Biometric Points on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In order to identify a person, a
 The procedure is called enrollment and comprises the creation of an enrollment data record of the biometric data subject (the person to be enrolled) and its storage in a biometric enrollment database. The enrollment data record comprises one or multiple biometric references and arbitrary non-biometric data such as a name or a personnel number.
The procedure is called enrollment and comprises the creation of an enrollment data record of the biometric data subject (the person to be enrolled) and its storage in a biometric enrollment database. The enrollment data record comprises one or multiple biometric references and arbitrary non-biometric data such as a name or a personnel number.
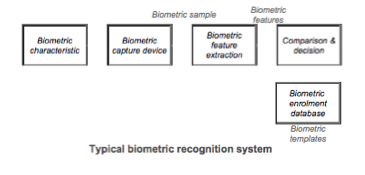 From this recognition biometric sample the biometric feature extraction software creates biometric features which are compared with one or multiple biometric templates from the biometric enrollment database. Due to the statistical nature of biometric samples there is generally no exact match possible. For that reason, the decision process will only assign the biometric data subject to a biometric template and confirm recognition if the comparison score exceeds an adjustable threshold.
From this recognition biometric sample the biometric feature extraction software creates biometric features which are compared with one or multiple biometric templates from the biometric enrollment database. Due to the statistical nature of biometric samples there is generally no exact match possible. For that reason, the decision process will only assign the biometric data subject to a biometric template and confirm recognition if the comparison score exceeds an adjustable threshold.
Biometric selection body partsKinect age verificationSANS Institute InfoSec Reading RoomHuman identificationCAESAR projectSilhouette-based Human Identification from Body
security" \n\n\nsecurity.txt is a proposed standard for websites' security information that is meant to allow security researchers to easily report security vulnerabilities. The standard prescribes a text file called \"security.txt\" in the well known locat ...
system has to compare personal characteristics with a database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases spa ...
. A scan of a person's iris, fingerprint
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfa ...
, face, or other distinguishing feature is created, and a series of biometric points are drawn at key locations in the scan. For example, in the case of a facial scan, biometric points might be placed at the tip of each ear lobe and in the corners of both eyes. Measurements taken between all the (possibly hundreds of) points of a scan are compiled and result in a numerical "score" (which can be quite large). This score is unique for every individual, but it can quickly and easily be compared to any compiled scores of the facial scans in the database to determine if there is a match.
Basic approach
For security systems usingcameras
A camera is an optical instrument that can capture an image. Most cameras can capture 2D images, with some more advanced models being able to capture 3D images. At a basic level, most cameras consist of sealed boxes (the camera body), with a ...
, people recognition has become, in recent years, one of the most common forms of identification. The successful identification
Identification or identify may refer to:
*Identity document, any document used to verify a person's identity
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''Identify'' (album) by Got7, 2014
* "Identify" (song), by Natalie Imbruglia, 1999
*Identification (a ...
of an individual requires comparing an image of the individual to a database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases spa ...
that contains the images of many people. However, comparing each image in its entirety, pixel by pixel, would be an extremely slow and expensive process. To solve this problem, biometrics are used. With biometrics, rather than comparing the entire image, biometric points are placed at key locations, measurements are taken between all the points, and the results are compiled into a "score." A score can be easily obtained from every image on file and stored in the database. When a new individual's image is obtained, the only requirement for successful identification
Identification or identify may refer to:
*Identity document, any document used to verify a person's identity
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''Identify'' (album) by Got7, 2014
* "Identify" (song), by Natalie Imbruglia, 1999
*Identification (a ...
is that the system needs to compile the score based on the image's biometrics and then to compare this new score to the scores in the database—an easy task for a modern computer or laptop.
The goal of a recognition system: given an image of an "unknown" person, to find a picture of the same person in a group of "known" or training images. The difficulty is ensuring that this process can be performed in real time. A biometric system identifies images or videos of people automatically. It can operate in two modes:
*Verification or authentication of individuals: a person's current image is compared with a stored image of the person to be identified. The system confirms or denies the identity of the person.
*ID or person recognition: the image of a stranger is compared with the images of known persons in the database to determine identity.
Biometrics
For the scientist,biometrics
Biometrics are body measurements and calculations related to human characteristics. Biometric authentication (or realistic authentication) is used in computer science as a form of identification and access control. It is also used to identify ...
is the science of measuring physical properties of living beings and for the engineer it is the automated recognition of individuals based on their behavioural and biological characteristics.
By measuring an individual's suitable behavioural
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as we ...
and biological
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary ...
characteristics in a recognition inquiry and comparing these data with the biometric reference data, which had been stored during a learning procedure, the identity of a specific user is determined.
Biometric characteristic
A biometric characteristic is biological or behavioural property of an individual that can be measured and from which distinguishing, repeatable biometric features can be extracted for the purpose of automated recognition of individuals. An example is the face. This characteristic, recorded with a capture device, can be compared with a biometric sample representation of biometric characteristics. The biometric features are information extracted from biometric samples, which can be used for comparison with a biometric reference. Examples are characteristic measurements extracted from a photograph of a face, such as eye distance or nose size. The aim of the extraction of biometric features from a biometric sample is to remove any information that does not contribute to biometric recognition. This enables a fast comparison, improved biometric performance, and may have privacy advantages.Well-known biometric characteristics
{, class="wikitable" , - ! Biometric characteristic !! Description of the features , - !Fingerprint
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfa ...
, Finger lines, pore structure
, -
! Signature (dynamic)
, Writing with pressure and speed differentials
, -
! Facial geometry
, Distances between specific facial features (eyes, nose, mouth)
, -
! Iris
Iris most often refers to:
*Iris (anatomy), part of the eye
*Iris (mythology), a Greek goddess
* ''Iris'' (plant), a genus of flowering plants
* Iris (color), an ambiguous color term
Iris or IRIS may also refer to:
Arts and media
Fictional ent ...
, Iris pattern
, -
! Retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
, Eye background (pattern of retina blood vessels)
, -
! Body geometry
, Distance between specific body features
, -
! Hand geometry
Hand geometry is a biometric that identifies users from the shape of their hands. Hand geometry readers measure a user's palm and fingers along many dimensions including length, width, deviation, and angle and compare those measurements to measu ...
, Measurement of fingers and palm
, -
! Vein structure of hand
, Vein structure of the back or palm of the hand
, -
! Ear
An ear is the organ that enables hearing and, in mammals, body balance using the vestibular system. In mammals, the ear is usually described as having three parts—the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear consists ...
form
, Dimensions of the visible ear
, -
! Voice
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound production ...
, Tone or timbre
, -
! DNA
, DNA code as the carrier of human hereditary
, -
! Keyboard strokes
, Rhythm of keyboard strokes (PC or other keyboard)
, -
! Gait Analysis
Gait analysis is the systematic study of animal locomotion, more specifically the study of human motion, using the eye and the brain of observers, augmented by instrumentation for measuring body movements, body mechanics, and the activity of the ...
, Variations in gait style or binary gait silhouette sequences
, -
!Touch screen (dynamic){{Citation, last=Kałużny, first=Piotr, title=Touchscreen Behavioural Biometrics Authentication in Self-contained Mobile Applications Design, date=2019, url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36691-9_56, work=Business Information Systems Workshops, series=Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing, volume=373, pages=672–685, place=Cham, publisher=Springer International Publishing, doi=10.1007/978-3-030-36691-9_56, isbn=978-3-030-36690-2, access-date=2020-10-22
, Interaction with touchscreens and swipe gestures
Process
To be able to recognize a person by biometric characteristics and derived biometric features, a learning phase must first take place. The procedure is called enrollment and comprises the creation of an enrollment data record of the biometric data subject (the person to be enrolled) and its storage in a biometric enrollment database. The enrollment data record comprises one or multiple biometric references and arbitrary non-biometric data such as a name or a personnel number.
The procedure is called enrollment and comprises the creation of an enrollment data record of the biometric data subject (the person to be enrolled) and its storage in a biometric enrollment database. The enrollment data record comprises one or multiple biometric references and arbitrary non-biometric data such as a name or a personnel number.
Biometric recognition work
For the purpose of recognition, the biometric data subject (the person to be recognized) presents his or her biometric characteristics to the biometric capture device, which generates a recognition biometric sample. From this recognition biometric sample the biometric feature extraction software creates biometric features which are compared with one or multiple biometric templates from the biometric enrollment database. Due to the statistical nature of biometric samples there is generally no exact match possible. For that reason, the decision process will only assign the biometric data subject to a biometric template and confirm recognition if the comparison score exceeds an adjustable threshold.
From this recognition biometric sample the biometric feature extraction software creates biometric features which are compared with one or multiple biometric templates from the biometric enrollment database. Due to the statistical nature of biometric samples there is generally no exact match possible. For that reason, the decision process will only assign the biometric data subject to a biometric template and confirm recognition if the comparison score exceeds an adjustable threshold.
Biometric points or shapes
In order to make an accurate comparison and determine if there is a match, the system requires a shape or points measurement to be compared against the information in the database. This process must be discriminating, quick to compute, concise to store, pose-independent and efficient to match.Head
The head shape is based in a spherical harmonics; the human head grid is mapped into a sphere and then expanded in the basics or spherical harmonics. For face recognition, the relationship between various points, such as the distance between the eyes, is compared.Body
For the body different kind of points are used, but, as with the head, the distances between these points are measured. Seventy-three so-called anthropometry landmarks were extracted from the scans of a database used to create this system. These are point-to-point distances. The landmarks identify key bone joint structure and are adequate to segment the body and produce anatomical reference axis systems for the key body segments and joints. Those points with separations that are pose-independent and feasibly findable in a camera’s field of view are connected by a single large bone. They form a biometric vector of twelve distances, , with , wrist to elbow, elbow to shoulder, d3 hip to knee, etc. for which the Euclidean distance is invariant across different poses. Distances such as chin-knee are avoided. All measurements are in millimeters (mm).Error
A computer-vision-based system will contain some errors in measurement of the landmark points. This is a complex function of the imaging system, image post-processing, and 3D calculation algorithm. For simplicity, the system does not analyze this process but instead specifies an equivalent error at the position of the landmarks, and studies the effect of this error on the recognizer.Conclusion
Biometrics points are useful for making identifications with cameras systems, but they depend on the existence of a previously generated database so that distances can be compared.Applications
Beside the most common use for people recognition in security systems, they can be used inKinect
Kinect is a line of motion sensing input devices produced by Microsoft and first released in 2010. The devices generally contain RGB cameras, and infrared projectors and detectors that map depth through either structured light or time of fl ...
for parental control. For example, the new data obtained is compared with previously stored data to determine if the person recognized is a minor or not.
References
Biometrics