Argentine ant on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Argentine ant (''Linepithema humile'', formerly ''Iridomyrmex humilis'') is an
brood
and the entire colony will move to dry ground. Austrian entomologist Gustav L. Mayr identified the first specimens of ''Hypoclinea humilis'' in the vicinity of
https://www.life.illinois.edu/suarez/publications/Holway_etal2002ARES.pdf (dead)
https://www.life.illinois.edu/suarez/publications/SuarezTsutsui2008MolEcol.pdf (dead)
...cite this study:
https://www.life.illinois.edu/suarez/Publications/Tsutsui_etal2001MolEcol.pdf (dead) which stretches across northern Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay, and southern Brazil. Within South America, this species has spread into parts of
 They have been extraordinarily successful, in part, because different nests of the introduced Argentine ants seldom attack or compete with each other, unlike most other species of ant. In their introduced range, their genetic makeup is so uniform that individuals from one nest can mingle in a neighboring nest without being attacked. Thus, in most of their introduced range, they form supercolonies.
The Very Large Colony, which covers territory from
They have been extraordinarily successful, in part, because different nests of the introduced Argentine ants seldom attack or compete with each other, unlike most other species of ant. In their introduced range, their genetic makeup is so uniform that individuals from one nest can mingle in a neighboring nest without being attacked. Thus, in most of their introduced range, they form supercolonies.
The Very Large Colony, which covers territory from
Kim McDonald, University of California, May 2000 In a series of experiments, ants of the same colony were isolated and fed different diets. The
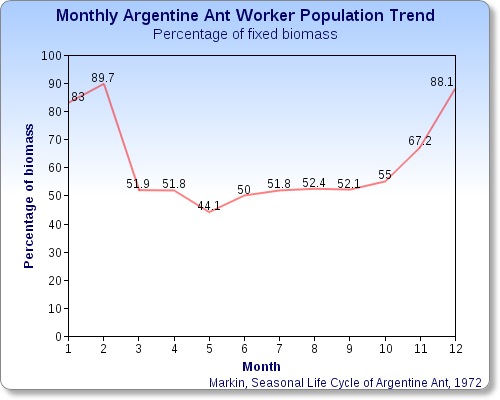 Like workers in many other ant species, Argentine ant workers are unable to lay reproductive eggs but can direct the development of eggs in reproductive females; the production of males appears to be controlled by the amount of food available to the larvae. Argentine ant colonies almost invariably have many reproductive queens, as many as eight for every 1,000 workers.
The seasonal low occurs in mid-winter, when 90% of a representative colony consists of workers and the remainder of queens, and no reproductive activity and minimal birthing. Eggs are produced in late-winter, nearly all of which hatch into sexual forms by May(*). Mating occurs after the females emerge. Worker production increases steadily from mid-March(*) to October(*), after which their numbers are not replenished; thus, their numbers drop steadily over the winter months.
((*) Note that the information regarding the months May, March, and October in this paragraph, as well as the entire Month axis in the graph, are not worldwide correct, in particular in Southern hemisphere, due to the shift of six months in seasons between the two hemispheres.)
Colonies in the Argentine ant's native habitat are kept within a range of ten to one hundred meters by colonies of interspecific and intraspecific rivals. As the colonies expand, they appear to form fluctuating territory borders, which contract and expand on a seasonal and conditional basis. There is an expansive push outward in the summer months, with a retreating motion in the winter. This has to do with
Like workers in many other ant species, Argentine ant workers are unable to lay reproductive eggs but can direct the development of eggs in reproductive females; the production of males appears to be controlled by the amount of food available to the larvae. Argentine ant colonies almost invariably have many reproductive queens, as many as eight for every 1,000 workers.
The seasonal low occurs in mid-winter, when 90% of a representative colony consists of workers and the remainder of queens, and no reproductive activity and minimal birthing. Eggs are produced in late-winter, nearly all of which hatch into sexual forms by May(*). Mating occurs after the females emerge. Worker production increases steadily from mid-March(*) to October(*), after which their numbers are not replenished; thus, their numbers drop steadily over the winter months.
((*) Note that the information regarding the months May, March, and October in this paragraph, as well as the entire Month axis in the graph, are not worldwide correct, in particular in Southern hemisphere, due to the shift of six months in seasons between the two hemispheres.)
Colonies in the Argentine ant's native habitat are kept within a range of ten to one hundred meters by colonies of interspecific and intraspecific rivals. As the colonies expand, they appear to form fluctuating territory borders, which contract and expand on a seasonal and conditional basis. There is an expansive push outward in the summer months, with a retreating motion in the winter. This has to do with
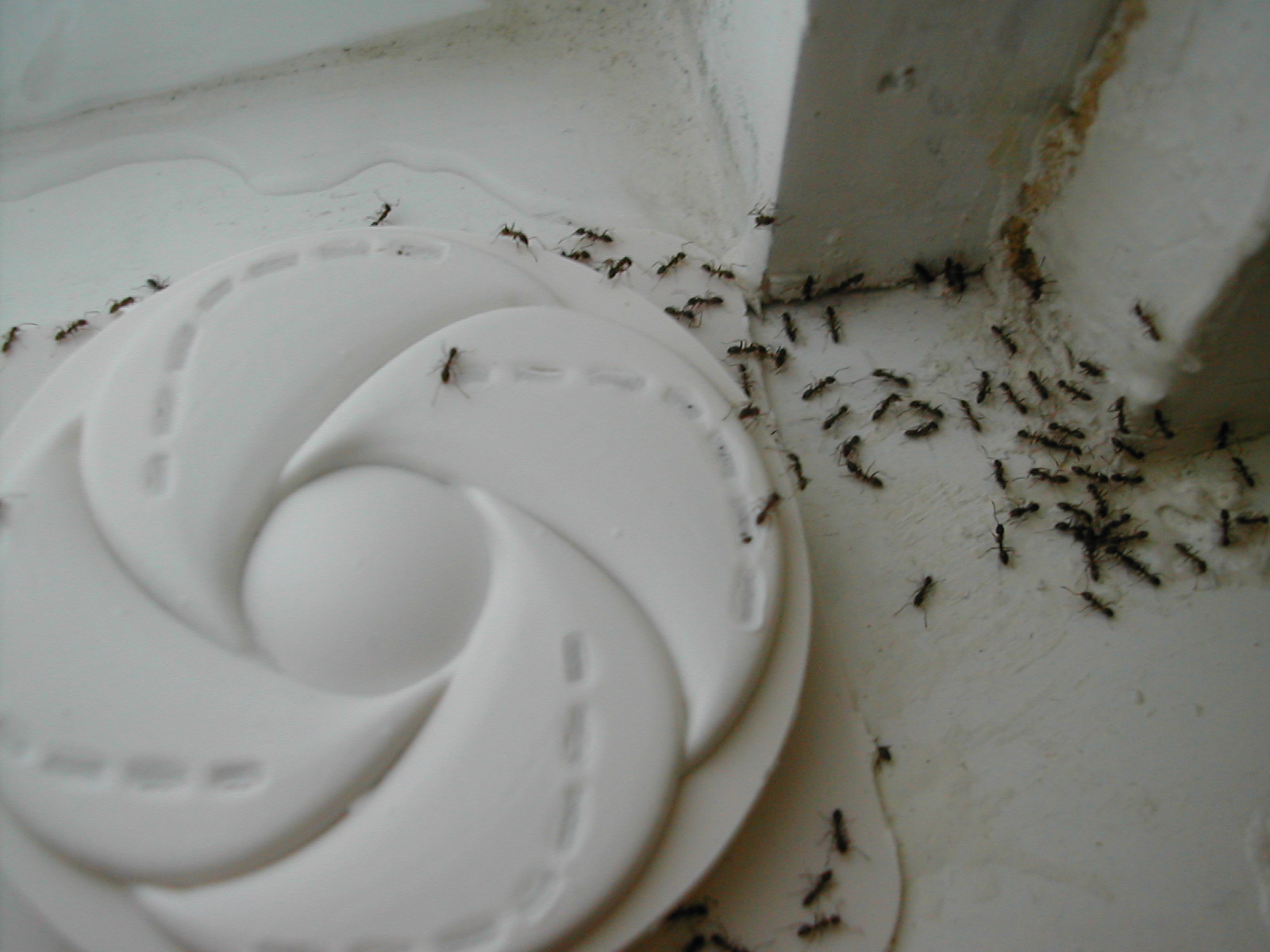 Argentine ants are a common household pest, often entering structures in search of food or water (particularly during dry or hot weather), or to escape flooded nests during periods of heavy rainfall. When they invade a kitchen, it is not uncommon to see two or three queens foraging along with the workers.
Argentine ants are a common household pest, often entering structures in search of food or water (particularly during dry or hot weather), or to escape flooded nests during periods of heavy rainfall. When they invade a kitchen, it is not uncommon to see two or three queens foraging along with the workers.
ant
Ants are Eusociality, eusocial insects of the Family (biology), family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the Taxonomy (biology), order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from Vespoidea, vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cre ...
native to northern Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
, Uruguay
Uruguay, officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast, while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the A ...
, Paraguay
Paraguay, officially the Republic of Paraguay, is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the Argentina–Paraguay border, south and southwest, Brazil to the Brazil–Paraguay border, east and northeast, and Boli ...
, Bolivia
Bolivia, officially the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is a landlocked country located in central South America. The country features diverse geography, including vast Amazonian plains, tropical lowlands, mountains, the Gran Chaco Province, w ...
and southern Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
. This invasive species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native spec ...
was inadvertently introduced by humans on a global scale and has become established in many Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate ( ), also called a dry summer climate, described by Köppen and Trewartha as ''Cs'', is a temperate climate type that occurs in the lower mid-latitudes (normally 30 to 44 north and south latitude). Such climates typic ...
areas, including South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
, New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
, Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, Easter Island
Easter Island (, ; , ) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is renowned for its nearly 1,000 extant monumental statues, ...
, Australia, the Azores
The Azores ( , , ; , ), officially the Autonomous Region of the Azores (), is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands in the Macaronesia region of the North Atl ...
, Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
, and the continental United States
The contiguous United States, also known as the U.S. mainland, officially referred to as the conterminous United States, consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the District of Columbia of the United States in central North America. The te ...
. Argentine ants are significant pests within agricultural and urban settings, and are documented to cause substantial harm to communities of native arthropods
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
, vertebrates, and plants within their invaded range.
Description
''Linepithema humile'' is a small-bodied (2.2–2.6 mm) ant species, dull light to dark brown in color. Within the invasion zone, ant colonies arelarge
Large means of great size.
Large may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Arbitrarily large, a phrase in mathematics
* Large cardinal, a property of certain transfinite numbers
* Large category, a category with a proper class of objects and morphisms (o ...
and include many workers and multiple queens.
Argentine ants are opportunistic with regard to nesting preferences. Colony nests have been found in the ground, in cracks in concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of aggregate bound together with a fluid cement that cures to a solid over time. It is the second-most-used substance (after water), the most–widely used building material, and the most-manufactur ...
walls, in spaces between boards and timbers, even among belongings in human dwellings. In natural areas, they generally nest shallowly in loose leaf litter
Plant litter (also leaf litter, tree litter, soil litter, litterfall, or duff) is dead plant material (such as leaves, bark, needles, twigs, and cladodes) that has fallen to the ground. This detritus or dead organic material and its constituen ...
or beneath small stones, due to their poor ability to dig deeper nests. However, if a deeper nesting ant species abandons their nest, Argentine ant colonies will readily take over the space. Because the native habitat for this species is within riparian floodplains, colonies are very sensitive to water infiltration within their nests; if their nests become inundated with water, workers will collect thbrood
and the entire colony will move to dry ground. Austrian entomologist Gustav L. Mayr identified the first specimens of ''Hypoclinea humilis'' in the vicinity of
Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires, controlled by the government of the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Argentina. It is located on the southwest of the Río de la Plata. Buenos Aires is classified as an Alpha− glob ...
, Argentina in 1866. This species was shortly transferred to the genus ''Iridomyrmex
''Iridomyrmex'' is a genus of ants called rainbow ants (referring to their blue-green iridescent sheen) first described by Austrian entomologist Gustav Mayr in 1862. He placed the genus in the subfamily Dolichoderinae of the family Formicida ...
'', and finally to ''Linepithema'' in the early 1990s.
Distribution
The native range of Argentine ants is limited toriparian
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a ripar ...
habitats in the lowland areas of the Paraná River
The Paraná River ( ; ; ) is a river in south-central South America, running through Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina for some ."Parana River". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online.
Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 2012. Web. ...
drainage,These reviews...
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
, Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
, Ecuador
Ecuador, officially the Republic of Ecuador, is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. It also includes the Galápagos Province which contain ...
, and Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
. ''Linepithema humile'' thrives in Mediterranean climates, and over the past century it has spread to across the globe by human-mediated transport. The species has become established to every continent except Antarctica and includes many oceanic islands
An island or isle is a piece of land, distinct from a continent, completely surrounded by water. There are continental islands, which were formed by being split from a continent by plate tectonics, and oceanic islands, which have never been ...
.
Global "mega-colony"
The absence of aggression within Argentine antcolonies
A colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule, which rules the territory and its indigenous peoples separated from the foreign rulers, the colonizer, and their '' metropole'' (or "mother country"). This separated rule was often or ...
was first reported in 1913 by Newell & Barber, who noted "…there is no apparent antagonism between separate colonies of its own kind".
Later studies showed that these " supercolonies" extend across hundreds or thousands of kilometers in different parts of the introduced range, first reported in California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
in 2000,
then in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
in 2002,
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
in 2009,
and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
in 2010.
Several subsequent studies used genetic, behavioral, and chemical analyses to show that introduced supercolonies on separate continents actually represent a single global supercolony.
The researchers stated that the "enormous extent of this population is paralleled only by human society", and had probably been spread and maintained by human travel.
Behavior
 They have been extraordinarily successful, in part, because different nests of the introduced Argentine ants seldom attack or compete with each other, unlike most other species of ant. In their introduced range, their genetic makeup is so uniform that individuals from one nest can mingle in a neighboring nest without being attacked. Thus, in most of their introduced range, they form supercolonies.
The Very Large Colony, which covers territory from
They have been extraordinarily successful, in part, because different nests of the introduced Argentine ants seldom attack or compete with each other, unlike most other species of ant. In their introduced range, their genetic makeup is so uniform that individuals from one nest can mingle in a neighboring nest without being attacked. Thus, in most of their introduced range, they form supercolonies.
The Very Large Colony, which covers territory from San Diego
San Diego ( , ) is a city on the Pacific coast of Southern California, adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a population of over 1.4 million, it is the List of United States cities by population, eighth-most populous city in t ...
to beyond San Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
, may have a population of nearly one trillion individuals.
Conflict does occur between members of different supercolonies. In 1997, UC San Diego
The University of California, San Diego (UC San Diego in communications material, formerly and colloquially UCSD) is a public land-grant research university in San Diego, California, United States. Established in 1960 near the pre-existing Sc ...
researchers observed fighting between different Argentine ants kept in lab, and in 2004 scientists began to map out the boundaries of the different supercolonies that clashed in San Diego. On the border of the Very Large Colony and the Lake Hodges Colony thirty million ants die each year, on a battlefront that covers many miles. While the battles of other ant species generally constitute colony raids lasting a few hours, or skirmishes that occur periodically for a few weeks, Argentine ants clash ceaselessly; the borders of their territory are a site of constant violence and battles can be fought on top of hundreds of dead ants. Fights may be halted by adverse weather such as rain.
In contrast, native populations are genetically more diverse and form colonies that are much smaller than the supercolonies that dominate the introduced range. Colonies living in close proximity are territorial and aggressive toward one another. Argentine ants in their native South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
also co-exist with many other species of ants, and do not attain the high population densities that characterize introduced populations.''Success of Introduced Argentine Ants Tied to Reduced Genetic Variation.''Kim McDonald, University of California, May 2000 In a series of experiments, ants of the same colony were isolated and fed different diets. The
hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and Hydrophobe, hydrophobic; their odor is usually fain ...
s from the diet were eventually incorporated into the cuticle of the subjects. Those that had the same diet appeared to recognize one another as kin. Those who had at least some overlap in dietary composition also appeared to react non-aggressively to one another. These interactions contrasts drastically with the groups that fed on completely different sources, such as those who lived off flies
Flies are insects of the Order (biology), order Diptera, the name being derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwin ...
and those that fed on grasshopper
Grasshoppers are a group of insects belonging to the suborder Caelifera. They are amongst what are possibly the most ancient living groups of chewing herbivorous insects, dating back to the early Triassic around 250 million years ago.
Grassh ...
s. The groups appeared to have incorporated hydrocarbons that were not similar to the others and created an unfamiliar identity cue. These groups reacted violently towards each other. This suggests that dietary factors affect the recognition cues for colony members.
Reproduction and seasonal colony trends
 Like workers in many other ant species, Argentine ant workers are unable to lay reproductive eggs but can direct the development of eggs in reproductive females; the production of males appears to be controlled by the amount of food available to the larvae. Argentine ant colonies almost invariably have many reproductive queens, as many as eight for every 1,000 workers.
The seasonal low occurs in mid-winter, when 90% of a representative colony consists of workers and the remainder of queens, and no reproductive activity and minimal birthing. Eggs are produced in late-winter, nearly all of which hatch into sexual forms by May(*). Mating occurs after the females emerge. Worker production increases steadily from mid-March(*) to October(*), after which their numbers are not replenished; thus, their numbers drop steadily over the winter months.
((*) Note that the information regarding the months May, March, and October in this paragraph, as well as the entire Month axis in the graph, are not worldwide correct, in particular in Southern hemisphere, due to the shift of six months in seasons between the two hemispheres.)
Colonies in the Argentine ant's native habitat are kept within a range of ten to one hundred meters by colonies of interspecific and intraspecific rivals. As the colonies expand, they appear to form fluctuating territory borders, which contract and expand on a seasonal and conditional basis. There is an expansive push outward in the summer months, with a retreating motion in the winter. This has to do with
Like workers in many other ant species, Argentine ant workers are unable to lay reproductive eggs but can direct the development of eggs in reproductive females; the production of males appears to be controlled by the amount of food available to the larvae. Argentine ant colonies almost invariably have many reproductive queens, as many as eight for every 1,000 workers.
The seasonal low occurs in mid-winter, when 90% of a representative colony consists of workers and the remainder of queens, and no reproductive activity and minimal birthing. Eggs are produced in late-winter, nearly all of which hatch into sexual forms by May(*). Mating occurs after the females emerge. Worker production increases steadily from mid-March(*) to October(*), after which their numbers are not replenished; thus, their numbers drop steadily over the winter months.
((*) Note that the information regarding the months May, March, and October in this paragraph, as well as the entire Month axis in the graph, are not worldwide correct, in particular in Southern hemisphere, due to the shift of six months in seasons between the two hemispheres.)
Colonies in the Argentine ant's native habitat are kept within a range of ten to one hundred meters by colonies of interspecific and intraspecific rivals. As the colonies expand, they appear to form fluctuating territory borders, which contract and expand on a seasonal and conditional basis. There is an expansive push outward in the summer months, with a retreating motion in the winter. This has to do with soil moisture
Soil moisture is the water content of the soil. It can be expressed in terms of volume or weight. Soil moisture measurement can be based on ''in situ'' probes (e.g., capacitance probes, neutron probes) or remote sensing methods.
Water that enters ...
and temperature conditions.
At the edges of these borders are either rival ''L. humile'' colonies or other obstacles that prevent further expansion, such as an inhospitable environment for nests.
Impact
The ants are ranked among the world's 100 worst invasive animal species. In its introduced range, the Argentine ant often displaces most or all native ants and can threaten native invertebrates and even small vertebrates that are not accustomed to defending against the aggressive ants. This can, in turn, imperil other species in theecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
, such as native plants that depend on native ants for seed dispersal, or lizard
Lizard is the common name used for all Squamata, squamate reptiles other than snakes (and to a lesser extent amphisbaenians), encompassing over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most Island#Oceanic isla ...
s that depend on native ants or invertebrates for food. For example, the recent severe decline in coastal horned lizard
''Phrynosoma'', whose members are known as the horned lizards, horny toads, or horntoads, is a genus of North American lizards and the type genus of the Family (biology), family Phrynosomatidae. Their common names refer directly to their horns or ...
s in southern California
Southern California (commonly shortened to SoCal) is a geographic and Cultural area, cultural List of regions of California, region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. Its densely populated coastal reg ...
is closely tied to Argentine ants displacing native ant species on which the lizards feed.
In South Africa, the Argentine ant has in some cases displaced native ants that disperse the seeds of Fynbos
Fynbos (; , ) is a small belt of natural shrubland or heathland vegetation located in the Western Cape and Eastern Cape provinces of South Africa. The area is predominantly coastal and mountainous, with a Mediterranean climate. The fynbos ...
plants like '' Mimetes cucullatus''. The Argentine ants don't take the seeds underground and are left on the surface, resulting in ungerminated plants and the dwindling of Fynbos seed reserves after veld fires.
Argentine ants sometimes tend aphid
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects in the Taxonomic rank, family Aphididae. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white Eriosomatinae, woolly ...
, mealybug
Mealybugs are insects in the family Pseudococcidae, unarmored scale insects found in moist, warm habitats. Of the more than 2,000 described species, many are considered pests as they feed on plant juices of greenhouse plants, house plants and ...
, and scale insect
Scale insects are small insects of the Order (biology), order Hemiptera, suborder Sternorrhyncha. Of dramatically variable appearance and extreme sexual dimorphism, they comprise the infraorder Coccomorpha which is considered a more convenient g ...
colonies,
sometimes relocating the parasites to unaffected plants, and their protection of these plant pests from predators
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill ...
and parasitoid
In evolutionary ecology, a parasitoid is an organism that lives in close association with its host (biology), host at the host's expense, eventually resulting in the death of the host. Parasitoidism is one of six major evolutionarily stable str ...
s can cause problems in agricultural areas.
In return for this protection, the ants benefit by feeding off honeydew.
There is also evidence that the presence of Argentine ant may decrease the number of pollinators that visit natural flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed with ...
s via predation on the larvae of the pollinator
A pollinator is an animal that moves pollen from the male anther of a flower to the female carpel, stigma of a flower. This helps to bring about fertilization of the ovules in the flower by the male gametes from the pollen grains.
Insects are ...
s.
Pest control
Borate
A borate is any of a range of boron oxyanions, anions containing boron and oxygen, such as orthoborate , metaborate , or tetraborate ; or any salt of such anions, such as sodium metaborate, and borax . The name also refers to esters of su ...
-sucrose water baits are toxic to Argentine ants, when the bait is 25% water, with 0.5–1.0% boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white ...
or borate salts.
In spring, during a colony's growth phase, protein based baits may be more effective due to much higher demand from the egg-laying queens.
Due to their nesting behavior and presence of numerous queens in each colony, it is generally impractical to spray Argentine ants with pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s or to use boiling water as with mound building ants. Spraying with pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s has occasionally stimulated increased egg-laying by the queens, compounding the problem. Pest control
Pest control is the regulation or management of a species defined as a pest (organism), pest; such as any animal, plant or fungus that impacts adversely on human activities or environment. The human response depends on the importance of the da ...
usually requires exploiting their omnivorous dietary habits, through use of slow-acting poison
A poison is any chemical substance that is harmful or lethal to living organisms. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figurati ...
bait (e.g. fipronil
Fipronil is a broad-spectrum insecticide that belongs to the phenylpyrazole insecticide class. Fipronil disrupts the insect central nervous system by blocking the ligand-gated ion channel of the GABAA receptor ( IRAC group 2B) and glutamate-g ...
, hydramethylnon, sulfluramid), which will be carried back to the nest by the workers, eventually killing all the individuals, including the queens.
Research
Researchers from theUniversity of California, Irvine
The University of California, Irvine (UCI or UC Irvine) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Irvine, California, United States. One of the ten campuses of the University of California system, U ...
, have developed a way to use the scent of Argentine ants against them. The exoskeleton
An exoskeleton () . is a skeleton that is on the exterior of an animal in the form of hardened integument, which both supports the body's shape and protects the internal organs, in contrast to an internal endoskeleton (e.g. human skeleton, that ...
s of the ants are covered with a hydrocarbon-laced secretion. They made a compound that is different, but similar, to the one that coats the ants. If the chemical is applied to an ant, the other members of the colony will kill it.
Another approach for a large scale control of the Argentine ant has been proposed by researchers from Japan, who showed that it is possible to disrupt its trails with synthetic pheromone
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavio ...
s. This has been confirmed in various later trials by a New Zealand-led team in Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
and by researchers from Victoria University of Wellington
Victoria University of Wellington (), also known by its shorter names "VUW" or "Vic", is a public university, public research university in Wellington, New Zealand. It was established in 1897 by Act of New Zealand Parliament, Parliament, and w ...
who showed that this approach is beneficial for other local ant species.
A multi-agency study at the environmentally-sensitive California Channel Islands in the mid-2010s eliminated the Argentine ant to sub-detectable levels. The ant was introduced to the islands in the early- to mid-1900s. Due to strict biosecurity measures, the risk of re-invasion was low and allowed for a controlled study. Four (4) km2, 2% of the island area, was treated with liquid bait pellets similar to off-the-shelf products, dispersed by helicopter. Cost of treatment ranged from $50000-$200000 USD (2015) per km2 including the cost of subsequent monitoring, and may serve as an initial guideline for other areas.
See also
* Linepithema humile virus 1, a virus carried by Argentine antsReferences
External links
* with information on habits, habitat and prevention * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Argentine Ant Dolichoderinae Agricultural pest insects Household pest insects Insects described in 1868 Hymenoptera of New Zealand Ants of New Zealand Taxa named by Gustav Mayr