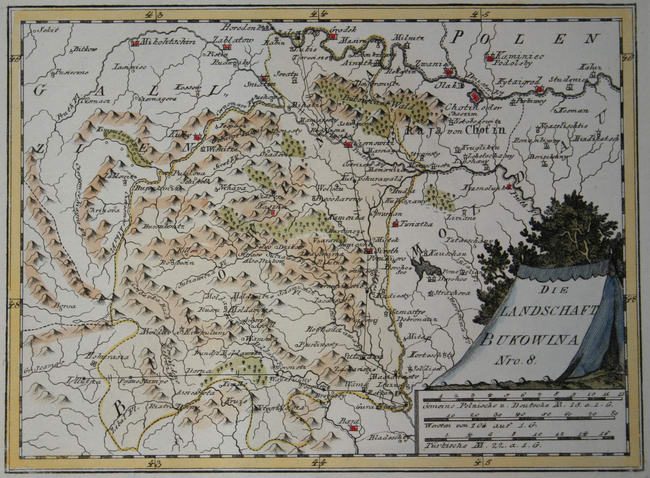
Bukovina on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bukovina or ; ; ; ; , ; see also other languages. is a historical region at the crossroads of Central and
 The name first appears in a document issued by the Voivode of Moldavia Roman I Mușat on 30 March 1392, by which he gives to Ionaș Viteazul three villages, located near the Siret river.
The name ''Bukovina'' came into official use in 1775 with the region's annexation from the
The name first appears in a document issued by the Voivode of Moldavia Roman I Mușat on 30 March 1392, by which he gives to Ionaș Viteazul three villages, located near the Siret river.
The name ''Bukovina'' came into official use in 1775 with the region's annexation from the
 In this period, the patronage of Stephen the Great and his successors on the throne of Moldavia saw the construction of the famous painted monasteries of Moldovița,
In this period, the patronage of Stephen the Great and his successors on the throne of Moldavia saw the construction of the famous painted monasteries of Moldovița,

 The 1871 and 1904 celebrations held at Putna Monastery, near the tomb of
The 1871 and 1904 celebrations held at Putna Monastery, near the tomb of
 Under Austrian rule, Bukovina remained ethnically mixed:
Under Austrian rule, Bukovina remained ethnically mixed:
 The Congress elected the Romanian Bukovinian politician Iancu Flondor as chairman, and voted for the union with the
The Congress elected the Romanian Bukovinian politician Iancu Flondor as chairman, and voted for the union with the
 As a result of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, the USSR demanded not only Bessarabia but also the northern half of Bukovina and Hertsa regions from Romania on 26 June 1940 (Bukovina bordered Eastern Galicia, which the USSR had annexed during the
As a result of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, the USSR demanded not only Bessarabia but also the northern half of Bukovina and Hertsa regions from Romania on 26 June 1940 (Bukovina bordered Eastern Galicia, which the USSR had annexed during the
 After the instauration of Soviet rule, under
After the instauration of Soviet rule, under

 In 1944 the
In 1944 the
 The region was occupied by several now extinct peoples. After which it was settled by both Romanians (Moldavians) and Ukrainians (Ruthenians) with the Antes controlling a large area that included Bukovina by the 6th century. Later, the region was part of Kievan Rus', and later still of the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia. During this period it reinforced its ties to other Ukrainian lands, with many Bukovinian natives studying in Lviv and Kyiv, and the Orthodox Bukovinian Church flourishing in the region. After passing to Hungary in the 14th century, the Hungarian king appointed Dragoș as his deputy forming the
The region was occupied by several now extinct peoples. After which it was settled by both Romanians (Moldavians) and Ukrainians (Ruthenians) with the Antes controlling a large area that included Bukovina by the 6th century. Later, the region was part of Kievan Rus', and later still of the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia. During this period it reinforced its ties to other Ukrainian lands, with many Bukovinian natives studying in Lviv and Kyiv, and the Orthodox Bukovinian Church flourishing in the region. After passing to Hungary in the 14th century, the Hungarian king appointed Dragoș as his deputy forming the 
 In 2011, an anthropological analysis of the Russian census of the population of Moldavia in 1774 asserted a population of 68,700 people in 1774, out of which 40,920 (59.6%) Romanians, 22,810 Ruthenians and Hutsuls (33.2%), and 7.2% Jews, Roma, and Armenians.
Based on the above anthropological estimate for 1774 as well as subsequent official censuses, the ethnic composition of Bukovina changed in the years after 1775 when the Austrian Empire occupied the region. The population of Bukovina increased steadily, primarily through immigration, which Austrian authorities encouraged to develop the economy.Raimund Friedrich Kaindl. ''Das Ansiedlungswesen in der Bukowina seit der Besitzergreifung durch Österreich.'' Innsbruck (1902), pp. 1–71 Indeed, the migrants entering the region came from Ukrainian Galicia, as well as from Romanian Transylvania and Moldavia. Another Austrian official report from 1783, referring to the villages between the Dniester and the Prut, indicated Ruthenian-speaking immigrants from Poland constituting a majority, with only a quarter of the population speaking Moldavian. The same report indicated that Moldavians constituted the majority in the area of Suceava. H.F. Müller gives the 1840 population used for purposes of military conscription as 339,669.
In 1843 the
In 2011, an anthropological analysis of the Russian census of the population of Moldavia in 1774 asserted a population of 68,700 people in 1774, out of which 40,920 (59.6%) Romanians, 22,810 Ruthenians and Hutsuls (33.2%), and 7.2% Jews, Roma, and Armenians.
Based on the above anthropological estimate for 1774 as well as subsequent official censuses, the ethnic composition of Bukovina changed in the years after 1775 when the Austrian Empire occupied the region. The population of Bukovina increased steadily, primarily through immigration, which Austrian authorities encouraged to develop the economy.Raimund Friedrich Kaindl. ''Das Ansiedlungswesen in der Bukowina seit der Besitzergreifung durch Österreich.'' Innsbruck (1902), pp. 1–71 Indeed, the migrants entering the region came from Ukrainian Galicia, as well as from Romanian Transylvania and Moldavia. Another Austrian official report from 1783, referring to the villages between the Dniester and the Prut, indicated Ruthenian-speaking immigrants from Poland constituting a majority, with only a quarter of the population speaking Moldavian. The same report indicated that Moldavians constituted the majority in the area of Suceava. H.F. Müller gives the 1840 population used for purposes of military conscription as 339,669.
In 1843 the
Bukovina Handbook
', prepared under the Direction of the Historical Section of the British Foreign Office No.6. Published in London, Feb.1919. Official censuses in the
52
Romanians made up 44.5% of the population, while 27.7% were Ukrainians/Ruthenians (plus 1.5% Hutsuls), 10.8% Jews, 8.9% Germans, 3.6% Poles, and 3.0% others or undeclared. According to estimates and censuses data, the population of Bukovina was: Note: e-estimate; c-census
 The present demographic situation in Bukovina hardly resembles that of the
The present demographic situation in Bukovina hardly resembles that of the
, at the 2011 census site; accessed 2 February 2012. However, Ukrainian nationalists of the 1990s claimed the region had 110,000 Ukrainians."The Ukrainians: Engaging the 'Eastern Diaspora'". By Andrew Wilson. (1999). In Charles King, Neil Melvin (Eds.) ''Nations Abroad''. Wesview Press, p. 119. The Ukrainian descendants of the Zaporozhian Cossacks who fled Russian rule in the 18th century, living in the
File:View on Suceava (Romania) from Fortess.jpg, The town of Suceava (German and Polish: ''Suczawa''), the largest in southern Bukovina
File:Palatul Administrativ din Suceava12.jpg, The Administrative Palace in Suceava (German and Polish: ''Suczawa'')
File:Fosta prefectură și hotel, Rădăuți (2).JPG, Rădăuți ()
File:Obcina Feredeului.JPG, Câmpulung Moldovenesc ()
File:RO SV Vatra Dornei street 1.jpg, Vatra Dornei ()
File:Gura Humorului - panoramio (3).jpg, Gura Humorului ()
File:Centrul orașului Frasin (4).jpg, Frasin ()
File:Biserica Nasterea Sf. Fecioare Maria din Siret16.jpg, Siret ()
File:Solca vue generale.jpg, Solca (German and Polish: ''Solka'')
File:Bukovina.JPG, The Carpathian Mountains in Bukovina
File:Karpatenlandschaft bei Slatioara.JPG, Slătioara secular forest,
13.4 Notele ultimate ale guvernului sovietic din 26–27 iunie și răspunsurile guvernului roman
(original version, in German – use English and French versions with caution) * Dumitru Covălciuc. Românii nord-bucovineni în exilul totalitarismului sovietic * Victor Bârsan "Masacrul inocenților", București, 1993, pp. 18–19 * Ștefan Purici. Represiunile sovietice... pp. 255–258; * Vasile Ilica. Fântâna Albă: O mărturie de sânge (istorie, amintiri, mărturii). – Oradea: Editura Imprimeriei de Vest, 1999. * Marian Olaru. Considerații preliminare despre demografie și geopolitică pe teritoriul Bucovinei. Analele Bucovinei. Tomul VIII. Partea I. București: Editura Academiei Române, 2001 * Țara fagilor: Almanah cultural-literar al românilor nord-bucovineni. Cernăuți-Târgu-Mureș, 1994 * Anița Nandris-Cudla. Amintiri din viață. 20 de ani în Siberia. Humanitas, Bucharest, 2006 (second edition), (in Romanian) *
City of Chernivtsy
The Metropolitanate of Moldavia and Bucovina (Romanian Orthodox Church)
* *
JEWISH GALICIA & BUKOVINAThings to do when visiting Bucovina
{{Authority control Historical regions in Romania Historical regions in Ukraine Historical regions Subdivisions of the Habsburg monarchy Moldavia Rusyn communities
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
. It is located on the northern slopes of the central Eastern Carpathians
Divisions of the Carpathians are a categorization of the Carpathian mountains system.
Below is a detailed overview of the major subdivisions and ranges of the Carpathian Mountains. The Carpathians are a "subsystem" of a bigger Alps-Himalaya Sy ...
and the adjoining plains, today divided between Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
and Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
.
Inhabited by many cultures and peoples, settled by both Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
( Ruthenians) and Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
(Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
ns), it became part of the Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus', also known as Kyivan Rus,.
* was the first East Slavs, East Slavic state and later an amalgam of principalities in Eastern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical At ...
and Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks, , Middle Turkic languages, Middle Turkic: , , , , , , ka, პაჭანიკი, , , ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Pečenezi, separator=/, Печенези, also known as Pecheneg Turks were a semi-nomadic Turkic peopl ...
' territory early on during the 10th century and an integral part of the Principality of Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially independent and later auto ...
in the 14th century where the capital of Moldavia, Suceava, was founded, eventually expanding its territory all the way to the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
.
Consequently, the culture of the Kievan Rus' spread in the region during the early Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
. During the time of the Golden Horde, namely in the 14th century (or in the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history between and ; it was preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended according to historiographical convention ...
), Bukovina became part of Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
under Hungarian suzerainty (i.e. under the medieval Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
).
According to the Moldo-Russian Chronicle, the Hungarian king Vladislav (Ladislaus) asked the Old Romans (i.e. Byzantines) and the New Romans (i.e. Vlachs) to fight the Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
. During the same event, it writes that Dragoș was one of the New Romans. Eventually, Dragoș dismounted Moldavia named from a river ( Moldova River) flowing in Bukovina. During a Vlach revolt in Bukovina against Balc, Dragoș's grandson, Bogdan the Founder joined the revolt and deposed Balc, securing independence from the Kingdom of Hungary. In 1497 a battle took place at the Cosmin Forest (the hilly forests separating in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Chernivtsi
Chernivtsi (, ; , ;, , see also #Names, other names) is a city in southwestern Ukraine on the upper course of the Prut River. Formerly the capital of the historic region of Bukovina, which is now divided between Romania and Ukraine, Chernivt ...
and Siret valleys), at which Stephen III of Moldavia (Stephen the Great), managed to defeat the much-stronger but demoralized army of King John I Albert of Poland. The battle is known in Polish popular culture as "the battle when the Knights have perished".
The territory of what became known as Bukovina was, from 1774 (officially May 7, 1775 Treaty of Kuchuk Kainarji) to 1919 ( Peace Treaty of Paris St Germain en Laye), an administrative division
Administrative divisions (also administrative units, administrative regions, subnational entities, or constituent states, as well as many similar generic terms) are geographical areas into which a particular independent sovereign state is divi ...
of the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
, the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
, and Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
. The first census that recorded ethnicity was made in 1851 and shows a population of 184,718 or 48.5% Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
, 144,982 or 38.1% Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
and 51,126 or 13.4% others, with a total population of 380,826 people. By 1910, Romanians and Ukrainians were almost in equal numbers with the Romanians concentrated mainly in the south and the Ukrainians mainly in the north. By 1930, following the Kingdom of Romania's acquisition of Bukovina, the region had a total population of 839,500. The region's ethnic composition was approximately 368,500 or 43% Romanian, 235,800 or 28% Ukrainian, 91,100 or 11% Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
, 75,000 or 9% German, 30,500 or 3.6% Polish, 12,400 or 1.5% Hutsul
The Hutsuls (Rusyn language, Hutsul/; ; ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group spanning parts of western Ukraine and northern Romania (i.e. parts of Bukovina and Maramureș).
In Ukraine, they have often been officially and administra ...
, and 11,800 or 1.4% Hungarian, with the remainder consisting of Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
, Romani, and other ethnic groups.
In 1940, the northern half of Bukovina was annexed by the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
in violation of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, a non-aggression pact between Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
and the Soviet Union. The region was temporarily recovered by Romania as an ally of Nazi Germany after the latter invaded the Soviet Union in 1941, but retaken by the Soviet army in 1944. Bukovina's population was historically ethnically diverse. Today, Bukovina's northern half is the Chernivtsi Oblast of Ukraine, while the southern part is Suceava County
Suceava County () is a county (') of Romania. Most of its territory lies in the southern part of the Historical regions of Romania, historical region of Bukovina, while the remainder forms part of Western Moldavia proper. The county seat and the ...
of Romania. Bukovina is sometimes known as the 'Switzerland of the East', given its diverse ethnic mosaic and deep forested mountainous landscapes.
Name
 The name first appears in a document issued by the Voivode of Moldavia Roman I Mușat on 30 March 1392, by which he gives to Ionaș Viteazul three villages, located near the Siret river.
The name ''Bukovina'' came into official use in 1775 with the region's annexation from the
The name first appears in a document issued by the Voivode of Moldavia Roman I Mușat on 30 March 1392, by which he gives to Ionaș Viteazul three villages, located near the Siret river.
The name ''Bukovina'' came into official use in 1775 with the region's annexation from the Principality of Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially independent and later auto ...
to the possessions of the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
, which became the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
in 1804, and Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
in 1867.
The official German name of the province under Austrian rule (1775–1918), , was derived from the Polish form , which in turn was derived from the common Slavic form of , meaning beech tree (compare Ukrainian ; German ; Hungarian ). Another German name for the region, , is mostly used in poetry, and means 'beech land', or 'the land of beech trees'. In Romanian, in literary or poetic contexts, the name ('the land of beech trees') is sometimes used. In some languages a definite article, sometimes optional, is used before the name: ''the Bukovina'', increasingly an archaism in English, which, however, is found in older literature.
In Ukraine, the name (''Bukovyna'') is unofficial, but is common when referring to the '' Chernivtsi Oblast'', as over two-thirds of the oblast
An oblast ( or ) is a type of administrative division in Bulgaria and several post-Soviet states, including Belarus, Russia and Ukraine. Historically, it was used in the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union. The term ''oblast'' is often translated i ...
is the northern part of Bukovina. In Romania, the term ''Northern Bukovina'' is sometimes synonymous with the entire Chernivtsi Oblast of Ukraine, while ''Southern Bukovina'' refers to the Suceava County
Suceava County () is a county (') of Romania. Most of its territory lies in the southern part of the Historical regions of Romania, historical region of Bukovina, while the remainder forms part of Western Moldavia proper. The county seat and the ...
of Romania (although 30% of the present-day Suceava County
Suceava County () is a county (') of Romania. Most of its territory lies in the southern part of the Historical regions of Romania, historical region of Bukovina, while the remainder forms part of Western Moldavia proper. The county seat and the ...
covers territory outside of the historical Bukovina).
History
The territory of Bukovina had been part ofKievan Rus'
Kievan Rus', also known as Kyivan Rus,.
* was the first East Slavs, East Slavic state and later an amalgam of principalities in Eastern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical At ...
since the 10th century. It then became part of the Principality of Galicia, and then part of Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
in the 14th century. It was first delineated as a separate district of the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria in 1775, and was made a nominal duchy
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a country, territory, fiefdom, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or Queen regnant, queen in Western European tradition.
There once existed an important differe ...
within the Austrian Empire in 1849.
Background
The region, which is made up of a portion of the northeastern Carpathian Mountains and the neighbouring plain, was settled by both Vlachs and Ruthenians. After being inhabited by ancient peoples and tribes ( Trypillian, Scythians, Dacians, Getae) starting from the Paleolithic, Germanic culture and language emerged in the region in the 4th century by the time of the Goths, archeological research has also indicated that the Romans had a presence in the region. Later, Slavic culture spread, and by the 10th century the region was part of Turkic, Slavic and Romance people like Pechenegs, Cumans, Ruthinians and Vlachs. Among the first references of the Vlachs (Romanians) in the region is in the 10th century by Varangian Sagas referring to the Blakumen people i.e. Vlachs in the land of Pechenegs. By late 12th century chronicle of Niketas Choniates, writes that some Vlachs seized the future Byzantine emperor, Andronikos Komnenos, when "he reached the borders of Halych" in 1164. In the Moldo-Russian Chronicle, writes the events of year 1342, that the Hungarian king Vladislav (Ladislaus) asked the Old Romans and the New Romans to fight the Tatars, by that they will earn a sit in Maramureș. During the same event, it writes that Dragoș was one of the Romans . In the year 1359 Dragoș dismounted Moldavia and took with him many Vlachs and German colonists from Maramureș to Moldavia.Early settlement
First traces of human occupation date back to the Paleolithic. The area was first settled by Trypillian culture tribes, in the Neolithic. It was then settled by now extinct tribes (Dacians
The Dacians (; ; ) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often considered a subgroup of the Thracians. This area include ...
/Getae
The Getae or Getai ( or , also Getans) were a large nation who inhabited the regions to either side of the Lower Danube in what is today northern Bulgaria and southern Romania, throughout much of Classical Antiquity. The main source of informa ...
, Thracian
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared between north-eastern Greece, ...
/ Scythian tribes). Meanwhile, many nomads crossed the region (3rd to 9th century A.D). By the 4th century, the Goths appeared in the region. And later by the 5th and 6th century Slavic people appeared in the region. They were part of the tribal alliance of the Antes. In the 9th century Tivertsi and White Croatians and Cowari composed the local population.
Kievan Rus
United by Prince Oleg in the 870s, Kievan Rus' was a loose federation of speakers of East Slavic and Uralic languages from the late 9th to the mid-13th century, under the reign of theRurik dynasty
The Rurik dynasty, also known as the Rurikid or Riurikid dynasty, as well as simply Rurikids or Riurikids, was a noble lineage allegedly founded by the Varangian prince Rurik, who, according to tradition, established himself at Novgorod in the ...
, founded by the Varangian prince Rurik
Rurik (also spelled Rorik, Riurik or Ryurik; ; ; died 879) was a Varangians, Varangian chieftain of the Rus' people, Rus' who, according to tradition, was invited to reign in Veliky Novgorod, Novgorod in the year 862. The ''Primary Chronicle' ...
. Bukovina gradually became part of Kievan Rus' from the late 10th century and Pechenegs. Parts of Bukovina were first conquered in 981 by Vladimir the Great
Vladimir I Sviatoslavich or Volodymyr I Sviatoslavych (; Christian name: ''Basil''; 15 July 1015), given the epithet "the Great", was Prince of Novgorod from 970 and Grand Prince of Kiev from 978 until his death in 1015. The Eastern Orthodox ...
. The rest was incorporated into the Principality of Terebovlia in 1084. When Kievan Rus' was partitioned at the end of the 11th century, Bukovina became part of the Principality of Galicia-Volhynia.
Principality of Galicia–Volhynia
After the fragmentation of Kievan Rus', Bukovina passed to the Principality of Galicia ( Principality of Galicia-Volhynia) in 1124. The Church in Bukovina was initially administered fromKiev
Kyiv, also Kiev, is the capital and most populous List of cities in Ukraine, city of Ukraine. Located in the north-central part of the country, it straddles both sides of the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2022, its population was 2, ...
. In 1302, it was passed to the Halych metropoly.
After the Mongols under Batu invaded Europe, with the region nominally falling into their hands, ties between Galician-Volhynian and Bukovina weakened. As a result of the Mongol invasion, the Shypyntsi land, recognizing the suzerainty of the Mongols, arose in the region.
Eventually, this state collapsed, and Bukovina passed to Hungary. King Louis I appointed Dragoș, Voivode of Moldavia as his deputy, facilitating the migration of the Romanians from Maramureș and Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
.
The Moldavian state was formed by the mid-14th century, eventually expanding its territory all the way to the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
. Upon its foundation, the Moldavian or Moldovan state recognized the supremacy of Poland, keeping on recognizing it from 1387 to 1497. Later (1514) it was vassalized by the Ottoman Empire. Bukovina and neighboring regions became the nucleus of the Moldavian Principality, with the capital successively moving from Baia, to Siret, Suceava, and finally in 1564 to Iași, where it would remain until the end of the principality's history. The name of Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
() is derived from the Moldova River in Bukovina.
Polish and Moldavian period
Petru II moved the seat of Moldova from Siret to Suceava in 1388. In the 15th century, Pokuttya, the region immediately to the north, became the subject of disputes between the Principality of Moldavia and the Polish Kingdom. Pokuttya was inhabited by Ruthenians (the predecessors of modern Ukrainians together with the Rus', and of theRusyns
Rusyns, also known as Carpatho-Rusyns, Carpatho-Russians, Ruthenians, or Rusnaks, are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group from the Carpathian Rus', Eastern Carpathians in Central Europe. They speak Rusyn language, Rusyn, an East Slavic lan ...
). In 1497 a battle took place at the Cosmin Forest (the hilly forests separating Chernivtsi
Chernivtsi (, ; , ;, , see also #Names, other names) is a city in southwestern Ukraine on the upper course of the Prut River. Formerly the capital of the historic region of Bukovina, which is now divided between Romania and Ukraine, Chernivt ...
and Siret valleys), at which Stephen III of Moldavia (Stephen the Great), managed to defeat the much-stronger but demoralized army of King John I Albert of Poland. The battle is known in Polish popular culture as "the battle when the Knights have perished". The region had been under Polish nominal suzerainty from its foundation (1387) to the time of this battle (1497). Shortly thereafter, it became a vassal of the Ottoman Empire (1514).
 In this period, the patronage of Stephen the Great and his successors on the throne of Moldavia saw the construction of the famous painted monasteries of Moldovița,
In this period, the patronage of Stephen the Great and his successors on the throne of Moldavia saw the construction of the famous painted monasteries of Moldovița, Sucevița
Sucevița () is a commune in Suceava County, in the historical region of Bukovina, northeastern Romania. It is composed of two villages, namely Sucevița and Voievodeasa (). Sucevița Monastery, part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site
Wor ...
, Putna, Humor
Humour ( Commonwealth English) or humor (American English) is the tendency of experiences to provoke laughter and provide amusement. The term derives from the humoral medicine of the ancient Greeks, which taught that the balance of fluids i ...
, Voroneț, Dragomirna, Arbore and others. With their renowned exterior fresco
Fresco ( or frescoes) is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaster, the painting become ...
es, these monasteries remain some of the greatest cultural treasures of Romania; some of them are World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
s, part of the painted churches of northern Moldavia. The most famous monasteries are in the area of Suceava, which today is part of Romania. Also part of Romania is the monastery of , an Orthodox saint and martyr, who was killed by the Tatars in Bilhorod-Dnistrovskyi.
From 1490 to 1492, the Mukha rebellion, led by the Ukrainian hero Petro Mukha, took place in Galicia. This event pitted the Moldavians against the oppressive rule of the Polish magnates. A rebel army composed of Moldavian peasants took the fortified towns of Sniatyn, Kolomyia, and Halych, killing many Polish noblemen and burghers, before being halted by the Polish Royal Army in alliance with a Galician '' levée en masse'' and Prussian mercenaries while marching to Lviv. Many rebels died in the Rohatyn Battle, with Mukha and the survivors fleeing back to Moldavia. Mukha returned to Galicia to re-ignite the rebellion, but was killed in 1492.
In May 1600 Mihai Viteazul (Michael the Brave), became the ruler the two Danubian principalities and Transylvania.
In the 16th and 17th centuries, Ukrainian warriors (''Cossacks
The Cossacks are a predominantly East Slavic languages, East Slavic Eastern Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of eastern Ukraine and southern Russia. Cossacks played an important role in defending the southern borde ...
'') were involved in many conflicts against the Turkish and Tatar invaders of the Moldavian territory. Notably, Ivan Pidkova, best known as the subject of Ukraine's bard Taras Shevchenko
Taras Hryhorovych Shevchenko (; ; 9 March 1814 – 10 March 1861) was a Ukrainian poet, writer, artist, public and political figure, folklorist, and ethnographer. He was a fellow of the Imperial Academy of Arts and a member of the Brotherhood o ...
's ''Ivan Pidkova'' (1840), led military campaigns in the 1570s. Many Bukovinians joined the Cossacks during the Khmelnytsky uprising
The Khmelnytsky Uprising, also known as the Cossack–Polish War, Khmelnytsky insurrection, or the National Liberation War, was a Cossack uprisings, Cossack rebellion that took place between 1648 and 1657 in the eastern territories of the Poli ...
. As part of the peasant armies, they formed their own regiment, which participated to the 1648 siege of Lviv. Ukrainian Hetman Bohdan Khmelnytsky himself led a campaign in Moldavia, whose result was an alliance between Khmelnytsky and its ''hospodar'' Vasile Lupu. Other prominent Ukrainian leaders fighting against the Turks in Moldovia were Severyn Nalyvaiko and Petro Konashevych-Sahaidachny.
For short periods of time (during wars), the Polish Kingdom (to which Moldavians were hostile) again occupied parts of northern Moldavia. However, the old border was re-established each time, as for example on 14 October 1703 the Polish delegate Martin Chometowski said, according to the Polish protocol, "Between us and Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Munteni ...
(i.e. the Moldavian region, vassal of the Turks) God himself set Dniester
The Dniester ( ) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and then through Moldova (from which it more or less separates the breakaway territory of Transnistria), finally discharging into the Black Sea on Uk ...
as the border" (''Inter nos et Valachiam ipse Deus flumine Tyras dislimitavit''). According to the Turkish protocol the sentence reads, "God (may He be exalted) has separated the lands of Moldavia ukovina, vassal of the Turksfrom our Polish lands by the river Dniester." Strikingly similar sentences were used in other sayings and folkloristic anecdotes, such as the phrase reportedly exclaimed by a member of the Aragonese Cortes in 1684.
In the course of the Russo-Turkish War of 1768–1774, the Ottoman armies were defeated by the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
, which occupied the region from 15 December 1769 to September 1774, and previously during 14 September–October 1769. Bukovina was the reward the Habsburgs received for aiding the Russians in that war. Prince Grigore III Ghica of Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
protested and was prepared to take action to recover the territory, but was assassinated, and a Greek-Phanariot
Phanariots, Phanariotes, or Fanariots (, , ) were members of prominent Greeks, Greek families in Fener, Phanar (Φανάρι, modern ''Fener''), the chief Greek quarter of Constantinople where the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople, Ecume ...
foreigner was put on the throne of Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially in ...
by the Ottomans.
Austrian Empire
Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
occupied Bukovina in October 1774. Following the First Partition of Poland
The First Partition of Poland took place in 1772 as the first of three partitions that eventually ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by 1795. The growth of power in the Russian Empire threatened the Kingdom of Prussia an ...
in 1772, the Austrians claimed that they needed it for ''a road between Galicia and Transylvania''. Bukovina was formally annexed in January 1775. On 2 July 1776, at Palamutka, Austrians and Ottomans signed a border convention, Austria giving back 59 of the previously occupied villages, retaining 278 villages.
Bukovina was a closed military district (1775–1786), then the largest district, Bukovina District (first known as the Czernowitz District), of the Austrian constituent Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria (1787–1849). On 4 March 1849, Bukovina became a separate Austrian Kronland 'crown land' under a '' Landespräsident'' (not a ''Statthalter'', as in other crown lands) and was declared the Duchy of Bukovina
The Duchy of Bukovina (; ; ) was a constituent land of the Austrian Empire from 1849 and a Cisleithanian crown land of Austria-Hungary from 1867 until 1918.
Name
The name ''Bukovina'' came into official use in 1775 with the region's annexation ...
''Herzogtum Bukowina'' (a nominal duchy, as part of the official full style of the Austrian Emperors). In 1860 it was again amalgamated with Galicia but reinstated as a separate province once again on 26 February 1861, a status that would last until 1918.
In 1849 Bukovina got a representative assembly, the ''Landtag'' ( diet). The Moldavian nobility had traditionally formed the ruling class in that territory. In 1867, with the re-organization of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, it became part of the Cisleithanian or Austrian territories of Austria-Hungary and remained so until 1918.
Late 19th to early 20th centuries
 The 1871 and 1904 celebrations held at Putna Monastery, near the tomb of
The 1871 and 1904 celebrations held at Putna Monastery, near the tomb of Stephen the Great
Stephen III, better known as Stephen the Great (; ; died 2 July 1504), was List of rulers of Moldavia, Voivode (or Prince) of Moldavia from 1457 to 1504. He was the son of and co-ruler with Bogdan II of Moldavia, Bogdan II, who was murdered in ...
, constituted tremendous moments for Romanian national identity in Bukovina. Since gaining its independence, the Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania () was a constitutional monarchy that existed from with the crowning of prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen as King of Romania, King Carol I of Romania, Carol I (thus beginning the Romanian royal family), until 1947 wit ...
had had designs on incorporating this province into its new Kingdom. Romanians considered it to be a core part of the old Principality of Moldavia, and of great significance to its history
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the Human history, human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some t ...
. It contained many prominent historical Moldavian monuments, art and architecture and remained a strong cultural anchor for Moldavians in particular.
During the Habsburg period, the Ukrainian population increased in the north of the region, while in the south the ethnic Romanian population remained the majority population. The Austrians "managed to keep a balance between the various ethnic groups." In the 1880 census, there were 239,690 Ruthenians and Hutzuls, or roughly 41.5% of the regions population, while Romanians were second with 190,005 people or 33%, a ratio that remained more or less the same until World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. The percentage of Romanians fell from 85.3% in 1774 to 34.1% in 1910. Ruthenians is an archaic name for Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
, while the Hutsul
The Hutsuls (Rusyn language, Hutsul/; ; ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group spanning parts of western Ukraine and northern Romania (i.e. parts of Bukovina and Maramureș).
In Ukraine, they have often been officially and administra ...
s are a regional Ukrainian subgroup.
Ukrainian national sentiment
Ukrainian national sentiment re-ignited in the 1840s. Officially started in 1848, the nationalist movement gained strength in 1869, when the Ruska Besida Society was founded inChernivtsi
Chernivtsi (, ; , ;, , see also #Names, other names) is a city in southwestern Ukraine on the upper course of the Prut River. Formerly the capital of the historic region of Bukovina, which is now divided between Romania and Ukraine, Chernivt ...
. By the 1890s, Ukrainians were represented in the regional diet and Vienna parliament, being led by Stepan Smal-Stotsky. Beside Stotsky, other important Bukovinian leaders were Yerotei Pihuliak, Omelian Popovych, Mykola Vasylko, , , Sylvester Nikorovych, Ivan and Petro Hryhorovych, and Lubomyr Husar. The first periodical in the Ukrainian language, ''Bukovyna'' (published from 1885 until 1918) was published by the populists since the 1880s. The Ukrainian populists fought for their ethnocultural rights against the Austrians.
Peasant revolts broke out in Hutsul areas in the 1840s, with the peasants demanding more rights, socially and politically. Likewise, nationalist sentiment spread among the Romanians. As a result, more rights were given to Ukrainians and Romanians, with five Ukrainians (including notably Lukian Kobylytsia), two Romanians and one German elected to represent the region. The Ukrainians won representation at the provincial diet as late as 1890, and fought for equality with the Romanians also in the religious sphere. This was partly achieved only as late as on the eve of World War I. However, their achievements were accompanied by friction with Romanians. Overpopulation in the countryside caused migration (especially to North America), also leading to peasant strikes. However, by 1914 Bukovina managed to get "the best Ukrainian schools and cultural-educational institutions of all the regions of Ukraine." Beside Ukrainians, also Bukovina's Germans and Jews, as well as a number of Romanians and Hungarians, emigrated in 19th and 20th century.
 Under Austrian rule, Bukovina remained ethnically mixed:
Under Austrian rule, Bukovina remained ethnically mixed: Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
were predominant in the south, Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
(commonly referred to as Ruthenians in the Empire) in the north, with small numbers of Hungarian Székelys, Slovak, and Polish peasants, and Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
, Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
and Jews in the towns. The 1910 census counted 800,198 people, of which: Ruthenians 38.88%, Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
34.38%, Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
21.24% (Jews 12.86% included), Polish people
Polish people, or Poles, are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation who share a common History of Poland, history, Culture of Poland, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Central Europe. The preamble t ...
4.55%, Hungarian people
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common culture, language and history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the U ...
1.31%, Slovaks
The Slovaks ( (historical Sloveni ), singular: ''Slovák'' (historical: ''Sloven'' ), feminine: ''Slovenka'' , plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history ...
0.08%, Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( ), are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, Slovenian culture, culture, and History of Slove ...
0.02%, Italian people
Italians (, ) are a European peoples, European ethnic group native to the Italian geographical region. Italians share a common Italian culture, culture, History of Italy, history, Cultural heritage, ancestry and Italian language, language. ...
0.02%, and a few Croat
The Croats (; , ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and other neighboring countries in Central Europe, Central and Southeastern Europe who share a common Croatian Cultural heritage, ancest ...
s, Romani people
{{Infobox ethnic group
, group = Romani people
, image =
, image_caption =
, flag = Roma flag.svg
, flag_caption = Romani flag created in 1933 and accepted at the 1971 World Romani Congress
, po ...
, Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Southeastern Europe who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of Serbia, history, and Serbian lan ...
and Turkish people
Turks (), or Turkish people, are the largest Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group, comprising the majority of the population of Turkey and Northern Cyprus. They generally speak the various Turkish dialects. In addition, centuries-old Turkish co ...
. While reading the statistics it should be mentioned that, due to "adverse economic conditions", some 50,000 Ukrainians left the region (mostly emigrating to North America) between 1891 and 1910, in the aforementioned migrations. Nonetheless, the percentage of Ukrainians has significantly grown since the end of the eighteenth century.
In 1783, by an imperial decree of Joseph II, the local Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
Eparchy of Bukovina (with its seat in Czernowitz) was placed under spiritual jurisdiction of the Metropolitanate of Karlovci. Some friction appeared in time between the church hierarchy and the Romanians, complaining that Old Church Slavonic
Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic ( ) is the first Slavic languages, Slavic literary language and the oldest extant written Slavonic language attested in literary sources. It belongs to the South Slavic languages, South Slavic subgroup of the ...
was favored to Romanian, and that family names were being slavicized
Slavicisation American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), or Slavicization, is the acculturation of something non-Slavic into a Slavs, Slavic culture, cuisine, region, or nation. The process can either be v ...
. In spite of Romanian-Slavic speaking frictions over the influence in the local church hierarchy, there was no Romanian-Ukrainian inter-ethnic tension, and both cultures developed in educational and public life. After the rise of Ukrainian nationalism in 1848 and the following rise of Romanian nationalism, Habsburg authorities reportedly awarded additional rights to Ukrainians in an attempt to temper Romanian ambitions of independence. On the other hand, the Ukrainians had to struggle against the Austrians, with the Austrians rejecting both nationalist claims, favoring neither Romanians nor Ukrainians, while attempting to "keep a balance between the various ethnic groups." Indeed, a group of scholars surrounding the Austrian Archduke Franz Ferdinand were planning to turn Austria-Hungary into a federation. These plans included creating a majority-Romanian state of ''Transylvania'' within the federation which would have included Bukovina with Czernowitz. After they acquired Bukovina, the Austrians opened only one elementary school in Czernowitz (Ukrainian 'Chernivsti', Romanian 'Cernăuți), which taught exclusively in Romanian. They later did open German schools, but no Ukrainian ones. Ukrainian language would appear in Chernivsti's schools as late as 1851, but only as a subject, at the local university (in spite of this, the city attracted students from other parts of Bukovina and Galicia, who would study in the German language of instruction). Lukjan Kobylytsia, a Ukrainian Bukovinian farmer and activist, died of torture-related causes after attempting to ask for more rights for the Bukovinian Ukrainians to the Austrians. He died of the consequence of torture in 1851 in Romania. At the end of the 19th century, the development of Ukrainian culture
The culture of Ukraine is composed of the material and spiritual values of the Ukrainian people that has formed throughout the history of Ukraine. Strong family values and religion, alongside the traditions of Ukrainian embroidery and Ukrainian ...
in Bukovina surpassed Galicia and the rest of Ukraine with a network of Ukrainian educational facilities, while Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
formed an archbishopric, later raised to the rank of ''Metropolitanate''.
In 1873, the Eastern Orthodox Bishop of Czernowitz (who was since 1783 under the spiritual jurisdiction of the Metropolitan of Karlovci) was elevated to the rank of Archbishop, when a new Metropolitanate of Bukovinian and Dalmatia was created. The new archbishop of Czernowitz gained supreme jurisdiction in all Cisleithania, over "Serbian" eparchies of Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
and Kotor
Kotor (Cyrillic script, Cyrillic: Котор, ), historically known as Cattaro (from Italian language, Italian: ), is a town in Coastal Montenegro, Coastal region of Montenegro. It is located in a secluded part of the Bay of Kotor. The city has ...
, which were also (until then) under the spiritual jurisdiction of the Patriarchate of Karlovci.
In the early 20th century, a group of scholars surrounding the Austrian Archduke Franz Ferdinand created a plan (that never came to pass) of United States of Greater Austria. The specific proposal was published in Aurel C. Popovici's book "Die Vereinigten Staaten von Groß-Österreich" he United States of Greater Austria Leipzig, 1906. According to it, most of Bukovina (including Czernowitz) would form, with Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
, a Romanian state, while the north-western portion (Zastavna, Kozman, Waschkoutz, Wiznitz, Gura Putilei, and Seletin districts) would form with the bigger part of Galicia a Ukrainian state, both in a federation with 13 other states under the Austrian crown.
Kingdom of Romania
InWorld War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, several battles were fought in Bukovina between the Austro-Hungarian, German, and Russian armies, which resulted in the Russian army invading Chernivtsi for three times (30 August to 21 October 1914, 26 November 1914 to 18 February 1915 and 18 June 1916 to 2 August 1917). The regime that had occupied the city pursued a policy of persecution of "nationally conscious Ukrainians". The situation was not improved until the February Revolution of 1917. The Russian were driven out in 1917. Bukovina suffered great losses during the war.
With the collapse of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
in 1918, both the local Romanian National Council and the Ukrainian National Council based in Galicia claimed the region. In the beginning, Bukovina joined the fledging West Ukrainian National Republic (November 1918), but it was occupied by the Romanian army immediately thereafter.
A Constituent Assembly on 14/27 October 1918 formed an executive committee, to whom the Austrian governor of the province handed power. After an official request by Iancu Flondor, Romanian troops swiftly moved in to take over the territory, against Ukrainian protest. Although local Ukrainians attempted to incorporate parts of Northern Bukovina into the short-lived West Ukrainian People's Republic
The West Ukrainian People's Republic (; West Ukrainian People's Republic#Name, see other names) was a short-lived state that controlled most of Eastern Galicia from November 1918 to July 1919. It included major cities of Lviv, Ternopil, Kolom ...
, this attempt was defeated by Polish and Romanian troops.
The Ukrainian Regional Committee, led by Omelian Popovych, organized a rally in Chernivtsi on 3 November 1918, demanding Bukovina's annexation to Ukraine. The committee took power in the Ukrainian part of Bukovina, including its biggest center Chernivtsi. The Romanian moderates, who were led by Aurel Onciul, accepted the division. However, the Romanian conservatives, led by Iancu Flondor, rejected the idea. In spite of Ukrainian resistance, the Romanian army occupied the Northern Bukovina, including Chernivtsi, on 11 November.
Under the protection of Romanian troops, the Romanian Council summoned a General Congress of Bukovina for 15/28 November 1918, where 74 Romanians, 13 Ruthenians, 7 Germans, and 6 Poles were represented (this is the linguistic composition, and Jews were not recorded as a separate group). According to Romanian historiography, popular enthusiasm swept the whole region, and a large number of people gathered in the city to wait for the resolution of the Congress. The council was quickly summoned by the Romanians upon their occupation of Bukovina.
 The Congress elected the Romanian Bukovinian politician Iancu Flondor as chairman, and voted for the union with the
The Congress elected the Romanian Bukovinian politician Iancu Flondor as chairman, and voted for the union with the Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania () was a constitutional monarchy that existed from with the crowning of prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen as King of Romania, King Carol I of Romania, Carol I (thus beginning the Romanian royal family), until 1947 wit ...
, with the support of the Romanian, German, and Polish representatives; the Ukrainians did not support this. The reasons stated were that, until its takeover by the Habsburg in 1775, Bukovina was the heart of the Principality of Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially independent and later auto ...
, where the ''gropnițele domnești'' (voivods' burial sites) are located, and ''dreptul de liberă hotărâre de sine'' (right of self-determination).''"Congresul general al Bucovinei, întrupând suprema putere a țării și fiind învestiți cu puterea legiuitoare, în numele suveranității naționale, hotărâm: Unirea necondiționată și pe vecie a Bucovinei în vechile ei hotare până la Ceremuș, Colacin și Nistru cu Regatul României".'' The General Congress of Bukovina, embodying the supreme power of the country ukovina and invested with legislative power, in the name of national sovereignty, we decide: Unconditional and eternal union of Bukovina, in its old boundaries up to Ceremuș iver
Iver is a civil parishes in England, civil parish in Buckinghamshire, England. In addition to the central nucleated village, clustered village, the parish includes the residential neighbourhoods of Iver Heath and Richings Park and the hamlets o ...
Colachin and Dniester iver
Iver is a civil parishes in England, civil parish in Buckinghamshire, England. In addition to the central nucleated village, clustered village, the parish includes the residential neighbourhoods of Iver Heath and Richings Park and the hamlets o ...
with the Kingdom of Romania. Romanian control of the province was recognized internationally in the Treaty of St. Germain in 1919. Bukovina's autonomy was undone during Romanian occupation, the region being reduced to an ordinary Romanian province. It was subject to martial law from 1918 to 1928, and again from 1937 to 1940.
The Ukrainian language was suppressed, "educational and cultural institutions, newspapers and magazines were closed."
Romanian authorities oversaw a renewed programme of Romanianization aiming its assimilationist policies at the Ukrainian population of the region. In addition to the suppression of the Ukrainian people, their language and culture, Ukrainian surnames were Rumanized, and the Ukrainian Orthodox Church was persecuted. In the 1930s an underground nationalist movement, which was led by Orest Zybachynsky and Denys Kvitkovsky, emerged in the region. The Romanian government suppressed it by staging two political trials in 1937.
At the same time, Ukrainian enrollment at the Cernăuți University fell from 239 out of 1671, in 1914, to 155 out of 3,247, in 1933, while simultaneously Romanian enrollment there increased several times to 2,117 out of 3,247. In part this was due to attempts to switch to Romanian as the primary language of university instruction, but chiefly to the fact that the university was one of only five in Romania, and was considered prestigious.
In the decade following 1928, as Romania tried to improve its relations with the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, Ukrainian culture was given some limited means to redevelop, though these gains were sharply reversed in 1938.
According to the 1930 Romanian census, Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
made up 44.5% of the total population of Bukovina, and Ukrainians (including Hutsuls) 29.1%. In the northern part of the region, however, Romanians made up only 32.6% of the population, with Ukrainians significantly outnumbering Romanians.
On 14 August 1938 Bukovina officially disappeared from the map, becoming a part of Ținutul Suceava, one of ten new administrative regions. At the same time, Cernăuți, the third most populous town in Romania (after Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ) is the capital and largest city of Romania. The metropolis stands on the River Dâmbovița (river), Dâmbovița in south-eastern Romania. Its population is officially estimated at 1.76 million residents within a greater Buc ...
and Chișinău
Chișinău ( , , ; formerly known as Kishinev) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Moldova, largest city of Moldova. The city is Moldova's main industrial and commercial centre, and is located in the middle of the coun ...
), which had been a mere county seat for the last 20 years, became again a (regional) capital. Also, Bukovinian regionalism continued under the new brand. During its first months of existence, Ținutul Suceava suffered far right (Iron Guard
The Iron Guard () was a Romanian militant revolutionary nationalism, revolutionary Clerical fascism, religious fascist Political movement, movement and political party founded in 1927 by Corneliu Zelea Codreanu as the Legion of the Archangel M ...
) uproars, to which the regional governor Gheorghe Alexianu (the future governor of the Transnistria Governorate) reacted with nationalist and anti-Semitic measures. Alexianu was replaced by Gheorghe Flondor on 1 February 1939.
Division of Bukovina
Invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland, also known as the September Campaign, Polish Campaign, and Polish Defensive War of 1939 (1 September – 6 October 1939), was a joint attack on the Second Polish Republic, Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany, the Slovak R ...
). Initially, the USSR wanted the whole of Bukovina. Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
, which was surprised by the Soviet claim to Bukovina, invoked the German ethnics living in the region. As a result, the USSR only demanded the northern, overwhelmingly Ukrainian part, arguing that it was a "reparation for the great loss produced to the Soviet Union and Bassarabia's population by twenty-two years of Romanian domination of Bassarabia". Following the Soviet ultimatum, Romania ceded Northern Bukovina, which included Cernăuți, to the USSR on 28 June 1940. The withdrawal of the Romanian Army, authorities, and civilians was disastrous. Mobs attacked retreating soldiers and civilians, whereas a retreating unit massacred Jewish soldiers and civilians in the town of Dorohoi. The Red Army occupied Cernăuți and Storojineț counties, as well as parts of Rădăuți and Dorohoi counties (the latter belonged to Ținutul Suceava, but not to Bukovina). The new Soviet-Romanian border was traced less than north of Putna Monastery. Until 22 September 1940, when Ținutul Suceava was abolished, the spa town Vatra Dornei served as the capital of Ținutul Suceava.
Second World War
In 1940, Chernivtsi Oblast ( of which is Northern Bukovina) had a population of circa 805,000, out of which 47.5% were Ukrainians and 28.3% were Romanians, with Germans, Jews, Poles, Hungarians, and Russians comprising the rest. The strong Ukrainian presence was the official motivation for the inclusion of the region into theUkrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as the Ukrainian SSR, UkrSSR, and also known as Soviet Ukraine or just Ukraine, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union from 1922 until 1991. ...
and not into the newly formed Moldavian SSR. Whether the region would have been included in the Moldavian SSR, if the commission presiding over the division had been led by someone other than the communist leader Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and the Premier of the Soviet Union, Chai ...
, remains a matter of debate among scholars. In fact, some territories with a mostly Romanian population (e.g., Hertsa region) were allotted to the Ukrainian SSR.
 After the instauration of Soviet rule, under
After the instauration of Soviet rule, under NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (, ), abbreviated as NKVD (; ), was the interior ministry and secret police of the Soviet Union from 1934 to 1946. The agency was formed to succeed the Joint State Political Directorate (OGPU) se ...
orders, thousands of local families were deported to Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
during this period, with 12,191 people targeted for deportation in a document dated 2 August 1940 (from all formerly Romanian regions included in the Ukrainian SSR), while a December 1940 document listed 2,057 persons to be deported to Siberia. The largest action took place on 13 June 1941, when about 13,000 people were deported to Siberia and Kazakhstan. The majority of those targeted were ethnic native Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
, but there were (to a lesser degree) representatives of other ethnicities, as well.
Until the repatriation convention of 15 April 1941, NKVD troops killed hundreds of Romanian peasants of Northern Bukovina as they tried to cross the border into Romania to escape from Soviet authorities. This culminated on 7 February 1941 with the Lunca massacre and on 1 April 1941 with the Fântâna Albă massacre.
During Soviet Communist rule in Bukovina, "private property was nationalized; farms were partly collectivized; and education was Ukrainianized. At the same time all Ukrainian organizations were disbanded, and many publicly active Ukrainians were either killed or exiled." A significant part of Ukrainian intelligentsia fled to Romania and Germany in the beginning of the occupation. When the conflict between the Soviets and Nazi Germany broke out, and the Soviet troops began moving out of Bukovina, the Ukrainian locals attempted to established their own government, but they were not able to stop the advancing Romanian army.
Almost the entire German population of Northern Bukovina was coerced to resettle in 1940–1941 to the parts of Poland then occupied by Nazi Germany, during 15 September 1940 – 15 November 1940, after this area was occupied by the Soviet Union. About 45,000 ethnic Germans had left Northern Bukovina by November 1940.
In the course of the 1941 attack on the Soviet Union by the Axis forces, the Romanian Third Army led by General Petre Dumitrescu (operating in the north), and the Fourth Romanian Army (operating in the south) regained Northern Bukovina, as well as Hertsa, and Bassarabia, during June–July 1941. It was organized as part of the Bukovina Governorate.
The Axis invasion of Northern Bukovina was catastrophic for its Jewish population, as conquering Romanian soldiers immediately began massacring its Jewish residents. Surviving Jews were forced into ghettoes to await deportation to work camps in Transnistria where 57,000 had arrived by 1941. One of the Romanian mayors of Cernăuți, Traian Popovici, managed to temporarily exempt from deportation 20,000 Jews living in the city between the fall of 1941 and the spring of 1942. Bukovina's remaining Jews were spared from certain death when it was retaken by Soviet forces in February 1944. In all, about half of Bukovina's entire Jewish population had perished. In southern Bukovina (the territory that is currently a part of Romania), in the counties of Campulung, Suceava and Radauti, there were 18,893 Jews according to the September 1, 1941 census; after the deportations to Transnistria later in the year, there were only 179 Jews in 1942. About 12,000 of the southern Bukovinian Jewish deportees survived the deportations to Transnistria. After the war and the return of the Soviets, most of the Jewish survivors from Northern Bukovina fled to Romania (and later settled in Israel).
After the war

Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
drove the Axis forces out and re-established Soviet control over the territory. Romania was forced to formally cede the northern part of Bukovina to the USSR
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
by the 1947 Paris peace treaty. The territory became part of the Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as the Ukrainian SSR, UkrSSR, and also known as Soviet Ukraine or just Ukraine, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union from 1922 until 1991. ...
as Chernivtsi Oblast (province
A province is an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire, Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
). While during the war the Soviet government killed or forced in exile a considerable number of Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
, after the war the same government deported or killed about 41,000 Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
. As a result of killings and mass deportations, entire villages, mostly inhabited by Romanians, were abandoned (Albovat, Frunza, I.G.Duca, Buci—completely erased, Prisaca, Tanteni and Vicov—destroyed to a large extent).Țara fagilor: Almanah cultural-literar al românilor nord-bucovineni. Cernăuți-Târgu-Mureș, 1994, p. 160. Men of military age (and sometimes above), both Ukrainians and Romanians, were conscripted into the Soviet Army. That did not protect them, however, from being arrested and deported for being "anti-Soviet elements".
As a reaction, partisan groups (composed of both Romanians and Ukrainians) began to operate against the Soviets in the woods around Chernivtsi
Chernivtsi (, ; , ;, , see also #Names, other names) is a city in southwestern Ukraine on the upper course of the Prut River. Formerly the capital of the historic region of Bukovina, which is now divided between Romania and Ukraine, Chernivt ...
, Crasna and Codrii Cosminului. In Crasna (in the former Storozhynets county) villagers attacked Soviet soldiers who were sent to "temporarily resettle" them, since they feared deportation. This resulted in dead and wounded among the villagers, who had no firearms.
Spring 1945 saw the formation of transports of Polish repatriates who (voluntarily or by coercion) had decided to leave. Between March 1945 and July 1946, 10,490 inhabitants left Northern Bukovina for Poland, including 8,140 Poles, 2,041 Jews and 309 of other nationalities. Most of them settled in Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
, near the towns: Bolesławiec
Bolesławiec (pronounced , ) is a historic city situated on the Bóbr River in the Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It is the administrative seat of Bolesławiec County, and of Gmina Bolesławiec, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Gm ...
, Dzierżoniów, Gubin, Lubań Śląski, Lwówek Śląski, Nowa Sól
Nowa Sól is a city on the Oder River in Lubusz Voivodeship, western Poland. It is the capital of Nowa Sól County and had a population of 38,763 (2019).
History
The territory became part of the emerging Polish state in the 10th century, and foll ...
, Oława, Prudnik, Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Eu ...
, Zielona Góra
Zielona Góra (; ''Green Mountain''; ) is the largest city in Lubusz Voivodeship, located in western Poland, with 140,403 inhabitants (). The region is closely associated with vineyards and holds an annual Zielona Góra Wine Fest, Wine Fest. Zie ...
, Żagań, Żary.
Overall, between 1930 (last Romanian census) and 1959 (first Soviet census), the population of Northern Bukovina decreased by 31,521 people. According to official data from those two censuses, the Romanian population had decreased by 75,752 people, and the Jewish population by 46,632, while the Ukrainian and Russian populations increased by 135,161 and 4,322 people, respectively.
After 1944, the human and economic connections between the northern (Soviet) and southern (Romanian) parts of Bukovina were severed. Today, the historically Ukrainian northern part is the nucleus of the Ukrainian Chernivtsi Oblast, while the southern part is part of Romania, though there are minorities of Ukrainians and Romanians in Romanian Bukovina and Ukrainian Bukovina respectively. Ukrainians are still a recognized minority in Romania, and have one seat reserved in the Romanian Chamber of Deputies.
In Romania, 28 November is a holiday observed as Bukovina Day. A popular Romanian-language song about the region is " Cântă cucu-n Bucovina" ("Sings the Cuckoo in Bukovina").
Geography
Bukovina proper has an area of . The territory of Romanian (or Southern) Bukovina is located in northeastern Romania and it is part of theSuceava County
Suceava County () is a county (') of Romania. Most of its territory lies in the southern part of the Historical regions of Romania, historical region of Bukovina, while the remainder forms part of Western Moldavia proper. The county seat and the ...
(plus three localities in Botoșani County
Botoșani County () is a county (județ) of Romania, in Western Moldavia (encompassing a few villages in neighbouring Suceava County from Bukovina to the west as well), with the county seat at Botoșani.
Demographics
As of 1st of December 20 ...
), whereas Ukrainian (or Northern) Bukovina is located in western Ukraine and it is part of the Chernivtsi Oblast.
Population
Historical population
 The region was occupied by several now extinct peoples. After which it was settled by both Romanians (Moldavians) and Ukrainians (Ruthenians) with the Antes controlling a large area that included Bukovina by the 6th century. Later, the region was part of Kievan Rus', and later still of the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia. During this period it reinforced its ties to other Ukrainian lands, with many Bukovinian natives studying in Lviv and Kyiv, and the Orthodox Bukovinian Church flourishing in the region. After passing to Hungary in the 14th century, the Hungarian king appointed Dragoș as his deputy forming the
The region was occupied by several now extinct peoples. After which it was settled by both Romanians (Moldavians) and Ukrainians (Ruthenians) with the Antes controlling a large area that included Bukovina by the 6th century. Later, the region was part of Kievan Rus', and later still of the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia. During this period it reinforced its ties to other Ukrainian lands, with many Bukovinian natives studying in Lviv and Kyiv, and the Orthodox Bukovinian Church flourishing in the region. After passing to Hungary in the 14th century, the Hungarian king appointed Dragoș as his deputy forming the principality of Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially independent and later auto ...
, following the revolt of Bogdan the Founder against the Kingdom of Hungary, Bukovina became an integral part of the principality of Moldavia. Suceava, in the south of the territory, was the capital of Moldavia from the late 14th to the mid-16th century. The only data we have about the ethnic composition of Bukovina are the Austrian censuses starting from the 1770s. The Austrians hindered both Romanian and Ukrainian nationalisms. On the other hand, they favored the migration in Bukovina of Ukrainians from Galicia as well as Romanians from Transylvania and Maramureș.
According to the 1775 Austrian census, the province had a total population of 86,000 (this included 56 villages which were returned to Moldavia one year later). The census only recorded social status and some ethno-religious groups (Jews, Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
, Roma, and German colonists). Historian Ion Nistor estimated that the 1774 population consisted of 52,750 Romanians (also called Moldavians) (73.5%), 15,000 Ruthenians and Hutsuls (20.9%) (of whom 6,000 were Hutsuls, and 9,000 were Ruthenian immigrants from Galicia and Podolia settled in Moldavia around 1766), and 4,000 others who "use the Romanian language in conversation" (5.6%), consisting of Armenians, Jews and Roma. Keith Hitchins on the other hand, estimated that in 1774 Bukovina's population consisted of 64,000 Romanians, 8,000 Ukrainians and 3,000 Germans, Jews, and Poles. According to Alecu Hurmuzaki, by 1848, out of a population of 377,581 people, 209,293 or 55.4% of the population was Romanian. At the same time, the Ukrainian population rose to 108,907 and the Jewish population surged from 526 in 1774, to 11,600 in 1848.

 In 2011, an anthropological analysis of the Russian census of the population of Moldavia in 1774 asserted a population of 68,700 people in 1774, out of which 40,920 (59.6%) Romanians, 22,810 Ruthenians and Hutsuls (33.2%), and 7.2% Jews, Roma, and Armenians.
Based on the above anthropological estimate for 1774 as well as subsequent official censuses, the ethnic composition of Bukovina changed in the years after 1775 when the Austrian Empire occupied the region. The population of Bukovina increased steadily, primarily through immigration, which Austrian authorities encouraged to develop the economy.Raimund Friedrich Kaindl. ''Das Ansiedlungswesen in der Bukowina seit der Besitzergreifung durch Österreich.'' Innsbruck (1902), pp. 1–71 Indeed, the migrants entering the region came from Ukrainian Galicia, as well as from Romanian Transylvania and Moldavia. Another Austrian official report from 1783, referring to the villages between the Dniester and the Prut, indicated Ruthenian-speaking immigrants from Poland constituting a majority, with only a quarter of the population speaking Moldavian. The same report indicated that Moldavians constituted the majority in the area of Suceava. H.F. Müller gives the 1840 population used for purposes of military conscription as 339,669.
In 1843 the
In 2011, an anthropological analysis of the Russian census of the population of Moldavia in 1774 asserted a population of 68,700 people in 1774, out of which 40,920 (59.6%) Romanians, 22,810 Ruthenians and Hutsuls (33.2%), and 7.2% Jews, Roma, and Armenians.
Based on the above anthropological estimate for 1774 as well as subsequent official censuses, the ethnic composition of Bukovina changed in the years after 1775 when the Austrian Empire occupied the region. The population of Bukovina increased steadily, primarily through immigration, which Austrian authorities encouraged to develop the economy.Raimund Friedrich Kaindl. ''Das Ansiedlungswesen in der Bukowina seit der Besitzergreifung durch Österreich.'' Innsbruck (1902), pp. 1–71 Indeed, the migrants entering the region came from Ukrainian Galicia, as well as from Romanian Transylvania and Moldavia. Another Austrian official report from 1783, referring to the villages between the Dniester and the Prut, indicated Ruthenian-speaking immigrants from Poland constituting a majority, with only a quarter of the population speaking Moldavian. The same report indicated that Moldavians constituted the majority in the area of Suceava. H.F. Müller gives the 1840 population used for purposes of military conscription as 339,669.
In 1843 the Ruthenian language
Ruthenian (see also #Nomenclature, other names) is an exonymic linguonym for a closely related group of East Slavic languages, East Slavic linguistic Variety (linguistics), varieties, particularly those spoken from the 15th to 18th centuries in ...
was recognized, along with the Romanian language
Romanian (obsolete spelling: Roumanian; , or , ) is the official and main language of Romania and Moldova. Romanian is part of the Eastern Romance languages, Eastern Romance sub-branch of Romance languages, a linguistic group that evolved fr ...
, as 'the language of the people and of the Church in Bukovina'.
During the 19th century, as mentioned, the Austrian Empire policies encouraged the influx of migrants coming from Transylvania, Moldavia, Galicia and the heartland of Austria and Germany, with Germans, Poles, Jews, Hungarians, Romanians, and Ukrainians settling in the region.Bukovina Handbook
', prepared under the Direction of the Historical Section of the British Foreign Office No.6. Published in London, Feb.1919. Official censuses in the
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
(later Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
) did not record ethnolinguistic data until 1850–1851. The 1857 and 1869 censuses omitted ethnic or language-related questions. 'Familiar language spoken' was not recorded again until 1880.
The Austrian census of 1850–1851, which recorded data regarding languages spoken, shows 48.50% Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
and 38.07% Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
. Subsequent Austrian censuses between 1880 and 1910 reveal a Romanian population stabilizing around 33% and a Ukrainian population around 40%. From 1774 to 1910, the percentage of Ukrainians increased, meanwhile the one of Romanians decreased.
According to the 1930 Romanian census, Bukovina had a population of 853,009.Livezeanu (1995), p52
Romanians made up 44.5% of the population, while 27.7% were Ukrainians/Ruthenians (plus 1.5% Hutsuls), 10.8% Jews, 8.9% Germans, 3.6% Poles, and 3.0% others or undeclared. According to estimates and censuses data, the population of Bukovina was: Note: e-estimate; c-census
Current population
 The present demographic situation in Bukovina hardly resembles that of the
The present demographic situation in Bukovina hardly resembles that of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
. The northern (Ukrainian) and southern (Romanian) parts became significantly dominated by their Ukrainian and Romanian majorities, respectively, with the representation of other ethnic groups being decreased significantly.
According to the data of the 2001 Ukrainian census, the Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
represent about 75% (689,100) of the population of Chernivtsi Oblast, which is the closest, although not an exact, approximation of the territory of the historic Northern Bukovina. The census also identified a fall in the Romanian and Moldovan populations to 12.5% (114,600) and 7.3% (67,200), respectively. Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
are the next largest ethnic group with 4.1%, while Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
, Belarusians
Belarusians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Belarus. They natively speak Belarusian language, Belarusian, an East Slavic language. More than 9 million people proclaim Belarusian ethnicity worldwide. Nearly 7.99&n ...
, and Jews comprise the rest 1.2%. The languages of the population closely reflect the ethnic composition, with over 90% within each of the major ethnic groups declaring their national language as the mother tongue ( Ukrainian, Romanian, and Russian, respectively).
The fact that Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
and Moldovans
Moldovans, sometimes referred to as Moldavians (, , ), are an ethnic group native to Moldova, who mostly speak the Romanian language, also referred to locally as Moldovan language, Moldovan. Moldovans form significant communities in Romania, It ...
, a self-declared majority in some regions, were presented as separate categories in the census results, has been criticized in Romania, where there are complains that this artificial Soviet-era practice results in the Romanian population being undercounted, as being divided between Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
and Moldovans
Moldovans, sometimes referred to as Moldavians (, , ), are an ethnic group native to Moldova, who mostly speak the Romanian language, also referred to locally as Moldovan language, Moldovan. Moldovans form significant communities in Romania, It ...
. The Romanian minority of Ukraine also claims to represent a 500,000-strong community.
The Romanians mostly inhabit the southern part of the Chernivtsi region, having been the majority in former Hertsa Raion and forming a plurality together with Moldovans in former Hlyboka Raion. Self-declared Moldovans were the majority in Novoselytsia Raion. In the other eight districts and the city of Chernivtsi
Chernivtsi (, ; , ;, , see also #Names, other names) is a city in southwestern Ukraine on the upper course of the Prut River. Formerly the capital of the historic region of Bukovina, which is now divided between Romania and Ukraine, Chernivt ...
, Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
were the majority. However, after the 2020 administrative reform in Ukraine, all these districts were abolished, and most of the areas merged into Chernivtsi Raion, where Romanians are not in majority anymore.
The southern, or Romanian Bukovina reportedly has a significant Romanian majority (94.8%) according to Romanian sources, the largest minority group being the Romani people
{{Infobox ethnic group
, group = Romani people
, image =
, image_caption =
, flag = Roma flag.svg
, flag_caption = Romani flag created in 1933 and accepted at the 1971 World Romani Congress
, po ...
(1.9%) and Ukrainians, who make up 0.9% of the population (2011 census). Other minor ethnic groups include Lipovans
The Lipovans or Lippovans are ethnic Russians, Russian Old Believers living in Romania, Ukraine, Moldova and Bulgaria who settled in the Principality of Moldavia, in the east of the Principality of Wallachia (Muntenia), and in the regions of D ...
, Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
(in Cacica, Mănăstirea Humorului, Mușenița, Moara, and Păltinoasa), Zipser Germans (in Cârlibaba and Iacobeni) and Bukovina Germans
The Bukovina Germans ( or ''Buchenlanddeutsche'', ), also known and referred to as Buchenland Germans, or Bukovinian Germans, are a German diaspora, German Ethnicity, ethnic group which settled in Bukovina, a historical region situated at the cro ...
(in Suceava, Rădăuți, and Câmpulung Moldovenesc), as well as Slovaks
The Slovaks ( (historical Sloveni ), singular: ''Slovák'' (historical: ''Sloven'' ), feminine: ''Slovenka'' , plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history ...
and Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
(almost exclusively in Suceava, Rădăuți and Siret).
Concerns have been raised about the way census are handled in Romania. For example, according to the 2011 Romanian census, Ukrainians of Romania number 51,703 people, making up 0.3% of the total population."Comunicat de presă privind rezultatele provizorii ale Recensământului Populației și Locuințelor – 2011", at the 2011 census site; accessed 2 February 2012. However, Ukrainian nationalists of the 1990s claimed the region had 110,000 Ukrainians."The Ukrainians: Engaging the 'Eastern Diaspora'". By Andrew Wilson. (1999). In Charles King, Neil Melvin (Eds.) ''Nations Abroad''. Wesview Press, p. 119. The Ukrainian descendants of the Zaporozhian Cossacks who fled Russian rule in the 18th century, living in the
Dobruja
Dobruja or Dobrudja (; or ''Dobrudža''; , or ; ; Dobrujan Tatar: ''Tomrîğa''; Ukrainian language, Ukrainian and ) is a Geography, geographical and historical region in Southeastern Europe that has been divided since the 19th century betw ...
region of the Danube Delta
The Danube Delta (, ; , ) is the second largest river delta in Europe, after the Volga Delta, and is the best preserved on the continent. Occurring where the Danube, Danube River empties into the Black Sea, most of the Danube Delta lies in Romania ...
, also complained similar practices. In 1992, their descendants numbered four thousand people according to official Romanian statistics.Calculated from statistics for the counties of Tulcea and Constanța from However, the local community claims to number 20,000, five times the number stated by Romanian authorities. Rumanization, with the closure of schools and suppression of the language, happened in all areas in present-day Romania where the Ukrainians live or lived. The very term "Ukrainians" was prohibited from the official usage and some Romanians of disputable Ukrainian ethnicity were rather called the "citizens of Romania who forgot their native language" and were forced to change their last names to Romanian-sounding ones.Oleksandr Derhachov (editor), "Ukrainian Statehood in the Twentieth Century: Historical and Political Analysis", Chapter: "Ukraine in Romanian concepts of the foreign policy", 1996, Kiev In Bukovina, the practice of Romanization dates to much earlier than the 20th century. Since Louis of Hungary appointed Dragoș, Voivode of Moldavia as his deputy, there was an introduction of Romanians in Bukovina, and a process of Romanization that intensified in the 1560s.
Places such as the etymologically Ukrainian Breaza and Moldovița (whose name in German is ''Russ Moldawitza'', and used to be ''Ruska Moldavyda'' in Ukrainian), Șerbăuți and Siret used to have an overwhelming Ukrainian majority. In some places in southern Bukovina, such as Balkivtsi (Romanian: ''Bălcăuți''), Izvoarele Sucevei, Ulma and Negostina, Ukrainian majority is still reported in Romanian census. On other hand in North Bukovina the Romanians used to be the biggest ethnic group in the city of Chernivtsi
Chernivtsi (, ; , ;, , see also #Names, other names) is a city in southwestern Ukraine on the upper course of the Prut River. Formerly the capital of the historic region of Bukovina, which is now divided between Romania and Ukraine, Chernivt ...
, as well as in the towns of Hlyboka and Storozhynets, and still are in Boiany and Krasnoilsk.
Urban settlements
Southern Bukovina
Northern Bukovina
Gallery
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
File:Voronet Intrare.JPG, Voroneț Monastery
The Voroneț Monastery is a medieval monastery in the Romanian village of Voroneț, now a part of the town Gura Humorului. It is one of the famous Painted churches of northern Moldavia, painted monasteries from southern Bukovina, in Suceava Co ...
, UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage site
File:Manastirea putna1.jpg, Medieval Putna Monastery in Putna, Suceava County
Suceava County () is a county (') of Romania. Most of its territory lies in the southern part of the Historical regions of Romania, historical region of Bukovina, while the remainder forms part of Western Moldavia proper. The county seat and the ...
File:HerrenGasse 830.jpg, The German House in Chernivtsi
Chernivtsi (, ; , ;, , see also #Names, other names) is a city in southwestern Ukraine on the upper course of the Prut River. Formerly the capital of the historic region of Bukovina, which is now divided between Romania and Ukraine, Chernivt ...
(, )
File:Chernivtsi_University.jpg, Residence of Bukovinian and Dalmatian Metropolitans, UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage site
File:Kirlibaba.jpg, Cârlibaba ()
File:Rumunia, Kaczyka, kościół rzymskokatolicki DSCF7626.jpg, The Polish basilica in Cacica ()
File:Romania Putna Biserica Coborârea Duhului Sfânt din Putna.jpg, The Roman Catholic church of the Bukovina Germans
The Bukovina Germans ( or ''Buchenlanddeutsche'', ), also known and referred to as Buchenland Germans, or Bukovinian Germans, are a German diaspora, German Ethnicity, ethnic group which settled in Bukovina, a historical region situated at the cro ...
in Putna
File:Fundu Moldovei town hall.jpg, Fundu Moldovei ()
File:RO SV Iacobeni (46).JPG, Iacobeni ()
File:SolonetuNou.jpg, Solonețu Nou () village
File:Biserica Sf. Mihail si Gavriil din Maneuti.jpg, Măneuți ()
File:Humor monastery5.jpg, Mănăstirea Humorului ()
File:Moldovita forest railway 2013-07-12 03.jpg, Mocănița-Huțulca-Moldovița narrow-gauge steam train in Suceava County
See also
*Principality of Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially independent and later auto ...
* Galicia, Central European historical region
* Bukovina Germans
The Bukovina Germans ( or ''Buchenlanddeutsche'', ), also known and referred to as Buchenland Germans, or Bukovinian Germans, are a German diaspora, German Ethnicity, ethnic group which settled in Bukovina, a historical region situated at the cro ...
* Székelys of Bukovina
Notes
References
Further reading
* *13.4 Notele ultimate ale guvernului sovietic din 26–27 iunie și răspunsurile guvernului roman
(original version, in German – use English and French versions with caution) * Dumitru Covălciuc. Românii nord-bucovineni în exilul totalitarismului sovietic * Victor Bârsan "Masacrul inocenților", București, 1993, pp. 18–19 * Ștefan Purici. Represiunile sovietice... pp. 255–258; * Vasile Ilica. Fântâna Albă: O mărturie de sânge (istorie, amintiri, mărturii). – Oradea: Editura Imprimeriei de Vest, 1999. * Marian Olaru. Considerații preliminare despre demografie și geopolitică pe teritoriul Bucovinei. Analele Bucovinei. Tomul VIII. Partea I. București: Editura Academiei Române, 2001 * Țara fagilor: Almanah cultural-literar al românilor nord-bucovineni. Cernăuți-Târgu-Mureș, 1994 * Anița Nandris-Cudla. Amintiri din viață. 20 de ani în Siberia. Humanitas, Bucharest, 2006 (second edition), (in Romanian) *
External links
*City of Chernivtsy
The Metropolitanate of Moldavia and Bucovina (Romanian Orthodox Church)
* *
JEWISH GALICIA & BUKOVINA
{{Authority control Historical regions in Romania Historical regions in Ukraine Historical regions Subdivisions of the Habsburg monarchy Moldavia Rusyn communities