astrological aspect on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
''Conjunctions of Jupiter and Saturn''
Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada, Vol. 94, p.174 Greater importance is attributed to the beginning of a new cycle, which may occur after all four Trigons have been visited, which occurs in ~900 years. Typically, medieval astrologers used 960 years as the length of the full cycle, because, in some cases, it took 240 years to pass from one trigon to the next. If a cycle is defined by when the Conjunctions return to the same right ascension rather than to the same constellation, the cycle is only ~800 years, because of
Astrodienst
/ref> Typically, with a Square, Trine or Sextile, the outer or superior planet has an effect on the inner or inferior planet. A Square creates a strong and usable tension. It may integrate between two different areas of your life or it may offer a turning point where an important decision needs to be made that involves an opportunity at a cost. Typically, if it involves
 A Semisextile or ''Duodecile'' is an angle of 30°, which is 1/12 of the 360°
A Semisextile or ''Duodecile'' is an angle of 30°, which is 1/12 of the 360°
 A
A
Regular star polygon 12-5.svg, Dodecagram
Regular star polygon 7-2.svg,
 An Octile or ''Semisquare'' is an angle of 45°, which is 1/8 of the 360°
An Octile or ''Semisquare'' is an angle of 45°, which is 1/8 of the 360°  A Sesquiquadrate or ''Trioctile'' is an angle of 135°, which is 3/8 of the 360° ecliptic. An orb of ±1.5° is allowed.
A Sesquiquadrate is a harmonic of a Semisquare, which involves challenge. It is not an exact division of the 360° ecliptic. Therefore, when a Semisquare is present, it does not function as a standalone aspect, but as part of a series.
A Sesquiquadrate or ''Trioctile'' is an angle of 135°, which is 3/8 of the 360° ecliptic. An orb of ±1.5° is allowed.
A Sesquiquadrate is a harmonic of a Semisquare, which involves challenge. It is not an exact division of the 360° ecliptic. Therefore, when a Semisquare is present, it does not function as a standalone aspect, but as part of a series.
Regular star polygon 8-3.svg,
Regular star polygon 9-2.svg, Enneagram
Regular star polygon 9-4.svg, Enneagram
 A Decile is an angle of 36°, which is 1/10 of the 360°
A Decile is an angle of 36°, which is 1/10 of the 360°  3 A Tridecile is an angle of 108°, which is 3/10 of the 360° ecliptic.
3 A Tridecile is an angle of 108°, which is 3/10 of the 360° ecliptic.
Regular star polygon 10-3.svg, Decagram
Regular star polygon 11-2.svg, Hendecagram
Regular star polygon 11-3.svg, Hendecagram
Regular star polygon 11-4.svg, Hendecagram
Regular star polygon 11-5.svg, Hendecagram
Regular star polygon 16-3.svg, Hexadecagram
Regular star polygon 16-5.svg, Hexadecagram
Regular star polygon 16-7.svg, Hexadecagram
''The Classical Origin & Traditional Use of Aspects''
Deborah Houlding
Online Ephemeris from Khaldea.com
��600BC to 2400AD—Calculated for Midnight
''Harmonices mundi''
("The Harmony of the Worlds") in fulltext facsimile;
astrology
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Di ...
, an aspect is an angle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays, called the '' sides'' of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the '' vertex'' of the angle.
Angles formed by two rays lie in the plane that contains the rays. Angles a ...
that planets make to each other in the Horoscope; as well as to the Ascendant
The ascendant (Asc, Asc or As) is the astrological sign on the eastern horizon when the person was born.
According to certain astrological theories, celestial phenomena reflect or influence human activity on the principle of " as above, so bel ...
, Midheaven
A horoscope (or other commonly used names for the horoscope in English include natal chart, astrological chart, astro-chart, celestial map, sky-map, star-chart, cosmogram, vitasphere, radical chart, radix, chart wheel or simply chart) is an ast ...
, Descendant, Lower Midheaven, and other points of astrological interest. As viewed from Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
, aspects are measured by the angular distance
Angular distance \theta (also known as angular separation, apparent distance, or apparent separation) is the angle between the two sightlines, or between two point objects as viewed from an observer.
Angular distance appears in mathematics (in par ...
in degrees and minutes of ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agains ...
longitude between two points. According to astrological tradition, they indicate the timing of transitions and developmental changes in the lives of people and affairs relative to the Earth.
For example, if an astrologer creates a Horoscope that shows the apparent positions of the celestial bodies at the time of a person's birth (Natal Chart
A horoscope (or other commonly used names for the horoscope in English include natal chart, astrological chart, astro-chart, celestial map, sky-map, star-chart, cosmogram, vitasphere, radical chart, radix, chart wheel or simply chart) is an ast ...
), and the angular distance between Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
and Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
is 92° ecliptic longitude, the chart is said to have the aspect "Venus Square
In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90- degree angles, π/2 radian angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length a ...
Mars" with an orb of 2° (i.e., it is 2° away from being an exact Square; a Square being a 90° aspect). The more exact an aspect, the stronger or more dominant it is said to be in shaping character or manifesting change.
With Natal charts, other signs may take precedence over a Sun sign. For example, an Aries may have several other planets in Cancer or Pisces. Therefore, the two latter signs may be more influential.
History and approach
In medieval astrology, certain aspects andplanet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a you ...
s were considered to be either favorable (benefic
Babylonian astrology was the first known organized system of astrology, arising in the second millennium BC.
In Babylon as well as in Assyria as a direct offshoot of Babylonian culture, astrology takes its place as one of the two chief means a ...
) or unfavorable ( malefic). Modern usage places less emphasis on these fatalistic distinctions. The more modern approach to astrological aspects is exemplified by research on astrological harmonics. In 1619, Johannes Kepler advocates this in his book ''Harmonice Mundi
''Harmonice Mundi (Harmonices mundi libri V)''The full title is ''Ioannis Keppleri Harmonices mundi libri V'' (''The Five Books of Johannes Kepler's The Harmony of the World''). (Latin: ''The Harmony of the World'', 1619) is a book by Johannes ...
''. Thereafter, John Addey was a major proponent. However, even in modern times, aspects are considered to be either easy (60° ''Sextile
In astrology, an aspect is an angle that planets make to each other in the Horoscope; as well as to the Ascendant, Midheaven, Descendant, Lower Midheaven, and other points of astrological interest. As viewed from Earth, aspects are measured ...
'' or
120° '' Trine'') or hard (90° ''Square
In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90- degree angles, π/2 radian angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length a ...
'' or 180° ''Opposition
Opposition may refer to:
Arts and media
* ''Opposition'' (Altars EP), 2011 EP by Christian metalcore band Altars
* The Opposition (band), a London post-punk band
* '' The Opposition with Jordan Klepper'', a late-night television series on Com ...
''). Depending on the involved planets, a ''Conjunction
Conjunction may refer to:
* Conjunction (grammar), a part of speech
* Logical conjunction, a mathematical operator
** Conjunction introduction, a rule of inference of propositional logic
* Conjunction (astronomy), in which two astronomical bodies ...
'' (0°, which is a discounting orb) may be in either category.
Easy aspects may be positive, because they enhance opportunity for talent to grow.
Hard aspects may be negative, because they enhance a challenge where an adjustment must be made to reach balance. Typically, manifestation may occur with a Conjunction, Square or Opposition.
Planets may be considered. Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
and Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus ( Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars), grandfather of Zeus (Jupiter) and father of ...
tend to ignite while Saturn and Neptune inhibit. Whether a planet is direct or retrograde is of great significance. An eclipse of the Sun or Moon is even more significant. The South Node of the Moon denotes innate wisdom from past experience while the North Node denotes karma and evolution.
Astrological Signs may be considered. For example, the fire signs of Aries, Leo and Sagittarius are more compatible with the air signs of Gemini
Gemini may refer to:
Space
* Gemini (constellation), one of the constellations of the zodiac
** Gemini in Chinese astronomy
* Project Gemini, the second U.S. crewed spaceflight program
* Gemini Observatory, consisting of telescopes in the Norther ...
, Libra
Libra generally refers to:
* Libra (constellation), a constellation
* Libra (astrology), an astrological sign based on the star constellation
Libra may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Libra'' (novel), a 1988 novel by Don DeLillo
Musi ...
and Aquarius
Aquarius may refer to:
Astrology
* Aquarius (astrology), an astrological sign
* Age of Aquarius, a time period in the cycle of astrological ages
Astronomy
* Aquarius (constellation)
* Aquarius in Chinese astronomy
Arts and entertainme ...
. The Earth signs of Taurus
Taurus is Latin for 'bull' and may refer to:
* Taurus (astrology), the astrological sign
* Taurus (constellation), one of the constellations of the zodiac
* Taurus (mythology), one of two Greek mythological characters named Taurus
* '' Bos tauru ...
, Virgo
Virgo may refer to:
*Virgo (astrology), the sixth astrological sign of the zodiac
* Virgo (constellation), a constellation
*Virgo Cluster, a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Virgo
*Virgo Stellar Stream, remains of a dwarf galaxy
* Virgo Su ...
and Capricorn are more compatible with the water signs of Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
, Scorpio and Pisces. The mutable signs of Gemini, Virgo, Sagittarius and Pisces may be flexible. The cardinal signs of Aries, Cancer, Libra and Capricorn may change their mind. The fixed signs of Taurus, Leo, Scorpio and Aquarius may be difficult.
Astrological Houses
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
may be considered.
Ptolemaic Aspects
Since they were defined and used byPtolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
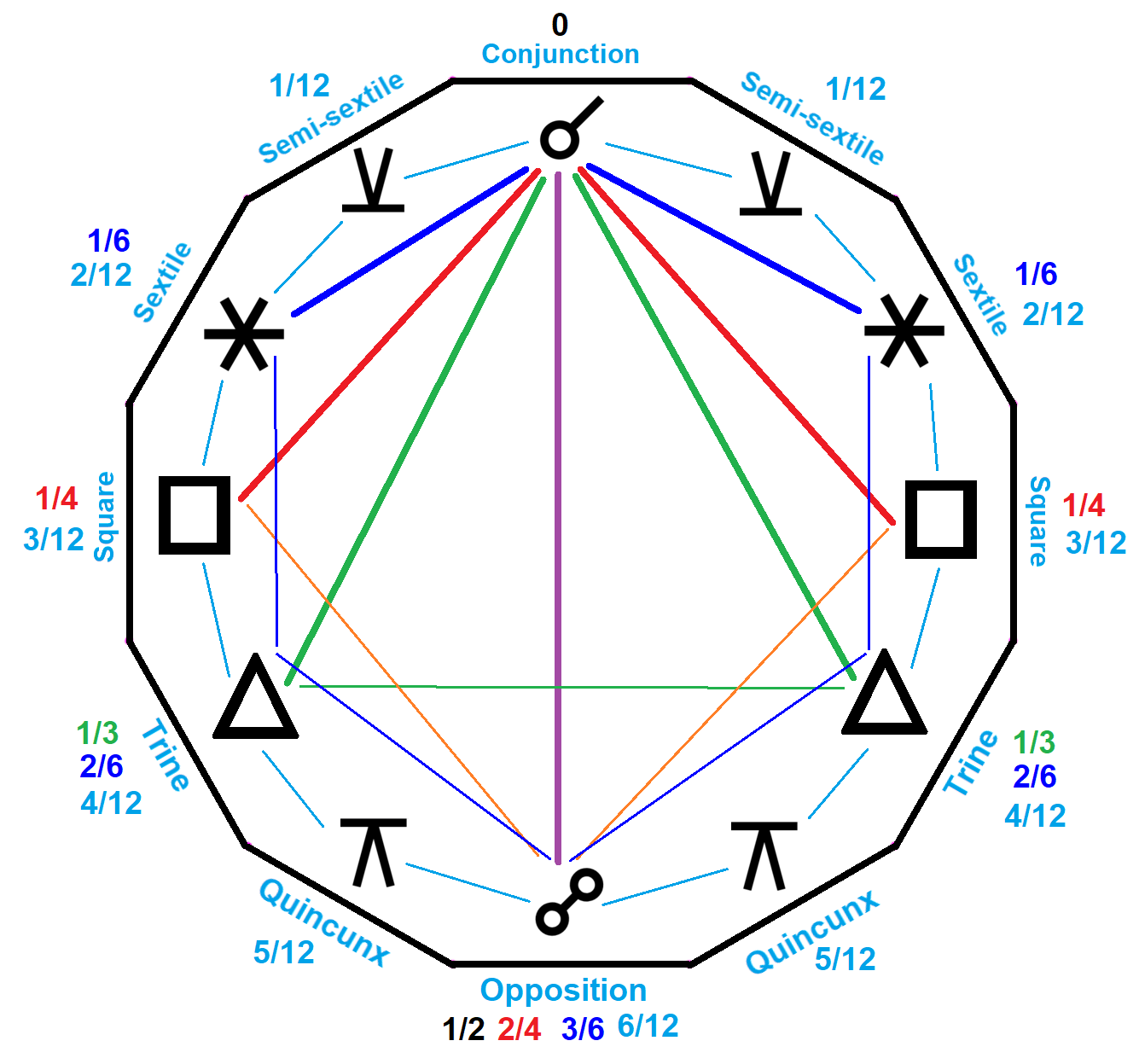
in the 1st Century AD, the traditional major aspects are sometimes called Ptolemaic Aspects. These aspects are the Conjunction (0°), Sextile (60°), Square (90°), Trine (120°), and Opposition (180°). Major aspects are those that are divisible by 10 and evenly divided in relation to 360° (with the exception of the Semisextile).
When calculating or using aspects, it is important to note that different astrologers and separate astrological systems/traditions utilize differing orbs, which is the degree of separation between exactitude. Orbs may also be subject to variation, depending on the need for detail and personal preferences. Although, when compared to other aspects, almost all astrologers use a larger orb for a Conjunction.
Kepler's Aspects
Collective astrological data along with Johannes Kepler described 13 aspects in his book ''Harmonice Mundi
''Harmonice Mundi (Harmonices mundi libri V)''The full title is ''Ioannis Keppleri Harmonices mundi libri V'' (''The Five Books of Johannes Kepler's The Harmony of the World''). (Latin: ''The Harmony of the World'', 1619) is a book by Johannes ...
''. Astrological data grouped together in five degrees of influentially picked from symbol ratios encountered in geometry and music: 0/2, 1/2, 1/5, 2/6, 1/3, 1/12 along with 1/5, 2/5, 15/5, 10, 10/3, 8, and 8/3. The general names for whole divisors are (Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
) ''n''-ile for whole fractions 1/''n'', and ''m''-''n''-ile for fraction ''m''/''n''. A Semi-''n''-tile is a ''2n''-tile, 1/(2''n''), and Sesqui-n-tile is a Tri-2''n''-tile, 3/(2''n'').
All aspects can be seen as small whole number harmonics, (1/''n'' of 360°). Multiples of ''m''/''n'' create new aspects where there are no common factors between ''n'' and ''m'', gcd(n,m)=1.
Major Aspects

Conjunction
A Conjunction (abbreviated as "Con") is an angle of approximately (~) 0–10°. Typically, an orb of ~10° is considered to be a Conjunction. If neither theSun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
or Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
are involved, some astrologers consider a maximum orb of 8°.
Conjunctions are a major aspect in a horoscope chart. They are said to be the most powerful aspects, because they mutually intensify the effects of the involved planets.
Depending on the involved planets, a Conjunction may be beneficial or detrimental. Highly favourable Conjunctions may involve the Sun, Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
, and/or Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth t ...
as well as any of the three possible combinations. Highly ''un''favourable Conjunctions may involve the Moon, Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
, and/or Saturn as well as any of the three possible combinations.
Exceptionally, on November 9–10 of 1970, the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
, Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
, and Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth t ...
were in a 3-way beneficial Conjunction. In that same year, on March 10, the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
, Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
, and Saturn were in 3-way detrimental Conjunction.
If either of two planets involved in a Conjunction is also under tension from one or more hard aspects with one or more other planets, then the added presence of a Conjunction will further intensify the tension of that hard aspect.
If a planet is in ''very'' close Conjunction to the Sun (within 17 minutes of arc or only about 0.28°),
the Conjunction is of great strength. The planet is said to be ''Cazimi'', which is an ancient astrological term meaning "in the heart" (of the Sun). For example, "Venus ''Cazimi''" means Venus is in Conjunction with the Sun with an orb of less than ~0.28°.
If a planet is moderately close to the Sun, the specific orb limit may depend on the particular planet. It is said to be ''Combust''.
Every month of the year, during the New Moon, the Sun and Moon experience a Conjunction.
Great Conjunctions
In the past, Great Conjunctions between the two slowest classical planets,Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth t ...
and Saturn, have attracted considerable attention as celestial omens. This interest can be traced back to Arabic translations found in Europe; most notably Albumasar
Abu Ma'shar al-Balkhi, Latinized as Albumasar (also ''Albusar'', ''Albuxar''; full name ''Abū Maʿshar Jaʿfar ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿUmar al-Balkhī'' ;
, AH 171–272), was an early Persian Muslim astrologer, thought to be the greatest as ...
's book on Conjunctions. During the late Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
and the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
, these omens were a topic broached by most astronomers. This included scholastic thinkers, such as Roger Bacon and Pierre D'Ailly
Pierre d'Ailly (; Latin ''Petrus Aliacensis'', ''Petrus de Alliaco''; 13519 August 1420) was a French theologian, astrologer and cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church.
Academic career
D'Ailly was born in Compiègne in 1350 or 1351 of a prospero ...
. Omens are also mentioned in popular literary writings by authors, such as Dante
Dante Alighieri (; – 14 September 1321), probably baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante (, ), was an Italian people, Italian Italian poetry, poet, writer and philosopher. His ''Divine Comedy'', origin ...
Woody K., ''Dante and the Doctrine of the Great Conjunctions'', Dante Studies, with the Annual Report of the Dante Society, No. 95 (1977), pp. 119–134 and Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's natio ...
.Aston M., ''The Fiery Trigon Conjunction: An Elizabethan Astrological Prediction'', Isis, Vol. 61, No. 2 (Summer, 1970), pp. 158–187 This interest continued up to the times of Tycho Brahe
Tycho Brahe ( ; born Tyge Ottesen Brahe; generally called Tycho (14 December 154624 October 1601) was a Danish astronomer, known for his comprehensive astronomical observations, generally considered to be the most accurate of his time. He was ...
and Kepler
Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws o ...
.
Every 20 years, successive Great Conjunctions move retrograde ~120°. Sequential Conjunctions appear as triangular patterns. They repeat after every third Conjunction; they return after some 60 years to the vicinity of the first. These returns are observed to be shifted by ~8° relative to the fixed stars; no more than four of them occur in the same zodiac sign. Typically, Conjunctions occur in one of the following '' Triplicities'' or ''Trigons'' of Zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south (as measured in celestial latitude) of the ecliptic, the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. The pat ...
signs:
After about 220 years the pattern shifts to the next Trigon; in ~900 years, the pattern returns to the first Trigon.If and designate the periods of Jupiter and Saturn then the return takes which comes to 883.15 years, but to be a whole number of Conjunction intervals it must be sometimes 913 years and sometimes 854. See Etz.
To each triangular pattern, astrologers have ascribed one from a series of four elements
Classical elements typically refer to earth, water, air, fire, and (later) aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler substances. Ancient cultures in Greece, Tibet, and India had simi ...
. Particular importance has been accorded to the occurrence of a Great Conjunction in a new Trigon, which is bound to happen after ~240 years at most.Etz D., (2000)''Conjunctions of Jupiter and Saturn''
Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada, Vol. 94, p.174 Greater importance is attributed to the beginning of a new cycle, which may occur after all four Trigons have been visited, which occurs in ~900 years. Typically, medieval astrologers used 960 years as the length of the full cycle, because, in some cases, it took 240 years to pass from one trigon to the next. If a cycle is defined by when the Conjunctions return to the same right ascension rather than to the same constellation, the cycle is only ~800 years, because of
axial precession
In astronomy, axial precession is a gravity-induced, slow, and continuous change in the orientation of an astronomical body's rotational axis. In the absence of precession, the astronomical body's orbit would show axial parallelism. In partic ...
. Use of the Alphonsine tables apparently led to the use of precessing signs; Kepler
Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws o ...
gave a value of 794 years, which created 40 Conjunctions.
Up to the end of the 16th century, despite the inaccuracies and some disagreement about the beginning of the cycle, the belief in the significance of such events generated a steady stream of publications. In 1583, the last Great Conjunction occurred in the watery trigon. It was widely supposed to herald apocalyptic changes. In 1586, a Papal Bull was issued against divinations. By 1603, public interest rapidly died, because nothing really significant had happened with the advent of a new Trigon.
Opposition
An Opposition (abbreviated as "Opp") is an angle of 180°, which is 1/2 of the 360°ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agains ...
. Depending on the involved planets, an orb of 5-10° is allowed.
An Opposition is said to be the second most powerful aspect. It resembles a conjunction, but an Opposition is fundamentally relational and it is not unifying like a conjunction. Some astrologers say it is prone to exaggeration, because it has a dichotomous quality and an externalizing effect.
All important axes in astrology are essentially Oppositions. Therefore, at its most basic level, an Opposition may often signify a relationship that can be oppositional or complementary.
Sextile
A Sextile (abbreviated as "SXt or Sex") is an angle of 60°, which is 1/6 of the 360°ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agains ...
or 1/2 a trine (120°). Depending on the involved planets, an orb of 3-4° is allowed. The symbol is the radii of a hexagon.
Traditionally, a Sextile is said to be similar in influence to a Trine, but less intense. It indicates compatibility and harmony, which eases communication between the two involved elements. It also provides opportunity. To gain its benefit, make an expended effort. See information below on the Semisextile.
Square
A Square or ''Quartile'' (abbreviated as "SQr or Squ") is an angle of 90°, which is 1/4 of the 360°ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agains ...
or 1/2 an opposition (180°). Depending on the involved planets, an orb of 5-10° is allowed.Orbs used by Liz Greene, seAstrodienst
/ref> Typically, with a Square, Trine or Sextile, the outer or superior planet has an effect on the inner or inferior planet. A Square creates a strong and usable tension. It may integrate between two different areas of your life or it may offer a turning point where an important decision needs to be made that involves an opportunity at a cost. Typically, if it involves
Houses
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
in different quadrants
Quadrant may refer to:
Companies
* Quadrant Cycle Company, 1899 manufacturers in Britain of the Quadrant motorcar
* Quadrant (motorcycles), one of the earliest British motorcycle manufacturers, established in Birmingham in 1901
* Quadrant Privat ...
, it is the smallest major aspect.
Trine
A Trine (abbreviated as "Tri") is an angle of 120°, which is 1/3 of the 360°ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agains ...
. Depending on the involved planets, an orb of 5-10° is allowed.
Traditionally, a Trine is extremely beneficial. It indicates harmony, ease and what is natural. A Trine may involve innate talent or ability. In transit
Transit may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Transit'' (1979 film), a 1979 Israeli film
* ''Transit'' (2005 film), a film produced by MTV and Staying-Alive about four people in countries in the world
* ''Transit'' (2006 film), a 2006 ...
, an event may emerge from a current or past situation in a natural way.
Minor Aspects
Semisextile
ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agains ...
. An orb of ±1.2° is allowed. The symbol is 1/2 a Sextile (60°), which is the top radii of a hexagon; the internal angles are 60°.
Of the minor aspects, it may be the most often used, because it can be easily seen. It indicates a mental interaction between planets; it is more sensually than externally experienced.
With a Semisextile, energy gradually builds and potentiates. Consider other planets, Signs and Houses
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
. A major aspect transit may be involved. To gain its benefit, make an effort.
Quincunx
Quincunx
A quincunx () is a geometric pattern consisting of five points arranged in a cross, with four of them forming a square or rectangle and a fifth at its center. The same pattern has other names, including "in saltire" or "in cross" in heraldry (d ...
or ''Quinduodecile'' or ''Inconjunct'' is an angle of 150°, which is 5/12 of the 360° ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agains ...
. Depending on the involved planets, an orb of ±3.5° is allowed. The symbol is the bottom radii of a hexagon, which is 1/2 a Sextile (60°) less than a semicircle; the internal angles are 60°.
An interpretation of a Quincunx may mostly rely on the involved planets, Signs and Houses
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
. Different areas of your life, that are not usually in communication, may come together. Planets may be far apart in different house quadrants. With a shift in perspective, clarity may reveal what was not previously seen. If a third planet, in a major aspect, triangulates a Qunicunx, the effect may be very obvious.
For Quincunx, keywords are karmic, mystery, unpredictable, imbalance, surreal, resourceful, creative, and humor.
A Quincunx does not offer equal divisions of a circle. It represents the 150° turn angles of a Dodecagram, .
Other Minor Aspects
Septile
A Septile is an angle of about 51.43°, which is 1/7 of the 360°ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agains ...
. An orb of ±1° is allowed.
A Septile is a mystical aspect that indicates a hidden flow of energy between the involved planets. Often, it involves spiritual or energetic sensitivity as well as an inner awareness of a more subtle, hidden level of reality.
;Irreducible Multiples:
: A Biseptile is an angle of 102.86°, which is 2/7 of the 360° ecliptic.
: A Triseptile is an angle of 154.29°, which is 3/7 of the 360° ecliptic.
Heptagram
A heptagram, septagram, septegram or septogram is a seven-point star drawn with seven straight strokes.
The name ''heptagram'' combines a numeral prefix, ''hepta-'', with the Greek suffix ''-gram''. The ''-gram'' suffix derives from ''γρ� ...
Regular star polygon 7-3.svg, Heptagram
A heptagram, septagram, septegram or septogram is a seven-point star drawn with seven straight strokes.
The name ''heptagram'' combines a numeral prefix, ''hepta-'', with the Greek suffix ''-gram''. The ''-gram'' suffix derives from ''γρ� ...
Octile
ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agains ...
. An orb of ±2° is allowed. The symbol is drawn with a 60-90° angle; the original angle is 90°, which is 1/2 a Square.
An Octile is an important minor aspect. It indicates stimulating or challenging energy. It is similar to a Square, but less intense and more internal.
A Semisquare is considered to be a minor hard aspect
In astrology, an aspect is an angle that planets make to each other in the Horoscope; as well as to the Ascendant, Midheaven, Descendant, Lower Midheaven, and other points of astrological interest. As viewed from Earth, aspects are measured b ...
, because it causes friction and prompts action to reduce that friction. For example, a Semisquare may occur if the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
is 10° Aquarius
Aquarius may refer to:
Astrology
* Aquarius (astrology), an astrological sign
* Age of Aquarius, a time period in the cycle of astrological ages
Astronomy
* Aquarius (constellation)
* Aquarius in Chinese astronomy
Arts and entertainme ...
and Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
is 25° Pisces. This may indicate unhappiness in love
Love encompasses a range of strong and positive emotional and mental states, from the most sublime virtue or good habit, the deepest interpersonal affection, to the simplest pleasure. An example of this range of meanings is that the love o ...
. Incompatibility may prompt action to reduce friction.
;Irreducible Multiples:
Octagram
In geometry, an octagram is an eight-angled star polygon.
The name ''octagram'' combine a Greek numeral prefix, '' octa-'', with the Greek suffix '' -gram''. The ''-gram'' suffix derives from γραμμή (''grammḗ'') meaning "line".
Deta ...
Novile
A Novile is an angle of 40°, which is 1/9 of the 360°ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agains ...
. An orb of ±1° is allowed.
A Novile indicates an energy of perfection and/or idealization.
;Irreducible Multiples:
: A Binovile is an angle of 80°, which is 2/9 of the 360° ecliptic.
: A Quadnovile is an angle of 160°, which is 4/9 of the 360° ecliptic.
Decile
ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agains ...
.
;Irreducible Multiples:
: Undecile
An Undecile or ''Elftile'' is an angle of 32.73°, which is 1/11 of the 360°ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agains ...
. An orb of ±1° is allowed.
;Irreducible Multiples:
: A Biundecile is an angle of 65.45°, which is 2/11 of the 360° ecliptic.
: A Triundecile is an angle of 98.18°, which is 3/11 of the 360° ecliptic.
: A Quadundecile is an angle of 130.91°, which is 4/11 of the 360° ecliptic.
: A Quinundecile is an angle of 163.63°, which is 5/11 of the 360° ecliptic.
Semioctile
A Semioctile or ''Sexdecile'' is an angle of 22.5°, which is 1/16 of the 360°ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agains ...
. An orb of ±0.75° is allowed.
A Semioctile is part of the square family. It is considered to be a more minor version of the Semisquare, which triggers challenge. Its harmonic aspects are 45°, 67.5°, 90°, 112.5°, 135°, 157.5° and 180°. It was discovered by Uranian astrologers.
;Irreducible Multiples:
: A Sesquioctile or ''Bisexdecile'' is an angle of 67.5°, which is 3/16 of the 360° ecliptic.
: A Quinsemioctile or ''Quinsexdecile'' is an angle of 112.5°, which is 5/16 of the 360° ecliptic.
: A Sepsemioctile or ''Sepsexdecile'' is an angle of 157.5°, which is 7/16 of the 360° ecliptic.
Declinations
The Parallel and Contraparallel or ''Antiparallel'' are two other aspects which refer to degrees of declination above or below theCelestial Equator
The celestial equator is the great circle of the imaginary celestial sphere on the same plane as the equator of Earth. This plane of reference bases the equatorial coordinate system. In other words, the celestial equator is an abstract proj ...
. They are not widely used by astrologers.
Parallel
A Parallel may be similar to a Semisquare or Quincunx, because it is not clearly seen. It represents an opportunity for perspective and communication between energies that requires some work to be made conscious. An orb of the same degree ±1° with a 12-minute arc is allowed.Contraparallel
A Contraparallel may be similar to the Parallel. Some astrologers that use the Parallel do not consider the Contraparallel to be an aspect. An orb of the opposite degree ±1° with a 12-minute arc is allowed.See also
*Astrological symbols
Historically, astrological and astronomical symbols overlapped. Frequently used symbols include signs of the zodiac and classical planets. These originate from medieval Byzantine codices. Their current form is a product of the European Renaissa ...
*Conjunction
Conjunction may refer to:
* Conjunction (grammar), a part of speech
* Logical conjunction, a mathematical operator
** Conjunction introduction, a rule of inference of propositional logic
* Conjunction (astronomy), in which two astronomical bodies ...
*Opposition
Opposition may refer to:
Arts and media
* ''Opposition'' (Altars EP), 2011 EP by Christian metalcore band Altars
* The Opposition (band), a London post-punk band
* '' The Opposition with Jordan Klepper'', a late-night television series on Com ...
* Cosmobiology
*Hamburg School of Astrology
The Hamburg School of Astrology originated in Hamburg, Germany, and revolved around the research and teachings of surveyor/astrologer/amateur astronomer Alfred Witte. The term ''Hamburg School'' as an astrological method originated in 1923 at ...
*Quadrature (astronomy)
In spherical astronomy, quadrature is the configuration of a celestial object in which its elongation is perpendicular to the direction of the Sun. It is applied especially to the position of a superior planet or the Moon at its first and last ...
References
External links
''The Classical Origin & Traditional Use of Aspects''
Deborah Houlding
Online Ephemeris from Khaldea.com
��600BC to 2400AD—Calculated for Midnight
GMT
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is the mean solar time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London, counted from midnight. At different times in the past, it has been calculated in different ways, including being calculated from noon; as a cons ...
; also with an Aspectarian included for years 1900 to 2005
''Harmonices mundi''
("The Harmony of the Worlds") in fulltext facsimile;
Carnegie-Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. One of its predecessors was established in 1900 by Andrew Carnegie as the Carnegie Technical Schools; it became the Carnegie Institute of Technology ...
{{Authority control
Technical factors of Western astrology