Battery Electric Vehicles on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of
A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of
 Battery electric trains in the form of BEMUs (battery electric multiple units) are operated commercially in
Battery electric trains in the form of BEMUs (battery electric multiple units) are operated commercially in

 The same technology is used to power the Mountain View Community Shuttles. This technology was supported by the California Energy Commission, and the shuttle program is being supported by Google.
The same technology is used to power the Mountain View Community Shuttles. This technology was supported by the California Energy Commission, and the shuttle program is being supported by Google.


 India is the world's biggest market for bicycles at 22 million units per year. By 2024, electric two-wheelers will be a $2 billion market with over 3 million units being sold in India.
The Indian government is launching schemes and incentives to promote the adoption of electric vehicles in the country, and is aiming to be a manufacturing hub for electric vehicles within the next five years.
China has experienced an explosive growth of sales of non-assisted e-bikes including the scooter type, with annual sales jumping from 56,000 units in 1998 to over 21 million in 2008, and reaching an estimated 120 million e-bikes on the road in early 2010. China is the world's leading manufacturer of e-bikes, with 22.2 million units produced in 2009.
India is the world's biggest market for bicycles at 22 million units per year. By 2024, electric two-wheelers will be a $2 billion market with over 3 million units being sold in India.
The Indian government is launching schemes and incentives to promote the adoption of electric vehicles in the country, and is aiming to be a manufacturing hub for electric vehicles within the next five years.
China has experienced an explosive growth of sales of non-assisted e-bikes including the scooter type, with annual sales jumping from 56,000 units in 1998 to over 21 million in 2008, and reaching an estimated 120 million e-bikes on the road in early 2010. China is the world's leading manufacturer of e-bikes, with 22.2 million units produced in 2009.
 Most electric vehicles today use an
Most electric vehicles today use an
Building Better Batteries for Electric Cars
''
Electrically Propelled Perambulator
', 1894 * , Hiram Percy Maxim, ''Motor vehicle'', 1897 * , Hiram Percy Maxim et al.,
Electric motor vehicle
', 1904 ;Organizations
Battery Vehicle Society (UK)
Zap-Map – the UK national directory of recharging points
The European Association for Battery, Hybrid and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (AVERE)
Czech EV Club – (CZ) Eng. section in photogallery
Alternative Technology Association Electric Vehicle Interest Group
Australian Electric Vehicle Association
Electric Car Society
;News
(Green Car Congress) * [https://web.archive.org/web/20110815220501/http://www.dailytech.com/Ford+Focus+Electric+to+go+GridNeutral+With+the+Help+of+SunPower+Panels/article22416.htm Solar charging station for Ford Focus Electric Vehicle] ;Studies * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Battery Electric Vehicle Battery electric vehicles, Automotive technologies Sustainable technologies


 A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of
A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of electric vehicle
An electric vehicle (EV) is a motor vehicle whose propulsion is powered fully or mostly by electricity. EVs encompass a wide range of transportation modes, including road vehicle, road and rail vehicles, electric boats and Submersible, submer ...
(EV) that uses electrical energy
Electrical energy is the energy transferred as electric charges move between points with different electric potential, that is, as they move across a voltage, potential difference. As electric potential is lost or gained, work is done changing the ...
exclusively from an on-board battery pack to power one or more electric
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
traction motor
A traction motor is an electric motor used for propulsion of a vehicle, such as locomotives, electric vehicle, electric or hydrogen vehicles, or electric multiple unit trains.
Traction (engineering), Traction motors are used in electrically powe ...
s, on which the vehicle solely relies for propulsion
Propulsion is the generation of force by any combination of pushing or pulling to modify the translational motion of an object, which is typically a rigid body (or an articulated rigid body) but may also concern a fluid. The term is derived from ...
.
This definition excludes hybrid electric vehicle
A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) is a type of hybrid vehicle that couples a conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) with one or more electric engines into a hybrid vehicle drivetrain, combined propulsion system. The presence of the electri ...
s (HEVs; including mild, full and plug-in hybrid
A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) or simply plug-in hybrid is a type of hybrid electric vehicle equipped with a rechargeable battery pack that can be directly replenished via a charging cable plugged into an external electric power so ...
s), which use internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal comb ...
s (ICEs) in adjunct to electric motors for propulsion; and fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) and range-extended electric vehicles (REEVs), which consume fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work (physics), work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chem ...
through a fuel cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most bat ...
or an ICE-driven generator to produce electricity needed for the electric motors. BEVs have no fuel tank
A fuel tank (also called a petrol tank or gas tank) is a safe container for Flammability, flammable fluids, often gasoline or diesel fuel. Though any storage tank for fuel may be so called, the term is typically applied to part of an engine sys ...
s and replenish their energy storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an Accumulator (energy), accumulator or Batte ...
by plugging into a charging station
A charging station, also known as a charge point, chargepoint, or electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE), is a power supply electrical device, device that supplies electrical power for recharging plug-in electric vehicles (including batter ...
, electrical grid
An electrical grid (or electricity network) is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids consist of power stations, electrical substations to step voltage up or down, electric power tran ...
or getting a new battery at a battery swap station, and use motor controller
A motor controller is a device or group of devices that can coordinate in a predetermined manner the performance of an electric motor. A motor controller might include a manual or automatic means for starting and stopping the motor, selecting forw ...
s to modulate the output engine power
Engine power is the power that an engine can develop. It can be expressed in power units, most commonly kilowatt, metric horsepower (often abbreviated PS), or horsepower. In terms of internal combustion engines, the engine power usually describ ...
and torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. Wh ...
, thus eliminating the need for clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that allows an output shaft to be disconnected from a rotating input shaft. The clutch's input shaft is typically attached to a motor, while the clutch's output shaft is connected to the mechanism that does th ...
es, transmissions and sophisticated engine cooling as seen in conventional ICE vehicles. BEVs include – but are not limited to – all battery-driven electric car
An electric car or electric vehicle (EV) is a passenger car, passenger automobile that is propelled by an electric motor, electric traction motor, using electrical energy as the primary source of propulsion. The term normally refers to a p ...
s, bus
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a motor vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van, but fewer than the average rail transport. It is most commonly used ...
es, truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport freight, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame construct ...
s, forklift
A forklift (also called industrial truck, lift truck, jitney, hi-lo, fork truck, fork hoist, and forklift truck) is a powered industrial truck used to lift and move materials over short distances. The forklift was developed in the early 20th c ...
s, motorcycles and scooters, bicycle
A bicycle, also called a pedal cycle, bike, push-bike or cycle, is a human-powered transport, human-powered or motorized bicycle, motor-assisted, bicycle pedal, pedal-driven, single-track vehicle, with two bicycle wheel, wheels attached to a ...
s, skateboard
A skateboard is a type of sports equipment used for skateboarding. It is usually made of a specially designed 7–8-ply maple plywood deck and has polyurethane wheels attached to the underside by a pair of skateboarding trucks.
The skateboard ...
s, railcar
A railcar (not to be confused with the generic term railroad car or railway car) is a self-propelled railway vehicle designed to transport passengers. The term "railcar" is usually used in reference to a train consisting of a single coa ...
s, boat
A boat is a watercraft of a large range of types and sizes, but generally smaller than a ship, which is distinguished by its larger size or capacity, its shape, or its ability to carry boats.
Small boats are typically used on inland waterways s ...
and personal watercraft
A personal watercraft (PWC), also called Jet Ski or water scooter, is a primarily recreational watercraft that is designed to hold only a small number of occupants, who sit or stand on top of the craft, not within the craft as in a boat.
P ...
, although in common usage the term usually refers specifically to passenger cars.
In 2016, there were 210 million electric bikes worldwide used daily. Cumulative global sales of highway-capable light-duty pure electric car
An electric car or electric vehicle (EV) is a passenger car, passenger automobile that is propelled by an electric motor, electric traction motor, using electrical energy as the primary source of propulsion. The term normally refers to a p ...
vehicles passed the one million unit milestone in September 2016. , the world's top-selling all-electric car in history is the Tesla Model Y, with an estimated 3.4 million sales, followed by the Tesla Model 3
The Tesla Model 3 is a Battery electric vehicle, battery electric powered Mid-size car, mid-size sedan with a fastback body style built by Tesla, Inc., introduced in 2017. The vehicle is marketed as being more affordable to more people than pr ...
with over 2.6 million sales, and the Wuling Hongguang Mini EV with 1.4 million sales .
History
During the 1880s,Gustave Trouvé
Gustave Pierre Trouvé (2 January 1839 – 27 July 1902) was a French electrical engineer and inventor in the 19th century. A polymath, he was highly respected for his innovative skill in miniaturization.
Early life and education
Gustave Trouvé ...
, Thomas Parker and Andreas Flocken built experimental electric cars, but the first practical battery electric vehicles appeared during the 1890s. Battery vehicle milk float
A milk float is a vehicle specifically designed for the Delivery (commerce), delivery of fresh milk. Today, milk floats are usually battery electric vehicles (BEV), but they were formerly Float (horse-drawn), horse-drawn floats. They were ...
s expanded in 1931, and by 1967, gave Britain the largest electric vehicle fleet in the world.
Terminology
Hybrid electric vehicle
A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) is a type of hybrid vehicle that couples a conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) with one or more electric engines into a hybrid vehicle drivetrain, combined propulsion system. The presence of the electri ...
s use both electric motors and internal combustion engines, and are not considered pure or all-electric vehicles.
Hybrid electric vehicles whose batteries can be charged externally are called plug-in hybrid
A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) or simply plug-in hybrid is a type of hybrid electric vehicle equipped with a rechargeable battery pack that can be directly replenished via a charging cable plugged into an external electric power so ...
electric vehicles (PHEV) and run as BEVs during their charge-depleting mode. PHEVs with a series
Series may refer to:
People with the name
* Caroline Series (born 1951), English mathematician, daughter of George Series
* George Series (1920–1995), English physicist
Arts, entertainment, and media
Music
* Series, the ordered sets used i ...
powertrain
In a motor vehicle, the powertrain comprises the main components that generate engine power, power and deliver that power to the road surface, water, or air. This includes the internal combustion engine, engine, transmission (mechanics), trans ...
are also called range-extended electric vehicles (REEVs), such as the Chevrolet Volt
The Chevrolet Volt is an electric vehicle car that was manufactured by General Motors, and also marketed in rebadged variants as the Holden Volt in Australia and New Zealand and the Buick Velite 5 in China, and with a different fascia as the ...
and Fisker Karma
The Fisker Karma is a luxury vehicle, luxury plug-in Range extender (vehicle), range-extended electric sports sedan produced by Fisker Automotive between 2011 and 2012. The cars were manufactured at Valmet Automotive in Finland.
The United St ...
.
Plug-in electric vehicle
A plug-in electric vehicle (PEV) is any road vehicle that can utilize an external source of electricity (such as a wall socket that connects to the power grid) via an detachable power cable to store electrical energy within its onboard rechar ...
s (PEVs) are a subcategory of electric vehicle
An electric vehicle (EV) is a motor vehicle whose propulsion is powered fully or mostly by electricity. EVs encompass a wide range of transportation modes, including road vehicle, road and rail vehicles, electric boats and Submersible, submer ...
s that includes battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid vehicles
Plug-in, plug in or plugin may refer to:
* Plug-in (computing), a software component that adds a specific feature to an existing computer program
** Audio plug-in, adds audio signal processing features
** Photoshop plugin, a piece of software tha ...
(PHEVs).
The electric vehicle conversion
In automobile engineering, electric vehicle conversion is the replacement of a car's combustion engine and connected components with an electric motor and batteries, to create a battery electric vehicle (BEV).
There are two main aims for conver ...
s of hybrid electric vehicles and conventional internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal comb ...
vehicles (aka all-combustion vehicles) belong to one of the two categories.''See definition on pp. 2.''
In China, plug-in electric vehicles, together with hybrid electric vehicles are called new energy vehicles (NEVs). ''See Acronyms and Key Terms, pp. v'' However, in the United States, neighborhood electric vehicles (NEVs) are battery electric vehicles that are legally limited to roads with posted speed limits no higher than , are usually built to have a top speed of , and have a maximum loaded weight of .
Vehicles by type
The concept of battery electric vehicles is to use charged batteries on board vehicles for propulsion. Battery electric cars are becoming more and more attractive with the higher oil prices and the advancement of new battery technology (lithium-ion
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible Intercalation (chemistry), intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically Electrical conductor, conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are c ...
) that have higher power and energy density
In physics, energy density is the quotient between the amount of energy stored in a given system or contained in a given region of space and the volume of the system or region considered. Often only the ''useful'' or extractable energy is measure ...
(i.e., greater possible acceleration and more range with fewer batteries). Compared to older battery types such as lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, energy ...
for example now have an energy density of 0.9–2.63 MJ/L whereas lead-acid batteries had an energy density of 0.36 MJ/L (so 2.5 to 7.3x higher). There is still a long way to go if comparing it to petroleum-based fuels and biofuels, however (gasoline having an energy density of 34.2 MJ/L -38x to 12.92x higher- and ethanol having an energy of 24 MJ/L -26x to 9.12x higher-). This is partially offset by higher conversion efficiency of electric motors – BEVs travel roughly 3x further than similar-size internal combustion vehicles per MJ of stored energy.
BEVs include automobile
A car, or an automobile, is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars state that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, peopl ...
s, light trucks
Light truck or light-duty truck is a US classification for vehicles with a gross vehicle weight up to and a payload capacity up to . Similar goods vehicle classes in the European Union, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand are termed light ...
, and neighborhood electric vehicles.
Rail
* Battery electric railcars:Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
. They are charged via pantographs, either when driving on electrified railway lines or during stops at specially equipped train stations. They use battery power for propulsion when driving on railway lines that are not electrified, and have successfully replaced diesel multiple units on some such lines.
Other countries have also tested or ordered such vehicles.
* Locomotives:
* Electric rail trolley
Bus
Chattanooga, Tennessee
Chattanooga ( ) is a city in Hamilton County, Tennessee, United States, and its county seat. It is located along the Tennessee River and borders Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the south. With a population of 181,099 in 2020, it is Tennessee ...
, operates nine zero-fare
Free public transport, often called fare-free public transit or zero-fare public transport, is public transport which is fully funded by means other than collecting fares from passengers. It may be funded by national, regional or local governme ...
electric buses, which have been in operation since 1992 and have carried 11.3 million passengers and covered a distance of . They were made locally by Advanced Vehicle Systems. Two of these buses were used for the 1996 Summer Olympics
The 1996 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXVI Olympiad, also known as Atlanta 1996 and commonly referred to as the Centennial Olympic Games) were an international multi-sport event held from July 19 to August 4, 1996, in Atlanta, ...
in Atlanta.
Beginning in the summer of 2000, Hong Kong Airport
Hong Kong International Airport is an international airport on the island of Chek Lap Kok in western Hong Kong. The airport is also referred to as Chek Lap Kok International Airport or Chek Lap Kok Airport, to distinguish it from its predec ...
began operating a 16-passenger Mitsubishi Rosa
The Mitsubishi Fuso Rosa () is a Japanese minibus based on the Mitsubishi Fuso Canter manufactured by Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus Corporation. The Mitsubishi Fuso Rosa was launched in 1960 and is now in its fifth generation, known as the BE7 ...
electric shuttle bus, and in the fall of 2000, New York City began testing a 66-passenger battery-powered school bus
A school bus is any type of bus owned, leased, contracted to, or operated by a school or school district. It is regularly used to Student transport, transport students to and from school or school-related activities, but not including a charter ...
, an all-electric version of the Blue Bird TC/2000. A similar bus was operated in Napa Valley, California, for 14 months ending in April 2004.
The 2008 Beijing Olympics
The 2008 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XXIX Olympiad () and officially branded as Beijing 2008 (), were an international multisport event held from 8 to 24 August 2008, in Beijing, China. A total of 10,942 athletes fro ...
used a fleet of 50 electric buses, which have a range of with the air conditioning on. They use lithium-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, energy ...
, and consume about . The buses were designed by the Beijing Institute of Technology and built by the Jinghua Coach. The batteries are replaced with fully charged ones at the recharging station to allow 24-hour operation of the buses.
In France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, the electric bus phenomenon is in development, but some buses are already operating in numerous cities. PVI, a medium-sized company located in the Paris region, is one of the leaders of the market with its brand Gepebus (offering Oreos 2X and Oreos 4X).
In the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, the first battery-electric, fast-charge bus has been in operation in Pomona, California
Pomona ( ) is a city in eastern Los Angeles County, California, United States. Pomona is located in the Pomona Valley, between the Inland Empire and the San Gabriel Valley. At the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the city's population was ...
, since September 2010 at Foothill Transit
Foothill Transit is a public transit agency that is government funded by 22 member cities in the San Gabriel and Pomona valleys. It operates a fixed-route bus public transit service in the San Gabriel Valley region of eastern Los Angeles Cou ...
. The Proterra EcoRide BE35 uses lithium-titanate batteries and is able to fast-charge in less than 10 minutes.
In 2012, heavy-duty trucks and buses contributed 7% of global warming emissions in California.
In 2014, the first production model all-electric school bus was delivered to the Kings Canyon Unified School District in California's San Joaquin Valley
The San Joaquin Valley ( ; Spanish language in California, Spanish: ''Valle de San Joaquín'') is the southern half of California's Central Valley (California), Central Valley. Famed as a major breadbasket, the San Joaquin Valley is an importa ...
. The bus was one of four the district ordered. This battery-electric school bus, which has four sodium nickel batteries, is the first modern electric school bus approved for student transportation by any state.
In 2016, including the light heavy-duty vehicles, there were roughly 1.5 million heavy-duty vehicles in California.
 The same technology is used to power the Mountain View Community Shuttles. This technology was supported by the California Energy Commission, and the shuttle program is being supported by Google.
The same technology is used to power the Mountain View Community Shuttles. This technology was supported by the California Energy Commission, and the shuttle program is being supported by Google.
Thunder Sky
Thunder Sky (based in Hong Kong) buildslithium-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, energy ...
used in submarines and has three models of electric buses, the 10/21 passenger EV-6700 with a range of under 20 mins quick-charge, the EV-2009 city buses, and the 43 passenger EV-2008 highway bus, which has a range of under quick-charge (20 mins to 80 percent), and under full charge (25 mins). The buses will also be built in the United States and Finland.
Free Tindo
Tindo is an all-electric bus fromAdelaide, Australia
Adelaide ( , ; ) is the list of Australian capital cities, capital and most populous city of South Australia, as well as the list of cities in Australia by population, fifth-most populous city in Australia. The name "Adelaide" may refer to ei ...
. The Tindo (aboriginal word for sun) is made by Designline International in New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
and gets its electricity from a solar PV system on Adelaide's central bus station
A bus station, bus depot, or bus interchange is a structure where city buses or intercity buses stop to pick up and drop off passengers. A bus station is larger than a bus stop, which is usually simply a place on the roadside, where buses can st ...
. Rides are zero-fare
Free public transport, often called fare-free public transit or zero-fare public transport, is public transport which is fully funded by means other than collecting fares from passengers. It may be funded by national, regional or local governme ...
as part of Adelaide's public transport system.
First Fast-Charge, Battery-Electric Transit Bus
Proterra's EcoRide BE35 transit bus, called the Ecoliner by Foothill Transit in West Covina, California, is a heavy-duty, fast charge, battery-electric bus. Proterra's ProDrive drive-system uses a UQM motor and regenerative braking that captures 90 percent of the available energy and returns it to the TerraVolt energy storage system, which in turn increases the total distance the bus can drive by 31–35 percent. It can travel on a single charge, is up to 600 percent more fuel-efficient than a typical diesel or CNG bus, and produces 44 percent less carbon than CNG. Proterra buses have had several problems, most notably in Philadelphia where the entire fleet was removed from service.Trucks
For most of the 20th century, the majority of the world's battery electric road vehicles were Britishmilk float
A milk float is a vehicle specifically designed for the Delivery (commerce), delivery of fresh milk. Today, milk floats are usually battery electric vehicles (BEV), but they were formerly Float (horse-drawn), horse-drawn floats. They were ...
s. The 21st century saw the massive development of BYD electric trucks.
Vans
In March 2012,Smith Electric Vehicles
Smith Electric Vehicles (also known as Smith's) was a manufacturer of electric trucks. The company, founded in 1920 in the north of England, moved its headquarters to Kansas City, Missouri in 2011. Smith suspended all operations in 2017.
Smith ...
announced the release of the Newton Step-Van, an all-electric, zero-emission vehicle built on the versatile Newton platform that features a walk-in body produced by Indiana-based Utilimaster.
BYD supplies DHL
DHL (originally named after founders Dalsey, Hillblom and Lynn) is a multinational Import-Export Expert Company, founded in the United States and headquartered in Bonn, Germany. It provides courier, package delivery, and express mail service, ...
with electric distribution fleet of commercial BYD T3.
Cars
Although electric cars often give good acceleration and have generally acceptable top speed, the lower electricpotential energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy of an object or system due to the body's position relative to other objects, or the configuration of its particles. The energy is equal to the work done against any restoring forces, such as gravity ...
of production batteries available in 2015 compared with the chemical potential energy of carbon-based fuel Carbon-based may refer to:
* Biology
* based on Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to fo ...
s means that electric cars need batteries that are a fairly large fraction of the vehicle mass but still often give a relatively low range between charges. Recharging can also take significant lengths of time. For journeys within a single battery charge, rather than long journeys, electric cars are practical forms of transportation and can be recharged overnight.
Electric cars can significantly reduce city pollution by having zero emissions. Vehicle greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
savings depend on how the electricity is generated.
Electric cars are having a major impact in the auto industry given advantages in city pollution, less dependence on oil and combustion, and scarcity and expected rise in gasoline prices. World governments are pledging billions to fund development of electric vehicles and their components.
Formula E
Formula E, officially the ABB FIA Formula E World Championship, is an open-wheel single-seater motorsport championship for electric cars. The racing series is the highest class of competition for electrically powered single-seater racing cars ...
is a fully electric international single-seater championship. The series was conceived in 2012, and the inaugural championship started in Beijing on 13 September 2014. The series is sanctioned by the FIA. Alejandro Agag is the current CEO of Formula E.
The Formula E championship is currently contested by ten teams with two drivers each (after the withdrawal of Team Trulli, there are temporarily only nine teams competing). Racing generally takes place on temporary city-center street circuits which are approximately long. Currently, only the Mexico City ePrix takes place on a road course, a modified version of the Autódromo Hermanos Rodríguez.
Special-purpose vehicles
Special-purpose vehicle
A special-purpose entity (SPE), also called a special-purpose vehicle (SPV) or a financial vehicle corporation (FVC), is a legal entity (usually a limited company of some type or, sometimes, a limited partnership) created to fulfill narrow, speci ...
s come in a wide range of types, ranging from relatively common ones such as golf carts, things like electric golf trolleys, milk float
A milk float is a vehicle specifically designed for the Delivery (commerce), delivery of fresh milk. Today, milk floats are usually battery electric vehicles (BEV), but they were formerly Float (horse-drawn), horse-drawn floats. They were ...
s, all-terrain vehicle
An all-terrain vehicle (ATV), also known as a light utility vehicle (LUV), a quad bike or quad (if it has four wheels), as defined by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), is a vehicle that travels on low-pressure tires, has a seat ...
s, neighborhood electric vehicles, and a wide range of other devices. Certain manufacturers specialize in electric-powered "in plant" work machines.
Motorcycles, scooters and rickshaws
Three-wheeled vehicles include electric rickshaws, a powered variant of thecycle rickshaw
The cycle rickshaw is a small-scale local means of transport. It is a type of tricycle designed to carry passengers on a vehicle for hire, for-hire basis. It is also known by a variety of other names such as bike taxi, velotaxi, pedicab, bi ...
. The large-scale adoption of electric two-wheelers can reduce traffic noise and road congestion but may necessitate adaptations of the existing urban infrastructure and safety regulations.
Ather Energy
Ather Energy is an Indian electric two-wheeler manufacturer headquartered in Bengaluru. It was founded by Tarun Mehta and Swapnil Jain in 2013. It manufactures electric scooters including the Ather 450 series and Ather Rizta. It has EV man ...
from India has launched their BLDC motor powered Ather 450 electric scooter with Lithium Ion batteries in 2018. Also from India, AVERA – a new and renewable energy company is going to launch two models of electric scooters at the end of 2018, with Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery
The lithium iron phosphate battery ( battery) or LFP battery (''lithium ferrophosphate'') is a type of lithium-ion battery using lithium iron phosphate () as the cathode material, and a graphitic carbon electrode with a metallic backing as t ...
technology.
Bicycles

 India is the world's biggest market for bicycles at 22 million units per year. By 2024, electric two-wheelers will be a $2 billion market with over 3 million units being sold in India.
The Indian government is launching schemes and incentives to promote the adoption of electric vehicles in the country, and is aiming to be a manufacturing hub for electric vehicles within the next five years.
China has experienced an explosive growth of sales of non-assisted e-bikes including the scooter type, with annual sales jumping from 56,000 units in 1998 to over 21 million in 2008, and reaching an estimated 120 million e-bikes on the road in early 2010. China is the world's leading manufacturer of e-bikes, with 22.2 million units produced in 2009.
India is the world's biggest market for bicycles at 22 million units per year. By 2024, electric two-wheelers will be a $2 billion market with over 3 million units being sold in India.
The Indian government is launching schemes and incentives to promote the adoption of electric vehicles in the country, and is aiming to be a manufacturing hub for electric vehicles within the next five years.
China has experienced an explosive growth of sales of non-assisted e-bikes including the scooter type, with annual sales jumping from 56,000 units in 1998 to over 21 million in 2008, and reaching an estimated 120 million e-bikes on the road in early 2010. China is the world's leading manufacturer of e-bikes, with 22.2 million units produced in 2009.
Personal transporters
An increasing variety ofpersonal transporter
A personal transporter (also powered transporter, electric rideable, personal light electric vehicle, personal mobility device, etc.) is any of a class of compact, mostly recent (21st century), motorised micromobility vehicle for transporting an ...
s are being manufactured, including the one-wheeled self-balancing unicycle
An electric unicycle (often initialized as EUC or acronymized yuke or Uni) is a self-balancing personal transporter with a unicycle, single wheel. The rider controls speed by leaning forwards or backwards, and steers by twisting or tilting the uni ...
s, self-balancing scooter
A self-balancing scooter (also hoverboard, self-balancing board, electric scooter board, or swegway) is a self-balancing personal transporter consisting of two motorized wheels connected to a pair of articulated pads on which the rider places the ...
s, electric kick scooters, and electric skateboard
An electric skateboard is a personal transporter based on a skateboard. The speed is usually controlled by a wireless hand-held throttle remote, or rider body weight-shifting between front of the board for forward motion and rear for braking. As ...
s.
Boats
Several battery electric ships operate throughout the world, some for business. Electricferries
A ferry is a boat or ship that transports passengers, and occasionally vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A small passenger ferry with multiple stops, like those in Venice, Italy, is sometimes referred to as a water taxi or water bus.
...
are being operated and constructed.
Technology
Motor controllers
The motor controller receives a signal from potentiometers linked to the accelerator pedal, and it uses this signal to determine how much electric power is needed. This DC power is supplied by the battery pack, and the controller regulates the power to the motor, supplying either variable pulse width DC or variable frequency variable amplitude AC, depending on the motor type. The controller also handlesregenerative braking
Regenerative braking is an energy recovery mechanism that slows down a moving vehicle or object by converting its kinetic energy or potential energy into a form that can be either used immediately or stored until needed.
Typically, regenerativ ...
, whereby electrical power is gathered as the vehicle slows down and this power recharges the battery. In addition to power and motor management, the controller performs various safety checks such as anomaly detection, functional safety tests and failure diagnostics.
Battery pack
 Most electric vehicles today use an
Most electric vehicles today use an electric battery
An electric battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices. When a battery is supplying power, its positive Terminal (electronics), terminal is the ...
, consisting of electrochemical cell
An electrochemical cell is a device that either generates electrical energy from chemical reactions in a so called galvanic cell, galvanic or voltaic cell, or induces chemical reactions (electrolysis) by applying external electrical energy in an ...
s with external connections in order to provide power to the vehicle.
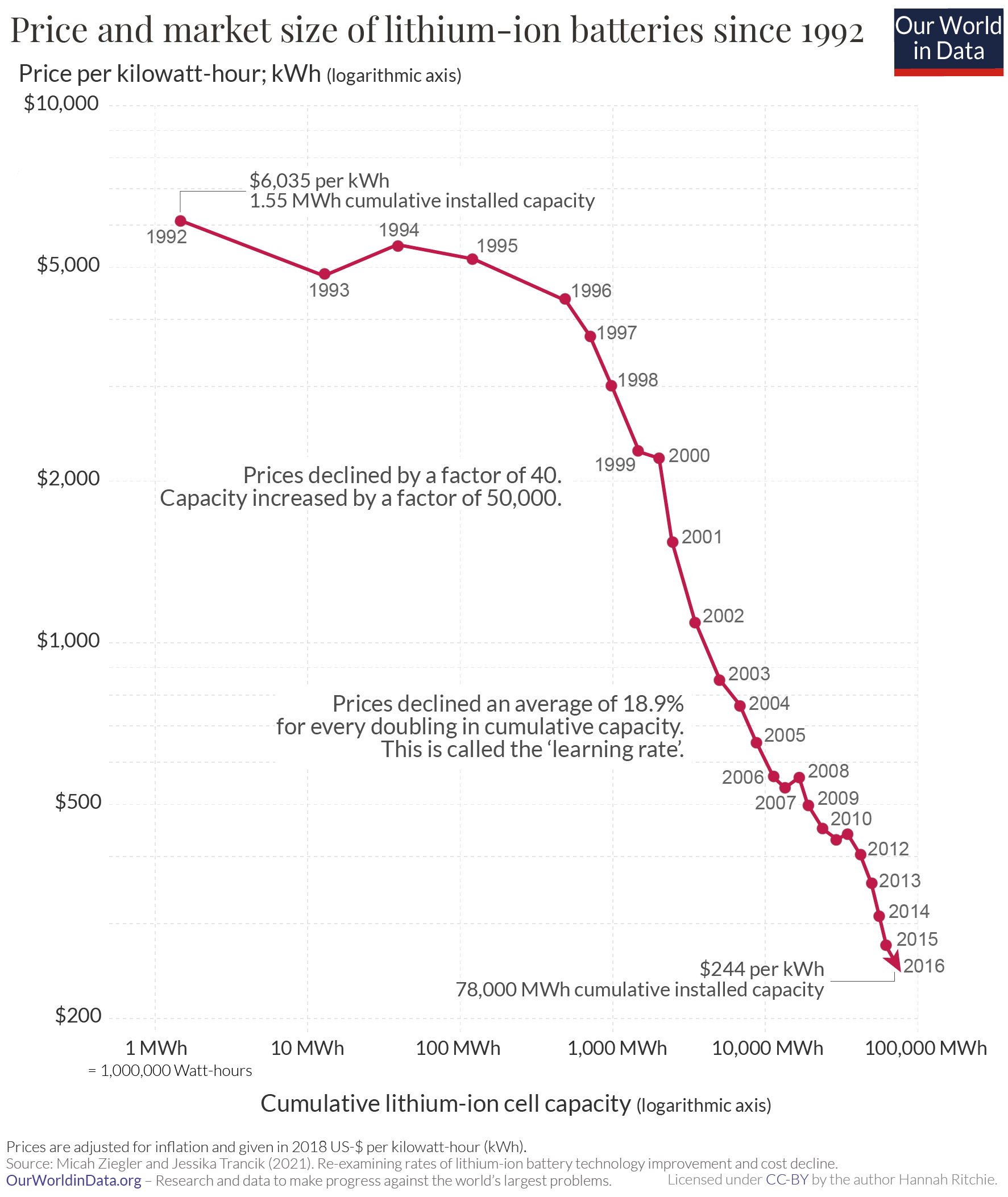
Battery technology for EVs has developed from early lead-acid batteries used in the late 19th century to the 2010s, to lithium-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, energy ...
which are found in most EVs today. The overall battery is referred to as a battery pack
A battery pack is a set of any number of (preferably) identical Battery (electricity), batteries or individual battery cells. They may be configured in a series, parallel or a mixture of both to deliver the desired voltage and current. The term ' ...
, which is a group of multiple battery modules and cells. For example, the Tesla Model S battery pack has up to 7,104 cells, split into 16 modules with 6 groups of 74 cells in each. Each cell has a nominal voltage of 3–4 volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, Voltage#Galvani potential vs. electrochemical potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units, International System of Uni ...
s, depending on its chemical composition.
Motors
Electric cars have traditionally used series wound DC motors, a form of brushed DC electric motor. Separately excited and permanent magnet are just two of the types of DC motors available. More recent electric vehicles have made use of a variety ofAC motor
An AC motor is an electric motor driven by an alternating current (AC). The AC motor commonly consists of two basic parts, an outside stator having coils supplied with alternating current to produce a rotating magnetic field, and an inside roto ...
types, as these are simpler to build and have no brushes that can wear out. These are usually induction motor
An induction motor or asynchronous motor is an AC motor, AC electric motor in which the electric current in the rotor (electric), rotor that produces torque is obtained by electromagnetic induction from the magnetic field of the stator winding ...
s or brushless AC electric motors which use permanent magnets. There are several variations of the permanent magnet motor which offer simpler drive schemes and/or lower cost including the brushless DC electric motor.
Once electric power is supplied to the motor (from the controller), the magnetic field interaction inside the motor will turn the drive shaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft (Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power (physics), power, torque, and rotation, usually ...
and ultimately the vehicle's wheels.
Economy
EV battery storage is a key element for the globalenergy transition
An energy transition (or energy system transformation) is a major structural change to energy supply and consumption in an energy system. Currently, a transition to sustainable energy is underway to limit climate change. Most of the sustainab ...
which is dependent on more electricity storage right now. As energy availability is the most important factor for the vitality of an economy the mobile storage infrastructure of EV batteries can be seen as one of the most meaningful infrastructure projects facilitating the energy transition to a fully sustainable economy based on renewables. A meta-study graphically showing the importance of electricity storage depicts the technology in context.
Environmental impact
Power generation
Electric vehicles produce no greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in operation, but the electricity used to power them may do so in its generation. The two factors driving the emissions of battery electric vehicles are thecarbon intensity
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. It belongs to grou ...
of the electricity used to recharge the Electric Vehicle (commonly expressed in grams of per kWh) and the consumption of the specific vehicle (in kilometers/kWh).
The carbon intensity of electricity varies depending on the source of electricity where it is consumed. A country with a high share of renewable energy
Renewable energy (also called green energy) is energy made from renewable resource, renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human lifetime, human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind pow ...
in its electricity mix will have a low C.I. In the European Union, in 2013, the carbon intensity had a strong geographic variability but in most of the member states, electric vehicles were "greener" than conventional ones. On average, electric cars saved 50–60% of emissions compared to diesel and gasoline fuelled engines.
Moreover, the de-carbonisation process is constantly reducing the GHG emissions due to the use of electric vehicles. In the European Union, on average, between 2009 and 2013 there was a reduction in the electricity carbon intensity of 17%. In a life-cycle assessment
Life cycle assessment (LCA), also known as life cycle analysis, is a methodology for assessing the impacts associated with all the stages of the life cycle of a commercial product, process, or service. For instance, in the case of a manufact ...
perspective, considering the GHG necessary to build the battery and its end-of-life, the GHG savings are 10–13% lower.
The open source VencoPy model framework can be used to study the interactions between vehicles, owners, and the electricity system at large.
Vehicle construction
GHGs are also emitted when the electric vehicle is being manufactured. The lithium-ion batteries used in the vehicle take more materials and energy to produce because of the extraction process of the lithium and cobalt essential to the battery. This means the bigger the electric vehicle, the more carbon dioxide emitted. The same size-to-emission relationship applies to manufacturing of all products.Terrestrial Mining
The mines that are used to produce the lithium and cobalt used in the battery are also creating problems for the environment, as fish are dying up to downstream from mining operations due to chemical leaks and the chemicals also leak into the water sources the people that live near the mines use, creating health problems for the animals and people that live nearby.Deep sea mining
Along with terrestrial mining, deep sea mining is a means by which vital minerals such as nickel, copper, cobalt, manganese, zinc, gold and rare-earth metals can be procured. As the name suggests, large robotic cutting machines are used to strip away large areas of the ocean floor in search of minerals embedded within it. These minerals appear as mineral formations such as polymetallic nodules that are roughly the size of a potato. Currently, sea mining projects are underway in areas such as the Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ) in the Pacific Ocean. While there is an abundance of minerals to be found in the ocean, there are many concerns in regards to the environmental impact of deep sea mining. Marine habitats and ecosystems are not only widely understudied, they are also extremely temperamental and even slight disturbances can be incredibly destructive. Deep sea mining affects the quality of the water through sediment plumes and the release of carbon dioxide trapped within ocean floors, directly endangering marine life in the area. Sound pollution is also harmful to marine life in many mining sites, such as dolphins and whales.Barriers to adoption
Current research suggests that BEVs (battery electric vehicles) are the most efficient in reducing GHGs (greenhouse gases). However, adoption of BEVs has varied globally, with China and Europe leading the world in BEV diffusion (''see also'': Electric car use by country) For other nations that have found diffusion more difficult, buyers generally express one or more of four main reasons for their hesitance in purchasing battery electric vehicles. These include: the cost of this type of vehicle, the availability of charging stations, their range versus that of an internal combustion engine, and the cost of repairs/replacement parts. Other factors affecting the adoption of BEV technology are more nuanced or political.United States
In the United States, political ideology impacts the adoption of BEVs. Those who identify as Republican are less likely to purchase BEVs than those who identify as Democrats. This phenomenon likely has its roots in the positions of the parties regarding environmentalism and climate change. Historically, Republicans have expressed negative attitudes towards environmental and climate change policies; conversely, Democrats tend to be in favor of these types of policies A current example of this polarity can be found within both party's 2024 platforms. The preamble for the Democratic platform states, “We're fighting climate change, reducing pollution, and fueling a clean energy boom.” The preamble for the Republican platform states, “we must unleash American Energy…We will DRILL, BABY, DRILL and we will become Energy Independent, and even Dominant again." Moreover, a 2021 article titled, “7 Ways Oil and Gas Drilling is Bad for the Environment”, published by American non-profit The Wilderness Society states in its introduction that, “ l and gas drilling has a serious impact on our wildlands and communities. Drilling projects operate around the clock generating pollution, fueling climate change, disrupting wildlife and damaging public lands that were set aside to benefit all people.” A result of this political dichotomy, those who identify as members of the two main American parties will similarly have either a greater support or a greater opposition to such policies and, subsequently, of BEVs. Another important occurrence in recent years is the rise of right-wing populism within the Republican party under the leadership of Donald Trump. Trump and those within his party known as “MAGA-Republicans” have espoused greater skepticism of the effects of climate change and policies that aim to regulate industries such as that of fossil fuel. However, there are Republicans and other conservatives that are working towards changing these attitudes within party lines, which may allow for bipartisan cooperation in adopting cleaner energy technologies.Japan
In Japan, where EV technology started developing after World War II, there is domestic resistance to the diffusion of this technology that results from both the general public's wariness and the unique composition of the automotive industry in this country. Concerns from Japanese citizens are similar to those of the global public (i.e. infrastructure, price, grid capacity, performance, etc.) For automotive manufacturers, however, the diffusion of BEV technology has disruptive effects on the current infrastructure of automotive production. Known as the KEIRETSU system, the major car companies in Japan (i.e. Toyota, Honda, and Nissan imitedly subcontract the production of specific parts to smaller, independent companies in an effort to make the overall production process more efficient. This system creates a top-down (“vertical”), hierarchical division of labor that includes hundreds of smaller Japanese manufacturing companies. The more “horizontal,” global cooperation-based model that EV production currently employs could be detrimental to those smaller Japanese companies employed by the major auto manufacturers. Automotive business leader, Akio Toyoda, chairman of Toyota stated recently that there are roughly 5.5 million jobs in jeopardy amidst the country's transition to EV and BEV technology. Groups such as The Japanese Automobile Manufacturers Association (JAMA), who serve the interest of Japan's auto industry, have also argued that a transition to BEVs puts large amounts of jobs in the automotive industry at risk.See also
* All-electric range *Automotive battery
An automotive battery, or car battery, is a usually 12 Volt lead-acid rechargeable battery that is used to start a motor vehicle, and to power lights, screen wiper etc. while the engine is off.
Its main purpose is to provide an electric curren ...
*Battery balancing
Battery balancing and battery redistribution refer to techniques that improve the available capacity of a battery pack with multiple cells (usually in series) and increase each cell's longevity. A ''battery balancer'' or ''regulator'' is a ...
* Capa vehicle
* Electric Drive Transportation Association (EDTA)
*Electric vehicle battery
An electric vehicle battery is a rechargeable battery used to power the electric motors of a battery electric vehicle (BEV) or hybrid electric vehicle (HEV).
They are typically lithium-ion batteries that are designed for high power-to-weigh ...
* Electric vehicle warning sounds
* Global Electric Motorcars
*Government incentives for plug-in electric vehicles
Government incentives for plug-in electric vehicles have been established around the world to support policy-driven adoption of plug-in electric vehicles. These incentives mainly take the form of purchase rebates, tax exemptions and tax credi ...
* Greenpower
*Hydrogen vehicle
A hydrogen vehicle is a vehicle that uses hydrogen to move. Hydrogen vehicles include some road vehicles, rail vehicles, space rockets, forklifts, ships and aircraft. Motive power is generated by converting the chemical energy of hydrogen to me ...
* List of battery electric vehicles
* List of electric vehicle battery manufacturers
* List of production battery electric vehicles
* Miles per gallon gasoline equivalent
* Patent encumbrance of large automotive NiMH batteries
*Phase-out of fossil fuel vehicles
A phase-out of fossil fuel vehicles are proposed bans or discouragement (for example via taxes) on the sale of new fossil-fuel powered vehicles or use of existing fossil-fuel powered vehicles, as well the encouragement of using modal share, oth ...
* Road-powered electric vehicle
* Short-commute vehicles
*Supercapacitor
alt=Supercapacitor, upright=1.5, Schematic illustration of a supercapacitor
upright=1.5, A diagram that shows a hierarchical classification of supercapacitors and capacitors of related types
A supercapacitor (SC), also called an ultracapacitor, ...
* Think Global
*Tokyo Electric Power Company
is a Japanese electric utility holding company servicing Japan's Kantō region, Yamanashi Prefecture, and the eastern portion of Shizuoka Prefecture. This area includes Tokyo. Its headquarters are located in Uchisaiwaicho, Chiyoda, Tokyo, an ...
* Wireless charging
* Personal electric vehicle (PEV)
References
Further reading
* Witkin, JimBuilding Better Batteries for Electric Cars
''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'', 31 March 2011, p. F4. Published online 30 March 2011. Discusses rechargeable batteries
A rechargeable battery, storage battery, or secondary cell (formally a type of energy accumulator), is a type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or prima ...
and the new-technology lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, energy d ...
.
External links
;Patents * , Emil E. Keller,Electrically Propelled Perambulator
', 1894 * , Hiram Percy Maxim, ''Motor vehicle'', 1897 * , Hiram Percy Maxim et al.,
Electric motor vehicle
', 1904 ;Organizations
Battery Vehicle Society (UK)
Zap-Map – the UK national directory of recharging points
The European Association for Battery, Hybrid and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (AVERE)
Czech EV Club – (CZ) Eng. section in photogallery
Alternative Technology Association Electric Vehicle Interest Group
Australian Electric Vehicle Association
Electric Car Society
;News
(Green Car Congress) * [https://web.archive.org/web/20110815220501/http://www.dailytech.com/Ford+Focus+Electric+to+go+GridNeutral+With+the+Help+of+SunPower+Panels/article22416.htm Solar charging station for Ford Focus Electric Vehicle] ;Studies * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Battery Electric Vehicle Battery electric vehicles, Automotive technologies Sustainable technologies