Battle of Megiddo (1918) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of Megiddo ( tr, ), also known in Turkish as the ("Rout of Nablus") or the ("Breakthrough at Nablus"), was fought between 19 and 25 September 1918, on the
 These various deceptions could not have been successful without the Entente forces' undisputed air supremacy west of the Jordan. The squadrons of the
These various deceptions could not have been successful without the Entente forces' undisputed air supremacy west of the Jordan. The squadrons of the
 At 1:00 am on 19 September, the RAF Palestine Brigade's single Handley Page O/400 heavy bomber dropped its full load of sixteen bombs on the main telephone exchange and railway station in Al-Afuleh. This cut communications between Liman's headquarters at Nazareth and Ottoman Seventh and Eighth Armies for the following vital two days, dislocating the Ottoman command. DH.9s of No. 144 Squadron also bombed El Afule telephone exchange and railway station, Messudieh railway junction and the Ottoman Seventh Army headquarters and telephone exchange at Nablus.
At 1:00 am on 19 September, the RAF Palestine Brigade's single Handley Page O/400 heavy bomber dropped its full load of sixteen bombs on the main telephone exchange and railway station in Al-Afuleh. This cut communications between Liman's headquarters at Nazareth and Ottoman Seventh and Eighth Armies for the following vital two days, dislocating the Ottoman command. DH.9s of No. 144 Squadron also bombed El Afule telephone exchange and railway station, Messudieh railway junction and the Ottoman Seventh Army headquarters and telephone exchange at Nablus.
 During the early hours of 20 September 1918, the Desert Mounted Corps secured the defiles of the Carmel Range. The 4th Mounted Division passed through these to capture Afulah and Beisan, complete with the bulk of two depot regiments. A brigade of the 5th Mounted Division attacked Nazareth, where Liman von Sanders's HQ was situated, although Liman himself escaped. In the late afternoon a brigade from the Australian Mounted Division occupied Jenin, capturing many retreating Ottomans. The 15th Imperial Service Cavalry Brigade, of the 5th Mounted Division, captured the port of Haifa on 23 September.Liddell Hart, p. 438
Once nothing stood between Allenby's forces and Mustafa Kemal's Seventh Army in Nablus, Kemal decided that he lacked sufficient men to fight the British forces. With the railway blocked, the Seventh Army's only escape route lay to the east, along the Nablus-Beisan road that led down the Wadi Fara into the Jordan valley.
During the early hours of 20 September 1918, the Desert Mounted Corps secured the defiles of the Carmel Range. The 4th Mounted Division passed through these to capture Afulah and Beisan, complete with the bulk of two depot regiments. A brigade of the 5th Mounted Division attacked Nazareth, where Liman von Sanders's HQ was situated, although Liman himself escaped. In the late afternoon a brigade from the Australian Mounted Division occupied Jenin, capturing many retreating Ottomans. The 15th Imperial Service Cavalry Brigade, of the 5th Mounted Division, captured the port of Haifa on 23 September.Liddell Hart, p. 438
Once nothing stood between Allenby's forces and Mustafa Kemal's Seventh Army in Nablus, Kemal decided that he lacked sufficient men to fight the British forces. With the railway blocked, the Seventh Army's only escape route lay to the east, along the Nablus-Beisan road that led down the Wadi Fara into the Jordan valley.
 On the night of 20–21 September the Seventh Army began to evacuate Nablus. By this time it was the last formed Ottoman army west of the Jordan and although there was a chance that Chetwode's XX Corps might cut off their retreat, its advance had been slowed by Ottoman rearguards. On 21 September, the Seventh Army was spotted by aircraft in a defile west of the river. The RAF proceeded to bomb the retreating army and destroyed the entire column. Waves of bombing and strafing aircraft passed over the column every three minutes and although the operation had been intended to last for five hours, the Seventh Army was routed in 60 minutes. The wreckage of the destroyed column stretched over . British cavalry later found 87 guns, 55 motor-lorries, 4 motor-cars, 75 carts, 837 four-wheeled wagons, and scores of water-carts and field-kitchens destroyed or abandoned on the road. Many Ottoman soldiers were killed and the survivors were scattered and leaderless. Lawrence later wrote that "the RAF lost four killed. The Turks lost a corps."
According to Chauvel's biographer, Allenby's plan for the Battle of Megiddo was as "brilliant in execution as it had been in conception; it had no parallel in France or on any other front, but rather looked forward in principle and even in detail to the Blitzkrieg of 1939." Over the next four days, the 4th Cavalry Division and Australian Mounted Division rounded up large numbers of demoralised and disorganised Ottoman troops in the
On the night of 20–21 September the Seventh Army began to evacuate Nablus. By this time it was the last formed Ottoman army west of the Jordan and although there was a chance that Chetwode's XX Corps might cut off their retreat, its advance had been slowed by Ottoman rearguards. On 21 September, the Seventh Army was spotted by aircraft in a defile west of the river. The RAF proceeded to bomb the retreating army and destroyed the entire column. Waves of bombing and strafing aircraft passed over the column every three minutes and although the operation had been intended to last for five hours, the Seventh Army was routed in 60 minutes. The wreckage of the destroyed column stretched over . British cavalry later found 87 guns, 55 motor-lorries, 4 motor-cars, 75 carts, 837 four-wheeled wagons, and scores of water-carts and field-kitchens destroyed or abandoned on the road. Many Ottoman soldiers were killed and the survivors were scattered and leaderless. Lawrence later wrote that "the RAF lost four killed. The Turks lost a corps."
According to Chauvel's biographer, Allenby's plan for the Battle of Megiddo was as "brilliant in execution as it had been in conception; it had no parallel in France or on any other front, but rather looked forward in principle and even in detail to the Blitzkrieg of 1939." Over the next four days, the 4th Cavalry Division and Australian Mounted Division rounded up large numbers of demoralised and disorganised Ottoman troops in the
Plain of Sharon
The Sharon plain ( ''HaSharon Arabic: سهل شارون Sahel Sharon'') is the central section of the Israeli coastal plain. The plain lies between the Mediterranean Sea to the west and the Samarian Hills, to the east. It stretches from Nahal T ...
, in front of Tulkarm
Tulkarm, Tulkarem or Tull Keram ( ar, طولكرم, ''Ṭūlkarm'') is a Palestinian city in the West Bank, located in the Tulkarm Governorate of the State of Palestine. The Israeli city of Netanya is to the west, and the Palestinian cities o ...
, Tabsor and Arara in the Judean Hills
The Judaean Mountains, or Judaean Hills ( he, הרי יהודה, translit=Harei Yehuda) or the Hebron Mountains ( ar, تلال الخليل, translit=Tilal al-Khalīl, links=, lit=Hebron Mountains), is a mountain range in Palestine and Israel wh ...
as well as on the Esdralon Plain at Nazareth, Afulah, Beisan, Jenin and Samakh. Its name, which has been described as "perhaps misleading" since very limited fighting took place near Tel Megiddo
Tel Megiddo ( he, תל מגידו; ar, مجیدو, Tell el- Mutesellim, ''lit.'' "Mound of the Governor"; gr, Μεγιδδώ, Megiddo) is the site of the ancient city of Megiddo, the remains of which form a tell (archaeological mound), situa ...
, was chosen by Allenby for its biblical and symbolic resonance.
The battle was the final Allied offensive of the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. The contending forces were the Allied Egyptian Expeditionary Force
The Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) was a British Empire military formation, formed on 10 March 1916 under the command of General Archibald Murray from the Mediterranean Expeditionary Force and the Force in Egypt (1914–15), at the beginning ...
, of three corps
Corps (; plural ''corps'' ; from French , from the Latin "body") is a term used for several different kinds of organization. A military innovation by Napoleon I, the formation was first named as such in 1805. The size of a corps varies great ...
including one of mounted troops, and the Ottoman Yildirim Army Group
The Yildirim Army Group or Thunderbolt Army Group of the Ottoman Empire ( Turkish: ''Yıldırım Ordular Grubu'') or Army Group F (German: ''Heeresgruppe F'') was an Army Group of the Ottoman Army during World War I. While being an Ottoman unit, ...
which numbered three armies
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
, each the strength of barely an Allied corps. The series of battles took place in what was then the central and northern parts of Ottoman Palestine and parts of present-day Israel, Syria and Jordan. After forces of the Arab Revolt
The Arab Revolt ( ar, الثورة العربية, ) or the Great Arab Revolt ( ar, الثورة العربية الكبرى, ) was a military uprising of Arab forces against the Ottoman Empire in the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I. On ...
attacked the Ottoman lines of communication, distracting the Ottomans, British and Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
infantry divisions attacked and broke through the Ottoman defensive lines in the sector adjacent to the coast in the set-piece Battle of Sharon
The Battle of Sharon fought between 19 and 25 September 1918, began the set piece Battle of Megiddo (1918), Battle of Megiddo half a day before the Battle of Nablus (1918), Battle of Nablus, in which large formations engaged and responded to mov ...
. The Desert Mounted Corps
The Desert Mounted Corps was an army corps of the British Army during the First World War, of three mounted divisions renamed in August 1917 by General Edmund Allenby, from Desert Column. These divisions which served in the Sinai and Pales ...
rode through the breach and almost encircled the Ottoman Seventh
Seventh is the ordinal form of the number seven.
Seventh may refer to:
* Seventh Amendment to the United States Constitution
* A fraction (mathematics), , equal to one of seven equal parts
Film and television
*"The Seventh", a second-season e ...
and Eighth armies still fighting in the Judean Hills. The subsidiary Battle of Nablus was fought virtually simultaneously in the Judean Hills in front of Nablus and at crossings of the Jordan River. The Ottoman Fourth Army was subsequently attacked in the Hills of Moab at Es Salt
Al-Salt ( ar, السلط ''As-Salt'') is an ancient salt trading city and administrative centre in west-central Jordan. It is on the old main highway leading from Amman to Jerusalem. Situated in the Balqa (region), Balqa highland, about 790–1, ...
and Amman.
These battles resulted in many tens of thousands of prisoners and many miles of territory being captured by the Allies. Following the battles, Daraa
Daraa ( ar, دَرْعَا, Darʿā, Levantine Arabic: , also Darʿā, Dara’a, Deraa, Dera'a, Dera, Derʿā and Edrei; means "''fortress''", compare Dura-Europos) is a city in southwestern Syria, located about north of the border with Jord ...
was captured on 27 September, Damascus on 1 October and operations at Haritan, north of Aleppo, were still in progress when the Armistice of Mudros
Concluded on 30 October 1918 and taking effect at noon the next day, the Armistice of Mudros ( tr, Mondros Mütarekesi) ended hostilities in the Middle Eastern theatre between the Ottoman Empire and the Allies of World War I. It was signed by th ...
was signed ending hostilities between the Allies and Ottomans.
The operations of General Edmund Allenby
Field Marshal Edmund Henry Hynman Allenby, 1st Viscount Allenby, (23 April 1861 – 14 May 1936) was a senior British Army officer and Imperial Governor. He fought in the Second Boer War and also in the First World War, in which he led th ...
, the British commander of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force, achieved decisive results at comparatively little cost, in contrast to many offensives during the First World War. Allenby achieved this through the use of creeping barrages to cover set-piece infantry attacks to break a state of trench warfare and then use his mobile forces ( cavalry, armoured cars and aircraft) to encircle the Ottoman armies' positions in the Judean Hills, cutting off their lines of retreat. The irregular forces of the Arab Revolt also played a part in this victory.
Background
The ancient fortress ofMegiddo Megiddo may refer to:
Places and sites in Israel
* Tel Megiddo, site of an ancient city in Israel's Jezreel valley
* Megiddo Airport, a domestic airport in Israel
* Megiddo church (Israel)
* Megiddo, Israel, a kibbutz in Israel
* Megiddo Junctio ...
stands on Tell el-Mutesellim (Tel Megiddo
Tel Megiddo ( he, תל מגידו; ar, مجیدو, Tell el- Mutesellim, ''lit.'' "Mound of the Governor"; gr, Μεγιδδώ, Megiddo) is the site of the ancient city of Megiddo, the remains of which form a tell (archaeological mound), situa ...
), at the mouth of the Musmus Pass near al-Lajjun, controlling the routes to the north and the interior by dominating the Plain of Armageddon
According to the Book of Revelation in the New Testament of the Christian Bible, Armageddon (, from grc, Ἁρμαγεδών ''Harmagedōn'', Late Latin: , from Hebrew: ''Har Məgīddō'') is the prophesied location of a gathering of armies ...
or of Megiddo. Across this plain several armies, from the ancient Egyptians to the French under Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
, had fought on their way towards Nazareth in the Galilean Hills. By 1918 this plain, known as the Plain of Esdraelon (the Jezreel Valley
The Jezreel Valley (from the he, עמק יזרעאל, translit. ''ʿĒmeq Yīzrəʿēʿl''), or Marj Ibn Amir ( ar, مرج ابن عامر), also known as the Valley of Megiddo, is a large fertile plain and inland valley in the Northern Distr ...
in Israeli terms) was still strategically important as it linked the Jordan Valley
The Jordan Valley ( ar, غور الأردن, ''Ghor al-Urdun''; he, עֵמֶק הַיַרְדֵּן, ''Emek HaYarden'') forms part of the larger Jordan Rift Valley. Unlike most other river valleys, the term "Jordan Valley" often applies just to ...
and the Plain of Sharon
The Sharon plain ( ''HaSharon Arabic: سهل شارون Sahel Sharon'') is the central section of the Israeli coastal plain. The plain lies between the Mediterranean Sea to the west and the Samarian Hills, to the east. It stretches from Nahal T ...
behind the Ottoman front line, and together, these three valleys formed a semicircle round the main Ottoman positions in the Judean Hills held by their Seventh and Eighth armies.
Allied situation
TheEntente Powers
The Triple Entente (from French '' entente'' meaning "friendship, understanding, agreement") describes the informal understanding between the Russian Empire, the French Third Republic, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland as well a ...
had declared war on the Ottoman Empire in November 1914. In early 1915 and in August 1916 the Ottomans, with German commanders, aid and encouragement, had attacked the Suez Canal, a vital link between Britain and India, Australia and New Zealand. Under General Archibald Murray
General Sir Archibald James Murray, (23 April 1860 – 21 January 1945) was a British Army officer who served in the Second Boer War and the First World War. He was Chief of Staff to the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) in August 1914 but ...
, the British Egyptian Expeditionary Force
The Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) was a British Empire military formation, formed on 10 March 1916 under the command of General Archibald Murray from the Mediterranean Expeditionary Force and the Force in Egypt (1914–15), at the beginning ...
(EEF) stopped the Ottoman army at the Battle of Romani
The Battle of Romani was the last ground attack of the Central Powers on the Suez Canal at the beginning of the Sinai and Palestine campaign during the First World War. The battle was fought between 3 and 5 August 1916 near the Egyptian town ...
and drove them back to Magdhaba and across the Sinai to Rafa to reoccupy Egyptian territory and secure the safety of the Suez Canal. Having constructed a railway and water pipeline across the desert, Murray then attacked southern Palestine. In the First Battle of Gaza
The First Battle of Gaza was fought on 26 March 1917 during the first attempt by the Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF), which was a British Empire military formation, formed on 10 March 1916 under the command of General Archibald Murray from th ...
and the Second Battle of Gaza
The Second Battle of Gaza was fought on 17-19 April 1917, following the defeat of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) at the First Battle of Gaza in March, during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of the First World War. Gaza was defended by ...
in March and April 1917, the British attacks were defeated.
In 1916, the Arab Revolt
The Arab Revolt ( ar, الثورة العربية, ) or the Great Arab Revolt ( ar, الثورة العربية الكبرى, ) was a military uprising of Arab forces against the Ottoman Empire in the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I. On ...
against Ottoman rule had broken out in the Hejaz, led by Hussein bin Ali, Sharif of Mecca
Hussein bin Ali al-Hashimi ( ar, الحسين بن علي الهاشمي, al-Ḥusayn bin ‘Alī al-Hāshimī; 1 May 18544 June 1931) was an Arab leader from the Banu Hashim clan who was the Sharif and Emir of Mecca from 1908 and, after procl ...
. Although the Ottomans defended Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
, at the end of the Hejaz Railway against them, part of the Sherifian Army, led by Hussein's son, the Emir Feisal, and British liaison officer T. E. Lawrence, extended the revolt northwards. Finally, Lawrence and bedouin tribesmen won the Battle of Aqaba
The Battle of Aqaba (6 July 1917) was fought for the Red Sea port of Aqaba (now in Jordan) during the Arab Revolt of World War I. The attacking forces, led by Sherif Nasir and Auda abu Tayi and advised by T. E. Lawrence ("Lawrence of Arabia"), ...
in July 1917. The capture of the port of Aqaba
Aqaba (, also ; ar, العقبة, al-ʿAqaba, al-ʿAgaba, ) is the only coastal city in Jordan and the largest and most populous city on the Gulf of Aqaba. Situated in southernmost Jordan, Aqaba is the administrative centre of the Aqaba Govern ...
allowed the Allies to supply Feisal's forces and deprived the Ottomans of a position behind the right flank of the EEF.
General Allenby had been appointed to succeed Murray in command of the EEF, and was encouraged to renew the offensive. After receiving reinforcements, he broke through the Ottoman defences in the Third Battle of Gaza
The Third Battle of Gaza was fought on the night of 1–2 November 1917 between British and Ottoman forces during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of World War I and came after the British Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) victory at the ...
and defeated an Ottoman attempt to make a stand to the north at the Battle of Mughar Ridge
The Battle of Mughar Ridge, officially known by the British as the action of El Mughar, took place on 13 November 1917 during the Pursuit phase of the Southern Palestine Offensive of the Sinai and Palestine Campaign in the First World War. Figh ...
. Despite Ottoman counter-attacks, the EEF captured Jerusalem in the second week in December 1917.
After a pause of several weeks caused by bad weather and the need to repair his lines of communication, Allenby advanced eastward to capture Jericho in February 1918. However, in March, the Germans launched their spring offensive on the Western Front, intending to defeat the Allied armies in France and Belgium. Allenby was ordered to send reinforcements (two complete divisions, another 24 infantry battalion
A battalion is a military unit, typically consisting of 300 to 1,200 soldiers commanded by a lieutenant colonel, and subdivided into a number of companies (usually each commanded by a major or a captain). In some countries, battalions a ...
s from other divisions and nine dismounted yeomanry
Yeomanry is a designation used by a number of units or sub-units of the British Army Reserve, descended from volunteer cavalry regiments. Today, Yeomanry units serve in a variety of different military roles.
History
Origins
In the 1790s, f ...
regiment
A regiment is a military unit. Its role and size varies markedly, depending on the country, service and/or a specialisation.
In Medieval Europe, the term "regiment" denoted any large body of front-line soldiers, recruited or conscript ...
s) to the Western Front. Allenby's tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engi ...
force was also returned to France. In total approximately 60,000 officers and men were transferred to the Western Front in 1918.
However, Allenby maintained pressure on the Ottoman armies by twice sending mounted and infantry divisions across the Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
. The first attack briefly cut the Hejaz Railway near Amman before the attackers retreated. In the second attack, Allenby's troops captured Es Salt
Al-Salt ( ar, السلط ''As-Salt'') is an ancient salt trading city and administrative centre in west-central Jordan. It is on the old main highway leading from Amman to Jerusalem. Situated in the Balqa (region), Balqa highland, about 790–1, ...
on the road to Amman, but fell back when their communications were threatened. Despite these failures, Allenby had established two bridgeheads across the Jordan north of the Dead Sea which were retained during the ensuing occupation of the southern Jordan Valley
The Jordan Valley ( ar, غور الأردن, ''Ghor al-Urdun''; he, עֵמֶק הַיַרְדֵּן, ''Emek HaYarden'') forms part of the larger Jordan Rift Valley. Unlike most other river valleys, the term "Jordan Valley" often applies just to ...
.
Ottoman situation
At the same time (effectively from 8 March 1918), the Ottoman command changed.Erickson 2001, p. 194 The highest level Ottoman headquarters in Palestine was the Yıldırım Army Group. The army group had originally been formed to recaptureBaghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
which had been captured by the British in March 1917. Instead, it had been diverted to Palestine where the British were close to capturing Jerusalem. The army group's commander was the German general, Erich von Falkenhayn
General Erich Georg Sebastian Anton von Falkenhayn (11 September 1861 – 8 April 1922) was the second Chief of the German General Staff of the First World War from September 1914 until 29 August 1916. He was removed on 29 August 1916 after t ...
, who wished to continue a policy of " yielding defence" rather than hold all positions at all costs. He was also prepared to retreat to shorten his lines of communication and reduce the need for static garrisons. However, he was unpopular among Ottoman officers, mainly because he relied almost exclusively on German rather than Ottoman staff officers, and was blamed for the defeats at Gaza and Jerusalem. He was replaced by another German General, Otto Liman von Sanders
Otto Viktor Karl Liman von Sanders (; 17 February 1855 – 22 August 1929) was an Imperial German Army general who served as a military adviser to the Ottoman Army during the First World War. In 1918 he commanded an Ottoman army during the Sin ...
, who had commanded the Ottoman defence during the Gallipoli Campaign. Liman reasoned that continued retreat in Palestine would demoralise the troops, ruin their draught animal
A working animal is an animal, usually domesticated, that is kept by humans and trained to perform tasks instead of being slaughtered to harvest animal products. Some are used for their physical strength (e.g. oxen and draft horses) or for t ...
s, encourage the Arab Revolt to spread further north into the Ottoman rear areas and also lead to all the Ottoman forces to the south in the Hejaz being finally isolated.Liddell Hart, p. 437 His forces halted their retreat and dug in to resist the British, even reoccupying some ground near the Jordan as Allenby's two raids across the Jordan were repulsed.
Until late September 1918, the strategic situation of the Ottoman Empire appeared to be better than that of the other Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
. Their forces in Mesopotamia were holding their ground, while in the Caucasus they had captured Armenia, Azerbaijan and much of Georgia in an advance towards the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
. Liman von Sanders was expected to repeat his defence of Gallipoli and defeat the British invasion in Palestine.
However, some other commanders were worried about an assault on their extended front in Palestine. They wished to pull their troops back, so an attack would have to cross undefended ground and lose any tactical surprise. However, Liman would have had to abandon what seemed to be good defences and he decided that it was too late to pull back.
Allied reorganisation
During the summer of 1918, Allenby's forces were built back up to full strength. Two British Indian Army cavalry divisions, the 4th Cavalry Division and 5th Cavalry Division, arrived from the Western Front and were reorganised to include one Britishyeomanry
Yeomanry is a designation used by a number of units or sub-units of the British Army Reserve, descended from volunteer cavalry regiments. Today, Yeomanry units serve in a variety of different military roles.
History
Origins
In the 1790s, f ...
regiment in five of their six brigades. Two Indian infantry divisions, the 3rd (Lahore) Division
The 3rd (Lahore) Division was an infantry division of the British Indian Army, first organised in 1852. It saw service during World War I as part of the Indian Corps in France before being moved to the Middle East where it fought against troops ...
and the 7th (Meerut) Division, were transferred from the Mesopotamian Campaign
The Mesopotamian campaign was a campaign in the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I fought between the Allies represented by the British Empire, troops from Britain, Australia and the vast majority from British India, against the Central Po ...
to replace two divisions which had been sent to the Western Front.Perrett 1999, p. 24 Four of Allenby's infantry divisions (the 10th
10 (ten) is the even natural number following 9 and preceding 11. Ten is the base of the decimal numeral system, by far the most common system of denoting numbers in both spoken and written language. It is the first double-digit number. The re ...
, 53rd, 60th and 75th) were reformed on the pattern of British Indian Army, with three Indian and one British infantry battalion in each brigade except one brigade in the 53rd Division which had one British, one South African and two Indian battalions. The remaining British infantry division, the 54th (East Anglian) Division, retained its all-British composition, although the brigade-sized Détachement Français de Palestine et de Syrie was attached to the division.
There was a comparative lull in activity while Allenby's divisions were reorganised and retrained, but some local attacks were made, especially in the Judean Hills. On 19 July, the Ottomans and Germans mounted a brief attack at Abu Tellul near the Jordan, but were defeated by Australian Light Horse
Australian Light Horse were mounted troops with characteristics of both cavalry and mounted infantry, who served in the Second Boer War and World War I. During the inter-war years, a number of regiments were raised as part of Australia's part-t ...
regiments with heavy casualties to the German 11th Reserve '' Jäger'' battalion, which was subsequently withdrawn from Palestine.
Arab Northern Army
As Allenby's reorganisation proceeded, the Arab Northern Army (part of the Arab Revolt) was operating east of the Jordan under the overall leadership of the Emir Feisal. Feisal's headquarters were at Aba el Lissan, about south-west of the Ottoman position atMa'an
Ma'an ( ar, مَعان, Maʿān) is a city in southern Jordan, southwest of the capital Amman. It serves as the capital of the Ma'an Governorate. Its population was approximately 41,055 in 2015. Civilizations with the name of Ma'an have existe ...
, and his army received support from the British through the port of Aqaba. Assistance to Feisal included liaison officers, detachments of armoured cars, Indian machine gunners and a French Algerian mountain battery,Wavell 1968 pp. 199–200 2,000 camels from three disbanded battalions of the Imperial Camel Corps Brigade
The Imperial Camel Corps Brigade (ICCB) was a camel-mounted infantry brigade that the British Empire raised in December 1916 during the First World War for service in the Middle East.
From a small beginning the unit eventually grew to a bri ...
, weapons, ammunition and above all, money (almost always in coin). In mid-1916, this had started as a monthly subsidy of £30,000. By the time Allenby launched his Megiddo offensive, it had grown to £220,000 a month.
The 2,000 regular soldiers of the Arab Northern Army maintained a blockade of the Ottoman garrison at Ma'an after an unsuccessful attack at Khirbet es-Samra earlier in the year. They were commanded by Jaafar Pasha
Ja'far Pasha al-Askari ( ar, جعفر العسكري; 15 September 1885 – 29 October 1936) served twice as prime minister of Iraq: from 22 November 1923 to 3 August 1924; and from 21 November 1926 to 31 December 1927.
Al-Askari served in th ...
, formerly an Ottoman officer who had been sent to lead a rebellion against the British by the Senussi in Egypt, but had joined the Arab Revolt after being captured. Most of these regulars were former Arab conscripts in the Ottoman Army who had deserted or, like Jaafar, had changed sides after becoming prisoners of war.
Meanwhile, Arab irregulars raided the Hejaz Railway from Aba-el-Lissan and Aqaba, often accompanied by Lawrence and other British liaison officers. In particular, in the weeks following the failure of Allenby's second attack across the Jordan, they carried out demolitions on an stretch of line around Mudawara, due east of Aqaba, effectively closing the line for a month and ending Ottoman operations around Medina at the end of the railway.
Prelude
Allenby's plan
Allenby intended to break through the western end of the Ottoman line, where the terrain was favourable to cavalry operations. His horsemen would pass through the gap to seize objectives deep in the Ottoman rear areas and isolate theirSeventh
Seventh is the ordinal form of the number seven.
Seventh may refer to:
* Seventh Amendment to the United States Constitution
* A fraction (mathematics), , equal to one of seven equal parts
Film and television
*"The Seventh", a second-season e ...
and Eighth Armies.Liddell Hart, p. 435
As a preliminary move, the Arab Northern Army would attack the railway junction at Daraa
Daraa ( ar, دَرْعَا, Darʿā, Levantine Arabic: , also Darʿā, Dara’a, Deraa, Dera'a, Dera, Derʿā and Edrei; means "''fortress''", compare Dura-Europos) is a city in southwestern Syria, located about north of the border with Jord ...
beginning on 16 September, to interrupt the Ottoman lines of communication and distract the Yildirim headquarters.Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 448
The two divisions of XX Corps, commanded by Lieutenant General Philip Chetwode
Field Marshal Philip Walhouse Chetwode, 1st Baron Chetwode, 7th Baronet of Oakley, (21 September 1869 – 6 July 1950), was a senior British Army officer. He saw action during the Second Boer War, during which he was present at the Siege of Ladys ...
, would make an attack in the Judean Hills beginning on the night of 18 September, partly to further distract Ottoman attention to the Jordan Valley sector, and partly to secure positions from which their line of retreat across the Jordan could be blocked. Once the main offensive by XXI Corps and the Desert Mounted Corps
The Desert Mounted Corps was an army corps of the British Army during the First World War, of three mounted divisions renamed in August 1917 by General Edmund Allenby, from Desert Column. These divisions which served in the Sinai and Pales ...
was launched, XX Corps was to block the Ottoman escape route from Nablus to the Jordan crossing at Jisr ed Damieh
Jisr ed-Damiye ( ar, جسر الدامية , Jisr ed-Damieh, Bridge of ed-Damieh), known in English as Damiyah Bridge, as Prince Muhammad Bridge in Jordan, and as Gesher Adam ( he, גשר אדם, , Adam Bridge) in Israel, stretches over the Jordan ...
and if possible capture the Ottoman Seventh Army's headquarters in Nablus.
The main breakthrough was to be achieved on the coast on 19 September by four infantry divisions of XXI Corps, commanded by Lieutenant General Edward Bulfin, massed on a front wide. The fifth division of XXI Corps (the 54th) was to make a subsidiary attack inland of the main breach. Once the breakthrough was achieved, the corps, with the 5th Light Horse Brigade
The 5th Light Horse Brigade was a mounted infantry brigade of the First Australian Imperial Force (AIF) that served during World War I. The brigade was initially formed as a part-time militia formation in the early 1900s in Queensland. During Wor ...
attached, would advance to capture the headquarters of the Ottoman Eighth Army at Tulkarm
Tulkarm, Tulkarem or Tull Keram ( ar, طولكرم, ''Ṭūlkarm'') is a Palestinian city in the West Bank, located in the Tulkarm Governorate of the State of Palestine. The Israeli city of Netanya is to the west, and the Palestinian cities o ...
and the lateral railway line by which the Ottoman Seventh and Eighth Armies were supplied, including the important railway junction at Messudieh.Carver 2003 p. 232Falls 1930 Vol. 2 Part II pp. 455–456
The strategic move was to be made by the Desert Mounted Corps, commanded by Lieutenant General Harry Chauvel
General Sir Henry George Chauvel, (16 April 1865 – 4 March 1945) was a senior officer of the Australian Imperial Force who fought at Gallipoli and during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign in the Middle Eastern theatre of the First World W ...
. Its three mounted divisions were massed behind the three westernmost infantry divisions of XXI Corps. As soon as XXI Corps had breached the Ottoman defences, they were to march north to reach the passes through the Carmel Range before Ottoman troops could forestall them, and pass through these to seize the communication centres of Al-Afuleh and Beisan. These two communication centres were within the radius of a strategic cavalry "bound", the distance mounted units could cover before being forced to halt for rest and to obtain water and fodder for the horses. If they were captured, the lines of communication and retreat for all Ottoman troops west of the Jordan would be cut.
Finally, a detachment consisting of the Anzac Mounted Division, the 20th Indian Infantry Brigade, two battalions of the British West Indies Regiment, and two battalions of Jewish Volunteers in the Royal Fusiliers, amounting to 11,000 men commanded by Major General Edward Chaytor
Major General Sir Edward Walter Clervaux Chaytor, (21 June 1868 – 15 June 1939) was a farmer, and a military commander of New Zealand troops in the Boer War and the First World War.
Early life
Born in Motueka, New Zealand, Chaytor was the so ...
and known as Chaytor's Force, was to capture the Jisr ed Damieh bridge and fords in a pincer movement
The pincer movement, or double envelopment, is a military maneuver in which forces simultaneously attack both flanks (sides) of an enemy formation. This classic maneuver holds an important foothold throughout the history of warfare.
The pin ...
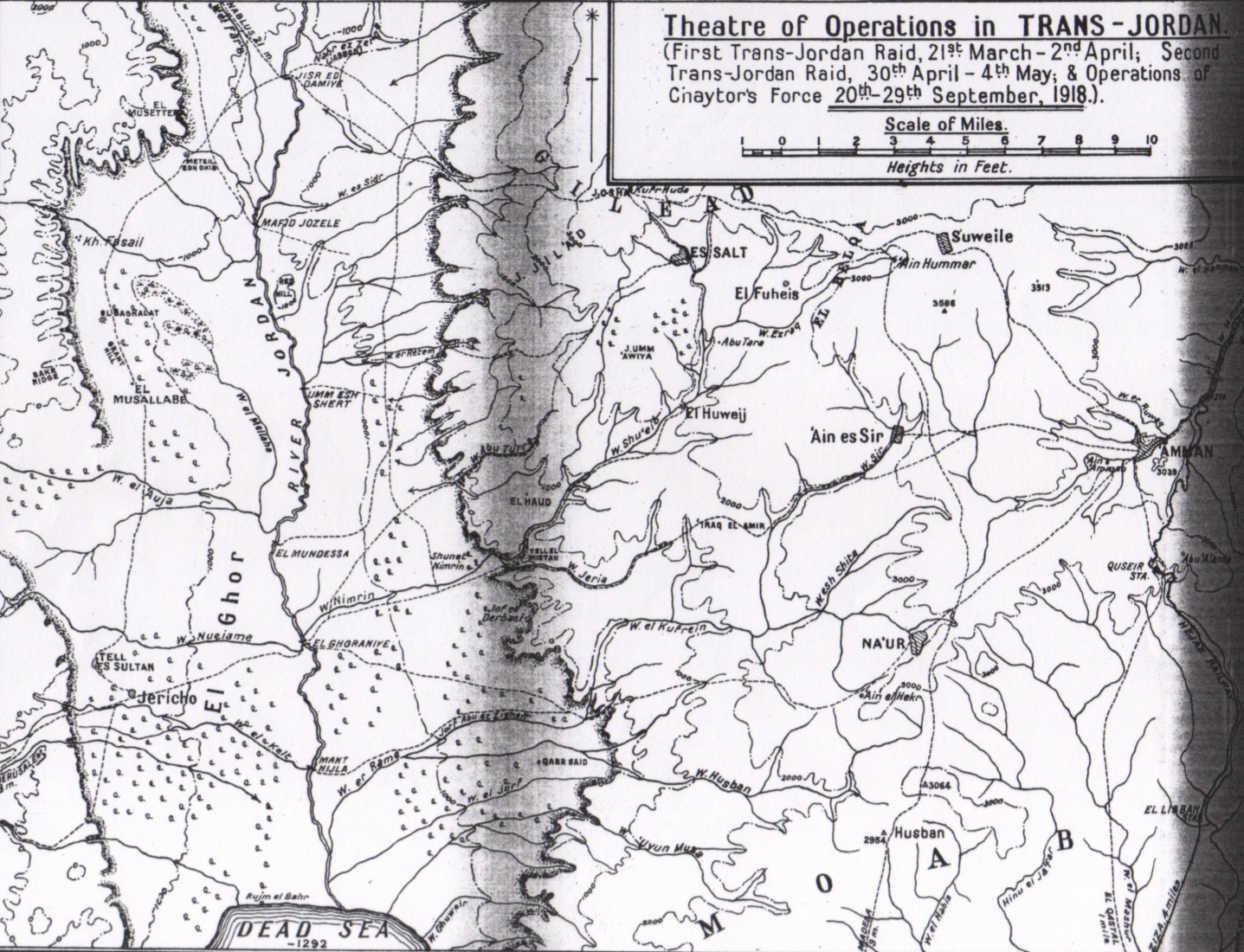
. This important line of communication between the Ottoman Armies on the west bank of the Jordan with the Ottoman Fourth Army at Es Salt, was required by Allenby before Chaytor could proceed to capture Es Salt and Amman.Allenby 24 July 1918 in Hughes 2004 pp. 168–169
Entente deceptions
Secrecy was an essential part, as it had been at the Battle of Beersheba the preceding year. It was feared that the Ottomans could thwart the preparations for the attack by making a withdrawal in the coastal sector. Laborious efforts were therefore made to prevent the Ottomans discerning Allenby's intentions and to persuade them that the next Entente attack would be made in the Jordan Valley. All westward movements of personnel and vehicles from the Jordan Valley towards the Mediterranean coast were made during the night while all movements eastwards were made during daytime. The detached Anzac Mounted Division in the Jordan Valley simulated the activity of the entire mounted corps. Troops marched openly down to the valley by day, and were secretly taken back by lorry at night to repeat the process the next day. Vehicles or mules dragged harrows along tracks to raise dust clouds, simulating other troop movements. Dummy camps and horse lines were constructed and a hotel in Jerusalem was ostentatiously commandeered for an Expeditionary Force headquarters. Meanwhile, the 2nd (British) Battalion of the Imperial Camel Corps joined Arab irregulars in a raid east of the Jordan. They first captured and destroyed the railway station at Mudawara, finally cutting the Hejaz Railway, and then mounted a reconnaissance near Amman, scattering corned beef tins and documents as proof of their presence. Lawrence sent agents to openly buy up huge quantities of forage in the same area. As a final touch, British newspapers and messages were filled with reports of a race meeting to take place on 19 September, the day on which the attack was to be launched. Though Allenby's deceptions did not induce Liman to concentrate his forces against the River Jordan flank, Allenby was nevertheless able to concentrate a force superior to the Ottoman XXII Corps by nearly five to one in infantry and even more in artillery on the Mediterranean flank, where the main attack was to be made, undetected by the Ottomans. Earlier in the year (on 9 June), units of the 7th (Meerut) Division had captured two hills just inland from the coast, depriving the Ottomans of two important observation points overlooking the Allied bridgehead north of the Nahr-el-Auja. Also, the Royal Engineers had established a bridging school on the Nahr-al-Auja much earlier in the year, so the sudden appearance of several bridges across it on the eve of the assault did not alert any other Ottoman observers.Entente air superiority
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
and the Australian Flying Corps
The Australian Flying Corps (AFC) was the branch of the Australian Army responsible for operating aircraft during World War I, and the forerunner of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). The AFC was established in 1912, though it was not until ...
outnumbered and outclassed the Ottoman and German aircraft detachments in Palestine.Falls (1964), p. 39 During the weeks before the September attack, enemy aerial activity dropped markedly. Although during one week in June hostile aeroplanes crossed the British front lines 100 times, mainly on the tip–and–run principle at altitudes of , by the last week in August this number had dropped to 18 and during the three following weeks of September it was reduced to just four enemy aircraft. During the 18 days before the start of the battle, only two or three German aircraft were seen flying. Eventually, Ottoman and German reconnaissance aircraft could not even take off without being engaged by British or Australian fighters, and could therefore not see through Allenby's deceptions, nor spot the true Allied concentration which was concealed in orange groves and plantations.
Ottoman dispositions
Under the Yildirim Army Group were, from west to east: the Eighth Army ( Jevad Pasha) which held the front from theMediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
coast to the Judean Hills
The Judaean Mountains, or Judaean Hills ( he, הרי יהודה, translit=Harei Yehuda) or the Hebron Mountains ( ar, تلال الخليل, translit=Tilal al-Khalīl, links=, lit=Hebron Mountains), is a mountain range in Palestine and Israel wh ...
with five divisions (one of which had recently arrived at Et Tire, a few miles behind the front lines), a cavalry division and the German "Pasha II" detachment, equivalent to a regiment; the Seventh Army (Mustafa Kemal Pasha
Mustafa ( ar, مصطفى
, Muṣṭafā) is one of the names of Prophet Muhammad, and the name means "chosen, selected, appointed, preferred", used as an Arabic given name and surname. Mustafa is a common name in the Muslim world.
Given name Mou ...
) which held the front in the Judean Hills to the Jordan River with four divisions and a German regiment; and the Fourth Army ( Jemal Mersinli Pasha), which was divided into two groups: one faced the bridgeheads which Allenby's forces had seized over the Jordan with two divisions, while the other defended Amman and Ma'an and the Hejaz Railway against attacks by Arab forces with two divisions, a cavalry division and some miscellaneous detachments.
In August 1918, the Yildirim Army Group's front-line strength was 40,598 infantrymen armed with 19,819 rifles, 273 light and 696 heavy machine guns,Erickson 2001, p. 196 and 402 guns.Liddell Hart, p. 432 fn
Although the Ottomans had fairly accurately estimated the total Allied strength, Liman lacked intelligence on the Allied plans and dispositions and was forced to dispose his forces evenly along the entire length of his front. Moreover, almost his entire fighting strength was in the front line. The armies' only operational reserves were the two German regiments and the two understrength cavalry divisions. Further back there were no strategic reserves other than some "Depot Regiments", not organised as fighting units, and scattered garrisons and line of communication units.
After four years of warfare, most Ottoman units were understrength and demoralised by desertions, sickness and shortage of supplies (although supplies were not short at Damascus when Desert Mounted Corps arrived there on 1 October 1918. It was possible to find food and forage for three cavalry divisions; 20,000 men and horses "without depriving the inhabitants of essential food."). Liman nevertheless relied on the determination of the Turkish infantry and the strength of their front-line fortifications. Although the numbers of artillery pieces and especially of machine guns among the defenders were unusually high, the Ottoman lines had only thin belts of barbed wire compared with those on the Western Front,Erickson 2001, p. 198 and Liman was unable to take into account the improved British tactical methods in set-piece offensives, involving surprise and short but accurate artillery preparation based on aerial reconnaissance.
Battle
Opening attacks
On 16 September 1918, Arabs under T. E. Lawrence andNuri as-Said
Nuri Pasha al-Said CH (December 1888 – 15 July 1958) ( ar, نوري السعيد) was an Iraqi politician during the British mandate in Iraq and the Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq. He held various key cabinet positions and served eight terms as ...
began destroying railway lines around the vital rail centre of Daraa, at the junction of the Hedjaz Railway which supplied the Ottoman army at Amman and the Palestine Railway which supplied the Ottoman armies in Palestine. Lawrence's initial forces (a Camel Corps unit from Feisal's Army, an Egyptian Camel Corps unit, some Gurkha
The Gurkhas or Gorkhas (), with endonym Gorkhali ), are soldiers native to the Indian subcontinent, Indian Subcontinent, chiefly residing within Nepal and some parts of Northeast India.
The Gurkha units are composed of Nepalis and Indian Go ...
machine gunners, British and Australian armoured cars and French mountain artillery) were soon joined by up to 3,000 Ruwallah
The Ruwallah ( ar, الرولة, singular Ruweili/Ruwaili) are a large Arab tribe of northern Arabia and the Syrian Desert, including modern-day Jordan.
History
Until the demarcation of borders in the Middle East in the early 20th century, the Ruw ...
and Howeitat
The Howeitat or Huwaitat ( ar, الحويطات ''al-Ḥuwayṭāt'', Northwest Arabian dialect: ''ál-Ḥwēṭāt'') are a large Judhami tribe, that inhabits areas of present-day southern Jordan, the Sinai Peninsula and Sharqia governate in Eg ...
tribesmen under noted fighting chiefs such as Auda abu Tayi and Nuri al-Shaalan
Nuri is a place in modern Sudan on the west side of the Nile, near the Fourth Cataract. Nuri is situated about 15 km north of Sanam, and 10 km from Jebel Barkal.
Nuri is the second of three Napatan burial sites and the construction of p ...
. Although Lawrence was ordered by Allenby only to disrupt communications around Daraa for a week and Lawrence himself had not intended a major uprising to take place in the area immediately, to avoid Ottoman reprisals, a growing number of local communities spontaneously took up arms against the Turks.Erickson 2001 p. 198
As the Ottomans reacted, sending the garrison of Al-Afuleh to reinforce Daraa, the units of Chetwode's Corps made attacks in the hills above the Jordan on 17 and 18 September. The 53rd Division attempted to seize ground commanding the road system behind the Ottoman front lines. Some objectives were captured but a position known to the British as "Nairn Ridge" was defended by the Ottomans until late on 19 September. Once it was captured, roads could be constructed to link the British road systems with those newly captured.
At the last minute, an Indian deserter had warned the Turks about the impending main attack. Refet Bey, the commander of the Ottoman XXII Corps on the Eighth Army's right flank, wished to withdraw to forestall the attack but his superiors Jevad Pasha, commanding the Ottoman Eighth Army, and Liman (who feared that the deserter was himself an attempted intelligence bluff) forbade him to do so.
 At 1:00 am on 19 September, the RAF Palestine Brigade's single Handley Page O/400 heavy bomber dropped its full load of sixteen bombs on the main telephone exchange and railway station in Al-Afuleh. This cut communications between Liman's headquarters at Nazareth and Ottoman Seventh and Eighth Armies for the following vital two days, dislocating the Ottoman command. DH.9s of No. 144 Squadron also bombed El Afule telephone exchange and railway station, Messudieh railway junction and the Ottoman Seventh Army headquarters and telephone exchange at Nablus.
At 1:00 am on 19 September, the RAF Palestine Brigade's single Handley Page O/400 heavy bomber dropped its full load of sixteen bombs on the main telephone exchange and railway station in Al-Afuleh. This cut communications between Liman's headquarters at Nazareth and Ottoman Seventh and Eighth Armies for the following vital two days, dislocating the Ottoman command. DH.9s of No. 144 Squadron also bombed El Afule telephone exchange and railway station, Messudieh railway junction and the Ottoman Seventh Army headquarters and telephone exchange at Nablus.
Breakthrough of Ottoman line
At 4:30 am, Allenby's main attack by XXI Corps opened. A barrage by 385 guns (the field artillery of five divisions, five batteries of 60-pounder guns, thirteen siege batteries of medium howitzers and seven batteries of theRoyal Horse Artillery
The Royal Horse Artillery (RHA) was formed in 1793 as a distinct arm of the Royal Regiment of Artillery (commonly termed Royal Artillery) to provide horse artillery support to the cavalry units of the British Army. (Although the cavalry link r ...
),Falls, p. 37 60 trench mortars
Mortar may refer to:
* Mortar (weapon), an indirect-fire infantry weapon
* Mortar (masonry), a material used to fill the gaps between blocks and bind them together
* Mortar and pestle, a tool pair used to crush or grind
* Mortar, Bihar, a villag ...
and two destroyers off the coast fell on the Ottoman 7th and 20th Divisions' front-line positions defending Nahr el Faliq
Poleg ( he, נחל פולג, Naḥal Poleg) is a stream in the Sharon plain in Israel that empties into the Mediterranean Sea between Netanya and the Wingate Institute.
Geography
The stream starts between Tira and Ramat HaKovesh, east of Mish ...
. As the opening bombardment turned to a "lifting" barrage at 4:50 am, the British and Indian infantry advanced and quickly broke through the Ottoman lines. Within hours, the Desert Mounted Corps were moving north along the coast, with no Ottoman reserves available to check them.
According to Woodward, "concentration, surprise, and speed were key elements in the '' blitzkrieg'' warfare planned by Allenby." By the end of the first day of battle, the left flank unit of the British XXI Corps (the 60th Division) had reached Tulkarm and the remnants of the Ottoman Eighth Army were in disorderly retreat under air attack by Bristol F.2 Fighter
The Bristol F.2 Fighter is a British First World War two-seat biplane fighter and reconnaissance aircraft developed by Frank Barnwell at the Bristol Aeroplane Company. It is often simply called the Bristol Fighter, ''"Brisfit"'' or ''"Bif ...
s of No. 1 Australian Squadron, through the defile at Messudieh and into the hills to the east, covered by a few hastily organised rearguards. Jevad Pasha, the army commander, had fled, and Mustafa Kemal Pasha at Seventh Army headquarters was unable to re-establish control over Eighth Army's troops.
Throughout the day, the RAF prevented any of the German aircraft based at Jenin from taking off and interfering with the British land operations. Relays of two S.E.5s from Nos. 111 and 145 Squadrons, armed with bombs, circled over the German airfield at Jenin all day on 19 September. Whenever they spotted any movement on the ground, they bombed the airfield. Each pair of aircraft were relieved every two hours, machine-gunning the German hangars before departing.
Encirclement of two Ottoman Armies
 During the early hours of 20 September 1918, the Desert Mounted Corps secured the defiles of the Carmel Range. The 4th Mounted Division passed through these to capture Afulah and Beisan, complete with the bulk of two depot regiments. A brigade of the 5th Mounted Division attacked Nazareth, where Liman von Sanders's HQ was situated, although Liman himself escaped. In the late afternoon a brigade from the Australian Mounted Division occupied Jenin, capturing many retreating Ottomans. The 15th Imperial Service Cavalry Brigade, of the 5th Mounted Division, captured the port of Haifa on 23 September.Liddell Hart, p. 438
Once nothing stood between Allenby's forces and Mustafa Kemal's Seventh Army in Nablus, Kemal decided that he lacked sufficient men to fight the British forces. With the railway blocked, the Seventh Army's only escape route lay to the east, along the Nablus-Beisan road that led down the Wadi Fara into the Jordan valley.
During the early hours of 20 September 1918, the Desert Mounted Corps secured the defiles of the Carmel Range. The 4th Mounted Division passed through these to capture Afulah and Beisan, complete with the bulk of two depot regiments. A brigade of the 5th Mounted Division attacked Nazareth, where Liman von Sanders's HQ was situated, although Liman himself escaped. In the late afternoon a brigade from the Australian Mounted Division occupied Jenin, capturing many retreating Ottomans. The 15th Imperial Service Cavalry Brigade, of the 5th Mounted Division, captured the port of Haifa on 23 September.Liddell Hart, p. 438
Once nothing stood between Allenby's forces and Mustafa Kemal's Seventh Army in Nablus, Kemal decided that he lacked sufficient men to fight the British forces. With the railway blocked, the Seventh Army's only escape route lay to the east, along the Nablus-Beisan road that led down the Wadi Fara into the Jordan valley.
 On the night of 20–21 September the Seventh Army began to evacuate Nablus. By this time it was the last formed Ottoman army west of the Jordan and although there was a chance that Chetwode's XX Corps might cut off their retreat, its advance had been slowed by Ottoman rearguards. On 21 September, the Seventh Army was spotted by aircraft in a defile west of the river. The RAF proceeded to bomb the retreating army and destroyed the entire column. Waves of bombing and strafing aircraft passed over the column every three minutes and although the operation had been intended to last for five hours, the Seventh Army was routed in 60 minutes. The wreckage of the destroyed column stretched over . British cavalry later found 87 guns, 55 motor-lorries, 4 motor-cars, 75 carts, 837 four-wheeled wagons, and scores of water-carts and field-kitchens destroyed or abandoned on the road. Many Ottoman soldiers were killed and the survivors were scattered and leaderless. Lawrence later wrote that "the RAF lost four killed. The Turks lost a corps."
According to Chauvel's biographer, Allenby's plan for the Battle of Megiddo was as "brilliant in execution as it had been in conception; it had no parallel in France or on any other front, but rather looked forward in principle and even in detail to the Blitzkrieg of 1939." Over the next four days, the 4th Cavalry Division and Australian Mounted Division rounded up large numbers of demoralised and disorganised Ottoman troops in the
On the night of 20–21 September the Seventh Army began to evacuate Nablus. By this time it was the last formed Ottoman army west of the Jordan and although there was a chance that Chetwode's XX Corps might cut off their retreat, its advance had been slowed by Ottoman rearguards. On 21 September, the Seventh Army was spotted by aircraft in a defile west of the river. The RAF proceeded to bomb the retreating army and destroyed the entire column. Waves of bombing and strafing aircraft passed over the column every three minutes and although the operation had been intended to last for five hours, the Seventh Army was routed in 60 minutes. The wreckage of the destroyed column stretched over . British cavalry later found 87 guns, 55 motor-lorries, 4 motor-cars, 75 carts, 837 four-wheeled wagons, and scores of water-carts and field-kitchens destroyed or abandoned on the road. Many Ottoman soldiers were killed and the survivors were scattered and leaderless. Lawrence later wrote that "the RAF lost four killed. The Turks lost a corps."
According to Chauvel's biographer, Allenby's plan for the Battle of Megiddo was as "brilliant in execution as it had been in conception; it had no parallel in France or on any other front, but rather looked forward in principle and even in detail to the Blitzkrieg of 1939." Over the next four days, the 4th Cavalry Division and Australian Mounted Division rounded up large numbers of demoralised and disorganised Ottoman troops in the Jezreel Valley
The Jezreel Valley (from the he, עמק יזרעאל, translit. ''ʿĒmeq Yīzrəʿēʿl''), or Marj Ibn Amir ( ar, مرج ابن عامر), also known as the Valley of Megiddo, is a large fertile plain and inland valley in the Northern Distr ...
. Many of the surviving refugees who crossed the Jordan were attacked and captured by Arabs as they approached or tried to bypass Daraa.
Liman deployed a rearguard to hold Samakh, on the Sea of Galilee. This town was to be the centre of a line stretching from Lake Hula
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
to Daraa
Daraa ( ar, دَرْعَا, Darʿā, Levantine Arabic: , also Darʿā, Dara’a, Deraa, Dera'a, Dera, Derʿā and Edrei; means "''fortress''", compare Dura-Europos) is a city in southwestern Syria, located about north of the border with Jord ...
. A charge by one and a half Australian Light Horse regiments before dawn on 25 September, followed by intense hand-to-hand fighting, eventually captured the town. This victory broke the proposed defensive line and ended the Battle of Sharon.
Judean Hills fighting
As the Desert Mounted Corps and XXI Corps achieved their objectives, the units of XX Corps resumed their advance. Nablus was captured about noon on 21 September by the 10th Division and the Australian 5th Light Horse Brigade from XXI Corps. The British 53rd Division halted its advance towards the Wadi el Fara road when it became clear that the retreating Ottomans had effectively been destroyed by aerial attacks.
Later operations around Daraa
German and Ottoman aircraft had continued to operate from Daraa, harassing the Arab irregulars and insurgents still attacking railways and isolated Ottoman detachments about the town. At Lawrence's urging, British aircraft began operating from makeshift landing strips at Um el Surab nearby from 22 September. Three Bristol F.2 Fighters shot down several of the Ottoman aircraft. The Handley Page 0/400 ferried across petrol, ammunition and spares for the fighters and two Airco DH.9s, and itself bombed the airfield at Daraa early on 23 September and nearbyMafraq
Mafraq ( ar, المفرق ''Al-Mafraq'', local dialects: ''Mafrag'' or ''Mafra''; ) is the capital city of Mafraq Governorate in Jordan, located 80 km to the north from the capital Amman in crossroad to Syria to the north and Iraq to the east ...
on the following night.
Capture of Amman
On 22 September, on the western side of the Jordan River, the Ottoman 53rd Division was attacked at its headquarters near the Wadi el Fara road, by units from Meldrum's Force. This force consisted of the New Zealand Mounted Brigade (commanded by Brigadier General W. Meldrum), the Machine Gun Squadron, the mounted sections of the 1st and 2nd British West Indies Regiment, the 29th Indian Mountain Battery and Ayrshire (or Inverness) Battery RHA. Meldrum's force captured the commander of the 53rd Division, its headquarters and 600 prisoners, before defeating determined Ottoman rearguards to capture the Jisr ed Damieh bridge.Wavell 1968 p. 221 The Ottoman Fourth Army had remained in its positions until 21 September, apparently unaware of the destruction of the Ottoman armies west of the Jordan until refugees reached them. That day, Liman ordered the Fourth Army to retreat to Daraa and Irbid, about to the west. The Fourth Army began to retreat from the Jordan and Amman on 22 September in increasing disorder due to attacks by British and Australian aircraft on 23 September which caused heavy casualties to the retreating troops on the roads between Es Salt and Amman. On the same day, Chaytor's Force advanced across the Jordan River to capture Es Salt.Cutlack 1941 pp. 165–167Falls 1964, pp. 97–99 On 25 September the Ottoman troops who had reached Mafraq by train from Amman, but who could proceed no further because the railway ahead was demolished, came under heavy aerial attack which caused many casualties and much disorder. Many Ottoman soldiers fled into the desert but several thousand maintained some order and, having abandoned their wheeled transport, continued to retreat northwards towards Daraa on foot or horseback, under constant air attack. Chaytor's Force captured Amman on 25 September. The Ottoman detachment from Ma'an, also trying to retreat northwards, found its line of retreat blocked at Ziza, south of Amman, and surrendered intact to the Anzac Mounted Division on 28 September, rather than risk slaughter by Arab irregulars.Aftermath
Capture of Damascus
Allenby now ordered his cavalry to cross the Jordan, to capture Daraa and Damascus. Meanwhile, the 3rd (Lahore) Division advanced north along the coast towardsBeirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint o ...
and the 7th (Meerut) Division advanced on Baalbek in the Beqaa Valley, where the rearmost Ottoman depots and reinforcement camps were situated.
On 27 September, the 4th Mounted Division moved to Daraa, which had already been abandoned to Arab forces, and then advanced north on Damascus in company with them. The retreating Ottomans committed several atrocities against hostile Arab villages; in return, the Arab forces took no prisoners. Almost an entire Ottoman brigade (along with some German and Austrians) was massacred near the village of Tafas
Tafas ( ar, طفس, also spelled Tafs or Tuffas) is a town in southern Syria, administratively part of the Daraa Governorate, located north of Daraa. Nearby localities include al-Shaykh Saad and Nawa to the north, Da'el, Abtaa and al-Shaykh Mas ...
on 27 September, with the commander Jemal Pasha narrowly escaping. The Arabs repeated the performance the next day, losing a few hundred casualties while wiping out nearly 5,000 Turks in these two battles.
The 5th Mounted and Australian Mounted Divisions advanced directly across the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
towards Damascus. They fought actions at Benat Yakup, Kuneitra, Sasa and Katana, before they reached and closed the north and north-west exits from Damascus on 29 September. On 30 September, the Australians intercepted the garrison of Damascus as they tried to retreat through the Barada gorge. Damascus was captured the next day, with the Allies capturing 20,000 prisoners.Liddell Hart, p. 439 Jemal Pasha fled, having failed to inspire last-ditch resistance.
Overall, the campaign to the fall of Damascus resulted in the surrender of 75,000 Ottoman soldiers.
Pursuit to Aleppo
After the fall of Damascus, the 5th Mounted Division and some detachments of the Arab Northern Army advanced north through Syria, capturing Aleppo on 26 October. They subsequently advanced to Mouslimmiye, where Mustafa Kemal (who had replaced Liman von Sanders in command of the Yıldırım Army Group) had rallied some troops under XXII Corps HQ. Kemal held his positions until 31 October, when hostilities ceased following the signing of theArmistice of Mudros
Concluded on 30 October 1918 and taking effect at noon the next day, the Armistice of Mudros ( tr, Mondros Mütarekesi) ended hostilities in the Middle Eastern theatre between the Ottoman Empire and the Allies of World War I. It was signed by th ...
.
Effects
The successful action at Megiddo resulted in thebattle honour
A battle honour is an award of a right by a government or sovereign to a military unit to emblazon the name of a battle or operation on its flags ("colours"), uniforms or other accessories where ornamentation is possible.
In European military t ...
"Megiddo Megiddo may refer to:
Places and sites in Israel
* Tel Megiddo, site of an ancient city in Israel's Jezreel valley
* Megiddo Airport, a domestic airport in Israel
* Megiddo church (Israel)
* Megiddo, Israel, a kibbutz in Israel
* Megiddo Junctio ...
" being awarded to units of the British, Dominion and Empire forces participating in the battle. Battle honours for the two subsidiary battles of Sharon and Nablus were also awarded.Singh 1993, p. 166
Edward Erickson, a historian of the Ottoman Army, later wrote:
The Battle of the Nablus Plain ranks with Ludendorff's Black Days of the German Army in the effect that it had on the consciousness of the Turkish General Staff. It was now apparent to all but the most diehard nationalists that the Turks were finished in the war. In spite of the great victories in Armenia and in Azerbaijan, Turkey was now in an indefensible condition, which could not be remedied with the resources on hand. It was also apparent that the disintegration of the Bulgarian Army at Salonika and the dissolution of the Austro–Hungarian Army spelled disaster and defeat for the Central Powers. From now until the Armistice, the focus of the Turkish strategy would be to retain as much Ottoman territory as possible.The battle is commemorated in Thomas Hardy’s poem ''Jezreel: on its Seizure by the English under Allenby, September 1918''.
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* *External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Megiddo, Battle Of (1918) Conflicts in 1918 1918 in the Ottoman Empire Battles of the Sinai and Palestine Campaign Battles of World War I involving Australia Battles of World War I involving New Zealand Battles of World War I involving the United Kingdom Battles of World War I involving the Ottoman Empire Battles of World War I involving France Battles of World War I involving British India Battles of World War I involving Germany Aerial operations and battles of World War I History of the Royal Air Force during World War I Battles of World War I involving Indian Princely States September 1918 events Battles of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk