Bani Khalid on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bani Khalid ( ar, بني خالد) is an
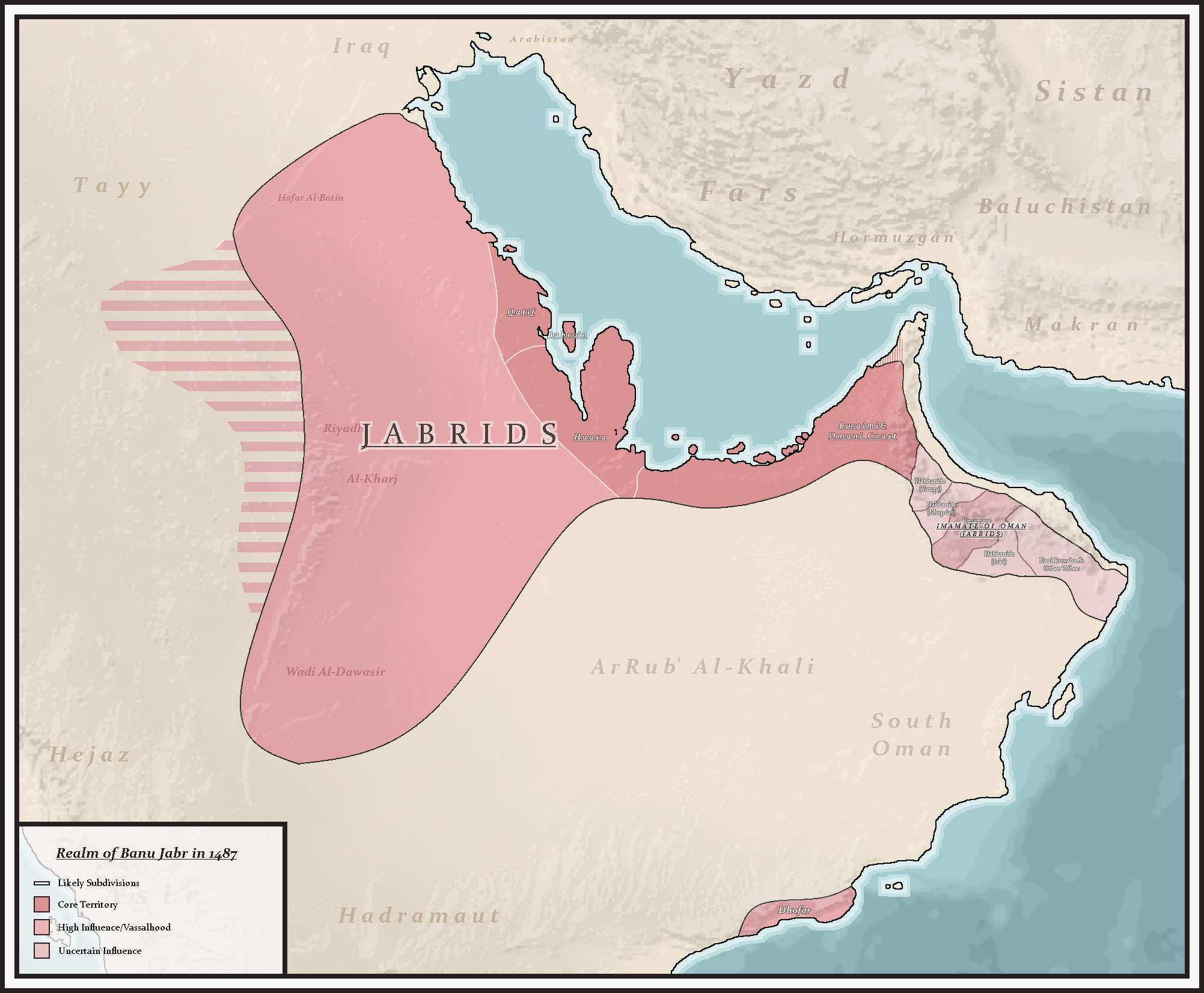 The Jabrids were the ruling class of the Bani Khaild tribe in Nejd.The Jabrids established the Arab dynasty that ruled Eastern Arabia and Nejd from the 15th to the 16th century.
Banu jabr followed the Maliki Sunni school, and made Al-Ahsa, the capital for their Emirate and the stronghold for the Bani Khaild tribe.
The descendants of Banu Jabr can still be found in Al-Qassim,
The Jabrids were the ruling class of the Bani Khaild tribe in Nejd.The Jabrids established the Arab dynasty that ruled Eastern Arabia and Nejd from the 15th to the 16th century.
Banu jabr followed the Maliki Sunni school, and made Al-Ahsa, the capital for their Emirate and the stronghold for the Bani Khaild tribe.
The descendants of Banu Jabr can still be found in Al-Qassim,
 The main branches of the tribe are the Al Humaid, the Juboor, the Du'um, the Al Janah, the Al suhoob, the Grusha, the Al Musallam, the 'Amayer, the Al Subaih and the Mahashir & Nahood.Al-Jassir The chieftainship of the Bani Khalid has traditionally been held by the clan of Al Humaid. The Bani Khalid dominated the deserts surrounding the Al-Hasa and
The main branches of the tribe are the Al Humaid, the Juboor, the Du'um, the Al Janah, the Al suhoob, the Grusha, the Al Musallam, the 'Amayer, the Al Subaih and the Mahashir & Nahood.Al-Jassir The chieftainship of the Bani Khalid has traditionally been held by the clan of Al Humaid. The Bani Khalid dominated the deserts surrounding the Al-Hasa and
 he Khalidis of Jerusalem rose to prominence during
he Khalidis of Jerusalem rose to prominence during  After the
After the
*Ibn Agil al-Zahiri, ''Ansab al-Usar al-Hakima fi al-Ahsa'' ("The Genealogies of the Ruling Families of al-Ahsa, Part II: Banu Humayd (Al 'Uray'ir)"), Dar al-Yamama,
* Hamad al-Jassir, Al-Jassir, Hamad, ''Jamharat Ansab al-Usar al-Mutahaddirah fi Nejd'' ("Compendium of the Geanologies of the Settled Families of Nejd"), entry on "Banu Khalid" (Arabic) *al-Juhany, Uwaidah, ''Najd Before the Salafi Reform Movement'', Ithaca Press, 2002 *Lorimer, John Gordon, ''
* Yitzhak Nakash, Nakash, Yitzhak, ''Reaching for Power: The Shi'a in the Modern Arab World'', Princeton University Press, 2006, online excerpt a
, retrieved 5 Dec 2007 *Oppenheim, Max Freiherr von, with Braunlich, Erich and Caskill, Werner, ''Die Beduinen'', 4 volumes, Otto Harrassowitz Wiesbaden 1952 (German) *Szombathy, Zoltan, Genealogy in Medieval Muslim Societies, ''Studia Islamica'', No. 95. (2002), pp. 5–35 * Madawi Al-Rasheed, Al-Rasheed, Madawi, ''A History of Saudi Arabia'', Cambridge University Press, 2002 (through GoogleBook
*Rentz, George, "Notes on Oppenheim's 'Die Beduinen'", ''Oriens'', Vol. 10, No. 1. (31 Jul. 1957), pp. 77–89 *Al-Wuhaby, Abd al-Karim al-Munif, ''Banu Khalid wa 'Alaqatuhum bi Najd'' ("Banu Khalid and their Relations with Nejd"), Dar Thaqif lil-Nashr wa-al-Ta'lif, 1989 (Arabic) :عبدالكريم الوهيبي، "بنو خالد وعلاقتهم بنجد"، دار ثقيف للنشر والتأليف، 1989 {{DEFAULTSORT:Khalid Arabs from the Ottoman Empire Tribes of Arabia Tribes of Iraq Ottoman Arabia Tribes of Kuwait Tribes of Saudi Arabia
Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
tribal confederation mainly inhabiting Eastern Arabia
Eastern Arabia, historically known as al-Baḥrayn ( ar, البحرين) until the 18th century, is a region stretched from Basra to Khasab along the Persian Gulf coast and included parts of modern-day Bahrain, Kuwait, Eastern Saudi Arabia, Unite ...
and Najd
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of Saudi Arabia, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the ...
. The tribe ruled southern Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
, Kuwait
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Ku ...
, and Eastern Arabia
Eastern Arabia, historically known as al-Baḥrayn ( ar, البحرين) until the 18th century, is a region stretched from Basra to Khasab along the Persian Gulf coast and included parts of modern-day Bahrain, Kuwait, Eastern Saudi Arabia, Unite ...
( al-Hasa and al-Qatif
Qatif or Al-Qatif ( ar, ٱلْقَطِيف ''Al-Qaṭīf'') is a governorate and urban area located in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. It extends from Ras Tanura and Jubail in the north to Dammam in the south, and from the Persian Gulf in the ...
) from the 15th century to the 18th century, and again under the auspices of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
during the early 19th century. At its greatest extent, the domain of Bani Khalid extended from Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
in the north to the borders of Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of ...
in the South, and Bani Khalid wielded political influence by ruling the region of Najd
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of Saudi Arabia, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the ...
in central Arabia. Most of the tribe's members presently reside in eastern and central Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Ara ...
, while others live in Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
, Kuwait
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Ku ...
, Qatar
Qatar (, ; ar, قطر, Qaṭar ; local vernacular pronunciation: ), officially the State of Qatar,) is a country in Western Asia. It occupies the Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it sh ...
, Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and a ...
, Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
and the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE; ar, اَلْإِمَارَات الْعَرَبِيَة الْمُتَحِدَة ), or simply the Emirates ( ar, الِْإمَارَات ), is a country in Western Asia (Middle East, The Middle East). It is ...
. Bani Khalid has both Shia Muslim
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, most ...
and Sunni Muslim
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagre ...
members.Lineage
The tribe traditionally claims descent fromKhalid ibn al-Walid
Khalid ibn al-Walid ibn al-Mughira al-Makhzumi (; died 642) was a 7th-century Arab military commander. He initially headed campaigns against Muhammad on behalf of the Quraysh. He later became a Muslim and spent the remainder of his career in ...
a senior companion of the Prophet Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monoth ...
, and esteemed general who was crucial in the Muslim conquest of Persia
The Muslim conquest of Persia, also known as the Arab conquest of Iran, was carried out by the Rashidun Caliphate from 633 to 654 AD and led to the fall of the Sasanian Empire as well as the eventual decline of the Zoroastrian religion.
The ...
and the Levant. This claim has been questioned by Arab genealogists who have suggested that the tribe may descend from his relatives from Banu Makhzum
The Banu Makhzum () was one of the wealthy clans of the Quraysh. They are regarded as being among the three most powerful and influential clans in Mecca before the advent of Islam, the other two being the Banu Hashim (the tribe of the Islamic proph ...
and not from Khalid himself, alternatively, they have largely been attributed to.
He mentioned in the lineage of Bani Khalid a number of sayings; Most notably:
* They are from the tribe of Banu Rabi'ah bin 'Amir bin Sa'sa'a from the Hawazin )
, type = Qaysi
, image = Hawazin Flag (20).png
, image_size =170px
, alt =
, caption = Banner of the Hawazin at the Battle of Siffin
, nisba =
, location =
, descended = Hawazin ibn Mansur ib ...
tribenihayat al'iirb (Arabic) page 226
* They are a tribe from Banu Ghazia from the Tayy
, location = 2nd century CE–10th century: Jabal Tayy and Syrian Desert
10th century–16th century: Jabal Tayy, Syrian Desert, Jibal al-Sharat, al-Balqa, Palmyrene Steppe, Upper Mesopotamia, Northern Hejaz, Najd
, parent_tribe = Madh ...
tribe
* They are a tribe from the offspring of Khalid ibn al-Walid, from Banu Makhzum
The Banu Makhzum () was one of the wealthy clans of the Quraysh. They are regarded as being among the three most powerful and influential clans in Mecca before the advent of Islam, the other two being the Banu Hashim (the tribe of the Islamic proph ...
, from the Quraysh
The Quraysh ( ar, قُرَيْشٌ) were a grouping of Arab clans that historically inhabited and controlled the city of Mecca and its Kaaba. The Islamic prophet Muhammad was born into the Hashim clan of the tribe. Despite this, many of the Qu ...
tribe
A number of lineages from the Quraish tribe mentioned the discontinuation of Khalid bin Al-Walid's offspring and the extinction of his son, and that his relative Ayoub bin Salama bin Abdullah bin Al-Walid bin Al-Walid bin Al-Mughirah Al-Makhzumi Al -Qurashi inherited the money of Khaled bin Al-Walid bin Al-Mughira, after the death of his last descendant.
The oldest historical text in which the tribe of Bani Khalid was mentioned is what was reported by Ibn al-Atheer in his book "Al-Kamil fi al-Tarikh", speaking about the events of the year 513 AH, saying: (a group of people known as Bani Khalid); It was mentioned that their homes are near Lake Tiberias in Palestine, but the Bani Khalid that Ibn al-Athir mentioned here is not necessarily the current tribe of Bani Khalid.
History
Jabrid Emirate
 The Jabrids were the ruling class of the Bani Khaild tribe in Nejd.The Jabrids established the Arab dynasty that ruled Eastern Arabia and Nejd from the 15th to the 16th century.
Banu jabr followed the Maliki Sunni school, and made Al-Ahsa, the capital for their Emirate and the stronghold for the Bani Khaild tribe.
The descendants of Banu Jabr can still be found in Al-Qassim,
The Jabrids were the ruling class of the Bani Khaild tribe in Nejd.The Jabrids established the Arab dynasty that ruled Eastern Arabia and Nejd from the 15th to the 16th century.
Banu jabr followed the Maliki Sunni school, and made Al-Ahsa, the capital for their Emirate and the stronghold for the Bani Khaild tribe.
The descendants of Banu Jabr can still be found in Al-Qassim, Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Ara ...
, mainly in the members of Al-Mohaimeed family, and the descendants of the Shiekh Sultan Bin Saud Al-Jabri in The Sultanate of Oman.
First Khalidi Emirate
 The main branches of the tribe are the Al Humaid, the Juboor, the Du'um, the Al Janah, the Al suhoob, the Grusha, the Al Musallam, the 'Amayer, the Al Subaih and the Mahashir & Nahood.Al-Jassir The chieftainship of the Bani Khalid has traditionally been held by the clan of Al Humaid. The Bani Khalid dominated the deserts surrounding the Al-Hasa and
The main branches of the tribe are the Al Humaid, the Juboor, the Du'um, the Al Janah, the Al suhoob, the Grusha, the Al Musallam, the 'Amayer, the Al Subaih and the Mahashir & Nahood.Al-Jassir The chieftainship of the Bani Khalid has traditionally been held by the clan of Al Humaid. The Bani Khalid dominated the deserts surrounding the Al-Hasa and Al-Qatif
Qatif or Al-Qatif ( ar, ٱلْقَطِيف ''Al-Qaṭīf'') is a governorate and urban area located in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. It extends from Ras Tanura and Jubail in the north to Dammam in the south, and from the Persian Gulf in the ...
during the 15th and 18th century. Under Barrak ibn Ghurayr of the Al Humaid, the Bani Khalid were able to expel Ottoman forces from the cities and towns in 1670 and proclaim their rule over the region.Ibn Agil, p. 78 Ibn Ghurayr made his capital in Al-Mubarraz
Al-Mubarraz is a city located at Al-Ahsa in the Eastern Province of The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia , and it's the north gate for Al-Ahsa governorate. With a population of 837,000 (as of 2020). Al-Mubarraz has historical importance because it was th ...
, where remnants of his castle stand today. According to Arabian folklore, one chief of the Bani Khalid attempted to protect the prized desert bustard
Bustards, including floricans and korhaans, are large, terrestrial birds living mainly in dry grassland areas and on the steppes of the Old World. They range in length from . They make up the family Otididae (, formerly known as Otidae). Bust ...
(Habari
Habari was a free and open source blog engine written in PHP and currently supports MySQL, SQLite and PostgreSQL for the database backend. It got its name from the Swahili greeting ''habari,'' which means "(what's the) news".
The last releas ...
) from extinction by prohibiting the bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu (; , singular ) are nomadic Arabs, Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia. The Bedouin originated in the Syrian Desert ...
in his realm from poaching the bird's eggs, earning the tribe the appellation of "protectors of the eggs of the Habari", an allusion to the chief's absolute supremacy over his realm. The first chieftain of the "Khawalid" was Haddori.
Fall to the Saudis
The Bani Khalid of eastern Arabia maintained ties with members of their tribe who had settled in Nejd during their earlier migration eastwards, and also cultivated clients among the rulers of the Najdi towns, such as the Al Mu'ammar of al-Uyayna. When the emir of Uyayna adopted the ideas ofMuhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab
Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab ibn Sulayman al-Tamimi ( ar, محمد بن عبد الوهاب بن سليمان , translit=Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhāb ibn Sulaymān al-Tamīmī; 1703–1792) was an Arabian Islamic scholar, theologian, preacher, ac ...
, the Khalidi chief ordered him to cease support for Ibn Abd al-Wahhab and expel him from his town. The emir agreed, and Ibn Abd al-Wahhab moved to neighboring Dir'iyyah
Diriyah ( ar, الدِرْعِيّة), formerly romanized as Dereyeh and Dariyya), is a town in Saudi Arabia located on the north-western outskirts of the Saudi capital, Riyadh. Diriyah was the original home of the Saudi royal family, and served ...
, where he joined forces with the Al Saud
The House of Saud ( ar, آل سُعُود, ʾĀl Suʿūd ) is the ruling royal family of Saudi Arabia. It is composed of the descendants of Muhammad bin Saud, founder of the Emirate of Diriyah, known as the First Saudi state (1727–1818), and ...
. The Bani Khalid remained staunch enemies of the Saudis
Saudis ( ar, سعوديون, Suʿūdiyyūn) are people identified with the country of Saudi Arabia. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. The Saudis are composed mainly of Arabs and primarily speak a regional dialect ...
and their allies and attempted to invade Nejd and Diriyyah
Diriyah ( ar, الدِرْعِيّة), formerly romanized as Dereyeh and Dariyya), is a town in Saudi Arabia located on the north-western outskirts of the Saudi capital, Riyadh. Diriyah was the original home of the Saudi royal family, and served ...
in an effort to stop Saudi expansion. Their efforts failed, however, and after conquering Nejd, the Saudis invaded the Bani Khalid's domain in al-Hasa and deposed the Al 'Ura'yir in 1793. In the early 1950s, many Al Arabi people originating from Iraq migrated to Saudi Arabia Al Qassim.
Khalidis of Jerusalem
 he Khalidis of Jerusalem rose to prominence during
he Khalidis of Jerusalem rose to prominence during Mamluk
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
rule. They became one of the most powerful families in Palestine, rivaled by the equally powerful Husayni
Husayni ( ar, الحسيني also spelled Husseini) is the name of a prominent Palestinian Arab clan formerly based in Jerusalem, which claims descent from Husayn ibn Ali (the son of Ali).
The Husaynis follow the Hanafi school of Sunni Islam, ...
clan as well as the Nashashibi
Nashashibi ( ar, النشاشيبي; transliteration, Al-Nashāshībī) is the name of a prominent Palestinian family based in Jerusalem.
After the First World War, during the British period, Raghib al-Nashashibi was Mayor of Jerusalem (1920– ...
s. The Khalidi family held the banner of the Qaysi faction in Jerusalem while the Husaynis held the banner of the Yamanis. After the fall of Egypt and the Levant to the Ottomans, the Khalidis grew in power, with many of them holding key offices.
 After the
After the Tanzimat
The Tanzimat (; ota, تنظيمات, translit=Tanzimāt, lit=Reorganization, ''see'' nizām) was a period of reform in the Ottoman Empire that began with the Gülhane Hatt-ı Şerif in 1839 and ended with the First Constitutional Era in 187 ...
reforms were completed in the Ottoman Empire, it adopted a new government type, modeled on that of the average European nation. In accordance with the Ottoman Constitution of 1876, which had turned the Ottoman Empire into a constitutional monarchy, the Ottoman Empire now had a parliament with representatives from every Province. Yusuf Dia-Uddin Pasha Al Khalidi was the representative of Jerusalem in the Parliament, he was also the mayor of Jerusalem from 1870 to 1876 and 1878 to 1879. Yusuf Dia Pasha, had studied in Malta and learned English and French. He received a letter from Zadok Kahn
Zadoc Kahn (18 February 1839 in Mommenheim, Alsace – 8 December 1905 in Paris) was an Alsatian- French rabbi and chief rabbi of France.
Life
In 1856 he entered the rabbinical school of Metz, finishing his theological studies at the sam ...
Chief Rabbi of France, calling him to the Zionist
Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת ''Tsiyyonut'' after '' Zion'') is a nationalist movement that espouses the establishment of, and support for a homeland for the Jewish people centered in the area roughly corresponding to what is known in Je ...
cause. He replied with a letter, "In the Name of God, Leave Palestine Alone". Zadok Kahn showed the letter to Theodor Herzl
Theodor Herzl; hu, Herzl Tivadar; Hebrew name given at his brit milah: Binyamin Ze'ev (2 May 1860 – 3 July 1904) was an Austro-Hungarian Jewish lawyer, journalist, playwright, political activist, and writer who was the father of modern po ...
the founder of political Zionism, Herzl replied "If we are not wanted in Palestine, we will search and we will find elsewhere what we seek".
Ruhi al-Khalidi
Yusuf Dia Pasha's nephew, Ruhi al Khalidi was the mayor of Jerusalem from 1899 to 1907 and the deputy of the head of parliament in 1911, he wrote extensively on early Zionism and the threats they posed, he was known to be very cross with the ruling political party the Ittihad ve Terraki for their lack of seriousness with dealing with the Zionist threat. His rising political career ended with his death to typhoid
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by ''Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several d ...
in 1913. Both Yusuf and Ruhi were part of the Ittihad be Terraki, a right wing party believing in Ottoman Islamist Nationalism, as opposed to their Husseini rivals who were Arab Nationalists.
After the Collapse of the Ottomans in WW1 due to the Great Arab Revolt, a British Mandate was set up in Palestine, charged with modernizing Palestine and granting it Independence when it was "ready". This time period was marked by Arab Nationalists strengthening their regime under the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem Amin al-Husseini
Mohammed Amin al-Husseini ( ar, محمد أمين الحسيني 1897
– 4 July 1974) was a Palestinian Arab nationalist and Muslim leader in Mandatory Palestine.
Al-Husseini was the scion of the al-Husayni family of Jerusalemite Arab notab ...
. Due to the Khaldis opposition to Nationalism, they had difficult times getting back into politics. With the exceptions of Hussein al-Khalidi who was mayor from 1934 to 1937, and Mustafa al-Khalidi who was the last Arab Mayor of Jerusalem from 1938 to 1944. Mustafa was like his relatives accused of Zionism, he replied by saying,"We must recognise the facts; the Zionists have migrated to this country, become citizens, have become Palestinians, and they cannot be thrown into the sea. Likewise, some of them have bought land and received deeds in exchange for money and we must recognize them. There is no point in closing our eyes about such things". After the creation of the State of Israel, most Arab countries had turned into monarchies, meaning ascension into the political system was no easy task. Hussein al-Khalidi had managed to be appointed Prime Minister of Jordan, his cabinet was rejected multiple times however, and was forced to give up the position. His memoirs "An era of courtesies went on" were published by the Khalidi Library
The Khalidi Library ( ar, المكتبة الخالدية ) is a library and archive in the Old City of Jerusalem. It was established in 1900, under Ottoman rule.
Location
The Turba Baraka Khan/Khalidi Library is on the south side of the Chain G ...
in Jerusalem. Descendants of the Jerusalemite branch have become highly influential academics. Walid Khalidi
Walid Khalidi ( ar, وليد خالدي, born 1925 in Jerusalem) is an Oxford University-educated Palestinian historian who has written extensively on the Palestinian exodus. He is a co-founder of the Institute for Palestine Studies, establish ...
is a professor of history at Oxford University
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
. The nephew of Hussein al-Khalidi, Rashid Khalidi, is a professor at Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
and has written extensively on the Palestinian Exodus.
The Khalidis of Jerusalem established the famous Khalidi Library
The Khalidi Library ( ar, المكتبة الخالدية ) is a library and archive in the Old City of Jerusalem. It was established in 1900, under Ottoman rule.
Location
The Turba Baraka Khan/Khalidi Library is on the south side of the Chain G ...
near the Aqsa Mosque, which is open till this day.
Return and fall from power
When theOttomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
invaded Arabia and overthrew the Al Saud
The House of Saud ( ar, آل سُعُود, ʾĀl Suʿūd ) is the ruling royal family of Saudi Arabia. It is composed of the descendants of Muhammad bin Saud, founder of the Emirate of Diriyah, known as the First Saudi state (1727–1818), and ...
in 1818, they conquered al-Hasa, al-Qatif and reinstated members of the Al 'Uray'ir as rulers of the region. The Bani Khalid were no longer the potent military force they once were at this time, and tribes such as the Ajman
Ajman ( ar, عجمان, '; Gulf Arabic: عيمان ʿymān) is the capital of the emirate of Ajman in the United Arab Emirates. It is the fifth-largest city in UAE after Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Sharjah and Al Ain. Located along the Persian Gulf, ...
, the Dawasir
Al-Dawasir
Al-Dawasir (Arabic: الدواسر) i is an Arab tribe whose main base is in the south of Najd in the governorates of Wadi Al-Dawasir, Al-Sulail , Al-Aflaj, and Al-Kharj. The tribe is divided into two groups, namely Al Zayed ( Azd) an ...
, Subay'
Subaie' ( ar, سبيع, also spelled Alsubaie', Sbei', and Subei) is an Arabian tribe living in the center of southern Najd.Hamad Al-Jassir, Dictionary of the tribes of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, p.123
History
The family is of North Arabia ...
and Mutayr
Mutayr () is an Arab tribe that originated in the northern Hejaz near Medina. The tribe mainly inhabits Saudi Arabia (Najd), Kuwait, Iraq, Morocco, and Tunisia.
Genealogy
Ahmad al-Qalqashandi who died in 1418 stated that al-Mutayr tribe belongs ...
began encroaching on the Bani Khalid's desert territories. They were also beset by internal quarrels over leadership. Though the Bani Khalid were able to forge an alliance with the 'Anizzah tribe in this period, they were eventually defeated by an alliance of several tribes along with the Al Saud
The House of Saud ( ar, آل سُعُود, ʾĀl Suʿūd ) is the ruling royal family of Saudi Arabia. It is composed of the descendants of Muhammad bin Saud, founder of the Emirate of Diriyah, known as the First Saudi state (1727–1818), and ...
, who had reestablished their rule in Riyadh
Riyadh (, ar, الرياض, 'ar-Riyāḍ, lit.: 'The Gardens' Najdi pronunciation: ), formerly known as Hajr al-Yamamah, is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyadh Province and the centre of the ...
in 1823. A battle with an alliance led by the Mutayr
Mutayr () is an Arab tribe that originated in the northern Hejaz near Medina. The tribe mainly inhabits Saudi Arabia (Najd), Kuwait, Iraq, Morocco, and Tunisia.
Genealogy
Ahmad al-Qalqashandi who died in 1418 stated that al-Mutayr tribe belongs ...
and 'Ajman tribes in 1823, and another battle with the Subay'
Subaie' ( ar, سبيع, also spelled Alsubaie', Sbei', and Subei) is an Arabian tribe living in the center of southern Najd.Hamad Al-Jassir, Dictionary of the tribes of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, p.123
History
The family is of North Arabia ...
and the Al Saud
The House of Saud ( ar, آل سُعُود, ʾĀl Suʿūd ) is the ruling royal family of Saudi Arabia. It is composed of the descendants of Muhammad bin Saud, founder of the Emirate of Diriyah, known as the First Saudi state (1727–1818), and ...
in 1830, brought the rule of the Bani Khalid to a close. The Ottomans appointed a governor from Bani Khalid over al-Hasa once more in 1874, but his rule was also short-lived.Al-Rasheed, p. 36
Present
Many clans and sections of the Bani Khalid had already settled in al-Hasa and Nejd by this time, but many of those who remained leaving east Arabia after their military defeats againstIbn Saud
Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman Al Saud ( ar, عبد العزيز بن عبد الرحمن آل سعود, ʿAbd al ʿAzīz bin ʿAbd ar Raḥman Āl Suʿūd; 15 January 1875Ibn Saud's birth year has been a source of debate. It is generally accepted ...
, eventually settled in Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
, Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
. The clan today consists of important rulers, and members of government. Many families from Bani Khalid can be found today in Kuwait
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Ku ...
, Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and a ...
, Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Ara ...
and Qatar
Qatar (, ; ar, قطر, Qaṭar ; local vernacular pronunciation: ), officially the State of Qatar,) is a country in Western Asia. It occupies the Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it sh ...
Notable people
Among the tribe's members are: *Shaykh Ahmad
Sheikh (pronounced or ; ar, شيخ ' , mostly pronounced , plural ' )—also transliterated sheekh, sheyikh, shaykh, shayk, shekh, shaik and Shaikh, shak—is an honorific title in the Arabic language. It commonly designates a chief of a ...
, Shia Muslim theologian and jurist
* Wadha bint Muhammad Al Orair, mother of Prince Turki and King Saud
Saud bin Abdulaziz Al Saud ( ar, سعود بن عبد العزيز آل سعود ''Suʿūd ibn ʿAbd al ʿAzīz Āl Suʿūd'', Najdi Arabic pronunciation: ; 15 January 1902 – 23 February 1969) was King of Saudi Arabia from 9 November 1953 ...
* Ahmed Juffali, Saudi businessman
* Salman al-Ouda, Saudi Muslim scholar
* Ibrahim bin Abdullah Al Suwaiyel, Saudi Minister of Foreign Affairs
A foreign affairs minister or minister of foreign affairs (less commonly minister for foreign affairs) is generally a cabinet minister in charge of a state's foreign policy and relations. The formal title of the top official varies between co ...
and Minister of Environment, Water and Agriculture
Notes
References
*Anscombe, Frederick F., ''The Ottoman Gulf: the creation of Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Qater, 1870–1914'',Columbia University Press
Columbia University Press is a university press based in New York City, and affiliated with Columbia University. It is currently directed by Jennifer Crewe (2014–present) and publishes titles in the humanities and sciences, including the fie ...
, New York 1997
*Fattah, Hala Mundhir, ''The Politics of Regional Trade in Iraq, Arabia, and the Gulf, 1745–1900'', SUNY Press, 199*Ibn Agil al-Zahiri, ''Ansab al-Usar al-Hakima fi al-Ahsa'' ("The Genealogies of the Ruling Families of al-Ahsa, Part II: Banu Humayd (Al 'Uray'ir)"), Dar al-Yamama,
Riyadh
Riyadh (, ar, الرياض, 'ar-Riyāḍ, lit.: 'The Gardens' Najdi pronunciation: ), formerly known as Hajr al-Yamamah, is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyadh Province and the centre of the ...
, Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Ara ...
(Arabic)
:أبو عبدالرحمن بن عقيل الظاهري، "أنساب الأسر الحاكمة في الأحساء، القسم الثاني: بنو حميد (آل عريعر)"، من منشورات دار اليمامة، الرياض، المملكة العربية السعودية
*Ingham, B. "Muṭayr." Encyclopaedia of Islam. Edited by: P. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel and W.P. Heinrichs. Brill, 2007. Brill Online. 1 December 200* Hamad al-Jassir, Al-Jassir, Hamad, ''Jamharat Ansab al-Usar al-Mutahaddirah fi Nejd'' ("Compendium of the Geanologies of the Settled Families of Nejd"), entry on "Banu Khalid" (Arabic) *al-Juhany, Uwaidah, ''Najd Before the Salafi Reform Movement'', Ithaca Press, 2002 *Lorimer, John Gordon, ''
Gazetteer of the Persian Gulf, Oman and Central Arabia
The ''Gazetteer of the Persian Gulf, Oman and Central Arabia'' (nicknamed ''Lorimer'') is a two-volume encyclopedia compiled by John Gordon Lorimer. The ''Gazetteer'' was published in secret by the British government in India in 1908 and 1915 a ...
'', republished by Gregg International Publishers Limited Westemead. Farnborough, Hants., England and Irish University Press, Shannon, Irelend. Printed in Holland, 1970
*Mandaville, Jon E., "The Ottoman Province of al-Hasā in the Sixteenth and Seventeenth Centuries", ''Journal of the American Oriental Society'', Vol. 90, No. 3. (Jul. - Sep., 1970), pp. 486–513
*Meglio, R. Di. "banū Ḵh̲ālid ." Encyclopaedia of Islam. Edited by: P. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel and W.P. Heinrichs. Brill, 2007. Brill Online. 1 December 200* Yitzhak Nakash, Nakash, Yitzhak, ''Reaching for Power: The Shi'a in the Modern Arab World'', Princeton University Press, 2006, online excerpt a
, retrieved 5 Dec 2007 *Oppenheim, Max Freiherr von, with Braunlich, Erich and Caskill, Werner, ''Die Beduinen'', 4 volumes, Otto Harrassowitz Wiesbaden 1952 (German) *Szombathy, Zoltan, Genealogy in Medieval Muslim Societies, ''Studia Islamica'', No. 95. (2002), pp. 5–35 * Madawi Al-Rasheed, Al-Rasheed, Madawi, ''A History of Saudi Arabia'', Cambridge University Press, 2002 (through GoogleBook
*Rentz, George, "Notes on Oppenheim's 'Die Beduinen'", ''Oriens'', Vol. 10, No. 1. (31 Jul. 1957), pp. 77–89 *Al-Wuhaby, Abd al-Karim al-Munif, ''Banu Khalid wa 'Alaqatuhum bi Najd'' ("Banu Khalid and their Relations with Nejd"), Dar Thaqif lil-Nashr wa-al-Ta'lif, 1989 (Arabic) :عبدالكريم الوهيبي، "بنو خالد وعلاقتهم بنجد"، دار ثقيف للنشر والتأليف، 1989 {{DEFAULTSORT:Khalid Arabs from the Ottoman Empire Tribes of Arabia Tribes of Iraq Ottoman Arabia Tribes of Kuwait Tribes of Saudi Arabia