all unsuccessful, and withdrew to the vicinity of the Open Knob at around 5:30 p.m. The assault by Maney's brigade over three hours was the bloodiest of the battle, and arguably its most crucial action. Historian Kenneth W. Noe describes Maney's final repulse as the " high-water mark of the Confederacy in the western theater, no less important than the Angle at Gettysburg."
At that time Brig. Gen. Terrill returned to the fight, leading his troops up the reverse slope of the hill. He was mortally wounded by an artillery shell exploding overhead and died at 2 a.m. the following day. Starkweather, meanwhile, was able to salvage six of his twelve guns and move them west to the next ridge. Col. Albert S. Hall began the day as regimental commander of the 105th Ohio, and with the deaths of Jackson, Terrill, and Col. George Webster, advanced all the way to command of the 10th Division by the end of the day.
Once again the Federals had a strong defensive position, with good artillery support and a stone wall at the top of a steep slope. Maney's and Stewart's men attempted three assaults, all unsuccessful, and withdrew to the vicinity of the Open Knob at around 5:30 p.m. The assault by Maney's brigade over three hours was the bloodiest of the battle, and arguably its most crucial action. Historian Kenneth W. Noe describes Maney's final repulse as the " high-water mark of the Confederacy in the western theater, no less important than the Angle at Gettysburg."
 Almost all of McCook's I Corps units were posted at the beginning of the battle on land owned by "
Almost all of McCook's I Corps units were posted at the beginning of the battle on land owned by " Sheridan's division did participate toward the end of the battle. The Confederate brigade of Col. Samuel Powel (Anderson's division) was ordered to advance in conjunction with Adams's brigade, on Cleburne's left. The two brigades were widely separated, however, with Powel's on Edwards House Hill, immediately west of Perryville. At about 4 p.m., Powel received orders from Bragg to advance west on the Springfield Pike to silence the battery of Capt. Henry Hescock, which was firing into the left flank of Bragg's assault. Bragg assumed this was an isolated battery, not the entire III Corps. Three regiments of Powel's brigade encountered Sheridan's division, and although Sheridan was initially concerned by the Confederates' aggressive attack and sent for reinforcements, the three regiments were quickly repulsed.
Sheridan, who would be characterized in later battles as very aggressive, hesitated to pursue the smaller force, and also refused a request by Daniel McCook to move north in support of his brother's corps. However, his earlier request for reinforcements bore fruit and the 31st Brigade of Col.
Sheridan's division did participate toward the end of the battle. The Confederate brigade of Col. Samuel Powel (Anderson's division) was ordered to advance in conjunction with Adams's brigade, on Cleburne's left. The two brigades were widely separated, however, with Powel's on Edwards House Hill, immediately west of Perryville. At about 4 p.m., Powel received orders from Bragg to advance west on the Springfield Pike to silence the battery of Capt. Henry Hescock, which was firing into the left flank of Bragg's assault. Bragg assumed this was an isolated battery, not the entire III Corps. Three regiments of Powel's brigade encountered Sheridan's division, and although Sheridan was initially concerned by the Confederates' aggressive attack and sent for reinforcements, the three regiments were quickly repulsed.
Sheridan, who would be characterized in later battles as very aggressive, hesitated to pursue the smaller force, and also refused a request by Daniel McCook to move north in support of his brother's corps. However, his earlier request for reinforcements bore fruit and the 31st Brigade of Col.
 Bragg's attack had been a large pincer movement, forcing both flanks of McCook's corps back into a concentrated mass. This mass occurred at the Dixville Crossroads, where the Benton Road crossed the Mackville Road. If the Confederates seized this intersection they could, conceivably, get around the right wing of McCook's corps and effectively cut them off from the rest of the army. The southern jaw of the pincer began to slow at the temporary line established at the Russell House. Harris's and Lytle's brigades defended until Cleburne's and Adams's attack ground to a halt. The northern jaw had been stopped by Starkweather's defense. The remaining attacks came from north of the Mackville Road by two fresh brigades from Buckner's division: Brig. Gen. St. John R. Liddell's and Brig. Gen. Sterling A. M. Wood's.
The initial target of the assault was Col. George Webster's 34th Brigade of Jackson's division. Webster was mortally wounded during the fighting. His death marked the final senior loss for the 10th Division—the division commander, Jackson, and the other brigade commander, Terrill, had also been mortally wounded. (The previous evening, Jackson, Terrill, and Webster had been idly discussing the possibility of all of them being killed in battle and they dismissed the thought as being mathematically negligible.) Webster's infantry and Capt. Harris's artillery battery posted on a hill near the Benton Road shot Wood's attackers to pieces and they were forced to fall back. They regrouped at the base of the hill and renewed their assault. Harris's battery ran low on ammunition and had to withdraw, and the Confederate attack pushed Webster's men back toward the crossroads. Col. Michael Gooding's 13th Brigade (Mitchell's division) arrived on the field from Gilbert's corps and took up the fight. Wood's men withdrew and were replaced by Liddell's.
The arrival of reinforcements was a result of McCook's belated attempts to secure aid for his beleaguered corps. At 2:30 p.m. he sent an aide to Sheridan on Peters Hill requesting that he secure I Corps' right flank. McCook dispatched a second staff officer at 3 p.m. to obtain assistance from the nearest III Corps unit. The officer encountered Brig. Gen. Albin F. Schoepf, commanding the 1st Division, the III Corps' reserve. Unwilling to act on his own authority, Schoepf referred the staff officer to Gilbert, who in turn referred him to Buell's headquarters more than away. The arrival of McCook's staff officer at about 4 p.m. surprised the army commander, who had heard little battle noise and found it difficult to believe that a major Confederate attack had been under way for some time. Nevertheless, Buell ordered two brigades from Schoepf's division to support I Corps. This relatively minor commitment indicated Buell's unwillingness to accept the reported dire situation at face value.
Liddell's men fired at an unknown unit less than east of the crossroads. Calls were heard, "You are firing upon friends; for God's sake stop!" Leonidas Polk, the wing commander, decided to ride forward to see who had been the victims of the supposedly friendly fire. Polk found that he had ridden by mistake into the lines of the 22nd Indiana and was forced to bluff his way out by riding down the Union line pretending to be a Union officer and shouting at the Federal troops to cease fire. When he had escaped he shouted to Liddell and the Confederates fired hundreds of muskets in a single volley, which killed Col. Squire Keith and caused casualties of 65% in the 22nd Indiana, the highest percentage of any Federal regiment engaged at Perryville. Although Liddell wanted to pursue the assault, Polk had been unnerved by his personal contact with the enemy and halted the attack, blaming the falling darkness. The Union units moved their supplies and equipment through the endangered intersection and consolidated their lines on a chain of hills northwest. McCook's corps had been badly damaged during the day, but was not destroyed.
Bragg's attack had been a large pincer movement, forcing both flanks of McCook's corps back into a concentrated mass. This mass occurred at the Dixville Crossroads, where the Benton Road crossed the Mackville Road. If the Confederates seized this intersection they could, conceivably, get around the right wing of McCook's corps and effectively cut them off from the rest of the army. The southern jaw of the pincer began to slow at the temporary line established at the Russell House. Harris's and Lytle's brigades defended until Cleburne's and Adams's attack ground to a halt. The northern jaw had been stopped by Starkweather's defense. The remaining attacks came from north of the Mackville Road by two fresh brigades from Buckner's division: Brig. Gen. St. John R. Liddell's and Brig. Gen. Sterling A. M. Wood's.
The initial target of the assault was Col. George Webster's 34th Brigade of Jackson's division. Webster was mortally wounded during the fighting. His death marked the final senior loss for the 10th Division—the division commander, Jackson, and the other brigade commander, Terrill, had also been mortally wounded. (The previous evening, Jackson, Terrill, and Webster had been idly discussing the possibility of all of them being killed in battle and they dismissed the thought as being mathematically negligible.) Webster's infantry and Capt. Harris's artillery battery posted on a hill near the Benton Road shot Wood's attackers to pieces and they were forced to fall back. They regrouped at the base of the hill and renewed their assault. Harris's battery ran low on ammunition and had to withdraw, and the Confederate attack pushed Webster's men back toward the crossroads. Col. Michael Gooding's 13th Brigade (Mitchell's division) arrived on the field from Gilbert's corps and took up the fight. Wood's men withdrew and were replaced by Liddell's.
The arrival of reinforcements was a result of McCook's belated attempts to secure aid for his beleaguered corps. At 2:30 p.m. he sent an aide to Sheridan on Peters Hill requesting that he secure I Corps' right flank. McCook dispatched a second staff officer at 3 p.m. to obtain assistance from the nearest III Corps unit. The officer encountered Brig. Gen. Albin F. Schoepf, commanding the 1st Division, the III Corps' reserve. Unwilling to act on his own authority, Schoepf referred the staff officer to Gilbert, who in turn referred him to Buell's headquarters more than away. The arrival of McCook's staff officer at about 4 p.m. surprised the army commander, who had heard little battle noise and found it difficult to believe that a major Confederate attack had been under way for some time. Nevertheless, Buell ordered two brigades from Schoepf's division to support I Corps. This relatively minor commitment indicated Buell's unwillingness to accept the reported dire situation at face value.
Liddell's men fired at an unknown unit less than east of the crossroads. Calls were heard, "You are firing upon friends; for God's sake stop!" Leonidas Polk, the wing commander, decided to ride forward to see who had been the victims of the supposedly friendly fire. Polk found that he had ridden by mistake into the lines of the 22nd Indiana and was forced to bluff his way out by riding down the Union line pretending to be a Union officer and shouting at the Federal troops to cease fire. When he had escaped he shouted to Liddell and the Confederates fired hundreds of muskets in a single volley, which killed Col. Squire Keith and caused casualties of 65% in the 22nd Indiana, the highest percentage of any Federal regiment engaged at Perryville. Although Liddell wanted to pursue the assault, Polk had been unnerved by his personal contact with the enemy and halted the attack, blaming the falling darkness. The Union units moved their supplies and equipment through the endangered intersection and consolidated their lines on a chain of hills northwest. McCook's corps had been badly damaged during the day, but was not destroyed.
 Braxton Bragg had arguably won a tactical victory, having fought aggressively and pushed his opponent back for over a mile. But his precarious strategic situation became clear to him as he found out about the III Corps advance on the Springfield Pike, and when he learned late in the day of the II Corps' presence on the Lebanon Pike. At 9 p.m. he met with his subordinates at the Crawford House and gave orders to begin a withdrawal after midnight, leaving a picket line in place while his army joined up with Kirby Smith's. As the army marched toward Harrodsburg, they were forced to leave 900 wounded men behind.
Bragg united his forces with Smith's at Harrodsburg, and the Union and Confederate armies, now of comparable size, skirmished with one another over the next week or so, but neither attacked. Bragg soon realized that the new infantry recruits he had sought from Kentucky would not be forthcoming, although many Kentuckians were willing to join the Confederate cavalry. Furthermore, Bragg concluded that he lacked the logistical support he needed to remain in the state. He made his way southeast to
Braxton Bragg had arguably won a tactical victory, having fought aggressively and pushed his opponent back for over a mile. But his precarious strategic situation became clear to him as he found out about the III Corps advance on the Springfield Pike, and when he learned late in the day of the II Corps' presence on the Lebanon Pike. At 9 p.m. he met with his subordinates at the Crawford House and gave orders to begin a withdrawal after midnight, leaving a picket line in place while his army joined up with Kirby Smith's. As the army marched toward Harrodsburg, they were forced to leave 900 wounded men behind.
Bragg united his forces with Smith's at Harrodsburg, and the Union and Confederate armies, now of comparable size, skirmished with one another over the next week or so, but neither attacked. Bragg soon realized that the new infantry recruits he had sought from Kentucky would not be forthcoming, although many Kentuckians were willing to join the Confederate cavalry. Furthermore, Bragg concluded that he lacked the logistical support he needed to remain in the state. He made his way southeast to
Civil War Trust "Saved Land" webpage.
Accessed Jan. 3, 2018 and November 24, 2021.
"The Battle of Perryville"
Accessed January 1, 2008. * Breiner, Thomas L
Accessed January 1, 2008. * Cameron, Robert S
''Staff Ride Handbook for the Battle of Perryville, 8 October 1862''
Fort Leavenworth, KS: Combat Studies Institute Press, 2005. . * Eicher, David J. ''The Longest Night: A Military History of the Civil War''. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2001. . * Esposito, Vincent J. ''West Point Atlas of American Wars''. New York: Frederick A. Praeger, 1959. . The collection of maps (without explanatory text) is available online at th
West Point website
* Hafendorfer, Kenneth A. ''Perryville: Battle for Kentucky''. Louisville, KY: K. H. Press, 1991. . * Kennedy, Frances H., ed. ''The Civil War Battlefield Guide''. 2nd ed. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Co., 1998. . * McDonough, James Lee. ''War in Kentucky: From Shiloh to Perryville''. Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 1994. . * McPherson, James M. '' Battle Cry of Freedom: The Civil War Era''. Oxford History of the United States. New York: Oxford University Press, 1988. . * Noe, Kenneth W. ''Perryville: This Grand Havoc of Battle''. Lexington: University Press of Kentucky, 2001. . * Prokopowicz, Gerald J. ''All for the Regiment: The Army of the Ohio, 1861–1862''. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 2001. . * Street, James Jr., and the Editors of Time-Life Books. ''The Struggle for Tennessee: Tupelo to Stones River''. Alexandria, VA: Time-Life Books, 1985. . * Watkins, Sam
''Co. Aytch Maury Grays, First Tennessee Regiment or, A Side Show of the Big Show''
Cumberland Presbyterian Publishing House, 1882. . * Woodworth, Steven E. ''Jefferson Davis and His Generals: The Failure of Confederate Command in the West''. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas, 1990. .
National Park Service battle description
''Battles and Leaders of the Civil War''
4 vols. New York: Century Co., 1884–1888. : ** Buell, Don Carlos
"East Tennessee and the Campaign of Perryville"
** Gilbert, Charles C
"On the Field of Perryville"
** Wheeler, Joseph
"Bragg's Invasion of Kentucky"
** Wright, J. Montgomery
"Notes of a Staff Officer at Perryville"
* Steely, Will Frank, and Orville W. Taylor. "Bragg's Kentucky Campaign: A Confederate Soldier's Account". ''The Register of the Kentucky Historical Society'' (1959): 49–55. . * U.S. War Department
''The War of the Rebellion: a Compilation of the Official Records of the Union and Confederate Armies''. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1880–1901.
Battle of Perryville
photos, history articles, and battlefield news ( Civil War Trust)
The Battle of Perryville, Kentucky
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20110716084401/http://www.civilwaralbum.com/misc/perry1.htm Modern Perryville photos
Perryville Order of Battle
{{DEFAULTSORT:Perryville 1862 in Kentucky 1862 in the American Civil War Perryville Perryville Boyle County, Kentucky Perryville October 1862 events Perryville
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
. Confederate Gen.
The Book of Genesis (from Greek ; Hebrew: בְּרֵאשִׁית ''Bəreʾšīt'', "In hebeginning") is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its first word, ( "In the beginning"). ...
Braxton Bragg
Braxton Bragg (March 22, 1817 – September 27, 1876) was an American army officer during the Second Seminole War and Mexican–American War and Confederate general in the Confederate Army during the American Civil War, serving in the Wester ...
's Army of Mississippi initially won a tactical victory against primarily a single corps of Maj. Gen. Don Carlos Buell
Don Carlos Buell (March 23, 1818November 19, 1898) was a United States Army officer who fought in the Seminole War, the Mexican–American War, and the American Civil War. Buell led Union armies in two great Civil War battles— Shiloh and Per ...
's Union Army of the Ohio
The Army of the Ohio was the name of two Union armies in the American Civil War. The first army became the Army of the Cumberland and the second army was created in 1863.
History
1st Army of the Ohio
General Orders No. 97 appointed Maj. Gen. ...
. The battle is considered a strategic Union victory, sometimes called the Battle for Kentucky, since Bragg withdrew to Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 36th-largest by ...
soon thereafter. The Union retained control of the critical border state of Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia ...
for the remainder of the war.
On October 7, Buell's army, in pursuit of Bragg, converged on the small crossroads town of Perryville in three columns. Union forces first skirmished with Confederate cavalry on the Springfield Pike before the fighting became more general, on Peters Hill, when the Confederate infantry arrived. Both sides were desperate to get access to fresh water. The next day, at dawn, fighting began again around Peters Hill as a Union division advanced up the pike, halting just before the Confederate line. After noon, a Confederate division struck the Union left flank—the I Corps I Corps, 1st Corps, or First Corps may refer to:
France
* 1st Army Corps (France)
* I Cavalry Corps (Grande Armée), a cavalry unit of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
* I Corps (Grande Armée), a unit of the Imperial French Ar ...
of Maj. Gen. Alexander M. McCook
Alexander McDowell McCook (April 22, 1831June 12, 1903) was a career United States Army officer and a Union general in the American Civil War.
Early life
McCook was born in Columbiana County, Ohio. A Scottish family, the McCooks were prominent i ...
—and forced it to fall back. When more Confederate divisions joined the fray, the Union line made a stubborn stand, counterattacked, but finally fell back with some units routed.NPSBuell, several miles behind the action, was unaware that a major battle was taking place and did not send any reserves to the front until late in the afternoon. The Union troops on the left flank, reinforced by two brigades, stabilized their line, and the Confederate attack sputtered to a halt. Later, three Confederate regiments assaulted the Union division on the Springfield Pike but were repulsed and fell back into Perryville. Union troops pursued, and skirmishing occurred in the streets until dark. By that time, Union reinforcements were threatening the Confederate left flank. Bragg, short of men and supplies, withdrew during the night, and continued the Confederate retreat by way of
Cumberland Gap
The Cumberland Gap is a pass through the long ridge of the Cumberland Mountains, within the Appalachian Mountains, near the junction of the U.S. states of Kentucky, Virginia, and Tennessee. It is famous in American colonial history for its r ...
into East Tennessee
East Tennessee is one of the three Grand Divisions of Tennessee defined in state law. Geographically and socioculturally distinct, it comprises approximately the eastern third of the U.S. state of Tennessee. East Tennessee consists of 33 count ...
.
Considering the casualties relative to the engaged strengths of the armies, the Battle of Perryville was one of the bloodiest battles of the Civil War. It was the largest battle fought in the state of Kentucky.
Background
Military situation
Kentucky campaign of 1862

 Situated between the Southern states of
Situated between the Southern states of Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 36th-largest by ...
and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
and the Northern states of Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rock ...
, Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th ...
, and Ohio
Ohio () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Of the List of states and territories of the United States, fifty U.S. states, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 34th-l ...
, the border state of Kentucky was coveted by both sides of the conflict because of its central location and its control of key rivers, particularly the Ohio
Ohio () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Of the List of states and territories of the United States, fifty U.S. states, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 34th-l ...
. In September 1861, Kentucky-born President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ...
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation throu ...
wrote in a private letter, "I think to lose Kentucky is nearly to lose the whole game."
Opposing political elements within the state vied for control during the early part of the war, and the state legislature declared official neutrality to keep out both the Union and the Confederate armies. This neutrality was first violated on September 3, 1861, when Confederate Maj. Gen. Leonidas Polk
Lieutenant-General Leonidas Polk (April 10, 1806 – June 14, 1864) was a bishop of the Episcopal Diocese of Louisiana and founder of the Protestant Episcopal Church in the Confederate States of America, which separated from the Episcopal Ch ...
occupied Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
, considered key to controlling the Lower Mississippi
The Lower Mississippi River is the portion of the Mississippi River downstream of Cairo, Illinois. From the confluence of the Ohio River and Upper Mississippi River at Cairo, the Lower flows just under 1000 miles (1600 km) to the Gulf of ...
. Two days later Union Brig. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union A ...
seized Paducah. Henceforth, the proclaimed neutrality was a dead letter. While the state never seceded from the Union, Confederate sympathizers who were members of the legislature set up a temporary Confederate capital in Bowling Green
A bowling green is a finely laid, close-mown and rolled stretch of turf for playing the game of bowls.
Before 1830, when Edwin Beard Budding of Thrupp, near Stroud, UK, invented the lawnmower, lawns were often kept cropped by grazing sheep ...
in November 1861. It never wielded significant power inside the state. The Confederate States recognized Kentucky and added a star representing the state to the Confederate flag
The flags of the Confederate States of America have a history of three successive designs during the American Civil War. The flags were known as the "Stars and Bars", used from 1861 to 1863; the "Stainless Banner", used from 1863 to 1865; and ...
.
After the Battle of Shiloh
The Battle of Shiloh (also known as the Battle of Pittsburg Landing) was fought on April 6–7, 1862, in the American Civil War. The fighting took place in southwestern Tennessee, which was part of the war's Western Theater. The battlefield i ...
on April 6-7, the beaten Confederate army under Maj. Gen Pierre G.T. Beauregard retreated down into Corinth, very slowly pursued by the combined Union forces under Maj. Gen Henry Halleck--the armies of Grant, Buell, and John Pope. Although Halleck had 100,000 men under his command and Beauregard half or less of that number, it took him 51 days to march the 20 miles from Pittsburg Landing to Corinth, which was abandoned by the Confederates on May 29. Confederate president Jefferson Davis
Jefferson F. Davis (June 3, 1808December 6, 1889) was an American politician who served as the president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the United States Senate and the House of Representatives as ...
, unhappy with Beauregard's retreat, removed him from command and gave Braxton Bragg the army, which he renamed the Army of Tennessee. Bragg spent most of June drilling and reorganizing the army in camp at Tupelo, Mississippi
Tupelo () is a city in and the county seat of Lee County, Mississippi, United States. With an estimated population of 38,300, Tupelo is the sixth-largest city in Mississippi and is considered a commercial, industrial, and cultural hub of North ...
. The Union armies ignored him and the war in Tennessee virtually ground to a halt during the summer months. Grant's Army of the Tennessee was scattered about western Tennessee and northern Mississippi, while Buell's Army of Ohio was moving towards Chattanooga
Chattanooga ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Hamilton County, Tennessee, United States. Located along the Tennessee River bordering Georgia, it also extends into Marion County on its western end. With a population of 181,099 in 2020, ...
at an incredibly slow pace, spending much of that time rebuilding railroad lines. While Halleck had had overall command of the Union war effort in the West since spring, he was summoned to Washington DC in July to become general-in-chief of the armies, leaving Grant and Buell to their separate independent commands--Pope was also called east to take command of the Union war effort in Virginia and his former army added to Grant's and put under the command of William Rosecrans.
The initiative to invade Kentucky came primarily from Confederate Maj. Gen. Edmund Kirby Smith
General Edmund Kirby Smith (May 16, 1824March 28, 1893) was a senior officer of the Confederate States Army who commanded the Trans-Mississippi Department (comprising Arkansas, Missouri, Texas, western Louisiana, Arizona Territory and the India ...
, commander of the Department of East Tennessee. He believed the campaign would allow them to obtain supplies, enlist recruits, divert Union troops from Tennessee, and claim Kentucky for the Confederacy. In July 1862 Col. John Hunt Morgan carried out a successful cavalry raid in the state, venturing deeply into the rear areas of Buell's department. The raid caused considerable consternation in Buell's command and in Washington, D.C. During the raid, Morgan and his forces were cheered and supported by many residents. He added 300 Kentucky volunteers to his 900-man force during the raid. He confidently promised Kirby Smith, "The whole country can be secured, and 25,000 or 30,000 men will join you at once."
Bragg considered various options, including an attempt to retake Corinth, Mississippi
Corinth is a city in and the county seat of Alcorn County, Mississippi, United States. The population was 14,573 at the 2010 census. Its ZIP codes are 38834 and 38835. It lies on the state line with Tennessee.
History
Corinth was founded i ...
, or to advance against Buell's army through Middle Tennessee
Middle Tennessee is one of the three Grand Divisions of the U.S. state of Tennessee that composes roughly the central portion of the state. It is delineated according to state law as 41 of the state's 95 counties. Middle Tennessee contains the ...
. He eventually heeded Kirby Smith's calls for reinforcement and decided to relocate his Army of Mississippi to join with him. He moved 30,000 infantrymen in a tortuous railroad journey from Tupelo, Mississippi
Tupelo () is a city in and the county seat of Lee County, Mississippi, United States. With an estimated population of 38,300, Tupelo is the sixth-largest city in Mississippi and is considered a commercial, industrial, and cultural hub of North ...
, through Mobile and Montgomery to Chattanooga
Chattanooga ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Hamilton County, Tennessee, United States. Located along the Tennessee River bordering Georgia, it also extends into Marion County on its western end. With a population of 181,099 in 2020, ...
. Supply wagons, cavalry, and artillery moved overland under their own power through Rome, Georgia
Rome is the largest city in and the county seat of Floyd County, Georgia, United States. Located in the foothills of the Appalachian Mountains, it is the principal city of the Rome, Georgia, metropolitan statistical area, which encompasses all ...
. Although Bragg was the senior general in the theater, Confederate President
The president of the Confederate States was the head of state and head of government of the Confederate States. The president was the chief executive of the federal government and was the commander-in-chief of the Confederate Army and the Confed ...
Jefferson Davis
Jefferson F. Davis (June 3, 1808December 6, 1889) was an American politician who served as the president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the United States Senate and the House of Representatives as ...
had established Kirby Smith's Department of East Tennessee as an independent command, reporting directly to Richmond
Richmond most often refers to:
* Richmond, Virginia, the capital of Virginia, United States
* Richmond, London, a part of London
* Richmond, North Yorkshire, a town in England
* Richmond, British Columbia, a city in Canada
* Richmond, Californi ...
. This decision caused Bragg difficulty during the campaign.
Smith and Bragg met in Chattanooga on July 31, and devised a plan for the campaign: The newly created Army of Kentucky, including two of Bragg's brigade
A brigade is a major tactical military formation that typically comprises three to six battalions plus supporting elements. It is roughly equivalent to an enlarged or reinforced regiment. Two or more brigades may constitute a division.
...
s and approximately 21,000 men, would march north under Kirby Smith's command into Kentucky to dispose of the Union defenders of Cumberland Gap. (Bragg's army was too exhausted from its long journey to begin immediate offensive operations.) Smith would return to join Bragg, and their combined forces would attempt to maneuver into Buell's rear and force a battle to protect his supply lines. Any attempt by Ulysses S. Grant to reinforce Buell from northern Mississippi would be handled by the two small armies of Maj. Gens. Sterling Price
Major-General Sterling "Old Pap" Price (September 14, 1809 – September 29, 1867) was a senior officer of the Confederate States Army who commanded infantry in the Western and Trans-Mississippi theaters of the American Civil War. Prior to ...
and Earl Van Dorn
Earl Van Dorn (September 17, 1820May 7, 1863) started his military career as a United States Army officer but joined Confederate forces in 1861 after the Civil War broke out. He was a major general when he was killed in a private conflict.
A g ...
.
The first indication that something was happening came in late June when Col. Phil Sheridan, commanding a cavalry demi-brigade (two regiments) in the Army of the Tennessee, went on a reconnaissance mission to discover that the Confederates had abandoned their camp at Tupelo and began moving towards Chattanooga, while another Confederate army under Sterling Price
Major-General Sterling "Old Pap" Price (September 14, 1809 – September 29, 1867) was a senior officer of the Confederate States Army who commanded infantry in the Western and Trans-Mississippi theaters of the American Civil War. Prior to ...
was gathering in Mississippi. Several captured letters from Confederate soldiers boasted that the Yankees would be given the slip (Maj. Gen William Rosecrans was impressed with Sheridan's foray and recommended him for promotion to brigadier general).
Once the armies were combined, Bragg's seniority would apply and Smith would be under his direct command. Assuming that Buell's army could be destroyed, Bragg and Smith would march north into Kentucky, a movement they assumed would be welcomed by the local populace. Any remaining Federal force would be defeated in a grand battle in Kentucky, establishing the Confederate frontier at the Ohio River.
The campaign plan was bold but risky, requiring perfect coordination between multiple armies that would initially have no unity of command. Bragg almost immediately began to have second thoughts, despite pressure from President Davis to take Kentucky. Smith quickly abandoned the agreement, foreseeing that a solo adventure in Kentucky would bring him personal glory. He deceived Bragg as to his intentions and requested two additional brigades, ostensibly for his expedition to Cumberland Gap
The Cumberland Gap is a pass through the long ridge of the Cumberland Mountains, within the Appalachian Mountains, near the junction of the U.S. states of Kentucky, Virginia, and Tennessee. It is famous in American colonial history for its r ...
. On August 9, Smith informed Bragg that he was breaking the agreement and intended to bypass Cumberland Gap, leaving a small holding force to neutralize the Union garrison, and to move north. Unable to command Smith to honor their plan, Bragg focused on a movement to Lexington
Lexington may refer to:
Places England
* Laxton, Nottinghamshire, formerly Lexington
Canada
* Lexington, a district in Waterloo, Ontario
United States
* Lexington, Kentucky, the largest city with this name
* Lexington, Massachusetts, the oldes ...
instead of Nashville
Nashville is the capital city of the U.S. state of Tennessee and the seat of Davidson County. With a population of 689,447 at the 2020 U.S. census, Nashville is the most populous city in the state, 21st most-populous city in the U.S., and th ...
. He cautioned Smith that Buell could pursue and defeat his smaller army before Bragg's army could join up with them.
Smith marched north with 21,000 men from Knoxville on August 13; Bragg departed from Chattanooga on August 27, just before Smith reached Lexington. The beginning of the campaign coincided with Gen.
The Book of Genesis (from Greek ; Hebrew: בְּרֵאשִׁית ''Bəreʾšīt'', "In hebeginning") is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its first word, ( "In the beginning"). ...
Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, towards the end of which he was appointed the overall commander of the Confederate States Army. He led the Army of Nor ...
's offensive in the northern Virginia campaign (second Manassas campaign) and with Price's and Van Dorn's operations against Grant. Although not centrally directed, it was the largest simultaneous Confederate offensive of the war.
Meanwhile, Buell was forced to abandon his slow advance toward Chattanooga. Receiving word of the Confederate movements, he decided to concentrate his army around Nashville. The news that Smith and Bragg were both in Kentucky convinced him of the need to place his army between the Confederates and the Union cities of Louisville
Louisville ( , , ) is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Kentucky and the 28th most-populous city in the United States. Louisville is the historical seat and, since 2003, the nominal seat of Jefferson County, on the Indiana border.
...
and Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Hamilton County. Settled in 1788, the city is located at the northern side of the confluence of the Licking and Ohio rivers, the latter of which marks the state line w ...
. On September 7, Buell's Army of the Ohio left Nashville and began racing Bragg to Louisville.
On the way, Bragg was distracted by the capture of a Union fort at Munfordville. He had to decide whether to continue toward a fight with Buell (over Louisville) or rejoin Smith, who had gained control of the center of the state by capturing Richmond
Richmond most often refers to:
* Richmond, Virginia, the capital of Virginia, United States
* Richmond, London, a part of London
* Richmond, North Yorkshire, a town in England
* Richmond, British Columbia, a city in Canada
* Richmond, Californi ...
and Lexington, and threatened to move on Cincinnati. Bragg chose to rejoin Smith.
Buell reached Louisville, where he gathered, reorganized, and reinforced his army with thousands of new recruits. He dispatched 20,000 men under Brig. Gen. Joshua W. Sill toward Frankfort, hoping to distract Smith and prevent the two Confederate armies from joining against him. Meanwhile, Bragg left his army and met Smith in Frankfort, where they attended the inauguration
In government and politics, inauguration is the process of swearing a person into office and thus making that person the incumbent. Such an inauguration commonly occurs through a formal ceremony or special event, which may also include an inaugu ...
of Confederate Governor Richard Hawes
Richard Hawes Jr. (February 6, 1797 – May 25, 1877) was a United States representative from Kentucky and the second Confederate Governor of Kentucky. He was part of the politically influential Hawes family. His brother, uncle, and cousin a ...
on October 4. The inauguration ceremony was disrupted by the sound of cannon fire from Sill's approaching division, and organizers canceled the inaugural ball scheduled for that evening.
Prelude to battle
When he departed for Frankfort on September 28, Bragg left his army under Polk's command. On October 3, the approach of the large Union force caused the Confederates to withdraw eastward and Bardstown was occupied on October 4. Hardee's wing stopped at Perryville and requested reinforcements from Bragg. Although Bragg wished to concentrate his army atVersailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, ...
, the quickly approaching Federal III Corps forced the concentration at Perryville and Harrodsburg.
Geography and location
 Hardee had selected Perryville for a few reasons. The village of approximately 300 residents had an excellent road network with connections to nearby towns in six directions, allowing for strategic flexibility. It was located to prevent the Federals from reaching the Confederate supply depot in Bryantsville. Finally, it was a potential source of water. An extremely wet winter and spring of 1862, believed caused by the eruption of Mt. Dubbi in East Africa in May 1861, gave way to dry conditions during June which stayed that way throughout the summer and into early fall. The Southern states remained locked under a stagnant high pressure ridge that sent daytime temperatures soaring with little rain to cool things down.The heat was oppressive for both men and horses, and the few sources of drinking water provided by the rivers and creeks west of town—most reduced to isolated stagnant puddles—were desperately sought after.
Hardee had selected Perryville for a few reasons. The village of approximately 300 residents had an excellent road network with connections to nearby towns in six directions, allowing for strategic flexibility. It was located to prevent the Federals from reaching the Confederate supply depot in Bryantsville. Finally, it was a potential source of water. An extremely wet winter and spring of 1862, believed caused by the eruption of Mt. Dubbi in East Africa in May 1861, gave way to dry conditions during June which stayed that way throughout the summer and into early fall. The Southern states remained locked under a stagnant high pressure ridge that sent daytime temperatures soaring with little rain to cool things down.The heat was oppressive for both men and horses, and the few sources of drinking water provided by the rivers and creeks west of town—most reduced to isolated stagnant puddles—were desperately sought after.
Disposition of armies
On October 7, Buell reached the Perryville area as Union cavalry clashed with Wheeler's rearguard throughout the day. Accompanying III Corps, Buell learned that the Confederates had halted at Perryville and were deploying their infantry. He therefore planned an attack. The enemy force was his principal objective, but the availability of water also made control of the town and surrounding area desirable. Buell issued orders for all corps to move at 3 a.m. the next day and attack at 10 a.m. However, movements of the I and II Corps were delayed, having deviated several miles from their line of march in search of water. Buell decided to delay his attack until October 9 to complete his army's deployment and ordered each corps commander to avoid a general engagement on October 8. Buell was unable to oversee the deployment of his arriving corps. Thrown from his horse, he suffered injuries that prevented him from riding. He established his headquarters at the Dorsey house, about due west of town. Hardee established a line of defense across the three roads leading into Perryville from the north and west. Until reinforcements could arrive, he was limited to three of the four brigades of Buckner's division. Brig. Gen. Sterling A. M. Wood was placed at the north of town. Brig. Gen.Bushrod Johnson
Bushrod Rust Johnson (October 7, 1817 – September 12, 1880) was a Confederate general in the American Civil War and an officer in the United States Army. As a university professor he had been active in the state militias of Kentucky and Tenn ...
was to Wood's right, east of the Chaplin River
The Chaplin River is an U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed May 13, 2011 tributary of the Beech Fork of the Salt River in the U.S. state of Kentucky.
The name comes from Ca ...
near the Harrodsburg Pike. Brig. Gen. St. John R. Liddell's Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
Brigade formed on the crest of Bottom Hill, just east of Bull Run Creek, a tributary of Doctor's Creek, with one regiment, the 7th Arkansas, sent forward to Peters Hill on the other side of the creek. On the evening of October 7 the final Confederate forces began to arrive. The first of Patton Anderson's four brigades reached the area around 3 p.m. Brig. Gen. Patrick Cleburne
Major-General Patrick Ronayne Cleburne ( ; March 16, 1828November 30, 1864) was a senior officer of the Confederate States Army who commanded infantry in the Western Theater of the American Civil War.
Born in Ireland, Cleburne served in ...
's brigade, the remainder of Buckner's division, followed. Around midnight, three brigades of Frank Cheatham's division arrived, moving quickly and enthusiastically, having left their baggage train behind; his fourth brigade, under Brig. Gen. Preston Smith, received orders to return to Harrodsburg.
Opposing forces
Union
On October 1, Buell'sArmy of the Ohio
The Army of the Ohio was the name of two Union armies in the American Civil War. The first army became the Army of the Cumberland and the second army was created in 1863.
History
1st Army of the Ohio
General Orders No. 97 appointed Maj. Gen. ...
left Louisville with Maj. Gen. George H. Thomas as his second in command. (Two days earlier, Buell had received orders from Washington relieving him of command, to be replaced by Thomas. Thomas demurred, refusing to accept command while the campaign was underway, leaving Buell in place.) The 55,000 troops—many of whom Thomas described as "yet undisciplined, unprovided with suitable artillery, and in every way unfit for active operations against a disciplined foe"—advanced toward Bragg's veteran army in Bardstown
Bardstown is a home rule-class city in Nelson County, Kentucky, United States. The population was 11,700 in the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Nelson County.
Bardstown is named for the pioneering Bard brothers. David Bard obtained a l ...
on three separate roads.
* The I Corps I Corps, 1st Corps, or First Corps may refer to:
France
* 1st Army Corps (France)
* I Cavalry Corps (Grande Armée), a cavalry unit of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
* I Corps (Grande Armée), a unit of the Imperial French Ar ...
, commanded by Maj. Gen. Alexander M. McCook
Alexander McDowell McCook (April 22, 1831June 12, 1903) was a career United States Army officer and a Union general in the American Civil War.
Early life
McCook was born in Columbiana County, Ohio. A Scottish family, the McCooks were prominent i ...
, marched on the left, along the Mackville Road. His 13,000 men consisted of the 3rd Division, under Brig. Gen. Lovell H. Rousseau
Lovell Harrison Rousseau (August 4, 1818 – January 7, 1869) was a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War, as well as a lawyer and politician in Kentucky and Indiana.
Early life and career
Born near Stanford, Kentucky, on Augus ...
, and the 10th Division, under Brig. Gen. James S. Jackson.
* The II Corps 2nd Corps, Second Corps, or II Corps may refer to:
France
* 2nd Army Corps (France)
* II Cavalry Corps (Grande Armée), a cavalry unit of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
* II Corps (Grande Armée), a unit of the Imperial French ...
, commanded by Maj. Gen. Thomas L. Crittenden
Thomas Leonidas Crittenden (May 15, 1819 – October 23, 1893) was a lawyer, politician, and Union general during the American Civil War.
Early life
Crittenden was born in Russellville, Kentucky, the son of U.S. Senator John J. Crittenden, who ...
, marched on the right, along the Lebanon Road. His 20,000 men were in three divisions: the 4th, commanded by Brig. Gen. William Sooy Smith
William Sooy Smith (July 22, 1830 – March 4, 1916) was a West Point graduate and career civil engineer who became a brigadier general in the Union Army during the American Civil War.
In civilian life, he was a renowned engineer involved in ...
; the 5th, Brig. Gen. Horatio P. Van Cleve; and the 6th, Brig. Gen. Thomas J. Wood
Thomas John Wood (September 25, 1823 – February 26, 1906) was a career United States Army officer. He served in the Mexican–American War and as a Union general during the American Civil War.
During the Mexican–American War, Wood served on ...
.
* The III Corps 3rd Corps, Third Corps, III Corps, or 3rd Army Corps may refer to:
France
* 3rd Army Corps (France)
* III Cavalry Corps (Grande Armée), a cavalry unit of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
* III Corps (Grande Armée), a unit of t ...
, commanded by Maj. Gen. Charles Champion Gilbert, took the center, along the Springfield Pike. Just a few weeks earlier, Gilbert had been a captain, but was elevated to acting major general and corps command following the death by murder of the previous commander, Maj. Gen. William "Bull" Nelson. Gilbert's 22,000 men were also in three divisions: the 1st, under Brig. Gen. Albin F. Schoepf; 9th, Brig. Gen. Robert B. Mitchell; and the 11th, Brig. Gen. Philip H. Sheridan.
Confederate
Bragg's Army of Mississippi consisted of about 16,800 men in two wings: * Right Wing, commanded by Maj. Gen.Leonidas Polk
Lieutenant-General Leonidas Polk (April 10, 1806 – June 14, 1864) was a bishop of the Episcopal Diocese of Louisiana and founder of the Protestant Episcopal Church in the Confederate States of America, which separated from the Episcopal Ch ...
, consisted of a single division under Maj. Gen. Benjamin F. Cheatham
Benjamin Franklin "Frank" Cheatham (October 20, 1820 – September 4, 1886) was a Tennessee planter, California gold miner, and a general in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. He served in the Army of Tennessee, inflicting ...
;
* Left Wing, commanded by Maj. Gen. William J. Hardee, consisted of the divisions of Brig. Gen. J. Patton Anderson and Maj. Gen. Simon B. Buckner.
Battle
Morning actions
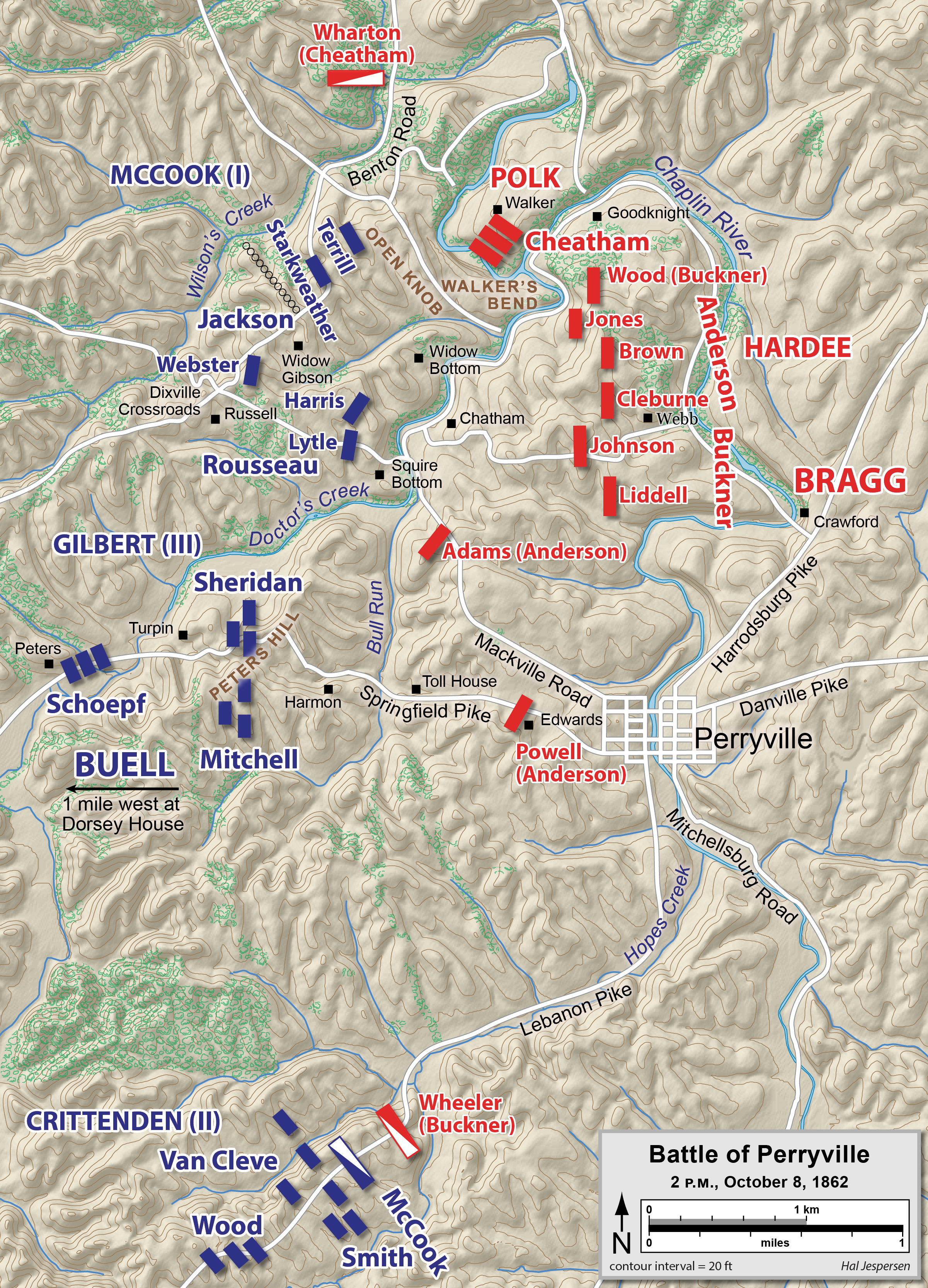
The first shots of the battle were fired early on the morning of October 8. Finding that there were algae-covered pools of water in the otherwise dry bed of Doctor's Creek, troops from the 10th Indiana advanced to take advantage of them. They encountered the forward men of the 7th Arkansas and some shots were exchanged. At 2 a.m., Buell and Gilbert, the III Corps commander, ordered newly promoted Brig. Gen. Phil Sheridan to seize Peters Hill; Sheridan started off with the brigade of Col. Daniel McCook (the younger brother of the I Corps commander). Sheridan seized the hill, driving the Arkansans back to the main line of their brigade, but continued to push across the creek. Liddell's brigade could not check the momentum of Sheridan's thirsty soldiers and Buckner, Liddell's division commander, was ordered by Polk not to reinforce him, but to pull his brigade back. Polk was concerned about starting a general engagement to the west of the Chaplin River, fearing he was outnumbered. Meanwhile, on the Union side, a nervous Gilbert ordered Sheridan to return to Peters Hill. For the preceding few days, Braxton Bragg had been deceived by the diversion launched by Sills against Frankfort, assuming that it was the major thrust of Buell's army. He wanted Polk to attack and defeat what he considered to be a minor force at Perryville and then immediately return so that the entire army could be joined with Kirby Smith's. Polk sent a dispatch to Bragg early that morning that he intended to attack vigorously, but he quickly changed his mind and settled on a defensive posture. Bragg, angered that he was not hearing the sounds of battle, rode from Harrodsburg to Perryville to take charge, arriving about 10 a.m. and establishing his headquarters at the Crawford house on the Harrodsburg Pike. Bragg was appalled at the condition of Polk's battle line, which contained gaps and was not properly anchored on the flanks. As he rode in, he observed some of McCook's I Corps troops north of town, but he assumed that the primary threat continued to be on the Springfield Pike, where the action against the III Corps had taken place early that morning. (He had no knowledge of Crittenden's II Corps approaching on the Lebanon Pike.) He gave orders to realign his army into a north–south line and prepare to attack ''en echelon''. Cheatham's division marched north from town and prepared to open the attack on the Union left—which Bragg assumed to be on the Mackville Road—beginning a large "left wheel" movement. Two brigades from Patton Anderson's division would then strike the Union center and Buckner's division would follow up on the left. Another of Anderson's brigades, commanded by Col. Samuel Powel, would attack farther to the south along the Springfield Pike. The large clouds of dust raised by Cheatham's division marching north at the double-quick prompted some of McCook's men to believe the Confederates were starting to retreat, which increased the surprise of the Rebel attack later in the day. By the afternoon of October 8, most of Buell's army had arrived. They were positioned with McCook's I Corps on the left from the Benton Road to the Mackville Road; Gilbert's III Corps in the center, on the Springfield Pike; Crittenden's II Corps on the right, along the Lebanon Pike. The vast majority of action during the battle would be against McCook's corps. Because of an unusualacoustic shadow An acoustic shadow or sound shadow is an area through which sound waves fail to propagate, due to topographical obstructions or disruption of the waves via phenomena such as wind currents, buildings, or sound barriers.
Short-distance acoustic shado ...
, few sounds from the battle reached Buell's headquarters only away; he did not exert effective control over the battle and committed no reserves until late in the day.
Attack from the Confederate right
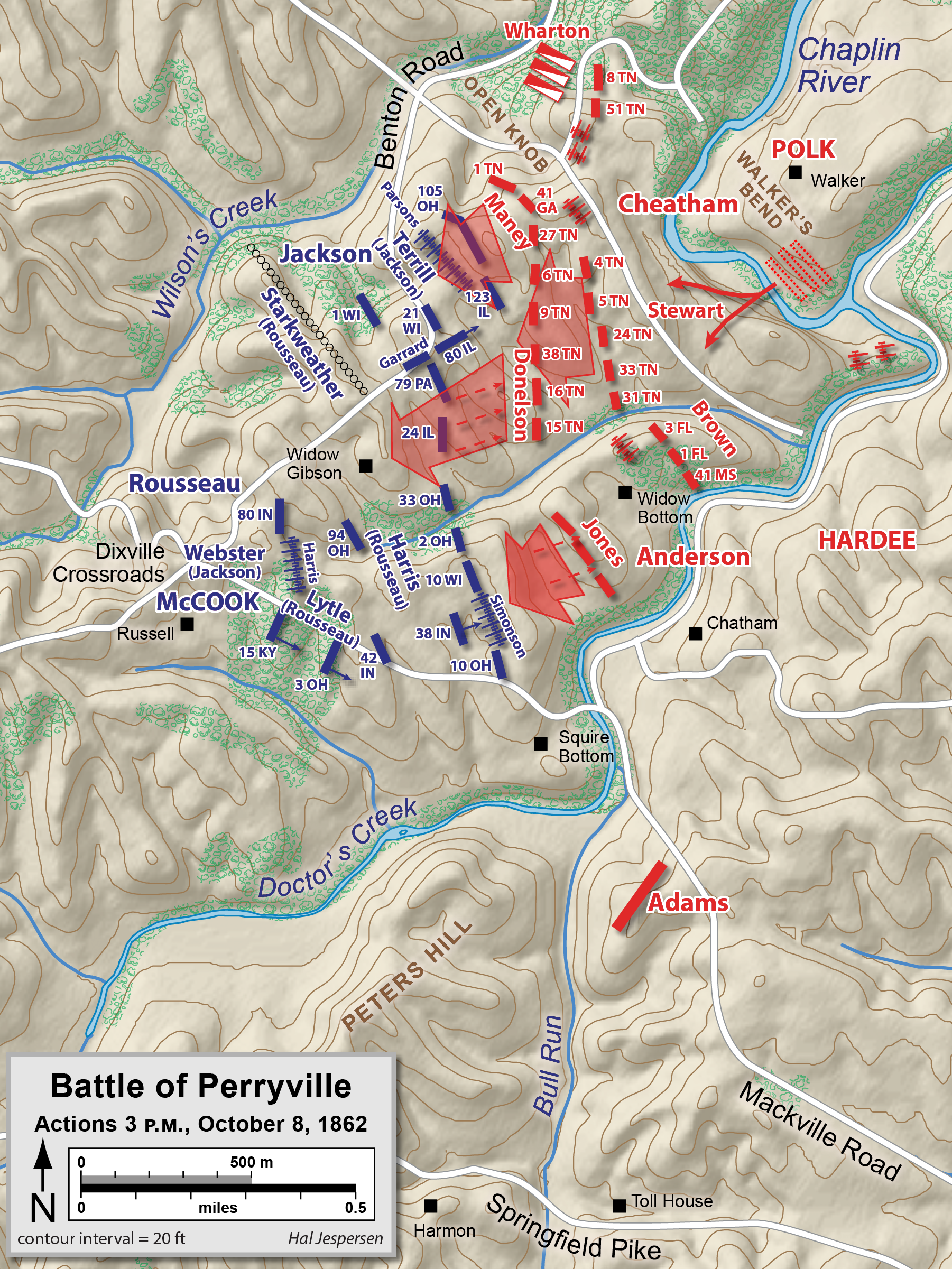
 Cheatham's artillery bombardment began at 12:30 p.m., but he did not immediately order his infantry forward. Union troops continued to file into line, extending their flank to the north, beyond the intended avenue of attack. Bragg moved Cheatham's division into Walker's Bend, assuming the redirected attack would now strike the Union's open flank. Unfortunately for the Confederates, their cavalry reconnaissance withdrew before McCook placed an artillery battery under Lt. Charles Parsons and the brigade of Brig. Gen. William R. Terrill onto the Open Knob, a prominent hill on the northern end of the battlefield.
The brigade of Brig. Gen. Daniel S. Donelson was the first to cross the Chaplin River, climb the bluffs on the west bank, and began its attack around 2 p.m. Two of the brigade's regiments had been detached, leaving only three for the attack. Cheatham shouted, "Give 'em hell, boys!" One of the enduring legends of the Civil War is that Gen. Polk, who was also an Episcopal
Cheatham's artillery bombardment began at 12:30 p.m., but he did not immediately order his infantry forward. Union troops continued to file into line, extending their flank to the north, beyond the intended avenue of attack. Bragg moved Cheatham's division into Walker's Bend, assuming the redirected attack would now strike the Union's open flank. Unfortunately for the Confederates, their cavalry reconnaissance withdrew before McCook placed an artillery battery under Lt. Charles Parsons and the brigade of Brig. Gen. William R. Terrill onto the Open Knob, a prominent hill on the northern end of the battlefield.
The brigade of Brig. Gen. Daniel S. Donelson was the first to cross the Chaplin River, climb the bluffs on the west bank, and began its attack around 2 p.m. Two of the brigade's regiments had been detached, leaving only three for the attack. Cheatham shouted, "Give 'em hell, boys!" One of the enduring legends of the Civil War is that Gen. Polk, who was also an Episcopal bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ...
, was nearby and seconded the cheer: "Give it to 'em boys; give 'em what General Cheatham says!" The brigade found that instead of striking the open flank it had expected, it was performing a frontal assault on the center of the Union position. The 16th Tennessee Infantry, under Col. John H. Savage, raced ahead of the other two regiments, attempting to reach the artillery battery of Capt. Samuel J. Harris. (Savage held Donelson in disdain, considering him a drunkard with limited military ability, and often paid little attention to orders from his commander. He considered Donelson's order to attack Harris's battery to be a death sentence against him.) As it moved west into a depression, it came under crossfire from the 33rd Ohio Infantry
The 33rd Ohio Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War.
Service
The 33rd Ohio Infantry Regiment was organized at Portsmouth, Ohio, from August 5 through September 13, 1861. It was mustered ...
and the eight guns of Parsons' artillery on Open Knob, to the north. Cheatham ordered the brigade of Brig. Gen. George E. Maney forward to deal with Parsons on the Open Knob, but Donelson's brigade could not withstand the fire and withdrew to its starting point at 2:30 p.m. with about 20% casualties; Savage's regiment lost 219 of its 370 men.
 Parsons' eight guns on the Open Knob were manned by inexperienced soldiers, some of whom were infantry recruits from the
Parsons' eight guns on the Open Knob were manned by inexperienced soldiers, some of whom were infantry recruits from the 105th Ohio Infantry
The 105th Ohio Infantry Regiment, sometimes 105th Ohio Volunteer Infantry (or 105th OVI) was an infantry regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War.
Service
The 105th Ohio Infantry was organized at Cleveland, Ohio, and mustered in f ...
. Terrill's 33rd Brigade was posted to defend the guns. Meanwhile, Confederate Brigadier General George Maney's brigade was able to approach the Knob undetected through the woods, as the Union troops' attention was focused on Donelson's attack. Eventually, the Union artillery redirected their guns and a fierce firefight ensued. Brig. Gen. Jackson, the 10th Division commander, was killed in the action, and command fell to Terrill, who immediately made a poor command decision. Obsessed with the safety of his artillery, he ordered the 123rd Illinois to mount a bayonet charge down the hill. The 770 raw Union troops suffered heavy casualties at the hands of the 1,800 veteran Confederates. As reinforcements arrived from the 80th Illinois and a detachment of infantry commanded by Col. Theophilus T. Garrard, the two sides were briefly stalemated. Maney's artillery, commanded by Lt. William Turner, pounded the inexperienced defenders, and Maney ordered a charge up the steep slope, which swept the Union men from the hill and captured most of Parsons' guns; the tenacious Parsons had to be dragged away from the scene by his retreating soldiers.
 Maney's attack continued to the west, down the reverse slope of the Open Knob, through a cornfield, and across the Benton Road, after which was another steep ridge, occupied by the 2,200 men in the Union 28th Brigade of Col. John C. Starkweather (Rousseau's division), and twelve guns. Those guns made the Open Knob an untenable position. Starkweather had placed his 21st Wisconsin in the cornfield about the time that Maney was attacking Parsons' position. The inexperienced men of the 21st—some of whom had never fired their weapons before, the regiment having been formed less than a month earlier—could see little through the 10- to high cornstalks of the cornfield. They were surprised as the remnants of Terrill's brigade retreated through their position. As Terrill himself retreated, he shouted, "The Rebels are advancing in terrible force!" Terrill convinced the regimental adjutant to order yet another bayonet charge; 200 men advanced and were quickly smashed by the oncoming Confederates. While the Union men had to hold their fire to keep from shooting their retreating comrades, artillery fire from Starkweather's batteries caused numerous
Maney's attack continued to the west, down the reverse slope of the Open Knob, through a cornfield, and across the Benton Road, after which was another steep ridge, occupied by the 2,200 men in the Union 28th Brigade of Col. John C. Starkweather (Rousseau's division), and twelve guns. Those guns made the Open Knob an untenable position. Starkweather had placed his 21st Wisconsin in the cornfield about the time that Maney was attacking Parsons' position. The inexperienced men of the 21st—some of whom had never fired their weapons before, the regiment having been formed less than a month earlier—could see little through the 10- to high cornstalks of the cornfield. They were surprised as the remnants of Terrill's brigade retreated through their position. As Terrill himself retreated, he shouted, "The Rebels are advancing in terrible force!" Terrill convinced the regimental adjutant to order yet another bayonet charge; 200 men advanced and were quickly smashed by the oncoming Confederates. While the Union men had to hold their fire to keep from shooting their retreating comrades, artillery fire from Starkweather's batteries caused numerous friendly fire
In military terminology, friendly fire or fratricide is an attack by belligerent or neutral forces on friendly troops while attempting to attack enemy/hostile targets. Examples include misidentifying the target as hostile, cross-fire while en ...
casualties. The 21st managed to fire a volley into the Confederate ranks, but it was answered by a 1,400-musket volley that decimated the Union regiment, and the survivors fled toward the Benton Road.
 To fill a gap in the Confederate line where Donelson's brigade had fought, Cheatham deployed the Tennessee brigade of Brig. Gen.
To fill a gap in the Confederate line where Donelson's brigade had fought, Cheatham deployed the Tennessee brigade of Brig. Gen. Alexander P. Stewart
Alexander Peter Stewart (October 2, 1821 – August 30, 1908) was a career United States Army officer, college professor, and a general in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. He fought in many of the most significant ba ...
and they joined Maney's brigade in the advance against Starkweather. The 1st Tennessee attacked the northern end of the hill while the remainder of Maney's brigade assaulted directly up the slope. Starkweather's position was a strong one, however, and the Confederates were initially repulsed by strong infantry and artillery fire. A second charge and vicious hand-to-hand fighting brought the Confederates to the crest, among the batteries.
 At that time Brig. Gen. Terrill returned to the fight, leading his troops up the reverse slope of the hill. He was mortally wounded by an artillery shell exploding overhead and died at 2 a.m. the following day. Starkweather, meanwhile, was able to salvage six of his twelve guns and move them west to the next ridge. Col. Albert S. Hall began the day as regimental commander of the 105th Ohio, and with the deaths of Jackson, Terrill, and Col. George Webster, advanced all the way to command of the 10th Division by the end of the day.
Once again the Federals had a strong defensive position, with good artillery support and a stone wall at the top of a steep slope. Maney's and Stewart's men attempted three assaults, all unsuccessful, and withdrew to the vicinity of the Open Knob at around 5:30 p.m. The assault by Maney's brigade over three hours was the bloodiest of the battle, and arguably its most crucial action. Historian Kenneth W. Noe describes Maney's final repulse as the " high-water mark of the Confederacy in the western theater, no less important than the Angle at Gettysburg."
At that time Brig. Gen. Terrill returned to the fight, leading his troops up the reverse slope of the hill. He was mortally wounded by an artillery shell exploding overhead and died at 2 a.m. the following day. Starkweather, meanwhile, was able to salvage six of his twelve guns and move them west to the next ridge. Col. Albert S. Hall began the day as regimental commander of the 105th Ohio, and with the deaths of Jackson, Terrill, and Col. George Webster, advanced all the way to command of the 10th Division by the end of the day.
Once again the Federals had a strong defensive position, with good artillery support and a stone wall at the top of a steep slope. Maney's and Stewart's men attempted three assaults, all unsuccessful, and withdrew to the vicinity of the Open Knob at around 5:30 p.m. The assault by Maney's brigade over three hours was the bloodiest of the battle, and arguably its most crucial action. Historian Kenneth W. Noe describes Maney's final repulse as the " high-water mark of the Confederacy in the western theater, no less important than the Angle at Gettysburg."
Attack from the Confederate center
The ''en echelon'' attack continued with Anderson's division in the center. At about 2:45 p.m., the same time that Maney's first attack was being repulsed on the Open Knob, the brigade of Col. Thomas M. Jones began its attack across a valley commanded by a large sinkhole. Jones had no orders to attack from Anderson or Hardee, but moved forward on his own initiative when he heard the sound of firing to his right. As they entered the valley, his men were cut down by musketry and fire from twelve artillery pieces on the next ridge, where the Union 9th Brigade (Rousseau's division) under Col. Leonard A. Harris was posted. Confederate artillery attached to Jones's brigade, Capt. Charles Lumsden's Alabama Light Artillery, returned fire, but due to an optical illusion that made two successive ridges look the same, were unable to fix on the appropriate range and their fire had no effect on the Federal line. At 3:30 p.m., the Confederate brigade of Brig. Gen.John C. Brown
John Calvin Brown (January 6, 1827August 17, 1889) was a Confederate Army officer and an American politician and businessman. Although he originally opposed secession, Brown fought for the Confederacy during the American Civil War, eventually ...
moved up to take the place of Jones's retreating men. By this time, most of the Union artillery had had to withdraw to replenish their ammunition, so Brown's men did not suffer the same fate as Jones's. Nevertheless, they made no headway against the infantry units in place until successes on the Confederate left put pressure on the Union position.
Attack from the Confederate left
 Almost all of McCook's I Corps units were posted at the beginning of the battle on land owned by "
Almost all of McCook's I Corps units were posted at the beginning of the battle on land owned by "Squire
In the Middle Ages, a squire was the shield- or armour-bearer of a knight.
Use of the term evolved over time. Initially, a squire served as a knight's apprentice. Later, a village leader or a lord of the manor might come to be known as ...
" Henry P. Bottom. The corps' right flank, Col. William H. Lytle's 17th Brigade, was posted on a ridge on which Squire Bottom's house and barn were situated, overlooking a bend in the Chaplin River and a hill and farm owned by R. F. Chatham on the other side. At about 2:30 p.m. Major John E. Austin's 14th Battalion of Louisiana Sharpshooters, screening Brig. Gen. Daniel W. Adams's Confederate brigade, engaged the 42nd Indiana as it was collecting water in the ravine of Doctor's Creek. This began a Confederate attack against this area with Brig. Gen. Bushrod R. Johnson
Bushrod Rust Johnson (October 7, 1817 – September 12, 1880) was a Confederate general in the American Civil War and an officer in the United States Army. As a university professor he had been active in the state militias of Kentucky and Tenn ...
's brigade descending from Chatham House Hill at about 2:45 p.m., crossing the almost-dry riverbed and attacking the 3rd Ohio Infantry, commanded by Col. John Beatty. The attack was disorganized; last-minute changes of orders from Buckner were not distributed to all of the participating units and friendly fire from Confederate artillery broke their lines while still on Chatham House Hill. When the infantry attack eventually moved up the hill, fighting from stone wall to stone wall, Confederate artillery bombarded the 3rd Ohio and set afire Squire Bottom's log barn. Some of the Union wounded soldiers had sought refuge in the barn and many were burned to death.
The Ohioans withdrew and were replaced in their position by the 15th Kentucky. As Johnson's men ran low on ammunition, Brig. Gen. Patrick R. Cleburne
Major-General Patrick Ronayne Cleburne ( ; March 16, 1828November 30, 1864) was a senior officer of the Confederate States Army who commanded infantry in the Western Theater of the American Civil War.
Born in Ireland, Cleburne served in the ...
's brigade entered the battle at about 3:40 p.m. Cleburne's horse, Dixie, was killed by an artillery shell, which also wounded Cleburne in the ankle, but he kept his troops moving forward. As they advanced up the slope, they were subjected to Confederate artillery fire; Cleburne later surmised that the friendly fire was caused by his men wearing blue uniform trousers, which had been captured from Union soldiers at Richmond. On Cleburne's left, Brig. Gen. Daniel W. Adams's brigade joined the attack against the 15th Kentucky, which had been reinforced by three companies of the 3rd Ohio. The Union troops retreated to the west toward the Russell House, McCook's headquarters. Lytle was wounded in the head as he attempted to rally his men. He was left on the field for dead, and was captured.
While Lytle's brigade was being beaten back, the left flank of Phil Sheridan's division was only a few hundred yards to the south on Peters Hill. One of the lingering controversies of the battle has been why he did not choose to join the fight. Earlier in the day he had been ordered by Gilbert not to bring on a general engagement. At around 2 p.m., the sound of artillery fire reached army headquarters where Buell was having dinner with Gilbert; the two generals assumed that it was Union artillery practicing and sent word to Sheridan not to waste gunpowder. Sheridan did project some artillery fire into the Confederate assault, but when Gilbert finally arrived from the rear, he feared that Sheridan would be attacked and ordered him back to his entrenchments.
 Sheridan's division did participate toward the end of the battle. The Confederate brigade of Col. Samuel Powel (Anderson's division) was ordered to advance in conjunction with Adams's brigade, on Cleburne's left. The two brigades were widely separated, however, with Powel's on Edwards House Hill, immediately west of Perryville. At about 4 p.m., Powel received orders from Bragg to advance west on the Springfield Pike to silence the battery of Capt. Henry Hescock, which was firing into the left flank of Bragg's assault. Bragg assumed this was an isolated battery, not the entire III Corps. Three regiments of Powel's brigade encountered Sheridan's division, and although Sheridan was initially concerned by the Confederates' aggressive attack and sent for reinforcements, the three regiments were quickly repulsed.
Sheridan, who would be characterized in later battles as very aggressive, hesitated to pursue the smaller force, and also refused a request by Daniel McCook to move north in support of his brother's corps. However, his earlier request for reinforcements bore fruit and the 31st Brigade of Col.
Sheridan's division did participate toward the end of the battle. The Confederate brigade of Col. Samuel Powel (Anderson's division) was ordered to advance in conjunction with Adams's brigade, on Cleburne's left. The two brigades were widely separated, however, with Powel's on Edwards House Hill, immediately west of Perryville. At about 4 p.m., Powel received orders from Bragg to advance west on the Springfield Pike to silence the battery of Capt. Henry Hescock, which was firing into the left flank of Bragg's assault. Bragg assumed this was an isolated battery, not the entire III Corps. Three regiments of Powel's brigade encountered Sheridan's division, and although Sheridan was initially concerned by the Confederates' aggressive attack and sent for reinforcements, the three regiments were quickly repulsed.
Sheridan, who would be characterized in later battles as very aggressive, hesitated to pursue the smaller force, and also refused a request by Daniel McCook to move north in support of his brother's corps. However, his earlier request for reinforcements bore fruit and the 31st Brigade of Col. William P. Carlin
William Passmore Carlin (November 23, 1829 – October 4, 1903) was a career soldier from the state of Illinois who served as a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War and then in the postbellum United States Army. He led a brigad ...
(Mitchell's division) moved up on Sheridan's right. Carlin's men moved aggressively in pursuit of Powel, chasing them as fast as they could run toward Perryville. As they reached the cemetery on the western outskirts of town, fierce artillery dueling commenced. Carlin pressed forward and was joined by the 21st Brigade of Col. George D. Wagner
George Day Wagner (September 22, 1829 – February 13, 1869) was an Indiana politician, farmer, and soldier, serving as a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War. His controversial actions at the Battle of Franklin in 1864 o ...
(Wood's division, II Corps). They were poised to capture the town and the critical crossroads that dominated Braxton Bragg's avenue of withdrawal, but an order from Gilbert to Mitchell curtailed the advance, despite Mitchell's furious protestations.
Dixville Crossroads
 Bragg's attack had been a large pincer movement, forcing both flanks of McCook's corps back into a concentrated mass. This mass occurred at the Dixville Crossroads, where the Benton Road crossed the Mackville Road. If the Confederates seized this intersection they could, conceivably, get around the right wing of McCook's corps and effectively cut them off from the rest of the army. The southern jaw of the pincer began to slow at the temporary line established at the Russell House. Harris's and Lytle's brigades defended until Cleburne's and Adams's attack ground to a halt. The northern jaw had been stopped by Starkweather's defense. The remaining attacks came from north of the Mackville Road by two fresh brigades from Buckner's division: Brig. Gen. St. John R. Liddell's and Brig. Gen. Sterling A. M. Wood's.
The initial target of the assault was Col. George Webster's 34th Brigade of Jackson's division. Webster was mortally wounded during the fighting. His death marked the final senior loss for the 10th Division—the division commander, Jackson, and the other brigade commander, Terrill, had also been mortally wounded. (The previous evening, Jackson, Terrill, and Webster had been idly discussing the possibility of all of them being killed in battle and they dismissed the thought as being mathematically negligible.) Webster's infantry and Capt. Harris's artillery battery posted on a hill near the Benton Road shot Wood's attackers to pieces and they were forced to fall back. They regrouped at the base of the hill and renewed their assault. Harris's battery ran low on ammunition and had to withdraw, and the Confederate attack pushed Webster's men back toward the crossroads. Col. Michael Gooding's 13th Brigade (Mitchell's division) arrived on the field from Gilbert's corps and took up the fight. Wood's men withdrew and were replaced by Liddell's.
The arrival of reinforcements was a result of McCook's belated attempts to secure aid for his beleaguered corps. At 2:30 p.m. he sent an aide to Sheridan on Peters Hill requesting that he secure I Corps' right flank. McCook dispatched a second staff officer at 3 p.m. to obtain assistance from the nearest III Corps unit. The officer encountered Brig. Gen. Albin F. Schoepf, commanding the 1st Division, the III Corps' reserve. Unwilling to act on his own authority, Schoepf referred the staff officer to Gilbert, who in turn referred him to Buell's headquarters more than away. The arrival of McCook's staff officer at about 4 p.m. surprised the army commander, who had heard little battle noise and found it difficult to believe that a major Confederate attack had been under way for some time. Nevertheless, Buell ordered two brigades from Schoepf's division to support I Corps. This relatively minor commitment indicated Buell's unwillingness to accept the reported dire situation at face value.
Liddell's men fired at an unknown unit less than east of the crossroads. Calls were heard, "You are firing upon friends; for God's sake stop!" Leonidas Polk, the wing commander, decided to ride forward to see who had been the victims of the supposedly friendly fire. Polk found that he had ridden by mistake into the lines of the 22nd Indiana and was forced to bluff his way out by riding down the Union line pretending to be a Union officer and shouting at the Federal troops to cease fire. When he had escaped he shouted to Liddell and the Confederates fired hundreds of muskets in a single volley, which killed Col. Squire Keith and caused casualties of 65% in the 22nd Indiana, the highest percentage of any Federal regiment engaged at Perryville. Although Liddell wanted to pursue the assault, Polk had been unnerved by his personal contact with the enemy and halted the attack, blaming the falling darkness. The Union units moved their supplies and equipment through the endangered intersection and consolidated their lines on a chain of hills northwest. McCook's corps had been badly damaged during the day, but was not destroyed.
Bragg's attack had been a large pincer movement, forcing both flanks of McCook's corps back into a concentrated mass. This mass occurred at the Dixville Crossroads, where the Benton Road crossed the Mackville Road. If the Confederates seized this intersection they could, conceivably, get around the right wing of McCook's corps and effectively cut them off from the rest of the army. The southern jaw of the pincer began to slow at the temporary line established at the Russell House. Harris's and Lytle's brigades defended until Cleburne's and Adams's attack ground to a halt. The northern jaw had been stopped by Starkweather's defense. The remaining attacks came from north of the Mackville Road by two fresh brigades from Buckner's division: Brig. Gen. St. John R. Liddell's and Brig. Gen. Sterling A. M. Wood's.
The initial target of the assault was Col. George Webster's 34th Brigade of Jackson's division. Webster was mortally wounded during the fighting. His death marked the final senior loss for the 10th Division—the division commander, Jackson, and the other brigade commander, Terrill, had also been mortally wounded. (The previous evening, Jackson, Terrill, and Webster had been idly discussing the possibility of all of them being killed in battle and they dismissed the thought as being mathematically negligible.) Webster's infantry and Capt. Harris's artillery battery posted on a hill near the Benton Road shot Wood's attackers to pieces and they were forced to fall back. They regrouped at the base of the hill and renewed their assault. Harris's battery ran low on ammunition and had to withdraw, and the Confederate attack pushed Webster's men back toward the crossroads. Col. Michael Gooding's 13th Brigade (Mitchell's division) arrived on the field from Gilbert's corps and took up the fight. Wood's men withdrew and were replaced by Liddell's.
The arrival of reinforcements was a result of McCook's belated attempts to secure aid for his beleaguered corps. At 2:30 p.m. he sent an aide to Sheridan on Peters Hill requesting that he secure I Corps' right flank. McCook dispatched a second staff officer at 3 p.m. to obtain assistance from the nearest III Corps unit. The officer encountered Brig. Gen. Albin F. Schoepf, commanding the 1st Division, the III Corps' reserve. Unwilling to act on his own authority, Schoepf referred the staff officer to Gilbert, who in turn referred him to Buell's headquarters more than away. The arrival of McCook's staff officer at about 4 p.m. surprised the army commander, who had heard little battle noise and found it difficult to believe that a major Confederate attack had been under way for some time. Nevertheless, Buell ordered two brigades from Schoepf's division to support I Corps. This relatively minor commitment indicated Buell's unwillingness to accept the reported dire situation at face value.
Liddell's men fired at an unknown unit less than east of the crossroads. Calls were heard, "You are firing upon friends; for God's sake stop!" Leonidas Polk, the wing commander, decided to ride forward to see who had been the victims of the supposedly friendly fire. Polk found that he had ridden by mistake into the lines of the 22nd Indiana and was forced to bluff his way out by riding down the Union line pretending to be a Union officer and shouting at the Federal troops to cease fire. When he had escaped he shouted to Liddell and the Confederates fired hundreds of muskets in a single volley, which killed Col. Squire Keith and caused casualties of 65% in the 22nd Indiana, the highest percentage of any Federal regiment engaged at Perryville. Although Liddell wanted to pursue the assault, Polk had been unnerved by his personal contact with the enemy and halted the attack, blaming the falling darkness. The Union units moved their supplies and equipment through the endangered intersection and consolidated their lines on a chain of hills northwest. McCook's corps had been badly damaged during the day, but was not destroyed.
Aftermath
Casualties
Union casualties totaled 4,276 (894 killed, 2,911 wounded, 471 captured or missing). Confederate casualties were 3,401 (532 killed, 2,641 wounded, 228 captured or missing). In all, casualties totaled one-fifth of those involved.Reactions and effects
 Braxton Bragg had arguably won a tactical victory, having fought aggressively and pushed his opponent back for over a mile. But his precarious strategic situation became clear to him as he found out about the III Corps advance on the Springfield Pike, and when he learned late in the day of the II Corps' presence on the Lebanon Pike. At 9 p.m. he met with his subordinates at the Crawford House and gave orders to begin a withdrawal after midnight, leaving a picket line in place while his army joined up with Kirby Smith's. As the army marched toward Harrodsburg, they were forced to leave 900 wounded men behind.
Bragg united his forces with Smith's at Harrodsburg, and the Union and Confederate armies, now of comparable size, skirmished with one another over the next week or so, but neither attacked. Bragg soon realized that the new infantry recruits he had sought from Kentucky would not be forthcoming, although many Kentuckians were willing to join the Confederate cavalry. Furthermore, Bragg concluded that he lacked the logistical support he needed to remain in the state. He made his way southeast to
Braxton Bragg had arguably won a tactical victory, having fought aggressively and pushed his opponent back for over a mile. But his precarious strategic situation became clear to him as he found out about the III Corps advance on the Springfield Pike, and when he learned late in the day of the II Corps' presence on the Lebanon Pike. At 9 p.m. he met with his subordinates at the Crawford House and gave orders to begin a withdrawal after midnight, leaving a picket line in place while his army joined up with Kirby Smith's. As the army marched toward Harrodsburg, they were forced to leave 900 wounded men behind.
Bragg united his forces with Smith's at Harrodsburg, and the Union and Confederate armies, now of comparable size, skirmished with one another over the next week or so, but neither attacked. Bragg soon realized that the new infantry recruits he had sought from Kentucky would not be forthcoming, although many Kentuckians were willing to join the Confederate cavalry. Furthermore, Bragg concluded that he lacked the logistical support he needed to remain in the state. He made his way southeast to Knoxville, Tennessee
Knoxville is a city in and the county seat of Knox County in the U.S. state of Tennessee. As of the 2020 United States census, Knoxville's population was 190,740, making it the largest city in the East Tennessee Grand Division and the stat ...
through the Cumberland Gap
The Cumberland Gap is a pass through the long ridge of the Cumberland Mountains, within the Appalachian Mountains, near the junction of the U.S. states of Kentucky, Virginia, and Tennessee. It is famous in American colonial history for its r ...
. Bragg was quickly called to the Confederate capital, Richmond, Virginia
(Thus do we reach the stars)
, image_map =
, mapsize = 250 px
, map_caption = Location within Virginia
, pushpin_map = Virginia#USA
, pushpin_label = Richmond
, pushpin_m ...
, to explain to Jefferson Davis
Jefferson F. Davis (June 3, 1808December 6, 1889) was an American politician who served as the president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the United States Senate and the House of Representatives as ...
the charges brought by his officers about how he had conducted his campaign, who were demanding that he be replaced as head of the army. Although Davis decided to leave the general in command, Bragg's relationship with his subordinates would be severely damaged. Upon rejoining the army, he ordered a movement to Murfreesboro, Tennessee
Murfreesboro is a city in and county seat of Rutherford County, Tennessee, United States. The population was 152,769 according to the 2020 census, up from 108,755 residents certified in 2010. Murfreesboro is located in the Nashville metropol ...
.
Buell conducted a half-hearted pursuit of Bragg and returned to Nashville
Nashville is the capital city of the U.S. state of Tennessee and the seat of Davidson County. With a population of 689,447 at the 2020 U.S. census, Nashville is the most populous city in the state, 21st most-populous city in the U.S., and th ...
, rather than pushing on to East Tennessee as the Lincoln administration had wished. Pent-up dissatisfaction with Buell's performance resulted in a reorganization of the Western departments. On October 24, a new Department of the Cumberland was formed under Maj. Gen. William S. Rosecrans, and Buell's Army of the Ohio was assigned to it, redesignated the XIV Corps 14 Corps, 14th Corps, Fourteenth Corps, or XIV Corps may refer to:
* XIV Corps (Grande Armée), a unit of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
* XIV Corps (German Empire), a unit of the Imperial German Army prior to and during World ...
. (After the Battle of Stones River
The Battle of Stones River, also known as the Second Battle of Murfreesboro, was a battle fought from December 31, 1862, to January 2, 1863, in Middle Tennessee, as the culmination of the Stones River Campaign in the Western Theater of the Am ...
at Murfreesboro in late December, another strategic defeat for Braxton Bragg, it would receive its more familiar name, the Army of the Cumberland
The Army of the Cumberland was one of the principal Union armies in the Western Theater during the American Civil War. It was originally known as the Army of the Ohio.
History
The origin of the Army of the Cumberland dates back to the creation ...
.) Buell was ordered to appear before a commission investigating his conduct during the campaign. He remained in military limbo for a year and a half, his career essentially ruined. He resigned from the service in May 1864.
Subsequent events
Following the Battle of Perryville, the Union maintained control of Kentucky for the rest of the war. HistorianJames M. McPherson
James Munro McPherson (born October 11, 1936) is an American Civil War historian, and is the George Henry Davis '86 Professor Emeritus of United States History at Princeton University. He received the 1989 Pulitzer Prize for '' Battle Cry ...
considers Perryville to be part of a great turning point of the war, "when battles at Antietam
The Battle of Antietam (), or Battle of Sharpsburg particularly in the Southern United States, was a battle of the American Civil War fought on September 17, 1862, between Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia and Union G ...
and Perryville threw back Confederate invasions, forestalled European mediation and recognition of the Confederacy, perhaps prevented a Democratic victory in the northern elections of 1862 that might have inhibited the government's ability to carry on the war, and set the stage for the Emancipation Proclamation
The Emancipation Proclamation, officially Proclamation 95, was a presidential proclamation and executive order issued by United States President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863, during the American Civil War, Civil War. The Proclamation c ...
which enlarged the scope and purpose of the conflict."
Only two days after the battle, the drought suddenly ended as a cold front pushed through the region and brought rain and cool temperatures across Kentucky.
Battlefield preservation
Portions of the battlefield of Perryville are preserved by the state of Kentucky asPerryville Battlefield State Historic Site
Perryville Battlefield State Historic Site is a park near Perryville in Boyle County, Kentucky. The park continues to expand with purchases of parcels by the Office of Kentucky Nature Preserves' Kentucky Heritage Land Conservation Fund and the ...
. Also the Perryville Historic District covering downtown Perryville includes buildings which had roles in the battle, including the Elmwood mansion which was pressed into use as a field hospital during the battle. The American Battlefield Trust
The American Battlefield Trust is a charitable organization (501(c)(3)) whose primary focus is in the preservation of battlefields of the American Civil War, the Revolutionary War and the War of 1812 through acquisition of battlefield land. T ...
, its members and the Office of Kentucky Nature Preserves’ Kentucky Heritage Land Conservation Fund have saved 1,202 acres at the Perryville Battlefield through late 2021.Accessed Jan. 3, 2018 and November 24, 2021.
See also
* List of American Civil War battles * List of battles fought in Kentucky * List of costliest American Civil War land battles *Troop engagements of the American Civil War, 1862
The following is a list of engagements that took place in 1862 during the American Civil War. During the summer and early spring of the year, Union forces gained several successes over the Confederacy, seizing control of Missouri, northern Arkans ...
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* Breiner, Thomas L"The Battle of Perryville"
Accessed January 1, 2008. * Breiner, Thomas L
Accessed January 1, 2008. * Cameron, Robert S
''Staff Ride Handbook for the Battle of Perryville, 8 October 1862''
Fort Leavenworth, KS: Combat Studies Institute Press, 2005. . * Eicher, David J. ''The Longest Night: A Military History of the Civil War''. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2001. . * Esposito, Vincent J. ''West Point Atlas of American Wars''. New York: Frederick A. Praeger, 1959. . The collection of maps (without explanatory text) is available online at th
West Point website
* Hafendorfer, Kenneth A. ''Perryville: Battle for Kentucky''. Louisville, KY: K. H. Press, 1991. . * Kennedy, Frances H., ed. ''The Civil War Battlefield Guide''. 2nd ed. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Co., 1998. . * McDonough, James Lee. ''War in Kentucky: From Shiloh to Perryville''. Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 1994. . * McPherson, James M. '' Battle Cry of Freedom: The Civil War Era''. Oxford History of the United States. New York: Oxford University Press, 1988. . * Noe, Kenneth W. ''Perryville: This Grand Havoc of Battle''. Lexington: University Press of Kentucky, 2001. . * Prokopowicz, Gerald J. ''All for the Regiment: The Army of the Ohio, 1861–1862''. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 2001. . * Street, James Jr., and the Editors of Time-Life Books. ''The Struggle for Tennessee: Tupelo to Stones River''. Alexandria, VA: Time-Life Books, 1985. . * Watkins, Sam
''Co. Aytch Maury Grays, First Tennessee Regiment or, A Side Show of the Big Show''
Cumberland Presbyterian Publishing House, 1882. . * Woodworth, Steven E. ''Jefferson Davis and His Generals: The Failure of Confederate Command in the West''. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas, 1990. .
National Park Service battle description
Further reading
* Brown, Kent Masterson. ''The Civil War in Kentucky: Battle for the Bluegrass State''. Campbell, CA: Savas Publishing Company, 2000. . * Broadwater, Robert P. ''The Battle of Perryville, 1862: Culmination of the Failed Kentucky Campaign''. Jefferson, NC: McFarland & Company, 2005. . * Harrison, Lowell Hayes. ''The Civil War in Kentucky''. Lexington: University Press of Kentucky, 2010. . * Harrison, Lowell H. "The Civil War in Kentucky: Some Persistent Questions". ''The Register of the Kentucky Historical Society'' (1978): 1–21. . * * McWhiney, Grady. "Controversy in Kentucky: Braxton Bragg's Campaign of 1862". ''Civil War History'' (1960) 6 #1 pp. 5–42. * Wooster, Ralph A. "Confederate Success at Perryville". ''The Register of the Kentucky Historical Society'' (1961) 59 #4 pp. 318–323 . (University Press of Kentucky, 2001.) * Gillum, Jamie. "Understanding the Battle of Perryville: The Discovery of the Hafley Cabins and its Impact on Historiography of the Battlefield". Jamie Gillum, 2022. .Primary sources
* Johnson, Robert Underwood, and Clarence C. Buel, eds''Battles and Leaders of the Civil War''
4 vols. New York: Century Co., 1884–1888. : ** Buell, Don Carlos
"East Tennessee and the Campaign of Perryville"
** Gilbert, Charles C
"On the Field of Perryville"
** Wheeler, Joseph
"Bragg's Invasion of Kentucky"
** Wright, J. Montgomery
"Notes of a Staff Officer at Perryville"
* Steely, Will Frank, and Orville W. Taylor. "Bragg's Kentucky Campaign: A Confederate Soldier's Account". ''The Register of the Kentucky Historical Society'' (1959): 49–55. . * U.S. War Department
''The War of the Rebellion: a Compilation of the Official Records of the Union and Confederate Armies''. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1880–1901.
External links
Battle of Perryville
photos, history articles, and battlefield news ( Civil War Trust)
The Battle of Perryville, Kentucky
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20110716084401/http://www.civilwaralbum.com/misc/perry1.htm Modern Perryville photos
Perryville Order of Battle
{{DEFAULTSORT:Perryville 1862 in Kentucky 1862 in the American Civil War Perryville Perryville Boyle County, Kentucky Perryville October 1862 events Perryville