Arkansas River on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Arkansas River is a major
1
Its volume is much smaller than the Missouri and
 The Arkansas has three distinct sections in its long path through central North America. At its headwaters beginning near
The Arkansas has three distinct sections in its long path through central North America. At its headwaters beginning near
''Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture''. "Arkansas River.
These locks and dams enable the river to be navigable by barges and large river craft downriver of Muskogee, Oklahoma, where the McClellan-Kerr Arkansas River Navigation System joins the Verdigris River. Into western
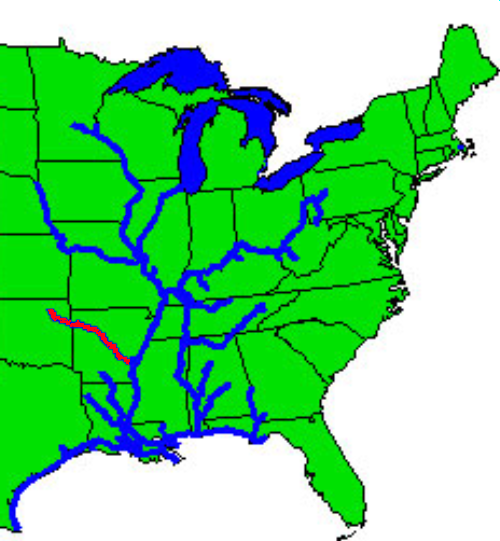 The
The
Oklahoma Department of Transportation. 2016. Accessed June 16, 2017. The McClellan–Kerr Arkansas River Navigation System diverts from the Arkansas River upstream of the
 Many nations of Native Americans lived near, or along, the 1,450-mile (2,334-km) stretch of the Arkansas River for thousands of years. The first Europeans to see the river were members of the
Many nations of Native Americans lived near, or along, the 1,450-mile (2,334-km) stretch of the Arkansas River for thousands of years. The first Europeans to see the river were members of the
Accessed January 26, 2017. French traders and trappers who had opened up trade with Indian tribes in Canada and the areas around the Great Lakes began exploring the Mississippi and some of its northern tributaries. They soon learned that the birchbark canoes, which had served them so well on the northern waterways, were too light for use on southern rivers such as the Arkansas. They turned to making and using dugout canoes, which they called ''pirogues'', made by hollowing out the trunks of cottonwood trees. Cottonwoods are plentiful along the streams of the southwest and grow to large sizes. The wood is soft and easily worked with the crude tools carried by both the French and Indians. The pirogues were sturdier and could be more useful to navigate the sandbars and snags of the Southern waterways.Wright, Muriel H. "Early Navigation and Commerce along the Arkansas and Red Rivers in Oklahoma." ''Chronicles of Oklahoma''. Volume 8, Number 1, March, 1930. p. 65.
Accessed September 29, 2017. In 1819, the Adams–Onís Treaty set the Arkansas as part of the frontier between the United States and Spanish
Accessed June 2, 2017. In mid-April 1822, the ''Robert Thompson'', towing a keelboat, was the first steamboat to navigate the Arkansas as far as Fort Smith. For five years, Fort Smith was known as the head of navigation for steamboats on the river. It lost the title to Fort Gibson in April 1832, when three steamboats, ''Velocipede'', ''Scioto'' and ''Catawba'', all arrived at Fort Gibson later that month. Later, the Santa Fe Trail followed the Arkansas through much of Kansas, picking it up near Great Bend and continuing through to La Junta, Colorado. Some users elected to take the challenging Cimarron Cutoff starting at Cimarron, Kansas.
Accessed June 4, 2017. Flooding in 1927 severely damaged or destroyed nearly every levee downstream of Fort Smith, and led to the development of the Arkansas River Flood Control Association. It also resulted in the Federal government assigning responsibility of flood control and navigation on the Arkansas river to the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACOE).
Colorado-Kansas Arkansas River Compact
Friends of the Arkansas River
Aquifer saturation map
for ''Equus Beds Aquifer Recharge Project''
Arkansas River Coalition
Full Scale Map
Santa Fe Trail Research
Wichita Water Center Tours
of navigation system
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20121024013411/http://www.library.okstate.edu/okmaps/ Oklahoma Digital Maps: Digital Collections of Oklahoma and Indian Territory* * * Arkansas River is discussed at the end of this article. * {{Authority control Rivers of Arkansas Rivers of Colorado Rivers of Kansas Rivers of Oklahoma Tributaries of the Mississippi River Regions of Arkansas Rivers of Edwards County, Kansas Rivers of Desha County, Arkansas Rivers of Arkansas County, Arkansas Rivers of Lincoln County, Arkansas Rivers of Jefferson County, Arkansas Rivers of Pulaski County, Arkansas Rivers of Faulkner County, Arkansas Rivers of Perry County, Arkansas Rivers of Conway County, Arkansas Rivers of Pope County, Arkansas Rivers of Yell County, Arkansas Rivers of Logan County, Arkansas Rivers of Johnson County, Arkansas Rivers of Franklin County, Arkansas Rivers of Crawford County, Arkansas Rivers of Sebastian County, Arkansas Rivers of Fremont County, Colorado Rivers of Sedgwick County, Kansas Geography of Tulsa, Oklahoma Rivers of Ford County, Kansas Rivers of Hamilton County, Kansas Rivers of Reno County, Kansas Rivers of Rice County, Kansas Rivers of Bent County, Colorado Rivers of Pueblo County, Colorado Mississippi River watershed
tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drai ...
of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
, Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to th ...
, Oklahoma, and Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
. The river's source basin lies in the western United States
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Far West, and the West) is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term ''the We ...
in Colorado, specifically the Arkansas River Valley. The headwaters derive from the snowpack in the Sawatch and Mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "li ...
mountain ranges. It flows east into the Midwest via Kansas, and finally into the South through Oklahoma and Arkansas.
At , it is the sixth-longest river in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, the second-longest tributary in the Mississippi–Missouri
Missouri is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee to the east, Arkansas t ...
system, and the 45th longest river in the world. Its origin is in the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
in Lake County, Colorado, near Leadville
The City of Leadville is a statutory city that is the county seat, the most populous community, and the only incorporated municipality in Lake County, Colorado, United States. The city population was 2,602 at the 2010 census and an estimated ...
. In 1859, placer gold discovered in the Leadville area brought thousands seeking to strike it rich, but the easily recovered placer gold was quickly exhausted. The Arkansas River's mouth is at Napoleon, Arkansas, and its drainage basin covers nearly .See watershed maps1
Its volume is much smaller than the Missouri and
Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
rivers, with a mean discharge of about .
The Arkansas from its headwaters to the 100th meridian west formed part of the U.S.–Mexico border from the Adams–Onís Treaty (in force 1821) until the Texas Annexation or Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ( es, Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo), officially the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits, and Settlement between the United States of America and the United Mexican States, is the peace treaty that was signed on 2 ...
.
Pronunciations
Name pronunciation varies by state. Generally, the river is pronounced inKansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to th ...
, but in Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
, Oklahoma, and Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
.
Physical geography
Course changes
The path of the Arkansas River has changed over time. Sediments from the river found in a palaeochannel next to Nolan, a site in the Tensas Basin, show that part of the river's meander belt flowed through up to 3200 BCE. While it was previously thought that this relict channel was active at the same time as another relict ofMississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
's meander belt, it has been shown that this channel of the Arkansas was inactive approximately 400 years before the Mississippi channel was active.
Hydrography
 The Arkansas has three distinct sections in its long path through central North America. At its headwaters beginning near
The Arkansas has three distinct sections in its long path through central North America. At its headwaters beginning near Leadville
The City of Leadville is a statutory city that is the county seat, the most populous community, and the only incorporated municipality in Lake County, Colorado, United States. The city population was 2,602 at the 2010 census and an estimated ...
, Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
, the Arkansas runs as a steep fast-flowing mountain river through the Rockies in its narrow valley, dropping in . This section supports extensive whitewater rafting
Rafting and whitewater rafting are recreational outdoor activities which use an inflatable raft to navigate a river or other body of water. This is often done on whitewater or different degrees of rough water. Dealing with risk is often a ...
, including The Numbers (near Granite, Colorado), Brown's Canyon, and the Royal Gorge.
At Cañon City, Colorado, the Arkansas River valley widens and flattens markedly. Just west of Pueblo, Colorado
Pueblo () is a home rule municipality that is the county seat and the most populous municipality of Pueblo County, Colorado, United States. The city population was 111,876 at the 2020 United States Census, making Pueblo the ninth most populo ...
, the river enters the Great Plains. Through the rest of Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
, Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to th ...
, and much of Oklahoma, it is a typical Great Plains riverway, with wide, shallow banks subject to seasonal flooding and periods of dwindling flow. Tributaries include the Cimarron and the Salt Fork Arkansas rivers.
In eastern Oklahoma the river begins to widen further into a more contained consistent channel. To maintain more reliable flow rates, a series of dams and large reservoir lakes have been built on the Arkansas and its intersecting tributaries, including the Canadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
, Verdigris, Neosho (Grand), Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockf ...
, and Poteau rivers.O'Dell, Larry''Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture''. "Arkansas River.
These locks and dams enable the river to be navigable by barges and large river craft downriver of Muskogee, Oklahoma, where the McClellan-Kerr Arkansas River Navigation System joins the Verdigris River. Into western
Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
, the river path works between the encroaching Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
and Ouachita mountains, including many isolated, flat-topped mesas, buttes, or monadnocks such as Mount Nebo
Mount Nebo ( ar, جَبَل نِيبُو, Jabal Nībū; he, , Har Nəḇō) is an elevated ridge located in Jordan, approximately above sea level. Part of the Abarim mountain range, Mount Nebo is mentioned in the Bible as the place where Moses ...
, Petit Jean Mountain, and Mount Magazine
Mount Magazine, officially named Magazine Mountain, is the highest point of the U.S. Interior Highlands and the U.S. state of Arkansas, and is the site of Mount Magazine State Park. It is a flat-topped mountain or mesa capped by hard rock and r ...
, the highest point in the state. The river valley expands as it encounters much flatter land beginning just west of Little Rock, Arkansas
( The "Little Rock")
, government_type = Council-manager
, leader_title = Mayor
, leader_name = Frank Scott Jr.
, leader_party = D
, leader_title2 = Council
, leader_name2 ...
. It continues eastward across the plains and forests of eastern Arkansas until it flows into the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
near Napoleon, Arkansas.
Water flow in the Arkansas River (as measured in central Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to th ...
) has dropped from approximately average from 1944–1963 to average from 1984–2003, largely because of the pumping of groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated ...
for irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
in eastern Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
and western Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to th ...
.
Important cities along the Arkansas River include Canon City, Pueblo
In the Southwestern United States, Pueblo (capitalized) refers to the Native tribes of Puebloans having fixed-location communities with permanent buildings which also are called pueblos (lowercased). The Spanish explorers of northern New Spain ...
, La Junta, and Lamar, Colorado
Lamar is the home rule municipality that is the county seat and the most populous municipality of Prowers County, Colorado, United States. The city population was 7,804 at the 2010 United States Census. The city was named after Confederate ...
; Garden City, Dodge City
Dodge City is the county seat of Ford County, Kansas, United States, named after nearby Fort Dodge. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 27,788. The city is famous in American culture for its history as a wild frontier town ...
, and Wichita, Kansas
Wichita ( ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Kansas and the county seat of Sedgwick County. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 397,532. The Wichita metro area had a population of 647,610 in 2020. It is located in ...
; Tulsa, Oklahoma
Tulsa () is the second-largest city in the state of Oklahoma and 47th-most populous city in the United States. The population was 413,066 as of the 2020 census. It is the principal municipality of the Tulsa Metropolitan Area, a region with ...
; and Fort Smith and Little Rock, Arkansas
( The "Little Rock")
, government_type = Council-manager
, leader_title = Mayor
, leader_name = Frank Scott Jr.
, leader_party = D
, leader_title2 = Council
, leader_name2 ...
.
The May 2002 I-40 bridge disaster
The I-40 bridge disaster was a bridge collapse that occurred southeast of Webbers Falls, Oklahoma, United States at 7:45 a.m. on May 26, 2002. Freight barges being transported on the Arkansas River collided with a pier supporting the Inters ...
took place on I-40
Interstate 40 (I-40) is a major east–west Interstate Highway running through the south-central portion of the United States. At a length of , it is the third-longest Interstate Highway in the country, after I-90 and I-80. From west to ea ...
's crossing of Kerr Reservoir on the Arkansas River near Webbers Falls, Oklahoma
Webbers Falls is a town in southeastern Muskogee County, Oklahoma, United States. The population was 616 at the 2010 census, a decline of 14.9 percent from the figure of 724 recorded in 2000.
The name comes from a seven-foot waterfall in the Arka ...
.
Table of primary tributaries
Allocation problems
Since 1902, Kansas has claimed that Colorado takes too much of the river's water; it has filed numerous lawsuits over this issue in the U.S. Supreme Court that continue to this day,'' Kansas v. Colorado'' 514 U.S. 673 (1995), 185 U.S. 125 (1902) generally under the name of '' Kansas v. Colorado''. The problems over the possession and use of Arkansas River water by Colorado and Kansas led to the creation of aninterstate compact
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. Th ...
or agreement between the two states. While Congress approved the Arkansas River Compact in 1949, the compact did not stop further disputes by the two states over water rights to the river.
The Kansas–Oklahoma Arkansas River Basin Compact was created in 1965 to promote mutual consideration and equity over water use in the basin shared by those states. The Kansas–Oklahoma Arkansas River Commission was established, charged with administering the compact and reducing pollution. The compact was approved and implemented by both states in 1970, and has been in force since then.
Riverway commerce
 The
The McClellan–Kerr Arkansas River Navigation System
The McClellan–Kerr Arkansas River Navigation System (MKARNS) is part of the United States inland waterway system originating at the Tulsa Port of Catoosa and running southeast through Oklahoma and Arkansas to the Mississippi River. The total ...
begins at the Tulsa Port of Catoosa
The primary facility of the Tulsa Ports, known as the Tulsa Port of Catoosa, is near the city of Catoosa in Rogers County, just inside the municipal fenceline of Tulsa, Oklahoma, United States. Located at the head of navigation for the McClell ...
on the Verdigris River
The Verdigris River is a tributary of the Arkansas River in southeastern Kansas and northeastern Oklahoma in the United States. It is about long.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, ...
, enters the Arkansas River near Muskogee, and runs via an extensive lock and dam system to the Mississippi River. Through Oklahoma and Arkansas, dams which artificially deepen and widen the river to sustain commercial barge traffic and recreational use give the river the appearance of a series of reservoirs."McClellan-Kerr Arkansas River Navigation System 2016 Inland Waterway Fact Sheet"Oklahoma Department of Transportation. 2016. Accessed June 16, 2017. The McClellan–Kerr Arkansas River Navigation System diverts from the Arkansas River upstream of the
Wilbur D. Mills Dam
Wilbur D. Mills Dam is a steel dam and generating facility located on the Arkansas River in Arkansas County and Desha County, Arkansas, United States.
The dam is part of the McClellan–Kerr Arkansas River Navigation System, and is named for ...
to avoid the long winding route which the lower Arkansas River follows. This circuitous portion of the Arkansas River between the Wilbur D. Mills Dam and the Mississippi River was historically bypassed by river vessels. Early steamboats instead followed a network of rivers—known as the Arkansas Post Canal—which flowed north of the lower Arkansas River and followed a shorter and more direct route to the Mississippi River. When the McClellan–Kerr Arkansas River Navigation System was constructed between 1963 and 1970, the Arkansas Post Canal was significantly improved, while the lower Arkansas River continued to be bypassed by commercial vessels.
In history
 Many nations of Native Americans lived near, or along, the 1,450-mile (2,334-km) stretch of the Arkansas River for thousands of years. The first Europeans to see the river were members of the
Many nations of Native Americans lived near, or along, the 1,450-mile (2,334-km) stretch of the Arkansas River for thousands of years. The first Europeans to see the river were members of the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
Coronado expedition on June 29, 1541. Also in the 1540s, Hernando de Soto discovered the junction of the Arkansas with the Mississippi. The Spanish originally called the river ''Napeste''. "The name "Arkansas" was first applied by French Father Jacques Marquette, who called the river ''Akansa'' in his journal of 1673. The Joliet-Marquette expedition travelled the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
from Prairie du Chien, Wisconsin
Prairie du Chien () is a city in and the county seat of Crawford County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 5,506 at the 2020 census. Its ZIP Code is 53821.
Often referred to as Wisconsin's second oldest city, Prairie du Chien was est ...
toward the Gulf of Mexico, but turned back at the mouth of the Arkansas River. By that time, they had encountered Native Americans carrying European trinkets, and feared confrontation with Spanish conquistadors.
Jean-Baptiste Bénard de la Harpe, a French trader, explorer and nobleman had led an expedition into what is now Oklahoma in 1718–19. His original objective was to establish a trading post near the present city of Texarkana, Arkansas
Texarkana is a city in the U.S. state of Arkansas and the county seat of Miller County, on the southwest border of the state. As of the 2020 census, it had a population of 29,387. The city is located across the state line from its twin city ...
, but he extended his trip overland as far north as the Arkansas River (which he designated as the ''Alcansas''). The explorer wrote that he and nine other men, including three Caddo guides and 22 horses loaded with trade goods, had come to a native settlement overlooking the river, where there were about 6,000 natives, who gave the strangers a warm welcome. La Harpe's party were honored with the calumet ceremony and spent ten days at this location.
In 1988, evidence of a native village was discovered along the Arkansas River south of present-day Tulsa, Oklahoma
Tulsa () is the second-largest city in the state of Oklahoma and 47th-most populous city in the United States. The population was 413,066 as of the 2020 census. It is the principal municipality of the Tulsa Metropolitan Area, a region with ...
. By then, the site was known as the Lasley Vore Site
The Lasley Vore Site is an archaeological site near the Arkansas River in Tulsa County, Oklahoma. Based on an archeological study in 1988 conducted by the University of Tulsa, this is believed to be the remains of a Wichita people, Wichita village ...
.Odell, George H. "Lasley Vore Site." ''Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture''.Accessed January 26, 2017. French traders and trappers who had opened up trade with Indian tribes in Canada and the areas around the Great Lakes began exploring the Mississippi and some of its northern tributaries. They soon learned that the birchbark canoes, which had served them so well on the northern waterways, were too light for use on southern rivers such as the Arkansas. They turned to making and using dugout canoes, which they called ''pirogues'', made by hollowing out the trunks of cottonwood trees. Cottonwoods are plentiful along the streams of the southwest and grow to large sizes. The wood is soft and easily worked with the crude tools carried by both the French and Indians. The pirogues were sturdier and could be more useful to navigate the sandbars and snags of the Southern waterways.Wright, Muriel H. "Early Navigation and Commerce along the Arkansas and Red Rivers in Oklahoma." ''Chronicles of Oklahoma''. Volume 8, Number 1, March, 1930. p. 65.
Accessed September 29, 2017. In 1819, the Adams–Onís Treaty set the Arkansas as part of the frontier between the United States and Spanish
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
. This continued until the United States annexed Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
after the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
, in 1846. The treaty was made shortly after "Old Settler" Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
were pushed out of Texas and moved to near what became known as Webbers Falls on the Arkansas River. They planned to reunite with the Cherokee who had moved there on the Trail of Tears in 1839. That area, then part of Arkansas Territory
The Arkansas Territory was a territory of the United States that existed from July 4, 1819, to June 15, 1836, when the final extent of Arkansas Territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Arkansas. Arkansas Post was the first territo ...
, would become Indian Territory
The Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the United States Government for the relocation of Native Americans who held aboriginal title to their land as a sovereign ...
and later Oklahoma.
This area had long been traditional territory of the Osage. They resisted the new Native Americans moving in with armed conflict. The US encouraged a peace treaty made in 1828 but the territory issue was still unresolved by the time thousands of additional Cherokee refugees moved to the area during the Trail of Tears
The Trail of Tears was an ethnic cleansing and forced displacement of approximately 60,000 people of the " Five Civilized Tribes" between 1830 and 1850 by the United States government. As part of the Indian removal, members of the Cherokee, ...
.
By the time Fort Smith was established in 1817, larger capacity watercraft became available to transport goods up and down the Arkansas. These included flatboats (''bateaus'') and keelboats
A keelboat is a riverine cargo-capable working boat, or a small- to mid-sized recreational sailing yacht. The boats in the first category have shallow structural keels, and are nearly flat-bottomed and often used leeboards if forced in open w ...
. Along with the pirogues, they transported piles of deer, bear, otter, beaver and buffalo skins up and down the river. Agricultural products such as corn, rice, dried peaches, beans, peanuts, snake root, sarsaparilla, and ginseng had grown in economic importance.
On March 31, 1820, the ''Comet'' became the first steamboat to successfully navigate part of the Arkansas River, reaching a place called Arkansas Post, about above the confluence of the Arkansas and the Mississippi rivers.U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Little Rock District/ Mission/Navigation.Accessed June 2, 2017. In mid-April 1822, the ''Robert Thompson'', towing a keelboat, was the first steamboat to navigate the Arkansas as far as Fort Smith. For five years, Fort Smith was known as the head of navigation for steamboats on the river. It lost the title to Fort Gibson in April 1832, when three steamboats, ''Velocipede'', ''Scioto'' and ''Catawba'', all arrived at Fort Gibson later that month. Later, the Santa Fe Trail followed the Arkansas through much of Kansas, picking it up near Great Bend and continuing through to La Junta, Colorado. Some users elected to take the challenging Cimarron Cutoff starting at Cimarron, Kansas.
American Civil War
During the American Civil War, each side tried to prevent the other from using the Arkansas River and its tributaries as a route for moving reinforcements. Initially, the Union Army abandoned its forts in the Indian Territory, including Fort Gibson and Fort Smith, in order to maximize its strength for campaigns elsewhere. The Confederate Army sent troops from Texas to support its Native American allies. Union troops returned to the area later in the war, after defeating the Confederates at theBattle of Pea Ridge
The Battle of Pea Ridge (March 7–8, 1862), also known as the Battle of Elkhorn Tavern, took place in the American Civil War near Leetown, Arkansas, Leetown, northeast of Fayetteville, Arkansas, Fayetteville, Arkansas. United States, Federal f ...
and the Battle of Fort Smith. They began recovering the position it had previously abandoned, most notably Fort Gibson, and reopened the Arkansas River as a supply route. In September 1864, a body of Confederate irregulars led by General Stand Watie (Cherokee) successfully ambushed a Union supply ship bound for Fort Gibson. The vessel was destroyed, and a part of its cargo was looted by the Confederates.
Post Civil War
In the 1880s, Charles "Buffalo" Jones, one of the cofounders of Garden City, Kansas, organized four irrigation companies to take water one hundred miles from the Arkansas River to cultivate of land. By 1890, water from the Arkansas was being used to irrigate more than of farmland in Kansas. By 1910, irrigation projects in Colorado had caused the river to stop flowing in July and August."History of the Arkansas River (1540 to 2000)". South Central Service Cooperative. 2017.Accessed June 4, 2017. Flooding in 1927 severely damaged or destroyed nearly every levee downstream of Fort Smith, and led to the development of the Arkansas River Flood Control Association. It also resulted in the Federal government assigning responsibility of flood control and navigation on the Arkansas river to the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACOE).

Angling
The headwaters of the Arkansas River in centralColorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
have been known for exceptional trout fishing, particularly fly fishing, since the 19th century, when greenback cutthroat trout
The greenback cutthroat trout (''Oncorhynchus clarkii stomias'') is the easternmost subspecies of cutthroat trout. The greenback cutthroat, once widespread in the Arkansas and South Platte River drainages of Eastern Colorado and Southeast Wyomin ...
dominated the river. Today, brown trout dominate the river, which also contains rainbow trout. '' Trout Unlimited'' considers the Arkansas one of the top 100 trout streams in America, a reputation the river has had since the 1950s. From Leadville to Pueblo, the Arkansas River is serviced by numerous fly shops and guides operating in Buena Vista, Salida, Cañon City and Pueblo. The Colorado Division of Wildlife provides regular online fishing reports for the river.
A fish kill occurred on December 29, 2010, in which an estimated 100,000 freshwater drum lined the Arkansas River bank
A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets.
Because ...
. An investigation, conducted by the Arkansas Game and Fish Commission, found the dead fish "... cover of river from the Ozark Lock and Dam downstream to River Mile 240, directly south of Hartman, Arkansas
Hartman is a city in Johnson County, Arkansas, United States. The population was 519 at the 2010 census.
Geography
Hartman is located in southwestern Johnson County on the west side of Horsehead Creek about north of the Arkansas River. U.S. Hig ...
." Tests later indicated the likely cause of the kill was gas bubble trauma caused by opening the spillways on the Ozark Dam.
Image gallery
Notes
See also
*Ackerman Island
Ackerman Island was a sandbar island located in the Arkansas River in downtown Wichita, Kansas, United States. It was located on the north side of the Douglas Street Bridge.
History
The sandbar started to form in the 1870s, supposedly due to a d ...
* '' Kansas v. Colorado''
* List of crossings of the Arkansas River
* List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem)
The longest rivers of the United States include 38 that have main stems of at least long. The main stem is "the primary downstream segment of a river, as contrasted to its tributaries". The United States Geological Survey (USGS) defines a main- ...
* Listing of rivers for each state: Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
, Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to th ...
, Oklahoma, Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
* McClellan–Kerr Arkansas River Navigation System
The McClellan–Kerr Arkansas River Navigation System (MKARNS) is part of the United States inland waterway system originating at the Tulsa Port of Catoosa and running southeast through Oklahoma and Arkansas to the Mississippi River. The total ...
References
External links
Colorado-Kansas Arkansas River Compact
Friends of the Arkansas River
Aquifer saturation map
for ''Equus Beds Aquifer Recharge Project''
Arkansas River Coalition
Full Scale Map
Santa Fe Trail Research
Wichita Water Center Tours
of navigation system
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20121024013411/http://www.library.okstate.edu/okmaps/ Oklahoma Digital Maps: Digital Collections of Oklahoma and Indian Territory* * * Arkansas River is discussed at the end of this article. * {{Authority control Rivers of Arkansas Rivers of Colorado Rivers of Kansas Rivers of Oklahoma Tributaries of the Mississippi River Regions of Arkansas Rivers of Edwards County, Kansas Rivers of Desha County, Arkansas Rivers of Arkansas County, Arkansas Rivers of Lincoln County, Arkansas Rivers of Jefferson County, Arkansas Rivers of Pulaski County, Arkansas Rivers of Faulkner County, Arkansas Rivers of Perry County, Arkansas Rivers of Conway County, Arkansas Rivers of Pope County, Arkansas Rivers of Yell County, Arkansas Rivers of Logan County, Arkansas Rivers of Johnson County, Arkansas Rivers of Franklin County, Arkansas Rivers of Crawford County, Arkansas Rivers of Sebastian County, Arkansas Rivers of Fremont County, Colorado Rivers of Sedgwick County, Kansas Geography of Tulsa, Oklahoma Rivers of Ford County, Kansas Rivers of Hamilton County, Kansas Rivers of Reno County, Kansas Rivers of Rice County, Kansas Rivers of Bent County, Colorado Rivers of Pueblo County, Colorado Mississippi River watershed